
DPC Elks Temple (Eureka Club), Rochester, NY 1908

Not a pretty picture.
• How Slow Is US Economic Growth? ‘Close To Zero’ (CNBC)
While 2016’s anemic growth level isn’t an automatic disqualifier for an interest rate increase, the bar just got a little higher. Friday’s GDP reading fell below even the dimming hopes on Wall Street. The 1.2% growth ratein the second quarter combined with a downward revision to the first three months of the year to produce an average growth rate of just 1%. In total, it was far below the Wall Street forecast of 2.6% second-quarter growth and didn’t lend a lot of credence to a Fed statement earlier this week that sounded more confident on the economy. (The Atlanta Fed was much closer, forecasting 1.8%.) In short, they are not numbers upon which a rate hawk would want to hang one’s hat.
“We’re tired of talking about rate hikes when it’s not going to happen for a while,” Diane Swonk of DS Economics told CNBC. “I really think the Fed is sidelined until the end of the year. Or, perhaps, longer. Market expectations for the next Fed hike had been sliding as the release of the GDP report got closer, and they plunged afterward. The fed funds futures market Friday morning was indicating just a 34.4% chance of a rate rise this year, with the next move pushed out until well into 2017. A day earlier, the futures market had moved to just over 50% for a 2016 move. The Fed last hiked in December 2015, which was the first move after eight years of keeping the overnight rate near zero.
To be sure, GDP growth is just one input for the central bank. Ostensibly, the Fed’s mandate is to ensure full employment and price stability, and it has come close to achieving the former while continually falling short of the latter. [..] .. the Fed has been warning about weak business investment, and Friday’s data showed those concerns were well-founded. Business investment fell 2.2%, its third consecutive quarterly decline. Gross private domestic investment tumbled 9.7%, and residential investment, which had been on the rise, reversed course and declined 6.1%, the first decrease since early 2014. Those numbers act as a counterweight to the declining jobless rate, which is down to 4.9%.
“What is really worrying is that pace has still been enough to reduce the unemployment rate further, suggesting that the economy’s potential growth rate could conceivably be close to zero,” Paul Ashworth, chief U.S. economist at Capital Economics, said in a note. The headline jobless rate has been declining, in part, due to a generational low in labor force participation, suggesting that outside a decline in labor slack, there’s little moving economic growth.

And consumer spending is set to contract sharply.
• US Non-Consumer Economy Is Now In A Recession (ZH)
While yesterday’s GDP report was an undisputed disappointment, printing at 1.2% or less than half the 2.5% expected following dramatic historical data revisions, an even more troubling finding emerged when looking at the annual growth rate of GDP. This is how Deutsche Bank’s Dominic Konstam summarized what we showed yesterday:
The latest GDP release favors our hypothesis of an imminent endogenous labor market slowdown over a more optimistic scenario in which productivity will replace employment as the engine for growth. With real GDP growing at just 1.2%, there is little evidence that productivity is ready to do the heavy lifting. We are particularly concerned because annual nominal growth has slowed to 2.4%, essentially a cyclical trough.
He was looking at the following chart (which as the BEA admitted yesterday, may be revised even lower in coming quarters).

However, as it turns out, that was not even the biggest risk. Recall that even as overall GDP rose a paltry 1.2%, somehow the consumer-driven portion of this number soared, with Personal Consumption Expenditures surging at an annualized 2.8% rate, nearly triple that recorded in the first quarter.

This means that the non-consumer part of the US economy subtracted 1.6% from GDP growth in the second quarter. In fact, as Deutsche Bank calculates, on an annual basis, the non-consumer portion of the economy is shrinking, i.e., in a recession, not only in real terms but also in nominal terms.


More parts of Stockman’s upcoming book ‘Trumped’.
• US Government Entitlements – Sixth Biggest Economy On Earth (Stockman)
……..Because the main street economy is failing, the nation’s entitlement rolls have exploded. About 110 million citizens now receive some form of means tested benefits. When social security is included, more than 160 million citizens get checks from Washington. The total cost is now $3 trillion per year and rising rapidly. America’s entitlements sector, in fact, is the sixth biggest economy in the world. Yet in a society that is rapidly aging to the tune of 10,000 baby boom retirees per day, this 50% dependency ratio is not even remotely sustainable. As we show in a later chapter, social security itself will be bankrupt within 10 years. Still, there is another even more important aspect of the mainstream narrative’s absolute radio silence about the monumental entitlements problem.
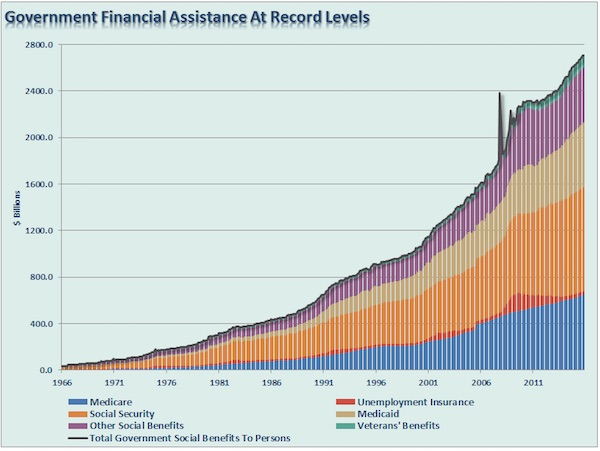
Like in the case of the nation’s 30-year LBO, the transfer payments crisis is obfuscated by the economic blind spots of our Keynesian central banking regime. Greenspan, Bernanke, Yellen and their posse of paint-by-the-numbers economic plumbers have deified the great aggregates of consumer, business and government spending as the motor force of economic life. As more fully deconstructed below, however, this boils down to a primitive notion of bathtub economics. In this bogus economic model, it is assumed that the supply-side of the economy is always fully endowed or even over-provided. By contrast, the perennial problem is purportedly a shortfall of an ether called “aggregate demand”.

Can we please stop talking about it, and do it already?
• Helicopter Money Talk Takes Flight As Bank of Japan Runs Out Of Runway (R.)
In the narrowest sense, a government can arrange a helicopter drop of cash by selling perpetual bonds, which never need to be repaid, directly to the central bank. Economists do not expect this in Japan, but they do see a high chance of mission creep, with the BOJ perhaps committing to buy municipal bonds or debt issued by state-backed entities, giving its interventions more impact than in the treasury bond market, where it is currently buying 80 trillion yen a year of Japanese government bonds (JGBs) from financial institutions. “Compared with government debt, these assets have low trading volume and low liquidity, so BOJ purchases stand a high chance of distorting these markets,” said Shinichi Fukuda, a professor of economics at Tokyo University.
“Prices would have an upward bias, so even if the BOJ bought at market rates, this would be considered close to helicopter money.” Other options include creating a special account at the BOJ that the government can always borrow from, committing to hold a certain%age of outstanding government debt or buying corporate bonds, economists say. With the BOJ’s annual JGB purchases already more than twice the volume of new debt issued by the government, Japan has already adopted something akin to helicopter money, said Etsuro Honda, a former special adviser to the Cabinet and a key architect of Abe’s reflationary economic policy. But it has not been enough to stop consumer prices falling in June at their fastest since the BOJ began quantitative easing in 2013.

And these are half-ass stress tests designed to let banks pass.
• No Clean Bill Of Health For EU Banks In Stress Test (R.)
Banks from Italy, Ireland, Spain and Austria fared worst in the latest European Union stress test, which the region’s banking watchdog said on Friday showed there was still work to do in order to boost credit to the bloc’s economy. Eight years since the collapse of Lehman Brothers sparked a global banking meltdown, many of Europe’s banks are still saddled with billions of euros in poorly performing loans, crimping their ability to lend and putting off investors. “While a number of individual banks have clearly fared badly, the overall finding of the European Banking Authority – that Europe’s banks are resilient to another crisis – is heartening,” Anthony Kruizinga at PwC said. Italy’s Monte dei Paschi, Austria’s Raiffeisen, Spain’s Banco Popular and two of Ireland’s main banks came out with the worst results in the EBA’s test of 51 EU lenders.
“Whilst we recognize the extensive capital raising done so far, this is not a clean bill of health,” EBA Chairman Andrea Enria said in a statement. “There remains work to do.” Italy’s largest lender, UniCredit, was also among those banks which fared badly, and it said it will work with supervisors to see if it should take further measures. Germany’s biggest banks, Deutsche Bank and Commerzbank, were also among the 12 weakest banks in the test, along with British rival Barclays. Monte dei Paschi, Italy’s third largest lender, had been scrambling to pull together a rescue plan and win approval for it from the ECB ahead of the test results. The Italian bank confirmed less than an hour before the results that it had finalised a plan to sell off its entire portfolio of non-performing loans and had assembled a consortium of banks to back a €5 billion capital increase.

More!
• Ireland Jails Three Top Bankers Over 2008 Banking Meltdown (R.)
Three senior Irish bankers were jailed on Friday for up to three-and-a-half years for conspiring to defraud investors in the most prominent prosecution arising from the 2008 banking crisis that crippled the country’s economy. The trio will be among the first senior bankers globally to be jailed for their role in the collapse of a bank during the crisis. The lack of convictions until now has angered Irish taxpayers, who had to stump up €64 billion – almost 40% of annual economic output – after a property collapse forced the biggest state bank rescue in the euro zone. The crash thrust Ireland into a three-year sovereign bailout in 2010 and the finance ministry said last month that it could take another 15 years to recover the funds pumped into the banks still operating.
Former Irish Life and Permanent Chief Executive Denis Casey was sentenced to two years and nine months following the 74-day criminal trial, Ireland’s longest ever. Willie McAteer, former finance director at the failed Anglo Irish Bank, and John Bowe, its ex-head of capital markets, were given sentences of 42 months and 24 months respectively. All three were convicted of conspiring together and with others to mislead investors, depositors and lenders by setting up a €7.2 billion circular transaction scheme between March and September 2008 to bolster Anglo’s balance sheet. Irish Life placed the deposits via a non-banking subsidiary in the run-up to Anglo’s financial year-end, to allow its rival to categorize them as customer deposits, which are viewed as more secure, rather than a deposit from another bank.

“..a couple of generations of Australians will be all the poorer for it…”
• Australia’s Property Market Is Completely Bonkers (Schwab)
House prices are no longer a function of value but rather of how much people are prepared to pay. That in turn is determined by how much banks are willing to lend. And that amount continues to rise. Before the current boom started in 1997, the ratio of household debt to GDP was around 40% — it’s now more than 100% (it’s the same story for household income to household debt). In short, the banks are lending Australians a whole load of cash, and we’re using that cash to bid up the price of an unproductive asset (established housing).
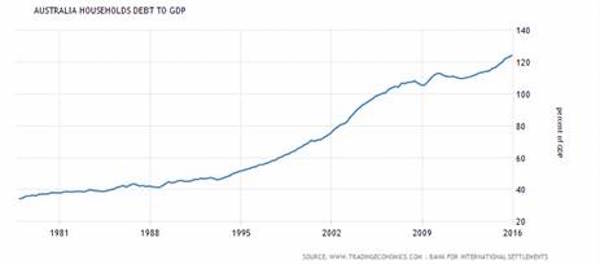
The removal of housing prices from reality is almost total. Most investment advisers will tell you that the price of an asset is dependent on the income that asset generates. For example, the more a company earns (or more specifically, the more investors think that company will earn in the future), the higher its share price will rise. Given house and apartment prices are currently high (based on their terrible net rental yield) one would expect rents to be increasing significantly to justify their price. However, the data tells a very different story. CoreLogic found that Australian dwellings increased in price by 10% in the past year. In Sydney and Melbourne the price rises were even more significant, with Sydney increasing by 13% and Melbourne by 13.9%.
If the market had any degree of rationality, given the market is already expensive, rentals would have needed to rise by around 20% during the year to justify those price increases. However, CoreLogic also reported that Sydney rents were up a mere 0.4% and Melbourne up by 1.7% (both well below the inflation rate). That means if the market was insane a year ago, it’s even worse now. Already overprice property is increasing, in Sydney’s case, 20 times as fast as underlying income. The problem is no one seems to care what the banks do (least of all the government, even though taxpayers are on the hook if any of the big banks fall over, which if the history of banking is anything to go by is a virtual certainty at some point).
Moreover, successive governments’ taxation policies (negative gearing, no capital gains tax, minimal land tax) serve to exacerbate the insanity. How long will the boom last? Potentially some time. There are a lot of vested interests (banks, real estate industry, state governments, the media) who are utterly reliant on the bubble continuing. Sadly, a couple of generations of Australians will be all the poorer for it.

“Economic stability breeds instability. Periods of prosperity give way to financial fragility. With overleveraged banks and no-money-down mortgages still fresh in the mind after the global financial crisis, Minsky’s insight might sound obvious.”
Minsky distinguished between three kinds of financing. The first, which he called “hedge financing”, is the safest: firms rely on their future cashflow to repay all their borrowings. For this to work, they need to have very limited borrowings and healthy profits. The second, speculative financing, is a bit riskier: firms rely on their cashflow to repay the interest on their borrowings but must roll over their debt to repay the principal. This should be manageable as long as the economy functions smoothly, but a downturn could cause distress. The third, Ponzi financing, is the most dangerous. Cashflow covers neither principal nor interest; firms are betting only that the underlying asset will appreciate by enough to cover their liabilities. If that fails to happen, they will be left exposed.
Economies dominated by hedge financing—that is, those with strong cashflows and low debt levels—are the most stable. When speculative and, especially, Ponzi financing come to the fore, financial systems are more vulnerable. If asset values start to fall, either because of monetary tightening or some external shock, the most overstretched firms will be forced to sell their positions. This further undermines asset values, causing pain for even more firms. They could avoid this trouble by restricting themselves to hedge financing. But over time, particularly when the economy is in fine fettle, the temptation to take on debt is irresistible. When growth looks assured, why not borrow more? Banks add to the dynamic, lowering their credit standards the longer booms last.
If defaults are minimal, why not lend more? Minsky’s conclusion was unsettling. Economic stability breeds instability. Periods of prosperity give way to financial fragility. With overleveraged banks and no-money-down mortgages still fresh in the mind after the global financial crisis, Minsky’s insight might sound obvious. Of course, debt and finance matter. But for decades the study of economics paid little heed to the former and relegated the latter to a sub-discipline, not an essential element in broader theories. Minsky was a maverick. He challenged both the Keynesian backbone of macroeconomics and a prevailing belief in efficient markets.

Yanis calling for heads to roll.
• The IMF Confesses It Immolated Greece On Behalf Of The Eurogroup (YV)
[..] an urgent apology is due to the Greek people, not just by the IMF but also by the ECB and the Commission whose officials were egging the IMF on with the fiscal waterboarding of Greece. But an apology and a collective mea culpa from the troika is woefully inadequate. It needs to be followed up by the immediate dismissal of at least three functionaries. First on the list is Mr Poul Thomsen – the original IMF Greek Mission Chief whose great failure (according to the IMF’s own reports never before had a mission chief presided over a greater macroeconomic disaster) led to his promotion to the IMF’s European Chief status.
A close second spot in this list is Mr Thomas Wieser, the chair of the EuroWorkingGroup who has been part of every policy and every coup that resulted in Greece’s immolation and Europe’s ignominy, hopefully to be joined into retirement by Mr Declan Costello, whose fingerprints are all over the instruments of fiscal waterboarding. And, lastly, a gentleman that my Irish friends know only too well, Mr Klaus Masuch of the ECB. Finally, and most importantly, the apology and the dismissals will count for nothing if they are not followed by a complete U-turn over macroeconomic, fiscal and reform policies for Greece and beyond.
Is any of this going to happen? Or will the IMF’s IEO report light up the sky fleetingly, to be forgotten soon? The omens are pointing to the latter. In which case, the EU’s chances of regaining the confidence of its citizens, chances that are already too slim, will run through our leaders’ fingers like thin, white sand.

“..the shift into an era of post-truth politics…”
• Econocracy Has Split Britain Into Experts And Ordinary People (G.)
During the EU referendum debate almost the whole global economic and financial establishment lined up to warn of the consequences of Brexit, and yet 52% of the country ignored them. For many Remain voters it is a clear sign of the shift into an era of post-truth politics. While economists developed rigorous, evidence-based arguments, Leave campaigners slandered experts and appeared to pluck numbers out of the air. Yet they won. Post-truth politics is indeed a scary prospect but to avoid such a future we cannot simply blame “populist politicians” or “ill-informed voters”. We must understand the referendum in its wider context; economists must realise that they are both part of the problem and a necessary part of the solution. We are living in an econocracy.
Such a society seems like a democracy, with political parties and elections, but political goals are expressed in terms of their effect on “the economy”, and economic policymaking is viewed as a technical, not a political, activity. Areas of political life are increasingly delegated to experts, whether at the Bank of England, the government’s behavioural insights team, the Competition Commission or the Treasury. As members of Rethinking Economics, an international student movement seeking to reform the discipline of economics, we are campaigning for a more pluralist, critical and participatory approach. We conduct workshops in schools, run evening crash courses for adults, and this year launched Economy, a website providing accessible economic analysis of current affairs and a platform for lively public debate.
We want economists and citizens to join us in our mission to democratise economics. That’s because the language of economics has become the language of government, and as the experts on “the economy”, economists have secured a position of prestige and authority. Their rise has gone hand in hand with the increasing importance over the 20th century and beyond of the idea of the economy in political and social life. This idea in its modern use took hold only in the 1950s but today GDP growth is one of the central indicators of success for governments, and it is unheard of for a political party to win a general election without being viewed as competent on the economy.
We have also seen the economisation of daily life, so that parts of society as diverse as the arts and healthcare now justify their value in terms of their contribution to the economy. But in this process economists have largely ignored citizens and failed to consider their right to participate in discussion and decision-making.

A bunch of dangerous sickos.
• Network Close To NATO Military Leader Fueled Ukraine Conflict (Spiegel)
The newly leaked emails reveal a clandestine network of Western agitators around the NATO military chief, whose presence fueled the conflict in Ukraine. Many allies found in Breedlove’s alarmist public statements about alleged large Russian troop movements cause for concern early on. Earlier this year, the general was assuring the world that US European Command was “deterring Russia now and preparing to fight and win if necessary.” The emails document for the first time the questionable sources from whom Breedlove was getting his information. He had exaggerated Russian activities in eastern Ukraine with the overt goal of delivering weapons to Kiev. The general and his likeminded colleagues perceived US President Barack Obama, the commander-in-chief of all American forces, as well as German Chancellor Angela Merkel as obstacles.
Obama and Merkel were being “politically naive & counter-productive” in their calls for de-escalation, according to Phillip Karber, a central figure in Breedlove’s network who was feeding information from Ukraine to the general. “I think POTUS sees us as a threat that must be minimized,… ie do not get me into a war????” Breedlove wrote in one email, using the acronym for the president of the United States. How could Obama be persuaded to be more “engaged” in the conflict in Ukraine – read: deliver weapons – Breedlove had asked former Secretary of State Colin Powell. Breedlove sought counsel from some very prominent people, his emails show. Among them were Wesley Clark, Breedlove’s predecessor at NATO, Victoria Nuland, the assistant secretary of state for European and Eurasian affairs at the State Department, and Geoffrey Pyatt, the US ambassador to Kiev.
One name that kept popping up was Phillip Karber, an adjunct assistant professor at Georgetown University in Washington DC and president of the Potomac Foundation, a conservative think tank founded by the former defense contractor BDM. By its own account, the foundation has helped eastern European countries prepare their accession into NATO. Now the Ukrainian parliament and the government in Kiev were asking Karber for help. On February 16, 2015, when the Ukraine crisis had reached its climax, Karber wrote an email to Breedlove, Clark, Pyatt and Rose Gottemoeller, the under secretary for arms control and international security at the State Department, who will be moving to Brussels this fall to take up the post of deputy secretary general of NATO.
Karber was in Warsaw, and he said he had found surreptitious channels to get weapons to Ukraine – without the US being directly involved. According to the email, Pakistan had offered, “under the table,” to sell Ukraine 500 portable TOW-II launchers and 8,000 TOW-II missiles. The deliveries could begin within two weeks. Even the Poles were willing to start sending “well maintained T-72 tanks, plus several hundred SP 122mm guns, and SP-122 howitzers (along with copious amounts of artillery ammunition for both)” that they had leftover from the Soviet era. The sales would likely go unnoticed, Karber said, because Poland’s old weapons were “virtually undistinguishable from those of Ukraine.”

What Trump said.
• America’s Military Is “Lender Of Last Resort” (Cate Long)
America is slowly awakening from its long debt-induced slumber. It has conducted two major wars, a bailout of banks and a major stimulus program without raising taxes to pay for them. Because the Federal Reserve kept interest rates low, it was easy for politicians to continue to raise the debt ceiling and spend without making reductions in other areas of the budget. But those days have ended, the punch bowl has been removed and a new sobriety has rolled into our national capital. Even with its massive deficit problems, America has been providing security for its global allies for decades at no cost to them.
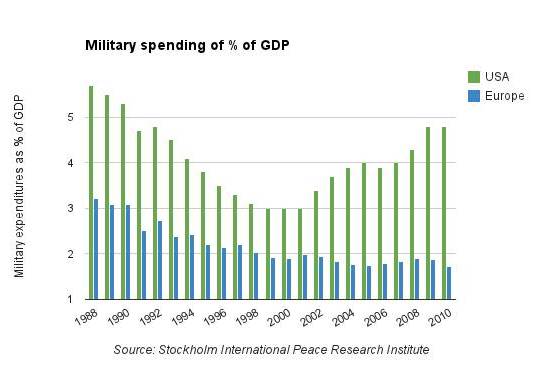
This resulted in spending 4.8% of GDP on U.S. military in 2010, which was ramped up from 3.0% in 2001, according to the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute. In contrast, you can see that European countries spent 1.73% of total GDP on military in 2010, which declined slightly from 1.99% in 2001. America has been subsidizing European military needs largely due to its role in the NATO alliance. The Council on Foreign Relations explains the new problems with this arrangement:
In 2011, then Secretary of Defense Robert Gates warned that ‘there will be dwindling appetite and patience in the U.S. . . . to expend increasingly precious funds on behalf of nations that are apparently unwilling to devote the necessary resources to be serious and capable partners in their own defense.’ France in Mali is now a case in point; the Obama administration is providing only grudging assistance to an under-resourced French intervention.
[…] French military spending…has since 2001 exhibited a marked constancy—one which is inconsistent with the country’s newfound passion for military engagement. (Libya in March 2011 was another example of the French, as well as British, military biting off more than it could chew). It also highlights the need for the Obama administration to address Gates’ prescient concern and to develop a clearer policy foundation for America’s global military ‘lender of last resort’ role.
America is woefully underfunded in infrastructure spending and many other social needs. A big question is whether it can also be the global military “lender of last resort” and still maintain its own house. The military contracting industry in America does create a lot of jobs, but in essence it also gives the benefits away free to its allies. Times must change. America must either charge for these services or understand more clearly what we gain from continued military involvement overseas.









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle July 31 2016