Bill Brandt After the celebration 1934

As Xi Jinping is being written into the Chinese constitution(!), Christopher Balding comes with a long and excellent expose of China’s real debt situation. Makes one wonder what Xi will actually be remembered for.
• Everything We Think We Know About Chinese Finances is Wrong (Balding)
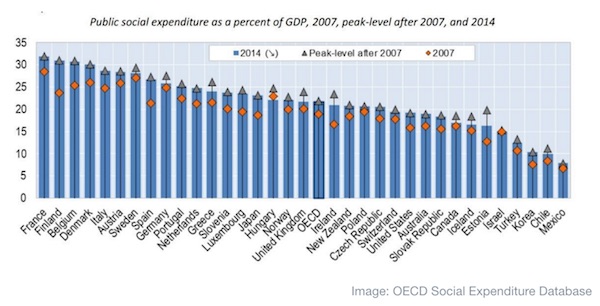
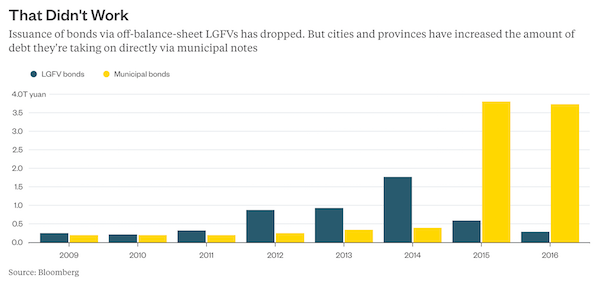
China has long faced doubts about the veracity of its economic data and concerns about its rapidly rising level of indebtedness. While defaults and individual incidents raised questions about debt discrepancies, there was no systematic evidence that the financial system faced systemic misstatement. The People’s Bank of China changed that with a few sentences. By some estimate, the widely watched debt to GDP metric in China has already surpassed 300%. While this is level is worrying given financial stress associated with countries that reached similar levels, this is only half the story. There have long been suspicions that Chinese debt numbers are not entirely accurate but data that would demonstrate a systemic difference from data has never emerged.
However, every time a company collapsed, there would inevitably come out a mountain of undeclared debt. While this raised suspicions, there was never systematic evidence. The Financial Stability Board (FSB), formed after the 2008 Global Financial Crisis, aggregates data for major countries that includes a broader measure of assets by banks, insurance companies, and other major asset holders. According to their data, at the end of 2015, China financial system assets had already reached 401% of GDP.
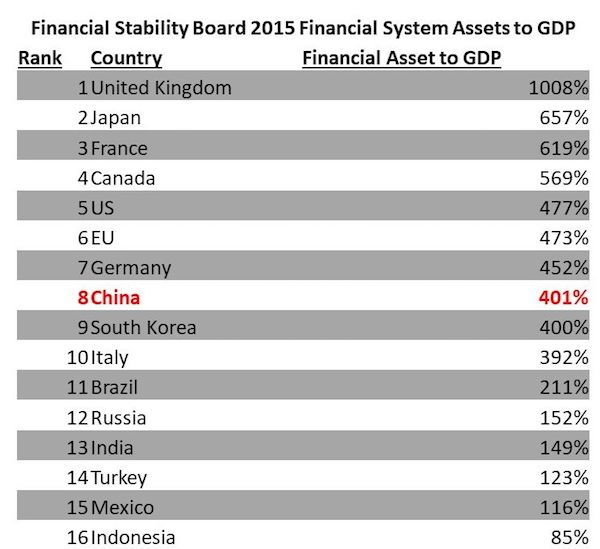
[..] China itself, gave us evidence that its financial data is wildly off. The annual PBOC Financial Stability Report with little fanfare more than doubled its estimates of financial system assets. In a little noticed paragraph the PBOC noted that “the outstanding balance of the off-balance sheet of banking institutions….registered 253.52 trillion yuan.” [..] Nor does the PBOC provide many clues as to what these off balance assets are holding. They do note that roughly two-thirds of the 253 trillion is held as “financial asset services” which may mean everything from structured products sold to clients who believe the bank will stand behind the product, special purpose vehicles holding non-traditional assets, or certain types of financial flows. If we revise our earlier estimate of financial system assets to GDP based upon the new PBOC numbers, China’s position changes dramatically.
[..] If we take the FSB data, add in the new PBOC data, and estimate forward to 2016 Chinese financial system assets are equal to 833% of nominal GDP ahead of Japan at 657% and behind only international banking center United Kingdom at 1008%. This level of asset accumulation imposes real costs. Where as Japan and Europe have close to zero or negative interest rates, China has significantly higher. If we make the simple cheap assumption that these assets earn the short term interbank deposit rate of return of 3.5%, this would imply a financial servicing cost to the economy of 29% of nominal GDP. Conversely, Japan with financial assets of 657% of GDP but using the higher long term loan rates of 1% instead, would need only 6.6% of GDP to service its asset costs.
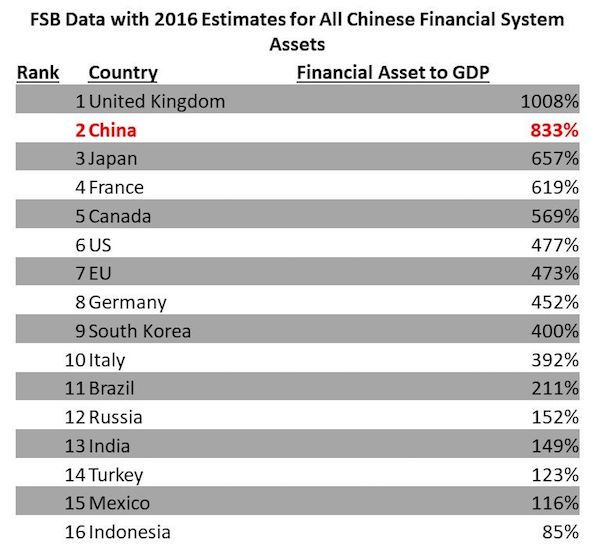
What makes this disclosure concerning is how extreme the numbers are. Even the FSB placed China among developed country financialization and well outside the range of other emerging markets. The new numbers place China on the extremity of all major economies behind only a major international banking center even in front of Japan who has run strongly expansionary monetary policy for years to try and push inflation. Many analysts have raised concerns about asset bubbles and debt growth in China but even the most bearish would have had trouble believing this level of financialization.

Victor Shih from the Mercator Institute for China Studies has a few subtle points on China as well.
• China’s Greatest Vulnerabilities (ZH)
[..] while some categories of shadow finance, including bill finance and non-loan trust credit, have actually declined in recent months (duly noted here), most other categories rose by double digits in percentage terms in the year and half between the end of 2015 and May 2017. Of note, credit held by funds, rose by 116%. So with credit soaring, Shih – like Goldman clients – asks “how much longer can this go on?” and answers that “the amount of interest that debtors in China must pay creditors provides clues on the costs of such a high debt level. If interest servicing exceeds incremental increase in nominal GDP, the debtor would need to pursue one of two courses of action to avoid a crisis. This ultimately goes to the question whether China has hit its “Minsky Moment” or is still in the Ponzi Finance stage, a discussion popularized by Morgan Stanley first in 2014.
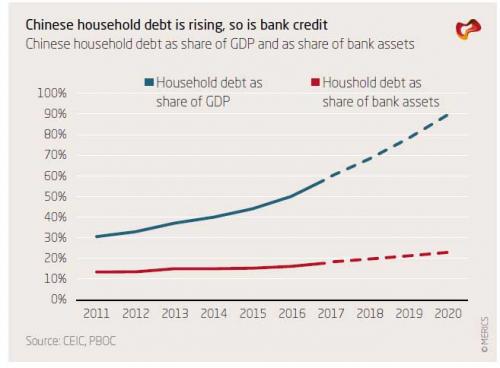
Here are Shih’s observations: First, creditors can extend even more credit to the debtors so that interest payments are serviced with new credit. This mechanism renders China more of a Ponzi unit, which requires new credit to service interest payments. Alternatively, a rising share of income for households, firms, or government will go toward servicing interest. While the first dynamic would cause the acceleration of debt accumulation, the second dynamic is tantamount to a massive tax which will slow growth for an extended period. The problem with both approaches is that China as a whole is a Ponzi unit. And, as Shih calculates and as shown in the chart below, total interest payments from June of 2016 to June of 2017 exceeded incremental increase in nominal GDP by roughly 8 trillion RMB.
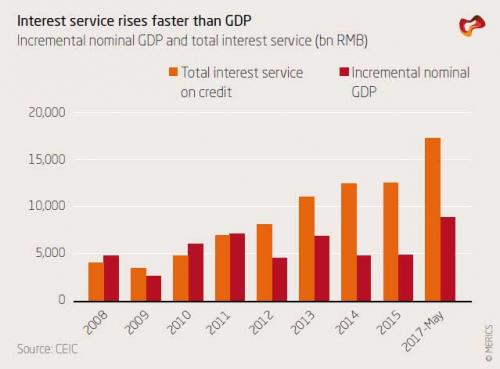
And since we have not see large-scale defaults in China, the new additional interest burden must have been financed in some way. Most likely, the Merics analysis notes, roughly this amount or more was capitalized as new loans, contributing to the rapid rise in total debt. As the chart above shows, this was not always the case. Prior to 2011, incremental nominal GDP roughly matched or even exceeded interest payments. The advent of high-yielding shadow banking led to the explosive growth in interest payments, and thus the need to capitalize interest payments, starting in 2012. This is a dynamic which will drive debt growth in China for years to come, or until the debt bubble ends.
So what ends the bubble? According to the Merics analysis, there are 4 possible channels for a financial crisis in China. First, it should be noted that despite the enormous debt load, a domestically triggered crisis is not likely in the next five years. Trouble is more likely to come from some combination of capital flight and sudden withdrawal of external credit.

Are people finally waking up to what makes societies viable, and what destroys them?
• Ray Dalio Explains Why 3 in 5 Americans Are Struggling (Fortune)
The founder of the world’s largest hedge fund has serious concerns about the U.S. economy. In a LinkedIn note published Monday, Ray Dalio, who founded Bridgewater Associates, said that average statistics about what’s going on in the economy mask deep divisions that could lead to “dangerous miscalculations.” To explain this divide, Dalio splits up the economy into two separate sections: the top 40% and the bottom 60%. He then runs through a number of different statistics showing that the economy for the bottom 60% of the population – or three in five Americans – is much less stable than that for those in the top bracket. For example, Dalio notes that, since 1980, real incomes have been flat or down for the average household in the bottom 60%.
Those in the top 40% also now have an average of 10 times as much wealth as households in the bottom 60% — an increase from six times as much in 1980. Other points include that only about one-third of people in the bottom 60% save any of their income and a similar number have retirement savings accounts. These three in five Americans have also seen an increasing rate of premature death and spend an average of four times less on education than those in the top 40%, Dalio wrote. Those without a college education see lower income rates and higher divorce rates. Dalio wrote that all of these concerns will likely intensify in the next five to 10 years, and that he believes policy makers need to take them into consideration. Dalio added that if he were running the Federal Reserve, he would “keep an eye on the economy of the bottom 60%.”

Can’t stop decentralization.
• To Understand the Next 10 Years, Study Spain (Krieger)
Some of you may be confused as to why a U.S. citizen living in Colorado has become so completely obsessed with what’s going on in Spain. Bear with me, there’s a method to my madness. I believe what’s currently happening in Spain represents a crucial microcosm for what we’ll see sweep across the entire planet over the next ten years. Some of you will want to have a discussion about who’s right and who’s wrong in this particular affair, but that’s besides the point. It doesn’t matter which side you favor, what matters is that Madrid/Catalonia is an example of the forces of centralization duking it out with forces of decentralization. Madrid represents the nation-state as we know it, with its leaders claiming Spain is forever indivisible according to the constitution.
Madrid has essentially proclaimed there’s no possible avenue to independence from a centralized Spain even if various regions decide in large number they wish to be independent. This sort of attitude will be seen as unacceptable and primitive by increasingly large numbers of humans in the years ahead. Catalonia should be seen as a canary in the coal mine. The forces of decentralization are rising, but entrenched centralized institutions and the bureaucrats running them will become increasingly terrified, panicked and oppressive. As I’ve discussed, this isn’t coming out of nowhere. Humanity’s current established centralized institutions and nation-states have become clownishly corrupt, merely existing to protect and enrich the powerful/connected as opposed to benefiting the population at large.
As such, legitimacy has been shattered and people have begun to demand a new way. Whether we see this with the rising popularity of Bitcoin, or the UK decision to leave the EU, evidence is everywhere and we’ve already passed the point of no return. This is precisely why EU leaders are rallying around Madrid. They’re scared to death and fear they might be next. They’re probably right.

Maybe this is good, though one must wonder why the case wasn’t brought before a UK court.
• HSBC Trader’s Conviction Will Rattle $5 Trillion FX Market (BBG)
Global currency traders and compliance officers who monitor them were put on high alert after a New York jury convicted a former HSBC executive of fraud for front-running a large client order. The verdict is a victory for U.S. prosecutors in their first attempt to hold individuals accountable since a global currency-rigging probe that led to banks paying more than $10 billion in penalties. Mark Johnson faces a maximum sentence of 20 years in prison, although he’s likely to get much less. Traders will almost certainly come under pressure to avoid conduct that could be seen as harming their clients and profiting unfairly at their expense, said Mayra Rodriguez Valladares, a former foreign-exchange analyst for the Federal Reserve Bank of New York.
“Front-running is a crime,” she said. “This should be a lesson to senior executives that they should invest in more training of ethics for traders and more in systems to detect irregularities.” The verdict is likely to echo worldwide. Although Johnson, HSBC’s global head of foreign exchange in 2011, was in New York at the time of the transaction, the trade was executed primarily in London, where Johnson’s co-defendant, Stuart Scott, was overseeing it. Scott, the bank’s former head of currency trading in Europe, remains in the U.K. as he fights extradition to the U.S. “This conviction will embolden the U.S. in other cases,” said Peter Henning, a law professor at Wayne State University in Detroit. “The U.S. authorities have shown they’re able to police global markets.”
“At its very essence,” he added, “this was a theft case.” Johnson, the first banker to go on trial following the investigation over foreign-exchange trading, was convicted of defrauding Cairn Energy Plc in what prosecutors said was a clear case of front-running the company’s $3.5 billion order. London-based HSBC wasn’t accused of wrongdoing, but the bank has been under investigation over currency trading and is in talks with the Justice Department and U.S. regulators to resolve the matters, according to a July 31 regulatory filing.

An absolutely crazy story. 145 Americans die every day from opioid overdoses.
• The Family That Built an Empire of Pain (New Yorker)
According to Forbes, the Sacklers are now one of America’s richest families, with a collective net worth of thirteen billion dollars—more than the Rockefellers or the Mellons. The bulk of the Sacklers’ fortune has been accumulated only in recent decades, yet the source of their wealth is to most people as obscure as that of the robber barons. While the Sacklers are interviewed regularly on the subject of their generosity, they almost never speak publicly about the family business, Purdue Pharma—a privately held company, based in Stamford, Connecticut, that developed the prescription painkiller OxyContin. Upon its release, in 1995, OxyContin was hailed as a medical breakthrough, a long-lasting narcotic that could help patients suffering from moderate to severe pain. The drug became a blockbuster, and has reportedly generated some thirty-five billion dollars in revenue for Purdue.
But OxyContin is a controversial drug. Its sole active ingredient is oxycodone, a chemical cousin of heroin which is up to twice as powerful as morphine. In the past, doctors had been reluctant to prescribe strong opioids—as synthetic drugs derived from opium are known—except for acute cancer pain and end-of-life palliative care, because of a long-standing, and well-founded, fear about the addictive properties of these drugs. “Few drugs are as dangerous as the opioids,” David Kessler, the former commissioner of the Food and Drug Administration, told me. Purdue launched OxyContin with a marketing campaign that attempted to counter this attitude and change the prescribing habits of doctors. The company funded research and paid doctors to make the case that concerns about opioid addiction were overblown, and that OxyContin could safely treat an ever-wider range of maladies.
Sales representatives marketed OxyContin as a product “to start with and to stay with.” Millions of patients found the drug to be a vital salve for excruciating pain. But many others grew so hooked on it that, between doses, they experienced debilitating withdrawal. Since 1999, two hundred thousand Americans have died from overdoses related to OxyContin and other prescription opioids. Many addicts, finding prescription painkillers too expensive or too difficult to obtain, have turned to heroin. According to the American Society of Addiction Medicine, four out of five people who try heroin today started with prescription painkillers. The most recent figures from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention suggest that a hundred and forty-five Americans now die every day from opioid overdoses.

They’re everywhere.
• America’s Forever Wars (NYT)
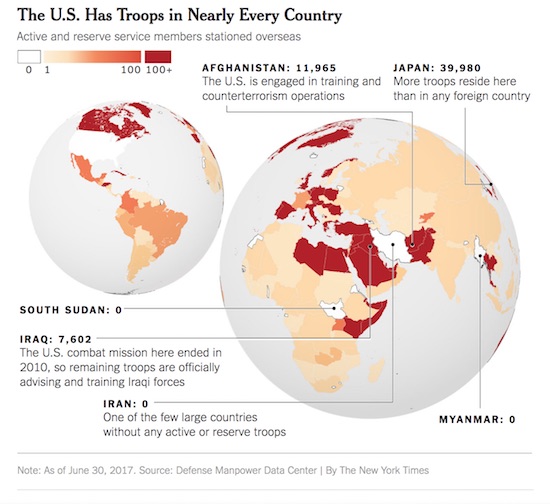
The United States has been at war continuously since the attacks of 9/11 and now has just over 240,000 active-duty and reserve troops in at least 172 countries and territories. While the number of men and women deployed overseas has shrunk considerably over the past 60 years, the military’s reach has not. American forces are actively engaged not only in the conflicts in Afghanistan, Iraq, Syria and Yemen that have dominated the news, but also in Niger and Somalia, both recently the scene of deadly attacks, as well as Jordan, Thailand and elsewhere.
An additional 37,813 troops serve on presumably secret assignment in places listed simply as “unknown.” The Pentagon provided no further explanation. There are traditional deployments in Japan (39,980 troops) and South Korea (23,591) to defend against North Korea and China, if needed, along with 36,034 troops in Germany, 8,286 in Britain and 1,364 in Turkey — all NATO allies. There are 6,524 troops in Bahrain and 3,055 in Qatar, where the United States has naval bases.

A quantum computer would turn the world upside down.
• China Speeds Ahead Of US As Quantum Race Escalates (McC.)
U.S. and other Western scientists voice awe, and even alarm, at China’s quickening advances and spending on quantum communications and computing, revolutionary technologies that could give a huge military and commercial advantage to the nation that conquers them. The concerns echo – although to a lesser degree – the shock in the West six decades ago when the Soviets launched the Sputnik satellite, sparking a space race. In quick succession, China in recent months has utilized a quantum satellite to transmit ultra-secure data, inaugurated a 1,243-mile quantum link between Shanghai and Beijing, and announced a $10 billion quantum computing center. “To me, what is alarming is the level of coordination of what they’ve done,” said Christopher Monroe, a physicist and pioneer in quantum communication at the University of Maryland.
Perhaps more than the accomplishments of the Chinese scientists, it is the resources that China is pouring into the research into how atoms, photons and other basic molecular matter can harness, process and transmit information. “It doesn’t necessarily mean that their scientists are better,” said Martin Laforest, a physicist and senior manager at the Institute for Quantum Computing at the University of Waterloo in Ontario, Canada. “It’s just that when they say, ‘We need a billion dollars to do this,’ bam, the money comes.” The engineering hurdles that China has cleared for quantum communication means that the United States will lag in that area for years.
But building a functioning quantum computer sets forth different kinds of challenges than mastering quantum communication, and may involve creating materials and processes that do not yet exist. Once thought to be decades off, scientists now presume a quantum computer may be built in a decade or less. The stakes are so high that advances by the U.S. government remain secret. “We don’t know exactly where the United States is. I fervently hope that a lot of this work is taking place in a classified setting,” said R. Paul Stimers, a lawyer at K&L Gates, a Washington law firm, who specializes in emerging technologies. “It is a race.”

“..its residues were recently found in 45% of Europe’s topsoil – and in the urine of three quarters of Germans tested, at five times the legal limit for drinking water.”
Seems a simple case. But it is not.
• EU On Brink Of Historic Decision On Pervasive Glyphosate Weedkiller (G.)
A pivotal EU vote this week could revoke the licence for the most widely used herbicide in human history, with fateful consequences for global agriculture and its regulation. Glyphosate is a weedkiller so pervasive that its residues were recently found in 45% of Europe’s topsoil – and in the urine of three quarters of Germans tested, at five times the legal limit for drinking water. Since 1974, almost enough of the enzyme-blocking herbicide has been sprayed to cover every cultivable acre of the planet. Its residues have been found in biscuits, crackers, crisps, breakfast cereals and in 60% of breads sold in the UK. But environmentalists claim that glyphosate is so non-selective that it can even kill large trees and is destructive to wild and semi-natural habitats, and to biodiversity.
The CEO of the Sustainable Food Trust, Patrick Holden, has said that a ban “could be the beginning of the end of herbicide use in agriculture as we know it, leading to a new chapter of innovation and diversity”. But industry officials warn of farmers in open revolt, environmental degradation and crops rotting in the fields if glyphosate is banned. Alarm at glyphosate’s ubiquity has grown since a 2015 study by the World Health Organisation’s IARC cancer agency found that it was “probably carcinogenic to humans”. More than a million people have petitioned Brussels for a moratorium. On Tuesday, MEPs will vote on a ban of the chemical by 2020 in a signal to the EU’s deadlocked expert committee, which is due to vote on a new lease the next day.
Anca Paduraru, an EC spokeswoman, said that a decision was needed before 15 December or “for sure the European commission will be taken to court by Monsanto and other industry and agricultural trade representatives for failing to act. We have received letters from Monsanto and others saying this.” France is resisting a new 10-year licence. Spain is in favour. Germany is in coalition talks and likely to abstain. The UK would normally push for a new lease of the licence but is less engaged due to Brexit. There may not be a qualified majority for any outcome.

And the EU dithers on glyphosate. Tragic species.
• Hidden Danger of Ecological Collapse (CP)
Is human society, en mass, committing suicide? The answer could be yes, humankind is committing harakari in the wide-open spaces for all to see, but nobody has noticed. Until now, as insect losses forewarn of impending ecosystem collapse. Loss of insects is certain to have deleterious effects on ecosystem functionality, as insects play a central role in a variety of processes, including pollination, herbivory and detrivory, nutrient cycling, and providing a food source for higher trophic levels such as birds, amphibians, and mammals. Harkening back to the Sixties, a strikingly similar issue was identified in Rachel Carson’s famous book Silent Spring (1962), the most important environmental book of the 20th century that exposed human poisoning of the biosphere through wholesale deployment of myriad chemicals aimed at pest control.
Carson’s fictional idyllic American town enriched with beautiful plant and animal life suddenly experienced a “strange blight,” leaving a swathe of inexplicable illnesses, birds found dead, farm animals unable to reproduce, and fruitless apple trees, a strange lifelessness. She wrote: “A grim specter has crept upon us to silence the voices of spring.” Today, scientists do not know the specific causes but speculate it could be simply that there is no food for insects; alternatively, the issue could be, specifically as well as more likely, exposure to chemical pesticides or maybe a combination, meaning too little food/too much pesticide. Not only that, flower-rich grasslands, the natural habitat for insects, have declined by 97% since early-mid 20th century whilst industrial pesticides literally cover the world.
Rachel Carson would be floored. That’s a sure-fire guaranteed formula for a tragic ending. Nature doesn’t have a snowball’s chance in hell.