
Elliott Erwitt Jack Kerouac 1953

The reality of -personal- debt.
• Nearly 40% May Default On Their Student Loans By 2023 (Brookings)
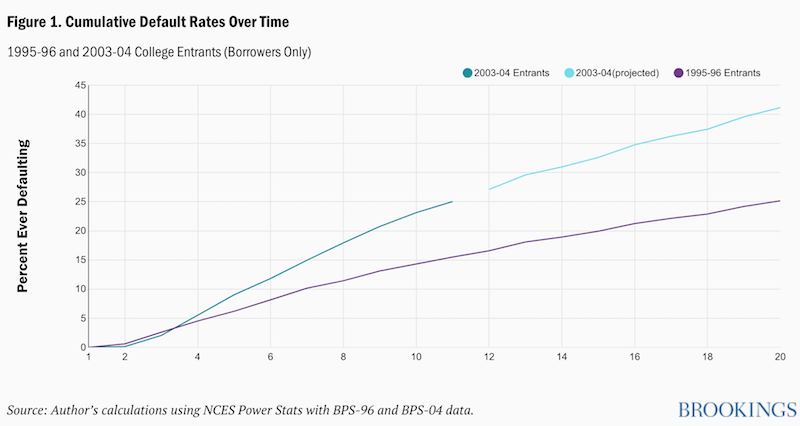
The best prior estimates of overall default rates come from Looney and Yannelis (2015), who examine defaults up to five years after entering repayment, and Miller (2017), who uses the new BPS-04 data to examine default rates within 12 years of college entry. These two sources provide similar estimates: about 28 to 29% of all borrowers ultimately default. But even 12 years may not be long enough to get a complete picture of defaults. The new data also allow loan outcomes to be tracked for a full 20 years after initial college entry, though only for the 1996 entry cohort. Still, examining patterns of default over a longer period for the 1996 cohort can help us estimate what to expect in the coming years for the more recent cohort.
If we assume that the cumulative defaults grow at the same rate (in percentage terms) for the 2004 cohort as for the earlier cohort, we can project how defaults are likely to increase beyond year 12 for the 2004 cohort. To compute these projections, I first use the 1996 cohort to calculate the cumulative default rates in years 13-20 as a percentage of year 12 cumulative default rates. I then take this percentage for years 13-20 and apply it to the 12-year rate observed for the 2004 cohort. So, for example, since the 20-year rate was 41% higher than the 12-year rate for the 1996 cohort, I project the Year 20 cumulative default rate for the 2004 cohort is projected to be 41% higher than its 12-year rate.
Figure 1 plots the resulting cumulative rates of default relative to initial entry for borrowers in both cohorts, with the data points after year 12 for the 2003-04 cohort representing projections. Defaults increase by about 40% for the 1995-96 cohort between years 12 and 20 (rising from 18 to 26% of all borrowers). Even by year 20, the curve does not appear to have leveled off; it seems likely that if we could track outcomes even longer, the default rate would continue to rise. For the more recent cohort, default rates had already reached 27% of all borrowers by year 12. But based on the patterns observed for the earlier cohort, a simple projection indicates that about 38% of all borrowers from the 2003-04 cohort will have experienced a default by 2023.

The reality of central banking.
• 3 Years After Currency Shock, Swiss Central Bank Can’t Get Back To Normal (R.)
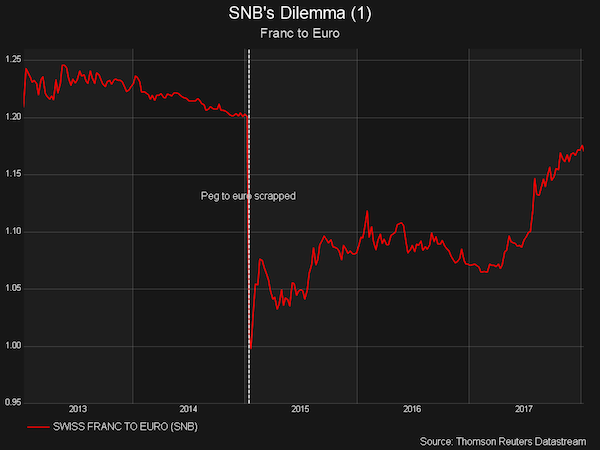
Three years after the Swiss National Bank shocked currency markets by scrapping the franc’s peg to the euro, it faces the toughest task of any major central bank in normalising ultra-loose monetary policy. If it raises rates, the Swiss franc strengthens. If it sells off its massive balance sheet, the Swiss franc strengthens. If a global crisis hits, the Swiss franc strengthens. And the abrupt decision to scrap the currency peg on Jan. 15, 2015, means it still has credibility issues with financial markets. “The SNB will most probably be one of the last central banks to change course, and it will take years or even decades for monetary policy to return to ‘normal’,” said Daniel Rempfler, head of fixed income Switzerland at Swiss Life Asset Managers.

The Bank of Japan illustrated the problem of reducing expansive policy when a small cut to its regular bond purchases sent the yen and bond yields higher. The scrapping of the cap – which sought to keep the franc at 1.20 to the euro to protect exporters and ward off deflationary pressure – sent it soaring. On the day of the announcement it went to 0.86 francs buying a euro before easing in later days. Although it weakened last year, SNB Chairman Thomas Jordan said in December it was too early to talk about normalising policy. The SNB has to wait for the European Central Bank to start raising interest rates before it can start hiking its own policy rate from minus 0.75%.
If the SNB acted first, the spread between Swiss and European market rates would narrow, making Swiss investments more attractive and boosting the franc. The ECB has already scaled back its asset purchasing programme, which is expected to end this year, but more action may be someway off. Meanwhile, any attempt by the SNB to cut its balance sheet – which has ballooned to 837 billion francs ($861 billion) – will be hard because 94% of its investments are in foreign currencies, held via bonds and shares in companies such as Apple and Starbucks.

The reality of Chinese borrowing.
• China Vows to Toughen Rules on $38 Trillion Banking Industry
China’s banking regulator pledged to continue its crackdown on malpractice in the $38 trillion industry in 2018, vowing to tackle everything from poor corporate governance and violation of lending policies to cross-holdings of risky financial products. The China Banking Regulatory Commission unveiled its regulatory priorities for the year in a statement on Saturday. They include: • Inspecting the funding source of banks’ shareholders and ensuring they have obtained their stakes in a regular manner • Examining banks’ compliance with rules restricting loans to real estate developers, local governments, industries burdened by overcapacity, and some home buyers • Looking into banks’ interbank activities and wealth management businesses.
The statement comes after China’s financial regulators started 2018 with a flurry of rules to plug loopholes uncovered in last year’s deleveraging campaign, showcasing their determination to limit broader risks to the financial system. Still, analysts have warned that the moves will make it more difficult for companies to obtain financing from loans, equities and bonds and could undermine economic growth. The “CBRC’s regulatory storm continues” with the weekend announcement covering almost all aspects of banks’ daily operations, Bocom International analysts Jaclyn Wang and Hannah Han wrote in a note. “We believe challenges for smaller banks in the current regulatory environment remain high,” they wrote, noting that curbs on off-balance-sheet lending and interbank activities may drag on profitability.

There’s no such thing as the reality of crypto.
• Bitcoin Not Even In Top 10 Of Crypto World’s Best Performers (AFP)
Bitcoin may be the most famous cryptocurrency but, despite a dizzying rise, it’s not the most lucrative one and far from alone in a universe that counts 1,400 rivals, and counting. Dozens of crypto units see the light of day every week, as baffled financial experts look on, and while none can match Bitcoin’s €200 billion ($242 bilion) market capitalisation, several have left the media darling’s profitability in the dust. In fact, bitcoin is not even in the top 10 of the crypto world’s best performers. Top of the heap is Ripple which posted a jaw-dropping 36,000% rise in 2017 and early this year broke through the €100 billion capitalisation mark, matching the value of blue-chip companies such as, say, global cosmetics giant L’Oreal.
“Its value shot up when a newspaper said that around 100 financial institutions were going to adopt their system,” said Alexandre Stachtchenko, co-founder of specialist consulting group Blockchain Partners. Using Ripple’s technology framework, however, is not the same as adopting the currency itself, and so the Ripple’s rise should be considered as “purely speculative”, according to Alexandre David, founder of sector specialist Eureka Certification. Others point out that Ripple’s market penetration is paper-thin as only 15 people hold between 60 and 80% of existing Ripples, among them co-founder Chris Larsen. But it still got him a moment of fame when, according to Forbes magazine, Larsen briefly stole Facebook founder Mark Zuckerberg’s spot as the fifth-wealthiest person in the US at the start of the year.
Ether is another rising star, based on the Ethereum protocol created in 2009 by a 19-year old programmer and seen by some specialists as a promising approach. Around 40 virtual currencies have now gone past the billion-euro mark in terms of capitalisation, up from seven just six months ago. The Cardano cryptocurrency’s combined value even hit €15 billion only three months after its creation. In efforts to stand out from the crowd, virtual currency founders often concentrate on the security of their systems, such as Cardano, which has made a major selling point of its system’s safety features.

After having been given numerous gov’t contracts just to stay alive. Biy, that country is sick.
• UK’s Carillion Files for Liquidation After Failing to Get Bailout (BBG)
Carillion, a U.K. government contractor involved in everything from hospitals to the HS2 high-speed rail project, has filed for compulsory liquidation after a last-ditch effort to shore up finances and get a government bailout failed. The company, which employs 43,000 people worldwide – 20,000 of them in the U.K. – had held talks with the government Sunday to ask for the 300 million pounds ($412 million) it needed by the end of the month to stay afloat, the Mail on Sunday reported. On Monday morning, the board of Carillion said in a statement it had “concluded that it had no choice but to take steps to enter into compulsory liquidation with immediate effect,” adding that it has obtained court approval for the move.
The challenge for liquidators and the government is now to ensure that the company’s break-up is orderly, with contracts and staff moved to rivals. For Prime Minister Theresa May, the collapse comes as opposition Labour Party leader Jeremy Corbyn questions the longstanding British policy of getting private sector contractors to deliver public sector projects. “This is very worrying for a lot of groups,” Labour’s business spokeswoman Rebecca Long-Bailey told the BBC. “We expect the government to step up now and take these contracts back into government control. Where it’s possible to take those back in-house it should do.” She also questioned why the company had been awarded further government contracts despite issuing profit warnings.
[..] Carillion’s struggles posed a conundrum for May over the political cost of using public money to assist a private company, or allowing it to fail, putting public services and infrastructure projects nationwide in danger. The company has contracts with many wings of government, including building roads, managing housing for the armed services, and running facilities for schools and hospitals.

Timber!
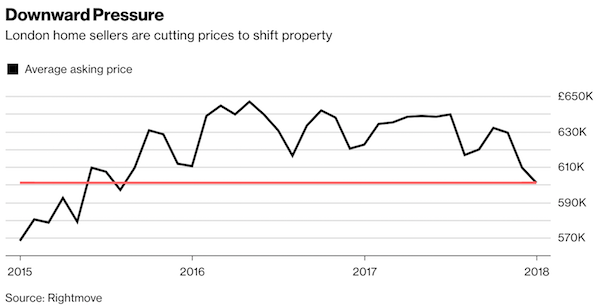
• London Housing Woe Endures as Prices Drop to 2 1/2-Year Low (BBG)
The new year brought little cheer for London’s housing market with asking prices dropping to the lowest since August 2015. New sellers cut prices 1.4% in January to an average of 600,926 pounds ($821,500), according to a report by Rightmove on Monday. In a further concerning sign for the market, the average number of days required to sell a house jumped to the longest since January 2012, reaching 78 from 71 a month earlier. The report suggests 2018 won’t be any brighter for the capital’s housing market, which was the worst performing in the U.K. in 2017. Asking prices are down 3.5% from a year ago, according to the report, with the slowdown due to factors including an inflation squeeze, Brexit uncertainty and tax changes affecting landlords and owners of second homes.

Now find the language that the people respond to.
• Let’s Wrench Power Back From The Billionaires (Bernie Sanders)
[..] all over the world corrupt elites, oligarchs and anachronistic monarchies spend billions on the most absurd extravagances. The Sultan of Brunei owns some 500 Rolls-Royces and lives in one of the world’s largest palaces, a building with 1,788 rooms once valued at $350m. In the Middle East, which boasts five of the world’s 10 richest monarchs, young royals jet-set around the globe while the region suffers from the highest youth unemployment rate in the world, and at least 29 million children are living in poverty without access to decent housing, safe water or nutritious food. Moreover, while hundreds of millions of people live in abysmal conditions, the arms merchants of the world grow increasingly rich as governments spend trillions of dollars on weapons.
In the United States, Jeff Bezos – founder of Amazon, and currently the world’s wealthiest person – has a net worth of more than $100bn. He owns at least four mansions, together worth many tens of millions of dollars. As if that weren’t enough, he is spending $42m on the construction of a clock inside a mountain in Texas that will supposedly run for 10,000 years. But, in Amazon warehouses across the country, his employees often work long, gruelling hours and earn wages so low they rely on Medicaid, food stamps and public housing paid for by US taxpayers. Not only that, but at a time of massive wealth and income inequality, people all over the world are losing their faith in democracy – government by the people, for the people and of the people.
They increasingly recognise that the global economy has been rigged to reward those at the top at the expense of everyone else, and they are angry. Millions of people are working longer hours for lower wages than they did 40 years ago, in both the United States and many other countries. They look on, feeling helpless in the face of a powerful few who buy elections, and a political and economic elite that grows wealthier, even as their own children’s future grows dimmer. In the midst of all of this economic disparity, the world is witnessing an alarming rise in authoritarianism and rightwing extremism – which feeds off, exploits and amplifies the resentments of those left behind, and fans the flames of ethnic and racial hatred.

Typical? Sign of the times? Laurie Kellman and Jonathan Drew for AP prove their own point by pretending to write about Americans from all stripes losing faith in news media, but then turn it into a one-sided Trump hit piece anyway.
• Trust in News Media Takes a Hit During Trump Presidency (AP)
When truck driver Chris Gromek wants to know what’s really going on in Washington, he scans the internet and satellite radio. He no longer flips TV channels because networks such as Fox News and MSNBC deliver conflicting accounts tainted by politics, he says. “Where is the truth?” asks the 47-year-old North Carolina resident. Answering that question accurately is a cornerstone of any functioning democracy, according to none other than Thomas Jefferson. But a year into Donald Trump’s fact-bending, media-bashing presidency, Americans are increasingly confused about who can be trusted to tell them reliably what their government and their commander in chief are doing. Interviews across the polarized country as well as polling from Trump’s first year suggest people seek out various outlets of information, including Trump’s Twitter account, and trust none in particular.
Many say that practice is a new, Trump-era phenomenon in their lives as the president and the media he denigrates as “fake news” fight to be seen as the more credible source. “It has made me take every story with a large grain, a block of salt,” said Lori Viars, a Christian conservative activist in Lebanon, Ohio, who gets her news from Fox and CNN. “Not just from liberal sources. I’ve seen conservative ‘fake news.'” Democrat Kathy Tibbits of Tahlequah, Oklahoma, reads lots of news sources as she tries to assess the accuracy of what Trump is reported to have said. “I kind of think the whole frontier has changed,” said the 60-year-old lawyer and artist. “My degree is in political science, and they never gave us a class on such fiasco politics.”
Though Trump’s habit of warping facts has had an impact, it’s not just him. Widely shared falsehoods have snagged the attention of world leaders such as Pope Francis and former President Barack Obama. Last year, false conspiracy theories led a North Carolina man to bring a gun into a pizza parlor in the nation’s capital, convinced that the restaurant was concealing a child prostitution ring. Just last week, after the publication of an unflattering book about Trump’s presidency, a tweet claiming that he is addicted to a TV show about gorillas went viral and prompted its apparent author to clarify that it was a joke. Trump has done his part to blur the lines between real and not. During the campaign, he made a practice of singling out for ridicule reporters covering his raucous rallies.
As president, he regularly complains about his news coverage and has attacked news outlets and journalists as “failing” and “fake news.” He’s repeatedly called reporters “the enemy of the people” and recently renewed calls to make it easier to sue for defamation. About 2 in 3 American adults say fabricated news stories cause a great deal of confusion about the basic facts of current affairs, according to a Pew Research Center report last month. The survey found that Republicans and Democrats are about equally likely to say that “fake news” leaves Americans deeply confused about current events. Despite the concern, more than 8 in 10 feel very or somewhat confident that they can recognize news that is fabricated, the survey found.

Greece will be monitored till 2060. I’m going to bet that’s not going to happen.
• Outgoing EWG Chief Says Greece May Get Debt Relief With Conditions Attached (K.)
Greece could receive debt relief but with terms attached when its bailout program is concluded in August, according to the outgoing chief of the Eurogroup Working Group (EWG), Thomas Wieser. In an interview in Sunday’s Greek edition of Kathimerini, Wieser said that despite there being no discussion about post-bailout arrangements, he expects that debt relief would be granted conditionally. “If there should be further debt relief after the end of the program then it’s only logical there will be some kind of additional agreements.” His comments imply there will be no clean exit from the bailout program as envisioned in the government’s narrative. Greece’s post-bailout status was raised at last week’s EWG meeting in Brussels where, according to sources, the taboo issue of Greece debt relief was raised.
It was noted in the meeting that if there is to be debt relief, then questions regarding Greece’s post-bailout framework have to be addressed. According to EU regulations, bailout countries including Ireland, Spain, Portugal, Cyprus – as well as Greece in the near future – will be monitored until 75% of their loans have been repaid. This means in Greece’s case that it will be monitored until 2060. Wieser added that one of Greece’s biggest problems, which remains unresolved despite eight years of fiscal adjustment programs, is that it doesn’t lure foreign investments like other countries. “I still have the feeling that foreign direct investment is not welcomed in Greece as it is in many other countries,” Wieser said.
While adding that he has the feeling that many domestic rules and regulations over the last eight years have indeed changed, he bemoaned the fact that investments have not picked up. “I think it’s only very recently that international and national investors trust that Greece is finally approaching the time where it can stand on its own feet again financially and that it is not a huge risk to invest in its economy,” he said, adding that one of the main reasons that investors have been reluctant to do business in Greece is its justice system.

Unlimited?
• Berlin Worried EU Reform Will Boost Immigration Influx (DS)
The European Parliament is planning to amend the Dublin Regulation, which requires asylum seekers to register in the first European Union member state they set foot on. That state would also be responsible for processing these requests. The proposed amendment, however, could possible shift that responsibility to wherever any asylum seeker claims to have family in the EU. Under such a change, “Germany would have to accommodate significantly more asylum seekers,” said an Interior Ministry memo, quoted by Der Spiegel. Furthermore, any and all caps on refugees and immigrant intakes would be nullified. This would effectively render Germany’s decision to cap immigrations influxes at around 180,000 to 220,000 as agreed upon by the working groups aiming to form a new German government.
Germany has been struggling to form a new government since the Sept. 24th elections; however, Chancellor Angela Merkel’s Christian Democrats (CDU), their sister party the CSU and Social Democrat Party leader Martin Schultz have agreed to go into official coalition talks, now made harder by the proposed EU bill. The proposed reform of the Dublin Agreement was put forth last November and now has to be approved by the European Council, which is composed of every single member states’ government leaders. Despite Germany’s worries, given the circumstances, the proposal is not expected to have much support. Between the nations of Eastern Europe, who never wanted any immigration at all, and the ever-more skeptical western nations, as well as the ones in Southern Europe, such as Greece, Italy and Spain that became the frontlines of the crisis, the proposed reform is not guaranteed to pass.
While the exact number of people that have entered Europe since 2015 is unknown, it is estimated that it is about 2 to 3 million, with the United Nations Human Rights Commission reporting that tens of millions more are on the move, mainly from sub-Saharan Africa. While Germany was probably Europe’s biggest supporter of asylum seekers and chain-migration, it now worries that it in particular will be negatively affected by what it sees as immigration on “an entirely different scale.” The German Interior Ministry noted that it was particularly worried by a section of the proposal that stated: “The mere assertion of a family connection was enough.” “As a result, a member state hosting many so-called ‘anchor persons’ will take over responsibility for far-reaching family associations.”
“If every one of the more than 1.4 million people who have applied for asylum in Germany since 2015 becomes an anchor for newcomers arriving in the EU, then we’re dealing with [numbers] on an entirely different scale compared to family reunifications,” said Ole Schröder, a parliamentary state secretary in Germany’s Interior Ministry.

It only gets messier.
• A New Refugee Flow To Europe: Turkish Refugees (AM)
This past November, three bodies were found washed ashore the Greek island of Lesbos. They were later identified as a Turkish husband and wife, Huseyin and Nur Maden, and one of their three children. The Madens were teachers in Turkey, but they were among the 150,000 civil servants dismissed from their jobs after the failed coup in July 2016. Some of those dismissed tried to flee to Greece to avoid arrest or find work. More than 12,000 Turks applied for asylum in Europe for the first time in 2017, according to Eurostat. This figure is triple what it was the year preceding the failed coup and is the highest it has been in the past decade. Since July 2016, Turkish authorities have arrested over 50,000 people, including journalists and intellectuals.
Around 150,000 Turks have both had their passports revoked and lost their jobs as police officers, soldiers, teachers and public servants. For some, the solution was to leave Turkey and find work in another country, where they could have a better life and avoid prosecution. With their passports revoked by the Turkish government, Turks prefer to go to Greece as opposed to other European countries since they can arrange transport by boat via smugglers. The journey from the Turkish coast to certain Greek islands can be short, distance-wise. “Turkish refugees [in Athens] are the most educated and intellectual segment of Turkish society,” said Murat, who fled Turkey for Greece after July 2016. “We can learn a new language or adapt to the culture in Europe really fast.”
Murat has been a member of the Gulen movement since 1994. He worked alongside his wife as a teacher in the Gulen schools in southeastern Turkey, but they were both dismissed from their jobs after the 2016 coup attempt, which the government claims was planned by the Gulen movement. Their children’s school was shut down after the coup attempt, and they were denied registration at a new school in their hometown due to their parent’s affiliation with the Gulen movement. “We tried to start over, but we were already marginalized in the community as ‘putschists,’” said Murat. “Our children were not accepted to schools, and finally, when 50 police arrived at our parent’s village to detain my wife, by chance we were not there. I sold my car within a week and with that money, we came to Greece.”
The Gulenists are not the only ones who have had to leave Turkey following the coup attempt. There are others, like Merve, 21, and her uncle Hasan. Merve was only 19 when she was arrested after the coup attempt and put in jail for a year. “I was studying philosophy in Tunceli and was part of a left-wing student organization at my university,” she said. “Now there are only two possibilities left for us Kurds in Turkey. If you don’t want to be jailed, you should either join the PKK [Kurdistan Workers Party] fighters or flee into exile.”

Nope, there is no war on plastic. So we can’t be losing it either.
• Why We’re Losing the War on Plastic (BBG)
T.V. naturalist Sir David Attenborough made his viewers weep last month with an exposé on how plastics are polluting the oceans, harming marine animals and fish. Last week, British prime minister Theresa May announced a slew of new measures to discourage plastics use, including plastic-free supermarket aisles and an expanded levy on plastic bags. A ban on microbeads in cosmetics came into force this year. Not to be outdone, the EU is mulling plastics taxes to cut pollution and packaging waste. Is this industry the new tobacco?It’s no wonder politicians feel compelled to act. About 60% of all the plastics produced either went to landfill or have been dumped in the natural environment. At current rates there will be more plastic than fish in the ocean by 2050 by weight, much of it in the form of small particles, ingestible by wildlife and very difficult to remove.
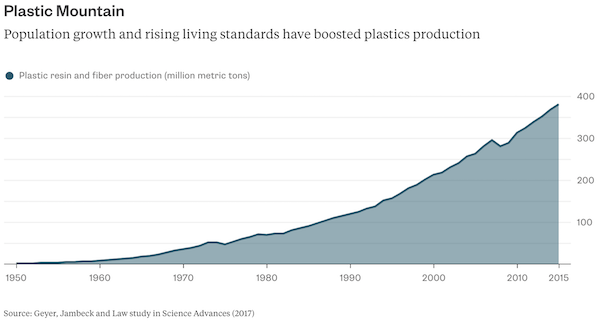
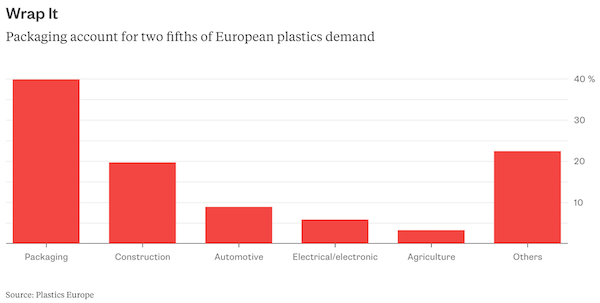
Public awareness has increased in recent years, yet that hasn’t led to falling consumption. More than half of the total plastics production has occurred since the turn of the millennium. Producers such as DowDuPont, Exxon Mobil, LyondellBasell and Ineos, as well as packaging manufacturers like Amcor, Berry Global and RPC have been happy to meet that demand. They don’t plan on it ending suddenly. Plastic packaging is an almost $290 billion-a-year business and sales are forecast to expand by almost 4 percent a year until 2022, according to research firm Smithers Pira. Demand for polyethylene, the most used plastic, is set to rise at a similar rate, meaning total consumption will rise to 118 million metric tons in 2022, according to IHS Markit. In the U.S., the shale gas boom has encouraged the construction of new ethylene plants. Oil companies are counting too on rising plastics consumption to offset the spread of electric vehicles, as my colleague Julian Lee has explained.
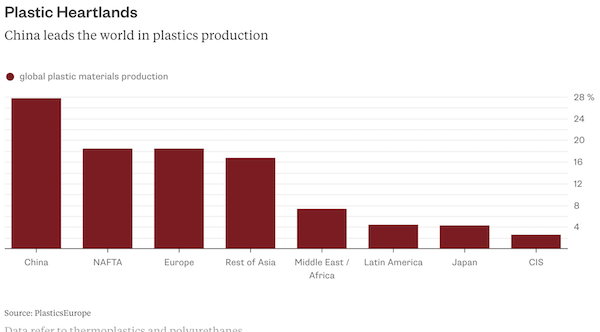
The reasons for the bullishness are obvious. Growing populations, rising living standards and the march of e-commerce mean more demand. In developed countries, per capita polyethylene use is as much as 40 kg per person, whereas in poorer countries like India the figure is just one tenth of that, according to IHS Markit. Plastics are displacing materials like glass and paper because they tend to be cheap, lightweight and sturdy. That plastics don’t easily decompose is an asset – it prevents food going bad – as well as a liability for the natural environment. Cutting consumption will be difficult. While bioplastics are an alternative, they make up only about 1 percent of global plastics demand. Quality and cost issues have prevented wider adoption. “A lot of these materials aren’t really competitive in a world of low to mid oil prices,” says Sebastian Bray, analyst at Berenberg.









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle January 15 2018