
Russell Lee Hollywood, California. Used car lot. 1942

As Gilts sell off… Very reassuring.
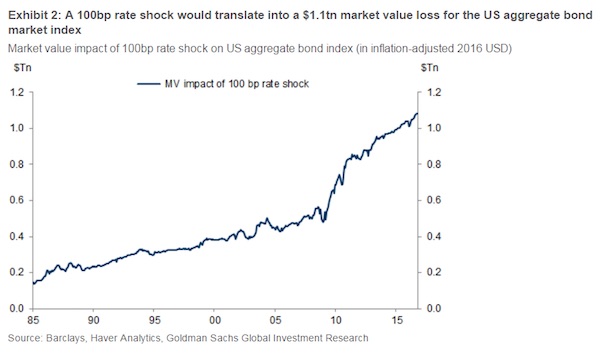
• US Bondholders Risk a $1.1 Trillion Hit if Rates Spike (BBG)
First they came for the yield, then they came for the duration. A Goldman Sachs analysis says investors could be mired in a world of pain if yields on long-dated assets snap higher. Just a modest backup in rates could inflict outsized losses on bond portfolios — a sobering prospect in light of the recent jump in longer-dated bond yields that’s already eating into bondholders’ capital returns. A 1% increase in interest rates could inflict a $1.1 trillion loss to the Bloomberg Barclays U.S. Aggregate Index, analysts at Goldman calculate, representing a larger loss for bondholders than at any other point in history. With the bank predicting the selloff in bonds has further to run, that remains “far from a tail scenario,” its analysts write.
Bets on longer-maturity obligations had paid off handsomely for most of the year amid a global bond rally triggered by expectations that weak economic activity will persuade central banks in advanced economies to postpone tightening monetary policy. Asset purchases by the BOJ, BOE and the ECB helped the average maturity of new U.S. corporate bonds climb to a peak of 11.3 years in August. With average bond maturities worldwide now more than double the inflation-adjusted level of 2009, and three times that of 1994, Goldman says there’s an elevated risk of losses if rates spike higher. “We see potential for the rates market to continue to sell off, and the notional amount of duration dollars at risk is unprecedentedly large,” Goldman fixed-income analysts, led by Marty Young, wrote in the report on Monday.

“..lack of affordability. “We have our eye on the wrong ball..”
• US First Home Buyers Even More Leveraged Than During Housing Bubble (MW)
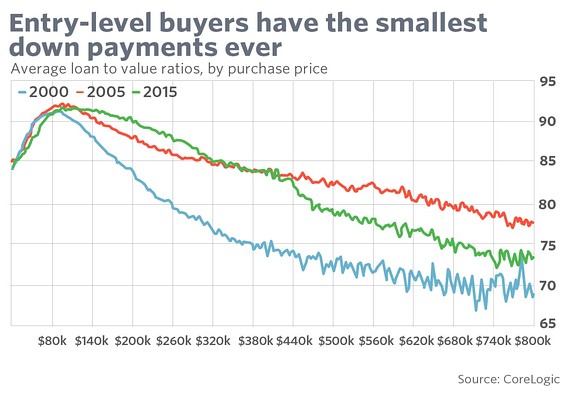
Ever since the shock of the financial crisis ebbed and buyers began to return to the housing market, one truth has dominated: mortgage lending is tight. But is it? It’s true that only the borrowers with the highest credit scores get home loans now. So much lending to people with higher credit scores and so little to those on the lower end of the spectrum has shifted the average FICO score up about 40 points since before the bubble burst. But measured in another way, lending is shockingly loose. And, according to one economist, that tells us a lot not just about the housing market, but about the economy as a whole. The 20% down payment may linger in Americans’ imagination, but it’s even less real today than Jimmy Stewart’s small-town banker from 1946.
American homeowners, particularly those at the lower end of the market, are increasingly leveraged to pay for their houses, says Sam Khater, deputy chief economist at data provider CoreLogic. In fact, owners of entry-level homes, those in the $150,000 to $300,000 range — have more debt and less equity now than they did in 2005, at the height of mortgage mania. For Khater, that says less about credit markets and more about another defining feature of the post-recession housing market — its lack of affordability. “We have our eye on the wrong ball,” he told MarketWatch. “What I worry about is the leverage not from a default perspective but from an affordability perspective. Demand for credit has been weak. But the much bigger issue is the supply of housing, not supply of credit.”

Swaps won’t rescue China’s bad debt. It’s just multiple state-owned firms selling each other the things.
• China’s Bad Credit (Balding)
There is good news when it comes to China’s scary and still-growing pile of debt: At least the government recognizes the problem. Its attempts to mitigate those risks, however, seem doomed to fall short. The government’s recent decision to create a market for credit default swaps is a case in point. The idea, as elsewhere, is to give banks and investors a means of pricing and trading the risk of Chinese companies defaulting on their debts. The need is obvious: Official measures of non-performing loans are worsening, while unofficial estimates say their share may have reached anywhere from 8% to 20%. Anything that spreads that risk should improve financial stability. Yet, as envisioned, this new CDS market is unlikely to do much to improve the situation.
For one thing, all but the largest companies already have to purchase credit insurance when taking out loans from giant state banks. There’s no pricing differential on this insurance, of course. But for the new system to function effectively, the government would have to let markets freely set the price of credit risk. China doesn’t exactly have a stellar record of allowing markets to set prices in any field, whether in stocks, real estate or currencies. If credit default swaps started to indicate a rising risk of default at a major state-owned company, it’s hard to imagine officials wouldn’t intervene to reverse that impression. This is dangerous on multiple levels. Already, several Chinese credit insurance firms have collapsed because they underestimated credit risk, forcing government bailouts. Continuing to underprice risk will only encourage the over-allocation of credit that’s gotten China into trouble thus far.
There’s also little reason to think that creating a CDS market would shift risk away from the most vulnerable banks. In a heavily concentrated banking and lending market such as China, where major financial institutions all trade with each other, swaps are likely to produce no net change to risk levels. Think of a simple example. Assume that Bank A has loans totaling 100 billion yuan but wants to protect itself against the risk of default by buying a CDS from Bank B that covers these companies. Now assume that Bank B does the same to cover its 100 billion yuan of loans, with A as the counter-party. If we assume these are similar baskets of loans – a reasonable assumption for major banks within a single country – then there’s been no net change in credit risk for either bank.

It doesn’t get much more serious than this: “The UK faces a balance of payments crisis..”
• Foreigners Shun Gilts On Hard Brexit Talk, As Hallowe’en Verdict Awaits (AEP)
The bond vigilantes are sharpening their knives. The last five trading sessions have seen a sudden and potentially ominous shift in the reflexes of the Gilts market, a sign that ‘hard Brexit’ rhetoric has rattled global debt managers. “For the first time, foreign investors are beginning to question the credit-worthiness of the United Kingdom,“ said Vatsala Datta, UK rates strategist at RBC. We will find out how serious it is on October 31 – Hallowe’en day – when the UK Debt Management Office publishes its monthly data on foreign holdings of Gilts. Central banks, sovereign wealth funds, and the like, currently hold £503bn of British public debt or 27pc of the total, a bigger share than UK pension funds and insurance companies.
Yields on 10-year Gilts have spiked by 62 basis points to 1.14pc from their trough in August. Until last week this was pure a ‘reflation trade’, a turbo-charged variant of what has been happening in the US and other parts of the world as markets price in accelerating global growth and a commodity rebound. Britain got a double-dose because the sharp fall in sterling automatically pushed up the likelihood of future inflation, and that is what bondholders hate most. It is easy to measure the inflation component of moves by tracking how the ‘break-even inflation rate’ rises in tandem with the headline bond yield. “The correlation was exact. It has now broken down,” said Ms Datta. Break-even rates stopped rising last week, yet this time Gilt yields spiked higher, a divergence of 18 basis points.
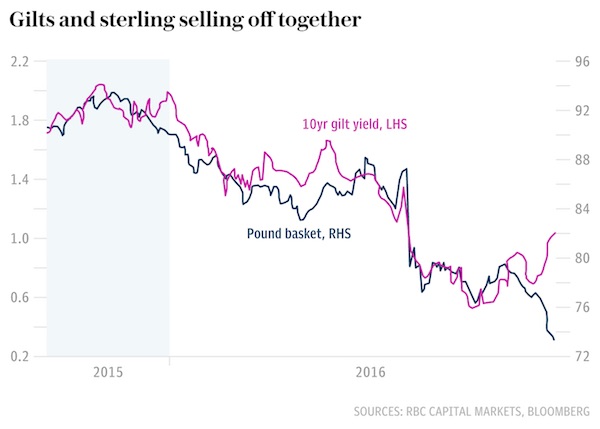
RBC said the pattern in the interlocking currency and debt markets is clear: sterling is no longer trading like a bona fide reserve currency. “The parallel sell-off in gilts and sterling is potentially a worrying development, consistent with the UK’s having growing difficulty funding its internal and external deficits,” it said. What typically happens when a blue chip currency like the US dollar or the Swiss franc falls is that central banks and fund managers buy more of that country’s bonds to keep a constant weighting. This is a mechanical practice. It happens unless managers take a conscious decision to override their model. It is why foreign holdings of UK Gilts have risen by 20pc over the last year, and why they surged at an even faster rate after the referendum.
This foreign rush into Gilts happened not in spite of the falling pound, but because of it. All of a sudden this has stopped. Loose proxies such as ‘swap spreads’ suggest an outright exodus from Gilts even as the pound weakens. It is symptomatic that the Japanese bank Nomura has issued a string of tough reports about what could happen if the British government opts to leave the EU single market, warning that an erratic UK can no longer count on the “kindness of strangers” to fund its current account deficit. “The UK faces a balance of payments crisis,” it says, menacingly.

“..if we’re going to cite unlawful transactions as a rationale for banning cash, it only makes sense to ban banks and accounting firms first.”
• The Cashless Society Is a Creepy Fantasy (BBG)
It’s fun to imagine a world without cash. Liberated from the burden of physical currency, consumers could make purchases from the convenience of a mobile device. Every transaction would come equipped with fraud protection, reward points and a digital record of its time and location. Comprehensive tracking could help the Internal Revenue Service reclaim billions of tax dollars lost to unreported income, like the $80 I made selling a used refrigerator on Craigslist. Drug dealers, helpless without an anonymous medium of exchange, would acquire wholesome professions. El Chapo might become a claims adjuster. Such is the utopia recently described by Nathan Heller in the New Yorker and by a former chief economist of the International Monetary Fund, Kenneth Rogoff, in a new book, “The Curse of Cash.”
But this universe is missing one of the fundamental aspects of human civilization. A world without cash is a world without money. Money belongs to its current holder. It doesn’t matter if a banknote was lost or stolen at some point in the past. Money is current; that’s why it’s called currency! A bank deposit, however, grants custody of money to the bank. An account balance is not actually money, but a claim on money. This is an important distinction. A claim is only as good as its enforceability, and in a cashless society every transaction must pass through a financial gatekeeper. Banks, being private institutions, have the right to refuse transactions at their discretion. We can’t expect every payment to be given due process.
This means that politically unpopular organizations could easily be deprived of economic access. Past attempts to curb money laundering have already inadvertently cut off financial services for legitimate individuals, businesses, and charities. The removal of paper currency would undoubtedly leave similar collateral damage. The crime-fighting case against cash is overstated. Last year, a risk assessment of money laundering and terrorist financing conducted by the U.K. government found that regulated institutions such as banks (like HSBC) and accountancy service providers (like the Panamanian tax-shelter specialist Mossack Fonseca) posed the highest risk of facilitating the illicit storage or movement of funds. Cash came in a close third, but if we’re going to cite unlawful transactions as a rationale for banning cash, it only makes sense to ban banks and accounting firms first.

Extrapolating trends is a pretty much useless exercise.
• Greece in 2050: A Country For Old Men (Kath.)
By 2050, Greece’s population is expected to shrink by 800,000 to 2.5 million people to between 8.3 and 10 million, and one in three of its residents will be over the age of 65 (30-33% compared to the present 21% and 7% in 1951), while under-14s will represent just 12-14.8% from 15% today and 28% in 1951. This dystopian view of the country – with empty schools and offices – emerges from a recent study on Greece’s demographic prospects, presented by the Athens-based Dianeosis research organization. The study explored eight different scenarios, all of which calculated a significant drop in the population by 2050. The most optimistic saw a reduction of 800,000 people and the rapid aging of society. The median age is seen reaching 49-52 years from 44 today and 26 in 1951.
By then, the study says, 50-year-olds will be the young ’uns. The number of school-age children (3-17) will drop from 1.6 million today to 1.4 million in the optimistic scenario and 1 million in the pessimistic one and the economically active population will shrink from 4.7 million people today to between 3 and 3.7 million, meaning that a much lower number of people will be able to work to cover the country’s needs. The study by Dianeosis reflects trends that are already being noted: On January 1, 2015, Greece’s population came to 10.8 million from 11.1 million in 2011, marking the first time since 1951 that the number of the country’s residents has gone down.
There are three factors that affect population fluctuations – births, deaths and migration – which can be separated into two categories, the natural process of births and deaths, and the migration factor, which includes both inflows and outflows. Today, births are decreasing and deaths going up due to sliding standards of living and a crumbling public healthcare system. Meanwhile, the outflow of mainly young Greeks and foreigners from the country is on the rise, while, despite the arrival of thousands of migrants, the crisis is preventing their numbers from being made up by fresh inflows.

It helps when politicians actually know the law.
• Judge Rejects Riot Charges For Journalist Amy Goodman On Pipeline Protest (G.)
A North Dakota judge rejected prosecutors’ “riot” charges against Democracy Now! host Amy Goodman for her reporting on the oil pipeline protests, a decision that advocates hailed as a major victory for freedom of the press. After the award-winning broadcast journalist filmed security guards working for the Dakota access pipeline using dogs and pepper spray on protesters, authorities issued a warrant for Goodman’s arrest and alleged that she participated in a “riot”, a serious offense that could result in months in jail. On Monday, judge John Grinsteiner ruled that the state lacked probable cause for the riot charge, blocking prosecutors from moving forward with the controversial prosecution.
“I feel vindicated. Most importantly, journalism is vindicated,” Goodman told reporters and supporters on a live Facebook video Monday afternoon. “We have a right to report. It’s also critical that we are on the front lines. Today, the judge sided with … freedom of the press.” The case stems from a 3 September report when Goodman traveled to the Native American-led protest against a controversial $3.8bn oil pipeline that the Standing Rock Sioux tribe says is threatening its water supply and cultural heritage. Goodman’s dispatch on the use of dogs went viral and has since garnered 14m views on Facebook and also prompted coverage from many news outlets, including CBS, NBC, NPR and CNN.

I picked the Reuters take on this. There are many others, some much more negative. The crux: This is getting way out of hand. Trying to interfere with classified material is crazy and desperate. And very illegal.
• State Department Official Pressured FBI To Declassify Clinton Email (R.)
A senior State Department official sought to shield Hillary Clinton last year by pressuring the FBI to drop its insistence that an email on the private server she used while secretary of state contained classified information, according to records of interviews with FBI officials released on Monday. The accusation against Patrick Kennedy, the State Department’s most senior manager, appears in the latest release of interview summaries from the Federal Bureau of Investigation’s year-long investigation into Clinton’s sending and receiving classified government secrets via her unauthorized server.
Although the FBI decided against declassifying the email’s contents, the claim of interference added fuel to Republicans’ belief that officials in President Barack Obama’s administration have sought to protect Clinton, a Democrat, from criminal liability as she seeks to succeed Obama in the Nov. 8 election. The FBI recommended against bringing any charges in July and has defended the integrity of its investigation. Clinton has said her decision to use a private server in her home for her work as the U.S. secretary of state from 2009 to 2013 was a mistake and has apologized. One FBI official, whose name is redacted, told investigators that Kennedy repeatedly “pressured” the various officials at the FBI to declassify information in one of Clinton’s emails.
The email was about the deadly 2012 attack on a U.S. compound in Benghazi, Libya, and included information that originated from the FBI, which meant that the FBI had final say on whether it would remain classified. The dispute began in the summer of 2015 as officials were busy reviewing the roughly 30,000 emails Clinton returned to the State Department ahead of their court-ordered public release in batches in 2015 and 2016. The official said the State Department’s office of legal counsel called him to question the FBI’s ruling that the information was classified, but the FBI stood by its decision. Soon after that call, one of the official’s FBI colleagues received a call from Kennedy in which Kennedy “asked his assistance in altering the email’s classification in exchange for a ‘quid pro quo.'”

From the Times (behind paywall): “The state-owned bank withdrew its planned punitive action after Moscow claimed it would freeze the BBC’s finances in Russia and report Britain to international watchdogs for breaching commitments to freedom of speech.”
• RBS Backtracks Over Closure Of RT Bank Accounts (RT)
The Royal Bank of Scotland (RBS) appears to have backtracked from its earlier statement that the looming closure of RT accounts is not up for discussion. In a letter to RT, the bank said the situation is being reviewed and the bank is contacting the customer. The e-mailed response began with apologies for the delay in the reply. These decisions are not taken lightly. We are reviewing the situation and are contacting the customer to discuss this further. The bank accounts remain open and are still operative,” Sarah Hinton-Smith, Head of Corporate & Institutional, Commercial & Private Media at RBS Communications, wrote. However, the response by Hinton-Smith contradicted an earlier statement by RBS, which said that the decision to suspend banking services to RT was final and not up for discussion.
The broadcaster addressed the Royal Bank of Scotland representative over the contradiction, pointing out that “your statement seems to suggest that the bank will contact RT and that there will be a review and further discussion.” “There’s not much more of a steer I can give other than what is in the statement,” Hinton-Smith replied via email. Earlier Monday, the National Westminster Bank (NatWest), which is part of RBS Group, informed RT UK’s office in London that it will no longer have the broadcaster among its customers, without providing any explanation for the decision.

“..the fact that the US polity now so desperately has to fight for survival shows how frail its legitimacy is.”
• The Odor of Desperation (Jim Kunstler)
It must be obvious even to nine-year-old casual observers of the scene that the US national election is hacking itself. It doesn’t require hacking assistance from any other entity. The two major parties could not have found worse candidates for president, and the struggle between them has turned into the most sordid public spectacle in US electoral history. Of course, the Russian hacking blame-game story emanates from the security apparatus controlled by a Democratic Party executive establishment desperate to preserve its perks and privileges . (I write as a still-registered-but-disaffected Democrat).
The reams of released emails from Clinton campaign chairman John Podesta, and other figures in HRC’s employ, depict a record of tactical mendacity, a gleeful eagerness to lie to the public, and a disregard for the world’s opinion that are plenty bad enough on their own. And Trump’s own fantastic gift for blunder could hardly be improved on by a meddling foreign power. The US political system is blowing itself to pieces. I say this with the understanding that political systems are emergent phenomena with the primary goal of maintaining their control on the agencies of power at all costs. That is, it’s natural for a polity to fight for its own survival. But the fact that the US polity now so desperately has to fight for survival shows how frail its legitimacy is.
It wouldn’t take much to shove it off a precipice into a new kind of civil war much more confusing and irresolvable than the one we went through in the 1860s. Events and circumstances are driving the US insane literally. We can’t construct a coherent consensus about what is happening to us and therefore we can’t form a set of coherent plans for doing anything about it. The main event is that our debt has far exceeded our ability to produce enough new wealth to service the debt, and our attempts to work around it with Federal Reserve accounting fraud only make the problem worse day by day and hour by hour. All of it tends to undermine both national morale and living standards, while it shoves us into the crisis I call the long emergency.

If anything ever smelled like a flase flag, it was this. Mere days after the world turned on the US and its Saudi friends for bombing a funeral procession, the Houthis supposedly shot at a US destroyer, missed by a mile and a half, and next thing you knew all of a sudden the US was itself involved in the so-called war, which is really just slaughter.
• Pentagon Backtracks, Voices Caution On Latest Yemen Missile Incident (R.)
The Pentagon declined to say on Monday whether the USS Mason destroyer was targeted by multiple inbound missiles fired from Yemen on Saturday, as initially thought, saying a review was under way to determine what happened. Any determination that the USS Mason guided-missile destroyer was targeted on Saturday could have military repercussions, since the United States has threatened to retaliate again should its ships come under fire from territory in Yemen controlled by Iran-aligned Houthi fighters. The United States carried out cruise missile strikes against radar sites in Yemen on Thursday after two confirmed attempts last week to hit the USS Mason with coastal cruise missiles. “We are still assessing the situation. There are still some aspects to this that we are trying to clarify for ourselves given the threat – the potential threat – to our people,” Pentagon spokesman Peter Cook told a news briefing.

Unfortunately, Curtis’ film Hypernormalization is for now still only available in Britain. Far as I know.
• We Have To Begin To Look Outside. Because There Is More Out There (Adam Curtis)
Power is all around us. It’s just that it has shifted and mutated into a massive system of management and control, whose tentacles reach into all parts of our lives. But we can’t see it because we still think of power in the old terms – of politicians telling us what to do. The aim of the film I have made – HyperNormalisation – is to bring that new power into focus, and show its true dimensions. It ranges from a giant computer high up in the mountains of northeast America that manages and controls over 7% of the worlds total wealth, to the complex algorithms that constantly monitor every move and choice you make online, to modern scientific ideas about what the normal human being should be – in their weight and in their feelings and moods.
What links all these systems is an overriding aim is to keep the world stable. To avoid all change. The giant computer constantly compares events happening around the world to events in the past. If it sees a dangerous pattern, it immediately adjusts its trillions of dollars to keep things stable. That is real power. The algorithms on social media constantly look at the patterns of what you like and then feed you more of that – so you enter into an echo chamber that constantly feeds you back to you. So again nothing changes – and you learn nothing new that would contradict how you feel. That too is real power. What results is a system which cocoons us and makes us feel safe. And that means we have become terrified of all change.
But that fear of change is in the interest of a system that wants to hold everything stable. And stops us from ever challenging it. But it is impossible to keep things frozen forever. The world is dynamic. Things happen that you can never predict just by reading the past. This is why more and more we are being hit by events – the horror in Syria, Brexit, Trump, the waves of refugees – that neither we nor our leaders have the mental map to understand let alone deal with. Because we have bought into the dream that the world can be held stable and safe. The short film I have made for VICE is about how, if you pull back and look at the everyday life all around you, you can see the cracks appearing through the shiny surface of the cocoon we are living in.
So much of the modern world is beginning to feel odd, unreal and sometimes fake. I think these are the dynamic forces outside beginning to pierce through as the system begins to fail. It will fail – because a system of power that has no vision of the future can never last. It cannot deal with change. We have to begin to look outside. Because there is more out there…









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle October 18 2016