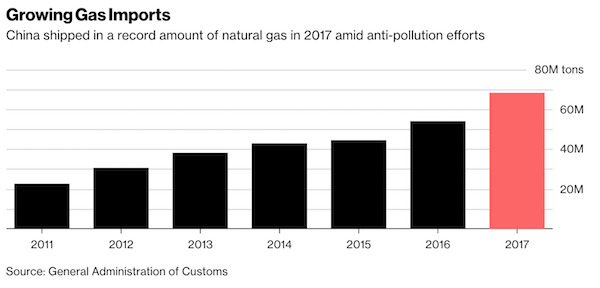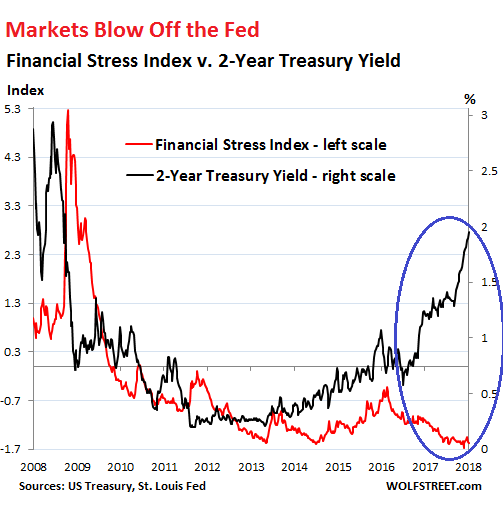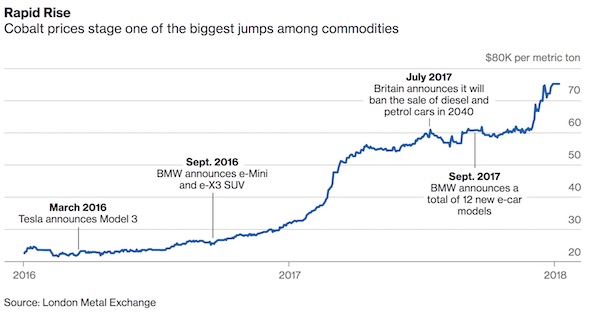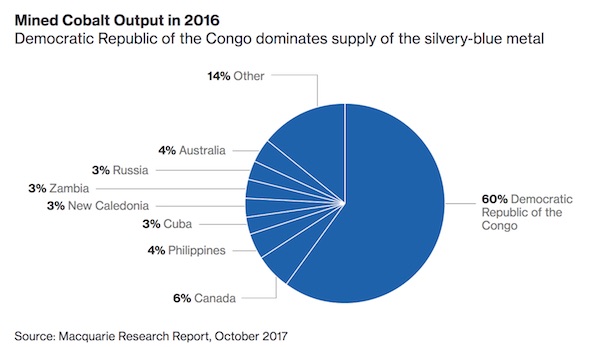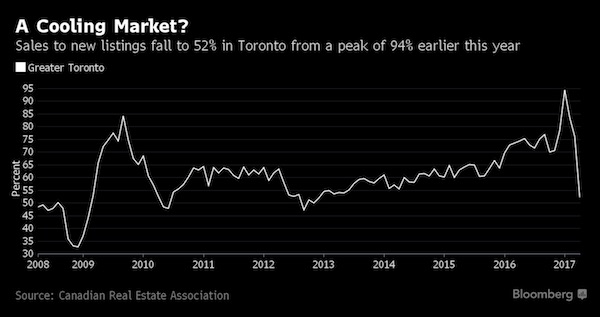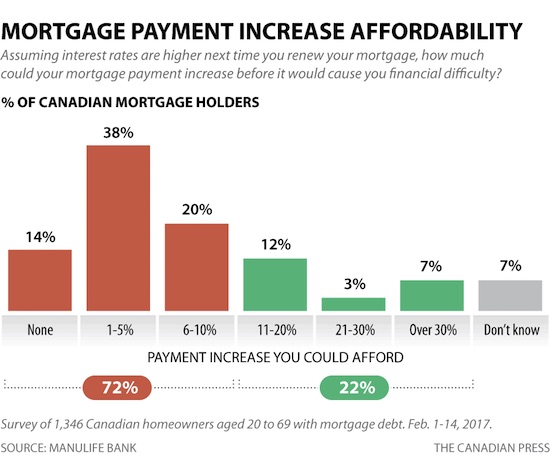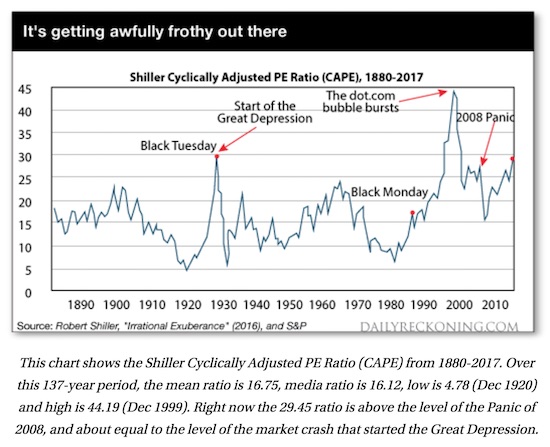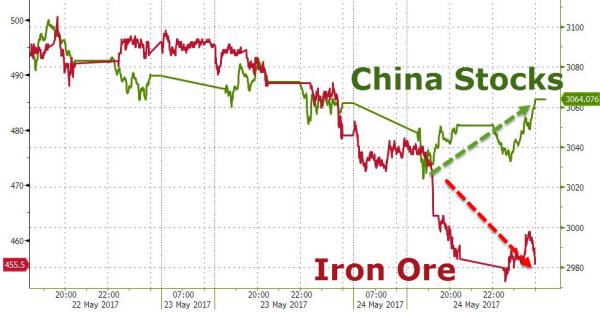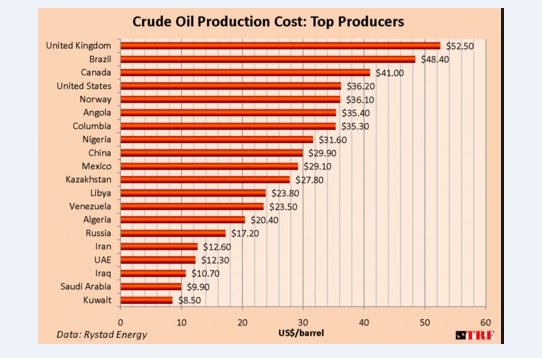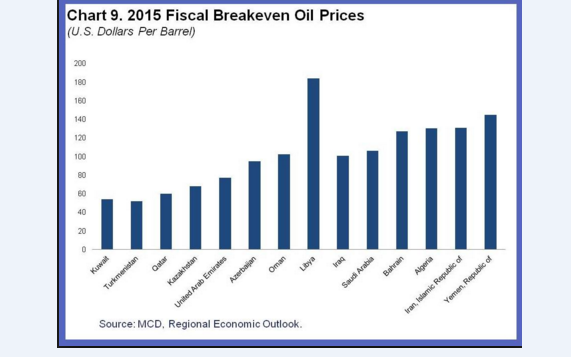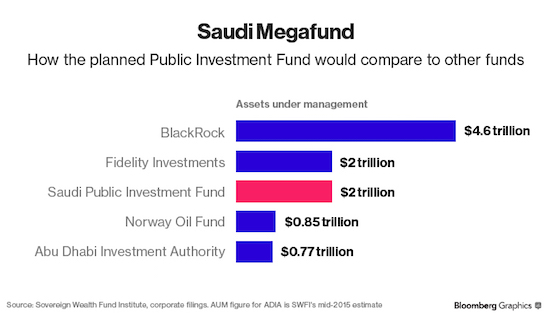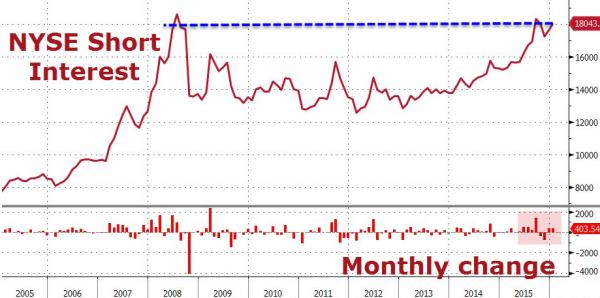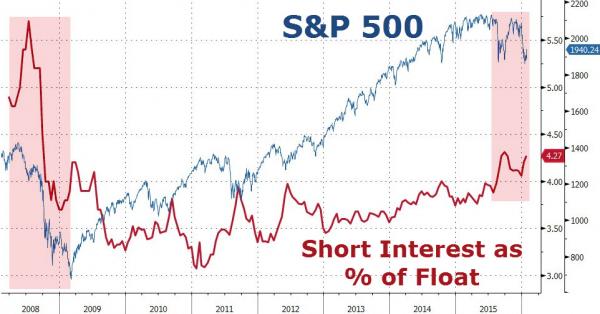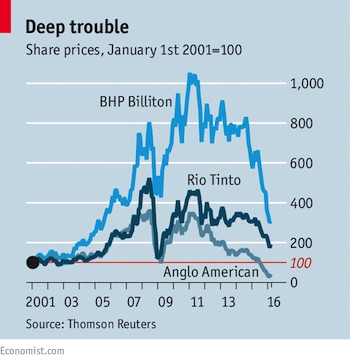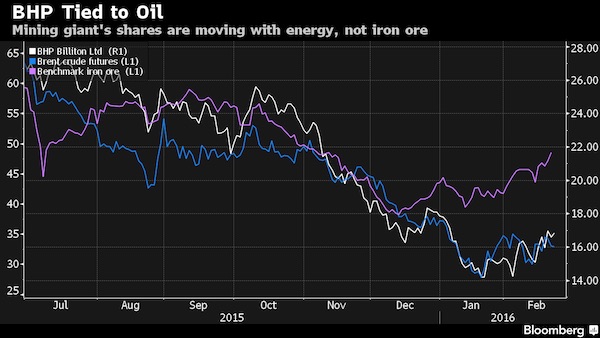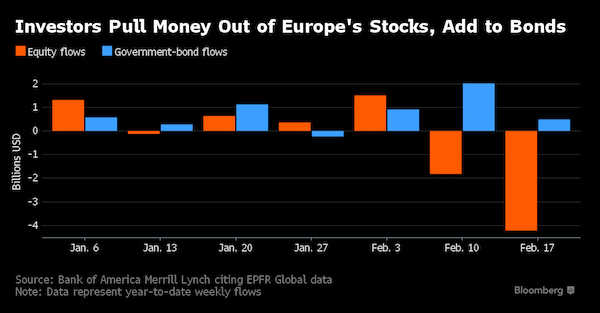

4% is nothing.
• Dow Jones Hit By Biggest Single-Day Points Drop Ever (Ind.)
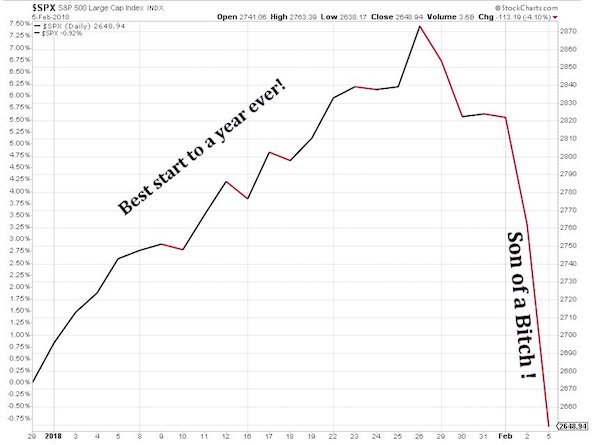
Newfound market volatility has shattered what had been a long period of stability and mounting value. The Dow’s dive erased gains for the year so far and extended a multi-day slump that saw the Dow drop by some 600 points on Friday. In addition setting a new record for number of points dropped in a day, the Dow’s 4.6% decline in value was the most substantial since 2011. It was still less severe than declines during market-rocking events like the 2008 financial crisis, when the Dow shed 7% of its value in its worst single-day hit. Earlier in the day the Dow had plummeted by nearly 1,600 points before recovering much of that value. It has swung some 2,100 points in the last week of trading, a slide approaching 8%.
In addition to the Dow shedding value, the S&P 500 index and the Nasdaq both saw declines of around 4%. The S&P 500 declined to about 7.8% below its all-time high. With thriving markets toppling records in recent months, some analysts said the pullback was all but inevitable. After cresting to a record high in January, the Dow has retreated by 8.5% from that apex. “It’s like a kid at a child’s party who, after an afternoon of cake and ice cream, eats one more cookie and that puts them over the edge,” David Kelly, the chief global strategist for JPMorgan Asset Management, told the Associated Press.

Worldwide.
• Stocks Crumble In Vicious Sell-off As ‘Goldilocks’ Trade Unravels (R.)
A rout in global equities deepened in Asia on Tuesday as inflation worries gripped financial markets, sending U.S. stock futures sinking further into the red after Wall Street suffered its biggest decline since 2011 in a vicious sell-off. S&P mini futures fell as much as 3.0% to four-month lows in Asia, extending their losses from the record peak hit just over a week ago to 12%. MSCI’s broadest index of Asia-Pacific shares outside Japan slid 4.3%, which would be its biggest fall since the yuan devaluation shock in August 2015, turning red on the year for the first time in 2018. Japan’s Nikkei dived 6.8% to near four-month lows while Taiwan shares lost 5.5% and Hong Kong’s Hang Seng Index dropped 4.9%.
Monday’s stock market rout left two of the most popular exchange-traded products that investors use to benefit from calm rather than volatile conditions facing potential liquidation, market participants said. The ructions in markets come after investors have ridden a nearly nine-year bull run, with low global rates sparking a revival in economic growth and bright corporate earnings. That good times may be nearing at end if Wall Street is anything to go by. U.S. stocks plunged in highly volatile trading on Monday, with the Dow industrials falling nearly 1,600 points during the session, its biggest intraday decline in history, as investors grappled with rising bond yields and potentially higher inflation.

They’ll all keep claiming that fundamentals are solid.
• Europe Joins Global Stock Selloff With Biggest Drop in 20 Months (BBG)
European stocks headed for their worst drop since the aftermath of the Brexit referendum as traders in the region caught up with an overnight selloff in the U.S. and Asia. The Stoxx Europe 600 Index fell 2.6% as of 8:16 a.m. in London, with all industry groups firmly in the red. After a strong start to 2018, most European stock benchmarks have wiped out gains for the year in a rout that is extending into a seventh day for the broader regional benchmark. Sentiment has been hurt by worries over rising government bond yields and the outlook for the trajectory of interest rates. “There is a sense out there that this is, in a way, a release of some of the pent-up low volatility we’ve seen over the past year,” said Ben Kumar, an investment manager at Seven Investment Management in London, which oversees about 12 billion pounds.
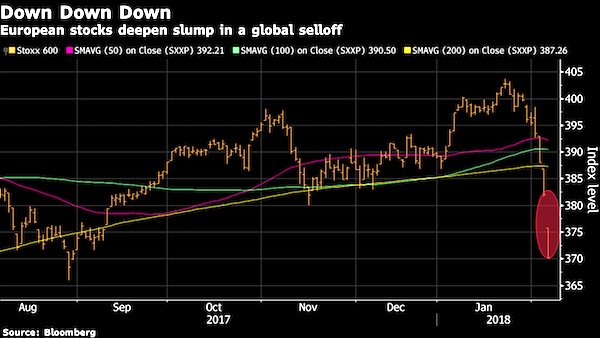
“We have been sitting on quite a large cash pile for some time and at some point, we will look to invest that. There may be a bit more pain to come before we start seeing a real dip to buy.” Cyclicals including automakers, technology and basic resources were among the worst sector performers. Still, data on Monday showed economic momentum in the euro-area climbed to the fastest pace in almost 12 years, and German factory orders surged in the last month of 2017. That’s leading some fund managers and traders to bet that equities are experiencing an overdue pullback rather than a deeper correction. “Market tops have probably been set for a pretty long time now on many equity indexes,” Stephane Barbier de la Serre, a strategist at Makor Capital Markets, said by phone.

They’ll have a hard time accepting the demise of easy money.
• ‘Short-Volatility Armageddon’ Craters Two Of Wall Street’s Favorite Trades (MW)
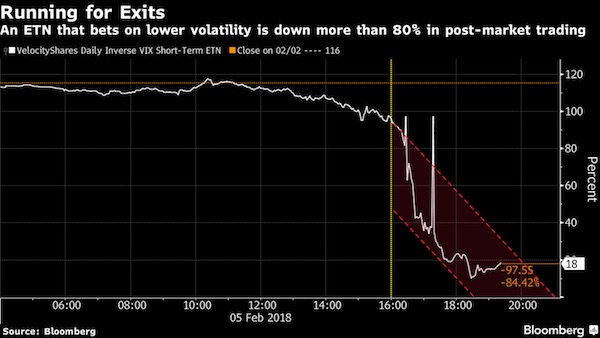
One of the most popular trades in the market, betting a period of unnatural calm would continue, may have amplified selling pressure in the stock market on Monday market participants said. At least two products tied to volatility bets were severely whacked with the hemorrhaging that could pose challenges to the exchange-traded notes. One popular product, the VelocityShares Daily Inverse VIX Short Term ETN, was down 90% in after-hours trade on Monday, following a session in which the Dow Jones Industrial plunged by 1,175 points, or 4.6%, while the S&P 500 index tumbled 4.1%—both benchmarks coughed up all of their gains for 2018.
The Cboe Volatility Index, meanwhile, skyrocketed by about 118%, marking its sharpest daily rise on record. The VIX uses bullish and bearish option bets on the S&P 500 to reflect expected volatility over the coming 30 days, and it typically rises as stocks fall. The XIV, meanwhile, was designed to allow investors to bet against a rise in volatility and such bets had been a winning proposition until recently, when equities accelerated a multisession unraveling fueled by fears that the Federal Reserve will be forced to raise borrowing costs faster than anticipated due to a potential resurgence in inflation, which had pushed Treasury yields higher. Monday’s stock-market drop may have been amplified because those making bets that volatility, as measured by the VIX, would remain relatively subdued, were caught wrong-footed.

Ultra low volatility is purely artificial.
• Volatility Spike Boosts US Options Hedging Activity (R.)
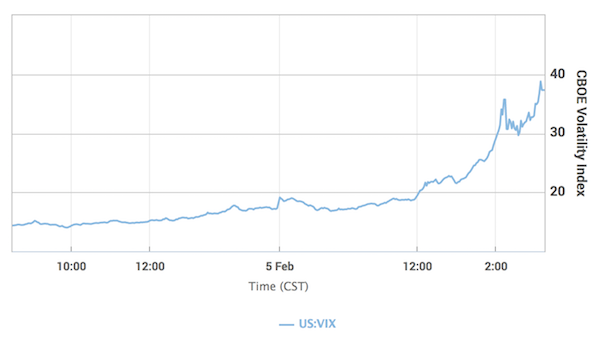
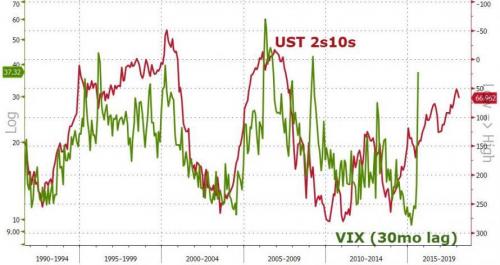
Wall Street’s “fear gauge” notched its biggest one-day jump on Monday in over two years, as U.S. stocks slumped and investors took to the options market in search of protection against a further slide in equities prices. Stocks slid in highly volatile trading on Monday, with the benchmark S&P 500 index and the Dow Jones Industrials suffering their biggest respective%age drops since August 2011 as a long-awaited pullback from record highs deepened. For the Dow, the fall at one point of nearly 1,600 points was the biggest intraday point loss in Wall Street history. The CBOE Volatility Index, better known as the VIX, is the most widely followed barometer of expected near-term volatility for the S&P 500 Index. On Monday, the index ended up 20.01 points at 37.32, its highest close since August 2015.
“The day started out fairly orderly, but somehow it took a turn for a worse, and then panic set in,” Randy Frederick, vice president of trading and derivatives for Charles Schwab. “There may have been some pretty sizeable program trades that were clicked in. It just looks like some institutional program selling,” he said. The intensity of the selloff drove traders to the options market and trading volume surged to 35.5 million contracts – the third busiest day ever and the busiest day since Aug. 21, 2015, according to options analytics firm Trade Alert. VIX call options, primarily used to protect against a spike in volatility, accounted for nine of Monday’s 10 most heavily-traded contracts. Overall VIX options volume hit 3.6 million contracts, or about three times its average daily volume.

VIX can trigger some pretty dramatic events.
• Traders Panic As XIV Disintegrates -90% After The Close (ZH)
Today’s market turmoil has left more questions than answers. “What was frightening was the speed at which the market tanked,” said Walter “Bucky” Hellwig, Birmingham, Alabama-based senior vice president at BB&T Wealth Management, who helps oversee about $17 billion. “The drop in the morning was caused by humans, but the free-fall in the afternoon was caused by the machines. It brought back the same reaction that we had in 2010, which was ‘What the heck is going on here?” Some tried to blame it on a fat-finger or ‘machines’, but in this case it was not the normal cuprits per se… “There was not a single self-help; there were no outs; there were no fat fingers that we saw,” Doug Cifu, CEO of high-speed trading firm Virtu, told CNBC. “There were no busted trades, no repricing. It was just an avalanche of orders around 3 o’clock-ish.”
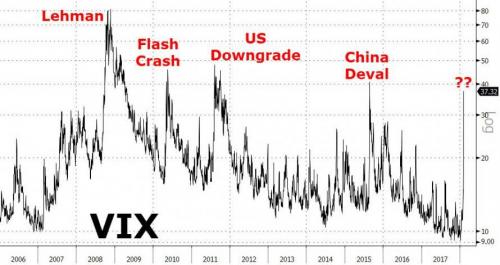
But while we noted earlier that US equity futures were extending losses after the close, but the real panic action is in the volatility complex. Putting today’s VIX move in context, this is among the biggest ever… And it appears Morgan Stanley was right to bet on VIX hitting 30…
But the real action is in the super-crowded short-vol space. XIV – The Short VIX ETF – after its relentless diagonal move higher as one after another Target manager sold vol for a living… just disintegrated after-hours, down a stunning 90% to $10.00.
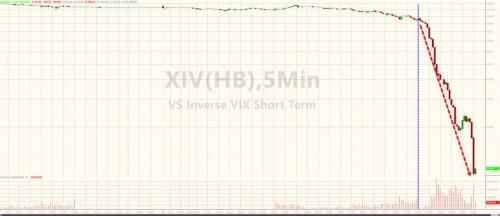
Which is a problem because as we explained last summer, the threshold for an XIV termination event is a -80% drop. What does this mean? Well, in previewing today’s events last July, Fasanara Capital explained precisely what is going on last July:
“Additional risks arise as ‘liquidity gates’ may be imposed, even in the absence of a spike in volatility. In 2012, for example, the price of TVIX ETN fell 60% in two days, despite relatively benign trading conditions elsewhere in the market. The reason was that the promoter of the volatility-linked note announced that it temporarily suspended further issuances of the ETN due to “internal limits” reached on the size of the ETNs. Furthermore, for some of the volatility-linked notes, the prospectus foresee the possibility of ‘termination events’: for example, for XIV ETF a termination event is triggered if the daily percentage drop exceeds 80%. Then a full wipe-out is avoided insofar as it is preceded by a game-over event.” The reaction of the investor base at play – often retail – holds the potential to create cascading effects and to send shockwaves to the market at large. This likely is a blind spot for markets.

Algorithms rule what is left.
• Machines Had Their Fingerprints All Over a Dow Rout for the Ages (BBG)
Risk parity funds. Volatility-targeting programs. Statistical arbitrage. Sometimes the U.S. stock market seems like a giant science project, one that can quickly turn hazardous for its human inhabitants. You didn’t need an engineering degree to tell something was amiss Monday. While it’s impossible to say for sure what was at work when the Dow Jones Industrial Average fell as much as 1,597 points, the worst part of the downdraft felt to many like the machines run amok. For 15 harrowing minutes just after 3 p.m. in New York a deluge of sell orders came so fast that it seemed like nothing breathing could’ve been responsible. The result was a gut check of epic proportion for investors, who before last week had been riding one of the most peaceful market advances ever seen. The S&P 500, which last week capped a record streak of never falling more than 3% from any past point, ended the day down 4.1%, bringing its loss since last Monday to 7.8%.
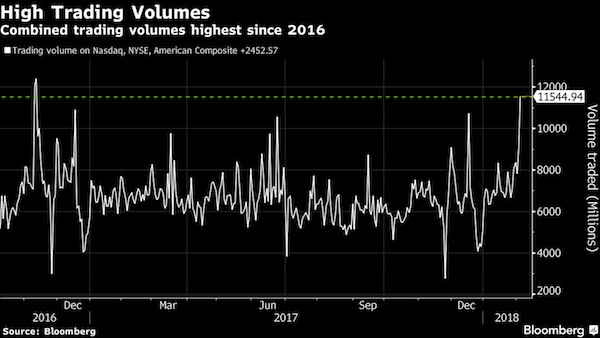
“We are proactively calling up our clients and discussing that a 1,600-point intraday drop is due more to algorithms and high-frequency quant trading than macro events or humans running swiftly to the nearest fire exit,” said Jon Ulin, of Ulin & Co. in an email. To be sure, not all of the rout requires inhuman agency to explain. Markets are jittery. Bond yields had been surging and stock valuations are approaching levels last seen in the internet bubble. Much of today’s selloff was perfectly rational, if harrowing – particularly coming after last week’s plunge in which the Dow fell 666 points on Friday. Observers looking for an electronic villain trained most of their attention on the roughest part of the tumble, a 15-minute stretch starting about an hour before the close. That’s when an orderly selloff snowballed, taking the Dow from down about 700 points to down a whopping 1,600. It quickly recovered.

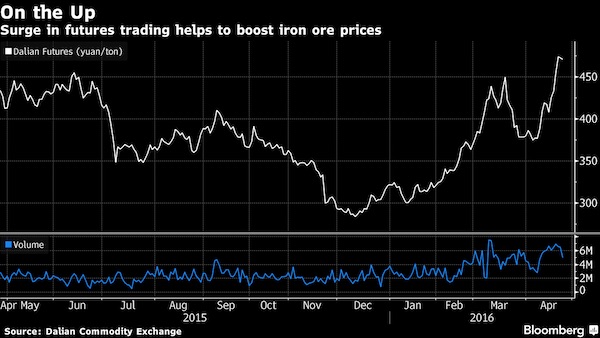
When commodities trade is separated from what industries actually use, and they become financial tools only, inevitable.
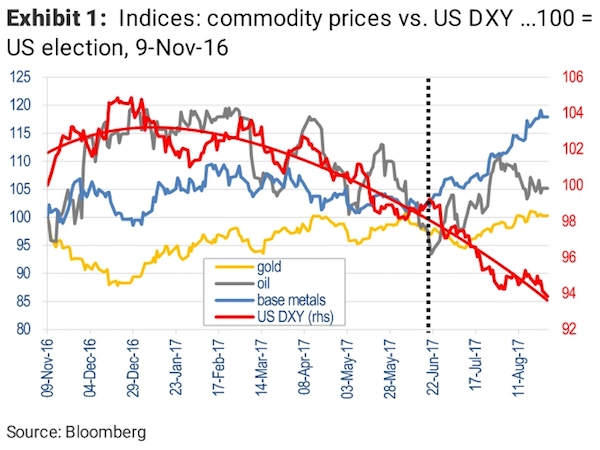
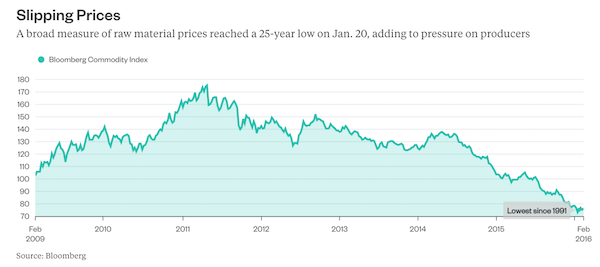
• Commodities Dragged Into Global Selloff as Oil to Copper Get Hit (BBG)
Commodities from crude oil to metals and iron ore dropped as the global equity rout and surge in market volatility spurred investors to pare risk, cutting positions in raw materials even as banks and analysts stood by the asset class given the backdrop of solid global growth. Brent crude slid as much as 1.2% to $66.82 a barrel, heading for a third daily drop and the longest losing run since November. On the London Metal Exchange, copper sank as much as 2% to $7,025 a metric ton as zinc, lead and nickel declined. Iron ore futures fell 1.2% in Singapore. Global equity markets are in retreat after Wall Street losses that began in the final session of last week worsened on Monday, with the Dow Jones Industrial Average posting its biggest intraday point drop in history.
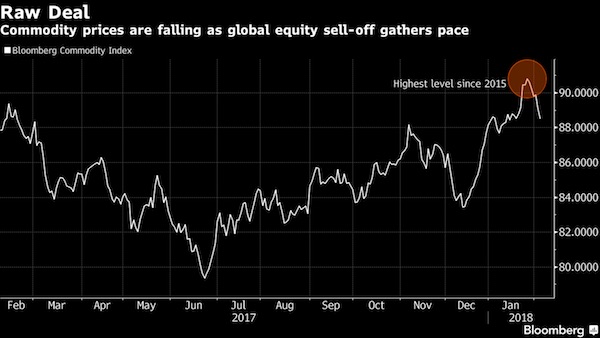
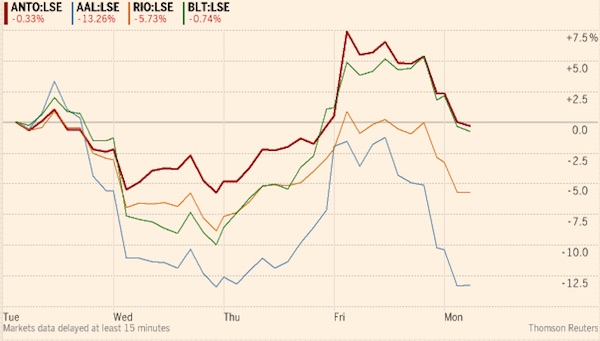
The selloff – triggered in part by an initial rise in bond yields and concerns about the pace at which the Federal Reserve will raise interest rates – is spilling into commodities, which rallied in late January to the highest level since 2015. Still, Citigroup said now’s the time for investors to add positions in metals. “Clearly there is a risk off tone in the markets that will weigh on the sector,” said Daniel Hynes at Australia & New Zealand Banking. “But there is no fundamental reason for this selloff to change our view of commodity markets.” Miners and energy companies fell as share benchmarks spiraled downward. In the U.S. on Monday, Exxon Mobil and Chevron were among the worst performers in the Dow. In Sydney, BHP Billiton, the world’s largest mining company, dropped 2.7% as Rio Tinto traded lower. Oil producer PetroChina lost as much as 7.3% in Hong Kong.

6,100 as I write this.
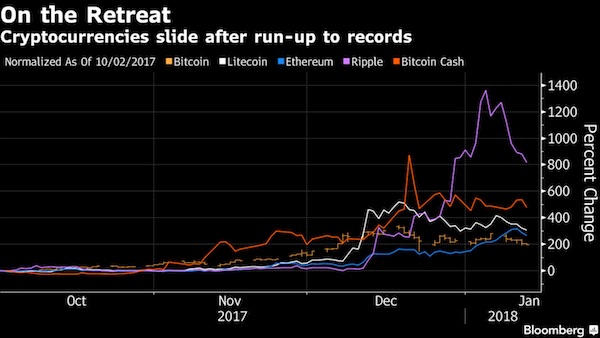
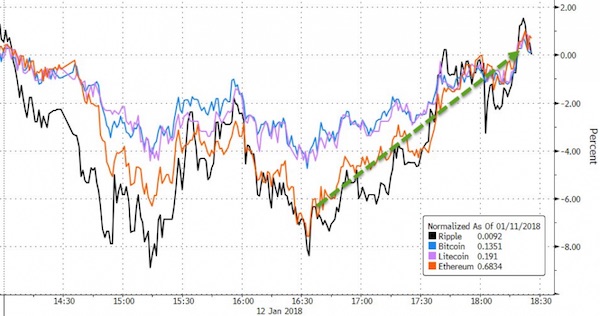
• Bitcoin Tumbles Almost 20% as Crypto Backlash Accelerates (BBG)
Bitcoin tumbled for a fifth day, dropping below $7,000 for the first time since November and leading other digital tokens lower, as a backlash by banks and government regulators against the speculative frenzy that drove cryptocurrencies to dizzying heights last year picks up steam. The biggest digital currency sank as much as 22% to $6,579, before trading at $7,054 as of 4:08 p.m. in New York. It has erased about 65% of its value from a record high $19,511 in December. Rival coins also retreated on Monday, with Ripple losing as much as 21% and Ethereum and Litecoin also weaker. “Although no fundamental change triggered this crash, the parabolic growth this market has experienced had to slow down at some point,” Lucas Nuzzi, a senior analyst at Digital Asset Research, wrote in an email. “All that it took this time was a large lot of sell orders.”
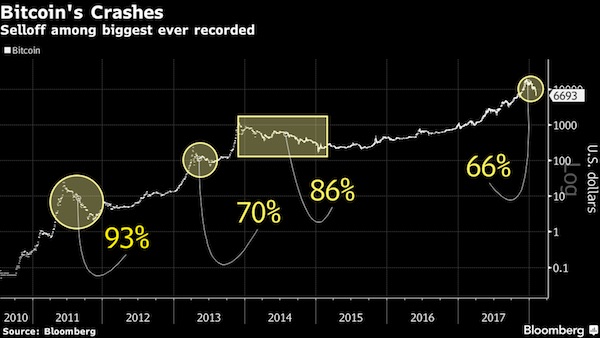
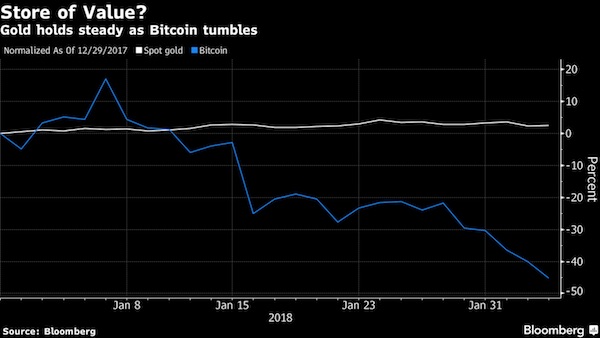
Weeks of negative news and commercial setbacks have buffeted digital tokens. Lloyds joined a growing number of big credit-card issuers have said they’re halting purchases of cryptocurrencies on their cards, including JPMorgan and Bank of America. Several cited risk aversion and a desire to protect their customers. SEC Chairman Jay Clayton said he supports efforts to bring clarity to cryptocurrency issues and that existing rules weren’t designed with such trading in mind, according to prepared remarks for a Senate Banking Committee hearing Tuesday on virtual currencies. Bitcoin’s longest run of losses since Christmas day has coincided with investors exiting risky assets across the board, with stocks retreating globally. Bitcoin so far seems to be struggling to live up to any comparison with gold as a store of value, which is an argument made by some of its supporters. Bullion edged higher as other safe havens – the yen, Swiss franc and bonds – also gained.

Stability breeds instability. Minsky.
• The Fed’s Dependence On Stability (Roberts)
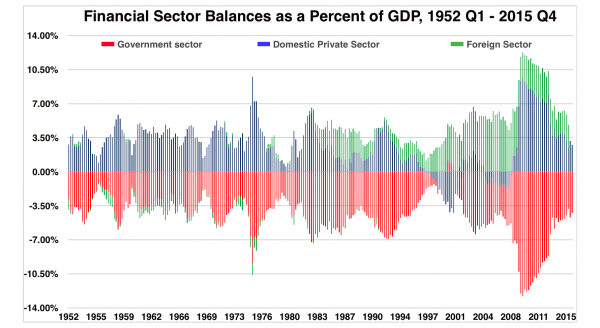
Last week, I discussed how the Federal Reserve will likely be the culprits of whatever sparks the next major financial crisis. To wit: “In the U.S., the Federal Reserve has been the catalyst behind every preceding financial event since they became ‘active,’ monetarily policy-wise, in the late 70’s. As shown in the chart below, when the Fed has lifted the short-term lending rates to a level higher than the 10-year rate, bad ‘stuff’ has historically followed.” This past week, as Ms. Yellen relinquished her control over the Federal Reserve to Jerome Powell, the Fed stood by its position they intend to hike rates 3-more times in 2018.
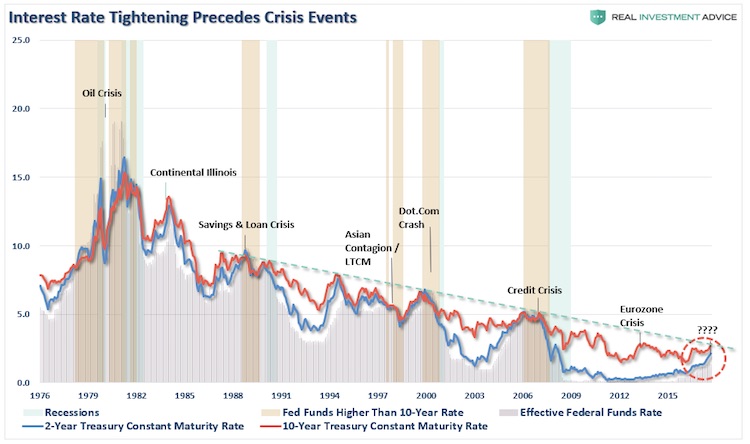
With the entirety of the financial ecosystem now more heavily levered than ever, due to the Fed’s profligate measures of suppressing interest rates and flooding the system with excessive levels of liquidity, the “instability of stability” is now the biggest risk. The “stability/instability paradox” assumes that all players are rational and such rationality implies avoidance of complete destruction. In other words, all players will act rationally and no one will push “the big red button.” The Fed is highly dependent on this assumption. After more than 9-years of the most unprecedented monetary policy program in human history, they are now trying to extricate themselves from it. The Fed is dependent on “everyone acting rationally,” particularly as they try to reduce their balance sheet. The first attempt was seen in January. Well…sort of…but not really.
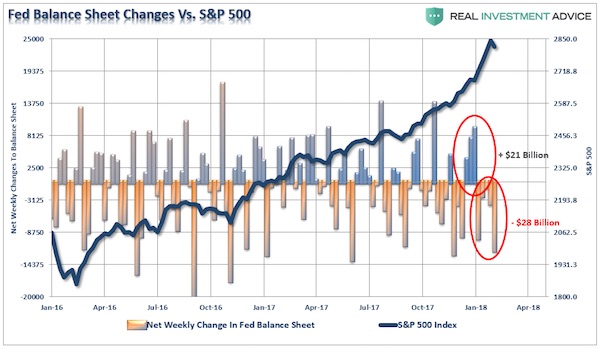
While the Fed did “reduce” their holding by $28 billion in January, it followed an increase of $21 billion in December. Which brings up several questions? Was the ramp up/run down just a test of the market’s stability? (Seems likely.) With the market throwing a “conniption fit” last week, will the Fed rethink their balance sheet reduction program? (Probably) More importantly, with the government on the verge of another “shut down” this coming week due to the expiration of the “continuing resolution” from three weeks ago, will the Fed continue its current path in the face of an event that could lead to fiscal instability? (Probably not) We will soon find out.

There will be a second Special Counsel.
The Resistance pulled out all the stops last week in its shrieking denunciation of the Nunes Memo, and the various complaints had one thing in common: a complete lack of interest in the facts of the matter, in particular the shenanigans in the upper ranks of the FBI. Give a listen, for instance, to last Thursday’s Slate’s Political Gabfest with David Plotz, John Dickerson, and Emily Bazelon, the three honey-badgers of Resistance Radio (like the fabled honey-badgers of the veldt, they don’t give a shit about any obstacles in pursuit of their quarry: Trump). They’ve even been able to one-up Nassim Taleb’s defined category of “intellectuals-yet-idiots” to intellectuals-yet-useful-idiots.
The New York Times, with its termite-mound of casuistry artists, managed to concoct a completely inside-out “story” alleging that the disclosure in the Nunes memo of official impropriety at the FBI was in itself an “obstruction of justice,” since making the FBI look bad might impede their ability to give Trump the much wished-for bum’s rush from the White House. There was already enough dishonesty in our national life before the Left side of the political transect decided to ally itself with the worst instincts of the permanent Washington bureaucracy: the faction devoted to ass-covering. The misconduct at the FBI and DOJ around the 2016 election is really quite startling.
How is it not disturbing that Associate Deputy Attorney General Bruce Ohr brokered the Steele Dossier between the Fusion GPS psy-ops company and the FBI, when Fusion GPS was employed by the Clinton campaign, and Ohr’s wife worked for Fusion GPS? How is it okay that this janky dossier was put over on a FISA court judge to get warrants to surveil US citizens in an election campaign? How was it okay for Deputy FBI Director Andrew McCabe’s wife to accept $700,000 from the Clinton family’s long-time bag-man, Terry McAuliffe, when she ran for a Virginia State Senate seat, a few months before McCabe assumed command of the Hillary email investigation? How was it not fishy that FBI Deputy Assistant Director of the Counterintelligence Division, Peter Strock, and his workplace girlfriend, FBI lawyer (for Andrew McCabe), Lisa Page appeared to plot against Trump in their many cell-phone text exchanges?

Deceit as the big killer.
• 21st Century Plague (MarkGB)
The Black Death was a medieval pandemic which swept through the ‘old world’ in the 14th Century. It arrived in Europe from Asia in the 1340s and killed an estimated 25 million people, about 50% of the population. The social and economic consequences of this were ‘permanent’: it created a labour shortage which ended the medieval institution of serfdom. In short: Increased demand for labour + reduced supply of labour + chaos = collapse of status quo. What emerged from the chaos was a rudimentary ‘free market’ in labour and goods. The age of capitalism had begun…the unforeseen consequence of a plague, borne on a creature that looked like this:
The pandemic we face in the 21st Century is a psychological phenomenon rather than a biological one, but in my view, it is equally parasitic. Its name is ‘deceit’, and our political & economic institutions are riddled with it. The majority of people I speak to know that something is badly wrong with our societies and our economies – they feel it when they pick up a newspaper, turn on the TV or engage with the internet. Some of us try to disconnect from the drama and the constant stream of claim and counterclaim, in order to try to ‘get on with normal lives’ – but we feel something is badly wrong nevertheless. Some of us gather ourselves into political parties, protest movements, and/or intellectual cliques in order to discuss how to ‘fix’ what ails us.
And every 4 or 5 years, the majority of us go out and vote for an individual or a group of people that we hope will bring change…and then…we get more of the same. We just got, for example, the 3rd president in a row who ran on a promise of peace, and then immediately went looking for war. What the majority of people have not yet realised is that the politician’s ‘promise’ is part of the deceit – it’s what keeps you coming back for more, hoping this time will be different. It never is – it’s just a new coat of paint on a crumbling wall. What the majority of people have not yet realised is that the politician’s ‘promise’ is part of the deceit – it’s what keeps you coming back for more
It matters little whether you believe an individual candidate is a ‘good’ person, or a ‘bad’ person. Once in office he or she becomes a tool for the maintenance of the status quo – evidently. Why is this? Because the system is not run for your benefit. Its primary function is the concentration of power and wealth within the system itself, to serve the vested interests of a relatively tiny group of people. These are the manifestations of the 21st-century plague – the institutions of deceit: 1) A monetary system rigged for the banks and globalised corporations. 2) A military-industrial complex that requires endless war. 3) Politicians that are controlled by 1 & 2. 4) A mainstream media that is complicit with 1 to 3.

Expect appeal after appeal.
• UK Court To Rule On Lifting Assange Arrest Warrant (AFP)
A British court is to decide Tuesday whether to lift a UK arrest warrant for Julian Assange, potentially paving the way for the WikiLeaks founder to leave the Ecuadorian embassy in London where he has spent the last five years. If the court rules in Assange’s favour, allowing him to leave the embassy in the British capital without fear of arrest, it would be the first time that he has stepped outside embassy grounds since seeking asylum there in June 2012. Assange entered the Ecuadoran embassy to dodge a European arrest warrant and extradition to Sweden over a 2010 probe in the Scandinavian country into rape and sexual assault allegations.
Sweden dropped its investigation last year, but British police are still seeking to arrest Assange for failing to surrender to a court after violating bail terms during his unsuccessful battle against extradition. Assange’s lawyer Mark Summers told a London court last week that the warrant had “lost its purpose and its function”. He said Assange had been living in conditions “akin to imprisonment” and his “psychological health” has deteriorated and was “in serious peril”. The court heard that the 46-year-old was suffering from a bad tooth, a frozen shoulder and depression. But prosecutor Aaron Watkins called Assange’s court bid “absurd”. “The proper approach is that when a discrete, standalone offence of failing to surrender occurs, it always remains open to this court to secure the arrest,” Watkins said.

You like this future? It’s all yours. Who needs people?
• Robots Will Care For 80% Of Elderly Japanese By 2020 (G.)
Japan’s elderly are being told to get used to being looked after by robots. With Japan’s ageing society facing a predicted shortfall of 370,000 caregivers by 2025, the government wants to increase community acceptance of technology that could help fill the gap in the nursing workforce. Developers have focused their efforts on producing simple robotic devices that help frail residents get out of their bed and into a wheelchair, or that can ease senior citizens into bathtubs. But the government sees a wider range of potential applications and recently revised its list of priorities to include robots that can predict when patients might need to use the toilet. Dr Hirohisa Hirukawa, director of robot innovation research at Japan’s National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, said the aims included easing the burden on nursing staff and boosting the autonomy of people still living at home.
“Robotics cannot solve all of these issues; however, robotics will be able to make a contribution to some of these difficulties,” he said. Hirukawa said lifting robotics had so far been deployed in only about 8% of nursing homes in Japan, partly because of the cost and partly because of the “the mindset by the people on the frontline of caregiving that after all it must be human beings who provide this kind of care”. He added: “On the side of those who receive care, of course initially there will be psychological resistance.” Hirukawa’s research centre has worked on a government-backed project to help 98 manufacturers test nursing-care robotic devices over the past five years, 15 of which have been developed into commercial products.

This is what Brussels and Berlin invite by ignoring the issue.
• Berlusconi Pledges To Deport 600,000 Illegal Immigrants From Italy (G.)
Silvio Berlusconi has pledged to deport 600,000 illegal immigrants from Italy should his centre-right coalition enter government after elections on 4 March, as tensions simmer over the shooting of six Africans by a far-right extremist on Saturday. The 81-year-old rightwing former prime minister said in a TV interview that immigration was a “social bomb ready to explode in Italy” and that the shooting in Macerata posed a security problem. “Immigration has become an urgent question, because after years with a leftwing government, there are 600,000 migrants who don’t have the right to stay,” said Berlusconi. “We consider it to be an absolute priority to regain control over the situation.” Berlusconi’s Forza Italia has forged an alliance with two far-right parties, the Northern League and the smaller Brothers of Italy, for the elections.
The three-time former prime minister is banned from running for office after being convicted of tax fraud, but could still end up pulling the strings of power should the coalition gain enough of a majority to govern. “When we’re in government we will invest many resources in security,” he said. “We will boost police presence and reintroduce the ‘Safe Streets’ initiative … Our soldiers will patrol the streets alongside police officers.” Berlusconi took a swipe at the EU for failing to share the burden of Italy’s migrant arrivals, saying: “Today, Italy counts for nothing in Brussels and the world. We will make it count again.” Italy is a favoured landing point on Europe’s southern coastline for people making the perilous journey across the Mediterranean, often on board unseaworthy boats, to enter the continent. However, 2017 was a turning point for Italy: the country went from large-scale arrivals in the first six months to a sharp drop-off, thanks to a controversial agreement between the EU and Libya.