
DPC “Wood Street, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania.” 1905



Again: this is just starting.
• Emerging Market Mayhem: Gross Sees “Debacle” As Currencies, Bonds Collapse (ZH)
One particularly alarming case that we’ve been keen to document lately is that of Brazil which, you’ll recall, is “up shit creek without a paddle” both figuratively and literally. For one thing, as Goldman recently noted, there’s not a single period in over a decade “with a strictly-worse growth-inflation outcome than that of 2Q2015.” In other words, “since 1Q2004 there has not been a single quarter in which we had simultaneously higher inflation and lower growth than during 2Q2015.” And here is what that looks like on a scale of 100 to -100 with 100 being “high growth, low inflation” and -100 being “stagflation nightmare”:
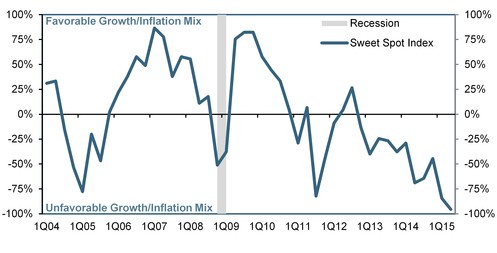
This helps to explain why CDS spreads have blown out to post-crisis wides. For those who favor a more qualitative approach to assessing an economy’s prospects, don’t forget that the Brazilian economy recently hit its metaphorical, and literal, bottom when AP reported that, with the Brazil Olympics of 2016 just about 1 year away, “athletes in next year’s Summer Olympics here will be swimming and boating in waters so contaminated with human feces that they risk becoming violently ill and unable to compete in the games.” So that’s Brazil, and while not every EM country is coping with the worst stagflation in 11 years while simultaneously trying to explain away rivers of raw sewage to the Olympic Committee, the combination of slumping commodity prices and the threat of an imminent Fed liftoff are wreaking havoc across the space.

Finally, we can let go of the nonsense? Or will the MSM keep reporting ‘official’ numbers?
• China Growth Probably Half Reported Rate Or Less, Say Sceptics (Reuters)
China’s economy is growing only half as fast as official data shows, or maybe even slower, according to foreign investors and analysts who increasingly challenge how the world’s second largest economy can be measured so swiftly and precisely. Beijing’s official statisticians reported last month that China’s economy grew by a steady 7.0% in the first two quarters of the year, spot on its official 2015 target. That statistical stability comes at a time when prices of global commodities, which China still hungers for despite a campaign to rebalance the economy away from investment and manufacturing toward consumer spending, have cratered.
But perhaps the biggest question is how a developing country of 1.4 billion people can publish its quarterly GDP statistics weeks before first drafts from developed economies like the United States, the euro zone or Britain, and then barely revise them later. “We think the numbers are fantasy,” said Erik Britton of Fathom Consulting, a London-based independent research firm and one of the more vocal critics of official Chinese data. “There is no way those numbers are even close to the truth.” The uncanny official calm in China GDP data may well be contributing to sceptics’ exit from Chinese assets just as the authorities struggle to manage a volatile stock market.
Fathom, which decided last year to stop publishing forecasts of the official GDP release and instead publish what it thinks is really happening, reckons growth will be 2.8% this year, slowing to just 1.0% next year. One issue is that so many other forecasters stick to the script. In the latest Reuters poll of mainly sell-side bank economists, based both inside and outside China, the range of opinion is 6.5-7.2%. For next year, it’s 6.3-7.5%.

China is due for epic unrest.
• The World Should Worry More About China’s Politics Than The Economy (Economist)
How much indeed has changed in China, Mr Xi might reflect, since he came to power nearly three years ago? The economy is on course for its slowest year of growth in a quarter of a century. The stockmarket, having risen to its highest level since the global financial crisis seven years ago, crashed last month. Once hailed as an economic miracle, China is now a source of foreboding: witness the latest falls in global commodity prices. Mr Xi likes to describe slower growth as the “new normal”—a welcome sign that the country is becoming less dependent on credit-fuelled investment. But debates rage within the party elite over how to keep the economy growing fast enough to prevent financial strains from erupting into a fully fledged crisis.
A year after he took over as China’s leader, Mr Xi promised to let market forces play a “decisive” role in shaping the economy. His government’s heavy-handed (and counterproductive) efforts to boost the price of shares have created doubts about his commitment to that aim. During discussions in Beidaihe, some officials will doubtless point to the stockmarket as evidence of what can go wrong when markets are given free rein. Others will suggest that, on the contrary, economic reform is still badly needed to help China avoid falling into the Japanese trap of long-term stagnation. Much depends on which camp Mr Xi heeds. During meetings in Beidaihe in 1988, China’s then leader, Deng Xiaoping, vacillated in the face of a backlash against his economic reforms.
By pandering to conservatives, he fuelled political divisions that erupted the following year into nationwide pro-democracy protests. The unrest, centred on Tiananmen Square, came close to toppling the party. It was not until 1992 that Deng was able to set his reforms back on track. China’s leadership does not appear anything like as divided as it did in the build-up to the Tiananmen upheaval. But appearances may be more deceptive now. Mr Xi is a leader of a very different hue from his predecessors. He has rewritten the rules of Chinese politics, in effect scrapping Deng’s system of “collective leadership” by taking on almost every portfolio himself, while waging a war on corruption of unprecedented scale and intensity.
The latest high-ranking official to be targeted, Guo Boxiong, was once the most senior general in the armed forces; he was expelled from the party on July 30th and now faces trial for graft. A dozen other generals, more than 50 ministerial-level officials and hundreds of thousands of lesser functionaries have met similar fates. That suggests Mr Xi is strong, but also that he has many enemies or is busy creating them. His rounding up of more than 200 civil-rights lawyers and other activists since early last month—the biggest such clampdown in years—hints at his insecurity.

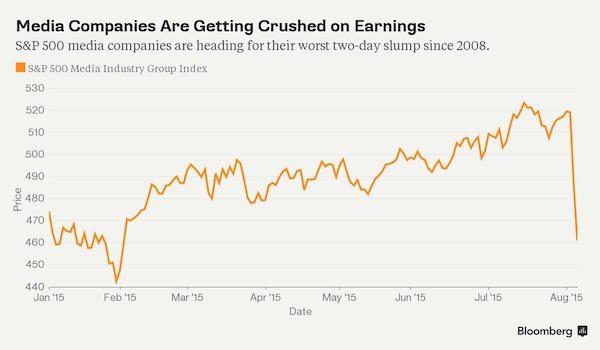
” In just five stocks – Disney, Time Warner, Fox, CBS and Comcast – almost $50 billion of value was erased in two days.”
• Another Major Pillar of the Bull Market Is Collapsing (Bloomberg)
A bull market without Apple is one thing. Removing cable television and movie stocks from the 6 1/2-year rally in U.S. equities is a little harder to imagine. Ignited by a plunge in Walt Disney, shares tracked by the 15-company S&P 500 Media Index have tumbled 8.2% in two days, the biggest slump for the group since 2008. The drop erased all of 2015’s gains for a group that has posted annualized returns of more than 33% since 2009. More than technology or even biotech, media stocks have ruled the roost during the share advance that restored $17 trillion to American equity prices since the financial crisis. Companies from CBS to Tegna and Time Warner Cable are among stocks with the 60 biggest increases during the stretch.
“This sector stripped out is certainly not going to help,” Larry Peruzzi, director of international trading at Cabrera Capital Markets LLC in Boston, said by phone. “There are a lot of companies adding pressure here and there’s an argument to be made that it’s an indicator of consumer sentiment, because that’s where media revenues come from.” Disappointing results from Disney after the close of trading Tuesday sparked the two-day rout. Selling spread to other television and publishing companies as quarterly reports from CBS to 21st Century Fox Inc. and Viacom Inc. were marked by shrinking U.S. ad sales and profits propped up by stock buybacks.
Until Tuesday, media shares were the best-performing shares of the bull market, rising 531% to eclipse automakers, retail stores and banks. The industry’s market capitalization was about $650 billion, compared with $135 billion in March 2009. That value is evaporating. In just five stocks – Disney, Time Warner, Fox, CBS and Comcast – almost $50 billion of value was erased in two days. Viacom slid 14% on Thursday alone, its biggest drop since October 2008.

Interesting developments. US interests are bound to keep resisting what is inevitable.
• How America Keeps The World’s Poor Downtrodden (Stiglitz)
Much has changed in the 13 years since the first International Conference on Financing for Development was held in Monterrey, Mexico, in 2002. Back then, the G-7 dominated global economic policy making; today, China is the world’s largest economy (in purchasing-power-parity terms), with savings some 50% larger than that of the U.S. In 2002, Western financial institutions were thought to be wizards at managing risk and allocating capital; today, we see that they are wizards at market manipulation and other deceptive practices. Gone are the calls for the developed countries to live up to their commitment to give at least 0.7% of their gross national income in development aid.
A few Northern European countries – Denmark, Luxembourg, Norway, Sweden and, most surprisingly, the United Kingdom in the midst of its self-inflicted austerity – fulfilled their pledges in 2014. But the United States (which gave 0.19% of GNI in 2014) lags far, far behind. Today, developing countries and emerging markets say to the U.S. and others: If you will not live up to your promises, at least get out of the way and let us create an international architecture for a global economy that works for the poor, too. Not surprisingly, the existing hegemons, led by the U.S., are doing whatever they can to thwart such efforts. When China proposed the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank to help recycle some of the surfeit of global savings to where financing is badly needed, the U.S. sought to torpedo the effort.
President Barack Obama’s administration suffered a stinging (and highly embarrassing) defeat. The U.S. is also blocking the world’s path toward an international rule of law for debt and finance. If bond markets, for example, are to work well, an orderly way of resolving cases of sovereign insolvency must be found. But today, there is no such way. Ukraine, Greece, and Argentina are all examples of the failure of existing international arrangements. The vast majority of countries have called for the creation of a framework for sovereign-debt restructuring. The U.S. remains the major obstacle.

Must read. Very good.
• Europeans Against the European Union (Village)
[..] since 2011, a rival, pro-European identity has emerged which is highly critical of the Troika and the increasingly undemocratic apparatus of the EU. Last month, in Greece, this movement was given a name: Generation No. The vote in Greece was striking in its breakdown. The average No voter rejecting the Troika’s ultimatum was young, working-class and held increasingly left-wing views. The percentage for ‘oxi’ under 25 was 85, under 35 was 78. These were a new generation, living in conditions of over 60% unemployment, often having to stretch out their studies over many years to afford to complete them, relying on cash from their parents to survive. But also, it is a generation increasingly willing to challenge the shibboleths of our societies – to experiment in unorthodox relationships to the economy, to housing, to politics.
The price of building up the reputation of the EU as an arena of opportunity for Europe’s periphery has been the weight of frustrated expectations when this turned out not to be the case. As a result not just in Greece but in an increasing number of states it isn’t Generation Yes which represents the future but Generation No. This shift in orientation towards the European project is not down to a turn against Europe. In fact, the Greek No vote enjoyed enormous support from across the continent – marches, direct actions, statements from social movements, trade unions, NGOs, academics and intellectuals. Instead what has happened is that the EU has been stripped back to its essence as a neoliberal economic project. Gone are the pretences of internationalism or a social element – the Greek crisis has demonstrated that bonds of solidarity stretch only as far as is profitable.
To understand why this disconnect between growing internationalism of European peoples and the European Union exists, we have to explore its economic basis. The idea of a ‘social Europe’ has never been at the heart of this market-oriented project of European integration. At the same time as Jacque Delors was seducing Europe’s social democrats into this myth in the 1980s, he was trapping them into arrangements they would never agree to without it. First in 1988 the directive mandating for extensive free movement of capital and then, in 1992, the Maastricht Treaty. These arrangements provided the foundation for the euro – a currency which was to drive the stake of neoliberalism into the heart of the European Union. The money in our pockets is the most right-wing currency ever designed, with a central bank that doesn’t care about unemployment and won’t act as a lender of last resort, modelled to work only in the free-market utopias predicted to arrive at Francis Fukuyama’s end of history.

Problems that are conveniently hidden behind ‘the Greece story’.
• Indebted Portugal Is Still The Problem Child Of The Eurozone (Telegraph)
Portugal must carry out a bold programme of deep spending cuts and tax hikes to tackle its perilously high debt levels, the IMF has warned. A former bail-out economy often hailed as a poster child for the eurozone’s austerity medicine, Portugal continues to have the highest public and private debt ratio in the eurozone at over 360pc of GDP. The IMF has now told the government to redouble its belt-tightening efforts to reduce its debt overhang and meet a mandated budget deficit target of 2.7pc of GDP this year. Should Lisbon fail to cut spending, the deficit is expected to balloon to 3.2pc of economic output. Portugal officially exited its €78bn international bail-out programme last year.
The economy is now expected to expand by 1.6pc in 2015, an upturn largely attributed to favourable external factors such as low commodity prices and a weak euro, said the IMF. Despite noting the recovery was broadly “on track”, the IMF painted a precarious picture of an economy heavily exposed to a downturn in global fortunes and fears over Greece’s future in the euro. “A sudden change in market sentiment due to concerns about the direction of economic policies or re-pricing of risk could render Portugal’s capacity to repay more vulnerable,” warned the report. Four years of Troika-imposed measures has seen government debt hit 127pc of GDP this year, leaving the country “vulnerable to any prolonged financial market turbulence”, according to the IMF’s monitoring report.
Prohibitive debt levels are now expected to dampen domestic demand, “constrain the pace of recovery and weigh on medium-term growth prospects”. In further worrying signs that the recovery has already lost steam, Portugal’s unemployment rate crept back up to 13.7pc in the first quarter of the year, up from 13.1pc in late 2014. Since the IMF’s assessment, joblessless has fallen back to 11.9pc in the three months to June. Last year, the government was forced to inject €5bn to stave off a collapse of Portugal’s biggest lender – Banco Espírito Santo. But the country’s financial system continues to be plagued by rising “bad” non-performing loans which grew by 12.3pc in the first three months of the year.
Political risk could also throw the country’s fragile recovery off track and precipate a fresh crisis for Brussels in the southern Mediterranean. Despite five years under a compliant centre-right government, progress on implementing structural reforms demanded by creditors has eased off, said the IMF. The country goes to the polls in October, where the anti-austerity Socialists are on course to win a parliamentary majority. Party leader Antonio Costa has vowed to roll back Troika-imposed reforms and end the country’s “obsession with austerity”.

The deal remains far from done. But Greece is set to receive ’emergency’ funds before it’s time to sign, and that is perhaps the pivotal event.
• Greece’s Tax Revenues Collapse As Debt Crisis Continues (Guardian)
Fresh evidence of the dramatic impact of the Greek debt crisis on the health of the country’s finances has emerged with official figures showing tax revenues collapsing. As talks continued over a proposed €86bn third bailout of the stricken state, the Greek treasury said tax revenues were 8.5% lower in the first six months of 2015 than the same period a year earlier. The bank shutdown that brought much economic activity to a halt began on 28 June. Public spending fell even more dramatically, by 12.3%, even before the new austerity measures the prime minister Alexis Tsipras has been forced to pass to win the support of his creditors for talks on a new bailout. Greece is due to make a €3.2bn repayment to the ECB on 20 August.
Talks with the quartet of creditors, which includes the ECB, the IMF, the European commission and Europe’s bailout fund, the European stability mechanism, are continuing, and Tsipras has suggested they are “in the final stretch”. However, it remains unclear whether the prime minister, who was only able to pass the latest package of austerity measures with the help of opposition MPs, will be able to win the backing of his radical Syriza party for new reforms, at a special conference due to be held next month. The IMF has made clear that it will refuse to commit any new funds until Greece has signed up to a new economic reform programme, and eurozone countries have made a concrete offer to write off part of the country’s debt burden.
Sweden’s representative on the 24-member IMF board, Thomas Östros, said there was strong support for a new Greek rescue, “but it will take time”. He told Swedish daily Dagens Nyheter: “There is going to be a discussion during the summer and autumn and then the board will make a decision during the autumn.” He also noted that Greece must adopt wide-ranging reforms first. “They have an inefficient public sector, corruption is a relatively big problem and the pension system is more expensive than other countries.” Despite the grim news on the public finances, Greek stock markets bounced back yesterday, after three straight days of decline, with the main Athens index closing up 3.65%.

Sorry, can’t really see that happen. The IMF will insist on debt relief, which the EU and ECB will resist, and SYRIZA will protest it all.
• Hollande And Tsipras Want Greek Bailout Agreed In Late August (Reuters)
A new bailout for Athens should be agreed by late August, Greek Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras and French President Francois Hollande said on Thursday. Greece is in negotiations with the European Union and International Monetary Fund for as much as €86 billion in fresh loans to stave off financial ruin and economic collapse. Tsipras said the new deal would be agreed soon after Aug. 15; Hollande said by the end of the month. The two men were speaking in Egypt on the sidelines of a ceremony to inaugurate the New Suez Canal. It will be Greece’s third bailout since its financial troubles became evident more than five years ago. Negotiations in the past have been heated, but all sides are reporting progress this time around.
An accord must be settled – or a bridge loan agreed – by Aug. 20, when a €5 billion debt payment to the ECB falls due. In a statement, Tsipras’s office in Athens said he and Hollande had agreed that the deal “should and could be concluded right after Aug. 15”. That would give enough time for the Greek parliament to approve it to enable the Aug. 20 repayment to the ECB. “They also agreed that everything should be done for the Greek economy to rebound, especially after the effects of the banking crisis,” the statement said. Greece’s banks are in need of recapitalization by €10 billion to 25 billion, according to the EU. France has been generally supportive of Greek requests for aid, contrasting with a harder line taken by Germany which has demanded stringent reform and austerity measures from Athens.

Greece can take the €10-15 billion and prepare to leave.
• German Finance Ministry Favors Bridge Loan For Greece (Reuters)
Germany’s Finance Ministry favors a bridge loan for Greece to give Athens and its creditors sufficient time to negotiate a comprehensive third bailout, the Sueddeutsche Zeitung daily reported on Friday. “A program that should last three years and be worth over €80 billion needs a really solid basis,” the paper quoted a ministry source as saying. “A further bridge loan is better than just a half-finished program.” Greece is in negotiations with the EU and IMF for as much as €86 billion in fresh loans to stave off financial ruin and economic collapse. A €3.5 billion debt payment to the ECB falls due on August 20 and without a bailout deal, Athens would need bridge financing. The reported German preference for a bridge loan contrasts with the view of Greek Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras and French President Francois Hollande, who said on Thursday a new bailout should be agreed by late August.

That “great” story is over too.
• German Industrial Output Slumps Unexpectedly (Marketwatch)
Germany’s industrial output and exports both slumped unexpectedly in June, a sign that growth in Europe’s largest economy failed to gather much momentum in the second quarter. Industrial production, adjusted for inflation and seasonal swings, declined 1.4% from May, leaving output in the second quarter flat from the previous period, the economics ministry said Friday. But strong manufacturing orders in June and healthy business sentiment indicate that “the modest upward trend in industry should be continued,” the ministry said. In a separate publication, the federal statistics office said Friday that German exports, adjusted for inflation and seasonal swings, dropped 1.0% from May; imports declined 0.5%. But Germany’s adjusted trade surplus, at €22 billion in June, remained near May’s record high of €22.6 billion, an indication that foreign demand underpinned economic activity in the second quarter.

Both the UK and US are far too focused on election entertainment.
• Corbyn’s “People’s QE” Could Actually Be A Decent Idea (Klein)
If Jeremy Corbyn becomes leader of the UK Labour Party, one positive consequence will be the ensuing discussion of the monetary policy transmission mechanism. It all started with his presentation on “The Economy in 2020” given on July 22:
The ‘rebalancing’ I have talked about here today means rebalancing away from finance towards the high-growth, sustainable sectors of the future. How do we do this? One option would be for the Bank of England to be given a new mandate to upgrade our economy to invest in new large scale housing, energy, transport and digital projects: Quantitative easing for people instead of banks. Richard Murphy has been one of many economists making that case.
That passage seems to have been mostly ignored until August 3, when Chris Leslie, Labour’s shadow chancellor, attacked the policy, which in turn led to a detailed response from the aforementioned Richard Murphy (see also here and here), at which point what seems like the bulk of the British economics commentariat erupted. Just search the internet for “Corbynomics” if you don’t believe us. Much of the commentary has been negative – former Bank of England economist Tony Yates concluded, for example, that “People’s QE” would be “the first step along the road to undermining the social usefulness of money” – although Chris Dillow gave an intelligent defense. We don’t understand the negativity. Some of the specific arguments justifying the proposal may be flawed, but the core idea is sound and possesses an impressive intellectual pedigree.
In fact, it could help solve one of the most troublesome questions in central banking: how policymakers can accomplish their objectives using the tools at their disposal, without producing too many unpleasant side effects. One of the oddities of “monetary policy” is that it has almost no direct impact on how much money there is to go around. Virtually all of what we commonly think of and use as money is actually short-term debt issued and retired at will by private financial firms. Monetary policymakers can affect the incentives of these profit-seeking entities but they have little control over the amount of nominal spending occurring in the economy. Nudging the unsecured overnight interbank lending rate up and down can encourage lenders to adjust their leverage, but good luck tying that to the traditional price stability mandate.

One among many.
• Indonesia’s Economy Has Stopped Emerging (Pesek)
Indonesia has come a long way since Oct. 20, when Joko Widodo was sworn in as president. Unfortunately, the distance the country has traveled has been in the wrong direction. Expectations were that Widodo, known as Jokowi, would accelerate the reforms of predecessor Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono – upgrading infrastructure, reducing red tape, curbing corruption. Who better to do so than Indonesia’s first leader independent of dynastic families and the military? In 10 years at the helm, Yudhoyono dragged the economy from failed-state candidate to investment-grade growth star. Jokowi’s mandate was to take Indonesia to the next level, honing its global competitiveness, creating new jobs, preparing one of the world’s youngest workforces to thrive and combating the remnants of the powerful political machine built by Suharto, the dictator deposed in 1998.
After 291 days, however, Jokowi seems no match for an Indonesian establishment bent on protecting the status quo. Growth was just 4.67% in the second quarter, the slowest pace in six years. What’s more, a recent MasterCard survey detected an “extreme deterioration” in consumer sentiment, which had plummeted to the worst levels in Asia. Investors are already voting with their feet. The Jakarta Composite Index has fallen 13% from its April 7 record high, one of Asia’s biggest plunges in that time. And foreign direct investment underwhelmed last quarter, coming in at $7.4 billion, little changed from a year earlier in dollar terms. Jokowi has plenty of time to turn things around; 1,535 days remain in his five-year term. But the “halo effect” Jokowi carried into office is fast fading as Indonesia’s 250 million people flirt with buyer’s remorse.
First, Jokowi must step up efforts to battle weakening exports. Indonesia’s weak government spending, stifling bureaucracy and conflicting regulations would be impediment enough; slowing world growth makes matters much worse. Jokowi must greenlight infrastructure projects to boost competitiveness and increase the number and quality of jobs. Next, Jokowi must decide what kind of leader he wants to be: a craven populist or the modernizer Indonesia needs. He has too often resorted to nationalistic rhetoric that hearkens to the Indonesian backwater of old – a turnoff for the multinational executives Jakarta should be courting. Last month, Jokowi raised import tariffs, while asking visiting U.K. Prime Minister David Cameron to do the opposite by cutting U.K. duties for Indonesian goods. Jokowi isn’t helping his constituents by driving up prices for goods while their currency is weakening.

These things should be held against daylight, but where?
• Malaysia Mess Puts Goldman Sachs In The Hot Seat (Reuters)
An unfolding political scandal in Malaysia is starting to reverberate far from Kuala Lumpur to the downtown New York headquarters of Goldman Sachs. State fund 1Malaysia Development Berhad (1MDB) is at the centre of allegations of graft and mismanagement. The furore has prompted renewed scrutiny of hefty fees the Wall Street bank led by Lloyd Blankfein earned selling bonds for 1MDB. The affair threatens to expose a blind spot in Goldman’s processes for vetting sensitive deals. The latest uproar was triggered by reports that almost $700 million landed in the personal accounts of Najib Razak, Malaysia’s Prime Minister. Najib denies taking any money from 1MDB for personal gain. The country’s anti-corruption commission says the funds came from an unnamed donor.
Even so, the investigations into the source of Najib’s mystery money have intensified questions about the management of the fund, which borrowed heavily to buy power assets and finance investments in recent years, but is now effectively being wound down. Goldman helped 1MDB raise a total of $6.5 billion from three bond issues in 2012 and 2013. Even at the time, the deals were controversial because they were so lucrative for the bank. Goldman earned roughly $590 million in fees, commissions and expenses from underwriting the bonds, according to a person familiar with the situation – a massive 9.1% of the total raised. That was almost four times the typical rate for a quasi-sovereign bond at the time.
It exceeds what Wall Street firms can charge in what has traditionally been their most lucrative work: taking companies public in the United States. Goldman was able to book hefty fees because it put its balance sheet at risk for 1MDB, which did not yet have a credit rating. And it wanted to raise a large amount of money very quickly. Yet the bonanza has left the bank exposed to its client’s woes. Malaysian opposition politician Tony Pua said earlier this year that 1MDB had been “royally screwed” by the deals.

Goes to show how bad things are.
• To Please Investors, Big Oil Makes Deepest Cuts in a Generation (Bloomberg)
Oil companies are making the largest cost cuts in a generation to reassure investors. They’re risking their own future growth. From Chevron to Shell, producers are firing thousands of workers and canceling investments to defend their dividends. Cutbacks across the industry total $180 billion so far this year, the most since the oil crash of 1986, according to Rystad Energy. BP CEO Bob Dudley said last week his “first priority” was payouts to shareholders. Chevron CFO Patricia Yarrington said her company was committed to continuing its 27-year record of annual dividend increases. While the dividend payouts please investors, the producers risk repeating the patterns of 1986 and 1999, when prices slumped and they slashed spending.
It took years for them to rebuild their pipelines of production growth. “You need to question whether it’s optimal to base the whole strategy on keeping the dividend,” said Thomas Moore, a director at U.K. fund manager Standard Life Investments. “The response to low oil prices has been savage cost-cutting.” Exxon Mobil, Shell, Chevron, BP and Total told investors last week that future growth plans aren’t imperiled and maintained their multi-year output targets. The history of previous cost-cutting is a cautionary tale.

Crazy wager.
• Inside Shell’s Extreme Plan to Drill for Oil in the Arctic (Bloomberg)
Chevron, ConocoPhillips, ExxonMobil, Statoil, and Total have all put Arctic plans on hold. “Given the environmental and regulatory risks in the Arctic and the cost of producing in that difficult setting, assuming they ever get to producing, Shell must anticipate an enormous find—and future oil prices much higher than they are today,” says Nick Butler, a former senior strategy executive at BP who does energy research at King’s College London. “It’s a dangerous wager.” One of the most powerful women executives in a decidedly masculine industry, Pickard, 59, meets a reporter visiting Anchorage in jeans and a blue button-down shirt.
Her rise through the ranks, first at the pre-merger Mobil and since 2000 at Shell, is especially impressive as she lacks the engineering or geology pedigree normally required of senior oil industry management. She has a graduate degree in international relations and has overseen exploration and production in Africa, Australia, Latin America, and Russia. “Ann doesn’t suffer fools,” says a (male) subordinate who pleads for anonymity. In 2005, Shell put Pickard in charge of sprawling operations in Nigeria long shadowed by pipeline thievery, militant attacks, and accusations—denied by Shell—of collaboration with brutal government crackdowns. Fortune magazine in 2008 labeled her “the bravest woman in oil”—a silly accolade, perhaps, but one that accurately reflects her reputation at Shell.
Most of the world’s “easy oil” has already been pumped or nationalized by resource-rich governments, Pickard says, leaving independent producers such as Shell no choice but to pursue “extreme oil” in dicey places. “I enjoy the challenge,” she says. That’s why in 2013, when she was planning to retire to spend more time with her husband, a retired Navy commander, and their two adopted children, she changed her mind and took over the troubled Arctic project.

Living on fumes: “Next year it’s really going to come to a head.”
• The Shale Patch Faces Reality (Bloomberg)
Not long ago the oil industry looked like it had dodged a bullet. After the worst bust in a generation cut crude prices from $100 a barrel last summer to $43 in March, the oil market rallied. By June, prices were up 40%, passing $60 for the first time since December. Oil companies that had cut costs began planning to deploy more rigs and drill more wells. “We didn’t think we’d be quite this good,” Stephen Chazen, chief executive officer of Occidental Petroleum, told analysts in May. The runup was short-lived. Fears over weak demand from China, along with rising production in the U.S., Saudi Arabia, and Iraq pushed prices back below $50. In July, even as the summer driving season boosted U.S. gasoline demand close to record highs, oil posted its biggest monthly drop since October 2008.
“The much feared double-dip is here,” Francisco Blanch at Bank of America wrote in a July 28 report. The largest oil companies are reporting their worst results in years. ExxonMobil’s second-quarter net income fell 52%; Chevron’s fell 90%. ConocoPhillips lost $180 million. Billions of dollars in capital spending have been cut, and more layoffs are likely. Part of the problem facing the majors is that they’re producing in some of the most expensive places on earth: deep water and the Arctic. With their healthy cash reserves the majors can hold out for higher prices, even if they’re years away. The same can’t be said for many of the smaller companies drilling in the U.S. shale patch.
Shale producers had bought themselves time by cutting costs, locking in higher prices with oil derivatives, and raising billions from big banks and investors. Many cut drilling costs by as much as 30%, fired thousands of workers, and renegotiated contracts with oilfield service companies. “That postponed the day of reckoning,” says Carl Tricoli at Denham Capital Management. But it’s not clear what’s left to cut. The futures contracts and other swaps and options they bought last year as insurance against falling prices are beginning to expire. During the first quarter, U.S. producers earned $3.7 billion from these hedges, crucial revenue for companies that often outspend their cash flow. “A year ago, you could hedge at $85 to $90, and now it’s in the low $60s,” says Chris Lang at Asset Risk Management. “Next year it’s really going to come to a head.”

Germans need to speak up against hatred.
• German TV Presenter Sparks Debate And Hatred With Support For Refugees (Guardian)
A television presenter in Germany has triggered a huge online debate after calling for a public stand against the growth of racist attacks towards refugees. Anja Reschke used a regular editorial slot on the evening news programme to lambast hate-filled commentators whose language she said had helped incite arson attacks on refugee homes. She said she was shocked at how socially-acceptable it had become to publish racist rants under real names. “Until recently, such commentators were hidden behind pseudonyms, but now these things are being aired under real names,” she said. “Apparently it’s no longer embarrassing anymore – on the contrary – in reaction to phrases like ‘filthy vermin should drown in the sea’, you get excited consensus and a lot of ‘likes’.
If up until then you had been a little racist nobody, of course you suddenly feel great,” she said in the two-minute commentary. The segment went viral within minutes of being broadcast, and by Thursday afternoon had been viewed more than 9m times, clocked up over 250,000 likes, 20,000 comments, and had been shared more than 83,000 times on Facebook. Reschke said the “hate-tirades” had sparked “group-dynamic processes” that had led to “a rise in extreme rightwing acts”. Calling on “decent” Germans to act, she said: “If you’re not of the opinion that all refugees are spongers, who should be hunted down, burnt or gassed, then you should make that known, oppose it, open your mouth, maintain an attitude, pillory people in public.”
Her appeal came a day after the head of the intelligence service, Hans-Georg Maassen, warned that a small group of rightwing extremists was in danger of escalating a wave of anti-asylum attacks. He made specific mention of the group Der III Weg or “The Third Way”, calling them “dangerous rabble-rousers”.

Europe’s biggest moral failure continues unabated. Blaming Tsipras, though, is nonsense.
• Migrant Crisis Overwhelms Greek Government (Kathimerini)
Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras is due to chair an emergency government meeting on Friday to address the refugee crisis facing Greece, which has been compounded by serious funding problems in Athens. The meeting was called in the wake of European Commissioner for Migration and Home Affairs Dimitris Avramopoulos informing Tsipras that Greece was missing out on more than €500 million in European Union funding because it has failed to set up a service to absorb and allocate this money for immigration and asylum projects. Kathimerini understands that Avramopoulos has told the prime minister Greece will be given as a down payment 4% of the total funding due over a six-year period. This will be followed by another 3% to cover actions this year.
Tsipras is due to discuss this issue, as well as the soaring number of refugees and migrants reaching Greece, with Alternate Minister for Immigration Policy Tasia Christodoulopoulou and several other cabinet members today. Christodoulopoulou admitted Thursday that the government has so far fallen short on this matter. “At the moment, nongovernmental organizations and charities are covering the gaps left by the state,” she told Mega TV. “Without them things would be worse.” The alternate minister said efforts were continuing to prepare a plot of land in Votanikos, near central Athens, so some 400 refugees currently living in tents in Pedion tou Areos park could be housed there. Authorities are currently carrying out work aimed at making the new site livable.
The refugees, including dozens of children, will be housed in prefabricated structures as well as large tents at Votanikos. Christodoulopoulou said the new site would operate as a reception, not detention, center. This means that up to 600 people who will be able to live there will be allowed to leave and enter the camp freely. The magnitude of the problem facing Greece was underlined by the United Nations on Thursday. A UN Refugee Agency (UNHCR) official told Agence-France Presse that by the end of July, around 224,000 refugees and migrants had arrived in Europe by sea and that of those, some 124,000 landed in Greece. More than 2,100 people have drowned or gone missing.

Margaret!!
• It’s Not Climate Change, It’s Everything Change (Margaret Atwood)
Oil! Our secret god, our secret sharer, our magic wand, fulfiller of our every desire, our co-conspirator, the sine qua non in all we do! Can’t live with it, can’t right at this moment live without it. But it’s on everyone s mind. Back in 2009, as fracking and the mining of the oil/tar sands in Alberta ramped up, when people were talking about Peak Oil and the dangers of the supply giving out, I wrote a piece for the German newspaper Die Zeit. In English it was called The Future Without Oil. It went like this:
The future without oil! For optimists, a pleasant picture: let’s call it Picture One. Shall we imagine it? There we are, driving around in our cars fueled by hydrogen, or methane, or solar, or something else we have yet to dream up. Goods from afar come to us by solar-and-sail-driven ship, the sails computerized to catch every whiff of air, or else by new versions of the airship, which can lift and carry a huge amount of freight with minimal pollution and no ear-slitting noise. Trains have made a comeback. So have bicycles, when it isn t snowing; but maybe there won’t be any more winter.
We ve gone back to small-scale hydropower, using fish-friendly dams. We re eating locally, and even growing organic vegetables on our erstwhile front lawns, watering them with greywater and rainwater, and with the water saved from using low-flush toilets, showers instead of baths, water-saving washing machines, and other appliances already on the market. We’re using low-draw lightbulbs; incandescents have been banned and energy-efficient heating systems, including pellet stoves, radiant panels, and long underwear. Heat yourself, not the room is no longer a slogan for nutty eccentrics: it’s the way we all live now.









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle August 7 2015