
William Henry Jackson New Orleans, “Canal Street from the Clay monument” 1890

“The saving grace would have been to invest in Detroit startups or other investments that successfully straddled wars, Russian revolution, crises..”
• A Black Swan The Size Of World War I (IBT)
To illustrate a strategic gap common to today’s portfolio managers, George Sokoloff, PhD, founder and CIO at Carmot Capital, proposes an interesting thought experiment – a breakdown of a typical, well-diversified investment strategy in 1912. Teetering on the cusp of revolution, war and depression, Sokoloff’s point is that, even following a modern portfolio management strategy, the manager would stand to lose the vast majority of their assets. People tend to rely on historically stable relationships between bonds and stocks, and when that relationship breaks down – as often happens in a liquidity event – even complicated strategies involving some arbitrage, essentially blow up. Imagine being a wealth manager out of Geneva in 1912, trying to create a nice diversified portfolio of developed market bonds, and emerging market bonds, says Sokoloff.
Say 39% of client assets would be split between stocks of Great Britain, France, German Empire, Austria-Hungary and Italy: truly mature, developed markets. Some 21% of assets would go into stocks of the two fastest growing economies: Russian Empire and North American United States. The wealth manager might also put a smidge into emerging economies like Argentina, Brazil or Japan. In bonds, allocation would be somewhat similar. Gilts with sub-3% yield would be the benchmark, with the rest of developed and emerging bonds trading at a spread. Alternatives investment could be in anything ranging from arable land in central Russia or the Great Plains, to shares of new automotive or aeroplane startups in Europe and America, to Japanese manufacturing ventures.
This well-intentioned, balanced portfolio would be in for a wild ride in the next decade and possibly drawdowns of as much as 80%. The saving grace would have been to invest in Detroit startups or other investments that successfully straddled wars, Russian revolution, crises and the technological boom of the early 20th century. Sokoloff told IBTimes UK: “That thought experiment is really frightening to me. You followed very sound modern portfolio management advice back then and still in ten years your portfolio is gone. I don’t think we are really learning the lessons of history, especially now that the global economy is so much more interconnected than it was before.”

Scary.
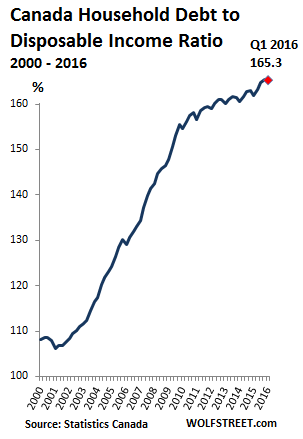
• Canadian Debt Slaves Pile it on (WS)
Consumer debt in Canada’s debt-fueled economy rose to a new record of C$1.67 trillion in the second quarter, according to Equifax. That’s up 3.0% from the prior quarter and 6.3% from a year ago. Excluding mortgages, consumer debt rose 3.4%, to C$21,878 per borrower on average. Folks 65 and over splurged the most with money they didn’t have and ended up increasing their debt by 8.2%. But Millennials had trouble. Their debts barely rose, and their delinquency rates have begun to jump. Equifax Canada, which based this report on its 25 million consumer credit files, doesn’t appear to capture the full extent of Canadian household debt: Statistics Canada’s most recent quarterly report pegged “total household credit market debt,” which includes mortgages, at a record C$1.933 trillion, up 5% year-over-year.
This gives Canadian households one of the highest debt-to-income ratios in the world. The ratio started soaring relentlessly 15 years ago, supporting the housing boom that barely took a breather during the Financial Crisis – a boom that now has turned into one of the globe’s most phenomenal and riskiest housing bubbles. Piling on debt to move the economy and the housing bubble forward was encouraged by record low borrowing rates. So at the end of the first quarter, the level of consumer debt was 165.3% of disposable income. It’s so high that it’s regularly subject of ineffectual hand-wringing in Canada’s central bank circles:

“..investment banking in Germany, for example, is down 45%…”
• Things Keep Getting Worse For EU Banks (CNBC)
European Union banks just can’t catch a break. Many of them are still slogging uphill to recoup share price losses incurred from the Brexit vote in the U.K. European investment banking revenue overall is down 23% this year compared with the same period in 2015, according to data tracker Dealogic. And all are lagging behind U.S. banks for wallet share, or how much revenue they take in from dealmaking compared to competitors. JPMorgan Chase tops every bank in the EU for wallet share, with 7.3% of deals, according to data from Dealogic this week. It’s followed by Goldman Sachs, which has 6.2% of deals, and only then, in third place, is an EU bank: Deutsche Bank has 5% of revenue on European mergers and acquisitions.
But European banks (and their American counterparts) are fighting off a rising tide of boutique banks that have taken a growingpercentage of M&A revenue from them over the last decade. Around the world, M&A levels have declined from recent record highs. But the pain is exacerbated in Europe, where big banks experienced a steeper drop off in revenue. Dealogic data show that investment banking in Germany, for example, is down 45%. Globally, European deals account for just 22% of banking revenue, the lowest margin since Dealogic began tracking investment banking wallet share. That comes in the wake of banks being hit especially hard on concerns about elevated loan losses, especially those coming from oil and gas assets.

For the love of Brexit.
• Brexit Armageddon Was A Terrifying Vision – But It Simply Hasn’t Happened (G.)
Unemployment would rocket. Tumbleweed would billow through deserted high streets. Share prices would crash. The government would struggle to find buyers for UK bonds. Financial markets would be in meltdown. Britain would be plunged instantly into another deep recession. Remember all that? It was hard to avoid the doom and gloom, not just in the weeks leading up to the referendum, but in those immediately after it. Many of those who voted remain comforted themselves with the certain knowledge that those who had voted for Brexit would suffer a bad case of buyer’s remorse. It hasn’t worked out that way. The 1.4% jump in retail sales in July showed that consumers have not stopped spending, and seem to be more influenced by the weather than they are by fear of the consequences of what happened on 23 June.
Retailers are licking their lips in anticipation of an Olympics feelgood factor. The financial markets are serene. Share prices are close to a record high, and fears that companies would find it difficult and expensive to borrow have proved wide of the mark. Far from dumping UK government gilts, pension funds and insurance companies have been keen to hold on to them. City economists had predicted an immediate rise in the claimant count measure of unemployment in July. That hasn’t happened either. This week’s figures show that instead of a 9,000 rise, there was an 8,600 drop.
Some caveats are in order. It is still early days. Hard data is scant. Survey evidence is still consistent with a slowdown in the economy in the second half of 2016. Brexit may be a slow burn, with the impact only becoming apparent in the months and years to come. But it is obvious that the sky has not fallen in as a result of the referendum, and those who said it would look a bit silly. By now, Britain was supposed to be reeling from the emergency budget George Osborne said would be necessary to fill a £30bn black hole in the public finances caused by a plunging economy. The emergency budget is history, as is Osborne.


Nobody should be buying a home in Britain.
• Over 500,000 UK First-Time Buyers Let Down By ‘Help To Buy’ Scheme (Sun)
The much-trumpeted Help to Buy Isa was branded a scandal last night as it emerged that first-time buyers will not be able to use it for a deposit. More than 500,000 savers opened accounts after George Osborne claimed it would provide ‘direct Government support’. But it has been revealed that a flaw in the scheme means a 25% Government bonus on savings will not be paid out until a house purchase has been completed. Experts said those struggling to find the money to buy a home would have to look to their parents for loans. The Help to Buy Isas, which launched last year, let customers save £200 a month, to which the Government adds £50, up to a final total of £15,000. Buyers are usually required to provide a 10% deposit when they exchange contacts.
But the small print shows the bonus cannot be used for the initial deposit and only spent as part of the purchase cost. So far, fewer than 1,500 people have used the Isas to help buy a home as the limit on how much can be paid in means they have only just got a realistic amount to put toward a deposit. Andrew Boast of SAM Conveyancing said: “It is a scandal. Unsuspecting first-time buyers are finding that they can’t use the bonus as part of the deposit.” Danny Cox of Hargreaves Lansdown financial advisers said: “Hundreds of thousands of Help to Buy Isa savers risk finding a last-minute hole in their finances.” A Treasury spokesman said: “It has always been the case that money saved in a Help to Buy Isa is for an exchange deposit, with the bonus of up to £3,000 per Isa going toward the total funds available for the property transaction.”

Fonterra was never going to last. Illusions of grandeur only go so far.
• A Dairy Firm at the End of the Earth Is Trying to Rule the World (BBG)
In the shadow of a snow-dusted volcano on a corner of New Zealand’s North Island, a sprawling expanse of stainless steel vats, chimneys and giant warehouses stands as a totem of the tiny nation’s dominance in the global dairy trade. The Whareroa factory was until recently the largest of its kind, churning out enough milk powder, cheese and cream to fill more than three Olympic-sized swimming pools a week. The plant has helped make owner Fonterra Cooperative Group the world’s top dairy exporter and its farmer-suppliers among the greatest beneficiaries of China’s emerging thirst for milk. Now, faced with reduced Chinese demand that’s eroded milk prices and helped drag 80% of New Zealand’s dairy farmers into the red, the 44-year-old factory has come to symbolize Fonterra’s struggle to climb the value chain.
While a global shift toward more natural foods has spurred even Coca-Cola to develop new milk products, Fonterra’s business remains largely wedded to commodities traded on often-volatile international markets. That’s frustrated the ranks of the cooperative’s 10,500 farmer-shareholders, who are set to receive the lowest return in nine years for the milking season just ended, and turned Fonterra’s strategy into the subject of national debate. “Fonterra hasn’t taken the opportunity to put itself in a position to really weather these storms as well as they should be able to,” said Harry Bayliss, 63, a former Fonterra director who still supplies the cooperative from farms about 30 kilometers west of the Whareroa factory. “What the board has focused on in the last 10 years haven’t been areas that have created real ongoing value for the shareholders or the company.”

Motorola borrows heavily to buy its own shares. If that isn’t liquidating your company, what is? “It’s a much weaker company than it was two or three years ago..”
• Does Motorola Need To Go To Rehab? (CCB)
How does Motorola Solutions CEO Greg Brown keep his company’s stock rising despite declining revenue and profit? Volume—of share repurchases. Since splitting off its mobile phone business in 2011, Motorola Solutions has spent $11.5 billion buying back stock. Earlier this month, the provider of products and services for government communications systems authorized another $2 billion in repurchases. The buybacks have reduced total share count by more than half, bolstering earnings per share even as actual profit declined to $613 million in 2015 from $1.16 billion in 2011. And because investors price shares on the basis of EPS, Motorola Solutions shares increased 90% in value over that period, to $75.99 yesterday, outpacing a 72% rise for the Standard & Poor’s 500 market.
Of course, Motorola Solutions is far from alone in gobbling its own shares as an antidote to sluggish growth. Companies in the Standard & Poor’s 500 repurchased a record amount in the 12 months through March 31. Still, Motorola ranks in the top 10% in terms of the percentage of outstanding shares repurchased over five years, according to Birinyi Associates. Buybacks are becoming more controversial as they consume a growing share of capital. Critics say companies are artificially burnishing their results rather than investing in business activities that would generate real long-term growth. Defenders say buybacks make sense for companies that generate more cash than they can reinvest profitably.
But Motorola Solutions has spent far more than excess cash flow on buybacks. Since the spinoff, the now Chicago-based maker of two-way radio systems has produced $2.7 billion in operating cash flow and collected $3.4 billion in proceeds from selling its enterprise business to Zebra Technologies in 2014. That $6.1 billion total represents a little more than half of Motorola’s buyback outlay. Brown has financed the rest with borrowed money, tripling long-term debt to $5 billion since the spinoff. Cash on hand dropped to $1.5 billion as of June 30, from $3.1 billion a year earlier. “It’s a much weaker company than it was two or three years ago,” says analyst David Novosel of Gimme Credit, a research firm in Chicago.

“When the financial bubble bursts, negative equity spreads as asset prices fall below the mortgages, bonds, and bank loans attached to the property.“
• Finance is Not the Economy (Hudson/Bezemer)
Analysis of private sector spending, banking, and debt falls broadly into two approaches. One focuses on production and consumption of current goods and services, and the payments involved in this process. Our approach views the economy as a symbiosis of this production and consumption with banking, real estate, and natural resources or monopolies. These rent-extracting sectors are largely institutional in character, and differ among economies according to their financial and fiscal policy. (By contrast, the “real” sectors of all countries usually are assumed to share a similar technology.)
Economic growth does require credit to the real sector, to be sure. But most credit today is extended against collateral, and hence is based on the ownership of assets. As Schumpeter (1934) emphasized, credit is not a “factor of production,” but a precondition for production to take place. Ever since time gaps between planting and harvesting emerged in the Neolithic era, credit has been implicit between the production, sale, and ultimate consumption of output, especially to finance long- distance trade when specialization of labor exists (Gardiner 2004; Hudson 2004a, 2004b). But it comes with a risk of overburdening the economy as bank credit creation affords an opportunity for rentier interests to install financial “tollbooths” to charge access fees in the form of interest charges and currency-transfer agio fees.
Most economic analysis leaves the financial and wealth sector invisible. For nearly two centuries, ever since David Ricardo published his Principles of Political Economy and Taxation in 1817, money has been viewed simply as a “veil” affecting commodity prices, wages, and other incomes symmetrically. Mainstream analysis focuses on production, consumption, and incomes. In addition to labor and fixed industrial capital, land rights to charge rent are often classified as a “factor of production,” along with other rent-extracting privileges. Also, it is as if the creation and allocation of interest-bearing bank credit does not affect relative prices or incomes.

Not exactly. The US is not some innocent bystander. Having the NYT write this up is maybe a sign, but it’s also double tongued.
• Saudi Arabia Kills Civilians, the US Looks the Other Way (NYT)
In the span of four days earlier this month, the Saudi Arabia-led coalition in Yemen bombed a Doctors Without Borders-supported hospital, killing 19 people; a school, where 10 children, some as young as 8, died; and a vital bridge over which United Nations food supplies traveled, punishing millions. In a war that has seen reports of human rights violations committed by every side, these three attacks stand out. But the Obama administration says these strikes, like previous ones that killed thousands of civilians since last March, will have no effect on the American support that is crucial for Saudi Arabia’s air war.
On the night of Aug. 11, coalition warplanes bombed the main bridge on the road from Hodeidah, along the Red Sea coast, to Sana, the capital. When it didn’t fully collapse, they returned the next day to destroy the bridge. More than 14 million Yemenis suffer dangerous levels of food insecurity — a figure that dwarfs that of any other country in conflict, worsened by a Saudi-led and American-supported blockade. One in three children under the age of 5 reportedly suffers from acute malnutrition. An estimated 90 percent of food that the United Nation’s World Food Program transports to Sana traveled across the destroyed bridge.

Too much publicity lately?
• US Withdraws Staff From Saudi Arabia Dedicated To Yemen Planning (R.)
The U.S. military has withdrawn from Saudi Arabia its personnel who were coordinating with the Saudi-led air campaign in Yemen, and sharply reduced the number of staff elsewhere who were assisting in that planning, U.S. officials told Reuters. Fewer than five U.S. service people are now assigned full-time to the “Joint Combined Planning Cell,” which was established last year to coordinate U.S. support, including air-to-air refueling of coalition jets and limited intelligence-sharing, Lieutenant Ian McConnaughey, a U.S. Navy spokesman in Bahrain, told Reuters. That is down from a peak of about 45 staff members who were dedicated to the effort full-time in Riyadh and elsewhere, he said.
The June staff withdrawal, which U.S. officials say followed a lull in air strikes in Yemen earlier this year, reduces Washington’s day-to-day involvement in advising a campaign that has come under increasing scrutiny for causing civilian casualties. A Pentagon statement issued after Reuters disclosed the withdrawal acknowledged that the JCPC, as originally conceived, had been “largely shelved” and that ongoing support was limited, despite renewed fighting this summer. “The cooperation that we’ve extended to Saudi Arabia since the conflict escalated again is modest and it is not a blank check,” Pentagon spokesman Adam Stump said. U.S. officials, speaking on condition of anonymity, said the reduced staffing was not due to the growing international outcry over civilian casualties in the 16-month civil war that has killed more than 6,500 people in Yemen, about half of them civilians.

The DoD simply does no accounting.
• US Army Fudged Its Accounts By Trillions Of Dollars (R.)
The United States Army’s finances are so jumbled it had to make trillions of dollars of improper accounting adjustments to create an illusion that its books are balanced.The Defense Department’s Inspector General, in a June report, said the Army made $2.8 trillion in wrongful adjustments to accounting entries in one quarter alone in 2015, and $6.5 trillion for the year. Yet the Army lacked receipts and invoices to support those numbers or simply made them up. As a result, the Army’s financial statements for 2015 were “materially misstated,” the report concluded. The “forced” adjustments rendered the statements useless because “DoD and Army managers could not rely on the data in their accounting systems when making management and resource decisions.”
Disclosure of the Army’s manipulation of numbers is the latest example of the severe accounting problems plaguing the Defense Department for decades. The report affirms a 2013 Reuters series revealing how the Defense Department falsified accounting on a large scale as it scrambled to close its books. As a result, there has been no way to know how the Defense Department – far and away the biggest chunk of Congress’ annual budget – spends the public’s money. The new report focused on the Army’s General Fund, the bigger of its two main accounts, with assets of $282.6 billion in 2015. The Army lost or didn’t keep required data, and much of the data it had was inaccurate, the IG said. “Where is the money going? Nobody knows,” said Franklin Spinney, a retired military analyst for the Pentagon and critic of Defense Department planning.

It’ll take a lot more than that to make cities liveable. How about a deep financial crisis?
• Netherlands On Brink Of Banning Sale Of Petrol-Fuelled Cars (Ind.)
Europe appears poised to continue its move towards cutting fossil fuel use as the Netherlands joins a host of nations looking to pass innovative green energy laws. The Dutch government has set a date for parliament to host a roundtable discussion that could see the sale of petrol- and diesel-fuelled cars banned by 2025. If the measures proposed by the Labour Party in March are finally passed, it would join Norway and Denmark in making a concerted move to develop its electric car industry. It comes after Germany saw all of its power supplied by renewable energies such as solar and wind power on one day in May as the economic powerhouse continues to phase out nuclear energy and fossil fuels.
And outside Europe, both India and China have demanded that citizens use their cars on alternate days only to reduce the exhaust fume production which is causing serious health problems for the populations of both nations. The consensus-oriented parties of the Netherlands are set to consider a total ban on petrol and diesel cars in a debate on 13 October. Richard Smokers, principle adviser in sustainable transport at the Dutch renewable technology company TNO, said the Dutch government was committed to meeting the Paris climate change agreement to reduce greenhouse emissions to 80% less than the 1990 level. The plan requires the majority of passenger cars to be run on CO2-free energy by 2050.
“Dutch cities still have some problems to meet existing EU air quality standards and have formulated ambitions to improve air quality beyond these standards,” he told The Independent, adding that the government had at the same time been reluctant to implement strict policies on the environment. “The current government embraces long term targets and strives at meeting EU requirements, but is hesistant about proposing ‘strong’ policy measures. “Instead it prefers to facilitate and stimulate initiatives from stakeholders in society.” If the law to ban the sale of new fossil-fuel cars by 2025 passes, a significant move will have been made towards phasing out all petrol and diesel cars by 2035, added Dr Smokers.









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle August 20 2016