
Dorothea Lange Water supply in squatter camp near Calipatria CA 1937



A Debt Rattle largely filled with central banks and various opinions and assumptions about them. Just happened that way.
• China’s Central Bank Says No Basis for Continued Yuan Decline (BBG)
China’s central bank governor said there was no basis for continued depreciation of the yuan as the balance of payments is good, capital outflows are normal and the exchange rate is basically stable against a basket of currencies, according to an interview published Saturday in Caixin magazine. Zhou Xiaochuan dismissed speculation that China planned to tighten capital controls and said there was no need to worry about a short-term decline in foreign-exchange reserves, adding that the country had ample holdings for payments and to defend stability. The comments come as Chinese financial markets prepare to reopen Monday after the week-long Lunar New Year holiday.
The country’s foreign-exchange reserves shrank to the smallest since 2012 in January, signaling that the central bank sold dollars as the yuan fell to a five-year low. The weakening exchange rate and declining share markets in China have fueled global turmoil and helped send world stocks to their lowest level in more than two years. The bank will not let “speculative forces dominate market sentiment,” Zhou said, adding that a flexible exchange rate should help efforts to combat speculation by effectively using “our ammunition while minimizing costs.”Policy makers seeking to support the yuan amid slower growth and increasing outflows have been using up reserves. The draw-down has continued since the devaluation of the currency in August and holdings fell by $99.5 billion in January to $3.23 trillion, according to the central bank on Feb. 7.
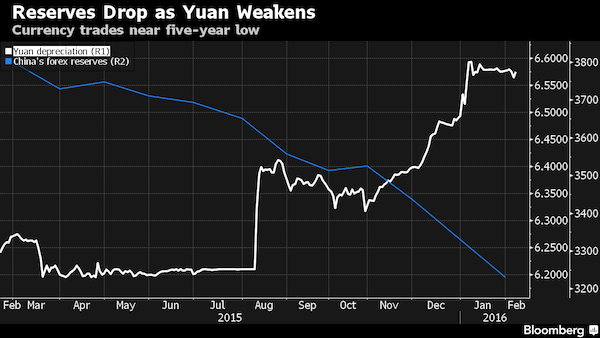
The stockpile slumped by more than half a trillion dollars in 2015. China has no incentive to depreciate the currency to boost net exports and there’s no direct link between the nation’s GDP and its exchange rate, Zhou said. Capital outflows need not be capital flight and tighter controls would be hard to implement because of the size of global trade, the movement of people and the number of Chinese living abroad, he added. The country will not peg the yuan to a basket of currencies but rather seek to rely more on a basket for reference and try to manage daily volatility versus the dollar, Zhou said. The bank will also use a wider range of macro-economic data to determine the exchange rate, he said.

By his own admission, no clue: “..what we have to do is to devise new tools, rather than give up the goal..”
• Why Kuroda’s ‘Bazooka’ May Be Out of Ammunition (WSJ)
Bank of Japan Gov. Haruhiko Kuroda once awed the markets. Now he looks like just another central banker running out of options. Mr. Kuroda took the helm of the BOJ in March 2013, vowing to do whatever it takes to vault Japan out of more than a decade of deflation. He fired one “monetary bazooka” and then another, seeming to bend markets to his will both times. Japanese stocks rose, and the yen sank, key developments for “Abenomics,” Prime Minister Shinzo Abe’s growth program. But the introduction of negative interest rates two weeks ago failed to impress—except in the minds of some as confirmation that what the BOJ had been doing for three years wasn’t working. Japan’s economy is sputtering and Mr. Kuroda’s primary target—2% inflation—is as far away as ever, heightening skepticism about the limits of monetary policy and the fate of Abenomics.
It is an ominous development for Mr. Kuroda. He sees Japan’s long bout of deflation as a psychological disorder as much as an economic disease. His job as BOJ chief has been part central banker, part national psychologist. It has been all about creating confidence. From the start, many said he was attempting the impossible. Deflation is notoriously difficult to escape, and had taken deep root in Japan after years of policy missteps. Last summer he invoked a fairy tale to describe his task. “I trust that many of you are familiar with the story of Peter Pan, in which it says, ‘The moment you doubt whether you can fly, you cease forever to be able to do it,’” Mr. Kuroda said in June last year. “Yes, what we need is a positive attitude and conviction.”
Answering questions in parliament Friday, Mr. Kuroda dismissed claims that the introduction of negative interest rates were to blame for the recent stock market selloff. He pointed to global market volatility, and said the negative rates have had their intended effects, driving down yields on short- and long-term government bonds. “I believe those effects will steadily spread through the economy and prices going forward,” he said. Mr. Kuroda has also repeatedly rejected the notion that the central bank is running out of ammunition, insisting that there is “no limit” to its policy options. “If we judge that existing measures in the tool kit are not enough to achieve the goal, what we have to do is to devise new tools, rather than give up the goal,” he said.

Peter Pan rules.
• BoJ Deputy Says Japan Needs Bolder Measures To Unlock Growth (FT)
The deputy governor of the Bank of Japan has called on the country’s government to pull its weight, as the central bank strains to haul the world’s third-largest economy decisively out of deflation. Last month the BoJ embarked on its latest round of easing, saying it would start charging for excess reserves deposited at the central bank. At the time, it said it wanted to provide a shot of stimulus at a critical moment, just ahead of the annual Spring round of wage negotiations between companies and workers’ groups. In a speech in New York on Friday, deputy governor Hiroshi Nakaso said that the government now needed to do more to boost Japan’s growth potential. He referred to a joint statement on overcoming deflation, signed by the BoJ and the government in January 2013, a few months before the bank embarked on its first round of easing under the current governor, Haruhiko Kuroda.
In it, the central bank pledged to stimulate demand through ultra-aggressive monetary policy while the government promised to pursue ‘all possible’ supply-side reforms. Now that the Bank of Japan has taken monetary easing one step further … I think that the original third arrow of Abenomics, the growth strategy, must also fly faster, he said. The unusually candid speech comes as the success of the mix of the policies pursued by prime minister, Shinzo Abe, remains in the balance. After three separate bursts of monetary stimulus from the BoJ, inflation has gained some momentum while corporate profits have been boosted by a sharp drop in the value of the yen. However, Japan’s potential growth rate remains so low — around or slightly below 0.5%, according to the BoJ’s estimate – that any setback has the potential to tip the country into recession.
Economists at Goldman Sachs expect that the first reading of GDP figures for the fourth quarter, due on Monday, will show an annualised contraction of 1.2% from the third quarter, hit by a slump in consumer spending due to a mild weather and smaller winter bonuses. The BoJ now fears that many cash-hoarding companies are set to resist calls for higher wages, as they assume that inflation will be kept in check by a combination of weak demand, a lower oil price and a stronger currency. The national trades union group, Rengo, has already signalled a less aggressive stance in this year’s negotiations, saying it is aiming at an across-the-board increase of “around 2%” — less than the 2015 demand for “at least” 2%. That could threaten progress toward the BoJ’s sole policy target: an inflation rate of 2%. In December Japan’s consumer price index stood at 0.1%, excluding fresh food, and 0.8% excluding energy.
“The sluggish increase in nominal wages is thought to reflect low productivity growth and the strong deflationary mindset,” said Mr Nakaso. “My answer to what kind of policies are needed, is that both monetary and fiscal policies and structural reforms are indispensable.” Mr Nakaso is likely to make similar remarks during a speech to business leaders next month in Okinawa, according to people familiar with his thinking, imploring the government to take bolder measures to unlock growth. Takuji Okubo, managing director at Japan Macro Advisors, a research boutique, said that the government’s ‘third arrow’ record has been poor, citing a lack of true reform of the labour market, the service sector or the public pension system. He added that the sharp sell-off in the Japanese stock market since the beginning of the year, coupled with a renewed appreciation of the yen, seems strong enough to put an end to the Abenomics boom. “The expiry date has now come to pass,” he said.

“What central bankers are doing now feels like a Jedi trick..”
• Swedish Central Bank Move Creates a Global Shudder (NY Times)
What if the bazooka is shooting blanks? Since the financial crisis, it has been gospel for many investors that some combination of actions by central banks — bond buying, bold promises or flirtations with negative interest rates — would be enough to keep the global economy out of recession. But investors’ distress over the latest volley by a major central bank, the surprise decision on Thursday by the Swedish central bank to lower its short-term rate to minus 0.50% from minus 0.35%, has heightened fears that brazen actions by central bankers are now making things worse, not better. Global stock markets sank, the price of oil plunged to a 13-year low and investors fled to safe haven instruments like gold and United States Treasury bills.
Markets generally embrace conviction and run away from indecision — which is what many see in the policy making of some of the large central banks these days. The Swedish central bank, the Riksbank, for example, has been criticized in the past for prematurely raising rates, and Thursday’s rate cut was opposed by two bank deputies. At the ECB Jens Weidmann, the head of the powerful German Bundesbank, remains at odds with the president, Mario Draghi, in terms of how loose the central bank’s policies should be. And in the United States, the Federal Reserve is seen by some market participants to be wavering in its commitment to higher rates in light of the market turmoil.
[..] “What central bankers are doing now feels like a Jedi trick,” said Albert Edwards, global strategist for Société Générale in London. “Everyone is in a currency war and inflation expectations are collapsing.” In other words, drastic steps by central bankers in Europe, Japan and China to keep their currencies weak and exports strong may not only be counterproductive in terms of stimulating global growth — someone has to buy all those Chinese and Japanese goods — but has other consequences as well. Negative interest rates, for example, are not only bad for bank profits and lending prospects, they can also make savers more fearful, hampering the central aim, which is to get people to spend, not hoard. All of which can lead to a global recession.
A perma-bear like Mr. Edwards is always in possession of a multitude of negative economic indicators to prove his thesis, which, in his case, is a fall of 75% in the S.&P. 500 from its peak last summer. Some are obvious and have been highlighted by most economists, like the increasing interest rates on corporate bonds in the United States — both investment grade and junk. But he also pointed to a recent release from the Fed that showed that loan officers at United States banks said that they had been tightening their loan standards for two consecutive quarters. “You tend to see that in a recession,” Mr. Edwards said. His prediction of a so-called deflationary ice age is still considered a fringe view of sorts, although he did say that a record 950 people (up from 700 the year before) attended his annual conference in London last month. Still, the notion that the global economy has not responded as it should to years of shock policies from central banks is more or less mainstream economic thinking right now.
[..] The well-known bond investor William H. Gross of Janus Capital took up this theme in his latest investment essay, arguing that there was no evidence to show that the financial wealth (and increased levels of debt) created by a long period of extra-low interest rates would spur growth in the real economy. As proof, he cited Japan’s persistent struggles to grow despite near-zero interest rates; subpar growth in the United States; and emerging market problems in China, Brazil and Venezuela. “There is a lot of risk in the global financial marketplace,” Mr. Gross said in an interview on Thursday. “It is incumbent on me to focus on safe assets now.”

Debt is king, and Draghi its oracle.
• Bond Investors Looking Out for Stimulus Hint in Draghi Testimony (BBG)
Investors will look next week for a whiff of confirmation from Mario Draghi that they weren’t wrong to push bond yields to record lows in anticipation of fresh stimulus from the ECB. The ECB president’s speech to European lawmakers in Brussels on Monday will come after a turbulent five days in which global markets exposed a schism in the euro region’s debt markets. German 10-year bund yields approached their record low from April while Portugal’s jumped by the most since May 2012, before Draghi made his famous “whatever it takes” speech in July that year. Investor demand for havens at these lower yields faces a challenge on Feb. 17 when Germany auctions €5 billion ($5.6 billion) of 10-year bonds.
That’s followed the next day by France selling up to €8.5 billion of conventional and inflation-linked bonds. The offerings come while the prospects of slowing growth and depressed inflation are prompting investors to pile into the region’s safer fixed-income assets, driving yields down toward levels that triggered a selloff last April and May. “Investors will keep a close eye for any hints for what type of policy easing will be forthcoming,” said Nick Stamenkovic at broker RIA Capital Markets. “People are plumping for safety, core government bonds and demanding a higher risk premium on peripherals in particular, and also some semi-core bonds. The upcoming auctions outside of Germany will be a good test of sentiment.”

“Pessimism is unwarranted.” Darn, and I though it was time to panic. Finally. They can’t even agree on that.
• There Are Still a Few Tricks Seen Up Central Bankers’ Sleeves
If one line of reasoning for the plunge in bank stocks is that monetary policy has lost its punch, investors would do well to recall a law of modern investing: “Don’t fight the Fed.” As the week draws to a close, some Wall Street economists and strategists say monetary authorities have plenty more tricks up their sleeve – even after more than 635 interest-rate cuts since the financial crisis by Bank of America’s reckoning and with central banks now sitting on more than $23 trillion of assets. “Time and time again policy makers have shown themselves to be bolder and more inventive than asset markets give them credit for,” Stephen Englander, Citigroup’s New York-based global head of Group-of-10 currency strategy, said in a report to clients late on Thursday. “Pessimism is unwarranted.”
His proposal is that officials focus their policy more on boosting demand rather than just increasing liquidity in the hope that consumers and companies will find a need for it. While he thinks targeted lending could help achieve that, he advocates what he calls “cold fusion” in which politicians would cut taxes and boost spending with central banks covering the resulting rise in borrowing by purchasing even more bonds. “The next generation of policy tools is likely to be designed to act more directly on final demand, using persistently below target inflation as a lever to justify policies that will be anathema otherwise,” Englander said. In a similar vein, Hans Redeker at Morgan Stanley in London, is declaring it’s time for central banks to begin using quantitative easing to buy private assets having previously focused on government debt.
“I would actually look into the next step of the monetary toolbox,” Redeker said in a Bloomberg Television interview. “We need to fight demand deficiency.” Critics say that’s the source of the problem. There’s little more bond-buying and rate cutting can do to stoke the real economy. And markets, they say, now recognize that. Part of this week’s pain in markets has stemmed from the concern that the negative interest rates increasingly embraced by the likes of the Bank of Japan and European Central Bank do more harm than good by hitting bank profits. That hasn’t stopped JPMorgan economists led by Bruce Kasman suggesting central banks could cut much deeper without any major side effects so long as they limit the reserves they are targeting. Citigroup said yesterday that Israel, the Czech Republic, Norway and perhaps Canada could also join the subzero club in the next couple of years.

“Look, these are very smart people..”
• Former Dallas Fed President Calls Out Central Banks (CNBC)
Are central banks’ aggressive monetary policies to blame for the today’s economic woes? Former Dallas Federal Reserve President Robert McTeer says yes. Speaking to CNBC’s “Fast Money” this week, McTeer explained that while the Fedis comprised of smart and carefully minded individuals, they dropped the ball when it comes to their current approach. “[The Fed] waited too long to begin the tightening process,” noted the former FOMC member and 36-year veteran of the Federal Reserve system. The central banker’s critique echoed that of other economists, whom have argued that the trillions of cheap dollars flooding the system have exacerbated the current downturn, and made the market addicted to the liquidity.
Known for his prolific writing and plain-speaking style while at the Fed, McTeer has been a critic of the Fed’s ultra-loose monetary policy, which he previously argued stayed too low for too long. However, McTeer admitted that bad luck and unfortunate timing has compounded the current undesirable circumstances. He told CNBC that “as soon as they took the first step [to tighten], international developments overwhelmed the situation.” At that time, China’s slowdown became more pronounced, upsetting markets. McTeer further believes that the Fed’s delay enabled other central banks—from Japan to the European Central Bank—to enact negative interest rates, a policy move with which he disagreed. Now, with international markets in crisis, McTeer says Fed chair Janet Yellen needs to take a more proactive approach in addressing global concerns.
The former central banker advised that “she should probably show more concern [related] to recent market turmoil” when speaking in the future. On Friday, international markets saw a sell-off in Asia where the Nikkei dropped 4.8% to 14,952, its lowest close since October, 2014. Additionally, the yen ended the week down 11%, unwinding some of the massive flight to safety buying that has recently boosted Japan’s currency. The Dow Jones Industrial Average, S&P 500 Index and Nasdaq all posted big gains, and snapped a five day losing streak. At the same time, the market’s latest mantra has become negative interest rates, which have been introduced in Japan and Europe. Earlier this week, Yellen refused to rule out the policy move for the world’s largest economy, but acknowledged the issue needed more study.
Negative rates, however, is an idea McTeer does not endorse. The central bank “is not going to do it, but furthermore they can’t do it,” he noted, speaking of the Fed’s next potential move. In McTeer’s interpretation, negative rates are not an options because the Fed has adopted a new mechanical procedure for establishing the Fed funds rate, which is the interest rate that banks use to calculate overnight loans to other institutions. The rate currently calls for a positivity on bank deposits. McTeer believes that if the Fed tries to go negative, it would take years to re-work the system.

Buybacks then! Solves everything.
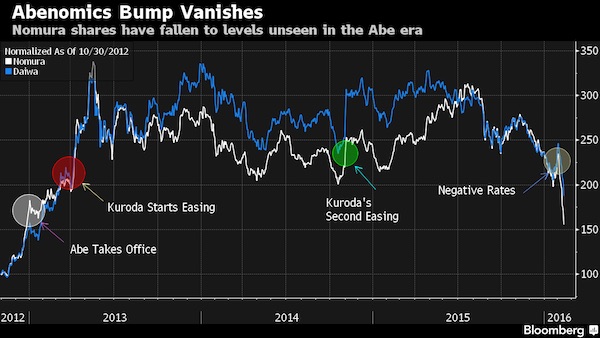
• Nomura Drops to Pre-Abenomics Level as Japan’s Brokers Slump (BBG)
It’s as if Abenomics never happened for Japan’s biggest brokerages. Nomura and Daiwa Securities fell for an eighth straight day in Tokyo as the deepening stock-market rout continues to pummel investment banks around the world. Nomura is now trading below its price when Shinzo Abe became prime minister in December 2012, ushering in an economic-stimulus policy that sparked a stock-market rally and a profit rebound at Japan’s largest securities firm. The selloff may be overdone because brokerages remain stronger than they were before the Abe administration, according to SBI Securities analyst Nobuyuki Fujimoto. “Their fundamentals haven’t deteriorated that much,” Fujimoto said by phone. “The tide will turn as overseas investors in particular decide whether their profitability is really worse than it was before Abenomics.”
Shares of Tokyo-based Nomura closed 9.2% lower Friday, extending their decline to 33% since the company posted worse-than-estimated earnings on Feb. 2. At 446.6 yen, the price is the lowest since Dec. 21, 2012. Daiwa dropped 8.2% to 591.1 yen, the weakest since the month before Bank of Japan Governor Haruhiko Kuroda unveiled his first round of monetary easing in April 2013. An index of securities firms was the third-worst performer on the benchmark Topix, which slumped 5.4%. Investors continued dumping Nomura shares even after Chief Executive Officer Koji Nagai said this week that the company is considering buying back stock while it’s cheap. “The brokerage must also be advising Japanese firms to consider share buybacks, if the CEO’s remarks are any guide,” said Fujimoto. “I wouldn’t be surprised to see companies start announcing such plans soon, which will be beneficial to brokerages.”
Nomura has announced five share buybacks since May 2013, including two last year. The company is now trading at 0.57 times the book value of its assets, the cheapest since November 2012, according to data compiled by Bloomberg. Daiwa has a price-to-book ratio of 0.80 “We’re considering returning profit appropriately” to shareholders, Nagai said in an interview on Tuesday. “There’s no doubt that it’s better for us to do it when they’re cheap,” he said, declining to comment on the timing and size of any buyback.

Oh wait, not everything…
• Deutsche Bank Buyback Sparks Backlash From Newest Investors (BBG)
Investors who scooped up bonds sold by Deutsche Bank last month are pushing for better terms in the bank’s $5.4 billion debt buyback plan, saying they were misled because the German lender failed to disclose its true financial position before the sale, according to people with knowledge of the matter. Some of the bondholders who participated in the $1.75 billion, two-part offering say the bank, which announced a fourth-quarter earnings loss less than two weeks after the sale, should’ve made that disclosure before selling the bonds, the people said, asking not to be identified as the discussions are private. Some investors are so upset that they may raise the issue with regulators, the people said.
The money managers are planning to hold discussions next week to explore their options on how best to challenge the bank, the people said. In addition to raising concern about disclosure, the bondholders are pushing for greater priority and better terms in the bank’s buyback offer announced Friday. Deutsche Bank’s buyback comes as the lender attempts to reassure investors who dumped European bank bonds and shares this week amid concerns over declining earnings and slowing global growth. The lender’s debt in a Bloomberg investment-grade bond index have dropped 2.7% in the past month compared with a 0.4% decline for all bank debt. The $750 million of 4.1% notes sold in January slumped 5.7%.
The firms that bought the biggest piece of the January offering at 100 cents on the dollar are now getting an offer to sell them back to the bank at as much as 97.3 cents, according to calculations by Bloomberg Intelligence analyst Arnold Kakuda. The securities traded at 95.6 cents on Thursday. Deutsche Bank, which unveiled the sale of the bonds on Jan. 8, said on Jan. 21 that it would post a €2.1 billion loss for the fourth quarter after setting aside more money for legal matters and taking a restructuring charge. Moody’s Investors Service cut its long-term debt rating on the bank to Baa1 from A3, citing structural issues that contributed to “weak profitability,” and the expense of maintaining a global capital-market footprint, the ratings firm said in a Jan. 25 statement.

Junk bonds will be back.
• This is How Financial Chaos Begins (WS)
There are over $1.8 trillion of US junk bonds outstanding. It’s the lifeblood of over-indebted corporate America. When yields began to soar over a year ago, and liquidity began to dry up at the bottom of the scale, it was “contained.” Yet contagion has spread from energy, metals, and mining to other industries and up the scale. According to UBS, about $1 trillion of these junk bonds are now “stressed” or “distressed.” And the entire corporate bond market, which is far larger than the stock market, is getting antsy. The average yield of CCC or lower-rated junk bonds hit the 20% mark a week ago. The last time yields had jumped to that level was on September 20, 2008, in the panic after the Lehman bankruptcy. Today, that average yield is nearly 22%! Today even the average yield spread between those bonds and US Treasuries has breached the 20% mark. Last time this happened was on October 6, 2008, during the post-Lehman panic:

At this cost of capital, companies can no longer borrow. Since they’re cash-flow negative, they’ll run out of liquidity sooner or later. When that happens, defaults jump, which blows out spreads even further, which is what happened during the Financial Crisis. The market seizes. Financial chaos ensues. It didn’t help that Standard & Poor’s just went on a “down-grade binge,” as S&P Capital IQ LCD called it, hammering 25 energy companies deeper into junk, 11 of them into the “substantial-risk” category of CCC+ or below. Back in the summer of 2014, during the peak of the wild credit bubble beautifully conjured up by the Fed, companies in this category had no problems issuing new debt in order to service existing debt, fill cash-flow holes, blow it on special dividends to their private-equity owners, and what not. The average yield of CCC or lower rated bonds at the time was around 8%.

Beware: “.. which would take their pension fund contribution rates from an average of about 18% of payroll to nearly 30%..”
• Pension Funds See 20% Spike In Deficit (AP)
Oregon Treasurer and Portland mayoral candidate Ted Wheeler issued a statement last week noting that the state pension fund’s investment returns were 2.1% in 2015. That beat the Standard & Poor’s 500 index and topped the performance of 88% of comparable institutional investment funds. What Wheeler’s statement didn’t mention was that investment returns for the year still fell 5.6 percentage points below the system’s 7.75% assumed rate of return for 2015. That’s terrible news for public employers and taxpayers. It means the pension system’s unfunded liability just increased by another 20% — growing from $18 billion at the end of 2014 to between $21 and $22 billion a year later. That will put renewed upward pressure on payments the system’s 925 public-sector employers are required to make.
Public employers had already been warned to expect maximum increases over the next six years, which would take their pension fund contribution rates from an average of about 18% of payroll to nearly 30%, redirecting billions of dollars out of public coffers and into the retirement system. In reality, those “maximum” increases could be a lot bigger. Milliman Inc., the actuary for the Public Employees Retirement System, told board members at their regular meeting Feb. 5 that the pension fund now has 71 to 72 cents in assets for every $1 in liabilities. That’s an average number across the entire system. Some individual employers’ accounts, including the system’s school district rate pool, are flirting with the 70% threshold that triggers larger maximum rate increases.
Here’s how it works: To prevent rate spikes, PERS limits the biennial change in employers’ payments to 20% of their existing rate. For example, if an employer is required to make contributions equal to 20% of payroll, the rate increase is “collared” to 20% of that number, or a 4 percentage-point increase. That 20% increase is what employers have been warned to expect every other year for the next six years. But when an employer’s funded status falls below 70%, that collar begins to widen on a sliding scale — up to a maximum of 40%.









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle February 14 2016