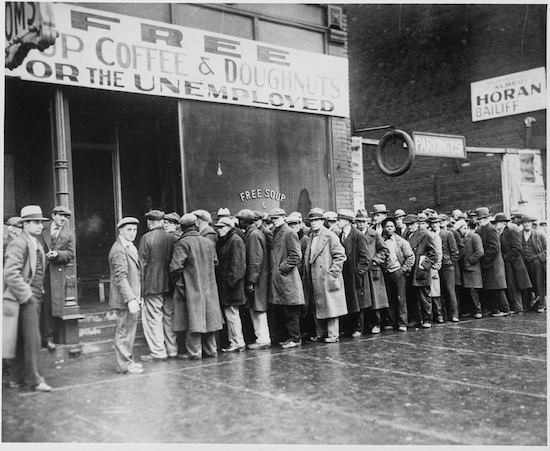

Al Capone’s free soup kitchen, Chicago, 1931

It is crucial for the US political system to be tested this way. So far, it seems to work, but we’re in very early innings. Important to recognize that Trump and Bannon merely attempt to use the broader executive powers developed under Clinton, Bush and Obama. A major problem can be that the judiciary has alredy become very politicized, with presidents getting to pick judges.
• US Appeals Court Upholds Suspension Of Trump Travel Ban (AP)
Trump’s ban on travelers from seven predominantly Muslim nations, dealing another legal setback to the new administration’s immigration policy. In a unanimous decision, the panel of three judges from the San Francisco-based 9th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals declined to block a lower-court ruling that suspended the ban and allowed previously barred travelers to enter the U.S. An appeal to the U.S. Supreme Court is possible. The court rejected the administration’s claim that it did not have the authority to review the president’s executive order. “There is no precedent to support this claimed unreviewability, which runs contrary to the fundamental structure of our constitutional democracy,” the court said. The judges noted that the states had raised serious allegations about religious discrimination.
Following news of the ruling, Trump tweeted, “See you in court, the security of our nation is at stake!” U.S. District Judge James Robart in Seattle issued a temporary restraining order halting the ban last week after Washington state and Minnesota sued. The ban temporarily suspended the nation’s refugee program and immigration from countries that have raised terrorism concerns. Justice Department lawyers appealed to the 9th Circuit, arguing that the president has the constitutional power to restrict entry to the United States and that the courts cannot second-guess his determination that such a step was needed to prevent terrorism. The states said Trump’s travel ban harmed individuals, businesses and universities. Citing Trump’s campaign promise to stop Muslims from entering the U.S., they said the ban unconstitutionally blocked entry to people based on religion.

“..the first half of the year will be consumed in nasty partisan battles over cabinet appointments, the Gorsuch nomination, interminable maneuvers over the travel ban and follow-on measures of extreme vetting and the Obamacare repeal/replace battle.”
• The Crash Will Be Violent (David Stockman)
[..] What will be coming soon, however, is the mother of all debt ceiling crises — an eruption of beltway dysfunction that will finally demolish the notion that Trump is good for the economy and the stock market. The debt ceiling holiday ends on March 15, and it appears that the rudderless Treasury Department — Mnuchin has not yet been approved as Treasury Secretary and there are no Trump deputies, either — may be engaging in a bit of sabotage. That is, the cash balance has run down from a peak of about $450 billion to just $304 billion as of last Friday. Unless reversed soon, this means that the Treasury will run out of cash by perhaps July 4th rather than Labor Day. After that, all hell will break loose.
Washington has been obviously dysfunctional for years, but the virtue of the Great Disrupter is that his tweets, tangents, inconsistencies and unpredictabilities guarantee that the system will soon shut down entirely. Consequently, the first half of the year will be consumed in nasty partisan battles over cabinet appointments, the Gorsuch nomination, interminable maneuvers over the travel ban and follow-on measures of extreme vetting and the Obamacare repeal/replace battle. Then, the second half of 2017 will degenerate into a non-stop battle over raising the debt ceiling and continuing resolutions for fiscal year (FY) 2018 which begins October 1. That will mean, in turn, that there is no budget resolution embodying the Trump/GOP fiscal agenda, and therefore no basis for filibuster-proof “reconciliation instructions” on the tax cut.
This latter point, in fact, needs special emphasis. The frail GOP majorities now in place will be too battered and fractured by the interim battles to coalesce around a ten-year budget resolution that embodies the $10 trillion of incremental deficits already built into the CBO baseline — plus trillions more for defense, veterans, border control, the Mexican Wall, an infrastructure bonanza and big tax cuts, too. It will never happen. There is not remotely a GOP majority for such a resolution. But without an FY 2018 budget resolution, inertia and the K-Street lobbies will rule. Without a 51-vote majority rule in the Senate, a material, deficit-neutral cut in the corporate tax rate would be absolutely impossible to pass. Yet that’s exactly what the casino is currently pricing-in.

Foreign investors.
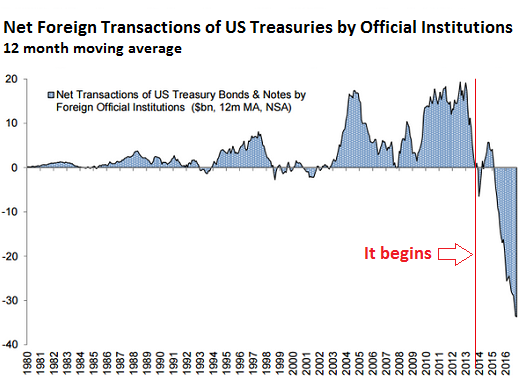
• Foreign Governments Dump US Treasuries as Never Before; Who is Buying? (WS)
It started with a whimper a couple of years ago and has turned into a roar: foreign governments are dumping US Treasuries. The signs are coming from all sides. The data from the US Treasury Department points at it. The People’s Bank of China points at it in its data releases on its foreign exchange reserves. Japan too has started selling Treasuries, as have other governments and central banks. Some, like China and Saudi Arabia, are unloading their foreign exchange reserves to counteract capital flight, prop up their own currencies, or defend a currency peg. Others might sell US Treasuries because QE is over and yields are rising as the Fed has embarked on ending its eight years of zero-interest-rate policy with what looks like years of wild flip-flopping, while some of the Fed heads are talking out loud about unwinding QE and shedding some of the Treasuries on its balance sheet.
Inflation has picked up too, and Treasury yields have begun to rise, and when yields rise, bond prices fall, and so unloading US Treasuries at what might be seen as the peak may just be an investment decision by some official institutions. The chart below from Goldman Sachs, via Christine Hughes at Otterwood Capital, shows the net transactions of US Treasury bonds and notes in billions of dollars by foreign official institutions (central banks, government funds, and the like) on a 12-month moving average. Note how it started with a whimper, bounced back a little, before turning into wholesale dumping, hitting record after record (red marks added):
The People’s Bank of China reported two days ago that foreign exchange reserves fell by another $12.3 billion in January, to $2.998 trillion, the seventh month in a row of declines, and the lowest in six years. They’re down 25%, or almost exactly $1 trillion, from their peak in June 2014 of nearly $4 trillion (via Trading Economics, red line added):
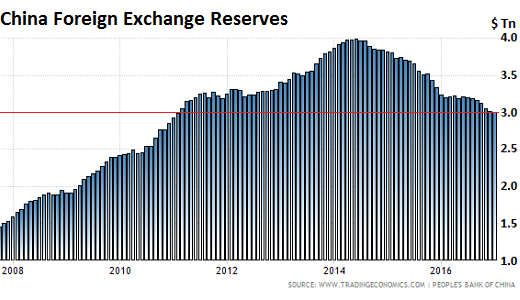
China’s foreign exchange reserves are composed of assets that are denominated in different currencies, but China does not provide details. So of the $1 trillion in reserves that it shed since 2014, not all were denominated in dollars. The US Treasury Department provides another partial view, based on data collected primarily from US-based custodians and broker-dealers that are holding these securities for China and other countries. But the US Treasury cannot determine which country owns the Treasuries held in custodial accounts overseas. Based on this limited data, China’s holdings of US Treasuries have plunged by $215.2 billion, or 17%, over the most recent 12 reporting months through November, to just above $1 trillion.

From a Mish article quoting an unpublished report. I wonder when all these people will begin to understand my point that growth is gone. Only then will the pieces fall into place. Note: calling Weak Global Growth and Impediment to Growth sounds a bit silly.
• Impediments to Growth (Lacy Hunt)
1. Unproductive Debt At the end of the third quarter, domestic nonfinancial debt and total debt reached $47.0 and $69.4 trillion, respectively. Neither of these figures includes a sizeable volume of vehicle and other leases that will come due in the next few years nor unfunded pension liabilities that will eventually be due. The total figure is much larger as it includes debt of financial institutions as well as foreign debt owed. The broader series points to the complexity of the debt overhang. Netting out the financial institutions and foreign debt is certainly appropriate for closed economies, but it is not appropriate for the current economy.
Total debt gained $3.1 trillion in the past four quarters, or $5.70 dollars for each $1.00 of GDP growth. From 1870 to 2015, $1.90 of total debt generated $1.00 dollar of GDP. We estimate that approximately $20 trillion of debt in the U.S. will reset within the next two years. Interest rates across the curve are up approximately 100 basis points from the lows of last year. Unless rates reverse, the annual interest costs will jump $200 billion within two years and move steadily higher thereafter as more debt obligations mature. This sum is equivalent to almost two-fifths of the $533 billion in nominal GDP in the past four quarters. This situation is the same problem that has constantly dogged highly indebted economies like the U.S., Japan and the Eurozone.
2. Record Global Debt The IMF calculated that the gross debt in the global non-financial sector was $217 trillion, or 325% of GDP, at the end of the third quarter of 2016. Total debt at the end of the third quarter 2016 was more than triple its level at the end of 1999. Debt in China surged by $3 trillion in just the first three quarters of 2016. Chinese debt at the end of the third quarter soared to 390% of GDP, an estimated 20% higher than U.S. debt-to-GDP. This debt surge explains the shortfall in the Chinese growth target for 2016, a major capital flight, a precipitous fall of the Yuan against the dollar and a large hike in their overnight lending rate. Such policies lose their effectiveness over time. [As stated by] Nobel laureate F. A. Hayek (1933):“To combat the depression by a forced credit expansion is to attempt to cure the evil by the very means which brought it about.”
3. Weak Global Growth Based on figures from the World Bank and the IMF through 2016, growth in a 60-country composite was just 1.1%, a fraction of the 7.2% average since 1961. Even with the small gain for 2016, the three-year average growth was -0.8%. As such, the last three years have provided more evidence that the benefits of a massive debt surge are elusive. World trade volume also confirms the fragile state of economic conditions. Trade peaked at 115.4 in February 2016, with September 2016 1.7% below that peak, according to the Netherlands Bureau of Economic Policy Analysis. Over the last 12 months, world trade volume fell 0.7%, compared to the 5.1% average growth since 1992.
4. Eroding Demographics World trade volume also confirms the fragile state of economic conditions. Trade peaked at 115.4 in February 2016, with September 2016 1.7% below that peak, according to the Netherlands Bureau of Economic Policy Analysis. Over the last 12 months, world trade volume fell 0.7%, compared to the 5.1% average growth since 1992.

Absolutely delightful.
Chess is a game where the number of possible positions rises at an astronomical rate. By the 2nd move of the game there are already 400 possible positions and after each person moves twice, that number rises to 8902. My coach explained to me that I was not trained enough to even begin to keep track of those things and that my only chance of ever winning was to take the initiative and never give it up. “You must know what your opponent will do next by playing his game for him.” was the advice I received. Now, I won’t bore you with the particulars but it boiled down to throwing punches each and every turn without exception. In other words, if my opponent must always waste his turn responding to what I am doing then he never gets an opportunity to come at me in the millions of possibilities that reside in the game. Again, if I throw the punch – even one that can be easily blocked, then I only have to worry about one combination and not millions.
My Russian chess coach next taught me that I should Proudly Announce what exactly I am doing and why I am doing it. He explained to me that bad chess players believe that they can hide their strategy even though all the pieces are right there in plain sight for anyone to see. A good chess player has no fear of this because they will choose positions that are unassailable so why not announce them? As a coach, I made all of my students tell each other why they were making the moves that they made as well as what they were planning next. It entirely removed luck from the game and quickly made them into superior players.
My Russian coach next stressed Time as something I should focus on to round out my game. He said that I shouldn’t move the same piece twice in a row and that my “wild punches” should focus on getting my pieces on to the board and into play as quickly as possible. So, if I do everything correctly, I have an opponent that will have a disorganized defense, no offense and few pieces even in play and this will work 9 out of 10 times. The only time it doesn’t work for me is when I go against players that have memorized hundreds of games and have memorized how to get out of these traps.
With all that said, let’s see if President Trump is playing chess. First, we can all agree that Trump, if nothing else, throws a lot of punches. We really saw this in the primaries where barely a day could go by without some scandal that would supposedly end his presidential bid. His opponents and the press erroneously thought that responding to each and every “outrage” was the correct thing to do without ever taking the time to think whether or not they had just walked into a trap. They would use their turn to block his Twitter attack but he wouldn’t move that piece again once that was in play but, instead, brought on the next outrage – just like my coach instructed me to do.
Second, Trump is very vocal in what he is going to do. Just like I had my students announced to each other their plans, Trump has been nothing but transparent about what he intends to do. After all, announcing your plans only works if your position is unassailable. It demoralizes your opponent. You rub their face in it. Another benefit to being vocal is that it encourages your opponent to bring out his favorite piece to deal with said announced plans. This is a big mistake as any good chess player will quickly recognize which piece his opponent favors and then go take them.

“Fraid Jim lost it.
• Biography of President Donald Trump, a.k.a. “Wayne Newton” (Jim Kunstler)
And so it happened years ago on the Trump family’s annual Christmas pilgrimage to Paraguay that Papa Fred and Mama Mary Anne fell in socially with the circle around Klaus Furtwänkler, Waffen-SS Gruppenführer (ret.) in the little resort village of Nueva Bavaria. The former commandant of the Flossenbürg work camp (granite quarries) introduced young Donald to the song “Danke Schoen” popularized by the vocalist Eva Braun at the 1936 Berlin Olympics. Since earliest childhood, with his love for the “spotlight,” Donald had entertained the family with renditions of Disney’s beloved hits, “Zip-a-dee-doo-dah,” “When I See an Elephant Fly,” and “Hi-Diddle-Dee-Dee (an Actor’s Life for Me).” The next evening, on Furtwänkler’s 3,000-hectare estancia, before an audience of fifty “special guests” at the Heiliger Abend buffet (Arapaima snapper with red cabbage and potato salad), Donald performed “Danke Schoen” to wild applause, propelling him into a career in show business. Not a few of the frauleins present fainted.

Young Donald or someone else?
To protect Papa’s real estate business interests in Queens, New York, Donald adopted the professional name “Wayne Newton” and was withdrawn from military school to perform on the county fair circuit across the states that would later self- identify by the color “red” — but which, given our adversarial relations with the USSR at the time, styled themselves red, white, and blue. Six month’s later, “Wayne” caught the eye of Las Vegas promoter Sal “Cukarach” Vaselino while playing the Refrigeration Engineers annual meet-up at the Sands Hotel, and then after a six-week smash engagement at the Golden Nugget in 1963, “Wayne” was inducted into the notorious Frank Sinatra / Dean Martin Rat-pack as its first underage member. (Rat-pack consigliere Peter Lawford introduced the talented lad to the concept of “sloppy seconds”).
[..] Back on the convention circuit with Jules the Singing Jackrabbit, Wayne played the 1983 National Realtors Association Pump-and-Dump Expo and was influenced to get his first real estate license. “Why pay for milk when you can own the cash cow,” keynote speaker Ivan Boesky advised “Wayne,” prompting him to return to his New York City “roots” and resume his identity as “The Donald,” son of “The Fred” Trump. A carefully orchestrated life of public appearances at Gotham charity events and a lavish wedding to model Ivana Zelníková reestablished Donald Trump as a fixture on the glittering Manhattan scene – meanwhile, a Greyhound Bus mechanic and aspiring country crooner named Bud Gorch, a “dead-ringer” look-alike for the erstwhile “Wayne Newton,” was recruited by the Trump Organization to impersonate the once-again in-demand Las Vegas star. Gorch-as-Wayne successfully premiered his new act at the National Colorectal Surgeons Association Chron’s and Colitis Congress and the “great switch” was achieved. The rest, as they say, is history!

Who actually was it onstage at the National Organ Transplant Association Convention, 1967?

The door is ajar.
• What Would it Cost a Country to Leave the Euro? (WS)
[Le Pen] is campaigning on taking France out of the euro (after holding a referendum) and re-denominating the entire €2.4 trillion pile of French government debt into new franc. Then the government can just print the money it wants to spend. There are some complications with her plan, including that the diverse and bickering French political class will unite into a slick monolithic bloc against her during the second round. And if she still wins, her government will face that bloc in parliament. But hey. And now people are seriously thinking about it. Greece was on the verge of leaving the euro, but then within a millimeter of actually taking the step, it blinked and inched back from the precipice in the hot summer of 2015. And so for now still no one knows what the cost would be to leave…
[..] Now ECB President Mario Draghi is stumbling into the fray. “The euro is irrevocable,” he told the European Parliament on Monday, to counter the populist rejection of the euro. “This is the treaty,” he said. Which evoked memories of the good ol’ days of the sovereign debt crisis, when, to put an end to it in July 2012, Draghi said that the euro was “irreversible” and that the ECB was “ready to do whatever it takes to preserve the euro.” At the time, the Spanish 10-year yield was above 7% and the Italian 10-year yield was above 6%. So now, same tune, different scenario. It’s not a debt crisis. It’s just a question of whether or not it’s possible to leave the euro, and if yes, how much it would cost. And that question has already been raised officially.
On January 18, Draghi had sent a letter to European Union lawmakers Marco Valli and Marco Zanni, telling them: “If a country were to leave the Eurosystem, its national central bank’s claims on or liabilities to the ECB would need to be settled in full.” That was the opening – the IF. “If a country were to leave…” It meant that a country could leave! It was the first official admission that this was actually possible. It was just a matter of cost. That’s how Zani saw Draghi’s response. Bloomberg: “I wanted to bring up the issue of exit from the euro and how it can happen,” he said in an interview before the testimony. “Draghi has now clearly admitted that such an exit is possible and now there is need to have more clarity about the cost. I’m sure that in case of Italy’s exit from the euro, benefits exceed costs.”
Alas, in his testimony before the European Parliament, Draghi refused to put a price tag on leaving the euro. Valli asked him whether the “liabilities” Draghi had referred to that would “need to be settled in full” were the so-called Target2 imbalances. These are a result of payment settlements within the European System of Central Banks. They’d soared during the debt crisis to hundreds of billions of euros, a sign of the underlying financial tensions between debtor and creditor countries. But Draghi dodged the question: “I cannot answer a question that is based on hypotheses, on assumptions which are not foreseen” by the European treaties, he said. “What I could do is send you a written answer which compares our Target2 system with the Federal Reserve-based system.” Which was very helpful.
But even though he refused to put a price tag on leaving the euro, the whole exchange confirmed that it’s possible to leave the euro, though there is nothing in the treaties that mentions leaving the euro.

Yanis is spot on right. The Greeks are now being sacrificed on the altar of incumbents afraid to lose elections. The insane narrative that Germans and Dutch ‘give’ billions to Greece persists. That says a lot about the press in these countries.
• Varoufakis Accuses Creditors Of Going After Greece’s ‘Little People’ (Ind.)
Former Greek finance minister Yanis Varoufakis has said that everyday life in Greece is unsustainable and that the country’s European creditors are going after the “little people” rather than “corrupt oligarchs”. Speaking to BBC Radio 4’s Today programme, the 55-year old economist said that the country has been put on a fiscal path which makes everyday life “unsustainable” in Greece. “The German finance minister agrees that no Greek government, however reformist it might be, can sustain the current debt obligations of Greece,” he said. Earlier in the day, Wolfgang Schäuble told German broadcaster ARD that Greece must reform or quit the euro. “A country in desperate need of reform has been made unreformable by unsustainable macroeconomic policies,” Mr Varoufakis said.
He said that “instead of attacking the worst cases of corruption, for six years now the creditors have been after the little people, the small pharmacists, the very poor pensioners instead of going for the oligarchies”. Greece in 2010 was given a huge loan that Mr Varoufakis said was not designed to save the bankrupt country but to “cynically transfer huge banking losses from the books of the Franco German banks onto the shoulders of the weakest taxpayers in Europe”. Earlier this week, the IMF warned Greece’s debts are on an “explosive” path, despite years of economic reform. The IMF has insisted on additional debt relief and reduced fiscal targets before it participates financially in Greece’s current bailout program. Germany, which faces national elections, has resisted such moves. Statistics agency ELSTAT said on Thursday that Greece’s jobless rate came in at 23% in November, unchanged from the previous month. But although the jobless rate has come down from record highs, it remains more than double the euro zone’s average of 9.8% in November.

Why try anymore?
• Greece Hopeful Of Imminent EU Debt Deal Despite German Warning (G.)
The Greek government has expressed hope of an imminent deal with its EU creditors, despite a warning from the German finance minister, Wolfgang Schäuble, that the country could cut its debts only by leaving the single currency. Athens is in a familiar stand-off with the German finance ministry as it seeks easier repayment terms on its €330bn debt pile, which the IMF has described as unsustainable and explosive. The IMF has so far declined to get involved in the latest Greek rescue effort, a three-year EU bailout worth €86bn set to run until August 2018. The fund says it will only join if Greece gets significant debt relief, although its board is split. Germany and the Netherlands, which both face elections this year, think the IMF’s involvement is crucial for the bailout plan to continue.
Tensions – and Greek borrowing costs – have risen in recent weeks, ahead of a meeting of eurozone finance ministers on 20 February, which is widely seen as the last moment to reach agreement before the eurozone election cycle. The Dutch go to the polls in March; French presidential elections follow in April-May and German elections in the autumn. George Katrougalos, Greece’s Europe minister, voiced confidence that a deal was within reach: “I am optimistic that we can have such an agreement before the Eurogroup of 20 February.” He told journalists in Brussels that Europe was not the problem. “If we had just to deal with the Europeans we would have already completed this review in December. All the delay is due to the ambivalence of the IMF to participate or not to participate.”

“Klaus Regling, the managing director of the European Stability Mechanism, argued that “Greece’s debt situation does not have to be cause for alarm”…
• Greek Crisis Descends Into Blame Game (Tel.)
Greece is under mounting pressure to embark on a new wave of economic reforms, as its international creditors demand extra efforts to drag the country out of its latest crisis. At the same time Germany is facing fresh demands from the International Monetary Fund (IMF) to write off some of the money it loaned to Greece in the most recent €86bn (£73bn) bailout. And the IMF has been forced to defend its dire predictions of permanent economic gloom as the Greek government rejects the IMF’s assessment of its reforms, public finances and economic performance. On top of that, the IMF itself is split, with a minority of directors pushing for extra spending cuts and tax hikes in Greece to try to improve its public finances. The IMF tried to address its internal splits, stressing that it wants debt relief for Greece combined with economic reforms, not austerity. It does still demand serious action, though – unless the economy picks up and debts are slashed, it has warned Greece’s debts are on an “explosive” path.
“Our strong preference is for a primary [Greek budget] surplus target of 1.5pc and that this should be accompanied by significant debt relief. We’ve referred to this as the ‘two legs’ of the programme that we think is required,” said Gerry RIce, the IMF’s spokesman. “We think this target, the 1.5, can be obtained by the policies envisaged by the current European Stability Mechanism programme – in short, the IMF is not asking for any more austerity for Greece.” That passes much of the pressure on to Germany and the other nations which have loaned Greece money, but are unwilling to write off the debt. Germany renewed the pressure on Greece to press ahead with more economic reforms. Its finance minister Wolfgang Schauble told a German TV station that the Lisbon Treaty prevents governments from writing off these debts.
Instead, he argued, Greece must continue reforming to make its economy more competitive. Meanwhile Klaus Regling, the managing director of the European Stability Mechanism, argued that “Greece’s debt situation does not have to be cause for alarm”. Writing in the Financial Times, he said that the IMF has failed to fully appreciate the amount of support on offer from other eurozone countries to Greece, largely in the form of very generous loans. “It is hard to overestimate the significance of this pledge, made by the finance ministers of the eurozone. Solidarity with Greece will continue,” he said. “We would not have lent this amount if we did not think we would get our money back,” he said, ruling out debt relief and backing more economic reforms.

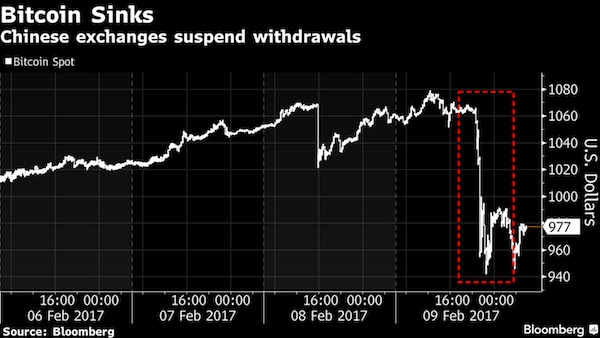
Beijing decides what bitcoin is.
• China Bitcoin Exchanges Halt Withdrawals After PBOC Talks (BBG)
China’s three biggest bitcoin exchanges took steps to prevent withdrawals of the cryptocurrency amid pressure from the nation’s central bank to clamp down on capital outflows. BTC China subjected all bitcoin withdrawals to a 72-hour review, while Huobi and OKCoin suspended them completely, the three venues said in separate statements on Thursday. They all said the measures were in response to central bank requirements. Conversion to and from the yuan is not affected and the curbs will be dropped after updates to compliance systems, the exchanges said. The People’s Bank of China told nine bitcoin venues at a meeting in Beijing on Wednesday that it will close exchanges that violate rules on foreign exchange management, money laundering, and payment and settlement.
Chinese authorities are scrutinizing the cryptocurrency amid concerns it’s being used to spirit money out of the country, undermining official efforts to clamp down on capital outflows and prop up the yuan. Demand from investors in Asia’s largest economy, home to most of the world’s bitcoin trades, has fueled a 160% rally versus the dollar over the past year. Huobi and OKCoin said it will take about a month to upgrade systems in line with new PBOC guidelines. BTC China did not give a timing for when any upgrade would be completed. “The Chinese government is worried about capital flight,” said Arthur Hayes, a former market maker at Citigroup who now runs BitMEX, a bitcoin derivatives venue in Hong Kong. “Bitcoin is seen as another way to move money out of China, even though most people trade it for onshore capital appreciation and as another asset in their portfolio.”

A long history of immgrant bans.
• Where US Immigrants Have Come From Over Time (BI)
President Donald Trump’s recent executive orders on immigration may have reignited public debate, but Americans have long harbored anti-immigrant sentiments. One-third of Americans said in a 2016 Pew Research Center survey that immigrants are a “burden on our country because they take our jobs, housing and health care,” and 38% say immigration should be decreased. On the flip side, 59% of Americans say immigrants “strengthen our country because of their hard work and talents” and either think immigration should stay at its present level or increase. Today, immigrants make up 13.5% of the US population — on par with the share in 1860, according to the Migration Policy Institute. The overall number of immigrants coming to the US peaked from 2000-05 at 5 million, and has been declining since then. Here are the major regions where immigrants entering the US have come from since 1820:
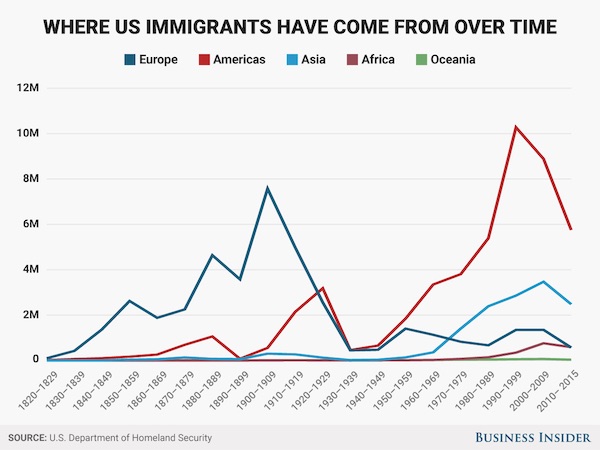
US immigrants were largely of European descent in the 1800s, and started coming from the Americas (largely Mexico) in the 1960s. The sharp decrease in the 1920s is due to Congress passing the Exclusion Act, which set limits on the number of immigrants who could enter the US, based on a quota system of the percentage of nationalities already in the country. Barely anyone from Asia could enter at all. Congress revised the law in 1952, and immigration started to tick up again.

Wonderful story.
• The World According to a Free-Range Short Seller (BBG)
Some of the most respected people in the investing industry say that, dating back to the 1980s, nobody has had a better nose for sniffing out fraud than the 56-year-old Cohodes. He’s exposed suspect accounting at a number of high-profile companies, including the Belgian speech-recognition software developer Lernout & Hauspie, which went bankrupt in 2001 after being valued at about $10 billion, and mortgage lender NovaStar Financial, where his efforts earned him a Harvard Business School case study published in 2013. “I would not want to be his adversary if I was still a criminal today,” says Sam Antar, who was sentenced to six months of house arrest and 1,200 hours of community service for cooking the books at New York consumer-electronics chain Crazy Eddie in one of the largest securities frauds unearthed in the 1980s. “A character like Marc”—the two crossed paths later in his life when both were focused on detecting fraud—“you stay away from.”
And that’s been relatively easy for at least part of the past eight years. In 2008 the hedge fund Cohodes worked at for more than two decades went out of business under controversial circumstances. He maintains that Goldman Sachs, its prime broker, closed it too hastily by making needless margin calls, a claim Goldman disputes. The fallout spurred a bout of what Cohodes likens to post-traumatic stress disorder. “What happened to me would put the average person under,” he says. He retreated to his farm, where he recuperated by spending his days delivering eggs to San Francisco, cheering on the Oakland Raiders, and traveling to see a friend’s rock band, Collective Soul. Besides, the vast majority of stocks were rising because of central bank stimulus, depriving him of ideal opportunities as a short seller.
Now Cohodes is back. His time among the horses and chickens—outside the money management industry—may even have helped him return to the top of his game. Slimmed down and fighting fit, he’s been winning big on a series of short bets against Canadian companies since he made his comeback. Cohodes says he’s been betting against embattled Valeant Pharmaceuticals International since the summer of 2015. Around the same time, he began shorting another debt-laden Canadian drugmaker, Concordia International, which he calls “the poor man’s Valeant.” Both stocks lost most of their value last year. Cohodes says he’s committed to exposing companies that he believes may be ripping off ordinary, unwary investors—“Joe Six-pack,” as he puts it. “Legitimate companies don’t know who the f— I am. And they don’t care,” Cohodes says. “The bad guys? They know. And they do care.”
And he’ll go to great lengths to chase them down: dumpster-diving to find clues of wrongdoing, lambasting enemies on Twitter (where his rambunctious character is on full display), and hotfooting it across Las Vegas to check whether new business offices reported by NovaStar were real. (They weren’t, according to Cohodes; one was a private home, another a massage parlor.) “I’m a pretty driven guy,” he says.

Still trying to find a good report on this, it’s frustrating. One detail: radiation levels are measured at a certain distance from the source, having some suggest real levels at that source could be 5000 sievert.
• Radiation at Japan’s Fukushima Reactor Is Now at ‘Unimaginable’ Levels (Fox)
The radiation levels at Japan’s crippled Fukushima nuclear power plant are now at “unimaginable” levels. Adam Housley, who reported from the area in 2011 following the catastrophic triple-meltdown, said this morning that new fuel leaks have been discovered. He said the radiation levels – as high as 530 sieverts per hour – are now the highest they’ve been since 2011 when a tsunami hit the coastal reactor. “To put this in very simple terms. Four sieverts can kill a handful of people,” he explained.
He said that critics, including the U.S. military in 2011, have long questioned whether Tokyo Electric Power Co. (TEPCO) and officials have been providing accurate information on the severity of the radiation. TEPCO maintains that the radiation is confined to the site and not a risk to the public. It’s expected to take at least $300 billion and four decades to fix it. Housley said small levels of radiation are still being detected off the coasts of California and Oregon and scientists fear it could get worse. “The worry is with 300 tons of radioactive water going into the Pacific every day, what is that doing to the Pacific Ocean?” said Housley. He added that critics are now questioning whether the radiation has been this severe all along.

Keep paying attention.
• Ground-Breaking Research Uncovers New Risks of GMOs, Glyphosate (NGR)
Within just a few weeks, two studies were published in the peer-reviewed journal Scientific Reports that cast new doubts on the safety of genetically modified foods and glyphosate herbicide. The first found that a genetically modified corn, NK 603, was not substantially equivalent to a non-GMO counterpart, which is contrary to claims of GMO proponents. The second study found that glyphosate, the main ingredient in Monsanto’s Roundup herbicide, can cause a serious liver disease at doses thousands of times lower than that allowed by law. Dr. Michael Antoniou, Head of the Gene Expression and Therapy Group at King’s College London in the United Kingdom, led the ground-breaking research.
The main focus of research within Dr. Antoniou’s group is the study of the molecular mechanisms of the regulation of gene function. He has used these discoveries to develop efficient gene expression systems for efficacious and safe biotechnological applications, including gene therapy. More recently, Dr. Antoniou has expanded his research program to include using molecular profiling “omics” methods in evaluating the safety of foods derived from GMO crops, low dose exposure from their associated pesticides, and other chemical pollutants. Dr. Antoniou is also a co-author of GMO Myths and Truths, an evidence-based examination of the claims made for the safety of genetically modified crops and foods.

Too many parties involved see misery as being a positive for their goals. Very few aim at actually solving the problems.
• ‘No One Accepts Responsibility’: Thirteen Refugees Dead In Greece (IRR)
The IRR has been trying to ascertain the circumstances in which thirteen refugees and migrants died since April 2016 in Greece, with six of these deaths occurring in hotspots. In only one of these cases are we in a position to provide the full name of the deceased; the only available identifier is nationality. At least six of the dead were refugees from Syria, including Syrian Kurds, three were from Afghanistan. Five of the dead were living at the hotspot at Moria, on the Greek island of Lesbos where over 3,000 refugees are accommodated, well above stated capacity. Those who died here did so because the heaters and gas canisters they had obtained in order to keep warm or cook food were faulty, or used in dangerous situations. An Iraqi man died of a cardiac arrest at a hotspot in Samos (refugee population around 1,800 in a place designed for less than half that number).
Since the Idomeni makeshift migrant camp close to the Macedonian border was cleared by police in May 2016, sub-standard government refugee camps lacking basic amenities have been set up, with three of the dead living in such facilities around Thessaloniki. The oldest to die was a grandmother of 66, the youngest a two-month-old baby. There are three children amongst the dead. The remaining two deaths we have recorded were of men who died of hypothermia after having crossed from Turkey via the river Evros. It’s likely that they made the perilous crossing in order to avoid being detained in the hotspots on the Greek islands. Autopsy results are shrouded in secrecy. Nevertheless, the facts speak for themselves. Overcrowded, unprotected and dangerous conditions are all symptoms of institutional neglect. The simple truth is that the securitisation of asylum policy has come at the expense of refugee protection, as well as basic human rights.
[..] The deaths that have occurred over the winter have at least been reported in the media, partly because human rights defenders, wary of the positive communication strategy of the UNHCR and the EU, issued a number of press releases. Even so, officialdom does not appear over- anxious to investigate. What is particularly worrying is the secrecy shrouding autopsy results, which, if left unchallenged, will ensure that completely avoidable deaths such as these become the new normal. Philippa Kempson, of the Eftalou/ Molovos refugee support group on Lesbos, told IRR News of her fear that the ‘deaths could be subject to cover ups’, and her particular concern that ‘the “accidental” deaths in Moria still do not have a conclusive cause of death’. She also drew attention to the escalation in suicide attempts, particularly amongst unaccompanied minors, at Moria. ‘No one accepts responsibility for what is going on, just a circle of blame,’ she said.
In fact, evading accountability is hard-wired into the way refugee reception is organised in Greece, as there is no central authority responsible for the camps’ administration but a number of actors – a mixture of EU officials, the Greek army and other Greek institutions, the Red Cross and the UNHCR. This means that when anything goes wrong, the various actors end up blaming each other – something academics refer to as a process of distanciation, in which complex chains of responsibility make it difficult to connect cause (ie, government policies) with effect (ie, border-related deaths). Guardian journalist Patrick Kingsley made a similar point in his recent exposé of how a multi-million pound fund administered by the EU’s aid department ECHO, implemented in Greece by UNHCR and aimed at creating adequate facilities to protect refugees from the winter, has been mishandled. Kingsley points out that as ‘no single actor has overall control of all funding and management decisions in the camps, this has allowed most parties to distance themselves from blame’.









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle February 10 2017