
Russell Lee Migrant family in trailer home near Edinburg, Texas Feb 1939

Very much in line with what I’ve been saying. China’s dollar reserves are plunging but its dollar-denominated debt soars. A devaluation looks inevitable, and it has to be big because having to do a second one is the worst of all worlds.
• China Approaches Maxi-Devaluation (DR)
The Institute of International Finance reports that capital outflows swelled to a record $725 billion last year. China’s desperate to keep that capital at home to support the economy. And it’s been burning holes in its dollar reserves to support the yuan. Selling its dollar holdings to buy yuan puts footings under the yuan. Makes it more attractive. Halts the capital flight. But the fire can only burn so long before it torches the remaining reserves… A $2.99 trillion war chest or a $3 trillion war chest sounds like plenty. But as Jim Rickards explained recently, it’s not nearly as much as it sounds: “Of the $3 trillion that China has left, only $1 trillion of that is a liquid. One trillion is invested in hedge funds, private equity funds, gold mines, et cetera. That money is not liquid. It cannot be used to support the currency, so remove a trillion.”
That leaves $2 trillion: “Another trillion has to be held on what’s called a precautionary reserve to bail out their banking system. The Chinese banks are completely insolvent. That system is going to need to be bailed out sooner rather than later.” Scratch another trillion: “That leaves only $1 trillion of the original $4 trillion in liquid form. The problem is that capital flight is continuing at a rate of $1 trillion per year, so China will be devoid of usable liquid assets by late 2017.” So now what? Jim has warned that Trump could soon label China a currency manipulator. That has vast implications, as you’ll see. But it’s not just Mr. Rickards. We learn today that a group of analysts at Deutsche Bank is piping an identical tune:
“Sometime in the next few weeks, President Trump or his Treasury secretary may declare China a currency manipulator and propose penalties including tariffs on some or all imports from China unless it ceases this and other alleged unfair trade policies.” And that would invite Chinese retaliation. Tariffs of their own on American goods. And then… China might reach for the nuclear option — a “maxi-devaluation.” Jim again: “We know what Donald Trump has said. China’s going to be labeled a currency manipulator. That’s like firing the first shot in a major currency war. We could see tariffs imposed in both directions, shots in retaliation, a financial war… China will retaliate with what I call their nuclear option, which is a maxi-devaluation of the Chinese yuan.”
If China’s going to be branded a currency manipulator and have its exports slapped with a steep tariff, why not go ahead and devalue? One, it would make Chinese exports more competitive. Two, China could stop depleting its dollar reserves. It would no longer have to burn through dollars to boost the yuan. And three, it could actually halt the capital outflows. How? Many Chinese fear the government will impose stricter capital controls as the situation worsens. So they move their capital out of the country in advance. That brings greater fear of capital controls. And more incentives for capital flight. It’s a vicious cycle. But if China devalues all at once, say, 25% or 30%, it sends this message: The worst is over. You may as well keep your capital in China. There will be no further devaluation.

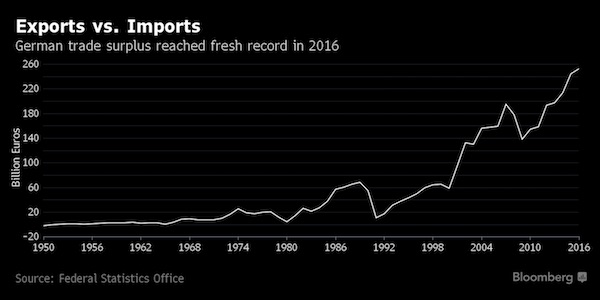
German trade surplus is bigger than the entire Greek economy. That is how the European Union ‘functions’.
• German Exports Break Record as Trump Targets Trade Balance (BBG)
Germany posted a record trade surplus in 2016, which may further fuel accusations by the Trump administration that Europe’s largest economy is exploiting a “grossly undervalued” euro. Exports climbed 1.2% last year to 1.2 trillion euros ($1.3 trillion), the Federal Statistics Office in Wiesbaden reported on Thursday, while imports rose 0.6% to 954.6 billion euros. That left Germany’s trade surplus at 253 billion euros in 2016. The report feeds into a debate kicked off late last month by Peter Navarro, the head of the White House National Trade Council, who told the Financial Times that Germany is gaining an unfair advantage over the U.S. and other nations with a weak currency.
ECB President Mario Draghi, Chancellor Angela Merkel and Finance Minister Wolfgang Schaeuble all rejected the claim that came on the back of President Donald Trump’s promises of renegotiating or tearing up free-trade treaties. “The fact that the German economy is exporting much more than it imports is a source of concern and no reason to be proud” because weak imports are the result of a lack of investment, Marcel Fratzscher, head of the DIW economic institute in Berlin, said in an e-mailed statement. “The record surplus will continue to fuel conflict with the U.S. and within the EU.” Exports fell 3.3% in December from the previous month, the report said, while imports were unchanged. The country’s current-account surplus reached 266 billion euros in 2016.

Zombies on life support.
• The Blood Bath Continues In The US Major Oil Industry (SRSrocco)
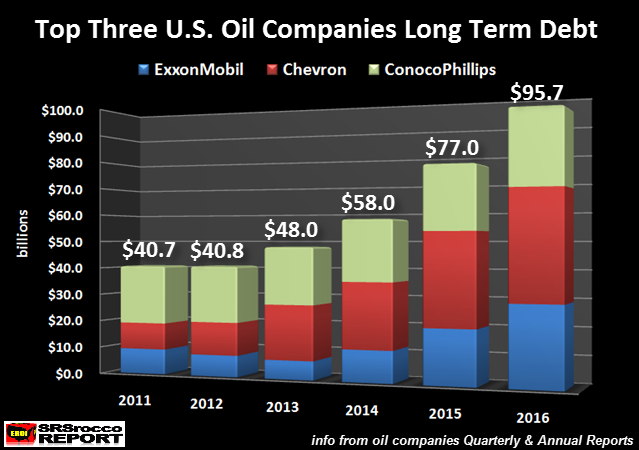
The carnage continues in the U.S. major oil industry as they sink further and further in the RED. The top three U.S. oil companies, whose profits were once the envy of the energy sector, are now forced to borrow money to pay dividends or capital expenditures. The financial situation at ExxonMobil, Chevron and ConocoPhillips has become so dreadful, their total long-term debt surged 25% in just the past year. [..] While the Federal Government could step in and bail out BIG OIL with printed money, they cannot print barrels of oil. Watch closely as the Thermodynamic Oil Collapse will start to pick up speed over the next five years. According to the most recently released financial reports, the top three U.S. oil companies combined net income was the worst ever. The results can be seen in the chart below:
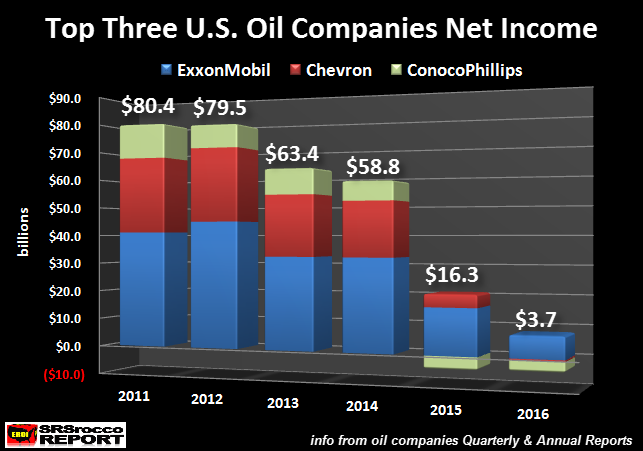
In 2011, ExxonMobil, Chevron and Conocophillips enjoyed a combined $80.4 billion in net income profits. ExxonMobil recorded the highest net income of the group by posting a $41.1 billion gain, followed by Chevron at $26.9 billion, while ConocoPhillips came in third at $12.4 billion. However, the rapidly falling oil price, since the latter part of 2014, totally gutted the profits at these top oil producers. In just five short years, ExxonMobil’s net income declined to $7.8 billion, Chevron reported its first $460 million loss while ConocoPhillips shaved another $3.6 billion off its bottom line in 2016. Thus, the combined net income of these three oil companies in 2016 totaled $3.7 billion versus $80.4 billion in 2011. Even though these three oil companies posted a combined net income profit of $3.7 billion last year, their financial situation is much worse when we dig a little deeper.
We must remember, net income does not include capital expenditures or dividend payouts. If we look at these oil companies Free Cash Flow, they have been losing money for the past two years. Their combined free cash flow fell from a healthy $46.3 billion in 2011 to a negative $8.7 billion in 2015 and a negative $7.3 billion in 2016. Now, their free cash flow would have been much worse in 2016 if theses companies didn’t reduce their CAPEX spending by nearly a whopping $20 billion.
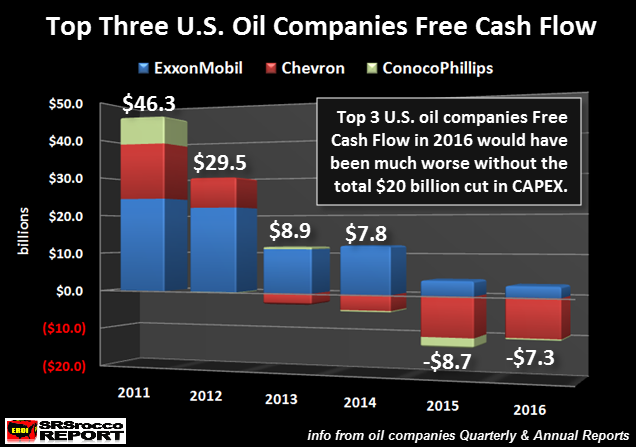
[..] the free cash flow minus dividend payouts provides us evidence that these oil companies have been seriously in the RED since 2013, not just the past two years displayed in the Free Cash Flow chart. As we can see, the group’s free cash flow minus dividends was a negative $32.8 billion in 2015 and a negative $29 billion last year. Of course, these three companies may have sold some financial investments or assets to reduce these negative values, but a company can’t stay in business for long by selling assets that it would need to use to produce oil in the future. So, what has falling free cash flow and dividends done to ExxonMobil, Chevron and ConocoPhillips long-term debt? You guessed it… it skyrocketed:

Does this sound like a good thing? : “..the environment remains highly favorable for junk-rated businesses..”
• Record $1 Trillion in US Junk Debt to Mature in Next 5 Years (WSJ)
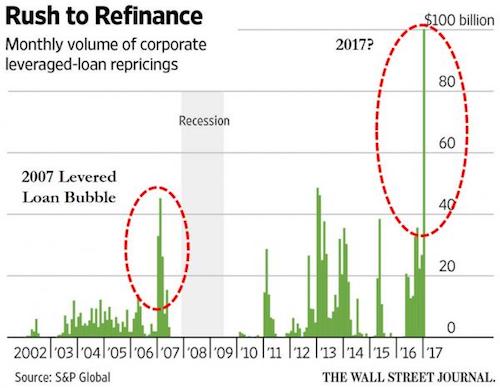
More than $1 trillion of junk-rated corporate debt is slated to mature over the next five years, creating a stiff challenge for heavily-indebted businesses if the market for riskier debt were to deteriorate, according to a new report from Moody’s Investors Service. The $1.063 trillion in maturing debt is the highest ever recorded by the ratings firm over a five-year period and also includes the highest single-year volume in 2021, when $402 billion of junk-rated corporate debt is scheduled to come due. Overall, a little more than $2 trillion of corporate debt is scheduled to mature by 2021 when factoring in $944 billion of investment-grade bonds. But it is the volume of junk-rated debt that could be of greater significance, given that investment-grade companies rarely have trouble extending debt maturities even in more difficult conditions.
As it stands, the environment remains highly favorable for junk-rated businesses, making it easy for most to access funds at their choosing. The average junk-bond yield was 5.72% Tuesday, the lowest level since September 2014. Buoyed by rising interest rates, junk-rated bank loans, which feature floating-rate coupons, have performed especially well of late, enabling U.S. companies to refinance $100 billion of loans in January, the largest monthly total in at least a decade, according to data from S&P Global Still, conditions can change quickly in the leveraged finance markets. A year ago, amid concerns that the U.S. was heading toward another recession, the average junk bond yield was nearly 10%, raising the risk that many borrowers would be unable to refinance bonds with looming maturities, hastening their descent into bankruptcy.

“..you might have to ask the question if what comes next could possibly be worse than what’s happening now.”
• Trump EU Envoy Says Greece Is Now More Likely To Leave The Euro (G.)
Donald Trump’s administration has put itself on a fresh collision course with the European Union after the president’s candidate to be ambassador in Brussels said Greece should leave the euro and predicted the single currency would not survive more than 18 months in its present form. Days after being accused of “outrageous malevolence” towards the EU for publicly declaring that it “needs a little taming”, Ted Malloch courted fresh controversy by saying Greece should have left the eurozone four years ago when it would have been “easier and simpler”. Malloch made his comments as financial markets began to take fright at the possibility of a fresh Greek debt crisis later this year. Shares fell and interest rates on Greek debt rose after it emerged that the EU was at loggerheads with the IMF over whether to give the country more generous debt relief.
“Whether the eurozone survives I think is very much a question that is on the agenda,” he told Greek Skai TV’s late-night chat show Istories. “We have had the exit of the UK, there are elections in other European countries, so I think it is something that will be determined over the course of the next year, year and a half. “Why is Greece again on the brink? It seems like a deja vu. Will it ever end? I think this time I would have to say that the odds are higher that Greece itself will break out of the euro,” Malloch said. The stridently Brexit-supporting businessman, who has yet to be confirmed as the US president’s EU ambassador and is seen by Brussels as a provocative nominee for the post, said he wholeheartedly agreed with Trump’s tweet from 2012 saying Greece should return to the drachma, its former currency.
“I personally think [Trump] was right. I would also say that this probably should have been instigated four years ago, and probably it would have been easier or simpler to do,” Malloch said in the interview with the show’s chief anchor, Alexis Papahelas. Seven years of arduous austerity – the price of the international bailout – had been so bad for the country that it was questionable whether what came next could possibly be worse, Malloch said. In the third bailout in as many years, Greece has lost more than 25% of its GDP due to austerity-fuelled recession, the biggest slump of any advanced western economy in modern times. Without further emergency funding from its €86bn rescue programme, Athens could face a default in July when debt repayments of about €7bn to the European Central Bank mature.
[..] The renewed focus came as the IMF revealed its board was split over how far spending cuts in the country should go, raising fresh doubts over the IMF’s participation in rescue plans for the struggling Greek economy. The IMF believes that the budgetary demands being imposed on Greece by Europe are unreasonable and that the country’s debts will hit 275% of national income by 2060 without fresh assistance. Malloch said: “I have travelled to Greece, met lots of Greek people, I have academic friends in Greece and they say that these austerity plans are really deeply hurting the Greek people, and that the situation is simply unsustainable. So you might have to ask the question if what comes next could possibly be worse than what’s happening now.” The biggest unknown was not a euro exit, but the chaos it would likely engender as Greece moved to a new currency, he said.

French revolution. Ironic that the central bank governor makes Le Pen’s point while trying to ‘push back’: “The Bank of France belongs to all French and is at the service of a French asset – our currency.” That’s exactly Le Pen’s point, it’s just that she doesn’t see the euro as ‘our currency’. For her, that means the franc.
• Le Pen Aide Briefed French Central Banker on Plan to Print Money (BBG)
Presidential candidate Marine Le Pen’s chief economic adviser Bernard Monot met with Bank of France Governor Francois Villeroy de Galhau in September and set out her party’s plans to take control of the central bank and use it to finance government spending. The meeting took place on the sidelines of Villeroy de Galhau’s public hearing in Brussels at the economic and monetary committee of the European Parliament, Monot, who also sits on the panel, said in a Feb. 4 interview. The central bank has become one of Le Pen’s key targets as she fleshes out her plans for taking control of the French economy and leaving the euro. She intends to revoke the Bank of France’s independence and use it to finance French welfare payments and service the government’s debts after abandoning the European monetary union.
While the National Front leader is ahead in polling for the first ballot on April 23, she’s still an outsider to become the next president because of the two-round system which requires broad-based support to win the run-off two weeks later. Villeroy de Galhau, who also sits on the governing council of the ECB, pushed back against her proposals in an interview on BFM television Thursday, though he didn’t mention her specifically. “It’s important that we have institutions and a currency that straddle daily turbulence,” the governor said. “The Bank of France belongs to all French and is at the service of a French asset – our currency.” The spread between French 10-year bonds and similarly dated German debt was the widest in more than four years earlier this week, as political uncertainty deterred investors. Villeroy de Galhau described the move as “temporary tension.”

The British economy will be healthier when its dependence on banking goes down. Not richer, but healthier. For instance, home prices can finally fall, a much needed development. There’s nothing good about a one-trick pony.
• Global Banks In London To Relocate $1.9 Trillion Of Assets After Brexit (BBG)
Global banks in London may have to relocate 1.8 trillion euros ($1.9 trillion) of assets to the continent after Britain withdraws from the European Union, putting as many as 30,000 U.K. jobs at risk, according to Brussels-based research group Bruegel. The assets potentially on the move represent 17% of the U.K. banking system, Bruegel said in a report published Wednesday. Based on discussions with market participants, the researchers estimate that 35% of wholesale banking activity in London can be attributed to dealings with customers inside the EU. Financial firms will have to move that business to countries inside the trading bloc after the U.K. leaves the EU in 2019, likely spelling the end of passporting, where firms seamlessly service the rest of the single market from their London hubs.
Banks, and their clients, are most concerned about a “cliff edge” Brexit, whereby all access is cut off after two years. To safeguard against that loss of access, banks are already in discussions with European regulators about setting up new bases inside the EU and have said they will start the process of moving people within weeks of the government triggering Brexit talks, expected in March. “At a minimum, it is expected that the new EU27-based entities will need to have autonomous boards, full senior management teams, senior account managers and traders, even though much of the back-office might stay in London or elsewhere in the world,” researchers led by Andre Sapir said in the report.
London-based firms will likely have to move about 10,000 employees into these new EU entities, Breugel estimates. An additional 18,000 to 20,000 people in associated professions, such as lawyers, consultants and accountants, may also have to relocate. Bruegel’s estimates are at the conservative end of the spectrum. TheCityUK industry lobby group forecasts as many as 35,000 banking jobs could be relocated, rising to 70,000 when including associated financial services. London Stock Exchange CEO Xavier Rolet has said Brexit would likely see 232,000 jobs leaving the U.K.

Both Danielle DiMartino Booth and Ann Pettifor have new books coming out. We need girl power, badly.
• Former Fed Staffer Says Central Bank Is Under the Thumb of Academics (WSJ)
The Federal Reserve is dominated by academics who don’t know how finance and the economy really work, according to a former Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas staffer in her new book. Danielle DiMartino Booth, an adviser to Richard Fisher when he was Dallas Fed president, says the economists who control most of the central bank’s seats of power filter their decision-making through theoretical models. That led the institution to miss the forces that created the financial crisis, and then adopt the wrong policies to put the economy back on track, she says. Ms. Booth makes her case in a book called “Fed Up: An Insider’s Take on Why the Federal Reserve Is Bad for America,” set to be published Tuesday. Her book comes as other Fed critics are pushing for more diversity at the central bank.
They often focus on the dearth of women and minorities among the top officials, but some have said a broader range of educational and professional backgrounds also would widen the central bank’s perspective. Of the 17 Fed governors and regional bank presidents, 16 are white, 13 are men, and 10 have a Ph.D. in economics. Ms. Booth’s arguments echo those of her former boss, who led the Dallas Fed from 2005 to 2015, and frequently voted against the central bank’s aggressive stimulus efforts during and after the financial crisis. “If you rely entirely on theory, you are not going to conduct the right policy, because policies have consequences” that in many cases people with real-world experience are particularly well-suited to spot, Mr. Fisher said in an interview late last year.
Mr. Fisher hired Ms. Booth, a former Wall Street trader turned financial journalist, to work at the Dallas Fed in 2006 on the strength of columns she had written warning about the state of the housing market and financial markets. She eventually rose to be his appointed eyes and ears on financial markets. In her book, Ms. Booth describes a tribe of slow-moving Fed economists who dismiss those without high-level academic credentials. She counts Fed Chairwoman Janet Yellen and former Fed leader Ben Bernanke among them. The Fed’s “modus operandi” is defined by “hubris and myopia,” Ms. Booth writes in an advance copy of the book. “Central bankers have invited politicians to abdicate leadership authority to an inbred society of PhD academics who are infected to their core with groupthink, or as I prefer to think of it: ‘groupstink.’”
“Global systemic risk has been exponentially amplified by the Fed’s actions,” Ms. Booth writes, referring to the central bank’s policies holding interest rates very low since late 2008. “Who will pay when this credit bubble bursts? The poor and middle class, not the elites.” Fed officials have defended their crisis-era stimulus policies, saying they lowered unemployment and helped the housing market recover. Opponents feared near-zero interest rates would cause excessive inflation and dangerous market bubbles, neither of which has happened. Ms. Booth also is among the Fed critics who see a worrisome revolving door between the central bank and the financial firms it regulates. She points to New York Fed President William Dudley, a former Goldman Sachs chief economist, as an illustration of a “codependent” relationship between the central bank and markets. He and three other regional Fed bank presidents have worked for or had associations with Goldman Sachs. With this in mind, she writes, “Goldman has positioned players on the Fed’s chessboard.”

“Italy was the second most pro-euro nation after Luxembourg, with 79% expressing a positive opinion.” But now: “only 41% said the euro was “a good thing”..”
• Out of Pocket, Italians Fall Out of Love With The Euro (R.)
When the Italian central bank’s deputy governor joined a radio phone-in show last week, many callers asked why Italy didn’t ditch the euro and return to its old lira currency. A few years ago such a scenario, that Salvatore Rossi said would lead to “catastrophe and disaster”, would not have been up for public discussion. Now, with the possibility of an election by June, politicians of all stripes are tapping into growing hostility towards the euro. Many Italians hold the single currency responsible for economic decline since its launch in 1999. “We lived much better before the euro,” says Luca Fioravanti, a 32-year-old real estate surveyor from Rome. “Prices have gone up but our salaries have stayed the same, we need to get out and go back to our own sovereign currency.”
The central bank is concerned about the rise in anti-euro sentiment, and a Bank of Italy source told Reuters Rossi’s appearance is part of a plan to reach out to ordinary Italians. Few Italians want to leave the European Union, as Britain chose to do in its referendum last year. Italy was a founding EU member in 1957 and Italians think it has helped maintain peace and stability in Europe. And the ruling Democratic Party (PD) is pro-euro and wants more European integration though it complains that the fiscal rules governing the euro are too rigid. But the three other largest parties are hostile, in various degrees, to Italy’s membership of the single currency in its current form. The PD is due to govern until early 2018, unless elections are called sooner. The PD’s prospects of victory have waned since its leader Matteo Renzi resigned as premier in December after losing a referendum on constitutional reform, and polls suggest that under the current electoral system no party or coalition is likely to win a majority.
Italians used to be among the euro’s biggest supporters but a Eurobarometer survey published in December by the European Commission showed only 41% said the euro was “a good thing”, while 47% called it “a bad thing.” In the Eurobarometer published in April 2002, a few months after the introduction of euro notes and coins, Italy was the second most pro-euro nation after Luxembourg, with 79% expressing a positive opinion. Italy is the only country in the euro zone where per capita output has actually fallen since it joined the euro, according to Eurostat data. Its economy is still 7% smaller than it was before the 2008 financial crisis, and youth unemployment stands at 40%.

They literally don’t know what they’re doing: “badly devised and even more badly executed”
• Italy’s “Bitter” Bank Rescue Tsar Bemoans Strategy Vacuum (R.)
The head of Italy’s bank-bailout fund said on Tuesday the country lacked a clear strategy for shifting 356 billion euros ($381 billion) in problem loans. In an extraordinary outburst from a man picked by Rome to help tackle the problem, Alessandro Penati, whose boutique asset management firm was chosen to raise private funds for struggling banks, said he felt “bitter and disillusioned”. His comments exposed tensions within the banking sector over Italy’s rescue efforts. “There is no clear vision of the problem and no strategy,” Penati said at a financial conference in Milan, suggesting that he was virtually working alone on rescues that had revealed “horror stories” within some banks. “There is simply a reaction to a problem and this has been the main difficulty for me over these past few months – I had nobody to relate to.”
The Atlante fund, created 10 months ago following pressure from the government, gathered 4.25 billion euros from around 70 mostly private investors, including Italy’s healthier lenders, to buy up bad loans and invest in weaker banks. But the fund’s investors are already making big writedowns on the value of their stakes in Atlante, which promised them annual returns of 6%. The fund faces ever greater demands for capital and no investors willing to stump up more money. In December, Penati’s plan to buy into Italy’s biggest-ever sale of bad debts – 28 billion euros worth of loans written by struggling bank Monte dei Paschi di Siena (BMPS.MI) — fell apart when the bank failed to find any other major investors.
Penati, a former economist who set up Milan-based Quaestio Capital Management, said the sale had collapsed because it had been tied to a capital raising that had been “badly devised and even more badly executed”. Monte dei Paschi (MPS) is now to be rescued by the state. “It would no longer make sense for Atlante to play a role now. The point is that state intervention is considered a way to solve all problems, but it isn’t … MPS’s bad loan problem remains and how they are going to solve it – I don’t know.”

Drilling has reportedly restarted. How bad can this get?
• Activists Plan Emergency Actions Across The Country To Protest DAPL (IC)
On Tuesday the Army Corps of Engineers gave notice to Congress that within 24 hours it would grant an easement allowing Energy Transfer Partners to move forward with construction on the Dakota Access Pipeline, which North Dakota’s Standing Rock Sioux tribe and thousands of allies have attempted to halt out of concern for water contamination, dangers to the climate, and damage to sites of religious significance to the tribe. The federal government dismissed those concerns in its filing. “I have determined that there is no cause for completing any additional environmental analysis,” Douglas Lamont, the acting assistant secretary of the Army, wrote in a memorandum. “The COE has full responsibility to take the reasonable steps necessary to execute the requested easement.”
Two weeks earlier, after only four days in office, Trump signed two memoranda instructing federal officials to ram forward approvals for the Dakota Access and Keystone XL pipelines, both of which had been halted by the Obama administration after people mobilized across the U.S. to stop them. On Dakota Access, the Army Corps did just what the president demanded, waiving the standard 14-day waiting period before such a permit becomes official. The tribe has been left with just one day to rally a legal response. Lawyers for the tribe say they will argue in court that an environmental impact statement, mandated by the Army Corps under Obama, was wrongfully terminated. They will likely request a restraining order while the legal battle ensues. Pipeline company lawyers have said that it would take at minimum 83 days for oil to flow from the date that an easement is granted.
Although the tribal government once supported the string of anti-pipeline camps that began popping up last spring, leaders have since insisted that pipeline opponents go home and stay away from the reservation. “Please respect our people and do not come to Standing Rock and instead exercise your First Amendment rights and take this fight to your respective state capitols, to your members of Congress, and to Washington, D.C.,” tribal chairman Dave Archambault said in a statement. Still, the easement announcement is already activating pipeline opponents to return. A “couple thousand people” are headed back to the camps, including contingents of veterans, said former congressional candidate Chase Iron Eyes, a member of the tribe, in a video posted to Facebook.

Boy, what a moral void.
• UK Government Backtracks On Pledge To Take Syrian Child Refugees (Ind.)
Hours before the final vote on the triggering of Article 50 the government quietly announced it would allow just 350 unaccompanied Syrian children to come to the UK, thousands short of the figure suggested by government sources last year. The statement from Immigration Minister Robert Goodwill said local authorities indicated “have capacity for around 400 unaccompanied asylum-seeking children until the end of this financial year” and said the country should be “proud” of its contribution to finding homes for refugees. Liberal Democrat leader Tim Farron called the decision “a betrayal of British values”. “Last May, MPs from all parties condemned the Government’s inaction on child refugees in Europe, and voted overwhelmingly to offer help to the thousands of unaccompanied kids who were stranded without their families backed by huge public support,” Mr Farron said.
“Instead, the Government has done the bare minimum, helping only a tiny number of youngsters and appearing to end the programme while thousands still suffer. At the end of December last year the Government had failed to bring a single child refugee to the UK under the Dubs scheme from Greece or Italy where many of these children are trapped.” Ministers introduced the programme last year after coming under intense pressure to give sanctuary to lone children stranded on the continent. Calls for the measure were spearheaded by Lord Dubs, whose amendment to the Immigration Act requires the Government to “make arrangements to relocate to the UK and support a specified number of unaccompanied refugee children from other countries in Europe”.

“This is not about supporting Bashar. This is about ending the war in Syria. We can’t continue like this, supporting regime change.”
• My Country Was Destroyed (Tima Kurdi)
I am the aunt of Alan Kurdi, the Syrian boy who tragically drowned September 2, 2015. The devastating image of my 2-year old nephew’s lifeless body, lying face-down on the beach in Turkey, was all over the news across the world. Two weeks ago, I got home from work and my husband showed me a video of Tulsi Gabbard talking about her visit to my home country of Syria. The things she was saying about the United States policy of regime change and how the West and the Gulf countries are funding the rebel groups who wind up with the terrorists are true. I was shocked because it’s something no other U.S. politician has the courage to say. Regime change policy has destroyed my country and forced my people to flee. Tulsi’s message was exactly what I have been trying to say for years, but no one wants to listen.
I live in Canada now, but I was born and raised in Damascus, Syria. Growing up, our country was peaceful, beautiful and safe. Our neighbors were Christian, Muslim, Sunni, Shia; all kinds of religion and color. We all lived together and respected each other. Syria is a secular country. In 2011, the war started in Syria. Most of my family was still in Damascus. I was always in close contact with them and talked to them on the phone on a daily basis. For a year, I heard many tragic stories of people, friends, and neighbors who I grew up with having died in this war. Ultimately, my family had to flee to Turkey. I did what everyone would do for their own family to help, I sent them money and I listened to their struggles to survive as refugees in Turkey.
In 2014, I went to Turkey to visit my family and tried to help them. What I saw and experienced is not what we all saw in the news or we heard in the radio. It was worse than I could ever have imagined. I saw people in the streets without homes, without hope. Children were hungry, begging for a piece of bread. I heard many heartbreaking stories from other refugees who were suffering so much and many who had lost loved ones in the war. After I returned to Canada, I decided I wanted to bring my family here as refugees, but I couldn’t get them approved to come in. Eventually, my brother Abdullah and his wife Rehana, like thousands of Syrians, decided they had to take the risk and trust a smuggler they thought would bring them to freedom, safety, and hope. In September 2, 2015, I heard the tragic news that my sister-in-law Rehana and her two sons drowned crossing from Turkey to Greece.
The image of my two year old nephew Alan Kurdi lying face down on a Turkish beach was all over the media across the world. It was the wake up call to the world. Enough suffering. Enough killing. And most importantly, it was my wake up call. [..] Like me, many Syrians are encouraged that Tulsi met with President Bashar Assad in Syria. Tulsi recognizes that we need to talk to him because a political solution is the only way to restore peace in Syria. If the West keeps funding the rebels, we will see more people flee, more bloodshed, and more suffering. My people have suffered for at least six years. This is not about supporting Bashar. This is about ending the war in Syria. We can’t continue like this, supporting regime change. We have seen it before in Iraq, in Libya, and look what happened to them.









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle February 9 2017