
Harris&Ewing Army surplus 1919

No matter what anybody does, the overbuilding, overcapacity and overconsumption in China can no longer be extended. Infrastructure investment in other countries won’t be enough to pick up the slack.
• Mining Giant BHP Slumps To Record Loss (BBC)
Mining giant BHP Billiton has reported a record loss for the past year following a mining disaster in Brazil and a slump in commodity prices. The Anglo-Australian commodities firm reported an annual net loss of $6.4bn (£5bn) for the year to 30 June. The global mining sector has seen years of weak demand attributed largely to slowing growth in China. BHP results were also hit by costs after the Samarco mining disaster in Brazil, which killed 19 people. The record losses come after the company had reported a $1.9bn net profit. “While commodity prices are expected to remain low and volatile in the short to medium term, we are confident in the long-term outlook for our commodities, particularly oil and copper,” chief executive Andrew Mackenzie said in a statement.
Underlying earnings for the past year, which strip out one-off costs, came in at $1.22bn. The financial fallout from the Samarco mining tragedy is still not clear though warns James Butterfill, head of research & investment strategy at ETF Securities. “There’s a huge uncertainty overhang,” he told the BBC. “The report hasn’t been published with regard to the Samarco dam collapse and there’s currently a $48bn lawsuit. It’s unrealistic to be that amount, but this is really BHP’s Macondo well incident theoretically that BP endured.”

As consumption and investment falls, so will prices. Commodity producers worldwide are sitting on huge overcapacity. They must shrink their operations, but the first reaction is always to produce more to make up for falling revenue.
• Chinese Traders Are Falling Out Of Love With Commodities (BBG)
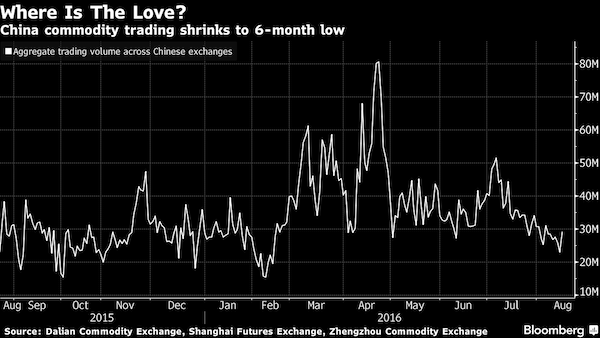
Chinese traders are falling out of love with commodities. Aggregate volumes across the nation’s three biggest exchanges have shrunk to the lowest level in six months, a shadow of the fevered trading in March and April when retail investors charged into markets for everything from iron ore to cotton, driving up prices and stoking fears of a bubble. Chinese authorities brought an end to the frenzy by introducing curbs on excessive speculation and trading has failed to recover since. Flush with record credit and hunting for returns, investors piled into commodities in the first half of the year, spurred by bets that China’s economic stimulus and industrial reforms would lead to shortages of raw materials. Now, there’s just not much for traders to get excited about, according to Wei Lai, an analyst with Cofco Futures.
Industrial production and fixed-asset investment slowed in July and a measure of new credit expanded the least in two years, spurring concern over growth in the world’s second-largest economy. “Investors are reluctant as there isn’t much information to play around with in the market,”’ Shanghai-based Wei said in an e-mail. High prices for some commodities may also be deterring traders, Wei said. Combined aggregate volume across the Shanghai Futures Exchange, Dalian Commodity Exchange and Zhengzhou Commodity Exchange slid to 23 million contracts as of Aug. 12, the lowest since February and compared with a peak of more than 80 million on April 22 when a total of $261 billion changed hands. Chinese exchanges double count trading volume and turnover.

China will become known for the biggest misallocation of investment in history.
• China’s Fading Animal Spirits (BBG)
The July wobble in China’s economy – like its multi-year slowdown – has much to do with the waning “animal spirits” of Chinese businesses caused by an historic shift in housing. That’s according to Chi Lo, greater China senior economist at BNP Paribas Investment Partners in Hong Kong. A property-led pick up in the first half lost momentum in July, suggesting the market is struggling to digest an overhang in supply of apartments. “In the past, the economic players expanded supply first and created jobs so as to create demand, but that is gone now,” Lo said in a telephone interview after Friday’s disappointing data. “It has to clean out the excess capacity, which means the supply-expansion model has to change.”
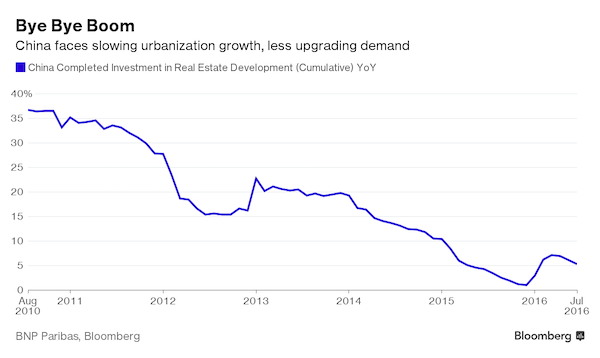
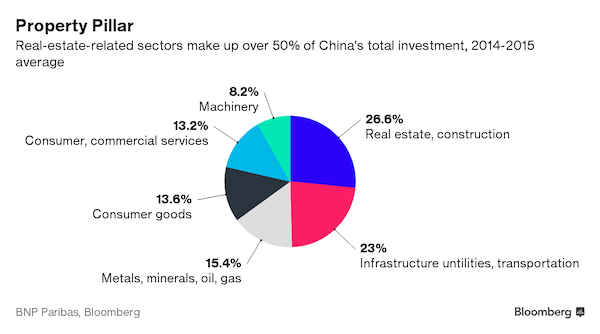
Another way of putting it: China’s build-it-and-they-will-come strategy needs to shift to one where demand, not supply, is in the drivers’ seat. It’s a change companies are struggling to come to terms with, leaving private investment in the doldrums. “Little attention has been paid to the underlying structural factor that is hurting private investment incentive,” Lo wrote in a research note ahead of the data last week. “This is the weakening of the final demand for output produced by the investment or capital-intensive sector in China. The key to understand this puzzle is China’s housing market.” That’s because it accounts for about half of all investment in China once spillovers into industries like metals and machinery are thrown in.
With such pervasive impact on everything from cement to cars, China’s property market was dubbed the most important sector in the universe back in 2011 by a UBS economist. BNP’s Lo says it’s unlikely to ever recapture the glory days of old. “China’s housing demand has likely passed its high-growth phase, with housing construction growth expected to go into a secular decline soon,” according to Lo. “This means that the capital-intensive sector, which has focused on producing all this housing units through the decades, is facing a structural decline in demand for its output.”

One might be forgiven for thinking Berlin is blowing up the eurozone on purpose. What is needed are transfer payments to southern Europe, but there is too much resistance to those.
• Germany Amassing Huge Surpluses – And Huge Risks (MW)
As one of the world’s largest exporters, Germany saw an important part of the political and economic rationale of entering European economic and monetary union in 1999 as lowering risks on its international commercial interactions. Nearly two decades later, Germany, more than ever, is an export champion. It is likely to register the world’s largest trade surplus this year, according to the OECD, at $324 billion (against China’s $314 billion), and will amass a record current-account surplus of 9.2% of gross domestic product. Yet, as a result of the large imbalances within EMU that these surpluses symbolize, Germany is a long way from insulating itself against foreign-currency risks.
The Bundesbank provides the strongest indicator of this change. The quintessentially hard-money central bank provided a role model for the ECB at the heart of the euro bloc. Yet the Bundesbank now confronts on its balance sheet a range of potential hazards that the euro’s founding fathers in the 1980s and 1990s would have regarded as inimical to economic stability and, for that reason, impossible to countenance. The Bundesbank’s balance sheet rose to €1.2 trillion in July from €222 billion when monetary union started in January 1999. Underlining the Bundesbank’s pivotal role in eurozone monetary operations, the German central bank’s balance sheet has expanded faster than that of the Eurosystem (the ECB and the constituent national central banks) as a whole.
The Bundesbank’s balance sheet now encompasses around 37% of Eurosystem assets of €3.3 trillion (computed on a net basis that strips out individual central banks’ claims and liabilities against each other under the Target-2 payments system), against 32% at the inception of EMU. The acceleration stands in marked contrast to the central bank’s stated desire, when monetary union started, to slim down its balance sheet and especially to economize on foreign-exchange reserves, held mostly in dollars. These have traditionally (together with gold) made up the lion’s share of the Bundesbank’s foreign assets, but have been cut from €45 billion to €50 billion when the euro was launched to only €30 billion to €35 billion in recent years.

You’re not going to solve the problems by tweaking the age; that merely shifts the issue into the future. Can, road.
• Bundesbank Floats Higher Retirement Age -69- in German Pension Debate (BBG)
Germany’s Bundesbank said raising the legal retirement age to 69 by 2060 could ease some of the pressure on the country’s state pension system as the population ages. Recent reforms won’t protect citizens from a drop in the level of pension payments from 2050, the central bank said in its monthly report published on Monday. Citizens who don’t opt for state-supported private insurance may face shortfalls a lot sooner. Low average interest rates could further reduce available provisions. While higher premiums could theoretically keep payouts stable, they would “raise the strain on those paying the contributions, and an increasing, high burden of payments overall has negative consequences on economic development,” the Bundesbank wrote. To avoid that, “the legal retirement age ultimately needs to be adjusted.”
The Bundesbank said the government’s current plans that include raising the retirement age to 67 by 2030 and increasing contributions don’t account for the fact that the ratio of retirees to contributors is set to widen further. Increasing life expectancy means retirees will draw from pension funds for a longer period of time, and a generation of baby boomers that retires post-2030 means there will be more pensioners to take care of per working adult, while birth rates remain low, according to the report. “Amid demographic change, the parameters of a contribution-based pension system can’t all be kept stable,” the Bundesbank said. “Confidence in pension insurance could be strengthened and uncertainty about financial stability at old age could be decreased if it were made clear how the parameters of retirement age, provision levels, and contribution rates can be adjusted in the long term.”

Short termism perfected.
• Top UK Firms Paid Five Times More In Dividends Than Into Pensions (G.)
Britain’s biggest companies paid five times more in dividends than they did pension contributions last year, according to a new report that highlights the pressure on retirement schemes. FTSE 100 companies paid £13.3bn towards their defined benefit pension schemes, compared with £71.8bn in payments to shareholders, according to the consultancy firm LCP’s annual study of pensions. The report has been published after Sir Philip Green was heavily criticised by a parliamentary investigation into the collapse of BHS for leaving the retailer with a £571m pension deficit, despite his family and other investors banking more than £400m in dividends. BHS’s 164 stores are all scheduled to close by 28 August, a week later than administrators planned last month as the retailer continues to sell its remaining stock.
Green remains locked in talks with the Pensions Regulator about a rescue deal for the BHS pension scheme. He has pledged to sort out the problems facing it, but the regulator has launched an investigation into whether the billionaire tycoon should be forced to make a financial contribution to fill the black hole. Other companies with large pension deficits could face action from the regulator if they are paying dividends, LCP says in its report. The 56 FTSE 100 companies that disclosed a pension deficit at the end of their 2015 financial year had a combined deficit of £42.3bn, but the same companies paid out dividends worth £53bn, 25% more than their pension contributions.

“..a $1BN pension that is fully funded at prevailing interest rates would be nearly $700mm underfunded if interest rates declined 300bps and all of their assets were invested in 30-year treasury bonds.”
• Pension Funds Are Driving The Biggest Bond Bubble In History (ZH)
We’ve frequently discussed the many problems faced by pension funds. Public and private pension funds around the globe are massively underfunded yet they continue to pay out current claims in full despite insufficient funding to cover future liabilities…also referred to as a ponzi scheme. In fact, we recently noted that the Central States Pension Fund pays out $3.46 in pension funds for every $1 it receives from employers. The pension problem is often attributed to low returns on assets. As Bill Gross frequently points out, low interest rates are the enemy of savers and pension funds have some of the biggest savings accounts around. That said, the impact of declining interest rates on the asset side of a pension’s net funded status is dwarfed by the much more devastating impact of declining discount rates used to value future benefit obligations.
The problem is one of duration. By definition, pension liabilities represent the present value of future benefit payments owed to retirees which is a virtually perpetual cash flow stream. Obviously, the longer the duration of a cash flow stream the larger the impact of interest rate swings on the present value of that stream. We created the chart below as a simplistic illustration of the pension “duration dilemma.” The chart graphs how a pension liability grows in a declining interest rate environment versus the value of 5-year and 30-year treasury bonds. As you can see, a $1BN pension that is fully funded at prevailing interest rates would be nearly $700mm underfunded if interest rates declined 300bps and all of their assets were invested in 30-year treasury bonds. The result is obviously even worse if the fund’s assets are invested in shorter duration 5-year treasuries.


How Abenomics gets strangled.
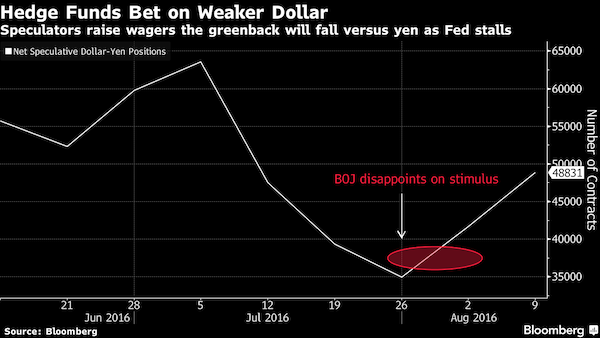
• Hedge Funds Bet Dollar Will Lose More Ground Versus Yen (BBG)
Hedge funds and other large speculators increased net bets the dollar will weaken against the yen to the highest level in a month, according to Commodity Futures Trading Commission data as of Aug. 9. Traders will focus on the meetings of the Federal Reserve and the Bank of Japan next month for direction, after disappointing stimulus announced last month by the BOJ failed to halt yen strength.

“Krugman would do himself a favor if he threw away what he thinks he knows about economics and went back for a nice 5th grade education.”
But the saddest part of course is that belugas are kept in an aquarium and learn tricks to amuse Japanese. Who are we?
• Krugman’s Arrow Theory Misses Target by Light Years (Mish)
With full employment, roads paved and repaved to nowhere, and bubble blowing beluga whales, just what the hell is Japan supposed to waste money on? Curiously, Krugman says it doesn’t matter. He once proposed a fake aliens from outer space scare as the solution to stimulate the economy. But roads and bridges and bubble blowing blowing beluga whales are surely better than fabricating space aliens or paying people to dig ditches and others to fill them up again. The problem is, it’s hard arguing with economic illiterates like Krugman. He can (and will) say “spending wasn’t enough”.
One can never prove him wrong. The implosion of Japan would not do it. His built-in excuse would be Japan did too little, too late. Just once I would like Krugman to address in his model what happens when the stimulus stops. He cannot and he won’t because he has no answer. The average 5th grader understands it’s absurd to pay money for something guaranteed to be useless, but the average Keynesian economist doesn’t. Krugman would do himself a favor if he threw away what he thinks he knows about economics and went back for a nice 5th grade education.


John Whitehead does not mince words.
• A Government of Scoundrels, Spies, Thieves, And Killers (JW)
“There is nothing more dangerous than a government of the many controlled by the few.”—Lawrence Lessig, Harvard law professor
The U.S. government remains the greatest threat to our freedoms. The systemic violence being perpetrated by agents of the government has done more collective harm to the American people and our liberties than any single act of terror. More than terrorism, more than domestic extremism, more than gun violence and organized crime, the U.S. government has become a greater menace to the life, liberty and property of its citizens than any of the so-called dangers from which the government claims to protect us. This is how tyranny rises and freedom falls.
As I explain in my book Battlefield America: The War on the American People, when the government views itself as superior to the citizenry, when it no longer operates for the benefit of the people, when the people are no longer able to peacefully reform their government, when government officials cease to act like public servants, when elected officials no longer represent the will of the people, when the government routinely violates the rights of the people and perpetrates more violence against the citizenry than the criminal class, when government spending is unaccountable and unaccounted for, when the judiciary act as courts of order rather than justice, and when the government is no longer bound by the laws of the Constitution, then you no longer have a government “of the people, by the people and for the people.”
What we have is a government of wolves. Worse than that, we are now being ruled by a government of scoundrels, spies, thugs, thieves, gangsters, ruffians, rapists, extortionists, bounty hunters, battle-ready warriors and cold-blooded killers who communicate using a language of force and oppression. Does the government pose a danger to you and your loved ones? The facts speak for themselves. We’re being held at gunpoint by a government of soldiers—a standing army. While Americans are being made to jump through an increasing number of hoops in order to exercise their Second Amendment right to own a gun, the government is arming its own civilian employees to the hilt with guns, ammunition and military-style equipment, authorizing them to make arrests, and training them in military tactics.
Among the agencies being supplied with night-vision equipment, body armor, hollow-point bullets, shotguns, drones, assault rifles and LP gas cannons are the Smithsonian, U.S. Mint, Health and Human Services, IRS, FDA, Small Business Administration, Social Security Administration, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Education Department, Energy Department, Bureau of Engraving and Printing and an assortment of public universities. There are now reportedly more bureaucratic (non-military) government civilians armed with high-tech, deadly weapons than U.S. Marines. That doesn’t even begin to touch on the government’s arsenal, the transformation of local police into extensions of the military, and the speed with which the nation could be locked down under martial law depending on the circumstances. Clearly, the government is preparing for war—and a civil war, at that—but who is the enemy?

2 weeks old, but highly relevant.
• Jimmy Carter: The US Is an ‘Oligarchy With Unlimited Political Bribery’ (IC)
Former president Jimmy Carter said on the nationally syndicated radio show the Thom Hartmann Program that the United States is now an “oligarchy” in which “unlimited political bribery” has created “a complete subversion of our political system as a payoff to major contributors.” Both Democrats and Republicans, Carter said, “look upon this unlimited money as a great benefit to themselves.” Carter was responding to a question from Hartmann about recent Supreme Court decisions on campaign financing like Citizens United. Transcript: HARTMANN: Our Supreme Court has now said, “unlimited money in politics.” It seems like a violation of principles of democracy. … Your thoughts on that?
CARTER: It violates the essence of what made America a great country in its political system. Now it’s just an oligarchy, with unlimited political bribery being the essence of getting the nominations for president or to elect the president. And the same thing applies to governors and U.S. senators and congress members. So now we’ve just seen a complete subversion of our political system as a payoff to major contributors, who want and expect and sometimes get favors for themselves after the election’s over. … The incumbents, Democrats and Republicans, look upon this unlimited money as a great benefit to themselves. Somebody’s who’s already in Congress has a lot more to sell to an avid contributor than somebody who’s just a challenger.

“..generate Money-Out-Of-Thin-Air (QE) for the purpose of allowing “liquidity” flows to end up in US equity and bond markets in order to paint a false picture of “recovery” so as to insure the election of Hillary Clinton.”
• Burning Down the House (Jim Kunstler)
There’s a new feature to the Anything-Goes-and-Nothing-Matters economy: Nothing-Adds-Up. The magicians who pretend to measure the growth of GDP (Gross Domestic Product — the monetary value of all the finished goods and services) came up with a second quarter “adjusted” figure of 1.2 percent. That would have to be construed by anyone acquainted with basic econ stats as perfectly dismal. And yet the Bureau of Labor Statistics put out a sparkly Nonfarm Payroll Report of 255,000 for July, way above the forecast 180,000. There were so many ways to game the jobs number — between people forced to work more than one shit job and the notorious “birth/death model” used to just make up any old number for political purposes — that no one can take this information seriously.
Anyway, the GDP number was instantly forgotten and the jobs number launched the stock markets to previously uncharted record altitude. It’s that time of the year for the hedge fund boys, with their testosterone flowing, to start burning down their house rentals in the Hamptons. And it’s also the time of year for an ever more stressed financial system to go down in flames. And, of course, it’s a presidential election season. Even for one allergic to conspiracy theories, it’s not farfetched to imagine a coordinated effort by central banks — under government direction — to generate Money-Out-Of-Thin-Air (QE) for the purpose of allowing “liquidity” flows to end up in US equity and bond markets in order to paint a false picture of “recovery” so as to insure the election of Hillary Clinton.
I think that is exactly behind the recent money-printing activities by the Japanese and European Central Banks, and the Bank of England. Why would it end up in US markets? For bonds, because the Euro and Japanese bond sovereign yields are in sub-zero territory and the BOE just cut its prime rate lower than the US Federal Reserve’s prime rate; and for stocks, because the value of the other three currencies is sliding down and the dollar has been rising — so, dump your falling currency for the rising dollar and jam it into rising US stocks. It’ll work until it doesn’t.
Why do this for Hillary? Because she represents the continuity of all the current rackets being used to prop up belief in the foundering business model of western civilization. If she doesn’t get into the White House there may be no backstopping of the insolvent banks and bankrupt governments and a TILT message will appear in the sky.

Australia is a private debt disaster. Public debt is much less important.
• Sleeping Bear Of Debt Set To Wake (Herald Sun)
The great sleeping bear of Australia’s economic future – of your economic future – is the current account deficit and our foreign debt. They have completely disappeared from the front page – indeed, even from the business pages. Nobody seems to mention them. But they most certainly haven’t disappeared in reality. And in reality, they’ve never been bigger. The deficit, the CAD, in the latest March quarter was more than $20 billion. It will top $80 billion for the full 2015-16 year. The net foreign debt sits at a tad more than $1 trillion. To give you a sense of the scale, that’s more than half the size of the Australian economy; more than double the total of all federal tax revenues in a year.
The CAD is the difference between what we earn from exports and from our international investments each year and what we pay for imports and to foreign investors in Australia. That last bit includes the interest we pay on our existing foreign debt. And the deficit each year is mostly covered by borrowing more from foreigners. In recent years, the biggest borrowers have been our banks. So we have this merry-go-round. The bigger the foreign debt, the bigger the deficit tends to be because of the interest paid on the debt. Then, the bigger the deficit, the bigger the foreign debt gets. Sound familiar? Because it’s exactly the same as the merry-go-round with the Budget deficit and the national debt. The deficit increases the national debt; and the interest on the debt increases the next year’s deficit; and that deficit further increases the debt.

“..as a society, are we really prepared to let our children grow up this way?”
• One-Third Of New Zealand Children Live Below The Poverty Line (G.)
One-third of New Zealand children, or 300,000, now live below the poverty line – 45,000 more than a year ago. Unicef’s definition of child poverty in New Zealand is children living in households who earn less than 60% of the median national income – NZ$28,000 a year, or NZ$550 a week. The fact that twice as many children now live below the poverty line than did in 1984 has become New Zealand’s most shameful statistic. “We have normalised child poverty as a society – that a certain level of need in a certain part of the population is somehow OK,” said Vivien Maidaborn, executive director of Unicef New Zealand. “The empathy Kiwis are famous for has hardened. Over the last 20 years we have increasingly blamed the people needing help for the problem.
“If you can’t afford your children to have breakfast, you’re a bad budgeter. If you aren’t working you’re lazy. But our subconscious beliefs about some people ‘deserving’ poverty because of poor life choices no longer apply in today’s environment. We have to ask ourselves as a society, are we really prepared to let our children grow up this way?” For a third of New Zealand children the Kiwi dream of home ownership, stable employment and education is just that – a dream. For poor children in the developed South Pacific nation of 4.5 million illnesses associated with chronic poverty are common, including third world rates of rheumatic fever (virtually unknown by doctors in comparable countries like Canada and the UK), and respiratory illnesses.









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle August 16 2016