Gottscho-Schleisner New York City views. Looking down South Street 1933



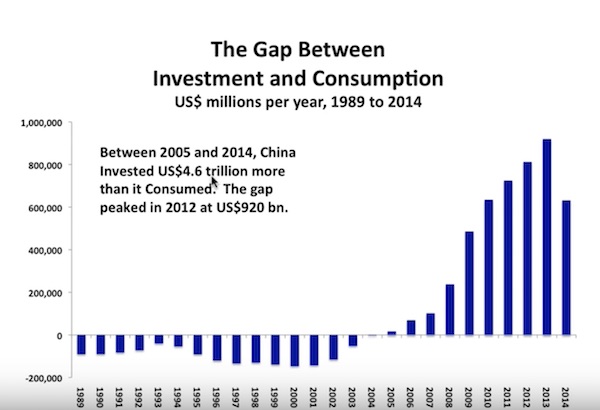
“Perhaps not since the Pharaohs built the pyramids with slave labour has investment made up such a large share of a country’s economy and household consumption made up so little..”
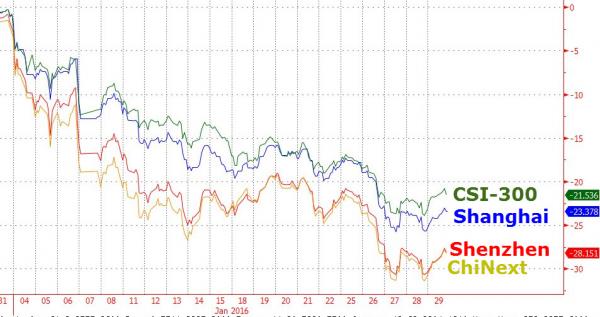
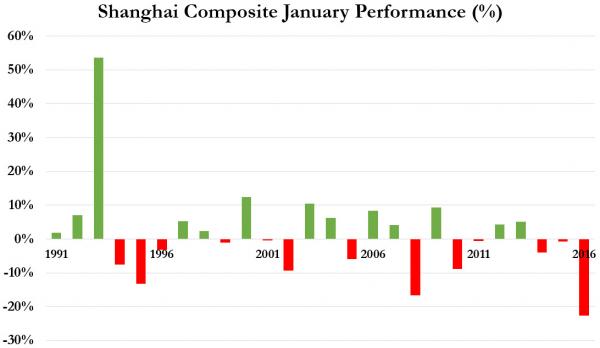
• China’s Hard Landing Began Last Year, And It’s Going To Get Worse (SCMP)
Economist and financial author Richard Duncan believes China’s economy entered into a hard landing in 2015, with the slowdown set to deepen into a slump that will prove to be “severe and protracted”. At its core, a growth model that relied too heavily on investment and exports has left the economy deeply imbalanced, with few drivers that can now take up the slack. Duncan has published a series of videos explaining why, in his opinion, China’s economic development model of export-led and investment-driven growth is now in crisis. The South China Morning Post brings you the second video in that series.
“Perhaps not since the Pharaohs built the pyramids with slave labour has investment made up such a large share of a country’s economy and household consumption made up so little,” Duncan said. “This enormous gap between investment and consumption means China’s economy is now wildly unbalanced.” Underscoring the scale of China’s reliance on investment as an engine of growth, consider how much it has ramped up spending in this area in just a few short years, compared to that of the US, the world’s largest economy. In 2014, investment in the US was US$177 billion higher than 2007, a growth rate of 6%. In 2014, the level of investment in China was US$3.2 trillion more than it was in 2007, representing growth of 236%.

Too much capital is fleeing.
• China’s Latest Export: Broken Deals (WSJ)
China’s global deal-making boom is coming undone. The mystery-shrouded Anbang Insurance is leading the way. It moved a step closer to hitting the trifecta of broken deals this week, just days after a major Chinese construction-equipment maker bailed on its bid to buy U.S. crane maker Terex. Announced overseas deals by Chinese companies topped 2015’s record before this year was half over, which would make China the world’s biggest buyer of foreign companies for the first time ever, according to Dealogic. Chinese companies have also failed to close on more deals than ever before, according to Dealogic.
It’s not a coincidence that the boom in Chinese overseas deal making occurred while businesses and individuals were pouring cash overseas, either to avoid an expected depreciation of the yuan or just to get assets out of the reach of Beijing. And the recent failures have happened while Beijing acts to stem the flow of these funds. That is just part of the weirdness that surrounds many of these deals, and their demise. Another is the opaque nature of the companies involved and the government owners or regulators that determine what is and isn’t allowed. Last are the reasons behind the deals, which have foreign regulators on edge. The latest deal on the ropes is Anbang’s planned $1.57 billion acquisition of U.S. insurer Fidelity & Guaranty Life, one of the biggest sellers of fixed indexed annuities.
Regulators in the U.S. have demanded but haven’t gotten detailed financial information from Anbang. Fidelity says it expects Anbang will try again to get the deal approved. It isn’t surprising that the company hasn’t provided the requested information. Efforts to figure out Anbang’s corporate structure or where its cash came from have so far failed to yield much clarity. This is the third proposed Anbang deal to run into trouble. First was its effort to buy Starwood Hotels & Resorts Worldwide Inc. After bidding up the price and threatening a rival deal, Anbang pulled out suddenly with little explanation.

Weather.
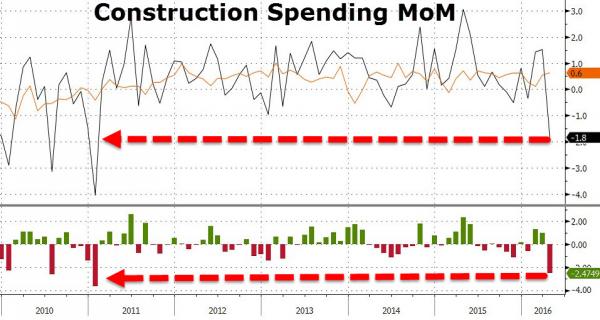
• US Construction Spending Collapses – Worst April Since 2009 (ZH)
Following a hope-strewn bounce in February and March, US Construction Spending plunged 1.8% in April (massively worse than the expected 0.6% rise). This is the biggest monthly drop since January 2011 as while religious construction surged 9.6%, Commercial, Healthcare, and Education construction all plunged with Communications and highway building collapsing 7.7% and 6.5% respectively. We are sure weather will be blamed but the 1.5% drop in residential construction is rather notable for an April – it is the weakest April since 2009.

Lend only to the rich.
• Banks’ Embrace of Jumbo Mortgages Means Fewer Loans for Blacks, Hispanics (WSJ)
Last decade’s financial crisis left many losers in banking. One winner is the jumbo. The biggest U.S. banks are tilting toward these high-dollar mortgages as they overhaul loan operations. And jumbo loans, which were less important during the subprime-loan boom, are helping banks take on less risk, as mandated by regulators in the postcrisis era. These loans, however, could put banks at odds with another federal regulatory mandate—one that says lenders should serve a racially diverse set of customers. As they approve relatively more jumbos, major banks are granting fewer mortgages to African-Americans and Hispanics than just before the crisis, a Wall Street Journal analysis found.
For banks, “it’s one of those damned if you do, damned if you don’t situations,” said Stu Feldstein, president at SMR Research Corp., a mortgage-research firm in Hackettstown, N.J. The Journal analyzed data on every mortgage approval reported to the federal government for home purchases in 2007 and 2014, the most recent available, including borrower race or ethnicity. In that period, each of the 10 biggest U.S. retail banks increased the share of its mortgage approvals that are jumbos. Jumbos, loans above $417,000 in most markets, are attractive because they typically feature high credit scores, big down payments and low default rates. And they aren’t linked to the government programs that cost banks tens of billions of dollars in fines related to the subprime-loan debacle.

Note: it’ll take the entire weekend.
• Brexit, Spexit, Grexit and Frexit Could All Collide In June 23 Weekend (MW)
The hedge funds will have prepped their positions. The investment banks will have ordered in pizza and extra coffee ready for a long night of dealing. Exit polls will have been commissioned, and currency traders will be ready to buy or sell sterling as soon as they start getting a clear idea of whether Britain has voted to stay in or get out of the EU on June 23. But hold on. In fact, it is not just the risk of Brexit that the markets need to be worrying about. In truth, the real drama is going to come over a long and difficult weekend, leading up to potentially wild day in European assets on Monday, June 27. Why? Over that weekend, Spanish voters will go back to the polls in another attempt to settle on a government, which may well see the far-left Podemos group make big gains.
Greece will be struggling to find the money to pay back its latest debts. And if the strikes in France escalate, the country may be close to running out of its strategic fuel reserves – and approaching a total meltdown. Brexit, Spexit, Grexit, and Frexit could all collide. The result? A car crash for the European markets. Brexit remains the most pressing worry for investors, and rightly so. With three weeks until the vote, the polls remain very close. The latest sample for the Daily Telegraph showed a five-point lead for “Remain,” and most have showed the two camps within five to 10 points of each other. But who knows what is going on? The UK hasn’t had a referendum like this for a generation. No one knows what questions to ask, what demographics to target and which side will be better at getting its people to the polling booths on the day.
Either side could win comfortably. Here is the interesting point, however. It may take until the weekend to work out what has happened. The TV networks have decided against an extensive exit poll, on the grounds that they don’t know how to make it accurate. The hedge funds are reported to be spending a lot of money on private exit polls, and the currency markets will tell us what those results look like.

Brilliant: “I think I would be a great uniter. I think that I would have great diplomatic skills; I would be able to get along with people very well,” Trump said. “I had great success [in my life]. I get along with people. People say, ‘Oh gee, it might be tough from that standpoint’, but actually I think the world would unite if I were the leader of the United States.”
• Donald Trump To Visit UK On Day Of EU Referendum Result
Donald Trump, the presumptive Republican nominee in the US presidential election, has confirmed he is to visit the UK later this month to attend the official reopening of his hotel and golf resort in Scotland. The billionaire property developer will be at the Turnberry hotel at the golf course in Ayrshire on 24 June for its official relaunch following a £200m redevelopment. Trump’s announcement throws up the question of whether David Cameron will meet him, as the visit comes the day after the UK’s referendum on EU membership on 23 June – a vote some polls suggest the prime minister faces losing. The Turnberry hotel, which Trump bought in 2014 for £35m, opened to guests on Wednesday. It features a £3,500-a-night presidential suite and, from August, the Donald J Trump ballroom – “the most luxurious meeting facility anywhere in Europe”, according to his publicists.
“Very exciting that one of the great resorts of the world, Turnberry, will be opening today after a massive £200m investment. I own it and I am very proud of it,” Trump said in a statement. He will not be officially confirmed as Republican nominee until the party’s convention in July. And his campaign did not say whether he planned any political activity while in the UK – or whether his trip was a coincidence. Trump has often weighed in on the referendum, and believes the UK should leave the EU. He told Fox News in May: “I know Great Britain very well. I know the country very well. I have a lot of investments there. I would say that they’re better off without it. But I want them to make their own decision.” He recently told Hollywood Reporter, “Oh yeah, I think they should leave”, after being initially unfamiliar with the term “Brexit”.

Ambrose on Brexit. I’m sure many Britons feel this has nothing to do with them, it’s just a bunch of middle-aged right wingers squaring off.
• Leave Camp Must Accept That Norway Model Is The Only Safe Way To Exit EU (AEP)
There have been two excellent reports on the EEA option, one by the Adam Smith Institute and another entitled ‘Flexcit’ by Richard North from the EU Referendum blog. The Adam Smith Institute starts from the premise that the EU is “sclerotic, anti-democratic, immune to reform, and a political relic of a post-war order that no longer exists.” It says the EEA option lets the public judge “what ‘out’ looks like” and keeps disruption to a minimum. “The economic risks of leaving would thus be neutralised – it would be solely a disengagement from political integration. All the business scare stories about being cut off from the single market would fade away,” it said. The report argues that everybody could live with an EEA compromise, whether the Civil Service, or the US, or the EU itself.
Britain would then be a sovereign actor, taking its own seat on the global bodies that increasingly regulate everything from car standards, to food safety, and banking rules. “As Britain is already a contracting party to the EEA Agreement there would be no serious legal obstacle,” it says. David Cameron disparages the Norwegian model as a non-starter. “While they pay, they don’t have a say,” he says. Actually they do. As our forensic report on Norway by Szu Ping Chan makes clear, they have a de facto veto over EU laws under Article 102 of the EEA agreement. Their net payments were £106 a head in 2014, a trivial sum.
They are exempt from the EU agricultural, fisheries, foreign, defence, and justice policies, yet they still have “passporting” rights for financial services. Their citizens can live in their Perigord moulins or on the Costa Del Sol just as contentedly as we can. They do not have to implement all EU law as often claimed. Norway’s latest report shows it has adopted just 1,349 of the 7,720 EU regulations in force, and 1,369 out of 1,965 EU directives. The elegance of the EEA option is that Britain would retain access to the EU customs union while being able to forge free trade deals with any other country over time.

Not the biggest fan of Wren-Lewis, but this is good.
• Greece Under Troika Rule (Wren-Lewis)
“The repayment of foreign loans and the return to stable currencies were recognized as the touchstones of rationality in politics; and no private suffering, no infringement of sovereignty was considered too great a sacrifice for the recovery of monetary integrity. The privations of the unemployed made jobless by deflation; the destitution of public servants dismissed without a pittance; even the relinquishment of national rights and the loss of constitutional liberties were judged a fair price to pay for the fulfilment of the requirements of sound budgets and sound currencies, these a priori of economic liberalism.” – Karl Polanyi (1944), “The Great Transformation” (p142)
This quote (HT Jeremy Smith) could almost be written today about Greece. I had once thought that the lessons of the interwar period and Great Depression had been well learnt, but 2010 austerity showed that was wrong. I therefore used in a 2014 post an earlier example of where one country allowed another to suffer for what was thought to be sound economics and their own ultimate good (‘a sharp but effectual remedy’): the British treatment of Ireland during the famine. The British held back relief because of a combination of laissez-faire beliefs and prejudice against Irish catholics. Replace famine relief with debt relief and Irish operating an inefficient agricultural system with lazy Greeks and an economy in need of structural reform, and the two stories have strong similarities, although of course the scale of the suffering is different.
To understand why the Greek crisis goes on you need to understand its history. That the Greek government borrowed too much is generally agreed. What is often ignored is that the scale of the excess borrowing meant default was pretty inevitable. But Eurozone leaders, worried about their banking system (which held a lot of Greek debt), first postponed default and then made it partial. The real ‘bailing out’ was for the European banks and others who had lent to the Greek government. The money the Eurozone lent to Greece largely went to pay off Greece’s creditors. There was absolutely nothing that obliged Eurozone leaders to lend their voters money to bail out these creditors. Pretty well all the analysis I saw at the time suggested it would be money that Greece would be unable to pay back.
If European leaders felt their banking systems needed support, they could have done this directly. But instead they convinced themselves that Greece could pay them back. It was a mistake they will do anything to avoid admitting. To try and ensure they got their money back, they along with the IMF effectively took over the running of the Greek economy. The result has been a complete disaster. The amount of austerity imposed caused great hardship, and crashed the economy. Whereas the Irish and Spanish economies are beginning to recover and regain market access, Greece is miles away from that, and the Troika’s structural reforms are partly to blame.

When will the Chinese start buying?
• Greek Home Prices Down 45%, Seen Dropping Another 20-25% By 2018 (Kath.)
Property market professionals are expecting house prices in Greece to drop further by up to 25% in the next few years, reporting a sudden rise in supply of properties owing to the upcoming repossessions, while demand will continue to fall due to the recessionary measures of the new bailout agreement. Since end-2008, house prices in the country’s two main cities, Athens and Thessaloniki, have fallen by an average of 45%, according to data from the Bank of Greece. The decline for the country as a whole comes to 41%. Therefore if the above estimate proves right, by the time the bailout period is supposed to be completed (in May 2018), the loss in residential properties’ market value will amount to 65-70%, or even more in some cases.
Giorgos Litsas, the head of chartered surveyors GLP Values, tells Kathimerini that “just under a year ago, when the agreement between the government and its creditors became known in the context of the capital controls, we estimated that the new bailout deal would entail a further 18% drop in home prices. Now, after the measures passed and under the threat of repossessions, we have had to revise the estimated drop in prices over the next couple of years to 20% or even 25%, particularly when taking into account the shift in supply of houses in a saturated market with no demand.”

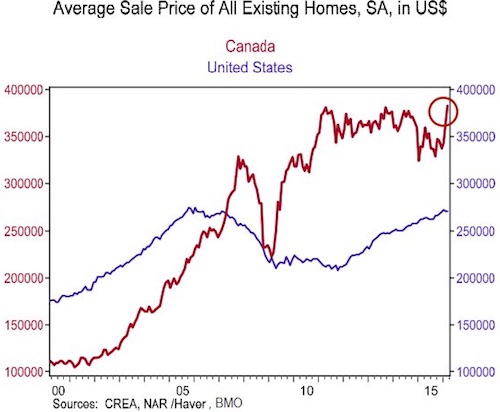
You don’t say: “We’re a little concerned about housing prices in the greater Vancouver area and Toronto..”
• OECD Warns Of “Disorderly Housing Market Correction” In Canada (ZH)
With regulators and local authorities unable or unwilling to crack down on the unprecedented housing bubble in select Canadian cities, increasingly used by Chinese oligarchs to park hot cash offshore, the local banks are starting to take action into their own hands. Case in point, Bank of Nova Scotia has decided to ease off on mortgage lending in Vancouver and Toronto due to soaring prices, Chief Executive Officer Brian Porter said. “We’re a little concerned about housing prices in the greater Vancouver area and Toronto,” Porter, 58, said Tuesday in an interview on Bloomberg TV Canada. “We just took our foot off the gas the last couple quarters in terms of mortgage growth for the reasons I cited, in terms of Vancouver and Toronto.”
Nationwide home sales in April jumped 10.3% from a year earlier, the most activity for that month and the second-highest level ever, according to the Canadian Real Estate Association. In Vancouver, prices rallied 25% in the month to an average of C$844,800 ($643,000) and sales climbed 15%. Toronto prices jumped 13% to C$614,700 and sales rose 7%, the association said. Then again, while Porter did tacitly admit that soaring housing prices are a threat, he also added that “generally, Canadians have a strong ability to self regulate and they’ve demonstrated that before.”
That may be in doubt, because none other than the OECD itself rang a alarm bells over the frothy nature of the Toronto and Vancouver housing markets and high levels of consumer debt. “Very low borrowing rates have encouraged household credit growth and underpinned rapidly rising housing prices, particularly in Vancouver and Toronto, which together are a third of the Canadian housing market,” the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development warned again today in its latest outlook quoted by the Globe and Mail.

Just drive up home prices high enough. And then there’s people saying: ‘we have to build our way out of this’. Oh, lord.
• Number Of Homeless People In Vancouver Reaches 10-Year High (G&M)
The number of homeless people in Vancouver is the highest in a decade, underscoring an affordability crunch that has worsened even as the local government has spent millions on new housing. Vancouver recorded 1,847 people without permanent housing during its annual homeless count in March – a 6-per-cent increase from a year earlier – in a city whose mayor came to office promising to end homelessness by the end of 2015. In releasing the tally on Tuesday, the city highlighted steps it had taken in recent years to build new homes and protect affordable housing, including changing its bylaws to make it more difficult for the owners of single-room occupancy hotels to evict low-income tenants.
But critics say those measures aren’t enough, especially when skyrocketing real estate prices make it tempting for building owners to evict tenants so they can sell or redevelop their properties. “We are not surprised by the numbers. What we are seeing in the Downtown Eastside – and it is happening across [Metro Vancouver] – is the loss of low-income housing,” Maria Wallstam, a spokeswoman for Carnegie Community Action Project, said Tuesday after the city released its report. “The existing low-income housing stock is being demolished, the rents are going up, or it’s being developed,” she added. “There are simply no options for people to live.” The homeless count, conducted over two nights in March, found 1,847 people who were homeless, compared with 1,746 in 2015.
The total comprises less than 1% of Vancouver’s population – 603,500 in the 2011 census – but is slightly higher than the level in several other Canadian cities, including Toronto and Saskatoon, the report said. The count showed that 61% had been homeless for less than a year and 78% were facing at least one physical or mental-health concern, or both. “What jumps out at me is the complexity of the issues behind these numbers,” said Jonathan Oldman, executive director of the Bloom Group, a non-profit organization that provides housing and support services in the Downtown Eastside.

All pigs are equal.
• EU Gives Budget Leeway To France ‘Because It Is France’ – Juncker (R.)
The European Commission has given France leeway on fiscal rules “because it is France,” the president of the EU executive Jean-Claude Juncker said on Tuesday, in a remark that may not go down well in Germany and other more thrifty euro zone states. The EU is debating how to best apply its fiscal rules, which require a budget deficit under 3% of GDP and public debt to fall, at a time when some argue that more public spending would help boost economic growth. The Commission, which is in charge of monitoring national budgets and recommending corrective measures, is sometimes accused by Germany and other northern euro zone governments of being to lenient in applying EU budget rules.
The EU executive arm gave France in 2015 two more years to bring its deficit below 3% of GDP, even though Paris appeared to miss agreed targets. Asked why the Commission, on several occasions, had turned a blind eye to French infractions, Juncker admitted candidly in an interview with the French Senate television Public Senate that it did so “because it is France”. “I know France well, its reflexes, its internal reactions, its multiple facets,” Juncker said, adding that fiscal rules should not be applied “blindly”. He then reiterated that France should respect its current commitment to bring its deficit below 3% next year.

It’s politics all the way down.
• The ECB’s Illusory Independence (Varoufakis)
A commitment to the independence of central banks is a vital part of the creed that “serious” policymakers are expected to uphold (privatization, labor-market “flexibility,” and so on). But what are central banks meant to be independent of? The answer seems obvious: governments. In this sense, the ECB is the quintessentially independent central bank: No single government stands behind it, and it is expressly prohibited from standing behind any of the national governments whose central bank it is. And yet the ECB is the least independent central bank in the developed world. The key difficulty is the ECB’s “no bailout” clause – the ban on aiding an insolvent member-state government. Because commercial banks are an essential source of funding for member governments, the ECB is forced to refuse liquidity to banks domiciled in insolvent members. Thus, the ECB is founded on rules that prevent it from serving as lender of last resort.
The Achilles heel of this arrangement is the lack of insolvency procedures for euro members. When, for example, Greece became insolvent in 2010, the German and French governments denied its government the right to default on debt held by German and French banks. Greece’s first “bailout” was used to make French and German banks whole. But doing so deepened Greece’s insolvency. It was at this point that the ECB’s lack of independence was fully exposed. Since 2010, the Greek government has been relying on a sequence of loans that it can never repay to maintain a façade of solvency. A truly independent ECB, adhering to its own rules, should have refused to accept as collateral all debt liabilities guaranteed by the Greek state – government bonds, treasury bills, and the more than €50 billion ($56 billion) of IOUs that Greece’s banks have issued to remain afloat.

Storm, teacup: 11 of the EU’s 28 members have recognized the Armenian killings as genocide and, despite initial protests, Turkey has maintained good relations with several of those countries.
• German Vote on Armenian Genocide Riles Tempers, and Turkey (NY Times)
If modern Germany has a mantra, it is that people should learn from their history. Yet Berlin’s latest attempt at reconciliation with the past focuses on the mass killing of Armenians by Ottoman Turks a century ago. And that gesture toward atonement has riled tempers on all sides of the already strained European relations with Turkey. The argument is set to peak on Thursday in a debate in the German Parliament, which is expected to overwhelmingly approve a resolution that officially declares the century-old Armenian massacres to be genocide — and condemns the then-German Empire, allied with Ankara, for failing to act on information it had at the time about the killings.
President Recep Tayyip Erdogan of Turkey said late Tuesday that he had warned Chancellor Angela Merkel of Germany in a telephone call that there could be consequences if the resolution passes. For Turkey, there is scarcely a more sensitive topic than what German and international historians say was the murder of more than a million Armenians and other Christian minorities from 1915 to 1916. The Turkish government has long rejected the term genocide, saying that thousands of people, many of them Turks, died in the civil war that destroyed the Ottoman Empire. For Germany, the resolution comes at a delicate time for Ms. Merkel.
She is relying on Turkey to stem the flow of migrants from the Middle East to Europe, a policy that has earned her criticism for allying with the increasingly authoritarian Mr. Erdogan. “If Germany is to be deceived by this, then bilateral, diplomatic, economic, trade, political and military ties — we are both NATO countries — will be damaged,” Mr. Erdogan told Turkish reporters before leaving on an official trip to Africa. To date, 11 of the European Union’s 28 members have recognized the Armenian killings as genocide and, despite initial protests, Turkey has maintained good relations with several of those countries.