
Keith Haring Retrospect 1989
Longtime and dear friend of the Automatic Earth, professor Steve Keen, wrote an article recently that everyone should read (that goes for everything Steve writes). It’s hard to select highlights, but I’ll give it a try. Steve explains where our housing markets went off the rails, what (short-sighted) interests politicians have in subverting them, and, something rarely addressed, why housing markets are unlike any other markets (the turnover of existing properties is financed with newly created money)
He then suggests some measures that might counter this subversion, with a twang of It’s a Wonderful Life nostalgia thrown in. That nostalgia, which will be seen by many as outdated and a grave mistake in these ‘modern times’, instead makes a lot of sense. We might even say it’s the only way to get back on our feet. It resides in the idea that money-circulating building societies, rather than money-creating banks should be in charge of the housing market.
Because it’s not supply and demand that rule the market today, it’s available debt (credit). And banks can, and will, always create more debt at the stroke of a keyboard. That is, until they can’t, and then house prices must and will of necessity fall off a cliff. In Steve’s words: “..mortgage credit causes house prices to rise, leading to yet more credit being taken on until, as in 2008, the process breaks down. And it has to break down, because the only way to sustain it is for debt to continue rising faster than income.
Still, it left me with a big question. But I’ll ask that at the end; here’s Steve first.
The Housing Crisis – There’s Nothing We Can Do… Or Is There?
[..] the UK data is remarkable, even in the context of a worldwide trend to higher levels of leverage. Between 1880 and 1980, private debt in the UK fluctuated as a percentage of GDP, but it never once reached 75% of GDP. But in 1982, both household and corporate debt took off. In 1982, total private debt was equivalent to 61% of GDP, split equally between households and corporations. 25 years later, as the global financial crisis unfolded, private debt was three times larger at 197% of GDP, again split 50:50 between households and corporations.
The key changes to legislation that occurred in 1982 is the UK let banks muscle into the mortgage market that was previously dominated by building societies. This was sold in terms of improving competition in the mortgage market, to the benefit of house buyers: allegedly, mortgage costs would fall. But its most profound impact was something much more insidious: it enabled the creation of credit money to fuel rising house prices, setting off a feedback loop that only ended in 2008.
Building societies don’t create money when they lend, because they lend from a bank account that stores the accumulated savings of their members. There’s no change in bank deposits, which are by far the largest component of the money supply.
However, banks do create money when they lend, because a bank records a loan as their asset when they make an identical entry in the borrower’s account, which enables the property to be bought. This dramatically inflates the price of housing, since, as the politicians themselves acknowledge – housing supply is inflexible, so prices increase far more than supply.
The supply side of the housing market has two main factors: the turnover of the existing stock of housing, and the net change in the number of houses (thanks to demolition of old properties and construction of new ones). The turnover of existing properties is far larger than the construction rate of new ones, and this alone makes housing different to your ordinary market. The demand side of the housing market has one main factor: new mortgages created by the banks.
Monetary demand for housing is therefore predominantly mortgage credit: the annual increase in mortgage debt. This also makes housing very different to ordinary markets, where most demand comes from the turnover of existing money, rather than from newly created money.
We can convert the credit-financed monetary demand for housing into a physical demand for new houses per year by dividing by the price level. This gives us a relationship between the level of mortgage credit and the level of house prices. There is therefore a relationship between the change in mortgage credit and the change in house prices. This relationship is ignored in mainstream politics and mainstream economics. But it is the major determinant of house prices: house prices rise when mortgage credit rises, and they fall when mortgage credit falls. This relationship is obvious even for the UK, where mortgage debt data isn’t systematically collected, and I am therefore forced to use data on total household debt (including credit cards, car loans etc.).
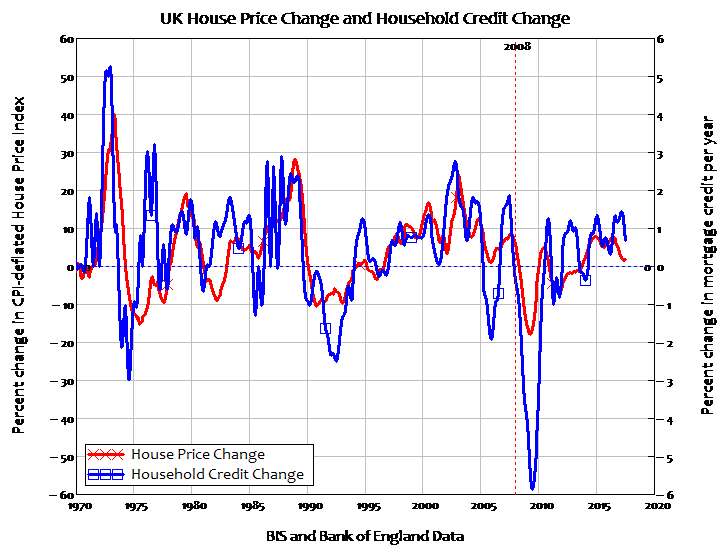
Even then, the correlation is obvious (for the technically minded, the correlation coefficient is 0.6). The US does publish data on mortgage debt, and there the correlation is an even stronger 0.78—and standard econometric tests establish that the causal process runs from mortgage debt to house prices, and not vice versa (the downturn in house prices began earlier in the USA, and was an obvious pre-cursor to the crisis there).
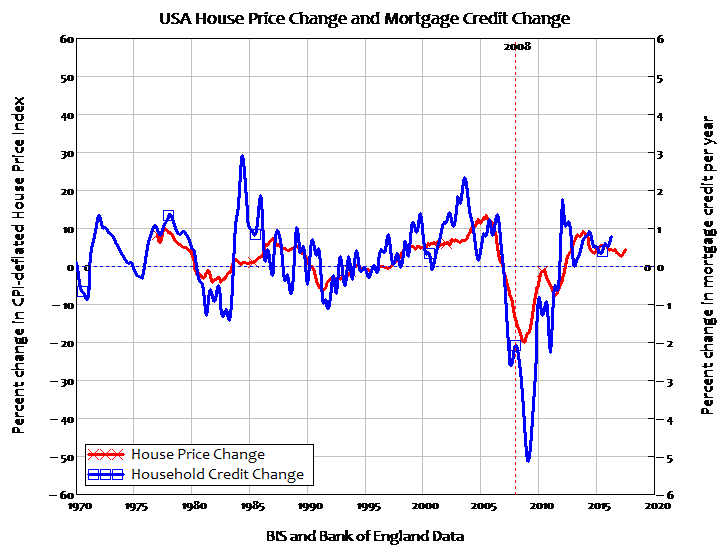
None of this would have happened – at least not in the UK – had mortgage lending remained the province of money-circulating building societies, rather than letting money-creating banks into the market. It’s too late to unscramble that omelette, but there are still things that politicians could do make it less toxic for the public.
The toxicity arises from the fact that the mortgage credit causes house prices to rise, leading to yet more credit being taken on until, as in 2008, the process breaks down.
And it has to break down, because the only way to sustain it is for debt to continue rising faster than income. Once that stops happening, demand evaporates, house prices collapse, and they take the economy down with them. That is no way to run an economy.
Yet far from learning this lesson, politicians continue to allow lending practices that facilitate this toxic feedback between leverage and house prices. A decade after the UK (and the USA, and Spain, and Ireland) suffered property crashes – and economic crises because of them – it takes just a millisecond of Internet searching to find lenders who will provide 100% mortgage finance based on the price of the property.
This should not be allowed. Instead, the maximum that lenders can provide should be limited to some multiple of a property’s actual or imputed rental income, so that the income-earning potential of a property is the basis of the lending allowed against it.
Two smaller points first: Steve doesn’t mention the role of ultra-low rates. Which is a huge factor leading the process. Second, he says his proposals will “..transition us from a world in which we treat housing as a speculative asset rather than what it really is, a long-lived consumption good”. I wonder if perhaps we should take this a step further.
We don’t see land as a consumption good either, or water sources. They are assets that belong to a given community. Or should. So shouldn’t buildings be too? A building society (or some local equivalent, It’s a Wonderful Life style) in a community can’t, won’t lend out money to build homes that serve the interests of the owner, but hamper those of the community. But now I sound even more commie than Steve for many, I know.
On to my main point: if you return mortgage lending to money-circulating building societies, rather than money-creating banks, who’s going to create the money? Don’t let’s forget that a huge part of our present money supply comes from those banks, and much of that from the mortgage loans they issue. Steve may well have thought about this (was he afraid to ask?), and I’d be curious to see his views.
Inflation/deflation is a function of money supply x money velocity (MxV). There are multiple ways to define this, and discuss it, but in the end this remains valid.
This is what the US money supply (stock) has done over the past 30-odd years
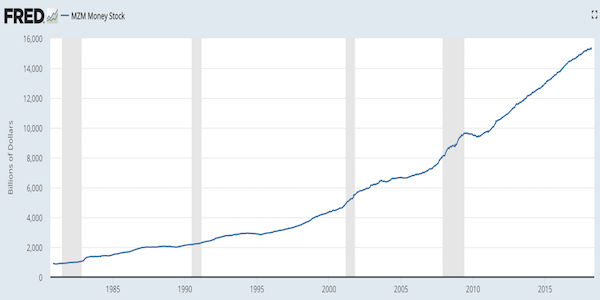
And here is the Case/Shiller home price index for the US over roughly that period. The correlation is painfully clear. Except maybe for that drop in 2008, but the Fed caught that one. Can’t let the money supply fall off a cliff.
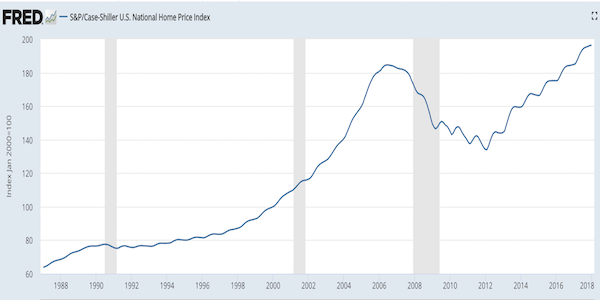
And why can’t we afford to let the money supply fall off a cliff? Because money velocity already has:
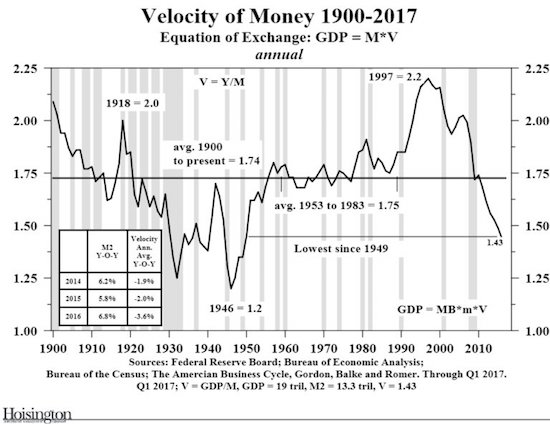
How dramatic that fall has been is perhaps even clearer on a shorter time-frame.
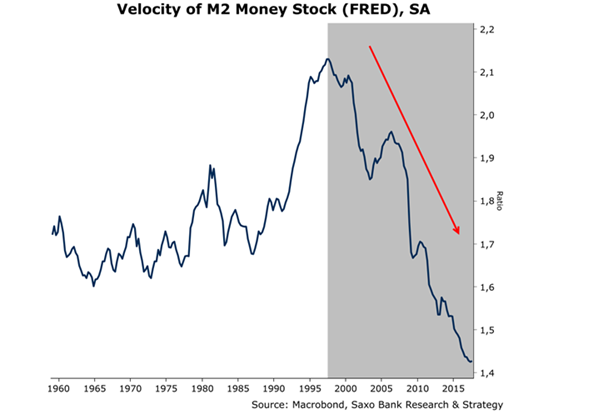
We can say that MV = GDP, or we can make it a bit more complex with MV=PT, where P is prices and T is transactions (or national output), and people can say that this is just one of many ways to define inflation, but when you have a drop in velocity as steep as that one, and you combine it with the rise in money supply we saw, the danger should be obvious.
We have made our economies fully dependent on banks creating loans out of thin air. Which is a ridiculous model, and as Steve says: “That is no way to run an economy”, but we still have. And if and when home prices start to fall, and fewer people buy homes, the money supply will first stop rising, and then start falling, and we will have the mother of all deflations.
If you take the MV = GDP formulation, GDP will go down right with the money supply, unless velocity (V) soars. Which it can’t, because people are maxed out on those mortgages. They can’t spend. If you go with MV=PT, then if money supply falls, so will prices. Unless transactions (output) is demolished, but that will just kill off velocity even more. Why many people see inflation in our future is hard to gauge.
We could, presumably, get our central banks to pump ginormous amounts of money into our societies, but where are they going to put it? Not into our banks(!), which wouldn’t create all those loans anymore, as It’s a Wonderful Life takes over that role, taking the banks and their present role down with it.
Because it’s starting to get obvious that the present ‘system’ is set to go down big time, since as Steve put it:the only way to sustain it is for debt to continue rising faster than income, and we all know where that goes, we can advocate a version of controlled demolition, but who would lead that?
The banks are the most powerful party at the table right now, and controlled demolition of what we have today, as sensible as it may be for society at large, is not for them. Which makes this not only a financial problem, but a political one too: where does power reside. Down the line, it doesn’t even seem to matter much who gives out the loans, there will be very few takers.
Let’s just say we’re open to suggestions. But they better be good.









Home › Forums › The Mother of All Deflations