
DPC Old Absinthe House, bar, New Orleans 1906



Because the entire system is leveraged to the hilt.
• Global Investors Are More Exposed To Interest-Rate Hikes Than Ever (BBG)
With any luck, the world economy will eventually be strong enough for central banks to follow the U.S. Federal Reserve in ending what has been an unprecedented period of extremely low interest rates. If and when they do, they’ll run straight into the same issue that the Fed now faces: Raising rates will precipitate unusually large losses for investors. Over the past several years, investors have gone to great lengths in their search for returns in a low-rate environment. They’ve done so in part by buying longer-maturity bonds, which tend to offer higher yields but are also more sensitive to changes in rates. One gauge of this risk is effective duration, which estimates the percentage decline in a bond’s price given a one-percentage-point increase in yield.
The measure is near all-time highs in the U.S., according to a report issued last week by the Office of Financial Research. The situation globally is no less precarious. Consider the effective duration for the BofA Merrill Lynch Global Broad Market Index, which tracks about $45 trillion in investment-grade bonds issued in major currencies – including government, corporate, mortgage and other asset-backed securities. As of last week, it stood at 6.6, meaning that a one-percentage-point increase in yield would wipe almost $3 trillion off the value of all the bonds included in the index. That’s a larger potential loss than at just about any point since the index’s inception in 1996. Here’s how that looks:
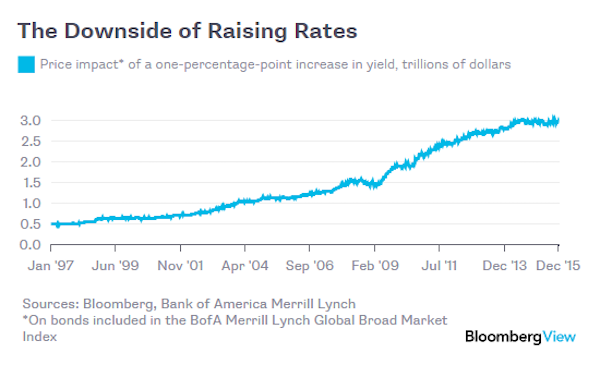
The high level of interest-rate risk illustrates a dilemma for central bankers everywhere. The power of traditional monetary stimulus depends in large part on the willingness of people and companies to borrow for new projects and purchases. But as the debt burden grows, it makes markets and the entire economy more susceptible to rate increases. It can also undermine the effect of rate cuts, as borrowers increasingly struggle under the weight of their existing obligations.

“These academic pettifoggers are so blinded by their tinker toy macro-model that they can’t even see the flashing red lights warning of recession just ahead.”
• The Keynesian Recovery Meme Is About To Get Mugged, Part 1 (Stockman)
Yellen said at least one thing of importance last week, but not in a good way. She confessed to the frightening truth that the FOMC formulates its policies and actions based on forecasts of future economic developments. My point is not simply that our monetary politburo couldn’t forecast its way out of a paper bag; that much they have proved in spades during their last few years of madcap money printing. Notwithstanding the most aggressive monetary stimulus in recorded history – 84 months of ZIRP and $3.5 trillion of bond purchases – average real GDP growth has barely amounted to 50% of the Fed’s preceding year forecast; and even that shortfall is understated owing to the BEA’s systemic suppression of the GDP deflator.
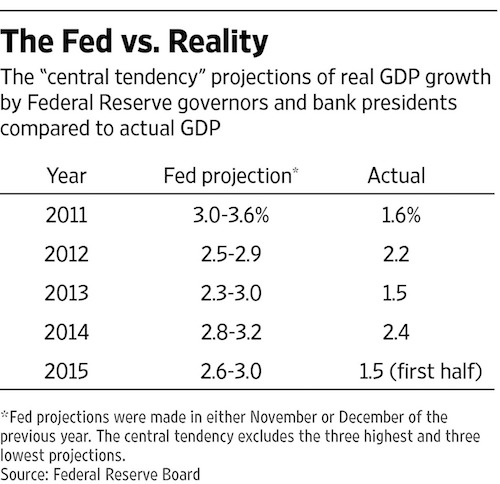
What I am getting at is that it’s inherently impossible to forecast the economic future, but that is especially true when the forecasting model is an obsolete Keynesian relic which essentially assumes a closed US economy and that balance sheets don’t matter. Actually, balance sheets now matter more than anything else. The $225 trillion of debt weighing on the world economy – up an astonishing 5.5X in the last two decades – imposes a stiff barrier to growth that our Keynesian monetary suzerains ignore entirely. Likewise, the economy is now seamlessly global, meaning that everything which counts such as labor supply and wage trends, capacity utilization and investment rates and the pace of business activity and inventory stocks is planetary in nature. By contrast, due to the narrow range of activity they capture, the BLS’ deeply flawed domestic labor statistics are nearly useless. And they are a seriously lagging indicator to boot.
Nevertheless, Yellen & Co. are obsessed with the immeasurable and largely irrelevant level of “slack” in the domestic labor market. They falsely view it as a proxy for the purported gap between potential and actual GDP. Not surprisingly, they are now under the supreme illusion that the labor slack has been largely absorbed and the output gap nearly closed. So they are raising money market rates by a smidgeon to confirm the US economy’s strength and that the Keynesian nirvana of full employment is near at hand. No it isn’t! These academic pettifoggers are so blinded by their tinker toy macro-model that they can’t even see the flashing red lights warning of recession just ahead.

Oil went up a whiff overnight. I always look at the spread between WTI and Brent. The smaller it gets, the higher the risks. Usually, it hovers between $2-3. Right now, it’s at 50 cents.
• Brent Oil Hits 11-Year Low As Global Supply Balloons (Reuters)
Brent oil cratered to its lowest price in more than 11 years on Monday, as demand for heating oil slumped on warmer-than-normal temperatures and traders tested for a bottom. U.S. crude remained above its 2009 low and settled up a penny a barrel as traders squared positions ahead of the January contract’s expiration. The February contract declined and analysts expect stockpiles to build again this week, signaling further oversupply in already glutted market. Concerns about swelling global crude supply and slow demand sparked by economic weakness in China have been recurring themes during this year’s rout. Analysts said the market was still testing for a bottom. “The key in finding the bottom of the market comes in a tightening of the supply side,” said Gene McGillian, senior analyst at Tradition Energy in Stamford, Connecticut.
OPEC and Russia will keep producing at high volumes, increasing pressure on U.S. producers to throttle back production, he said. “I think we’re getting ready for another round of capex cuts in North America,” he said. Heating oil futures weighed down the crude complex, hitting a new July 2004 low warmer-than-expected temperatures have hit seasonal demand. “The market is waiting for the next announcement,” said Tyche Capital Advisors senior research analyst John Macaluso. “The equity markets are waiting on crude oil, and crude oil is waiting for a bounce before shorts will come back into the market.” Crude short-sellers will be reluctant to return before U.S. crude recovers to $35.50, he said. Global oil production is running close to record highs. With more barrels poised to enter the market from nations such as Iran and Libya, the price of crude is set for its largest monthly percentage decline in seven years.

“..1% of stations selling gas at $1.59 a gallon..”
• US Gas Prices Fall Below $2 – In Some Places Under $1.60 (MarketWatch)
Christmas came early for U.S. drivers on Monday, as the national average gasoline price fell below $2 a gallon for the first time since March 2009. AAA put the average U.S. gas price at $1.998 per gallon on Monday, while fuel-price tracking service GasBuddy.com calculated the national average at $1.995 a gallon. That’s the lowest price by either measure since March 25, 2009. Unsurprisingly, drivers can credit a global glut of crude oil for the steady pressure on gas prices. Brent crude the global oil benchmark, plumbed levels last seen in 2004 on Monday, while the January contract for the U.S. benchmark CLF6, -0.20% West Texas Intermediate crude, was down 49 cents, or 1.4%, ahead of expiration at $34.24 a barrel on Nymex. The most-active February contract is down 1.3% at $35.58.
“In areas where there are no refinery bottlenecks, we’ve been able to see the falling price of crude oil translated directly into cheaper gas prices,” said Patrick DeHaan, senior petroleum analyst at GasBuddy.com, in a phone interview. Nymex reformulated gasoline futures for January delivery slumped 6.33 cents, or 5%, to $1.2114 a gallon. So how low are gas prices? In much of the country, the price is already well under $2 a gallon, AAA notes, with 1% of stations selling gas at $1.59 a gallon. On a state-by-state basis, Missouri has the lowest average price at $1.77, followed by Oklahoma and South Carolina at $1.78, and Tennessee and Kansas at $1.79.

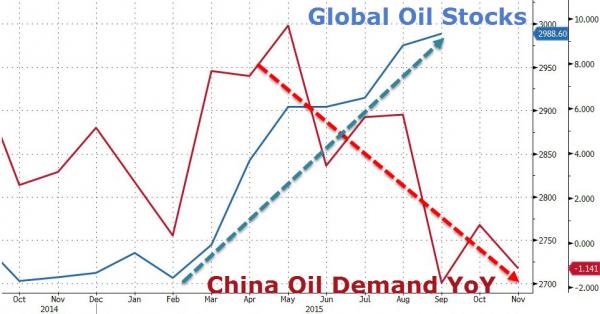
China. That’s all.
• The Real “Death Cross” Of Oil Markets (ZH)
The ‘death cross’ of these two energy market indicators is all one needs to know about the oil market… As Bloomberg notes, total industry oil stocks reported by the International Energy Agency rose for a third month, increasing by 0.5% to the highest on record at 2.99 billion barrels. China’s Beige Book, released last week, showed further economic deterioration in one of the world’s largest commodity-consuming nations in the fourth quarter. Until these two indicators change direction, lower-er for longer-er will remain.

Lots of last legs there.
• Risk Of Insolvency Hangs Over UK High Street Retailers (Guardian)
A string of retailers could face insolvency in the new year with tough trading on the high street in the run-up to Christmas leaving businesses fighting for survival, two influential industry bodies have warned. Widespread discounting and warmer-than-average weather have cranked up the pressure on high street retailers over the festive period. In the last few years a number of high street retailers have called in administrations either just before or after Christmas, including Woolworths, HMV, Zavvi, and Jessops. Retailers generate roughly 40% of their annual profits between October and December, underlining the importance of the period. However, if a high street business struggles during the festive season then its death knell is typically the quarterly rental payment they have to make to landlords at the end of December.
Atradius, one of the world’s largest trade credit insurers, has warned that retailers face a “perfect storm” that could lead to a bleak start to 2016 and a “fresh wave of insolvencies”. The comments from Atradius are significant because if a credit insurer refuses to back a retailer then suppliers will be unable to insure their orders with the business and could decide not to provide it with products. Owen Bassett, senior risk underwriter at Atradius, said: “Those who went into the fourth quarter needing – rather than wanting – a strong performance could be looking at a troubled future. “Experience tells us that when retailers need an exceptional seasonal sales period and then hit financial difficulty, we often see failures in the first quarter. It is not unusual in this sector to be loss-making during Q1 and with the first payment of quarterly rent due in January it can be difficult to survive after a poor Q4.”

Private debt. Should have a lot more attention. And not just in Britain.
• UK Economy Concerns As Household Debt Balloons To £40 Billion (PA)
Families are expected to run up £40bn of debt this year, sparking fears about Britain’s economic recovery. Labour raised concerns that millions of households would face “serious hardship” if interest rates rise and warned the borrowing trend could harm the economy. The latest Office for Budget Responsibility (OBR) forecasts have found that households have moved from a surplus of £67bn in 2010, the year the coalition took power, to a £40bn deficit this year. Unsustainable borrowing is on course to near the levels reached in the run-up to the 2008 financial crash, according to Labour. Seema Malhotra, the shadow chief secretary to the Treasury, said: “George Osborne is relying on millions of British families going further into debt to hit his growth targets.
“This is risky behaviour from a chancellor whose policy decisions are hurting, not helping, British families. Alarm bells should be ringing. There is a real risk that millions of families will face serious hardship if interest rates start to rise. “Of course families need access to credit and the ability to borrow to invest for the future. George Osborne should be seeking to rebalance the economy away from an over-reliance on borrowing and debt. “Labour is clear about the need for a strong and sustainable economic recovery. Osborne’s short-term political decisions risk real long-term damage to the finances of millions of British families and the nation’s economy.” The former business secretary Sir Vince Cable warned Britain was returning to “old and unhappily discredited” methods of economic growth. He told the Independent: “We’re back on the treadmill of growth being sustained by personal borrowing. Much of it is against an inflating housing stock.

Abenomics is a different way of saying anything goes.
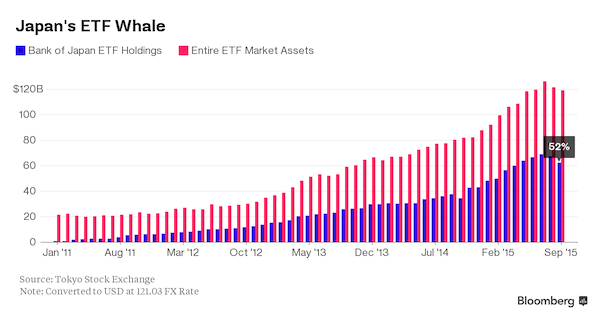
• The Bank of Japan’s $2.5 Billion Plan to Buy Non-Existent ETFs (BBG)
Haruhiko Kuroda has a new plan. He’s going to buy $2.5 billion of something that doesn’t exist. Markets were roiled Friday after the Bank of Japan unveiled measures including purchasing exchange-traded funds that track companies which are “proactively making investment in physical and human capital.” The central bank will spend 300 billion yen ($2.5 billion) a year from April buying such securities to offset the market impact as it resumes selling stocks purchased earlier from financial institutions. The only problem is such ETFs have never been made in Japan, at least not yet. Even as fund providers start hundreds of so-called “smart beta” products that choose stocks based on everything from dividends to volatility, ETFs that pick companies for how they deploy their cash are rare in global markets.
“These kinds of ETFs don’t exist now. Using capital spending as a factor in deciding what goes in an ETF is quite unusual,” said Koei Imai, who oversees $25 billion of ETFs at Nikko Asset Management Co. in Tokyo. “I think the message from the BOJ is for us to go out and make them.” The central bank is aware such products aren’t yet available and in the meantime will buy ETFs tracking the JPX-Nikkei Index 400, a government-backed equity measure started last year that chooses companies based on return on equity and operating profit. The BOJ also already purchases ETFs linked to the Nikkei 225 Stock Average and Topix index and owns roughly half of the market for ETFs in Japan.

How to kill confidence.
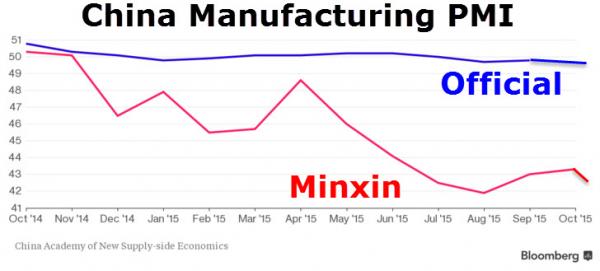
• China ‘Suspends’ Another Unofficial PMI Data Set For A ‘Major Adjustment’ (ZH)
For the second time in two months, an economic data series that indicate drastically weak performance in China has been “suspended.” Having seen Markit/Caixin’s flash gauge of China’s manufacturing discontinued in October (having plunged notably divergently from the government’s official data), Bloomberg reports that the publishers of the alternative China Minxin PMI will stop updating the series to make a “major adjustment.” Guess which time series was just “suspended”…
As Bloomberg details,
Release of the unofficial purchasing managers index jointly compiled by China Minsheng Banking Corp. and the China Academy of New Supply-side Economics will be suspended starting this month, the Beijing-based academy said in an e-mailed statement Monday, about six hours before the latest monthly data were scheduled for release.
Minxin’s suspension is the second in recent months as policy makers in the world’s second-largest economy struggle to arrest a deceleration in growth. Another early estimate of China’s manufacturing sector, a flash gauge of a purchasing managers index compiled by Markit Economics and sponsored by Caixin Media, was discontinued Oct. 1. Minxin’s PMI readings are based on a monthly survey covering more than 4,000 companies, about 70% of which are smaller enterprises. The private gauges have shown a more volatile picture than the official PMIs in the past year.
The manufacturing PMI declined to 42.4 in November from 43.3 in October, while the non-manufacturing reading fell to 42.9 from 44.2, according the the latest release. The factory gauge fell to a record low of 41.9 in August. China’s official PMI from the National Bureau of Statistics fell to a three-year low of 49.6 in November.

Humor?
• Zimbabwe To Make Chinese Yuan Legal Currency After Beijing Cancels Debts (AFP)
Zimbabwe has announced that it will make the Chinese yuan legal tender after Beijing confirmed it would cancel $40m in debts. “They [China] said they are cancelling our debts that are maturing this year and we are in the process of finalising the debt instruments and calculating the debts,” minister Patrick Chinamasa said in a statement. Chinamasa also announced that Zimbabwe will officially make the Chinese yuan legal tender as it seeks to increase trade with Beijing. Zimbabwe abandoned its own dollar in 2009 after hyperinflation, which had peaked at around 500bn%, rendered it unusable. It then started using a slew of foreign currencies, including the US dollar and the South African rand.
The yuan was later added to the basket of the foreign currencies, but its use had not been approved yet for public transactions in the market dominated by the greenback. Use of the yuan “will be a function of trade between China and Zimbabwe and acceptability with customers in Zimbabwe,” the minister said. Zimbabwe’s central bank chief John Mangudya was in negotiations with the People’s Bank of China “to see whether we can enhance its usage here,” said Chinamasa. China is Zimbabwe’s biggest trading partner following Zimbabwe’s isolation by its former western trading partners over Harare’s human rights record.

Europe’s dumb struggle with Moscow continues.
• Russia, EU Trade Talks Fail, Kiev Set To Face Retaliation (Reuters)
The EU failed to allay Russia’s concerns about Ukraine’s free-trade accord with the 28-nation bloc on Monday, leaving Kiev to face Russian retaliation through tighter bilateral trade rules from 2016. Closer ties between Ukraine and the EU, including the free trade deal, were at the heart of a battle for influence between Brussels and Moscow in Russia’s former satellite. When the then-Ukrainian president, Viktor Yanukovich, ditched the accord in early 2014 under pressure from Russia, protests erupted on the street of Kiev leading to a crisis in which he fled power and a pro-Europe leadership took over. The EU and Ukraine delayed implementation of their trade deal by a year out of deference to Moscow’s concerns that it could lead to a flood of European imports across its borders, damaging the competitiveness of Russian exports.
But comments by EU and Russian officials on Monday indicated that numerous meetings between the two sides to try to narrow differences and assuage Moscow’s concerns had failed. EU Trade Commissioner Cecilia Malmstrom raised doubts about the validity of the Russian concerns, saying some were “not real.” “We have been very open in listening to some of the concerns of Russia. Some of them we think are not real in economic terms. Some of them could potentially be real,” Malmstrom told a news conference following final talks in Brussels. Russian Economy Minister Alexei Ulyukayev, speaking in Brussels, said there was no deal and Moscow would scrap trade preferences dating back to 2011 for Ukraine as of 2016, when the bilateral EU-Ukraine deal will be implemented. “An agreement has not been reached. We were left with our concerns on our own and we are forced to safeguard our economic interest unilaterally,” Ulyukayev told reporters.

A stalemate that seems to end in either a fragile left government or new elections.
• Political Uprising In Spain Shatters Illusion Of Eurozone Recovery (AEP)
Spain risks months of political paralysis and a corrosive showdown with Germany over fiscal austerity after insurgent movements smashed the traditional two-party system, leaving the country almost ungovernable. The electoral earthquake over the weekend in one of the eurozone’s ‘big four’ states has echoes of the shock upsets in Greece and Portugal this year, a reminder that the delayed political fuse from years of economic depression and mass unemployment can detonate even once the worst seems to be over. Bank stocks plummeted on the Madrid bourse as startled investors awoke to the possibility of a Left-wing coalition that included the ultra-radical Podemos party, which won 20.7pc of the votes with threats to overturn the government’s bank bail-out and to restructure financial debt.
Pablo Iglesias, the pony-tailed leader of the Podemos rebellion, warned Brussels, Berlin, and Frankfurt that Spain was retaking control over its own destiny after years of kowtowing to eurozone demands. “Our message to Europe is clear. Spain will never again be the periphery of Germany. We will strive to restore the meaning of the word sovereignty to our country,” he said. The risk spread on Spanish 10-year bonds jumped eight basis points to 123 over German Bunds, though there is no imminent danger of a fresh debt crisis as long as the European Central Bank is buying Spanish bonds under quantitative easing. The IBEX index of equities slid 2.5pc, with Banco Popular and Caixabank both off 7pc. Premier Mariano Rajoy has lost his absolute majority in the Cortes.
Support for the conservative Partido Popular crashed from 44pc to 29pc, costing Mr Rajoy 5m votes as a festering corruption scandal took its toll. The electorate punished the two mainstream parties that have dominated Spanish politics since the end of the Franco dictatorship in the 1970s, and which by turns became the reluctant enforcers of eurozone austerity. The Socialists (PSOE) averted electoral collapse but have lost their hegemony over the Left and risk being outflanked and ultimately destroyed by Podemos, just as Syriza annihilated the once-dominant PASOK party in Greece. It had been widely assumed that Mr Rajoy would have enough seats to form a coalition with the free-market and anti-corruption party Ciudadanos, but this new reform movement stalled in the closing weeks of the campaign.
“There is enormous austerity fatigue and the country as a whole has clearly shifted to the Left,” said sovereign bond strategist Nicholas Spiro. Yet the Left has not won enough votes either to form a clear government. “The issue now is whether Spain is governable. All the parties are at daggers drawn and this could drag on for weeks. I don’t see any sustainable solution. We can certainly forget about reform,” he said. Mr Spiro said Spain has already seen a “dramatic deterioration” in the underlying public finances over the last eighteen months, although this has been disguised by a cyclical rebound, the stimulus of cheap oil and a weak euro, and QE from Frankfurt. “They have simply gone for growth,” he said.

Posterchild no more.
• Portugal Taxpayers Face €3 Billion Loss After 2nd Bank Bailout In 2 Years (ZH)
Back in August of 2014, Portugal had an idea. Lisbon would use some €5 billion from the country’s Resolution Fund to shore up (read: bailout) Portugal’s second largest bank by assets, Banco Espirito Santo. The idea, basically, was to sell off Novo Banco SA (the “good bank” that was spun out of BES) in relatively short order and use the proceeds to pay back the Resolution Fun. That way, the cost to taxpayers would be zero. You didn’t have to be a financial wizard or a fortune teller to predict what was likely to happen next. Unsurprisingly, the auction process didn’t go so well.
As we recounted in September, there were any number of reasons why Portugal had trouble selling Novo, not the least of which was that two potential bidders – Anbang Insurance Group and Fosun International which, you’re reminded, is run by the recently “disappeared” Chinese Warren Buffett – suddenly became far more risk-averse in the wake of the financial market turmoil in China. Talks with US PE (Apollo specifically) also went south, presumably because no one knows if this “good” bank will actually turn out to need more capital going forward given that NPLs sit at something like 20% while the H1 loss totaled €250 million thanks to higher provisioning for said NPLs. Now, the auction process has been mothballed and will restart in January. This matters because if the bank can’t be sold, the cost of the bailout ends up being tacked onto Lisbon’s budget.
The impact is substantial. In September, when the effort to sell Novo collapsed, the government restated its 2014 deficit which, after accounting for the bailout, ballooned to 7.2% of GDP from 4.5%. Portugal will tell you that this is only “temporary,” but let’s face it, if they haven’t managed to sell it by now, then one has to believe the prospects are grim – at least in terms of fetching anything that looks like a decent price. Well don’t look now, but Portugal’s seventh-largest bank, Banco Internacional do Funchal, now needs a bailout too. Banif (as it’s known) will be split into a “good” and “bad” bank, and its “healthy” assets will be sold to Banco Santander for €150 million. The government will inject up to €2.2 billion the European Commission said on Monday, to cover “future contingencies.”
Hilariously, the bailout was necessary because the bank was unable to repay a previous government cash injection. “The government injected €1.1 billion of fresh capital into the lender in January 2013 to allow it to meet minimum capital thresholds imposed by the banking regulator,” WSJ writes. For its trouble, Lisbon got a 60% stake in the bank and several hundred million worth of CoCos which the bank missed a payment on last year. “That,” WSJ goes on to note, “triggered close scrutiny by the European Commission, which opened an investigation into the legality of the state aid.” “The commission had said that Banif’s restructuring plan might not be enough to allow the bank to repay the state,” Bloomberg adds. “The Bank of Portugal said in the statement on Sunday that a ‘probable’ decision from the commission declaring the state aid illegal would create a shortage of capital at the bank.”

“We now enter the “discovery” phase of financial collapse, where things labeled “capital” and “credit” turn out to be mere holograms.”
• Christmas Present (Jim Kunstler)
Theory du jour: the new Star Wars movie is sucking in whatever meager disposable lucre remains among the economically-flayed mid-to-lower orders of America. In fact, I propose a new index showing an inverse relationship between Star Wars box office receipts and soundness of the financial commonweal. In other words, Star Wars is all that remains of the US economy outside of the obscure workings of Wall Street — and that heretofore magical realm is not looking too rosy either in this season of the Great Rate Hike after puking up 623 points of the DJIA last Thursday and Friday. Here I confess: for thirty years I have hated those stupid space movies, as much for their badly-written scripts (all mumbo-jumbo exposition of nonsensical story-lines between explosions) as for the degenerate techno-narcissism they promote in a society literally dying from the diminishing returns and unintended consequences of technology.
It adds up to an ominous Yuletide. Turns out that the vehicle the Federal Reserve’s Open Market Committee was driving in its game of “chicken” with oncoming reality was a hearse. The occupants are ghosts, but don’t know it. A lot of commentators around the web think that the Fed “pulled the trigger” on interest rates to save its credibility. Uh, wrong. They had already lost their credibility. What remains is for these ghosts to helplessly watch over the awesome workout, which has obviously been underway for quite a while in the crash of commodity prices (and whole national economies — e.g. Brazil, Canada, Australia), the janky regions of the bond markets, the related death of the shale oil industry, and the imploding hedge fund scene. As it were, all credit these days looks shopworn and threadbare, as if the capital markets had by stealth turned into a swap meet of previously-owned optimism.
Who believes in anything these days besides the allure of fraud? Capital is supposedly plentiful these days — look how much has rushed into the dollar from the nervous former go-go nations with their wobbling ziggurats of bad loans and surfeit of production capacity — but what actually constitutes that capital? Answer: the dwindling faith anyone will pay you back next Tuesday for a hamburger today. We now enter the “discovery” phase of financial collapse, where things labeled “capital” and “credit” turn out to be mere holograms. Fed Chair Janet Yellen herself had a sort of hologramatic look last Wednesday when she stepped onto her Delphic platform to reveal the long-heralded interest rate news. Perhaps Mrs. Yellen is a figment conjured by George Lucas’s Industrial Light & Magic shop (now owned by Disney). What could be more fitting in a smoke-and-mirrors culture?

Recognizable patterns.
• Et Tu, Brute? – How Empires Die (Thomas)
The state-owned Bank of China has been ordered by an American court to hand over customer information to the US. The bank has refused to comply, as to do so would violate China’s privacy law. The US court has subsequently ordered the Bank of China to pay a fine of $50,000 per day. Any guess as to how this is likely to turn out? China is a sovereign nation, halfway around the globe from the US, yet the US seems to feel that it’s somehow entitled to set the rules for China (as well as the other nations in the world). When China sees fit to develop islands in the South China Sea that it has laid claim to for centuries, it begins to hear threatening noises from the US military. A candidate for US president declares that he would buzz the islands with Air Force One, the Presidential jet, saying, “They’ll know we mean business.”
All over the world, those who live outside the US are increasingly observing that the US has become so drunk with power that they’re threatening both friend and foe with fines, trade restrictions, monetary sanctions, warfare, and invasions. And in so-observing, those of us who have studied the history of empires note that history is once again repeating itself. Time and time again, great empires build themselves up through industriousness and sound economic management only to subsequently decline into debt, complacency, and an entitlement mind-set. Over the millennia, empires as disparate as Persia, Rome, Spain, and Great Britain rose to dominate the world. Of course, we know how those empires turned out and, by extension, we might hazard an educated guess as to how the present American Empire will end.
In the final throes of empire-decline, we invariably observe the more sociopathic trends of a failing power, such as we’re seeing today from the US. First and foremost, any empire declines as a result of economic mismanagement. Decline from within (pandering to the populace with “bread and circuses”) and without (endless conquest and/or maintenance of dominance over far-flung geography) drain even the wealthiest government. Even eighteenth-century Spain, with all its billions in stolen New World gold, could not pay its ever-increasing bills and warfare-driven debt. Typically, the empire of the day enjoys the world’s greatest fighting force/armada/weapons build-up yet, when the money runs out, the war machine simply stops. Soldiers think more about their empty bellies than how much ammunition they have left.
Generals continue to issue orders, but they cease to be followed after the supply lines begin to dry up. And the leaders of a collapsing empire invariably make a fatal mistake: they assume that all the goodwill the empire gained when it was on its rise is permanent – that it will continue, even if the empire behaves like the world’s foremost bully. This is never the outcome. Invariably, as the decline nears its end, allies, without ever saying so, begin to withdraw their support. We see this today, as European leaders (America’s most essential allies) realise that the empire is becoming an arrogant liability and they begin cutting deals with the other side, as European leaders are now doing with Russia and others.

“The only way to avoid future crashes is for the Fed to stop creating inflation and bubbles.”
• Do We Need The Fed? (Ron Paul)
Stocks rose Wednesday following the Fed’s announcement of the first interest rate increase since 2006. However, stocks fell just two days later. One reason the positive reaction to the Fed’s announcement did not last long is that the Fed seems to lack confidence in the economy and is unsure what policies it should adopt in the future. At her Wednesday press conference, Fed Chair Janet Yellen acknowledged continuing “cyclical weakness” in the job market. She also suggested that future rate increases are likely to be as small, or even smaller, then Wednesday’s. However, she also expressed concerns over increasing inflation, which suggests the Fed may be open to bigger rate increases. Many investors and those who rely on interest from savings for a substantial part of their income cheered the increase.
However, others expressed concern that even this small rate increase will weaken the already fragile job market. These critics echo the claims of many economists and economic historians who blame past economic crises, including the Great Depression, on ill-timed money tightening by the Fed. While the Federal Reserve is responsible for our boom-bust economy, recessions and depressions are not caused by tight monetary policy. Instead, the real cause of economic crisis is the loose money policies that precede the Fed’s tightening. When the Fed floods the market with artificially created money, it lowers the interest rates, which are the price of money. As the price of money, interest rates send signals to businesses and investors regarding the wisdom of making certain types of investments.
When the rates are artificially lowered by the Fed instead of naturally lowered by the market, businesses and investors receive distorted signals. The result is over-investment in certain sectors of the economy, such as housing. This creates the temporary illusion of prosperity. However, since the boom is rooted in the Fed’s manipulation of the interest rates, eventually the bubble will burst and the economy will slide into recession. While the Federal Reserve may tighten the money supply before an economic downturn, the tightening is simply a futile attempt to control the inflation resulting from the Fed’s earlier increases in the money supply. After the bubble inevitably bursts, the Federal Reserve will inevitability try to revive the economy via new money creation, which starts the whole boom-bust cycle all over again. The only way to avoid future crashes is for the Fed to stop creating inflation and bubbles.

The more they can infringe on privacy, the more they will.
• Apple Says UK Surveillance Law Would Endanger All Customers (BBG)
Apple outlined its opposition to a proposed U.K. surveillance law, saying threats to national security don’t justify weakening privacy and putting the data of hundreds of millions of users at risk. The world’s most valuable company is leading a Silicon Valley challenge to the proposed U.K. law, called the Investigatory Powers bill, which attempts to strengthen the capabilities of law-enforcement agencies to investigate potential crimes or terrorist attacks. The bill would, among other things, give the government the ability to see the Internet browsing history of U.K. citizens. Apple said the U.K. government already has access to an unprecedented amount of data.
The Cupertino, California-based company is particularly concerned the bill would weaken digital privacy tools such as encryption, creating vulnerabilities that will be exploited by sophisticated hackers and government spy agencies. In response to the U.K. rules, other governments would probably adopt their own new laws, “paralyzing multinational corporations under the weight of what could be dozens or hundreds of contradictory country-specific laws,” Apple said. “The creation of backdoors and intercept capabilities would weaken the protections built into Apple products and endanger all our customers,” Apple said in an eight-page submission to the U.K. committee considering the bill. “A key left under the doormat would not just be there for the good guys. The bad guys would find it too.”

And that will not happen.
• Half of World’s Coal Must Go Unmined to Meet Paris Climate Target (BBG)
Coal, the fuel that powered the industrial revolution, is in hiding. While the world still has 890 billion tons of reserves, enough to last more than 65 years, about half must stay underground if nations are to meet environmental limits agreed to earlier this month in Paris, Bank of America Corp. said in a report. Burning less coal is the easiest way to lower emissions blamed for climate change, the bank said. The pact reached by 195 nations doesn’t target specific fuels, yet coal remains the world’s largest source of planet-warming carbon dioxide. A global oversupply of the power plant fuel has pushed producers into bankruptcy and sent prices to at least seven-year lows. The Paris agreement only further diminishes prospects for a recovery.
“The latest carbon initiatives are the nail in the coffin for global coal,” Sabine Schels, Peter Helles and Franciso Blanch, analysts at Bank of America said in the Dec. 18 report. If emissions limits take hold, “50% of the world’s current coal reserves may never be dug out.” Coal demand stopped growing in 2014 for the first time since the 1990s as China’s economy cooled, the Paris-based International Energy Agency said Dec. 18. Coal for delivery to Amsterdam, Rotterdam, and Antwerp, an Atlantic benchmark, is trading near an eight-year low. Newcastle coal, a barometer for the Asia-Pacific market, is at the cheapest in records going back to 2008, data compiled by Bloomberg show.

Last month, the warning came from China. Now it’s England and Wales.
• It’s ‘Almost Too Late’ To Stop A Global Superbug Crisis (PA)
It is “almost too late” to stop a global superbug crisis caused by the misuse of antibiotics, a leading expert has warned. Scientists have a “50-50” chance of salvaging existing antibiotics from bacteria which has become resistant to its effects, according to Dr David Brown. The director at Antibiotic Research UK, whose discoveries helped make more than £20bn ($30bn) in pharmaceutical sales, said efforts to find new antibiotics are “totally failing” despite significant investment and research. It comes after a gene was discovered which makes infectious bacteria resistant to the last line of antibiotic defence, colistin (polymyxins). The resistance to the colistin antibiotic is considered to be a “major step” towards completely untreatable infections and has been found in pigs and humans in England and Wales.
Public Health England said the risk posed to humans by the mcr-1 gene was “low” but was being monitored closely. Performing surgery, treating infections and even travelling abroad safely all rely to some extent on access to effective antibiotics. It is feared the crisis could further penetrate Europe as displaced migrants enter from a war-torn Middle East, where countries such as Syria have increasing levels of antibiotic resistance. Dr Brown told said: “It is almost too late. We needed to start research 10 years ago and we still have no global monitoring system in place. “The issue is people have tried to find new antibiotics but it is totally failing – there has been no new chemical class of drug to treat gram-negative infections for more than 40 years.









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle December 22 2015