Harris&Ewing Washington Monument, view from air 1919

“The workability of the institution breaks down when a different set of rules are seen to apply to governments versus those that apply to everyone else.”
• Bank of Japan’s Sovereign Debt Endgame Is The Naked Emperor (FP)
Last week, Bloomberg reported in depth on Japan’s miraculous diminishing debt load. Turns out, despite a steady rise in government borrowing, the burden of repayment is diminished because the buyer of 90% of that debt is the Bank of Japan. This has serious implications for Canadian investors, yet the full significance has not yet been thoroughly unpacked by media. My bet is most analysts and economists are aghast at this admission by a G7 government that debt could just be summarily forgiven. It suggests the notion of liability in credit does not apply to government, or its associated (yet private, to varying degree) central banks. But it’s really quite simple. The single most important rule upon which our global debt-driven economic growth equation is dependent is that debt is repaid.
If it isn’t, assets are confiscated. Just like if you don’t keep up with the mortgage payments on your house, you lose it. But what happens when the biggest creditor is also the debtor? The entire debtor/creditor relationship is rendered nonsensical. The size of the debt any one nation can undertake is directly related to its ability to repay any proposed amount over time. Its ability to repay its debt, in turn, is derived from the consensus of markets that demand a higher rate of interest the closer a debtor gets to defaulting. The debt limit is reached when no one will lend, because even at the highest rate of interest, the chance of default is greater. Or when the debtor misses a payment. This works well in a world ostensibly governed by free markets, and when the rules are universally applied. The workability of the institution breaks down when a different set of rules are seen to apply to governments versus those that apply to everyone else.
Read more …

BoJ buys everything. Banks have to deal with a monopoly, no profit in that.
• Japan’s Biggest Bank To Quit As JGB Primary Dealer (ZH)
Ever since the launch of Japan’s QE, and worsening in the aftermath of January’s shocking NIRP announcement, Japan’s bond market, which moments ago slid to new record lows yields across the curve, has had its share of near-death experiences: between repeated VaR shocks, to days in which not a single bond was traded, to trillions in bonds with negative yields, it has seemed that the Japanese Government Bond is on life support. That support may be ending. According to Nikkei, and confirmed by Bloomberg, Japan’s biggest bank, Bank of Tokyo-Mitsubishi UFJ, is preparing to quit its role as a primary dealer of Japanese government bonds as negative interest rates turn the instruments into larger risks, a fallout from massive monetary easing measures by the Bank of Japan.
While the role of a Primary Dealer comes with solid perks such as meetings with the Finance Ministry over bond issuance and generally being privy to inside information and effectively free money under POMO, dealers also are required to bid on at least 4% of a planned JGB issuance, which as the Nikkei reports has become an increasingly heavy burden for BTMU. In other words, one of the key links that provides liquidity and lubricates the Japanese government bond market has just decided to exit the market due to, among other thinks, lack of liquidity entirely due to the policy failure of Abenomics in general, and Kuroda’s disastrous monetary policies in particular.
One could, of course, ask just how does BTMU plan on also exiting the Japanese economy itself, if and when the country’s $8 trillion bond market implodes, but we doubt the bank will ever be able to answer that. The ministry is expected to let the bank resign. Japan has 22 primary dealers including megabanks and major brokerages. Several foreign brokerages had pulled out before as part of restructuring efforts at home or for other reasons, but BTMU will be the first Japanese institution to quit. In a revolutionary shift, one created by the Bank of Japan itself, banks, once the biggest buyers of JGBs, see little appeal in sovereign debt today. The bonds have very low yields, and a rise in interest rates could leave banks with vast unrealized losses.
Private-sector banks held just over 229 trillion yen ($2.13 trillion) in JGBs at the end of 2015, nearly 30% less than at the end of March 2013, before the BOJ launched massive quantitative and qualitative easing measures. Negative rates introduced this year by the BOJ reinforced the trend. The highest bid yield on benchmark 10-year JGBs sank to a record low of negative 0.092% on Thursday. BTMU was the fifth-largest buyer of Japanese government bonds among the 22 primary dealers until spring 2015, but ranked 10th or lower between October 2015 and March 2016 as shareholders turned up their nose on government debt.
Read more …

One day we’ll understand just how insane this is. One massive debt orgasm.
• Draghi Fires Starting Gun on Corporate Bond Purchases in Europe (BBG)
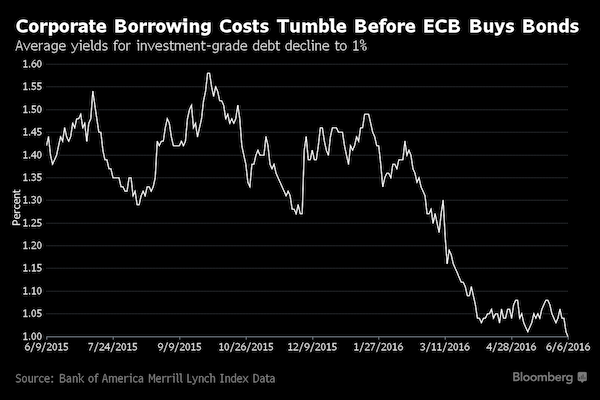
Investors will be watching Mario Draghi’s first corporate bond purchases on Wednesday for an indication of whether they were right to snap up the notes before the ECB. The ECB is adding investment-grade corporate notes to its €80 billion monthly purchase program, which already includes covered bonds, asset-backed securities and government debt, as part of efforts to encourage growth. The challenge will be buying enough bonds in increasingly illiquid markets, investors and analysts say. “There is a fair amount riding on this in terms of the ECB’s credibility,” said Victoria Whitehead at BNP Paribas Investment Partners. “The perception is that if they can’t buy at least €5 billion of bonds a month, the program will be seen as unsuccessful.” Investors have piled into investment-grade corporate bonds on the promise of central bank purchases, driving up prices and cutting borrowing costs.
The average yield for euro notes tumbled to 1.002% on Monday, the lowest in more than a year, according to BofAML index data. Companies responded to the surge in demand by selling more than €50 billion of bonds in the single currency in May, the second-busiest month on record. While purchases of more than €5 billion of bonds may boost the market, investors may be disappointed if the ECB bought less than €3 billion a month, CreditSights analysts wrote in a June 5 report. Commerzbank and Morgan Stanley don’t expect the monthly purchases to surpass €5 billion. “We’re worried that they won’t be able to buy quite as much as they want to,” said Tim Winstone at Henderson Global Investors. “If the buying underwhelms and reported volumes are less than most people expect, there is a risk of a selloff.”
Read more …

Dissolve the monster peacefully while you still can. Or else.
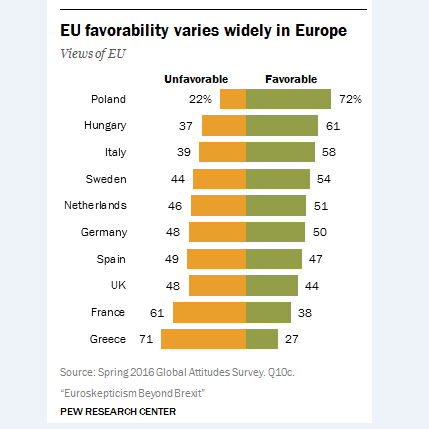
• Public Support For The EU Plunges Across Europe (R.)
Public support for the European Union has fallen sharply in its biggest member states over the past year, a survey showed on Tuesday, weeks before Britons vote on whether to leave the 28-nation bloc. The survey of 10 large EU states by the Washington-based Pew Research Center showed strong support for Britain to stay in the EU, with 89% of Swedes, 75% of Dutch and 74% of Germans viewing a so-called Brexit as a bad thing. But most striking was a plunge in the percentage of Europeans who view the EU favorably, a development which appears linked to the bloc’s handling of the refugee crisis and the economy. The fall was most pronounced in France, where only 38% of respondents said they had a favorable view of the EU, down 17 points from last year.
Favorability ratings also fell by 16 points in Spain to 47%, by eight points in Germany to 50%, and by seven points in Britain to 44%. Public support for the EU was strongest in Poland and Hungary, countries which ironically have two of the most EU-sceptical governments in the entire bloc. The Pew survey showed that 72% of Poles and 61% of Hungarians view the EU favorably. “The British are not the only ones with doubts about the European Union,” Pew said. “Much of the disaffection with the EU among Europeans can be attributed to Brussels’ handling of the refugee issue. In every country surveyed, overwhelming majorities disapprove of how Brussels has dealt with the problem.”
This was especially true in Greece, which has been overwhelmed by migrants crossing the Aegean Sea from Turkey. Some 94% of Greeks believe the EU has mishandled the refugee crisis. In Sweden it was 88%, in Italy 77% and in Spain 75%. At 92%, Greeks were also the most disapproving of the EU’s handling of the economy, followed by the Italians at 68% and French at 66%. Roughly two-thirds of Greeks and Britons said powers should be returned to national governments from Brussels, far higher than in the other surveyed countries.
Read more …

Close to what I’ve written before: “They may have to dissolve the EU as it is and try to reinvent it, both in order to bring the Brits back and because they fear that the whole political order will be swept away unless they do..”
• France Shuns Europe As Brexit Revolt Spreads (AEP)
France has turned even more viscerally eurosceptic than Britain over recent months, profoundly altering the political geography of Europe and making it impossible to judge how Paris might respond to Brexit. An intractable economic crisis has been eating away at the legitimacy of the French governing elites for much of this decade. This has now combined with a collapse in the credibility of the government, and mounting anger over immigration. A pan-European survey by the Pew Research Center released today found that 61pc of French voters have an “unfavourable” view, compared to 48pc in the UK. A clear majority is opposed to “ever closer union” and wants powers returned to the French parliament, a finding that sits badly with the insistence by President Francois Hollande that “more Europe” is the answer to the EU’s woes.
“It is a protest against the elites,” said Professor Brigitte Granville, a French economist at Queen Mary University of London. “There are 5000 people in charge of everything in France. They are all linked by school and marriage, and they are tight.” Prof Granville said the mechanisms of monetary union have upset the Franco-German strategic marriage, wounding the French psyche. “The EU was sold to the French people as a `partnership’ of equals with Germany. But it has been very clear since 2010 that this is not the case. Everybody could see that Germany decided everything in Greece,” she said. The death of the Monnet dream in the EU’s anchor state poses an existential threat to the European project and is running in parallel to what is happening in Britain.
The Front National’s Marine Le Pen is leading the polls for the presidential elections in 2017 with vows to restore the French franc and smash the EU edifice. While it has long been assumed that she could never win an outright majority, nobody is quite so sure after the anti-incumbent upset in Austria last month. “The Front National is making hay from the Brexit debate,” said Giles Merritt, head of the Friends of Europe think tank in Brussels. “The EU policy elites are in panic. If the British vote to leave the shock will be so ghastly that they will finally wake up and realize that they can no longer ignore demands for democratic reform,” he said.
“They may have to dissolve the EU as it is and try to reinvent it, both in order to bring the Brits back and because they fear that the whole political order will be swept away unless they do,” he said. Mr Merritt said it is an error to suppose that the EU would carry on as a monolithic bloc able to dictate terms after a Brexit vote. “The British would have pricked the bubble. The Germans are deeply alarmed at how suddenly the mood is shifting everywhere,” he said.
Read more …

It’s going to be so much fun, the next two weeks. Can the footballers save England at the Euro Cup?
• Billions Of Pounds Taken Out Of Britain Amid Fears Of Brexit (Ind.)
Investors are moving billions of pounds in assets out of British currency and assets ahead of the EU referendum, new figures suggest. An analysis by Sky News found £65bn left the UK or was converted into other currencies in March and April, the largest amount since the economic crash. In the six months to the end of April, £77bn was pulled out of British pounds, compared to just £2bn in the six months to the end of last October. The figures, published by the Bank of England, are consistent with investors worrying that the pound is due for a sharp fall should Brexit to occur. Because financial markets are prone to collective panic, investors’ views are the main factor in determining whether the pound will actually fall. Any perception that a fall was about to take place could end up becoming a self-fulfilling prophecy.
In February, HSBC warned that 20% could be wiped off the value of sterling were Britain to leave the EU. In May this figure was corroborated by the National Institute for Economic and Social Research. The pound plunged to a three-week low yesterday, probably partly in response to polls showing the Leave campaigning ahead. It hit a seven-year low against the dollar the day after the former Mayor of London, Boris Johnson, announced he was backing Brexit, and also suffered the biggest one-day fall since David Cameron become Prime Minister. The collapse of the pound at the end of June would mean Britons going abroad during the summer would have their spending power reduced. Imported goods such as electronics would also likely become significantly more expensive.
Read more …

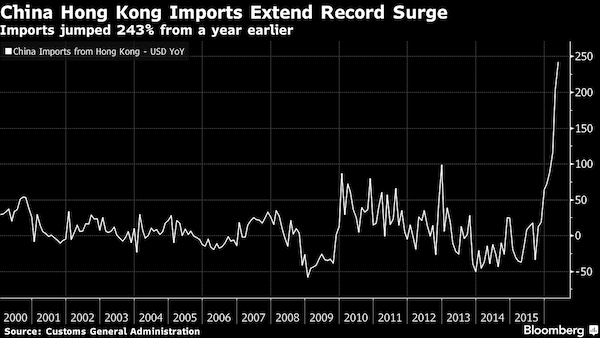
That is one damning graph. Where would China’s imports be without the fake invoices?
• China’s Exports Weaken, Signaling More Headwinds For Growth (BBG)
China’s exports stabilized in May, with a weakening currency giving some support to growth in the world’s biggest trading nation. Overseas shipments fell 4.1% in dollar terms from a year earlier, the customs administration said Wednesday. Imports slipped 0.4% – the smallest drop since late 2014 – to leave a trade surplus of $50 billion. Reflecting a weaker currency, both exports and imports fared better when measured in local currency terms. The Shanghai Composite Index pared losses and the Australian dollar rallied. “The worst time for Chinese exports has passed,” said Harrison Hu at Royal Bank of Scotland in Singapore, adding that the dollar-denominated export growth is slightly misleading due to the price changes.
“The quantity of exports actually showed a subdued increase. The yuan also depreciated against a basket of currencies, which supports exports.” Still, that support remains restrained. The World Bank on Tuesday cut its global growth estimate to 2.4% for this year, which would be the same as 2015, from the 2.9% projected in January. Ma Jun, chief economist of the People’s Bank of China’s research bureau, lowered his forecast for China’s exports this year to a 1% decline, versus a 3.1% increase seen previously, according to a work paper published Wednesday. “The weakening momentum of global growth is our main reason to lower the forecast,” he wrote. “A 10-percentage point decline in exports can drag GDP growth down by about 1%.”
Read more …

“China’s trade shrank 8% last year, compared with the government’s goal for 6% growth..”
• China Central Bank Holds Line On Growth Forecast, Sees More Pain To Come (R.)
China’s central bank slashed its forecast for exports on Wednesday, predicting a second straight annual fall in shipments, but said the economy will still grow 6.8% this year. The People’s Bank of China also warned in its mid-year work report that the government’s push to reduce debt levels and overcapacity could increase bond default risks and make it more difficult for companies to raise funds. And ahead of a meeting of the U.S. Federal Reserve’s policymaking board next week, it said the pace of U.S interest rate rises would affect global capital flows and emerging market currencies, but it did not mention the yuan. “Since the beginning of this year, the global and domestic economic environment has experienced a number of changes,” the PBOC said in the report.
“Reflecting these recent developments, we revised our China macroeconomic forecasts for 2016. Compared with our published forecasts in December last year, we maintain our baseline projection of 2016 real GDP growth at 6.8%.” The report was released shortly after monthly data showed China’s exports fell an annual 4.1% in May, more than expected and the 10th decline in the past 12 months. Imports were more encouraging, however, declining only marginally and much less than expected, pointing to improving domestic demand and adding to views that the economy may be slowly stabilizing. Preliminary commodity trade data showed sharp rises in imports of copper and iron ores.
[..] Despite cutting its forecast for exports to minus 1% from growth of 3.1%, the PBOC saw a domestic recovery remaining on track. It upgraded its forecast for fixed-asset investment growth to 11%, an increase of 0.2 percentage points from estimates it made late last year. A government spending spree on major infrastructure projects and a continuing recovery in the housing market have boosted demand for materials from cement to steel. China’s trade shrank 8% last year, compared with the government’s goal for 6% growth , in the worst performance since the global financial crisis.
Read more …

And those are here to stay. Sharply conflicting interests.
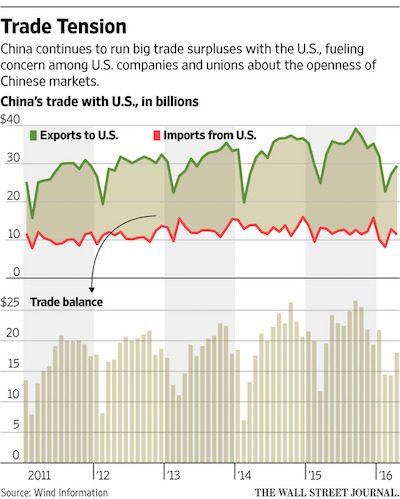
• US-China Talks Limited by Disagreements (WSJ)
The U.S. and China made little progress on a series of disagreements during two days of high-level economic and security talks, as both countries prepare for leadership change and further economic uncertainty. Statements by officials from both sides on Tuesday suggested mostly incremental results from the dialogue. U.S. Treasury Secretary Jacob Lew said Chinese officials reaffirmed a commitment not to devalue an already weakening yuan for competitive purposes and pledged not to “target” an expansion of the steel industry, whose surging production he previously called market-distorting. Beijing widened access to its tightly regulated financial markets, offering U.S. investors a quota of 250 billion yuan ($38.1 billion) to buy Chinese stocks and bonds.
The two governments agreed to designate clearing banks in the U.S. for settling yuan transactions, a move that would promote greater use of the Chinese currency. Mr. Lew said it was too early to say which U.S. financial institution might be chosen but said the U.S. will have the second-largest quota after Hong Kong. On the more contentious issues in the relationship, the senior officials appeared to restate positions and, in some cases, outright disagree. A new Chinese law that grants police the authority to monitor foreign nonprofits provoked sharp differences. This year’s meeting of the Strategic and Economic Dialogue is the last for the Obama administration, with the U.S. presidential election approaching. China soon will face its own important leadership transition.
In 2017, five of the seven members of the Politburo Standing Committee, China’s top decision-making body, are due to step down. The timing of the meetings, combined with tensions over the South China Sea—where the U.S. is challenging Beijing’s assertion of sovereignty over islands, reefs and surrounding waters claimed by other countries—limited prospects for breakthroughs on issues such as trade and investment barriers and China’s currency policy.
Read more …

TEXT
• Millions Around The World Are Fleeing Neoliberal Policy (RNN)
What it tells is almost identical to what has already been narrated for Russia and Greece. And what’s responsible for the increasing death rates is actually neoliberal economic policy, neoliberal trade policy, and the polarization and impoverishment of a large part of society. After the Soviet Union broke up in 1991, death rates soared, lifespans shortened, health standards decreased all throughout the Yeltsin administration, until finally President Putin came in and stabilized matters. Putin said that the destruction caused by neoliberal economic policies had killed more Russians than all of whom died in World War II, the 22 million people. That’s the devastation that polarization caused there.
Same thing in Greece. In the last five years, Greek lifespans have shortened. They’re getting sicker, they’re dying faster, they’re not healthy. Almost all of the British economists of the late 18th century said when you have poverty, when you have a transfer of wealth to the rich, you’re going to have shorter lifespans, and you’re also going to have immigration. The countries that have a hard money policy, a creditor policy, people are going to emigrate. Now, at that time that was why England was gaining immigrants. It was gaining skilled labor. It was gaining people to work in its industry because other countries were still in the post-feudal system and were driving them out. Russia had a huge emigration of skilled labor, largely to Germany and to the United States, especially in information technology. Greece has a heavy outflow of labor.
The Baltic states have had almost a 10% decline in their population in the last decade as a result of their neoliberal policies. Also, health problems are rising. Now, the question is, in America, now that you’re having as a result of this polarization shorter lifespans, worse health, worse diets, where are the Americans going to emigrate’ Nobody can figure that one out yet. There’s no, seems nowhere for them to go, because they don’t speak a foreign language. The Russians, the Greeks, most Europeans all somehow have to learn English in school. They’re able to get by in other countries. They’re not sure where on earth can the Americans come from’ Nobody can really figure this out.
Read more …
Curious ‘thingy’ from the Independent: somewhere in the article it says Iceland is the world’s most peaceful country, even though it’s not in that list of 10.
• Only 10 Countries In The World Are Not At War (Ind.)
The world is becoming a more dangerous place and there are now just 10 countries which can be considered completely free from conflict, according to authors of the 10th annual Global Peace Index. The worsening conflict in the Middle East, the lack of a solution to the refugee crisis and an increase in deaths from major terrorist incidents have all contributed to the world being less peaceful in 2016 than it was in 2015. And there are now fewer countries in the world which can be considered truly at peace – in other words, not engaged in any conflicts either internally or externally – than there were in 2014. According to the Institute for Economics and Peace, a think-tank which has produced the index for the past 10 years, only Botswana, Chile, Costa Rica, Japan, Mauritius, Panama, Qatar, Switzerland, Uruguay, and Vietnam are free from conflict.
Brazil is the country that has dropped out of the list, and as one of the worst performing countries year-on-year represents a serious concern ahead of the Rio Olympics, the IEP’s founder Steve Killelea told The Independent. But perhaps the most remarkable result from this year’s peace index, he said, was the extent to which the situation in the Middle East drags down the rest of the world when it comes to peacefulness. “If we look at the world overall, it has become slightly less peaceful in the last 12 months,” Mr Killelea said. “But if we took the Middle East out of the index over the last decade – and last year – the world would have become more peaceful,” he said. “It really highlights the impact the Middle East is having on the world.”
Read more …

Man was here.
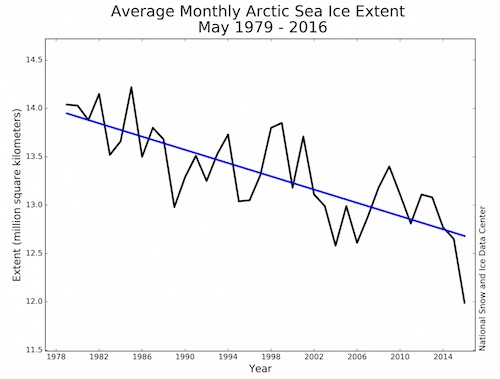
• Arctic Sea Ice Hit A Stunning New Low In May (WaPo)
The 2016 race downward in Arctic sea ice continued in May with a dramatic new record. The average area of sea ice atop the Arctic Ocean last month was just 12 million square kilometers (4.63 million square miles), according to the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC). That beats the prior May record (from 2004) by more than half a million square kilometers, and is well over a million square kilometers, or 500,000 square miles, below the average for the month. Another way to put it is this: The Arctic Ocean this May had more than three Californias less sea ice cover than it did during an average May between 1981 and 2010. And it broke the prior record low for May by a region larger than California, although not quite as large as Texas.
This matters because 2016 could be marching toward a new record for the lowest amount of ice ever observed on top of the world at the height of melt season — September. The previous record September low was set in 2012. But here’s what the National Snow and Ice Data Center has to say about that: Daily extents in May were also two to four weeks ahead of levels seen in 2012, which had the lowest September extent in the satellite record. The monthly average extent for May 2016 is more than one million square kilometers (386,000 square miles) below that observed in May 2012. In other words, for Arctic sea ice, May 2016 was more like June 2012 — the record-breaking year. Going into the truly warm months of the year, then, the ice is in a uniquely weak state.
Read more …

The whole thing is turning into such a mess you would think this is happening on purpose.
• Greek Legal Rulings Back 35 Refugees Appealing Deportation (Kath.)
Fears are rising about the possible breakdown of a deal between the European Union and Turkey for the return of migrants after legal committees in Greece upheld dozens of appeals by refugees against their deportation. By late Monday, Greek appeals committees had ruled in favor of 35 refugees, ruling that Turkey is “an unsafe country.” Only two rulings overturned appeals by refugees against their deportation. On Tuesday a crowd of refugees blocked the container terminal at the port of Thessaoniki to protest the slow pace at which asylum applications are being processed. Hundreds of applications are pending and there are fears that they too will result in rulings in favor of refugees, undercutting a deal signed between Ankara and Brussels in March to return migrants to Turkey.
Meanwhile there are also concerns about a pickup in arrivals from neighboring Turkey. For several weeks, a crackdown by Turkish authorities on smugglers had all but stopped the migrant influx. Now that ties between Turkey and the EU are strained over the former’s refusal to reform terrorism laws and its insistence that Turks be granted visa-free access to the bloc, more migrants have started arriving in Greece from Turkey. The total number of refugees in Greece is 57,458, according to government figures made public on Tuesday. The figure includes 5,700 people in rented accommodation arranged by the United Nations refugee agency, UNHCR. The remainder of the migrants are living in makeshift camps or state-run facilities on the Aegean islands or mainland Greece.
Read more …

When in a hole, keep digging. One deal with a madman is not enough.
• EU Considers Linking African Aid to Curbs on Migrant Flows (WSJ)
The European Union’s executive body on Tuesday presented plans linking trade and investment perks for African countries to their efforts in reducing migration to Europe, a controversial idea that still needs the backing of EU governments. While the bloc has managed to stem the influx of Syrian refugees and other migrants after striking a deal with Turkey in March, an increasing number of mostly African migrants are attempting to make the perilous journey via Libya across the Mediterranean Sea to Italy. Nearly 50,000 people were rescued and brought to Italy this year and over 2,000 are feared dead after several boats capsized off the Libyan coast, according the United Nations’ refugee agency.
“We must do in the southern Mediterranean what we’ve done in the Aegean,” European Commission Vice-President Frans Timmermans said Tuesday in the European Parliament in Strasbourg. Under the proposed measures from the European Commission, which still need the approval of EU governments and the European Parliament, EU development funding and trade incentives would be linked to the countries’ level of cooperation on migration. “We propose a mix of positive and negative incentives, to reward those countries willing to cooperate effectively with us and to ensure there are consequences for those who do not. This includes using our development and trade policies to create leverage,” Mr. Timmermans said.
EU diplomats in Brussels expect “quite heated discussions” on the idea of linking development aid and trade policies to cooperation on migration, as governments have different views on whether it is ethical to make aid conditional on countries taking people back or preventing them from leaving. EU interior ministers meeting in Luxembourg on Friday will have a first exchange of views on the topic.
Read more …