
Walker Evans Saint Charles Street. Liberty Theatre, New Orleans 1935



And all of your problems are solved. It was only a dream….
• Stocks Halt Brexit Selloff as Pound Rebounds With Commodities (BBG)
The pound, European stocks and commodities were all headed for their first gains since Britain’s shock vote to leave the European Union, while Asian shares erased losses amid signs policy makers are taking steps to limit any economic fallout. Sterling and the Stoxx Europe 600 Index both rebounded after tumbling 11% in the last two trading sessions. A gauge of the greenback’s strength snapped its steepest rally since 2011. The Bloomberg Commodity Index climbed from a three-week low as oil rose to about $47 a barrel and industrial metals rose. Sovereign bond yields plumbed new lows in Australia, Japan and South Korea as futures indicated that the next move in U.S. interest rates is now likely to be a cut.

What? “Japan’s Prime Minister Shinzo Abe said he wants his finance minister and the central bank governor to watch markets more closely.” You mean they didn’t?
• Asian Stocks Erase Losses as Japan Shares Gain on Stimulus Bets (BBG)
Asian stocks erased losses and most Tokyo shares rose amid speculation policy makers will move to shore up financial markets after Britain’s vote to leave the European Union. The MSCI Asia Pacific Index was little changed as of 4 p.m. in Tokyo after being down as much as 1.2% earlier. Most Japanese shares rose after a drop in the Nikkei 225 Stock Average below 15,000 spurred buying. South Korea’s Kospi index rose 0.5%, reversing a decline of 1%. Investors are watching closely for signs that central banks and governments will help to ease the post-Brexit market turmoil.
Japan’s Prime Minister Shinzo Abe said he wants his finance minister and the central bank governor to watch markets more closely. Toshihiro Nikai, chairman of the ruling party’s general council, proposed a 20 trillion yen ($196 billion) package to Abe, the Nikkei newspaper reported. South Korea said it’s planning a fiscal stimulus package of more than 20 trillion won ($17 billion). “We are probably going to have looser policy settings than before the vote,” said Tim Schroeders at Melbourne-based Pengana Capital. “You’d have to suspect that the bias is to the downside for global growth and as a result that stimulus remains in light of increased uncertainty.”

“The bear case is the pound disappears…” “The EU as we know it will not exist,” he said. “The euro as we know it will not exist…”
• Jim Rogers On Brexit: Worse Than Any Bear Market You’ve Seen In Your Life (Y!)
The UK’s decision to leave the European Union will lead to an economic crisis more severe than what the world faced in 2008, according to legendary investor Jim Rogers, chairman of Rogers Holdings. “This is going to be worse than any bear market you’ve seen in your lifetime,” he said. “2008 was bad because of debt. The debt all over the world is much, much higher now. Stocks in the US, for instance, have been going sideways for 18 months to 24 months. That’s called a distribution by many people. When you have distribution for a year and a half, it usually leads to bad things.” Rogers – who cofounded the Quantum Fund with George Soros in the 1970s – believes the “leave” movement’s victory last week may threaten the British union.
While any negotiated deal may help assuage the market’s Brexit fears, Rogers foresees a “bad case scenario” where Scotland and Northern Ireland leave the UK and London’s clout diminishes significantly as financial institutions move towards continental Europe. “The UK already has huge international debts and it has balance of trade problems and budget problems,” he said. “The bear case is the pound disappears. England becomes Spain or Poland or Italy or something.” While he doesn’t see an immediate collapse of England’s economy, Rogers anticipates a long-term decline in the country’s prospects.
“The deterioration will continue and make stocks go down a lot,” he warned. Brexit’s win will also embolden other countries to leave the EU and separatist movements to break up a few states, Rogers predicted. That could make the world to look significantly different in just a half a decade. “The EU as we know it will not exist,” he said. “The euro as we know it will not exist.

But no mea culpa. he wants to die a revered oracle.
• Greenspan Warns A Crisis Is Imminent, Urges A Return To The Gold Standard (ZH)
On Friday afternoon, after the shocking Brexit referendum, while being interviewed by CNBC Alan Greenspan stunned his hosts when he said that things are about as bad as he has ever seen. “This is the worst period, I recall since I’ve been in public service. There’s nothing like it, including the crisis — remember October 19th, 1987, when the Dow went down by a record amount 23%? That I thought was the bottom of all potential problems. This has a corrosive effect that will not go away. I’d love to find something positive to say.” Strangely enough, he was not refering to the British exodus but to America’s own economic troubles.
Today, Greenspan was on Bloomberg Surveillance where in an extensive, 30 minutes interview he was urged to give his take on the British referendum outcome. According to Greenspan, David Cameron miscalculated and made a “terrible mistake” in holding a referendum. That decision led to a “terrible outcome in all respects,” Greenspan said. “It didn’t have to happen.” Greenspan then noted that as a result of Brexit, “we are in very early days a crisis which has got a way to go”, and point to Scotland which he said will likely have another referendum on its own, predicting the vote would be successful, and Northern Ireland would “probably” go the same way.
His remarks then centered on the Eurozone which he defined as a truly “vulnerable institution,” primarily due to Greece’s inclusion in its structure. “Get Greece out. They’re a toxic liability sitting in the middle of a very important economic zone.” Ironically, the same Eurozone has spent countless hours doing everything in its power to show just how unbreakable the union is by preserving Greece, while it took the UK just one overnight session to break away. Luckily the UK was not part of the monetary union or else it would be game over. But speaking of crises, Greenspan warned that fundamentally it is not so much an issue of immigration, or even economics, but unsustainable welfare spending, or as Greenspan puts it, “entitlements.”
“The issue is essentially that entitlements are legal issues. They have nothing to do with economics. You reach a certain age or you are ill or something of that nature and you are entitled to certain expenditures out of the budget without any reference to how it’s going to be funded. Where the productivity levels are now, we are lucky to get something even close to two% annual growth rate. That annual growth rate of 2% is not adequate to finance the existing needs. I don’t know how it’s going to resolve, but there’s going to be a crisis. This is one of the great problems of democracy. It goes back to the founding fathers. How do you handle a situation like this? And it’s very troublesome, but eventually you get things like Margaret Thatcher showing up in Britain.”

Enter Captain Fantastic.
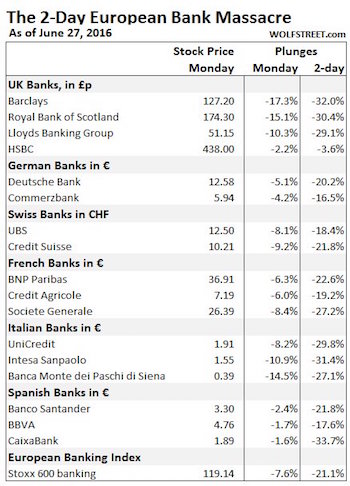
• European Banks Crash To Worst 2-Day Loss Ever As Default Risk Soars (ZH)
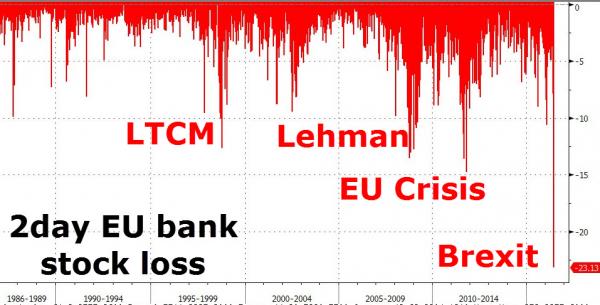
So much for George “Panic-Monger” Osborne’s calming statement this morning, European banks have collapsed this morning to close down between 20% and 30% since the Brexity vote. The last 2 days plunge in EU banks (down 23%) is the largest in history (double the size of Lehman) and pushes European bank equity market cap to its lowest (in USD terms) ever. Worst. Drop. Ever…

Giving people a vote in their lives is not Xi’s idea of fun…
• Brexit Is the Sum of China’s Fears (Balding)
In voting to leave the EU, the U.K. has confirmed many of the Chinese Communist Party’s worst fears about democracy. Now the question is whether Brexit will also impede its attempts at economic reform. At least one major target of “Leave” campaigners in the U.K. – an unaccountable bureaucracy in Brussels, enjoying the fruits of power – will certainly resonate with Chinese citizens. Despite a recent corruption crackdown, dissatisfaction with officials is simmering in many parts of China – over land grabs, unpaid wages, layoffs and more. For the Communist Party, a popular rejection of distant bureaucrats isn’t to be taken lightly. Brexit also confirms the party’s fears about the capriciousness of the people. As an editorial in the Global Times, a state-run tabloid, put it, Brexit is a “Pandora’s box,” a “lose-lose situation” and a “major setback.”
The Chinese people, it went on, “will continue to watch the consequence of Britain’s embracing of a `democratic’ referendum.” Such skepticism of the wisdom of crowds is widespread in Beijing’s halls of power – and it has real-world consequences for democracy advocates. A deeper worry for the party is instability. The political and business classes in China are extremely risk-averse. Banks lend to state-owned enterprises in the belief that the government stands behind them, students from the best schools aspire to the civil service, and changes to policy flow from on high. Party technocrats tend to see political and financial instability as intimately linked. And as Premier Li Keqiang stressed repeatedly yesterday at the World Economic Forum, Brexit has increased both.
The immediate economic consequences for China are likely to be minimal. As Bloomberg economists Tom Orlik and Fielding Chen have pointed out, only 2.6% of Chinese exports head to the U.K. But the indirect consequences could be substantial. After Britain voted out, the yuan suffered the biggest one-day drop since its devaluation last August. In the worst case, Brexit may act as a long-term drag on China’s exports, increase its spare capacity, spur capital flight, impede foreign direct investment and generally weaken the forces that have sustained its growth over the past few decades. Amid that kind of pressure, expect China’s leadership to double down on economic and financial policies intended to keep growth humming and minimize any disruption, no matter what the price.

“The FTSE 100 ended 2.6% lower [..] ..wiping off nearly $132 billion since the referendum results early on Friday..”
• Brexit To ‘Drive Tectonic Plate Shifts In European Bank Investing’ (R.)
Britain’s top share index extended the previous session’s steep losses on Monday as the country’s vote last week to leave the European Union hurled it into political and economic uncertainty, hitting banks, housebuilders and airlines hard. Some investors took refuge in firms producing gold, seen as a safe-haven asset, with Fresnillo closing up 7% after hitting a three-year high and Randgold Resources gaining 9%. The FTSE 100 ended 2.6% lower at 5,982.20 points, taking total losses to 5.6% in two sessions and wiping off nearly 100 billion pounds ($132 billion) since the referendum results early on Friday. Shares in easyJet recorded their biggest one-day percentage drop in 12 years.
The domestically-focused mid-cap index .FTMC lost nearly 7% after reaching its lowest since late 2014 following growing concerns about the country’s growth and earnings outlook after the poll outcome. “These uncertainties pose significant risks for the investment outlook,” said Larry Hatheway, chief economist and head of multi-asset portfolio solutions at GAM. “Against the backdrop of an already slowing UK economy, Brexit anxiety could precipitate a large enough reduction in consumer and business spending to tip the UK economy into recession.” British financial stocks declined the most, with the sector index ending 7.3% weaker after a seven-year low. RBS and Barclays dropped 15% and 17.3% respectively, also hit by broker downgrades and by JP Morgan’s cutting its rating on all domestic banks.
The mid-cap bank Shawbrook plummeted 30%. “The UK’s vote to leave the EU will drive tectonic plate shifts in European bank investing. We move to a slow growth/modestly recessionary scenario for UK banks,” analysts at Jefferies said in a note, downgrading RBS to “hold” and Barclays to “underperform”. Investors seemed to ignore finance minister George Osborne’s assertion on Monday that the British economy remained strong, his first public statement on the Brexit vote.

“Italian officials are studying a direct state recapitalisation of the banks, to be funded by a special bond issue.” Remember Cyprus. Italy wants to change bail-in rules, but it can’t.
• Italy Eyes €40 Billion Bank Rescue As First Brexit Domino Falls (AEP)
Italy is preparing a €40bn rescue of its financial system as bank shares collapse on the Milan bourse and the powerful after-shocks of Brexit shake European markets. An Italian government task force is watching events hour by hour, pledging all steps necessary to ensure the stability of the banks. “Italy will do everything necessary to reassure people,” said premier Matteo Renzi. “This is the moment of truth we have all been waiting for a long time. We just didn’t know it would be Brexit that set the elephant loose,” said a top Italian banker. The share price of banks crashed for a second trading day, with Intesa Sanpaolo off 12.5pc, and falls of 12pc for Banka MPS, 10.4pc for Mediobana, and 8pc for Unicredit. These lenders have lost a third of their value since Britain’s referendum.
“When Britain sneezes, Italy catches a cold. It is the weakest link in the European chain,” said Lorenzo Codogno, former director-general of the Italian treasury and now at LC Macro Advisors. The country is the first serious casualty of Brexit contagion and a reminder that the economic destinies of Britain and the rest of Europe are intimately entwined. Morgan Stanley warned in a new report that eurozone GDP would contract by almost as much as British GDP in a “high stress scenario”. Italian officials are studying a direct state recapitalisation of the banks, to be funded by a special bond issue. They also want a moratorium of so-called ‘bail-in’ rules and bondholder write-downs, but these steps are impossible under EU laws.
Mr Renzi raised the subject urgently at a meeting with Merkel and Hollande at a Brexit summit in Berlin on Monday. “There has to be a suspension of the bail-in rules and state aid rules at the highest political level in the EU, otherwise I don’t see how this can work,” said Mr Codogno. Unlike the eurozone debt crisis in 2011-2012, there is no serious trouble yet in the sovereign debt markets. The ECB is effectively capping yields under quantitative easing. The stress gauge in this episode is the health of the private banks. The Euro STOXX index of bank stocks has collapsed by half since last July, and is now probing depths seen in the white heat of the debt crisis. British bank shares have also plummeted since Brexit but this has no systemic implication so far.
It chiefly reflects recession fears, and potential loss of access to the EU market for business. Italy’s banks are the Achilles Heel of the eurozone financial system. Non-performing loans have ratcheted up to 18pc of total balance sheets as a result the country’s slide into depression after the Lehman crisis. The new bail-in reform this year has brought matters to a head, catching EU authorities off guard. It was intended to protect taxpayers by ensuring that creditors suffer major losses first if a bank gets into trouble, but was badly designed and has led to a flight from bank shares. The Bank of Italy has called for a complete overhaul of the bail-in rules. It is now almost impossible for Italian banks to raise capital.

Lots of bitter infighting will ensue. Sort of a cross between Coronation Street and Absolutely Fabulous.
• Preparing For Brexit, Britain May See New PM By Early September (R.)
Britain could have a new prime minister by early September, the ruling Conservative Party said on Monday, after David Cameron started laying the groundwork for his successor to trigger the country’s exit from the EU. The government is under pressure to fill a vacuum left when Cameron announced he would resign by October after Britain ignored his advice and voted to leave the 28-member bloc in last week’s referendum. Triggering a leadership battle that could draw in some of his closest advisers, Cameron urged ministers to work together in the meantime. But he also formed a separate unit, staffed by public servants, to help advise Britain on its departure and its options for a future outside the EU. “Although leaving the EU was not the path I recommended, I am the first to praise our incredible strengths as a country,” Cameron told parliament.
“As we proceed with implementing this decision and facing the challenges that it will undoubtedly bring, I believe we should hold fast to a vision of Britain that wants to be respected abroad, tolerant at home, engaged in the world.” Asked about the possibility of a second EU referendum, Cameron said the result of Thursday’s vote must be accepted. Graham Brady, chair of the “1922 Committee” of Conservative lawmakers, which sets the party’s ground rules in parliament, said the group had recommended that the leadership contest should begin next week and conclude no later than Sept. 2. That recommendation will almost certainly be passed. “Both the Conservatives and the country more generally really want certainty. We would like a resolution and we think it would be a good thing to conclude this process as soon as we practicably can,” Brady told Sky News.

There are so few AAAs left that it doesn’t matter much anymore. And to label Britain AAA is of course silly to begin with.
• S&P Strips UK of Last Top-Notch Credit Rating After Brexit (R.)
Ratings agency Standard & Poor’s stripped Britain of its last remaining top-notch credit rating on Monday, slashing it by two notches from AAA and warning more downgrades could follow after Britons voted to leave the European Union last week. “In our opinion, this outcome is a seminal event, and will lead to a less predictable, stable, and effective policy framework in the UK,” S&P said in a statement, adding it saw a higher risk of Scotland breaking away from the United Kingdom. S&P had warned that Britain’s coveted top-notch credit rating was no longer tenable after last Thursday’s referendum result.
The loss of the last remaining “AAA” rating represents a fresh blow to Britain’s economic standing after the referendum, with sterling tanking to a 31-year low against the dollar and the country’s stock markets plunging. Rival ratings agencies Fitch and Moody’s stripped Britain of their AAA ratings long before the referendum campaign began. They too have warned of further cuts to their gradings of Britain’s creditworthiness. Protecting Britain’s credit rating was a top priority of Conservative finance minister George Osborne when he came to power in 2010.

The kind of thing that can get very expensive very fast.
• UK Credit Default Swap Rates Spike After Wave Of Rating Downgrades (CNBC)
In case you’re wondering how Brexit impacts the U.K.’s creditworthiness, the derivatives market may offer different clues than the bond market. The cost of buying protection against a default on British sovereign debt using credit default swaps rose to a three-year high on Tuesday, after rating agencies rushed to slash the U.K.’s debt rating following last week’s vote to leave the EU. It now costs $48,500 a year to protect $10 million of U.K. sovereign debt for five years, compared with levels near $32,000 before the June 23 referendum. This came despite a sharp fall in yields on U.K. government debt, or gilts. On its own, the absolute cost of insurance remains low, especially when compared with euro zone countries such as Italy and Spain.
The sharp pace of the increase, however, underscored how uncertainty over the U.K.’s position in Europe had undermined its credit-worthiness. Sterling has already plunged to more-than-30-year lows and stock markets have tumbled. On Monday Standard & Poor’s downgraded the U.K.’s debt rating by two notches, from AAA to AA, citing last week’s referendum that approved a British exit from the EU, depriving the U.K. of its last triple A rating. Fitch Ratings, meanwhile, moved its rating from AA+ to AA. “In our opinion, this outcome is a seminal event, and will lead to a less predictable, stable, and effective policy framework in the U.K. We have reassessed our view of the U.K.’s institutional assessment and now no longer consider it a strength in our assessment of the rating,” S&P said in a news release.

“It’s become perilously fashionable all over the Western world to reach for non-democratic solutions whenever society drifts in a direction people don’t like…”
• The Reaction to Brexit Is the Reason Brexit Happened (Matt Taibbi)
Were I British, I’d probably have voted to Remain. But it’s not hard to understand being pissed off at being subject to unaccountable bureaucrats in Brussels. Nor is it hard to imagine the post-Brexit backlash confirming every suspicion you might have about the people who run the EU. Imagine having pundits and professors suggest you should have your voting rights curtailed because you voted Leave. Now imagine these same people are calling voters like you “children,” and castigating you for being insufficiently appreciative of, say, the joys of submitting to a European Supreme Court that claims primacy over the Magna Carta and the Bill of Rights. The overall message in every case is the same: Let us handle things. But whatever, let’s assume that the Brexit voters, like Trump voters, are wrong, ignorant, dangerous and unjustified.
Even stipulating to that, the reaction to both Brexit and Trump reveals a problem potentially more serious than either Brexit or the Trump campaign. It’s become perilously fashionable all over the Western world to reach for non-democratic solutions whenever society drifts in a direction people don’t like. Here in America the problem is snowballing on both the right and the left. Whether it’s Andrew Sullivan calling for Republican insiders to rig the nomination process to derail Trump’s candidacy, or Democratic Party lifers like Peter Orszag arguing that Republican intransigence in Congress means we should turn more power over to “depoliticized commissions,” the instinct to act by diktat surfaces quite a lot these days. “Too much democracy” used to be an argument we reserved for foreign peoples who tried to do things like vote to demand control over their own oil supplies.

A dead end street after all.
• Some Bad And Some Worse News For Stock Buybacks (ZH)
For those 17-year-old hedge fund managers used to BTFD on hopes corporate buybacks will “have their back” and provide the bid on which momentum-chasing HFT algos will piggyback, we have some bad news and some worse news. The bad news is that we are entering yet another quiet period for buybacks. This means that for the next 45 days, the biggest – and supposedly only – buyer of stocks will be mostly out of the market, and bank buyback desks will not be able to provide much needed support during distressed (read: more sellers than buyers) times. The worse news is that even without the buyback blackout period, following months of surging stock repurchasing activity by corporate treasurers… buybacks have now ground to a virtual halt.
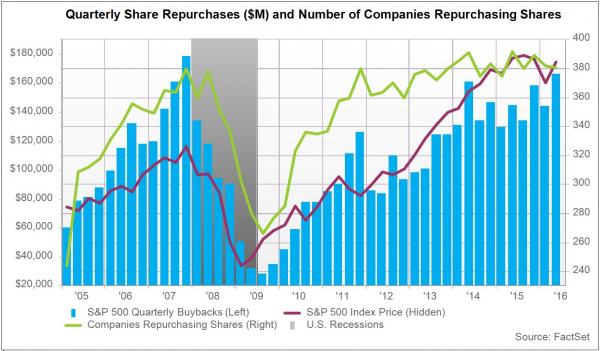
According to TrimTabs, stock buyback announcements by U.S. companies have fallen sharply, sending a longer-term negative signal for U.S. equities. “Corporate America announced $2.8 trillion in stock buybacks in the past five years, and these buybacks have provided a key source of fuel for the bull market,” said David Santschi, chief executive officer of TrimTabs. “Corporate actions this year suggest this support is going to diminish.” In a research note, TrimTabs reported that U.S. companies have announced a mere $11.8 billion in stock buybacks in June through Friday, June 24. This month’s pace is the lowest this year. Only four companies have announced plans to repurchase at least $1 billion this month.
“Even if some of the too-big-to-fails roll out buybacks after the release of the second part of the Fed’s stress test results, this month’s volume is likely to be among the lowest in the past three years,” noted Santschi. TrimTabs also explained that stock buyback announcements by U.S. companies have totaled $291.7 billion this year, which is 32% lower than the $432.0 billion in the same period last year. “The sharp decline in buyback announcements suggests corporate leaders are becoming more cautious, and it doesn’t bode well for the U.S. stock market,” said Santschi.









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle June 28 2016