
Pablo Picasso The Dream 1932

Xi has all the state media, and all Trump has is Twitter. Isn’t it fun? Then again, for Xi to let the Global Times come with this sort of childish language is below him.
• Chinese Media Say ‘Big Sticks’ Await Trump If He Seeks Trade War (BBG)
Chinese state media warned U.S. President-elect Donald Trump that he’ll be met with “big sticks” if he tries to ignite a trade war or further strain ties. “There are flowers around the gate of China’s Ministry of Commerce, but there are also big sticks hidden inside the door – they both await Americans,” the Communist Party’s Global Times newspaper wrote in an editorial Thursday in response to Trump’s plans to nominate lawyer Robert Lighthizer, who has criticized Beijing’s trade practices, as U.S. trade representative.
The latest salvo from state-run outlets followed others last month aimed at Peter Navarro, a University of California at Irvine economics professor and critic of China’s trade practices whom Trump last month named to head a newly formed White House National Trade Council. Those picks plus billionaire Wilbur Ross, the nominee for commerce secretary, will form an “iron curtain” of protectionism in Trump’s economic and trade team, the paper wrote. The three share Trump’s strong anti-globalization beliefs and seem unlikely to keep building the current trade order, it said, adding that they will be more interested in disrupting the world trade order.

Don’t think they saw this coming. And that’s perhaps not so intelligent. The CIA leaked a lot of wild anti-Trump stuff during the election campaign, and now claims he MUST trust them. But if he leaves the same people in place, when will they turn on him again?
• Donald Trump Plans Revamp of Top US Spy Agency and CIA (WSJ)
President-elect Donald Trump, a harsh critic of U.S. intelligence agencies, is working with top advisers on a plan that would restructure and pare back the nation’s top spy agency, people familiar with the planning said, prompted by a belief that the Office of the Director of National Intelligence has become bloated and politicized. The planning comes as Mr. Trump has leveled a series of social media attacks in recent months and the past few days against U.S. intelligence agencies, dismissing and mocking their assessment that the Russian government hacked emails of Democratic groups and individuals and then leaked them last year to WikiLeaks and others in an effort to help Mr. Trump win the White House.
One of the people familiar with Mr. Trump’s planning said advisers also are working on a plan to restructure the CIA, cutting back on staffing at its Virginia headquarters and pushing more people out into field posts around the world. The CIA declined to comment on the plan. “The view from the Trump team is the intelligence world [is] becoming completely politicized,” said the individual, who is close to the Trump transition operation. “They all need to be slimmed down. The focus will be on restructuring the agencies and how they interact.”
In one of his latest Twitter posts on Wednesday, Mr. Trump referenced an interview that WikiLeaks editor in chief Julian Assange gave to Fox News in which he denied Russia had been his source for the thousands of emails stolen from Democrats and Hillary Clinton advisers, including campaign manager John Podesta, that Mr. Assange published. Mr. Trump tweeted: “Julian Assange said ‘a 14 year old could have hacked Podesta’—why was DNC so careless? Also said Russians did not give him the info!”

This will dominate the news going forward. Main question: what crazy stories will the WaPo come up with to discredit the nominees? Should be interesting. Meanwhile: YOU LOST, Schumer. Big time. Stop digging.
• Schumer Calls Eight Trump Cabinet Picks ‘Troublesome’ (BBG)
Senate Democratic leader Chuck Schumer said his party views eight of Donald Trump’s Cabinet choices as being “the most troublesome” and wants at least two days of hearings for each of them. “We have asked for fair hearings on all of those nominees,” Schumer of New York told reporters Wednesday in Washington. “There are a lot of questions about these nominees.” Confirmation hearings begin next week for a number of the president-elect’s Cabinet picks, and several already overlap on a single day, Jan. 11. Majority Leader Mitch McConnell said minutes earlier that he hopes the Senate would be ready to confirm some of the nominees shortly after Trump is inaugurated on Jan. 20, just as it did when President Barack Obama first took office.
Under current Senate rules, Democrats can delay Senate confirmation of nominees but can’t block them on their own. Schumer’s office said the eight nominees targeted by Democrats for extra scrutiny are Rex Tillerson for secretary of State, Betsy DeVos for Education, Steven Mnuchin for Treasury, Scott Pruitt for the Environmental Protection Agency, Mick Mulvaney for budget director, Tom Price for Health and Human Services, Andy Puzder for Labor and Wilbur Ross for Commerce. Schumer said he wants their full paperwork before hearings are scheduled, adding that only a few have turned it in while most haven’t. Schumer said he also wants their tax returns, particularly because some are billionaires and given the potential for conflicts of interest.
The hearing for DeVos is scheduled for Jan. 11, “and we don’t have any information on her, and she in addition has a $5 million fine outstanding that she’s refused to pay,” Schumer said. Democrats have called on a political action committee led by DeVos to pay a $5.2 million fine imposed by Ohio officials over campaign finance violations in 2008. “There are so many issues about so many of them that to rush them through would be a disservice to the American people,” the Democratic leader said. While many of Obama’s nominees were confirmed quickly, his team had its paperwork in early, Schumer said.

Our God is the car.
• Ford’s Truck Trumps Mexico and Tesla (BBG)
On its first day back from the holidays, America’s auto industry began with a Mexican standoff and ended with Tesla just being off. Ford announced early on Tuesday it was scrapping plans to build a new plant in Mexico, apparently under pressure from President-elect Donald Trump. The PEOTUS then turned his signature industrial-policy-by-tweet on General Motors, threatening them over shipping Mexican-made Chevy Cruze cars back home .Meanwhile, after the market closed on Tuesday, Tesla Motors Inc. reported it missed its (reduced) guidance for vehicle deliveries in 2016. The stock fell in after-hours trading, as some were clearly caught by surprise – a reaction that, let’s face it, is itself a bit surprising at this point. In any case, a timely tour of the Gigafactory scheduled for Wednesday will no doubt snap the market’s attention back away from those pesky number thingies.
What links these stories is Ford’s other announcement on Tuesday morning, which got a bit lost in the shuffle; namely, its plans to electrify some of its marquee models – including the F-150 pickup truck.Rather than a battery-only version or even a plug-in hybrid model, Ford is committing merely to a basic hybrid version of the F-150 by 2020 – more Priusizing than Teslarizing it. So we aren’t about to see Ford’s trucks vanish from gasoline stations anytime soon. But this is still a big deal. The F-Series is America’s biggest-selling vehicle and represents one of every three full-size pickups sold. Also, pickups are archetypal gas guzzlers, and gas guzzlers are doing really well right now because of cheap gasoline. And even as Trump lobs Twitter-bombs at the car-makers’ foreign factories, his administration also looks likely to ease up on fuel-efficiency standards.

So What’s The Big Idea, Guardian? How can you have your own Jennifer Rankin in Brussels, Thomas Kirchner and Alexander Mühlauer of Suddeutsche Zeitung and Cécile Ducourtieux of Le Monde, all contribute to a long article, and still not touch on a single one prime issue with the EU? How do you do it?
• So What’s The Big Idea, European Union? (G.)
A few weeks ago, a significant anniversary in Maastricht slipped by almost unnoticed: 25 years ago, the historic treaty that ushered in the euro was drafted. But there was no fanfare, no commemoration in the European parliament, no mention at all by the commission. There was just a rather lacklustre speech by the EU president, Jean-Claude Juncker, in which he lamented that people were not sufficiently proud of what had been achieved on 9 December 1991. This air of resignation perfectly epitomises an EU in retreat. Battered, bothered and bewildered on all sides by a succession of crises – Brexit, the euro, refugees – the union is short of ideas, perhaps shorter than it has ever been. In his state of the union speech last autumn, the very best that Juncker could come up with was free Wi-Fi for every EU town and village by 2020, though even this sounded more like an aspiration than a concrete policy.

Oh, wait, that hollow ‘article’ on the EU was just a lead in to this Guardian smear piece in the honored tradition of the WaPo. Up to and including “Russian interference in Italian elections”.
• Italy’s 5 Star Movement Part Of Growing Club Of Putin Sympathisers In West (G.)
Ten years ago, in the wake of the murder of the leading Russian journalist Anna Politkovskaya, a popular comedian-turned-blogger in Italy named Beppe Grillo urged tens of thousands of his readers to go out and buy Putin’s Russia, her searing exposé of corruption under the leadership of Vladimir Putin. “Russia is a democracy based on the export of gas and oil. If they didn’t export that, they would go back to being the good old dictatorship of once upon a time,” Grillo wrote in a mournful 2006 post about the journalist’s murder. But today, Grillo’s position on Russia has radically changed. He is now part of a growing club of Kremlin sympathisers in the west – an important shift given that the comedian has become one of the most powerful political leaders in Italy and his Five Star Movement (M5S), the anti-establishment party he created in 2009, is a top contender to win the next Italian election.
[..] As the M5S’s rhetoric has become pro-Russian, it is simultaneously becoming more critical of the EU, including a vow to hold a referendum on the euro. Such a vote would be likely to have a destabilising effect on European unity, even if in practice it would be difficult to execute a departure from the single currency. Grillo has also called for a “review” of the EU’s open borders under the Schengen agreement, in response to the shooting in Milan of Anis Amri, the suspected terrorist behind last month’s attack on a Berlin Christmas market.
[..] Foreign diplomats in Rome said it was easy to overestimate the M5S’s chances of winning the next Italian election and that expected changes to Italy’s electoral rules would make an M5S victory difficult. That calculation is based on the fact that the M5S has always opposed forging governing alliances with other parties, which has made it impossible so far for the party to achieve a majority coalition in parliament. But a handful of diplomats have also suggested that the ruling Democratic party, which is still led by former prime minister Matteo Renzi, may not be fully alert to the potential threat of Russian interference in Italian elections, and is not as concerned about the issue as it should be.

This is Italy, so what does the other side say? Fascism. To propose a public jury on what news is false is fascism. As Italy is no. 77 in the World Press Freedom Index. This will get very ugly.
• Beppe Grillo Accuses Journalists Of ‘Manufacturing False News’ (DM)
The leader of Italy’s populist Five Star movement has caused a stir by accusing the country’s journalists of ‘manufacturing false news’. Comic Beppe Grillo, founder of the anti-euro movement, lashed out at print and TV journalists, accusing them of fabricating news to keep his party, the Five Stars, down. ‘Newspapers and television news programmes are the biggest manufacturers of false news in the country, with the aim of ensuring those who have power keep it,’ he said on his blog on Tuesday. He called for ‘a popular jury to determine the veracity of the news published,’ and said in cases of fake news ‘the editor must, head bowed, make a public apology and publish the correct version at the start of the programme or on the paper’s front page’.
Grillo said members of the general public ‘picked at random’ would be shown newspaper articles and programmes and asked ‘to determine their accuracy.’ The blog was accompanied by a montage of the banners and logos of Italy’s main newspapers and television news programmes. The media world was enraged by comments, as were politicians from Italy’s traditional parties. The news director of the private TG La7 channel, Enrico Mentana, said he would sue the comedian, while journalists’ union FNSI slammed the ‘lynching of all journalists’. The opposition Five Stars was running neck-and-neck with the ruling centre-left Democratic Party (PD) before Matteo Renzi’s downfall last month and Grillo is campaigning hard for the next general election, which could be held in coming months.
What Grillo is proposing ‘is called Fascism, and those who play it down are accomplices,’ PD senator Stefano Esposito said. The centre-right Forza Italia (FI) party, founded by ex-prime minister Silvio Berlusconi, said Grillo wanted a ‘minculpop 2.0’, a reference to the propaganda and censorship ministry under dictator Benito Mussolini. Grillo has had a difficult relationship with the media since launching the Five Stars (M5S) in 2009, banning members from appearing on talk shows and giving international media priority over their Italian counterparts at his rallies. His claim that journalists were to blame for the country’s poor standing on the World Press Freedom Index – where it ranks 77th – was dismissed by the editor in chief of the Repubblica daily.

The Crimeans voted in huge numbers to join -stay with- Russia, but you can’t say that. Not even if it’s true and you live 2000 miles away. I doubt Le Pen was planning any trips to Kyiv anytime soon to begin with, but so who’s next? She can’t go to Poland anymore either soon? But still get elected president of France? Bring it on.
• Ukraine Moves To Blacklist Le Pen Over Crimea Comments (R.)
Ukraine indicated on Wednesday it would bar French presidential candidate Marine Le Pen from entering the country after comments she made that appeared to legitimize Russia’s annexation of Crimea in 2014. Le Pen’s office dismissed the threat, saying she had no intention of visiting Ukraine. Kiev is nervous about the shifting political landscape in 2017. U.S. President-elect Donald Trump has adopted a friendlier tone toward Russia while another French presidential candidate, Francois Fillon, favours lifting sanctions against Moscow. Relations between Ukraine and Russia soured after Russia’s annexation of Crimea and the subsequent outbreak of pro-Russian separatist fighting in eastern Ukraine that has killed around 10,000 people, despite a ceasefire being notionally in place.
Alluding to Le Pen, the Ukrainian foreign ministry said in a statement: “Making statements that repeat Kremlin propaganda, the French politician shows disrespect for the sovereignty and territorial integrity of Ukraine and completely ignores the fundamental principles of international law. “…Such statements and actions in violation of the Ukrainian legislation will necessarily have consequences, as it was in the case of certain French politicians, who are denied entry to Ukraine,” it said. The far right leader was quoted by French television as saying Russia’s annexation of Crimea was not illegal because the Crimean people had chosen to join Russia in a referendum, a position Kiev vehemently disputes. The referendum was also declared illegal by the United Nations General Assembly.

What keeps Britain together. Credit and whining. And fog. Boy, what a sorrowful place it’s becoming.
• UK Credit Binge Approaching Levels Not Seen Since 2008 Crash (G.)
A credit boom that is close to levels not seen since the 2008 financial crash should set alarm bells ringing in Theresa May’s government, debt charities have warned. The latest figures from the Bank of England show unsecured consumer credit, which includes credit cards, car loans and second mortgages, grew by 10.8% in the year to November to £192.2bn, picking up pace on the previous month to grow at its fastest rate in more than 11 years. In September 2008, the month that Lehman Brothers collapsed and the banking crash triggered a worldwide recession, the level of UK consumer credit debt hit a peak of £208bn. Credit card debts, which accounted for £66.7bn of the total, hit a record high last month as Britons used the plastic to fund shopping as never before in the run-up to Christmas.
The debt charity StepChange said the rise in debt levels would leave thousands of families vulnerable to higher levels of inflation and changes in income from wage cuts, divorce or redundancy. Its head of policy, Peter Tutton, said: “Levels of outstanding borrowing are approaching the 2008 peak, and the growth rate of net lending is at its highest since 2005. Alarm bells should be ringing. “Previous experience shows how such increases in the levels of borrowing can leave households over-indebted and vulnerable to sudden changes in circumstances and drops in income that can pitch them into hardship. “Lenders, regulators and the government need to ensure that the mistakes made in the lead-up to the financial crisis are not repeated and that there are better policies in place to protect those who fall into financial difficulty.”

All you need, as if it wasn’t obvious: “..the link between the yuan and the dollar remains as tight as ever. In November 2016, 98% of turnover in China’s foreign-exchange market took place between those two currencies.”
• China Can’t Quit the Dollar (Balding)
China’s leaders are hardly disguising their fears about money leaving the country. They’ve just imposed new disclosure rules limiting how Chinese – who are allowed to convert up to $50,000 worth of yuan into foreign currency each year – can spend that money overseas. Simultaneously, they’re striving to tamp down worries about the tumbling yuan, which has fallen to an eight-year low against the U.S. dollar. At the end of December, the government added 11 currencies to the basket against which it now values the yuan. While the Chinese currency fell 6.5% against the dollar in 2016, its value measured against the broader basket has remained largely stable since July. The idea, at least in part, is to persuade ordinary Chinese that their nest eggs are safe in renminbi. Unfortunately, this latest effort isn’t likely to work any better than earlier ones.
The yuan remains inextricably bound to the U.S. dollar – and everyone knows it. The People’s Bank of China created the exchange-rate basket roughly a year ago. The goal was twofold – to shift attention away from the yuan’s precipitous decline against the dollar and to reduce China’s dependence on the U.S. currency. The latter was widely seen as humiliating – an affront to a rising superpower and the world’s second-largest economy. That resentment helped drive China’s effort – since stalled – to internationalize its currency. Yet any cursory review makes clear that the link between the yuan and the dollar remains as tight as ever. In November 2016, 98% of turnover in China’s foreign-exchange market took place between those two currencies. Flows of capital into and out of China show an only slightly less lopsided pattern.
Between them, the U.S. and Hong Kong dollars (the latter is hard-pegged to the U.S. currency) account for 91% of China’s non-yuan international bank transactions. The smaller currencies that make up nearly half of the basket comprise only 1.7% of international bank payments and receipts. Even the BIS estimates that 80% of China’s local loans in foreign currency are denominated in dollars. That’s the number that really matters: If the yuan continues to fall against the dollar, companies are going to have a harder time paying back those loans regardless of what the renminbi is or isn’t worth against the government’s official basket. All this is clear to ordinary investors. During my nearly eight years in China, I’ve never heard any Chinese citizen worry about the value of the yuan against the Emirati dirham.
So as long as the yuan continues to depreciate in dollar terms, Chinese are going to look for ways to get their money out of the country, despite any barriers the government might throw in their way. China’s options for preventing further outflows are limited. The PBOC could continue to deplete the country’s $3 trillion in foreign exchange reserves in an effort to prop up the yuan. That’s a risky game, though, as it reduces the stockpiles of hard currency needed to repay foreign-denominated debt and provide liquidity for international trade. As others have argued, reserves should be deployed strategically, not squandered defending bad policy.

I see helicopter money. Digital basic income will come too late. At the every least half the people don’t even have plastic. And Modi can’t afford to wait for that.
• India’s Cash Woes Are Just Beginning (BBG)
“Give me 50 days, friends,” Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi asked citizens after he canceled 86% of the country’s currency notes. After Dec. 30, if Indians saw his decision as flawed, he promised to “suffer any punishment.” But, he said confidently, if they could bear 50 days of disruption, they would have the “India of their dreams.” It is now January. While Modi’s deadline has passed, the pain hasn’t. Indeed, it may just be beginning: Measured by the purchasing managers’ index, or PMI, Indian manufacturing actually began to contract last month for the first time in all of 2016. This can’t be blamed on sluggish global demand; the equivalent measure from China suggested that manufacturing there is expanding quicker than expected. Indian companies are suffering from supply-chain disruptions and customers with no cash in their wallets.
True, in some ways things aren’t as bad, at least in metropolitan India, as they were a few weeks ago. The lines at ATMs are shorter and the government even felt comfortable enough to raise the limits for ATM withdrawals from 2,500 rupees a pop to 4,500 rupees (from $37 to $66). But overall cash limits haven’t been eased; most Indians can still only withdraw 24,000 of their own hard-earned rupees – a little over $350 – a week, or 50,000 rupees if one has a business account. That’s simply not enough cash to keep supply chains going. Lines at ATMs thus aren’t the most useful indicator. Even if more cash is getting into the economy, the question is whether Indians are still artificially constrained in how much cash they can access. If so, things haven’t returned to “normal.” And the longer there’s a cash constraint, the larger the ripple effect on the economy.
Here’s a thought experiment, based on how informal, cash-based economies work. For the first or second month that you’re short of cash, your creditors and your debtors, the people you buy from and the people you sell to, are all short of cash as well. Plus, everyone knows the cash crunch isn’t your fault; it doesn’t reveal any adverse information about how healthy your business is or isn’t. So you extend and receive credit relatively easily. Things can run on such relationships for awhile in the informal economy. But when the outside world – the formal economy – intrudes, the system breaks down. When it comes time to pay your electricity bill, or a loan installment to the banks, you’re forced to call in your debts. You may not face enough formal demands in the first month or two to pose a problem. But as time passes, they add up.

Way ahead of you! I wrote this in April 2015: Russia’s Central Bank Governor Is Way Smarter Than Ours.
• Head of Russian Central Bank Named European Banker of the Year (RT)
Elvira Nabiullina, the head of Russia’s central bank, has been named the best Central Bank Governor in Europe in 2016 by the international financial magazine, The Banker. The influential publication praised her for having “helped steer the country through the difficulties,” with Russia “set to return to economic growth in 2017.” “Having started 2016 with consumer price inflation of 12.9% – highs not seen since 2008 – Ms Nabiullina highlighted the need to lower inflation to improve economic growth in Russia,” the outlet writes in an article dedicated to the award. Established in 1926, The Banker is considered one of the leading international finance magazines, read in almost 180 countries.
“Ms Nabiullina’s efforts saw the rate drop below 6% by the end of 2016,” the magazine writes. This, as inflation in Russia “had never fallen under 6,1%”, according to the publication, citing figures by the International Monetary Fund going back to 1992. Nabiullina said she viewed the past year as a kind of turning point with regard to inflation. “Importantly, in 2016 there was a turning point in the sentiment of the population and professionals regarding inflation expectations,” she is quoted as saying by the outlet. “At the beginning of 2016, inflation expectations of market participants were well above our target, but now they have reduced to close to our [end-2017] 4% inflation target, at between 4.5% and 4.7%.”
In December last year, the chief of the IMF, Christine Lagarde lauded Nabiullina for doing “a fantastic job” while tackling the financial problems in Russia, and inflation in particular. Nabiullina served as economic adviser to Russian President Vladimir Putin between 2012 and 2013, when she was appointed to head Russia’s Central Bank. She was Minister of Economic Development and Trade for 5 years from September 2007 to May 2012. Forbes rates Nabiullina 56th among the world’s 100 most powerful women. In 2015, Nabiullina was named central bank governor of the year by Euromoney magazine.


Even on vacation he still finds a way to get his face in the media.
• Steve Keen: Rebel Economist With A Cause (AFR)
Keen’s views and policy prescriptions remain firmly and proudly unconventional – unworkable even. But as somebody who saw the GFC coming when most did not, and as a long-time disciple of the now in-vogue Austrian economist Hyman Minsky, it may be that Keen’s economic views are finally entering mainstream thought. In a sign of the times, none other than the new chief economist of the World Bank, Paul Romer, has admitted that “for more than three decades, macroeconomic theory has gone backwards”. In a piece titled The trouble with macroeconomics, Romer in September wrote that “theorists dismiss mere facts by feigning an obtuse ignorance about such simple assertions as ‘tight monetary policy can cause a recession’.”
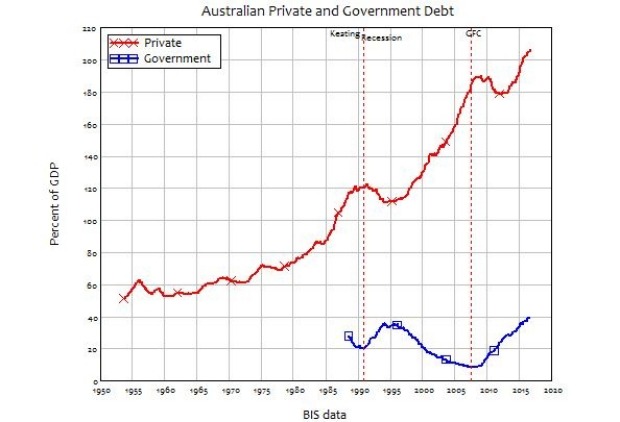
Australian private and government debt as a percentage of GDP. Steve Keen
And there is a strong need for fresh remedies. There is more debt in the world now than before the GFC – a crisis precipitated by excess borrowing. Low and zero interest rates and unconventional monetary policies such as QE have pumped up asset prices but done little to spark productivity gains or business investment in advanced economies. Private debt in Australia is now equivalent to around 210% of GDP, from 180% in 2007. Australian households are more indebted than ever, the RBA says. Keen is perhaps most critical of central bankers’ unwillingness to incorporate the link between credit growth and financial stability into their decision making. “Conventional economic thinking completely ignores where money comes from,” Keen says. “All this theory is effectively based on the idea that money is like nuts that chipmunks drop from trees and you can run out of it and if you don’t have enough of it you are going to starve over winter, and it’s a completely naive view of a monetary economy.”
While he acknowledges that RBA governor Philip Lowe has signalled a greater emphasis on “financial stability”, household indebtedness still continues to climb. “The Reserve Bank were so backward in their thinking. Their argument was, ‘oh well, the level of debt doesn’t matter because the households that have the debt are wealthy and they can continue servicing it’. But the real problem is demand for the economy comes out of turnover of the existing money plus credit. “Now, if you are relying on credit growth being equivalent to 15% of GDP, which is where it was in Australia just over six months ago, you’ve got to continue borrowing that 15% of GDP every year to maintain that trajectory. “If you simply stabilise, then, bang!, 15% of demand disappears. And that’s what we face and what I think will happen [in 2017].”









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle January 5 2017