Amedeo Modigliani Jeanne Hebuterne 1919

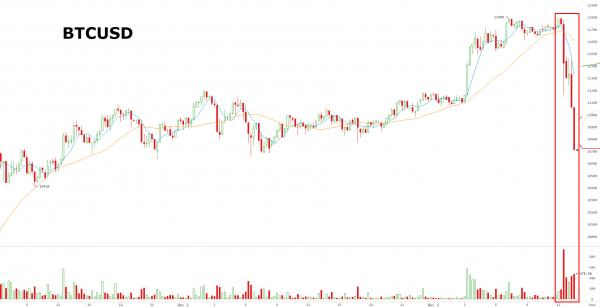
Wherever you stand on the issue, that is quite the graph. We’ll do a series on BTC soon.
• The Bitcoin Ramp – Is It Sustainable? (Lebowitz)
Believers in BTC claim it is quickly becoming a widely accepted global currency. To better understand their view let’s see how BTC meets the definition of a currency, both as a means of transacting (money) as well as a store of value. Money: money is anything that two parties can agree is acceptable in exchange for goods and services. For example, if I pay you a case of beer to mow my lawn, the beer, in this instance, is money. However, for “money” to be widely accepted, the masses must ascribe similar value to it. While there is an increasing number of vendors accepting BTC, it is nearly impossible to use BTC to meet your everyday needs. Further, the value, or price of money, needs to be relatively stable to be effective. If a dollar bill bought you a case of beer today, but only a single bottle tomorrow and a keg the following week, few consumer or vendors would trust the dollar’s value. BTC’s value can fluctuate 5-10% on an hourly basis.
Store of value: a store of value is something that allows one to save money and retain its value. When we save money we want comfort in knowing the money we earned can buy us the same amount of goods and services tomorrow that it can buy today. Again, the extreme volatility of the price of BTC makes it difficult to project how much purchasing power a BTC will buy you in the future. All currencies fluctuate but typically nowhere near the degree we are witnessing in BTC. If the extreme price movements of BTC subside it is possible that BTC can serve as a widely accepted currency and the believers could be correct.
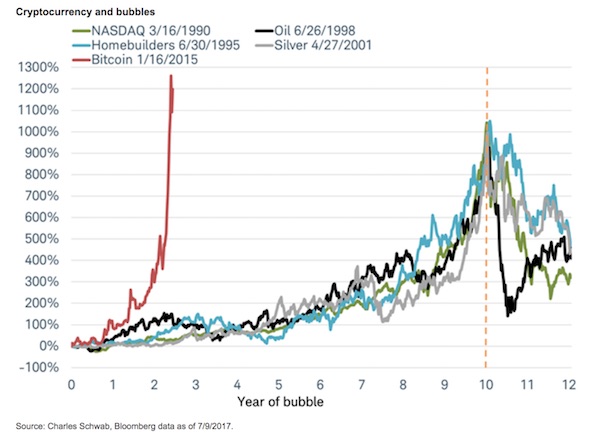
A second camp believes BTC is a financial bubble. The chart below compares BTC to other recent investment fads. You will notice in all instances above the bubbles rise steadily in price before transitioning to an exponential increase prior to collapse. Often, in the so-called euphoric phase, prices go well beyond the point most investors think is reasonable. In this respect, BTC is following the path of prior bubbles. Bubbles are not solely defined by price movements, but more importantly by a lack of supporting fundamental value. If you subscribe to the value of BTC as does the first camp, the rapid increase in price may well be justified. If you believe there is no value, BTC is showing the classic pattern of most bubbles.

Politicians, banks, they’re all trying to get control. But can they?
• UK, EU Plan Regulatory Crackdown On Cryptocurrencies (ZH)
However, in retrospect this appears to not have been the case, and as the Telegraph reported just around the time of the big drop, UK “ministers are launching a crackdown on the virtual currency Bitcoin amid growing concern it is being used to launder money and dodge tax.” Taking a page out of the Chinese playbook, the UK Treasury has announced plans to regulate the Bitcoin that will force traders in so-called crypto-currencies to disclose their identities and report suspicious activity. According to the Telegraph, while “until now, anybody buying and selling Bitcoins and other digital currencies have been able to do so anonymously, making it attractive to criminals and tax avoiders. But the Treasury has now said it intends to begin regulating the virtual currency, which has a total value of £145 billion, to bring it in line with rules on anti-money laundering and counter-terrorism financial legislation.”
“John Mann, a member of the Treasury select committee, said he expected to hold an inquiry into the need for better regulation of Bitcoin and other alternative currencies in the new year. He said: “These new forms of exchange are expanding rapidly and we’ve got to make sure we don’t get left behind – that’s particularly important in terms of money-laundering, terrorism or pure theft. “I’m not convinced that the regulatory authorities are keeping up to speed. I would be surprised if the committee doesn’t have an inquiry next year. “It would be timely to have a proper look at what this means. It may be that we want speed up our use of these kinds of thing in this country, but that makes it all the more important that we don’t have a regulatory lag.”
The proposed changes come amid increasing fears that Bitcoin is being used by gangs to launder the proceeds of crime while also attracting currency speculators – with the value of the coin soaring in the past 12 months. In other words, the same reason why the IRS is cracking down on Coinbase clients in the US is also why UK and European regulators are joining China in cracking down on capital flight. While such legislation by the UK alone would hardly have a major impact on crypto pricing – after all the UK is a very minor player in a market that is dominated by Korea and Japan (as proxies for China), and to a growing extent, the US, the new rules will also be applied across the European Union, and “are expected to come into force by the end of the year or early in 2018, the minister in charge has said.”

Backed by the world’s biggest oil reserves. But who’s going to buy?
• Venezuela To Launch Cryptocurrency To Combat US ‘Blockade’ (G.)
President Nicolas Maduro has said Venezuela would launch a cryptocurrency to combat a US-led financial “blockade,” although he provided few clues about how the economically crippled Opec member would pull off the feat. “Venezuela will create a cryptocurrency … the ‘petro,’ to advance in issues of monetary sovereignty, to make financial transactions and overcome the financial blockade,” leftist Maduro said during his weekly Sunday televised broadcast. The digital currency will be backed by Venezuelan reserves of gold, oil, gas, and diamonds, he said during the near five-hour show, which included traditional Christmas songs and dancing. “The 21st century has arrived!” Maduro added to cheers, without providing specifics about the currency launch.
Opposition leaders scorned the announcement, which they said needed congressional approval, and some cast doubt on whether the digital currency would ever see the light of day in tumultuous Venezuela. Still, the announcement highlights how US sanctions this year are hurting Venezuela’s ability to move money through international banks. Sources say compliance departments are scrutinising transactions linked to Venezuela, which has slowed some bond payments and complicated certain oil exports. Maduro’s move away from the US dollar comes after the recent spectacular rise of bitcoin, which has been fuelled by signs that the digital currency is slowly gaining traction in the mainstream investment world. Cryptocurrencies typically are not backed by any government or central banks.
Bitcoin already has a strong following among tech-savvy Venezuelans looking to bypass dysfunctional economic controls to obtain dollars or make internet purchases. Venezuela’s traditional currency, meanwhile, is in free fall. Currency controls and excessive money printing have led to a 57% depreciation of the bolivar against the dollar in the last month alone on the widely used black market. That has dragged down the monthly minimum wage to a mere $4.30.

A pretend free market suppressed close to a choking point. That cannot end well.
• Today’s Central Bank Vol Suppression Will End In Spectacular Fashion (Peters)
After his provocative admission published earlier that he now checks “Breitbart daily and InfoWars too… You can no longer understand America unless you do”, One River’s CIO Eric Peters published the following anecdote revealing an earlier moment of his life, when as a currency trader, he learned a valuable lesson following the spectacular blow up of Europe’s Exchange Rate Mechanism, or ERM, and why the lesson from some 25 years ago, leads Peters to conclude that “Today’s central bank volatility suppression regime resembles it, and will end in spectacular fashion”.
Anecdote: “Let’s step into my office,” he said. So I did. He was my boss. “The firm’s most important client needs help.” I listened, uninterested, unconcerned about clients, their problems. Barely cared about my boss. I had a game to play, solo sport, and loved it to the exclusion of all else. “They need to do a very large trade.” A twenty-six-year-old proprietary trader’s mind is rather primitive. Which is good and bad. Being young and dumb allows you to see things elders can’t. And take risks one rarely should. In 1992, I’d done both. “They need to buy three hundred million Mark/Lira.” Europeans established a mechanism to lock their exchange rates into narrow ranges to reduce market volatility and promote economic convergence. In theory it worked, in practice it didn’t. Politicians named it the ERM.
“What would you like to do?” he asked, calm. I stood there, processing. Such a sum was extraordinary even before the ERM blew up, which it just had. For months, I’d bought options in anticipation of its demise. Honestly, it was obvious. The ERM encouraged speculators to build massive leveraged carry positions, discouraged corporations from hedging exchange rate risk, suppressing volatility and interest rate spreads everywhere. The process was reflexive. Today’s central bank volatility suppression regime resembles it, and will end in spectacular fashion. All such things do. “I want to buy more!” I answered. My foreign-exchange options left me long the exact amount our client needed to buy. No other bank would sell them such a large sum. So naturally, I wanted more.
“You should sell them your whole position,” he told me, firm. I couldn’t understand, it made no sense. “Big customer orders like this usually mark the highs – never forget it,” he said. I left his office angry, irate, sold my whole position. And he was right.

There’s far too much crap out there for it all to escape through the emergency exits.
• Market Is Reminiscent Of 1999 Bubble, On Verge Of Significant Change (ZH)
Just hours after Neil Chriss announced that his $2.2 billion Hutchin Hill hedge fund is shuttering due to underperformance and admitted that “we fought hard, but did not deliver the performance that you expected from us”, another legendary hedge fund announced it was undergoing a significant restructuring as a result of relentless investor withdrawals: citing a November 30 letter, Bloomberg reported that Paul Tudor Jones’ Tudor Investment Corp, which lost 1.6% YTD, was closing its Discretionary Macro fund “and letting investors shift assets to the main BVI fund as of Jan. 1” with the letter clarifying that “Jones will also principally manage Tudor’s flagship BVI fund, which will be the firm’s only multi-trader fund next year.”
[..] while the internal reorganization of multi-billion hedge funds are hardly of material interest to ordinary retail, or even institutional, investors, PTJ’s outlook on the market always is, and it was concerning: frustrated by the collapse of market vol as a result of record central bank monetary easing, Jones said “the environment is on the verge of a significant change” and that the current market is reminiscent of the bubble of 1999. “That was a year in which Tudor BVI’s macro book was basically flat while U.S. equities experienced one of the greatest bubbles in history,” Jones, 63, wrote. “The termination of that bull market kicked off a three-year macro feast.” adding that “the plot is much the same today but we can substitute Bitcoin and fine art for the Nasdaq 100 of 1999.”
“In the face of a shock, investors may be surprised to find themselves jammed running for the exit,” he wrote. However, as Howard Marks has repeatedly cautioned in the past 3 years, this will be a problem as “the amount and quality of liquidity is lower than people recognize”, and “hidden leverage in the market will make a mass exit even more challenging.”

They are the central bank cheerleaders, who now try to issue a warning against what they were cheering for.
• BIS Joins Chorus Saying Stock Valuations Are Looking ‘Frothy’ (BBG)
The Bank for International Settlements added its voice to institutions questioning whether stocks have become too expensive, saying they look “frothy” – particularly in the U.S. The BIS weighed in on the debate just days after Goldman Sachs said a prolonged bull market across stocks, bonds and credit left its measure of average valuation at the highest since 1900. Stock prices are above historical averages and U.S. companies may struggle to continue their pace of dividend growth, the BIS said in its quarterly review on Sunday. Warnings on elevated asset prices have become more frequent as the world’s biggest central banks move toward tighter monetary policy. A Bank of America Merrill Lynch survey showed a record 48% of investors say equities are overvalued.
Nobel-Prize winning economist Richard H. Thaler said in October he can’t understand why stocks are still rising. The California State Teachers’ Retirement System CIO said last week that holding shares feels like “sitting on a pin cushion.” The paradox is that financial conditions have continued to ease even in the U.S., by far the most advanced in increasing interest rates, leaving investors struggling to judge how rates will drive prices. “Ultimately, the fate of nearly all asset classes appeared to hinge on the evolution of government bond yields,” the Basel, Switzerland-based institution said. “There is also significant uncertainty about the levels those yields will reach once monetary policies are normalized in the core jurisdictions.”
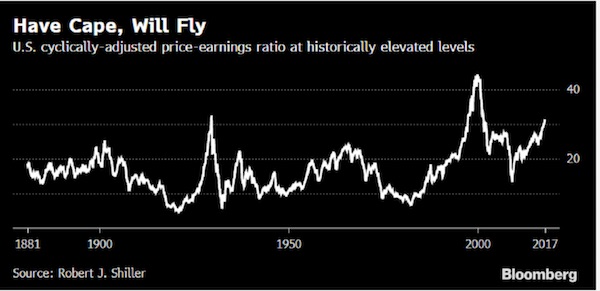
The price-earnings ratio of the U.S. stock market, cyclically adjusted, was recently above 30, exceeding its post-1982 average by almost 25%, the BIS said. While that’s below the peak of 45 reached in the dotcom bubble of the late 1990s, it’s nearly double the long-term average of 1881–2017. The gauges for European and U.K. equities were at their post-1982 averages.

More BIS. Woodford: “Investors have forgotten about risk and this is playing out in inflated asset prices and inflated valuations..”
• Financial Markets Could Be Over-Heating – BIS (G.)
Investors are ignoring warning signs that financial markets could be overheating and consumer debts are rising to unsustainable levels, the global body for central banks has warned in its quarterly financial health check. The Bank for International Settlements (BIS) said the situation in the global economy was similar to the pre-2008 crash era when investors, seeking high returns, borrowed heavily to invest in risky assets, despite moves by central banks to tighten access to credit. The BIS, known as the central bankers’ bank, said attempts by the US Federal Reserve and the Bank of England to choke off risky behaviour by raising interest rates had failed so far and unstable financial bubbles were continuing to grow.
Claudio Borio, the head of the BIS, said central banks might need to reconsider changing the way they communicated base interest rate rises or the speed at which they were increasing rates to jolt investors into recognising the need to calm asset markets. “The vulnerabilities that have built around the globe during the long period of unusually low interest rates have not gone away. High debt levels, in both domestic and foreign currency, are still there. And so are frothy valuations. “What’s more, the longer the risk-taking continues, the higher the underlying balance sheet exposures may become. Short-run calm comes at the expense of possible long-run turbulence,” he said. The warning came as Neil Woodford, one of the UK’s most high-profile fund managers, said stock markets were in danger of crashing, resulting in huge losses for millions of people.
The founder of Woodford Investment Management, which manages £15bn worth of assets, told the Financial Times that investors were at risk of the market experiencing a repeat of the dotcom crash of the early 2000s. Woodford said he was concerned that historically low levels of interest rates in most developed nations over the last decade were pushing asset prices to unsustainable levels. “Ten years on from the global financial crisis, we are witnessing the product of the biggest monetary policy experiment in history,” he said. “Investors have forgotten about risk and this is playing out in inflated asset prices and inflated valuations. “There are so many lights flashing red that I am losing count.”

I said this before: Merkel’s failure to form a coalition is a big deal all across Europe. Even if she succeeds the second time around. She leaves a big vacuum.
• Strong Leadership Across Europe Now Looks Like Wishful Thinking (CNBC)
Strong and stable leadership is difficult to come by these days across Europe. The countries that have traditionally been the bastion of reliable leadership – Germany and the U.K. — are leaving citizens feeling disappointed – and more worryingly, it is having spillover effects into matters outside of domestic politics. Brexit and U.K. leader Theresa May’s ill-fated snap election have left the Conservative government hamstrung and weakened, as the prime minister seems to be hanging onto her position by a thread. The latest installment of this political vacuum was showcased by Ireland, where the minority government was at risk of collapsing after a no-confidence motion was tabled against the Deputy Prime Minister Frances Fitzgerald over a police whistleblower scandal. This could have led to new elections in December.
And in Germany, which is usually considered an absolute beacon of stability, we are facing a political earthquake as exploratory talk on a potential “Jamaica” coalition have faltered spectacularly after the FDP’s (Free Democratic Party) Christian Lindner proclaimed blearily after another long night of talks that he would pull his support for further discussions to form a government. As I am writing this, the parties in Germany are under pressure to deal with shock of the unprecedented nature of the collapse and the utter lack of workable alternatives. New elections have been favored by Chancellor Angela Merkel but talks are still ongoing about a potential return of the much-loathed, yet functioning “grand coalition” between the CDU (Christian Democratic Union), its Bavarian sister party the Christian Social Union (CSU), and the Social Democratic Party (SPD). A revival of talks about a potential Jamaica coalition including the Greens, CDU/CSU and the liberal FDP party has now been ruled out by Lindner.
But surprisingly, the impact on the German economy is non-existent so far. Last month, we saw the German business morale hitting another record high in November, with the IFO Institute adding that the economy is “headed for a boom.” Just last week, data confirmed that the German economy grew by 0.8% in the third quarter, which led to the IFO Institute upgrading its growth forecast for the German economy to 2.3% this year, from 1.9% previously. Talking to me on CNBC, Clemens Fuest, the president of Munich-based IFO Institute, said that only a period of prolonged uncertainty brought about by new elections early next year might impact business sentiment, adding that “we are very far away from that scenario.” Even a minority government might work as this would “revitalize parliamentary debate,” he added.
In fact, when I asked Hans Redeker, head of foreign exchange strategy at Morgan Stanley, about a slowdown in investment in growth as a result of the collapse in coalition talks, he said: “When things are going well in the economy, you don’t necessarily need strong leadership – it is only when the economy isn’t doing well that you need leadership”.

What if talks with the EU today fall flat on their face? Will she still stay on?
• Theresa May Fails To Strike Border Deal With Irish Government (G.)
Theresa May and the Irish government have failed to reach a deal on the crucial Brexit issue of the Northern Ireland border ahead of a crunch meeting on Monday lunchtime with the European commission president, Jean-Claude Juncker. Despite intense efforts over the weekend to agree a proposal on how to avoid a hard border in Ireland, Irish officials revealed at midnight on Sunday that “there is still a way to go” to achieve a meeting of minds on the issue. “The Irish government remains hopeful – but at this stage it is very difficult to make a prediction,” said an official. The failure to seal a deal threatens to delay the progression of the Brexit negotiations to the second phase covering trade and the UK’s future relationship with the EU. May will meet Juncker with the UK’s final offer on the three main issues in the first round of Brexit talks – the Irish border, citizens’ rights and the financial settlement.
Talks could continue into Wednesday when the European commissioners are due to meet to discuss their recommendation to European leaders on whether “sufficient progress” has been achieved to move talks on to trade and transition arrangements. May had been given the deadline of Monday 4 December to table the offers before a European council summit on 14 December, when EU leaders will decide if “sufficient progress” has been made to proceed to the next phase. But although the money and citizens’ rights issues have been mostly resolved, the future arrangement with Ireland has remained a significant obstacle because the British government has yet to offer a firm commitment explaining how it will guarantee avoiding a return to a hard border after Brexit. For Ireland, and the EU27 as a whole, the problem has become a potential dealbreaker, with Dublin given an effective veto on progress of talks.

What hypocrisy is getting worked up about this.
• Nigel Farage Refuses To Give Up EU Pension (Ind.)
Nigel Farage has refused to give up his EU pension after Brexit, asking: “Why should my family and others suffer even more?” The former Ukip leader was asked on BBC One’s Andrew Marr Show whether he would stick to his principles and turn down his annual MEP pension. “All I can say is, given the arbitrary way the European Union behaves in terms of money, I’d be very surprised if I get any of it,” Mr Farage said. Mr Farage is entitled to an estimated annual pension of £73,000, The Times reports. The 53-year-old would be able to claim the pension at the age of 63.
Pressed by host Andrew Marr on whether he would stick to his principles and turn down the pension, Mr Farage said: “I’m not going to get it anyway. So I don’t think this would even occur.” When he was asked if he would take it, he said: “Of course I would take it. I’ve said that from day one. Why should my family and others suffer even more?” Replying to accusations of hypocrisy, Mr Farage said: “It is not hypocrisy. I’ve just voted to get rid of my job. I was the turkey that voted for Christmas. How is that hypocrisy? If it was hypocrisy, I’d have said we should stay in the EU.”

People should oinstead get worked up about Blair not being able to shut his face. He’s done enough damage.
• Tony Blair Confirms He Is Working To Reverse Brexit (G.)
Tony Blair has confirmed that he is trying to reverse Brexit, arguing that voters deserve a second referendum because the “£350m per week for the NHS” promise has now been exposed as untrue. In an interview with the BBC Radio 4’s The World This Weekend on Sunday, the former prime minister said that what was happening to the “crumbling” NHS was a “national tragedy” and that it was now “very clear” that the Vote Leave promise about Brexit leading to higher NHS spending would not be honoured. “When the facts change, I think people are entitled to change their mind,” said Blair, who has always been a strong opponent of Brexit but who has rarely been so explicit about being on a personal mission to stop it happening.
Asked if his purpose in relation to Brexit was to reverse it, Blair replied: “Yes, exactly so.” He added: “My belief is that, in the end, when the country sees the choice of this new relationship, it will realise that it’s either going to be something that does profound damage to the country, or alternatively, having left the European Union, left the single market, we will try and by some means recreate the benefit of that in some new relationship, in which case I think many people will think, ‘What’s the point?’” Blair rejected the argument that he was defying the will of the people. “The will of the people is not something immutable. People can change their mind if the circumstances change,” he said.

And certainly get worked up about this: ..400,000 more children and 300,000 more pensioners are now living in poverty than five years ago..”
• Fifth of UK Population Now Live In Poverty (Ind.)
Britain’s record on tackling poverty has reached a turning point and is at risk of unravelling, following the first sustained rises in child and pensioner poverty for two decades, a major report has warned. Nearly 400,000 more children and 300,000 more pensioners are now living in poverty than five years ago, during which time there have been continued increases in poverty across both age groups – prompting experts to warn that hard-fought progress towards tackling destitution is “in peril”. The report, by the independent Joseph Rowntree Foundation (JRF), shows that a total of 14 million people in the UK currently live in poverty – more than one in five of the population. While poverty levels fell in the years to 2011-12, changes to welfare policy – especially since the 2015 Budget – have seen the numbers creep up again.
The findings will fuel challenges currently facing Theresa May over failure to improve equality in the UK, after the entire board of her social mobility commission quit over the weekend at the lack of progress towards a “fairer Britain”. ..] The report echoes the concerns of the commission, warning that significant reductions in poverty levels – which researchers measured by the proportion of people in households with an income lower than 60 per cent of the median household income – are at risk of being reversed without immediate action. It warns that the squeeze on living standards now risks storing up problems for the future, with people being caught in a “standstill generation” – unable to build the foundations for a decent, secure life.
Debbie Abrahams MP, Shadow Work and Pensions Secretary, said the 700,000 increase in the number of children and older people in poverty was “totally unacceptable”, adding: “The past seven years of flat-lining wages and austerity cuts, now combined with sharply rising costs of household essentials, is a truly terrifying prospect for millions trying to make ends meet.

Attenborough has been in nature for 70 years. Imagine the changes he’s witnessed, the beauty he’s seen disappear.
• David Attenborough Issues Appeal To Save ‘The Future Of Humanity’ (Ind.)
Sir David Attenborough has urged people to take action to save the “future of humanity” as he opened up about the heartrending Blue Planet II scene in which a baby albatross was killed by a toothpick. The creature was shown lying dead after its mother had mistaken the plastic toothpick for healthy food. In a column in the Radio Times, the veteran presenter spoke of the threats earth is facing, including the eight million tonnes of plastic dumped into the sea each year, global warming and the rate of overfishing. There are concerns that more than a million birds and 100,000 sea mammals and turtles die every year from eating and getting tangled in plastic waste.
Sir David, 91, also echoed a previous call that he hoped US President Donald Trump would reconsider his threat to withdraw from the Paris Agreement on climate change. He wrote that “never before have we been so aware of what we are doing to our planet – and never before have we had such power to do something about it”. “Surely we have a responsibility to care for the planet on which we live? The future of humanity, and indeed of all life on Earth, now depends on us doing so,” he added. “Plastic is now found everywhere in the ocean, from its surface to its greatest depths,” Sir David wrote. “There are fragments of nets so big they entangle the heads of fish, birds and turtles, and slowly strangle them. Other pieces of plastic are so small that they are mistaken for food and eaten, accumulating in fishes’ stomachs, leaving them undernourished.”

When nations grow old
The arts grow cold
And commerce hangs on every tree
–William Blake