
NPC Daredevil John “Jammie” Reynolds, Washington DC 1917

Why does it seem so normal to use the word ‘magic’ in this context? When did that start?
• ECB’s Mario Draghi Has Run Out Of Magic As Deflation Closes In (AEP)
Large parts of the eurozone are slipping deeper into a deflationary trap despite negative interest rates and €1 trillion of quantitative easing by the ECB, leaving the currency bloc with no safety buffer when the next global recession hits. The ECB is close to exhausting its ammunition and appears increasingly powerless to do more under the legal constraints of its mandate. It has downgraded its growth forecast for the next two years, citing the uncertainties of Brexit, and admitted that it has little chance of meeting its 2pc inflation target this decade, insisting that it is now up to governments to break out of the vicious circle. Mario Draghi, the ECB’s president, said there are limits to monetary policy and called on the rest of the eurozone to act “much more decisively” to lift growth, with targeted spending on infrastructure.
“It is abundantly clear that Draghi is played out and we’re in the terminal phase of QE. The eurozone needs a quantum leap in the nature of policy and it has to come from fiscal policy,” said sovereign bond strategist Nicholas Spiro. Mr Draghi dashed hopes for an expansion of the ECB’s monthly €80bn programme of bond purchases, and offered no guidance on whether the scheme would be extended after it expires in March 2017. There was not a discussion on the subject. “The bar to further ECB action is higher than widely assumed,” said Ben May from Oxford Economics. The March deadline threatens to become a neuralgic issue for markets given the experience of the US Federal Reserve, which suggests that an abrupt stop in QE stimulus amounts to monetary tightening and can be highly disruptive.
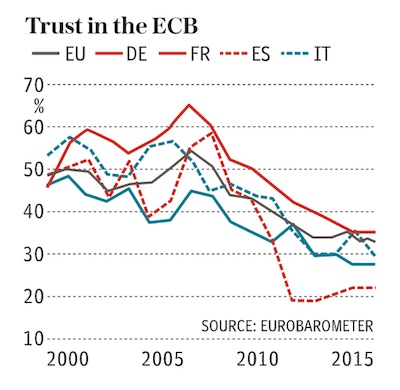
The ECB has pulled out all the stops to reflate the economy yet core inflation has been stuck at or below 1pc for three years. Officials are even more worried about the underlying trends. Data collected by Marchel Alexandrovich at Jefferies shows that the percentage of goods and services in the inflation basket currently rising at less than 1pc has crept up to 58pc. This is a classic precursor to deflation and suggests that the eurozone is acutely vulnerable to any external shock. The figure has spiked to 67pc in Italy, and is now significantly higher that it was when the ECB launched QE last year. The eurozone should have reached economic “escape velocity” by now after a potent brew of stimulus starting last year: cheap energy, a cheaper euro, €80bn a month of QE, and the end of fiscal austerity. [..] “The euro is far stronger than they want, and stronger than the economy deserves, but they don’t know how to weaken it. This is exactly what happened to the Japanese,” said Hans Redeker, currency chief at Morgan Stanley.

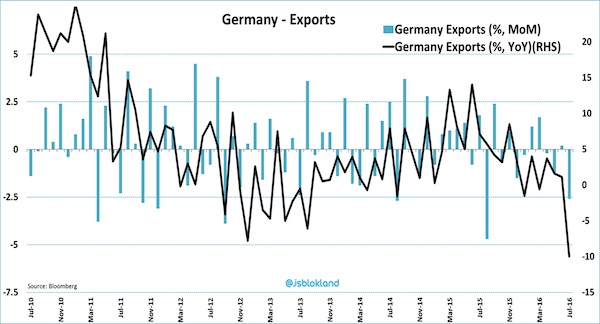
Draghi’s starting to come down on Germany, but it’s too late: their exports just fell 10%.
• ECB Stands Pat on Stimulus as Draghi Defends Policy (WSJ)
The ECB left its €1.7 trillion stimulus unchanged at a policy meeting Thursday, brushing off concerns over economic shock waves from Britain’s vote to leave the EU and disappointing investors expecting the ECB to act again soon. The decision to stand pat, even as new forecasts showed the ECB missing its inflation target for years, underlines how central banks are approaching the limits of what they can achieve without support from other policy areas, notably governments. In China earlier this month, Group of 20 leaders warned that monetary policy alone can’t fix the world’s economic ills, and pledged to boost spending and adopt overhauls aimed at boosting growth.
At a news conference here, ECB President Mario Draghi said he was concerned about persistently low eurozone inflation, which has fallen short of the ECB’s near-2% target for more than three years. Fresh ECB staff forecasts, published Thursday, showed inflation rising very gradually, to 1.2% next year and 1.6% in 2018. Despite that, Mr. Draghi said policy makers didn’t even discuss fresh stimulus, and praised the effectiveness of the bank’s existing policy measures, which include negative interest rates and €80 billion a month of bond purchases. He also aimed an unusually direct rebuke at Germany, criticizing Berlin for not boosting spending to support the economy. “Countries that have fiscal space should use it,” Mr. Draghi said. “Germany has fiscal space.”
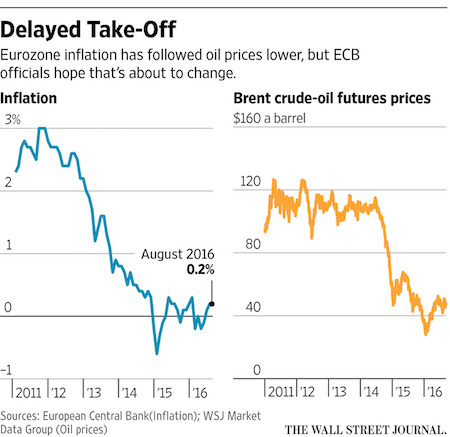

Germany looks a lot like Japan and China.
• German July Exports, Imports in Shock Plunge (Street)
German imports and exports unexpectedly shrunk in July, with a sharp export contraction causing a surprise narrowing in Germany’s trade balance. Federal Statistical Office data showed seasonally adjusted exports fell by 2.6% – analysts had expected about 0.3% growth – whereas imports fell by 0.7%, as against expectations for a 0.8% rise. On the year exports slumped by 10% and imports shriveled by 6.5%. The foreign trade balance shrunk to €19.4 billion from €21.4 billion in June, as against expectations for a balance of €22 billion. The Federal Statistical Office said the pace of German exports to other EU countries fell by 7% in July, while imports from the region fell by 4.5%. The falls were slightly narrower for trade with other eurozone countries.
German trade outside the 28-nation EU fared worse, with exports plunging by 13.8% and imports by 10.1%. Faltering German exports amid lackluster worldwide growth and emerging-market volatility has long been a drag on German growth. But the sharper-than-expected export fall challenges expectations of a second-half pickup in German trade with the rest of the world, and the surprise – albeit small -import decline suggests domestic demand isn’t robust enough to step into the breach. The trade data come in a week that the statistics office reported weaker-than-expected industrial output and manufacturing production for July. But the euro held firm against the dollar after the figures and was recently up 0.11% at $1.1272.

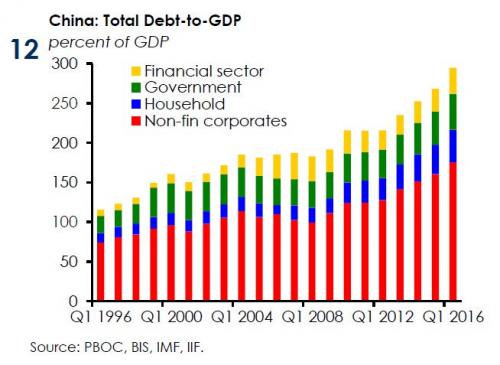
“..some time around 2019, China’s total Debt/GDP will be over 400%, an absolutely ridiculous number, and one which assures a banking, if not global, financial crisis.”
• Goldman Calculates True Growth Rate Of China’s Debt: 40% of GDP Per Year (ZH)
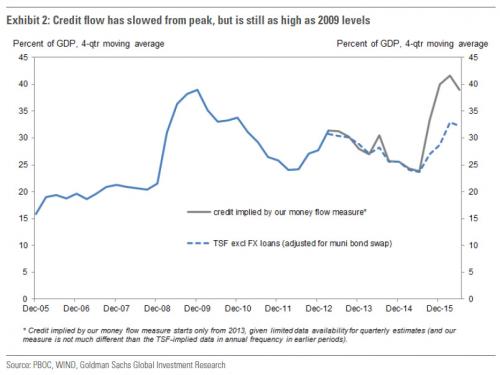
For a long time when it came to Chinese loan creation, analysts would only look at the broadest reported aggregate: the so-called Total Social Financing. And, for a long time, it was sufficient – TSF showed that in under a decade, China had created over $20 trillion in new loans, vastly more than all the “developed market” QE, the proceeds of which were used to kickstart growth after the 2009 global depression, to fund the biggest capital misallocation bubble the world has ever seen and create trillions in nonperforming loans. However, a problem emerged about a year ago, when it was revealed that not even China’s TSF statistic was sufficient to fully capture the grand total of total new loan creation in China.
[..] according to Goldman, “a substantial amount of money was created last year, evidencing a very large supply of credit, to the tune of RMB 25tn (36% of 2015 GDP).” This massive number was 9% higher than the TSF data, which implied that “only” a quarter of China’s 2015 GDP was the result of new loans. As Goldman further noted, the “divergence from TSF has been particularly notable since Q2 last year after a major dovish shift in policy stance.” In short, in addition to everything else, China has also been fabricating its loan creation data, and the broadest official monetary aggregate was undercutting the true new loan creation by approximately a third. The reason for this is simple: China does not want the world – or its own population – to realize just how reliant it is on creating loans out of thin air (and “collateralized” by increasingly more worthless assets), as it would lead to an even faster capital outflow by the local population sensing just how unstable the local banking system is.
Here is the good news: compared to late 2015, the record credit creation has slowed down fractionally, and the gap with the TSF total has shrunk. The smaller gap seems to be in line with recent reports that listed banks’ “investment receivables” expanded less rapidly in 2016 H1, and it might partly reflect the regulators’ tougher stance against shadow lending in recent months. And now, the bad news: this “tougher stance” has not been nearly tough enough, because as the following chart shows on a 1-year moving average, nearly 40% of China’s “economic growth” is the result of new credit creation, or in other words, new loans. What this really means, is that China’s debt/GDP, estimated most recently by the IIF at 300%…
… is now growing between 30% and 40% per year, when one accounts for the unaccounted for “shadow” credit conduits. Here is how Goldman concludes this stunning observation: “The PBOC appears to have shifted to a less dovish, though still supportive, policy bias in the last few months. However, given the prospective headwinds from slower housing construction and tighter on-budget fiscal stance in the coming months, there remains a clear need to sustain a high level of infrastructure investment, which is credit intensive, to achieve the minimum 6.5% full-year growth target. This poses constraints on how much further the PBOC can keep reining in credit, in our view.”
Translating Goldman, some time around 2019, China’s total Debt/GDP will be over 400%, an absolutely ridiculous number, and one which assures a banking, if not global, financial crisis.

The resounding success of globalization.
• China’s Reviving the American Heartland – One Low Wage at a Time (BBG)
For six years, the General Motors factory that used to make Chevy Trailblazers in Moraine, Ohio, sat abandoned, a rusting monument to the decline of the American auto industry. These days, the plant is humming again, fueled by a resurgent U.S. consumer – but now under Chinese management. On the shop floor, Chinese supervisors in sky-blue uniforms that carry the logo of the new owners, Fuyao Glass, teach American employees how to assemble windshields. Drive along Interstate 75, through America’s industrial heartland, and you’ll find no shortage of Chinese-owned firms like Fuyao. They’re setting up shop in states such as Ohio and Michigan, key voter battlegrounds in November, where traditional manufacturing has been hollowed out – in many cases, by trade. With China.
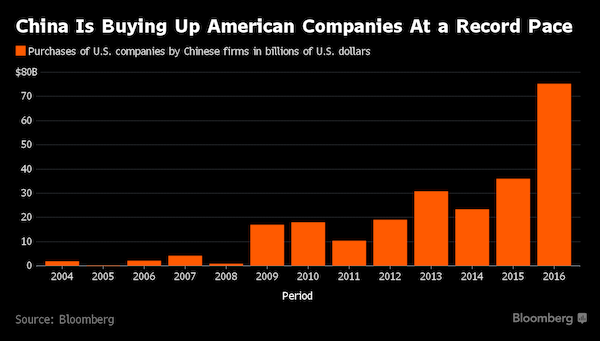
[..] Fuyao acquired roughly half the old GM plant in 2014, spending $450 million to buy and remodel it. For a company that started out as a small producer of covers for water-meters and is now the world’s second-biggest auto-glass supplier, the acquisition capped a decade-long push into U.S. markets. For the Dayton area, it meant employment: the city, hometown of the Wright brothers, was hit hard by the shutdown of the GM plant two days before Christmas in 2008. [..] “Hey, 1,700 jobs is 1,700 jobs,” said Shawn Kane, a 28-year-old chef shopping at the Kroger grocery store in Moraine last month. “At least it’s not sitting empty anymore.” They’re jobs that tend not to pay as well as factory work once did, though – and there probably aren’t as many of them.
To keep its production in the U.S. viable, Fuyao uses more automation than it does in China, said John Gauthier, president of Fuyao Glass America. “Our customers, all they care about is that their cost doesn’t increase,” he said. A line worker at Fuyao starts at $12 per hour, equivalent to an annual salary of about $25,000. GM workers at the old Moraine plant could make at least twice that, topped off by perks like defined-benefit pensions, according to union officials and former employees. “When you don’t have enough protections for American workers, and when you’ve got a globalized economy, this is what happens,” said Chris Baker, a 40-year-old sales rep based near Moraine. “This is the new normal. It’s very sad.”

WHen will they start buying people’s homes? Cars perhaps?
• Bank of Japan Risk: Running Out of Bonds to Buy (WSJ)
Japan’s central bank is facing a new problem: It could be running out of government bonds to buy. The Bank of Japan is snapping up the equivalent of more than $750 billion worth of government debt a year in an effort to spur inflation and growth. At that rate, analysts say, banks could run out of government debt to sell within the next 18 months. The looming scarcity is a powerful sign of the limits central banks face as they turn to ever-more aggressive means of stimulating their economies. The problem is mirrored in Europe, where self-imposed rules limit how many eurozone government bonds the ECB can buy from individual governments. Facing a diminishing supply of sovereign bonds, the ECB started buying corporate debt in June.
Some economists have even called for the ECB to start buying stocks. The central bank left its bond-buying program and interest-rate policy unchanged at its meeting Thursday. The Japanese central bank has fewer options if the country’s banks, which have to hold a certain amount of safe debt to use as collateral in everyday transactions, ever become unwilling to sell more of their holdings. Its most obvious alternatives—pushing rates deeper into negative territory or buying other types of assets—have practical limitations. Meanwhile, the BOJ’s economic goals remain out of reach: Inflation is stubbornly low, and the yen has strengthened about 18% this year.

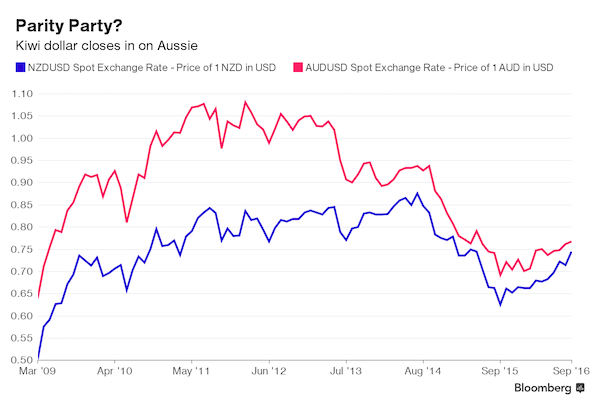
Does nobody have any common sense down under?
• Australia, New Zealand Housing Booms Set Currencies On Course For Parity (BBG)
Housing booms in New Zealand and Australia could be putting the neighbors’ currencies on course to reach parity for the first time ever. Both nations have seen house prices surge in recent years, but the underlying causes are fundamentally different, according to Deutsche Bank analysis. Australia’s boom is largely home-grown, whereas New Zealand’s is being fueled by record immigration. That’s affecting the countries’ current accounts differently. While Aussies are feeling richer due to house-price gains, prompting them to spend more on imports and boosting their current account deficit, New Zealand is sucking more offshore capital into its housing market, narrowing its current account gap. Currencies are sensitive to trends in the current account – a country’s balance with the rest of the world – because they are a gauge of risk for investors.
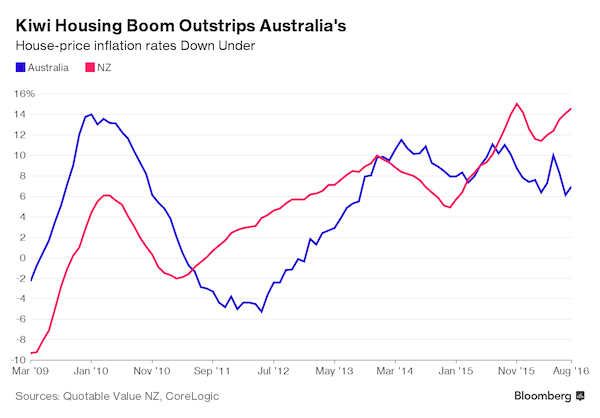
“The nature of the real estate boom in Australia should have bearish currency implications because it leads to deterioration in the basic balance,” Robin Winkler, a London-based strategist for Deutsche Bank, said in a research note. “This is not the case in New Zealand and adds to our conviction that AUD/NZD should drop to parity.” The two currencies have never converged in the free-floating era that began in the 1980s. They came close in April last year, when the kiwi briefly reached 99.79 Australian cents or, to express it the other way, the Aussie dollar fell below NZ$1.01. The New Zealand dollar was worth 96.8 Australian cents at 12:35p.m. in Wellington Friday.

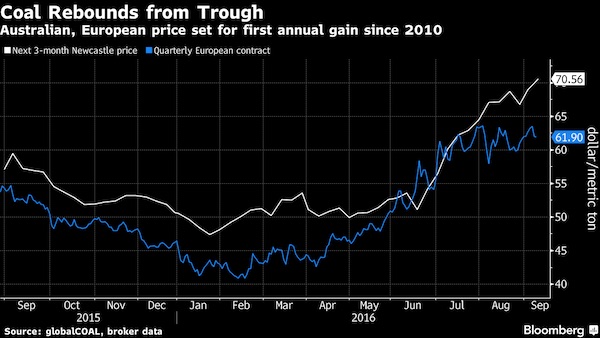
Burn baby burn.
• Coal Rises From the Grave to Become One of Hottest Commodities
For all the predictions about the death of coal, it’s now one of the hottest commodities in the world. The resurrection may have further to run. A surge in Chinese imports to compensate for lower domestic production has seen European prices jump to near an 18-month high, while Australia’s benchmark is set for the first annual gain since 2010. At the start of the year, prices languished near decade lows because of waning demand from utilities seeking to curb pollution and amid the International Energy Agency’s declaration that the fuel’s golden age in China was over. Now, traders are weighing the chances of extreme weather hitting major producers and China further boosting imports as factors that could push prices even higher.
“It’s a commodity that’s been on a slippery slide for the past four years and it’s making a remarkable recovery,” said Erik Stavseth, an analyst at Arctic Securities in Oslo, who’s tracked the market for almost a decade. “There’s a strong pulse.” What could light up the market further is the occurrence of a La Nina weather pattern later this year. Last time it happened in 2010 and 2011, heavy rains flooded mines in Australia and Indonesia, the world’s two largest exporters. While some meteorologists have toned down their predictions for the weather phenomenon forming, “another strong forecast” would cause prices to rise further, according to Fitch’s BMI Research.

Still don’t think I know what exactly the fraud was. Though I read the piece twice.
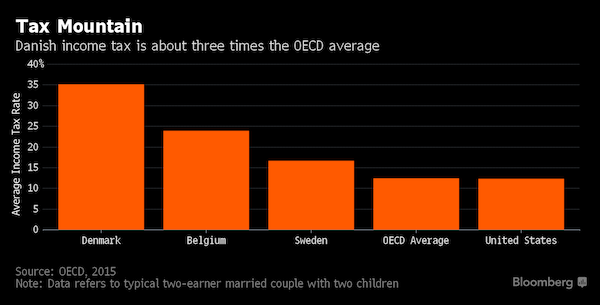
• Historic Tax Fraud Rocks Denmark As Loss Estimates Keep Growing (BBG)
About two weeks after Denmark revealed it had lost as much as $4 billion in taxes through a combination of fraud and mismanagement, the minister in charge of revenue collection says that figure may need to be revised even higher. Speaking to parliament on Thursday, Tax Minister Karsten Lauritzen said he “can’t rule out” that losses might be bigger than the most recent public estimates indicate. It would mark the latest in a string of revisions over the past year, in which Danes learned that losses initially thought to be less than $1 billion somehow ended up being about four times as big. The embarrassment caused by the tax fraud, which spans about a decade of successive administrations, has prompted Lauritzen to consider debt collection methods not usually associated with Scandinavian governments.
Denmark has long had one of the world’s highest tax burdens – government revenue as a percentage of GDP – and a well-functioning tax model is essential to maintaining its fabled welfare system. “We’re entertaining new ideas, considering more new measures,” Lauritzen told Bloomberg. Danish officials are now prepared to pay anonymous sources for evidence from the same database that generated the Panama Papers. Jim Soerensen, a director at Denmark’s Tax Authority, says the first batch of clues obtained using this method is expected by the end of the month.

Project Fear didn’t work in Britain either.
• Goldman Sachs Just Launched Project Fear in Italy (DQ)
Project Fear began two years ago in the run up to Scotland’s national referendum. It then spread to the rest of the UK in the lead up to this summer’s Brexit referendum. But it keeps on moving. Its latest destination is Italy, where the campaign to instill fear and trepidation in the hearts and souls of Italy’s voters was just inaugurated by the world’s most influential investment bank, Goldman Sachs. It just released a 14-page report warning about the potentially dire consequences of a “no” vote in Italy’s upcoming referendum on the government’s proposed constitutional reforms. The reforms seek, among other things, to streamline Italy’s government process by dramatically restricting the powers of the senate, a major source of political gridlock, while also handing more power to the executive.
The polls in Italy are currently neck and neck, though the momentum belongs to the reform bill’s opponents. If the Italian public vote against the bill, the response of the markets could be extremely negative, warns Goldman, putting in jeopardy the latest attempt to rescue Italy’s third largest and most insolvent bank, Monte dei Paschi di Siena. The rescue is being led by JP Morgan Chase and Italian lender Mediobanca, and includes the participation of a select group of global megabanks that are desperate to prevent contagion spreading from Italy’s banking system to other European markets, and beyond. In the event of a “no” vote, MPS’ planned €5 billion capital increase would have to be put on ice, while investors wait for the political uncertainty to clear before pledging further funds.
This being Italy, the wait could be interminable and the delay fatal for Monte dei Paschi and other Italian banks, Goldman warns. It also points out that Italy is the only European country where a substantial portion of its bank bonds are held in household portfolios (about 40% according to data from Moody’s, four times more than Germany and eight times more than France and Spain). In other words, things could get very ugly, very fast, if those bank bonds collapse! As for Italian government bonds and Europe’s broader debt markets, they would be insulated from any fallout by former Goldmanite Mario Draghi’s bond binge buying.

We are unstoppable.
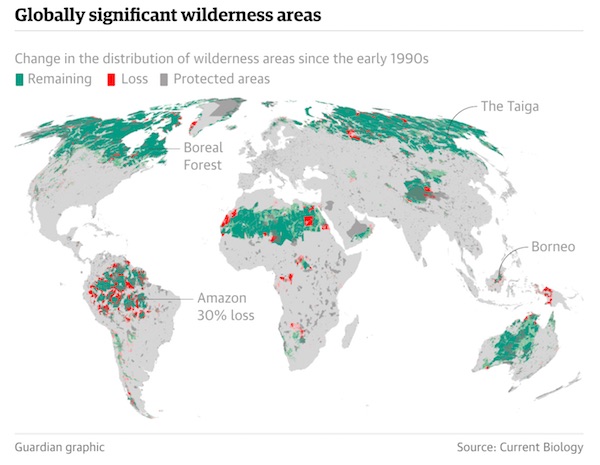
• Humans Have Destroyed A Tenth Of Earth’s Wilderness In 25 Years (G.)
Humans have destroyed a tenth of Earth’s remaining wilderness in the last 25 years and there may be none left within a century if trends continue, according to an authoritative new study. Researchers found a vast area the size of two Alaskas – 3.3m square kilometres – had been tarnished by human activities between 1993 and today, which experts said was a “shockingly bad” and “profoundly large number”. The Amazon accounted for nearly a third of the “catastrophic” loss, showing huge tracts of pristine rainforest are still being disrupted despite the Brazilian government slowing deforestation rates in recent years. A further 14% disappeared in central Africa, home to thousands of species including forest elephants and chimpanzees.
The loss of the world’s last untouched refuges would not just be disastrous for endangered species but for climate change efforts, the authors said, because some of the forests store enormous amounts of carbon. “Without any policies to protect these areas, they are falling victim to widespread development. We probably have one to two decades to turn this around,” said lead author Dr James Watson, of the University of Queensland and Wildlife Conservation Society. The analysis defined wilderness as places that are “ecologically largely intact” and “mostly free of human disturbance”, though some have indigenous people living within them. The team counted areas as no longer wilderness if they scored on eight measures of humanity’s footprint, including roads, lights at night and agriculture.









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle September 9 2016