
Louise Rosskam General store in Lincoln, Vermont Jul 1940



“Friday’s turbocharged jobs headline came thanks to seasonal adjustments and other wizardry at the Bureau of Labor Statistics ..”
• The ‘You Want Fries With That?’ Jobs Report (CNBC)
Consider it a brutal lesson in government math. Friday’s turbocharged jobs headline came thanks to seasonal adjustments and other wizardry at the Bureau of Labor Statistics, which reported that U.S. job growth hit 321,000 even as the unemployment rate held steady at 5.8%. Those numbers, courtesy of establishment survey estimates, sound nice on the surface, and they certainly present reasons if not for unbridled optimism then at least confidence that the job market continues to mend and is on a pretty steady trajectory higher. However, the household survey, which is an actual head count, presents details that show there’s still plenty of work to do. A few figures to consider: That big headline number translated into just 4,000 more working Americans. There were, at the same time, another 115,000 on the unemployment line. That disparity can be explained through an expanding labor force, which grew 119,000, though the participation rate among that group remained at 62.8%, which is just off the year’s worst level and around a 36-year low.
But wait, there’s more: The jobs that were created skewed heavily toward lower quality. Full-time jobs declined by 150,000, while part-time positions increased by 77,000. Analysts, though, mostly gushed over the report. Fixed income strategist David Harris at Schroders said it was “unquestionably strong and significantly exceeded expectations.” Economist Lindsey Piegza at Sterne Agee called it “impressive,” while Paul Ashworth at Capital Economics termed the headline gain “massive” with “labor market conditions improving at breakneck speed.” As for the unseemly nature of the internals, Michelle Meyer of BofAML said the “gift” of a report should override those concerns. “Household jobs were only up 4,000, which on the surface is a disappointment. However, this follows an outsized gain of 683,000 in October and 232,000 in September, leaving the three-month moving average still up a healthy 306,000,” Meyer said in a report for clients. “The monthly survey of household jobs tends to be quite noisy, suggesting caution when reacting to a given month of data.”
But there were several other points not to like in the report. Families, for instance, also were under pressure: There were 110,000 fewer married men at work, while married women saw their ranks shrink by 59,000. And there was an exceedingly huge disparity between expectations and results: ADP’s report Wednesday showed just 208,000 new private sector positions, compared with the 314,000 in the BLS report. That’s a miss of 51%, the worst showing for ADP’s count since April 2011 even though the firm has touted its partnership since then with Moody’s Analytics as a way to make its count more accurate. Some Wall Street analysts had been scaling back their calls, and Goldman Sachs, which has had a good history of picking the number, was expecting gains of 220,000. Even the most buoyant economist on the street, Joe LaVorgna at Deutsche Bank, was looking for 250,000. [..]
Finally, there was a rather startling numerical coincidence: That same 321,000 figure was repeated later in the report—as the total number of bar and restaurant jobs created over the past 12 months. Taken in total, a peek beneath the hood of these numbers suggests a job market that still has a ways to go.

“.. the Household Survey was nowhere close to confirming the Establishment Survey data, suggesting jobs rose only by 4K from 147,283K to 147,287K, and furthermore, the breakdown was skewed fully in favor of Part-Time jobs, which rose by 77K while Full-Time jobs declined by 150K.”
• Full-Time Jobs Down 150K, Participation Rate Stays At 35-Year Lows (Zero Hedge)
While the seasonally-adjusted headline Establishment Survey payroll print reported by the BLS moments ago may be indicative of an economy which the Fed will soon have to temper in an attempt to cool down, a closer read of the November payrolls report shows several other things that were not quite as rosy. First, the Household Survey was nowhere close to confirming the Establishment Survey data, suggesting jobs rose only by 4K from 147,283K to 147,287K, and furthermore, the breakdown was skewed fully in favor of Part-Time jobs, which rose by 77K while Full-Time jobs declined by 150K.
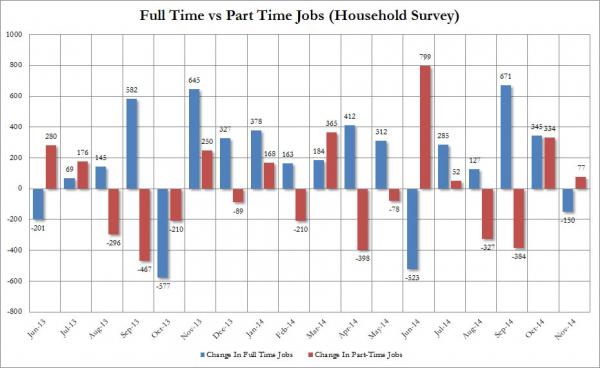
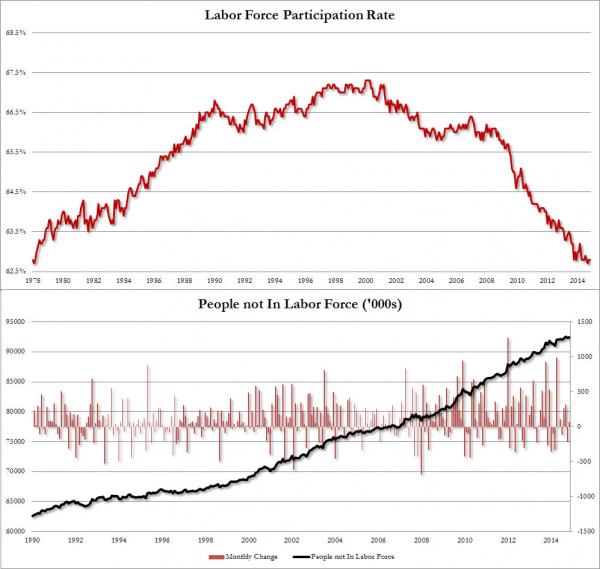
And then for those keeping tabs on the composition of the labor force, the same adverse trends indicated over the past 4 years have continued, with the participation rate remaining flat at 62.8%, essentially the lowest print since 1978, driven by a 69K worker increase in people not in the labor force.

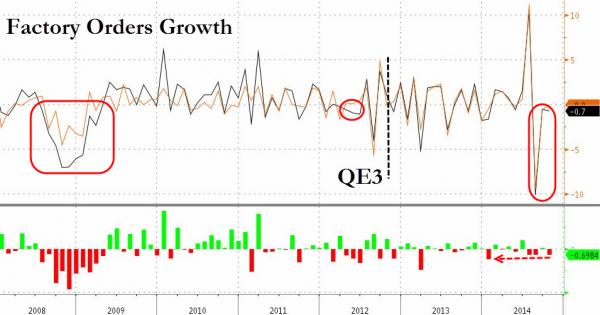
” .. the only other time we had 3 straight months of factory orders declines was in the recession and the 2012 decline was saved by QE3.”
• US Factory Orders Tumble, Miss By Most Since January (Zero Hedge)
But, but, but payrolls data was awesome!! US Factory Orders tumbled -0.7% in October (missing 0.0% expectations) for the 3rd month in a row (for the first time since June 2012). Rather notably, the only other time we had 3 straight months of factory orders declines was in the recession and the 2012 decline was saved by QE3. The data was ugly across the board: Non-durable orders -1.5%, non-defense, ex-air tumbled -1.6%, and inventories-to-shipments levels are at the year’s highs. More problematically for GDP enthusiasts, October inventories of manufactured nondurable goods decreased -0.5% to $249.0 billion driven by petroleum and coal products (but wait, lower oil prices are unequivocally good right?)

The Economist has no idea what is going on. Not the first time. All they see is a rising global GDP because of lower oil prices.
• The New Economics Of Oil (Economist)
The official charter of OPEC states that the group’s goal is “the stabilisation of prices in international oil markets”. It has not been doing a very good job. In June the price of a barrel of oil, then almost $115, began to slide; it now stands close to $70. This near-40% plunge is thanks partly to the sluggish world economy, which is consuming less oil than markets had anticipated, and partly to OPEC itself, which has produced more than markets expected. But the main culprits are the oilmen of North Dakota and Texas. Over the past four years, as the price hovered around $110 a barrel, they have set about extracting oil from shale formations previously considered unviable. Their manic drilling – they have completed perhaps 20,000 new wells since 2010, more than ten times Saudi Arabia’s tally – has boosted America’s oil production by a third, to nearly 9m barrels a day (b/d). That is just 1m b/d short of Saudi Arabia’s output. The contest between the shalemen and the sheikhs has tipped the world from a shortage of oil to a surplus.
Cheaper oil should act like a shot of adrenalin to global growth. A $40 price cut shifts some $1.3 trillion from producers to consumers. The typical American motorist, who spent $3,000 in 2013 at the pumps, might be $800 a year better off—equivalent to a 2% pay rise. Big importing countries such as the euro area, India, Japan and Turkey are enjoying especially big windfalls. Since this money is likely to be spent rather than stashed in a sovereign-wealth fund, global GDP should rise. The falling oil price will reduce already-low inflation still further, and so may encourage central bankers towards looser monetary policy. The Federal Reserve will put off raising interest rates for longer; the European Central Bank will act more boldly to ward off deflation by buying sovereign bonds.
There will, of course, be losers. Oil-producing countries whose budgets depend on high prices are in particular trouble. The rouble tumbled this week as Russia’s prospects darkened further. Nigeria has been forced to raise interest rates and devalue the naira. Venezuela looks ever closer to defaulting on its debt. The spectre of defaults and the speed and scale of the price plunge have unnerved financial markets. But the overall economic effect of cheaper oil is clearly positive. Just how positive will depend on how long the price stays low. That is the subject of a continuing tussle between OPEC and the shale-drillers. Several members of the cartel want it to cut its output, in the hope of pushing the price back up again. But Saudi Arabia, in particular, seems mindful of the experience of the 1970s, when a big leap in the price prompted huge investments in new fields, leading to a decade-long glut. Instead, the Saudis seem to be pushing a different tactic: let the price fall and put high-cost producers out of business. That should soon crimp supply, causing prices to rise.

But this the reality: loss of investment, defaults and job losses.
• More than $150 Billion of Oil Projects Face the Axe in 2015 (Reuters)
Global oil and gas exploration projects worth more than $150 billion are likely to be put on hold next year as plunging oil prices render them uneconomic, data shows, potentially curbing supplies by the end of the decade. As big oil fields that were discovered decades ago begin to deplete, oil companies are trying to access more complex and hard to reach fields located in some cases deep under sea level. But at the same time, the cost of production has risen sharply given the rising cost of raw materials and the need for expensive new technology to reach the oil. Now the outlook for onshore and offshore developments – from the Barents Sea to the Gulf or Mexico – looks as uncertain as the price of oil, which has plunged by 40% in the last five months to around $70 a barrel.
Next year companies will make final investment decisions (FIDs) on a total of 800 oil and gas projects worth $500 billion and totalling nearly 60 billion barrels of oil equivalent, according to data from Norwegian consultancy Rystad Energy. But with analysts forecasting oil to average $82.50 a barrel next year, around one third of the spending, or a fifth of the volume, is unlikely to be approved, head of analysis at Rystad Energy Per Magnus Nysveen said. “At $70 a barrel, half of the overall volumes are at risk,” he said. Around one third of the projects scheduled for FID in 2015 are so-called unconventional, where oil and gas are extracted using horizontal drilling, in what is known as fracking, or mining. Of those 20 billion barrels, around half are located in Canada’s oil sands and Venezuela’s tar sands, according to Nysveen.

“.. credit markets – the most sensitive to cashflows at this stage – are signalling either prices have considerably further to fall or will remain at these thinly-profitable-if-at-all prices for considerably longer ..”
• Energy Bond Crash Contagion Suggests Oil Will Stay Lower For Longer (Zero Hedge)
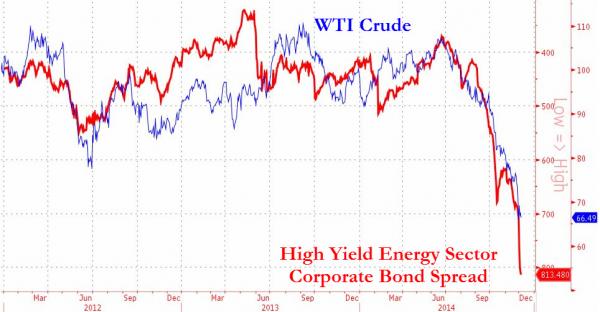
When we first explained to the public that the excessive leverage and currently squeezed cashflow of many US oil producers could “trigger a broader high-yield market default cycle,” the world’s smartest TV-anchors shrugged off lower oil prices as ‘unequivocally good’ for all. Now, as a 40% collapse in new well permits and liquidations occurring at the well-head, the world outside of credit markets is starting to comprehend the seriousness of the crash of a sector that was responsible for 93% of jobs created in this ‘recovery’. The credit risk of HY energy corporates has more than doubled to a record 815bps (over risk-free-rates) crushing any hopes of cheap funding/rolling debt loads. Suddenly expectations of 1/3rd of energy firms restructuring is not so crazy… The chart below suggests another problem for hopers… credit markets – the most sensitive to cashflows at this stage – are signalling either prices have considerably further to fall or will remain at these thinly-profitable-if-at-all prices for considerably longer…

.. “we’re setting ourselves up for a major fiasco“ ..
• Natural Gas: The Fracking Fallacy (Nature)
When US President Barack Obama talks about the future, he foresees a thriving US economy fuelled to a large degree by vast amounts of natural gas pouring from domestic wells. “We have a supply of natural gas that can last America nearly 100 years,” he declared in his 2012 State of the Union address. Obama’s statement reflects an optimism that has permeated the United States. It is all thanks to fracking — or hydraulic fracturing — which has made it possible to coax natural gas at a relatively low price out of the fine-grained rock known as shale. Around the country, terms such as ‘shale revolution’ and ‘energy abundance’ echo through corporate boardrooms.
Companies are betting big on forecasts of cheap, plentiful natural gas. Over the next 20 years, US industry and electricity producers are expected to invest hundreds of billions of dollars in new plants that rely on natural gas. And billions more dollars are pouring into the construction of export facilities that will enable the United States to ship liquefied natural gas to Europe, Asia and South America. All of those investments are based on the expectation that US gas production will climb for decades, in line with the official forecasts by the US Energy Information Administration (EIA). As agency director Adam Sieminski put it last year: “For natural gas, the EIA has no doubt at all that production can continue to grow all the way out to 2040.”
But a careful examination of the assumptions behind such bullish forecasts suggests that they may be overly optimistic, in part because the government’s predictions rely on coarse-grained studies of major shale formations, or plays. Now, researchers are analysing those formations in much greater detail and are issuing more-conservative forecasts. They calculate that such formations have relatively small ‘sweet spots’ where it will be profitable to extract gas. The results are “bad news”, says Tad Patzek, head of the University of Texas at Austin’s department of petroleum and geosystems engineering, and a member of the team that is conducting the in-depth analyses. With companies trying to extract shale gas as fast as possible and export significant quantities, he argues, “we’re setting ourselves up for a major fiasco”.

“.. a full six months after Mr Draghi first talked loosely of a €1 trillion blitz to head off deflation risks [..] the ECB balance sheet has shrunk by over €100bn.”
• Draghi’s Authority Drains Away As Half ECB Board Joins Mutiny (AEP)
The European Central Bank is facing a full-blown leadership crisis. Mario Draghi’s authority is ebbing, with powerful implications for financial markets and the long-term fate of monetary union. Both Die Zeit and Die Welt report that three members of the ECB’s six-strong executive board refused to sign off on Mr Draghi’s latest statement, an unprecedented mutiny in the sanctum sanctorum of the ECB’s policy making machinery. The dissenters are reportedly Germany’s Sabine Lautenschläger, Luxembourg’s Yves Mersch, and more surprisingly France’s Benoît Cœuré, an indication that Paris is still hoping to avoid a breakdown in relations with Berlin over the management of EMU. The reality is that a full six months after Mr Draghi first talked loosely of a €1 trillion blitz to head off deflation risks, almost nothing has actually happened. The ECB balance sheet has shrunk by over €100bn. Talk has achieved a weaker euro but that is not monetary stimulus. It does not offset the withdrawal of $85bn of net bond purchases by the US Federal Reserve for the global economy as a whole.
It is a zero-sum development. The clash comes at a delicate moment amid Italian press reports that Mr Draghi may soon go home, drafted to take over the Italian presidency as the 89-year old Giorgio Napolitano prepares to step down. Such an outcome is unlikely. Yet there is no doubt that Mr Draghi has pressing family reasons to return to Rome, and he barely disguises his irritation with Frankfurt any longer. This incendiary column in the ARD Tagesschau gives a flavour of what is being said in Germany. Fairly or not, Mr Draghi is accused of losing his temper, refusing to listen to objections, cutting off Bundesbank chief Jens Weidmann, and retreating to a “narrow kitchen cabinet”. The latest dispute was over a change in the wording of the ECB statement on its balance sheet. While it appears semantic and trivial – whether the €1 trillion boost is “expected” or “intended” – the underlying clash is serious. The hawks will not be bounced into full-fledged quantitative easing before they are ready. They are patently playing for time, still hoping that the Rubicon may never be crossed.
Mrs Lautenschläger raised eyebrows last weekend by violating the pre-meeting ‘Purdah’, warning that the bar on QE is still very high. She decried “activism” for the sake of it and warned that QE would do more harm than good at this point. Purchases of government bonds amount to fiscal transfer. They create a “serious incentive problem”, she said. She is of course backed by the Bundesbank’s Jens Weidmann, who said this morning that monetary policy is too loose for German needs – even as the Bundesbank halves its economic growth forecast for Germany to 1pc next year, and even as the share of goods in Germany’s price basket in deflation reaches 31.2pc. Mr Weidmann says the crash in oil prices is a “mini-stimulus”, seeming to imply that it therefore reduces any need for QE. The Germans suspect that Mr Draghi is trying rush through sovereign QE so that there will be a lender of last resort in place for Club Med bonds next year as banks sell their holdings, following the repayment of ECB loans (LTROs).
Italian lenders have doubled their portfolio of Italian state bonds (BTPs) to roughly €400bn since Mr Draghi launched his first €1 trillion carry trade three years ago. Mediobanca expects this to fall by €100bn in 2015. Who is going to buy this flood of supply on the market, and at what price? Mr Draghi made clear that the ECB can override Germany on bond purchases if need be. “We don’t need to have unanimity,” he said, though he could hardly have answered otherwise when questioned explicitly on the point. One can imagine the scandal if he had suggested instead that Germany has a veto.

Seen any coverage of this in the western press?
• EU Sanctions Relief For Russia’s Top Banks, Oil Companies (RT)
The European Union has amended sanctions against Russia’s biggest lenders like Sberbank and VTB on long-term financing, and eased some sanctions on the oil industry. The EU says Russia’s biggest lenders – Sberbank, VTB, Gazprombank, Vnesheconombank and Rosselkhozbank – will now be allowed access to long –term financing should the solvency of their European subsidiaries be at risk. The announcement released Friday refers to “loans that have a specific and documented objective to provide emergency funding to meet solvency and liquidity criteria for legal persons established in the Union, whose proprietary rights are owned for more than 50% by any entity referred to in Annex III [Russian banks – Ed.].” The EU has also specified the terms and conditions on which it can lift the ban on providing equipment for oil exploration.
Its supply is still banned to Russia itself, or the exclusive economic zone and offshore territories. However, EU said it may “grant an authorization where the sale, supply, transfer or export of the items is necessary for the urgent prevention or mitigation of an event likely to have a serious and significant impact on human health and safety or the environment.” This basically clarifies the position of the latest set of EU sanctions. The notion of “Arctic oil exploration” means the embargo is applied to oil exploration on the offshore Arctic. “Deep water exploration” means any operation extracting oil carried out deeper than 150 meters below the surface.
The sanctions target the finance, energy and defense sectors. In July 2014 the EU issued a “sectoral list” which includes Sberbank, VTB, Gazprombank, Russian Agricultural Bank (Rosselkhozbank) and Vnesheconombank. The lenders were cut off from long-term (over 30 days) international financing. The EU has banned three Russian energy companies Rosneft, Gazpromneft and Transneft from raising long-term debt on European capital markets. It has also halted services Russia needs to explore oil and gas in the Arctic, deep sea and shale extraction projects. On Friday Russia’s gas major Gazprom said it had inked a €390 million loan agreement with UniCredit bank. The EU however refused to comment on the news, with the EU foreign affairs department saying that the implementation of adopted restrictive measures is the responsibility of each EU country’s national authorities.

Well done Shinzo!
• Crashing Yen Leads To Record Number Of Japanese Bankruptcies (Zero Hedge)
Last week, Zero Hedge first showed a chart so simple, even a Krugman could get it: at this point (and really ever since USDJPY 110 and higher), any incremental Yen devaluation is destructive for the Japanese economy, leading to an unprecedented surge in corporate bankruptcies and, ultimately, economic depression.
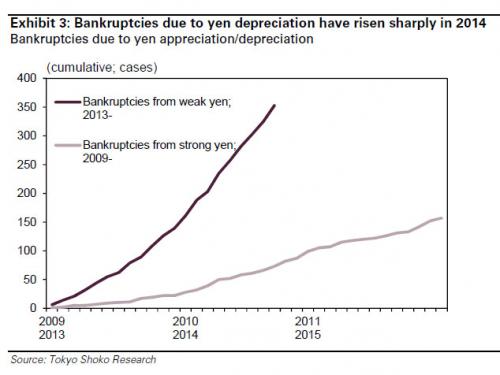
The obvious logic here led even the Keynesian studs at Goldman to declare that “Further yen depreciation could be a net burden.” Unfortunately for Abe and Kuroda, halting the Yen devaluation here would be suicide, as Japan now needs its currency to devalue every single day to mask the fact of the underlying economic devastation, or else the Japanese people may (and should) vote Abe out, which would lead to a prompt end to Abenomics, an epic collapse in the Nikkei, and put thousands of weak-Yen chasing Mrs. Watanabes in margin call purgatory. Sadly, that will not happen. We say “sadly” because an end end to Abenomics, which is really Krugmanomics now, is the only thing that could save Japan now. And just to prove that, here is Japan Times confirming what we said, with a report that “Corporate bankruptcies linked to the yen’s slide hit a new record in November, highlighting the strains on small and midsize companies as Prime Minister Shinzo Abe campaigns for re-election on his deflation-busting economic strategy.”
42 of the companies that failed in November cited the weakened currency as a contributing cause, bringing total bankruptcies associated with the yen so far this year to 301, almost triple that of the same period in 2013, according to a survey by Teikoku Databank Ltd. It said surging costs of imported food, metals and construction materials are squeezing small companies. The yen broke through 120 per dollar on Thursday in New York for the first time since 2007, as Abe’s handpicked Bank of Japan governor pumps a record amount of funds into the economy to stoke inflation. [..] “The business conditions for small and medium-size companies are severe,” said Norio Miyagawa, an economist at Mizuho Securities Co. “The more the yen weakens, the more the drawbacks will become evident, unless the benefits big companies are seeing spill over to consumption through an increase in wages.”

“There is simply no way to escape the need for ever more debt once you get locked into this economic catch 22.”
• A Comprehensive Breakdown of America’s Economic House of Cards (Beversdorf)
If we face the worse case projection, let’s call it 200% debt to GDP by 2039, 10 yr Treasuries cannot be more than around 2% yield in order to remain within the historical debt service to GDP range. This is where things really break down. Because if we cannot entice lenders today at 2.5% or 3% interest with 70% debt to GDP there is simply no way lenders will be attracted at 2% with debt to GDP at 200%. So let’s think about what this means. Now the CBO budget projections predict deficits will increase forever after 2018. And we will see why this is true shortly. This will require massive amounts of debt over the next 25 years.
And if we don’t have willing lenders we’re back to monetizing most of that debt as we’ve done for the past several years. This means massive amounts of money printing. And so we put ourselves into a downward spiral of devaluation, which means inflation. Inflation perpetuates larger deficits as spending increases and even more money printing and so the downward spiral worsens. This will be made much worse by the winding down currently taking place of the petrodollar as demand for dollars will see significant declines. Alternatively to monetizing debt, we can raise interest rates to attract lenders to the market. Let’s say we get to the 20 year average of 7.5%. That means 7.5% of 200% of GDP, so 15% of GDP. Well, we’ve already stated that total tax revenues equate to about 17% of GDP.
This means total debt service will eat up virtually every bit of tax revenue, again leading to massive deficits so even more debt will be required to cover all other expenditures. That leads to more borrowing and worsening balance sheet metrics requiring even higher interest rates. And so we can see very quickly this alternative also leads to a downward spiral. Further, we see that under both scenarios of monetizing debt or incentivizing lenders, a debt driven economy will result in endlessly rising deficits requiring ever more debt. There is simply no way to escape the need for ever more debt once you get locked into this economic catch 22.

And bond yields keep falling … A topsy turvy world, until it turns back around and right side up with a vengeance.
• S&P Wakes Up, Cuts Italy to One Notch Above Junk (WolfStreet)
Italy has one of the most troubled economies in the EU. Businesses and individuals are buckling under confiscatory taxes that everyone is feverishly trying to dodge. Banks are stuffed with non-performing loans that have jumped 20% from a year ago. The economy is crumbling under an immense burden of government debt that, unlike Japan, Italy cannot slough off the easy way by devaluing its own currency and stirring up a big bout of inflation – because it doesn’t have its own currency. Devaluation and inflation used to be Italy’s favorite methods of dealing with its economic problems. It went like this: Politicians made promises that they knew couldn’t be kept but that bought a lot of votes. When everything ground down as industries were getting hammered by competition from across the border, the government stirred up inflation, and then over some weekend, the lira would be devalued.
It was bitter medicine. It was painful. It didn’t even cure anything. It impoverished the people. But it temporarily made Italy competitive with its neighbors once again. Most recently, Italy devalued in 1990 and then again 1992 against the European Exchange Rate Mechanism, a predecessor to the euro. Having to take this bitter medicine time and again had made Italians the most eager to adopt the euro. The idea of a currency that would be out of reach of politicians and that would function as a reliable store of value, run by the Germans as if it were the mark, and in turn, keep politicians honest – all that seemed like paradise. But it just hasn’t kept Italian politicians honest. Only this time, their favorite tools are gone. The economy is now a mess.
Economic “growth” has been negative or zero for the last 13 quarters. And the country’s debt, no matter of how hard the government tries to fudge the numbers, just keeps ballooning. So, on Friday, ratings agency Standard & Poor’s woke up and cut Italy’s sovereign credit rating to BBB–, just one notch above junk, which is the dreaded BB. It cited the economy’s perennial shrinkage and lousy competitiveness. The deteriorating economic fundamentals and a political unwillingness to address the deficit were making the mountain of public debt increasingly unsustainable. The ECB has been busy doing “whatever it takes” to keep the cost of funding this wobbly construct as low as possible. It lowered its own benchmark interest rate to near zero. It instituted negative deposit rates, it’s contemplating a big round of QE, all to keep Italy (and some of its cohorts) afloat a little while longer.

Wonder where they got the money.
• Russia’s Gazprom Receives Prepayment From Ukraine For Gas Supplies (Reuters)
Russian natural gas producer Gazprom said on Saturday it had received a prepayment of $378.22 million from Ukraine for natural gas supplies, paving the way for the first shipments to Kiev since Moscow cut supplies in June. Ukraine’s state energy firm, Naftogaz, said on Friday it had transferred the sum to Gazprom for December. A Gazprom spokesman confirmed the money had been received. In line with a deal signed by Naftogaz and Gazprom in October, flows to Ukraine from Russia, which were severed in a dispute over prices and debts, will resume within 48 hours from when the Russian firm receives the transfer. Naftogaz did not say how much gas it planned to buy, but earlier the energy ministry said this could be about 1 billion cubic metres. Russian news agencies also put the amount at 1 billion cubic metres on Saturday.

Ron Paul has had it right all the way since this nonsense started. But the Putin bashing in the western media keeps running at a fever pitch.
• Reckless Congress ‘Declares War’ on Russia (Ron Paul)
Today the US House passed what I consider to be one of the worst pieces of legislation ever. H. Res. 758 was billed as a resolution “strongly condemning the actions of the Russian Federation, under President Vladimir Putin, which has carried out a policy of aggression against neighboring countries aimed at political and economic domination.” In fact, the bill was 16 pages of war propaganda that should have made even neocons blush, if they were capable of such a thing. These are the kinds of resolutions I have always watched closely in Congress, as what are billed as “harmless” statements of opinion often lead to sanctions and war. I remember in 1998 arguing strongly against the Iraq Liberation Act because, as I said at the time, I knew it would lead to war. I did not oppose the Act because I was an admirer of Saddam Hussein – just as now I am not an admirer of Putin or any foreign political leader – but rather because I knew then that another war against Iraq would not solve the problems and would probably make things worse.
We all know what happened next. That is why I can hardly believe they are getting away with it again, and this time with even higher stakes: provoking a war with Russia that could result in total destruction! If anyone thinks I am exaggerating about how bad this resolution really is, let me just offer a few examples from the legislation itself: The resolution (paragraph 3) accuses Russia of an invasion of Ukraine and condemns Russia’s violation of Ukrainian sovereignty. The statement is offered without any proof of such a thing. Surely with our sophisticated satellites that can read a license plate from space we should have video and pictures of this Russian invasion. None have been offered. As to Russia’s violation of Ukrainian sovereignty, why isn’t it a violation of Ukraine’s sovereignty for the US to participate in the overthrow of that country’s elected government as it did in February?
We have all heard the tapes of State Department officials plotting with the US Ambassador in Ukraine to overthrow the government. We heard US Assistant Secretary of State Victoria Nuland bragging that the US spent $5 billion on regime change in Ukraine. Why is that OK? The resolution (paragraph 11) accuses the people in east Ukraine of holding “fraudulent and illegal elections” in November. Why is it that every time elections do not produce the results desired by the US government they are called “illegal” and “fraudulent”? Aren’t the people of eastern Ukraine allowed self-determination? Isn’t that a basic human right? The resolution (paragraph 13) demands a withdrawal of Russia forces from Ukraine even though the US government has provided no evidence the Russian army was ever in Ukraine. This paragraph also urges the government in Kiev to resume military operations against the eastern regions seeking independence.

Wise man. So no-one will listen.
• Chief Constable Warns Against ‘Drift Towards (Thought) Police State’ (Guardian)
The battle against extremism could lead to a “drift towards a police state” in which officers are turned into “thought police”, one of Britain’s most senior chief constables has warned. Sir Peter Fahy, chief constable of Greater Manchester, said police were being left to decide what is acceptable free speech as the efforts against radicalisation and a severe threat of terrorist attack intensify. It is politicians, academics and others in civil society who have to define what counts as extremist ideas, he says. Fahy serves as chief constable of Greater Manchester police and also has national counter-terrorism roles. He is vice-chair of the police’s terrorism committee and national lead on Prevent, the counter radicalisation strategy. He stressed he supported new counter-terrorism measures unveiled by the government last week, including bans on alleged extremist speakers from colleges.
Fahy said government, academics and civil society needed to decide where the line fell between free speech and extremism. Otherwise, he warned, it would be decided by the security establishment, so-called “securocrats”, including the security services, government and senior police chiefs like Fahy. Speaking to the Guardian, Fahy said: “If these issues [defining extremism] are left to securocrats then there is a danger of a drift to a police state”. He added: “I am a securocrat, it’s people like me, in the security services, people with a narrow responsibility for counter-terrorism. It is better for that to be defined by wider society and not securocrats.” Fahy said officers were also having to decide issues such as when do anti-gay or anti-women’s rights sentiments cross the line, as well as when radical Islam veers into extremism: “There is a danger of us being turned into a thought police,” he said. “This securocrat says we do not want to be in the space of policing thought or police defining what is extremism.”

Der Spiegel has a go at this. Interesting in that it is a view from abroad, but not all that good.
• The Tragedy of America’s First Black President (Spiegel)
At the beginning of his term, Barack Obama likely never imagined that a new wave of violence would take place during his presidency. But it is not an accident. After all, he himself raised hopes that progress would be made. Yet after six years in office, little has changed for blacks in the US. Obama held the speech that raised the hopes of black Americans on March 18, 2008 as a candidate in Philadelphia. It was a reaction to comments made by his Chicago pastor and friend Jeremiah Wright, who had accused the US government of crimes against blacks. “God damn America … for killing innocent people,” he intoned from the pulpit in a sermon that threatened to derail Obama’s candidacy. “The profound mistake of Reverend Wright’s sermons is not that he spoke about racism in our society,” Obama said in his speech. “It’s that he spoke as if our society was static; as if no progress has been made; as if this country … is still irrevocably bound to a tragic past.”
Obama was referring to a time when blacks were forced to serve whites as slaves; a time when they weren’t even second-class citizens, instead being treated as commodities to be raised and sold at market. But he also was referring to the decades leading up to the 1960s when blacks were not allowed to use the same park benches as whites and were forced to sit at the back of the bus. In that speech, Obama promised to create “a more perfect union,” in reference to the preamble of the US Constitution. He sought to finally fulfill the promise made 50 years earlier by fellow Democrat Lyndon B. Johnson. In remarks at the signing of the Civil Rights Bill on July 2, 1964, Johnson said he hoped to “eliminate the last vestiges of injustice in our beloved country” and to “close the springs of racial poison.” Many observers believe that Obama’s speech was a decisive factor in his becoming the first black president in American history half a year later. It is still widely considered to be one of his best.
But the final push to realize Johnson’s dream has still not taken place. The situation today gives the impression that African-Americans are adequately represented “without giving them the possibility to really take advantage” of that representation, says Kareem Crayton, a law professor at the University of North Carolina. Eduardo Bonilla-Silva, sociology professor at Duke University, agrees. “Having a black president doesn’t mean much in our day-to-day lives.” [..] “It’s the age of Obama, and yet civil rights have gone backwards. What went wrong? asked the New Republic on its cover in August. The issue, which appeared after Michael Brown’s death in Ferguson, spoke of a “new racism.” Indeed, the kinds of deadly events that took place in Ferguson and Cleveland have now convinced many blacks that it wasn’t Obama who was right back in the spring of 2008. Rather, it was his angry pastor, Jeremiah Wright.

Attempts to put numbers on this don’t strike me as useful, they’ll just change all the time anyway. It seems far more important to make clear that this is not about money.
• Adapting To A Warmer Climate To Cost Three Times As Much As Thought (Guardian)
Adapting to a warmer world will cost hundreds of billions of dollars and up to three times as much as previous estimates, even if global climate talks manage to keep temperature rises below dangerous levels, warns a report by the UN. The first United Nations Environment Programme (Unep) ‘Adaptation Gap Report’ shows a significant funding gap after 2020 unless more funds from rich countries are pumped in to helping developing nations adapt to the droughts, flooding and heatwaves expected to accompany climate change. “The report provides a powerful reminder that the potential cost of inaction carries a real price tag. Debating the economics of our response to climate change must become more honest,” said Achim Steiner, Unep’s executive director, as ministers from nearly 200 countries prepare to join the high level segment of UN climate talks in Lima, Peru, next week.
“We owe it to ourselves but also to the next generation, as it is they who will have to foot the bill.” Without further action on cutting greenhouse gas emissions, the report warns, the cost of adaptation will soar even further as wider and more expensive action is needed to protect communities from the extreme weather brought about by climate change. Delegates from the Alliance of Small Islands States at the UN climate conference in Lima, which opened on Monday, are already feeling those impacts. They have appealed for adaptation funds for “loss and damage” as their homelands’ very existence is threatened by rising sea levels. “We’re keen to see the implementation of the Green Climate Fund – we’re still waiting,” Netatua Pelesikoti, director of the climate change office at the Secretariat of the Pacific Environment Programme, referring to a fund set up to hope poorer countries cope with global warming.
“The trickle down to each government in the Pacific is very slow but we can’t abandon the process at this stage,” said the Tongan delegate. Rich countries have pledged $9.7bn to the Green Climate Fund but the figure is well short of the minimum target of $100bn each year by 2020. The Adaptation Gap Report said adaptation costs could climb to $150bn by 2025/2030 and $250-500bn per year by 2050, even based on the assumption that emissions are cut to keep temperature rises below rises of 2C above pre-industrial levels, as governments have previously agreed. However, if emissions continue rising at their current rate – which would lead to temperature rises well above 2C – adaptation costs could hit double the worst-case figures, the report warned.

We need a lot more people like this man, or we will see the twilight of Africa’s wildlife in our lifetimes.
• One Man’s 40-Year Fight Against Africa’s Ivory Poachers (John Vidal)
Most tourists who walk into Hong Kong’s many licensed ivory stores and carving factories, browse the displays of statues, pendants and jewellery and accept the official assurances that it all comes from sustainable sources. But not the reserved middle-aged man who last month went into a Kowloon shop. What started with a few polite questions about the provenance of the objects on show turned swiftly to confrontation. Within minutes he was furious and the owner had threatened to call the police. Having spent nearly 40 years trying to protect elephants and other African wildlife from poachers, Richard Bonham says he was shocked to see, for the first time, the Hong Kong stores where most of the world’s ivory ends up. The statistics, he says, show that Africa’s elephant population has crashed from 1.3 million in 1979 to around 400,000 today.
In the last three years alone, around 100,000 elephants have been killed by poachers and more are now being shot than are being born. Rhinos are on the edge too. For a Hong Kong shopkeeper, each trinket is something to profit from. But for Bonham, they tell a story of cruelty, desperation and exploitation. “I wanted to see for myself. Yes, I was angry. There’s no other word for it. I saw the shops with huge stocks that, despite the import ban, are not dwindling. Yet the [Hong Kong] government has chosen not to recognise or address the lack of legitimacy of their trade. “The experience of seeing the end destination of ivory was important to me. It completed the circle from seeing elephant herds, stampeding in terror at the scent of man, from seeing the blood-soaked soil around lifeless carcasses to whimsical trinkets in glass display cases.”
In London last week to receive the Prince William lifetime achievement award conservation, he produced a Hong Kong government document that showed how the former British colony holds over 100 tonnes of ivory stocks despite a 25-year-old import ban that was meant to eliminate all stocks 10 years ago. It is proof, he says, that the Hong Kong government knows that its traders have been topping up their stocks with “black”, or illegal ivory from poached elephants, yet do nothing. Back in Africa, he said, the trade ends in carnage and impoverished environments. “I have watched elephants in the Selous game reserve in Tanzania drop from over 100,000 animals to probably less than 10,000 today and that number is still falling. During a one-hour drift down the Rufiji river three years ago I was seeing up to six different elephant herds coming down to drink.
Now I see none – they’ve gone, back to dust and into the African soil, with their ivory shipped off to distant lands. There is a silence on that river that will take decades to return – if at all.” But despite the statistics, he says he is upbeat for conservation, at least in the Amboseli national park in Kenya, where he lives among the Maasai. “It’s not all bad news, it’s not too late. We have got poaching there more or less under control. We are seeing elephants on the increase and lions, that 15 years ago where on the verge of local extinction, have increased by 300%. But probably more importantly we are seeing local communities setting aside land for conservancies and wildlife.









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle December 6 2014