Juan Gris Portrait of the artist’s mother 1912

No. The Fed took that leap in 2008. Bernanke himself talked about uncharted territory. Which is where they’ve been ever since. They literally don’t know what they’re doing.
• Fed To Take Historic Leap Into The Unknown (MW)
The Federal Reserve is set to take a leap into the unknown next week by beginning to sell some of the roughly $3.7 trillion of bonds and mortgage securities it amassed during the financial crisis. The Fed will meet on Tuesday and Wednesday and is widely expected at the end of the meeting to announce it plans to allow the run-off of its massive balance sheet beginning sometime in October. Fed Chairwoman Janet Yellen will hold a press conference afterwards to explain the decision. “It will be an historic day” for the Fed, said Lewis Alexander, chief U.S. economist at Nomura Securities, one the central bank has long thought about but was unsure when it would come. And still the final destination is unknown. “We are heading for a place that is very different from where we are now. It will take years to get there and figure out where we are,” Alexander said.
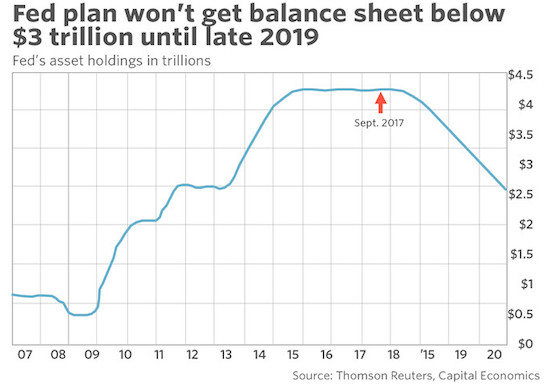
Trying to keep financial markets calm, the Fed is not celebrating this turning point. Officials have openly admitting they have designed the first steps to be so small it will be like watching paint dry. But economists have no doubt that bond yields will eventually move higher. “The Fed is just hoping desperately it has been transparent enough so that the adjustment will be orderly,” said Jim Glassman, head economist for the commercial bank at J.P. Morgan Chase. The central bank is trying to avoid a repeat “taper tantrum,” the swift run up of nearly 1 percentage point on the yield of the 10-year Treasury in 2013 after then-Chairman Ben Bernanke discussed the tapering of bond purchases for the first time. Fed officials have known they would have to reverse course eventually. Hawks and doves agree the policy is not sustainable over the medium term because it potentially adds too much stimulus to a healthy economy.

I don’t get how or why people can praise a man whose entire career has been one long litany of either wrong or intentionally bad decisions and policies. He was the teacher to all those central bankers who made all those decisions that the entire world will still be paying for many years from now. Fisher is the one outstanding symbol of everything that’s wrong in the shady area where finance touches politics.
• Janet Yellen’s Right-Hand Man Is Hanging Up His Boots (BI)
Federal Reserve Vice Chair Stanley Fischer announced last week he was resigning for personal reasons before the end of his term, opening yet another seat in the central bank’s powerful board for President Donald Trump to fill. The departure of Fischer, 73, represents a big loss of institutional knowledge and gravitas for the Fed at a time when many American institutions are sorely lacking in technocratic expertise. Fischer is considered the leader of a generation of prominent academic and professional economics, in part because he taught many of them at MIT. “He is often referred to as the dean of central bankers, having taught most central bankers including former Fed Chairman Ben Bernanke and ECB president Mario Draghi,” Shawn Baldwin, the chairman of AIA Group, wrote in a LinkedIn post. “Fischer’s departure creates a vacuum not easily filled, adding to the uncertainty in monetary policy.”
Larry Summers, the Harvard economist and former Treasury secretary, dubbed Fischer’s resignation “the end of an era.” Fischer, who was born in Zambia and later studied in London, started his career as an academic but became a policymaker at the World Bank and later the International Monetary Fund, where he rose to the role of first deputy managing director. Fischer then spent three years at Citigroup as a vice chairman before moving to Israel in 2005 to become the head of its central bank. Fischer returned to the US as Fed vice chairman in 2014. His term was not set to end until June 2018. “The Fed and the international monetary system will be weaker for his departure from official responsibility,” Summers wrote in a blog post. “Stan’s has been a singular career,” he said. “As an MIT professor he coauthored, with his close friend Rudi Dornbusch, the macro textbook that defined the basics of the field for a generation.
With Olivier Blanchard,” the former IMF chief economist, “he wrote the treatise that defined the state of the art for graduate students. His lectures were models of lucid exposition and balanced judgment. My view of monetary economics was shaped by my experience auditing his class in the Fall of 1978.” Not everyone is complimentary about the arc of Fischer’s career. To some, he represents the kind of establishment economics that led to financial instability and income inequality in many parts of the world. During his time at the IMF, Fischer became the face of austerity measures gone wrong. Many of his and the IMF’s recommendations for drastic spending cuts during the Asian financial crisis of the late 1990s have since been widely discredited as having made matters worse.

And that’s just the workers. Not their dependents. Or the unemployed.
• 97 Million American Workers Are Living Paycheck To Paycheck (ZH)
As we’ve noted time and time again, the number of Americans scraping by with almost no money in their savings account (if they even have a savings account) is staggeringly high – and growing. As the Motley Fool pointed out in a recent post, the St. Louis Federal Reserve, the personal saving rate in June 2017 was a measly 3.8%, or $3.80 for every $100 they earn. With the median household income in the US at just north of $50,000, that would amount to about $4,000 a year. And that’s when they’re saving money. Another study from GoBankingRates found that 69% of Americans surveyed had less than $1,000 in savings. And about one-third had no money in reserve.
Considering that the US economy is 70% based on consumption, Americans are probably over-consuming rather than saving. The Federal Reserve recently released data showing that aggregate credit card debt had hit an all-time high of $1.027 trillion, eclipsing the previous high that was set before the Great Recession. Add in another trillion of auto-loan debt and $1.4 trillion in student-loan debt, and the aggregate debt pile is not only larger than ever before – it’s growing at its fastest rate in decades. And in what’s perhaps the most troubling statistic highlighted by Motley Fool, a recent survey by CareerBuilder and The Harris Poll found that 78% of full-time US workers – nearly 100 million Americans – are now living paycheck to paycheck, up from 75% in 2016.
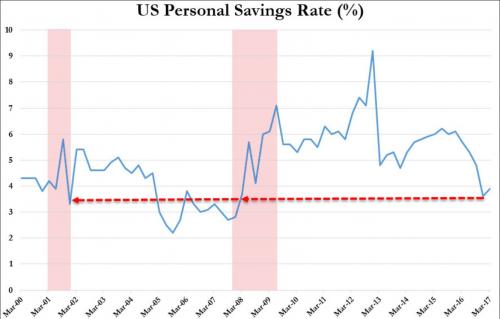
The survey suggested that only 19% of workers save more than $501 monthly, while at the other end of the spectrum, 56% were saving less than $100 a month, including 26% who saved nothing monthly. Fewer than one-third of respondents admitted to following a budget. Meanwhile, about half of respondents said they wouldn’t give up their internet, phone or car to save money. Maybe once the Federal Reserve has succeeded in “normalizing” interest rates, spendthrift Americans will have more of an incentive to save, while also making it more expensive to pay down debt – a powerful disincentive. Now, if only the central bank could find a way to revive stagnant wages…

Hendry has fallen prey to the central bankers. And shut his hedge fund.
• “Markets Are Wrong” (Hugh Hendry)
What if I was to tell you I wasn’t bearish on anything? Is that something you would be interested in? It wasn’t supposed to be like this and it is especially frustrating as nothing much has gone wrong with the economy over the summer. If anything we feel more convinced that our thesis of a healing global economy is understated: for the first time in an age all parts of the world are enjoying synchronised economic momentum and I can’t see it ending for some time. It’s just that our substantial risk book became strongly correlated over the short term to the maelstrom of President Trump and the daily news bombs emanating from the Korean Peninsula; that and the increasing regulatory burden which makes it almost impossible to manage small pools of capital today. Like I said, it wasn’t supposed to be like this…
But let me bow out by sharing my team’s views. For the implications of a sustained bout of economic growth are good for you. It’s good because it should continue to underwrite a continuation in the positive performance of global equities. I would stay long. It’s also good because I can’t see interest rates rising abruptly to interrupt the upward path of equities. And commodities have already acknowledged the upturn in the fortunes of the global economy and are likely to trend higher still. That’s a lot of good news. But it is bad news for me because funds like mine are required to demonstrate negative correlation with risk assets (when they go up like this I go down…), avoid large drawdowns and post consistent high risk adjusted returns. Oh, and I forgot, macro fund clients don’t like us investing in the stock market for the understandable fear that we concentrate their already considerable risk undertaking.
That proved to be an almighty puzzle for a fund like mine that has been proclaiming the stock market as a “safe-ish” bet ever since 2013. Let me explain the “markets are wrong and we boom now” argument. To begin with, and for the sake of clarity, I think we have to carefully go back and deconstruct the volatile engagement between capital markets and central banks for the last ten years for an understanding of where we stand today. The first die was cast by the central bankers in early 2009: having stared into the abyss of a deflationary spiral in 2008 the Fed and the BoE announced a radical new policy of bond purchases named Quantitative Easing. The bond market hated the idea as it was expected to cause a severe inflation problem.

Just yesterday I was telling a friend they would soon fire the next.
• Japanese Told To Find Shelter After North Korea ‘Fires New Missile’ (Y.)
North Korea has fired a ballistic missile directly over Japan. US Secretary of State Rex Tillerson branded the launch ‘reckless’ and called on China and Russia to take ‘direct action’ against Kim Jong-un, while Seoul responded to the test by launching the missiles of its own. The test sparked panic in Japan, where residents were immediately told to take shelter as the missile passed directly overhead – the second time Pyongyang has done so in the past few weeks. It flew over Hokkaido in northern Japan and fell into the Pacific Ocean, sparking a nationwide alert. South Korea said the missile probably reached an altitude of 770km and travelled 3,700km and called an urgent National Security Council meeting.
The North’s launch comes a day after it threatened to sink Japan and reduce the United States to “ashes and darkness” for supporting a U.N. Security Council resolution imposing new sanctions against it for its nuclear test on September 3. The severe sanctions include limits on imports of crude oil and a ban on exports of textiles – which is the country’s second biggest export, worth more than $700m a year. The North previously launched a ballistic missile from Sunan on August 29, which flew over Japan’s Hokkaido island and landed in the Pacific waters

Max is very crypto. But bitcoin et al had big overnight losses.
• JPMorgan Is In A Bubble And Not Bitcoin – Max Keiser (RT)
“JP Morgan, along with the entire finance sector, has been subsidized by the Federal Reserve’s corrupt practice of ‘financial repression’ that moves hundreds of billions from savers and pensioners, and workers, into JP Morgan and Jamie Dimon’s pocket. Jamie’s compensation is tied directly to manipulating JP Morgan’s stock and option prices, thanks to the Fed’s conflicted, corrupt, cozy malfeasance,” [..] “The US dollar, bond markets, and many property markets are in bubbles. Bitcoin and gold are the only financial assets not in bubbles.
To say bitcoin is fraudulent would be like saying gold is fraudulent. Some might say this, but no rational person would agree,” he said. “As the bubbles in fiat money, bonds and stocks pop, capital will flow into bitcoin, gold, and silver. At some point, when his customers start leaving JPMorgan and move to more bitcoin-focused options, Jamie will be forced to capitulate, or get replaced,”[..] “Bitcoin makes banks, essentially price gouging intermediaries and socially unacceptable leeches, obsolete. Bankers rightfully fear for their jobs as bitcoin replaces them,”

Nigel Gardner is a former European Commission spokesman.
• Why Europe Will Miss The Disruptive Brits (Gardner)
The UK’s constant digging-in of heels has allowed other governments to steer clear of negotiating clashes, safe in the knowledge that Britain and its Eurosceptic media would do the blocking of unpopular measures for them. Take the seemingly trivial example from 2013, of rules about how olive oil could be served in restaurants. “There was a daft proposal that it couldn’t be served in bowls or glass jugs at the table, but only in sealed sachets,” recalls a senior Dutch official. “We didn’t have to do anything – the Brits and their tabloids did the heavy lifting for us, and the proposal was withdrawn … Every time the European Commission proposes something, we know we can rely on the British to kick and shout so it’s blocked. With Brexit, that’s no longer going to be possible.”
Even that opt-out over the 48-hour week for which the UK fought its lonely battle is now – 20 years later – quietly being used by 15 other member states. So which country may end up replacing Britain as Europe’s new troublemaker-in-chief? Poland and Hungary are the obvious candidates because, across a whole range of areas, from civil liberties to media freedoms, the two countries find themselves at odds with the EU. As one senior EU official put it: “They are simply not in line with fundamental EU policies. As new member states they should be enthusiastic, but it’s the opposite.” Beata Szydlo, for example, tells us a lot about what the EU will look like after 2019 when Britain is supposed to exit. The Polish prime minister’s intemperate language at a recent European summit was previously the kind of thing the EU’s top brass expected only from the British.
She would not accept “blackmail from a leader with an approval rating of 4%” she raged against France’s then president François Hollande. Poland is now facing EU legal action over judicial reforms which Brussels says would undermine Polish democracy. Ironically, we may need to look to a more unlikely quarter to find Europe’s true new bad boy. Because post-Brexit, the Germans will end up being much more unpopular. “Without Britain,” one EU official told me, “they will have to assume the role they are historically reluctant to play.”
Indeed, the eurozone crisis provided a foretaste of how this could play out. With Britain outside the single currency, all the anger was directed against Germany and its chancellor, Angela Merkel, when things went wrong. Pictures of Merkel with a Hitler moustache were everywhere in the Greek press. And the old joke about Merkel arriving at Athens airport – the one where the border guard asks “Occupation?” and Merkel replies, “No, just visiting” – took on new life. Expect much more of this.

He might as well have called it Brexit’s British Question.
• Brexit’s Irish Question (Fintan O’Toole)
Brexit is, in a sense, a misnomer. There are five distinct parts of the UK: Scotland, Wales, Northern Ireland, the global metropolis that is Greater London, and what the veteran campaigner for democratic reform Anthony Barnett, in his excellent new book The Lure of Greatness, calls England-without-London. In three of these parts—Scotland, Northern Ireland, and London—Brexit was soundly rejected in last year’s referendum. Wales voted narrowly in favor of Brexit. But in England-without-London Brexit was triumphant, winning by almost 11%. It was moreover a classic nationalist revolt in that the support for Brexit in non-metropolitan England cut across the supposedly rigid divides of North and South, rich and poor. Every single region of England-without-London voted to leave the EU, from the Cotswolds to Cumbria, from the green and pleasant hills to the scarred old mining valleys.
This was a genuine nationalist uprising, a nation transcending social class and geographical divisions to rally behind the cry of “Take back control.” But the nation in question is not Britain, it is England. The problem with this English nationalism is not that it exists. It has a very long history (one has only to read Shakespeare) and indeed England can be seen as one of the first movers in the formation of the modern nation-state. The English have as much right to a collective political identity as the Irish or the Scots (and indeed as the Germans or the French) have. But for centuries, English nationalism has been buried in two larger constructs: the United Kingdom and the British Empire. These interments were entirely voluntary. The gradual construction of the UK, with the inclusion first of Scotland and then of Ireland, gave England stability and control in its own part of the world and allowed it to dominate much of the rest of the world through the empire.
Britishness didn’t threaten Englishness; it amplified it. Now, the empire is gone and the UK is slipping out of England’s control. Britain’s pretensions to be a global military power petered out in the sands of Iraq and Afghanistan: the British army was effectively defeated in both Basra and Helmand and had to be rescued by its American allies. The claim on Northern Ireland has been ceded, and Scotland, though not yet ready for independence, increasingly looks and sounds like another country. In retrospect, it is not surprising that the reaction to these developments has created a reversion to an English, rather than a British, allegiance. In the 2011 census, 32.4 million people (57.7% of the population of England and Wales) chose “English” as their sole identity, while just 10.7 million people (19.1%) associated themselves with a British identity only.

The torture never stops.
• IMF Is Set On Asset Quality Review For Greek Banks (K.)
Greece looks set for another difficult series of negotiations with its international creditors in the third review of its third bailout program, as IMF spokesman Gerry Rice made it clear on Thursday that the issue of the asset quality review of Greek banks (AQR) “will form part of the review.” He also said the Fund may demand new measures for next year, stressing that the programs evolve and conditions change. Citing the IMF report dated July 20 – when the Fund approved its participation in the Greek program “in principle” – Rice left no doubt as to whether the AQR would be discussed, branding it an important matter. This will likely cause friction with the European Central Bank, which has scheduled its own stress tests for the banks in 2018.
Sources in Frankfurt have noted that only if the Greek government asks for an AQR will the ECB authorize it. However, Athens, as a senior Finance Ministry official has said, has no such intention. Greek banks are obviously against any such project that would upset their operations, and had hoped that the IMF would eventually decide against raising the issue. In July the IMF had estimated that local lenders would need at least 10 billion euros in additional capital, raising the prospects of another recapitalization. Rice said on Thursday that the Fund is cooperating with the ECB and other European institutions on all issues, but added that “the stability of the credit system is of great significance for the program.”

For €45 million? An entire railway national company? How much is the kitchen sink?
• Greece Sells Its Railway Company To Italian State Operator (AP)
Greece has agreed to sell its railways company to Italy’s own state-owned operator for 45 million euros ($54 million) as part of its privatization drive. The country’s Asset Development Fund said Thursday that the sale of Trainose to Ferrovie Dello Stato Italiane completed a four-year process. Greece has pledged to carry out an ambitious privatization program as part of its international bailout, under which it has received billions of euros in emergency loans in return for overhauling its economy. Many of the privatizations have been met with resistance from unions. No trains were running on Thursday as the railway workers’ union called a 24-hour strike to protest the company’s sale.

An awful mess in more ways than one.
• Greek Oil Spill Forces Closure Of Athens Beaches (G.)
An emergency operation is under way to clean up an oil spill from a sunken tanker that has blackened popular beaches and bays in Athens’ Argo-Saronic gulf. What had been thought a containable spill is being described by officials as an ecological disaster after thick tar and oil pollution drifted toward residential coastal areas. By Thursday, four days after the 45-year-old Agia Zoni II sank off Salamína island, mayors in suburbs south of the capital were forced to close beaches, citing public health risks. “This is a major environmental disaster,” said the mayor of Salamína, Isidora Nannou-Papathanassiou. “Clearly the danger [of pollution] was not properly gauged, the currents have moved the spill.” The vessel sank while at anchor in the early hours of Sunday. It was carrying 2,500 tonnes of fuel oil and marine gas when it went down in mild weather.
It has emerged that only two of its 11-strong crew – the captain and chief engineer – were on board when it began to take on water. Both men have since been charged with negligence but freed on bail. The company operating the small, Greek-flagged vessel insisted it was seaworthy. Merchant marine officials said initial emphasis had been placed on sealing the vessel’s cargo holds to stop further leakage. The merchant marine minister, Panagiotis Kouroumblis, who has brought in help from abroad including an anti-pollution truck to collect the oil, ruled out further seepage on Tuesday, saying the ship’s hull had been secured. Late on Wednesday, however, the ministry’s general secretary, Dionysis Kalamatianos, raised the possibility that oil was still leaking from the vessel, telling Skai TV that efforts to seal it were “almost complete”.
The contradictory statements sparked accusations that authorities had not only underestimated the scale of the spill, but also lost valuable time in tackling it. The slick extends for miles, and some officials said the cleanup could last four months – much longer than the 20 days Kouroumblis estimated. In the Athens suburb of Glyfada, where floating dams have been set up and chemicals used to dissolve the spillage, the mayor, Giorgos Papanikolaou, said 28 tonnes of fuel had been removed from one beach alone. Images of of dead and oil-coated turtles and birds underscored the economic and environmental impact, and experts estimated it could take years before the affected area fully recovered.

The only good alternative energy is the one you don’t use.
• 100% Wishful Thinking: the Green-Energy Cornucopia (Cox)
At the People’s Climate March back last spring, all along that vast river of people, the atmosphere was electric. But electricity was also the focus of too many of the signs and banners. Yes, here and there were solid “System Change, Not Climate Change” – themed signs and banners. But the bulk of slogans on display asserted or implied that ending the climate emergency and avoiding climatic catastrophes like those that would occur a few months later—hurricanes Harvey and Irma and the mega-wildfires in the U.S. West—will be a simple matter of getting Donald Trump out of office and converting to 100-percent renewable energy.
The sunshiny placards and cheery banners promising an energy cornucopia were inspired by academic studies published in the past few years purporting to show how America and the world could meet 100% of future energy demand with solar, wind, and other “green” generation. The biggest attention-getters have been a pair of reports published in 2015 by a team led by Mark Jacobson of Stanford University, but there have been many others. A growing body of research has debunked overblown claims of a green-energy bonanza. Nevertheless, Al Gore, Bill McKibben (who recently expressed hope that Harvey’s attack on the petroleum industry in Texas will send a “wakeup call” for a 100-percent renewable energy surge), and other luminaries in the mainstream climate movement have been invigorated by reports like Jacobson’s and have embraced the 100-percent dream.
And that vision is merging with a broader, even more spurious claim that has become especially popular in the Trump era: the private sector, we are told, has now taken the lead on climate, and market forces will inevitably achieve the 100-percent renewable dream and solve the climate crisis on their own. [..] America does need to convert to fully renewable energy as quickly as possible. The “100-percent renewable for 100% of demand” goal is the problem. Scenarios that make that promise, along with the studies that dissect them, lead me to conclude that, at least in affluent countries, it would be better instead to transform society so that it operates on far less end-use energy while assuring sufficiency for all. That would bring a 100%-renewable energy system within closer reach and avoid the outrageous technological feats and gambles required by high-energy dogma. It would also have the advantage of being possible.

Quantum is per definition unbreakable. The CIA is not going to like it.
• China Takes The Lead In Building Quantum Data Security Networks (Axios)
For decades, physicists have looked to use the behavior of particles of light to securely send information. The basic science underlying quantum cryptography has been determined over the past 40 years, but a slew of papers published this summer by physicist Jian-Wei Pan establishes China as the early leader in deploying the technology on a global scale. Why it matters: Networks using quantum keys theoretically allow for very private communications and safe transactions — because if attacked, the key would be altered and the parties would know it wasn’t secure. That would be valuable for financial transactions or voting that involves transmitting information between two points. But beyond a handful of field tests, there hasn’t been a commitment to develop the technology at this scale until now.
How it works: Two people who want to communicate would share a number key encoded in a string of single photons (particles of light) that can be used to encrypt and decrypt a message. It’s secure because if someone tries to intercept the message, the photons would be physically altered and the key would no longer work, but the data would be secure. The vision: Optical fibers carry photons short distances on the ground (anything more than about 200 kilometers and the fiber absorbs the photon signal). So researchers want to pair them with satellites that can relay the signal and then drop it back down to a receiver on Earth. That goes on and on, ultimately carrying the information around the globe to the intended receiver. What they did: China built a 2,000-km fiber optic network between Beijing and Shanghai and launched a satellite last year — both dedicated to basic research on quantum satellite communications. So far, they’ve used it to:
• Send photons from the satellite to telescopes 1,200 km apart on the ground that acted as receivers. • Transmit quantum-encoded information from the ground to the satellite. • Distribute an actual quantum key string of photons from the satellite to the ground. • Shared the key between two ground receivers — during the day. (That’s key because light from the sun, moon and cities on Earth can drown out the photon signal. The current satellite only operates at night.) “They all together prove that a number of different concepts relevant for the quantum internet really do work in a space setting,” says Anton Zeilinger, a quantum physicist at the University of Vienna who was Pan’s advisor.
The bottom line: China’s achievements are more technological than scientific, but they represent a true advance in the development and deployment of these technologies, says Ray Newell of Los Alamos National Laboratory. He points out that many of the fundamental science and technologies for quantum key distribution were invented in the United States. (Satellite-based quantum key distribution was invented at Los Alamos, which holds the original patent for the technology.) Other countries possess the knowledge to build these systems, but China is the first to make a major investment. “In China, the decision to build it was done at the beginning, and then they went through with a lot of manpower and money,” says Norbert Lutkenhaus from the University of Waterloo.









