Mathew Brady Three captured Confederate soldiers, Gettysburg, PA 1863



Globalization has already died, it perished with the economic system. But it may take a long time until this is recognized, since that recognition would threaten vested interests.
• The Revenge Of Globalisation’s Losers (Münchau)
Globalisation is failing in advanced western countries, where a process once hailed for delivering universal benefit now faces a political backlash. Why? The establishment view, in Europe at least, is that states have neglected to forge the economic reforms necessary to make us more competitive globally. I would like to offer an alternative view. The failure of globalisation in the west is in fact down to democracies failure to cope with the economic shocks that inevitably result from globalisation — such as the stagnation of real average incomes for two decades. Another shock has been the global financial crisis — a consequence of globalisation — and its permanent impact on long-term economic growth.
In large parts of Europe, the combination of globalisation and technical advance destroyed the old working class and is now challenging the skilled jobs of the lower middle class. So voters’ insurrection is neither shocking nor irrational. Why should French voters cheer labour market reforms if it could result in the loss of their jobs, with no hope of a new one? Some reforms have worked, but ask yourself why. Germany’s acclaimed labour market reforms in 2003 succeeded in the short term because they raised the country’s cost competitiveness through lower wages relative to other advanced countries. The reforms produced a state of near full employment only because no other country did the same. If others had followed, there would have been no net gain. The reforms had a big downside.
They reduced relative prices in Germany and pushed up net exports in turn generating massive savings outflows, the deep cause of the imbalances that led to the eurozone crisis. Reforms such as these can hardly be the recipe for how advanced nations should address the problem of globalisation. Nor is there any factual evidence that countries that have reformed are performing better or are more able to cope with a populist insurrection. The US and the UK have more liberal market structures than most of continental Europe. Yet the UK may be about to exit the EU; in the US the Republicans may be about to nominate an extreme populist as their presidential candidate. Finland leads all the competitiveness rankings but the economy is a non-recovering basket case — and it has a strong populist party.
The economic impact of reforms is usually subtler than its advocates admit. And there is no straight connection between reforms and support for established political parties. My diagnosis is that globalisation has overwhelmed western societies politically and technically. There is no way we can, or should, hide from it. But we have to manage the change. This means accepting that the optimal moment for the next trade agreement, or market liberalisation, may not be right now.

TTiP is just a leftover chicken walking a few more steps after its head is chopped off.
• Obama and Merkel Unite Over TTiP (FT)
Barack Obama and Angela Merkel have called for talks over a transatlantic trade deal to be completed this year as fears mount that the opportunity to reach an agreement is slipping away. The US president used a visit to Hanover in Germany on Sunday to try to breathe new life into the Transatlantic Trade and Investment Partnership, which has been beset by political opposition in the US and Europe. “I am confident we will get this done,” Mr Obama said, talking about completing the negotiations this year. But he said time was “not on our side”, calling on all European leaders to support the deal and not “let this opportunity close”. President Obama was in Germany after a visit to Saudi Arabia and the UK where he waded into the Brexit debate, urging Britain to remain in the EU.
Speaking at a joint press conference, Mr Obama went out of his way to praise the German chancellor, who has been one of his closest confidants among international leaders but whose domestic political standing has been undermined by the migrant crisis. The German decision to allow more than 1m people to enter the country last year had put Ms Merkel “on the right side of history” despite the political backlash, he said. “She is giving voice to principles that bring people together rather than divide them. I’m very proud of her for that and I’m proud of the German people for that,” he added. In return, Ms Merkel showered her American counterpart with praise for his leadership on the Paris climate accords. “Barack, a personal thanks to you,” she said. “Without the United States of America, this would not have come to pass.”
The TTIP negotiations, which were launched in July 2013, have progressed slowly as opposition in Europe has grown and some member states have begun expressing scepticism. Ms Merkel said she wanted to speed up the negotiations, as a deal would be helpful in allowing the German and eurozone economies to grow. “We should do our bit,” she said. The chancellor added that she would canvas widely to get the deal back on track and pledged to “inject this with a new dynamism from the European side”. Mr Obama said that although he hoped the negotiations would be concluded this year, it would take longer for countries to ratify a deal.
[..] The closer the talks get to 2017, the more difficult life will become for EU trade negotiators. Chancellor Merkel faces re-election in parliamentary polls and French president François Hollande is at risk of losing in presidential elections, with National Front leader Marine Le Pen comfortably ahead in opinion polls. With TTIP divisive in both countries, officials, especially France, are unlikely to want to press ahead with the talks. Matthias Fekl, France’s trade minister, on Sunday reiterated previous threats to withdraw from the talks if there was not sufficient progress on a number of issues in the months to come. France has constantly put forward criteria, conditions, demands, Mr Fekl told the country’s i-Tele news channel. If these conditions are not fulfilled…France will withdraw.

Tyler Durden’s comment: the real debt is not 237% of GDP, but 350%.
• China Debt Load Reaches Record High As Risk To Economy Mounts (FT)
China’s total debt rose to a record 237% of GDP in the first quarter, far above emerging-market counterparts, raising the risk of a financial crisis or a prolonged slowdown in growth, economists warn. Beijing has turned to massive lending to boost economic growth, bringing total net debt to Rmb163 trillion ($25 trillion) at the end of March, including both domestic and foreign borrowing, according to Financial Times calculations. Such levels of debt are much higher as a proportion of national income than in other developing economies, although they are comparable to levels in the U.S. and the eurozone. While the absolute size of China’s debt load is a concern, more worrying is the speed at which it has accumulated — Chinese debt was only 148% of GDP at the end of 2007.
“Every major country with a rapid increase in debt has experienced either a financial crisis or a prolonged slowdown in GDP growth,” Ha Jiming, Goldman Sachs chief investment strategist, wrote in a report this year. The country’s present level of debt, and its increasing links to global financial markets, partly informed the International Monetary Fund’s recent warning that China poses a growing risk to advanced economies. Economists say it is difficult for any economy to deploy productively such a large amount of capital within a short period, given the limited number of profitable projects available at any given time. With returns spiralling downwards, more loans are at risk of turning sour. According to data from the Bank for International Settlements for the third quarter last year, emerging markets as a group have much lower levels of debt, at 175% of GDP.
The BIS data, which is based on similar methodology to the FT, put Chinese debt at 249% of GDP, which was broadly comparable with the euro zone’s figure of 270% and the US level of 248%. Beijing is juggling spending to support short-term growth and deleveraging to ward off long-term financial risk. Recently, however, as fears of a hard landing have intensified, it has shifted decisively towards stimulus. New borrowing increased by Rmb6.2tn in the first three months of 2016, the biggest three-month surge on record and more than 50% ahead of last year’s pace. Economists widely agree that the health of the country’s economy is at risk. Where opinion is divided is on how this will play out. At one end of the spectrum is acute financial crisis — a “Lehman moment” reminiscent of the U.S. in 2008, when banks failed and paralyzed credit markets.
Other economists predict a chronic, Japan-style malaise in which growth slows for years or even decades. Jonathan Anderson, principal at Emerging Advisors Group, belongs to the first camp. He warns that banks driving the huge credit expansion since 2008 rely increasingly on volatile short-term funding through sales of high-yielding wealth management products, rather than stable deposits. As Lehman and Bear Stearns proved in 2008, this kind of funding can quickly evaporate when defaults rise and nerves fray. “At the current rate of expansion, it is only a matter of time before some banks find themselves unable to fund all their assets safely,” Mr Anderson wrote last month. “And at that point, a financial crisis is likely.”

The greater fools are getting fleeced. “..But how much longer can Beijing go on creating debt at a breakneck pace?”
• China’s Fresh Boom Nears Peak Just As Amateurs Pile In (AEP)
Elite global banks have begun to warn clients that China’s latest credit-driven boom is nearing its peak and will lose momentum by late summer, dashing hopes for a genuine cycle of fresh economic growth and commodity demand. Morgan Stanley, Nomura, and Societe Generale have all issued cautionary notes just as amateur investors belatedly turn bullish again on China and start to pile into both commodities and emerging market equities. “While the mini-recovery is likely to last another 3-4 months, our economists expect a renewed slowdown in the second half of the year, as stimulus efforts fade,” said Morgan Stanley. The US bank said record credit growth over the last quarter will keep growth humming for a little longer but the fiscal blitz is already ebbing and the government is imposing property curbs in the Eastern cities to prevent a speculative bubble.
China’s reflation drive has been explosive. New home sales jumped 64pc in March from a year earlier. House prices have risen 28pc in Beijing, 30pc in Shanghai, and 63pc in the commercial hub of Shenzhen. The rush to buy has spread to the Tier 2 cities such as Hefei – up 9pc in a single month. “The housing market is on fire,” said Wei Yao, from Societe Generale. “In the first quarter, increases in total credit exploded to 7.5 trilion yuan, up 58pc year-on-year. There is no bigger policy lever than this kind of credit injection.” “This looks like an old-styled credit-backed investment-driven recovery, which bears an uncanny resemblance to the beginning of the“four trillion stimulus” package in 2009. The consequence of that stimulus was inflation, asset bubbles and excess capacity. We still think that this recovery will not last very long,” she said.
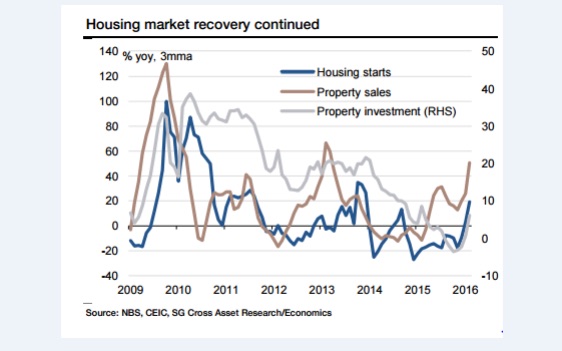
China’s housing market is on fire
The signs of excess are visible everywhere as the Communist Party once again throws caution to the wind . Cement production jumped 24pc in March and infrastructure investment rose 19pc. Yang Zhao from Nomura said the edifice is becoming more dangerously unstable with each of these stop-go mini-booms. “Structural problems and financial imbalances are worsening. We believe this debt-fueled growth is not sustainable,” he said. Nomura said the law of diminishing returns is setting in as the economy nears credit exhaustion. The ‘incremental credit-output ratio” has deteriorated to 5.0 from 2.3 in 2008. Loans are losing traction and the quality of investment is falling. “Be careful. We are nearing the point where things are as good as they get for the first half of 2016. We recommend taking some money off the table,” said Wendy Liu and Vicky Fung, the bank’s equity strategists.
Despite the stimulus, defaults among private companies and state entities (SOEs) have jumped to 11 so far this year from 17 last year, and the defaults are getting bigger. China Railway Materials has just suspended trading on $2.6bn of debt. Michelle Lam from Lombard Street Research said Beijing has retreated from reform and resorted to pump-priming again. “This may last for one or two quarters. But how much longer can Beijing go on creating debt at a breakneck pace?” she said. Capital Economics says there has typically been a lag of six to nine months after each burst of credit, suggesting that economic growth will roll over in the late Autumn. Markets do not move in lockstep, and may anticipate this.
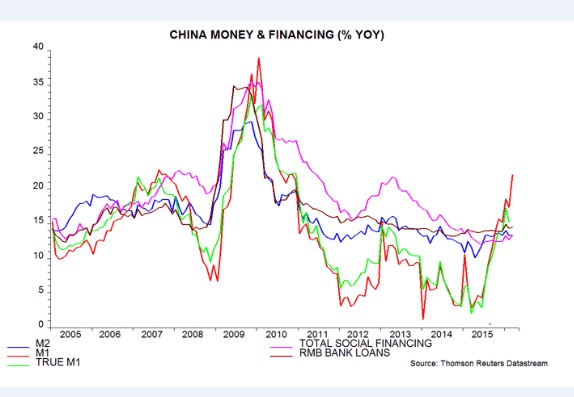
China’s M1 money supply is growing at the fastest pace since the post-Lehman stimulus

Must we wait till they run out of storage space for this too?
• Warnings Flash for China’s Red-Hot Steel Market on 47% Surge (BBG)
Warnings are stacking up fast after China’s eye-popping steel rally. Fitch Ratings said prices lifted in part by heightened speculation are destined to slump, while a bank in Singapore flagged the risk of a boom-bust cycle reminiscent of China’s equity market. The rapid advance isn’t sustainable as mills are expected to bring back idled capacity, raising supply, Fitch said in a report on Monday. Price gains have been driven by a seasonal recovery in activity that’s been exacerbated by increased speculation in the futures market, according to analyst Laura Zhai. Steel prices have surged in 2016, with reinforcement-bar up 47%, after policy makers in China talked up growth and added stimulus, helping to lift property prices and ignite a speculative frenzy. The gains have helped to restore mills’ profitability, boosting their incentive to increase output.
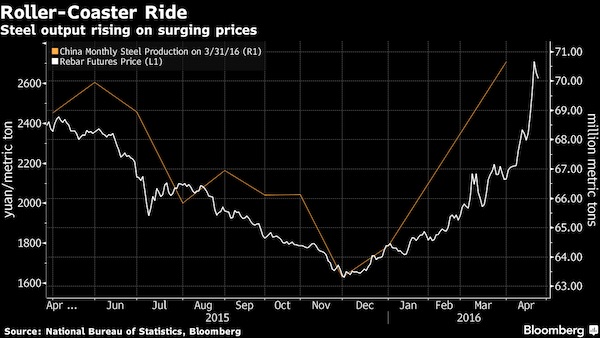
Singapore-based Oversea-Chinese Banking warned on Monday that there may be parallels between the sudden jump in steel trading and last year’s performance in equities, citing the potential for a boom-bust scenario. “The rapid increase in Chinese steel prices so far this year is not sustainable, as it is largely due to a seasonal pick-up in construction and elevated speculation in the steel futures market,” Fitch said. “With prices now surging, many of the suspended plants have resumed production.” Futures for rebar extended gains, rallying as much as 6.2% to 2,781 yuan ($427) a metric ton on the Shanghai Futures Exchange, before trading 0.2% higher on Monday. The price of the product used to strengthen concrete advanced for the 11th straight week through Friday, adding 14%. Steel output in the world’s largest supplier may see a further increase this month as more furnaces are fired up, according to Fitch.

Pon. Zi.
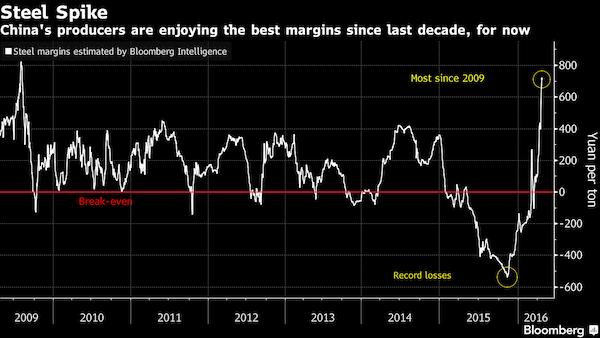
• China’s Steel Mill Margins Surge to 7-Year High on Boom (BBG)
China’s steel mills are making more money on each ton produced than at any time since 2009 after the government embarked on 4 trillion yuan ($615 billion) in infrastructure spending. A surprise rebound in China’s property and construction sectors has left steel buyers facing a shortage, and handed embattled mills a sudden boost to margins, according to data from Bloomberg Intelligence. The rally in steel prices is unsustainable as higher profits draw idled plants back into operation, says Fitch Ratings.

The lack of understanding of what inflation is, and what drives it, among both central bankers and media, is baffling.
• Draghi’s Growth and Inflation Conundrum Will Be Displayed Friday (BBG)
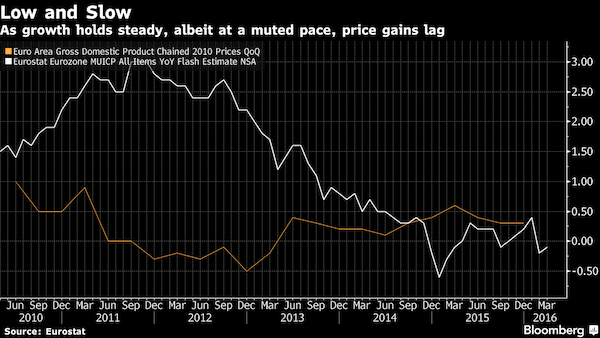
A suite of euro-area data on Friday will provide Mario Draghi with his first simultaneous dispatches from both fronts in his struggle to boost inflation – showing how he still has a fight on his hands. GDP numbers, in a newly accelerated publication just one month after the first quarter ended, will coincide with the usual end-of-the-month inflation statistics to present a snapshot of what the ECB president still has to achieve. It’s likely to show the euro area has now completed a dozen quarters of consecutive growth – though that momentum isn’t strong enough to produce faster price gains. Euro-area inflation hasn’t hit its target since 2013, when the economy was contracting. But now that it’s expanding, weak global demand, cheap commodity costs and a lack of investment are weighing down prices.
It’s a conundrum that Draghi hasn’t been able to solve, even after he’s cut interest rates to record lows, expanded bond purchases and started an additional loan program for banks. “The big story on inflation is that it’s flat, and going nowhere in the short term,” said Anatoli Annenkov, senior economist at Societe Generale in London, adding that cheap oil is behind the restraint and prices should move up later in the year. “We don’t doubt that the ECB’s measures are helping – they should have an impact on inflation and growth. The question is how big.” The region’s inflation rate probably stayed at zero in April, based on a Bloomberg survey of economists. That’s far below policy maker’s near-2% goal. By contrast, first-quarter growth probably picked up to 0.4% from 0.3% in the previous quarter.

Mystery? Not here.
• Stunted Growth: The Mystery Of The UK’s Productivity Crisis (G.)
Our economic future isn’t what it used to be. In March the Office for Budget Responsibility (OBR) revised down its growth estimates for each of the next five years. The chancellor was quick to blame a weakening world economy but the true driver lies closer to home. The problem isn’t a loud global economic crash but something much quieter: engine trouble. Productivity growth, the long-term motor of rising living standards, is slowing. The fact that this appears to be happening across the globe offers scant consolation. What’s worse is that no one is entirely sure what is causing the problem or how to fix it. And it is coming at about the worst time imaginable: global demographics are changing, with the supply of new workers set to slow and the older share of the population rising.
The future is of course inherently unknowable, but the reasons for longer-term pessimism on economic growth are starting to stack up. Productivity – the amount of output produced for each hour worked – rose at a fairly steady annual rate of about 2.2% in the UK for decades before the recession. Since the crisis though, that annual growth rate has collapsed to under 0.5%. The OBR has decided to revise down its future assumption on productivity from that pre-crisis 2.2% to a lower 2%. That small revision was enough to give the chancellor a large fiscal headache in his latest budget, but it still assumes a big rebound in productivity growth from its current level. What if that rebound doesn’t come? The near death of the British steel industry is a tragedy. But for all the political heat it has generated, its long-term consequences wouldn’t be as serious as the wider crisis. For while closing mills are highly visible, slipping productivity is not.
Looking at the global picture shows that while there are of course national nuances, the overall impression is grim and dates back to before the 2008 crash. Everywhere from the “dynamic” United States to “sclerotic” France, productivity growth has dropped considerably in recent years. The UK is an outlier with a bigger fall than many, but not by much. Some of this could be explained by measurement issues. To use every economist’s favourite example, it is straightforward to measure the inputs, the outputs – and hence the productivity – of a widget factory, even if no one is really sure what a widget is. It is harder to do the same with an online widget brand manager. But the mismeasurement would have to be on an unprecedented scale to explain away the problem.
What we are left with is a bewildering array of theories as to what has driven the fall but no clear answer. We know the productivity slowdown is broad based and happening across most sectors of the economy. Lower corporate and public investment than in the past almost certainly explains some of the shortfall. Weaker labour bargaining power than in previous decades might also be playing a role. Low wages are allowing low-skill, low-productivity business models to expand and deincentivising corporate spending on new kit. Why spend on expensive labour-saving technology when labour itself is cheap?

How does this differ from China again?
• The Tokyo Whale Is Quietly Buying Up Huge Stakes in Japan Inc. (BBG)
They may not realize it yet, but Japan Inc.’s executives are increasingly working for a shareholder unlike any other: the nation’s money-printing central bank. While the Bank of Japan’s name is nowhere to be found in regulatory filings on major stock investors, the monetary authority’s exchange-traded fund purchases have made it a top 10 shareholder in about 90% of the Nikkei 225 Stock Average, according to estimates compiled by Bloomberg from public data. It’s now a major owner of more Japanese blue-chips than both BlackRock, the world’s largest money manager, and Vanguard Group, which oversees more than $3 trillion. To critics already wary of the central bank’s outsized impact on the Japanese bond market, the BOJ’s growing influence in stocks risks distorting valuations and undermining efforts to improve corporate governance.
Proponents, meanwhile, say the purchases provide a much-needed boost to investor confidence. With the Nikkei 225 down 8.3% this year and inflation well below official targets, a majority of analysts surveyed by Bloomberg predict the BOJ will boost its ETF buying – a move that could come as soon as Thursday. “For those who want shares to go up at any cost, it’s absolutely fantastic that the BOJ is buying so much,” said Shingo Ide at NLI Research Institute in Tokyo. “But this is clearly distorting the sanity of the stock market.” Under the BOJ’s current stimulus plan, the central bank buys about 3 trillion yen ($27.2 billion) of ETFs every year.
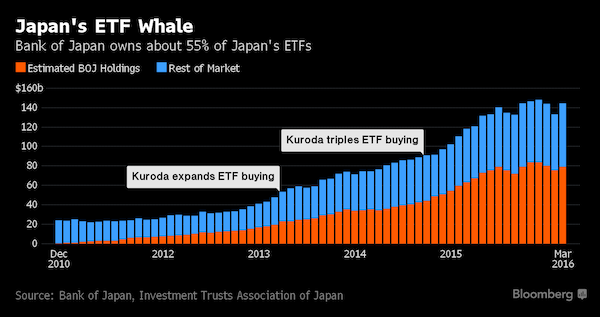
While policy makers don’t disclose how those holdings translate into stakes of individual companies, estimates can be gleaned from publicly available central bank records, regulatory filings by companies and ETF managers, and statistics from the Investment Trusts Association of Japan. The estimates reveal a presence in Japan’s top firms that’s rivaled by few others, with the BOJ ranking as a top 10 holder in more than 200 of the Nikkei gauge’s 225 companies. The central bank effectively controls about 9% of Fast Retailing, the operator of Uniqlo stores, and nearly 5% of soy sauce maker Kikkoman. It has an estimated shareholder rank of No. 3 in both Yamaha, one of the world’s largest makers of musical instruments, and Daiwa House, Japan’s biggest homebuilder.

A state run economy has a limited lifespan, but it can be stretched beyond expectations.
• Goldman Expects The Japanese Yen To Collapse Within 12 Months (ZH)
Forget the G-20 agreement on no “competitive devaluations” – the full court press on the Bank of Japan to engage in the next round of aggressive currency devaluation is on, just three months after Kuroda unveiled Japan’s first negative interest rate. Recall that it was Goldman who not only brought forward its forecast for a first rate hike from July to April and first suggested earlier this week that it is time for the Bank of Japan to forget about caution and to more than double its purchases of equities in the form of ETFs (and which the BOJ already owns a majority of all available securities) as doing either more NIRP and more QE may no longer have a favorable outcome:
… we think the BOJ is most likely to ease mainly via the qualitative measure, with increasing ETF purchasing the central pillar, with a view to improving business confidence. We think the market is already factoring in an increase in annual purchasing from ¥3.3 tn to ¥5-6 tn, and we thus think the BOJ may look to slightly more than double its current figure to around ¥7 tn.
This pushed both the USDJPY and the S&P off their overnight lows when it was first floated in the early morning of April 20. Then, on Friday, the Yen had its biggest one day surge since the announcement of the expanded QQE in October 2014 when Bloomberg reported of the latest BOJ trial balloon whereby “the Bank of Japan may consider helping banks lend by offering a negative rate on some loans, according to people familiar with talks at the BOJ.” This happened just as the net spec short position in the USDJPY hit record short, forcing yet another massive squeeze in the currency which soared higher by nearly 300 pips in one day.
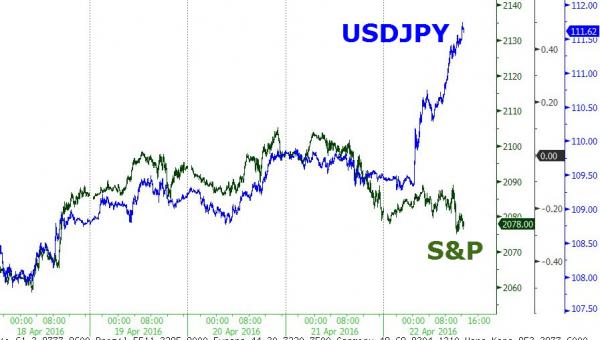
Which brings us to today, when in its latest attempt to throw everything at the wall and hope something sticks, Goldman Sachs’ FX team – whose trading recommendations in the past 6 months have been an unmitigated disaster – is predicting that the $/JPY will “move higher again in the near term and continue to forecast $/JPY at 130 a year from now.” Why does Goldman expect a collapse in the Yen by nearly 20 big figures? Because as analysts Sylvia Ardagna and Robin Brooks note, “the BoJ faces an important challenge: it needs to reaffirm that the monetary easing arrow of Abenomics is still on course, or the market will price that the central bank is backtracking from the 2% inflation goal. This could be extremely disruptive for the Japanese economy. Using markets jargon, the BoJ is already so long into ‘the reflationary trade’ that it has to continue to deliver further accommodation for the time being.”

The vulture as the Apex predator.
• How Argentina Settled a Billion-Dollar Debt & Paul Singer Made 392% (NY Times)
The Waldorf Astoria hotel in Manhattan has long been a location for secret diplomacy, but few meetings there would have seemed as unlikely as the one that took place one day in early December. In a hotel conference room, a top Argentine politician drank coffee with two hedge fund executives — a meeting that was nothing short of remarkable after more than a decade of bitter legal skirmishes between Argentina and a group of disgruntled debt holders who at one point seized an Argentine Navy ship. The previous Buenos Aires government reviled the hedge funds as “vultures.” That meeting on Dec. 7 between Luis Caputo, who days later would be sworn in as Argentina’s finance secretary, and Jonathan Pollock and Jay Newman from Elliott Management, the $27 billion hedge fund founded by Paul E. Singer, was the start of a rapprochement leading to a momentous debt deal that has now allowed Argentina to rejoin the global financial markets that it had been locked out of for 15 years.
Last week, Argentina successfully sold $16.5 billion in bonds to international investors, a record amount for any developing country. And on Friday, Elliott and the other bondholders finally received their reward in the form of billions of dollars in repayment, representing returns worth hundreds of times their original investments. “Today, we have put a definitive close to this chapter,” Alfonso Prat-Gay, Argentina’s economic minister, told an Argentine radio station on Friday. The negotiations that led to the deal were set in motion by the election in November of President Mauricio Macri, who ran on a promise to reignite Argentina’s flailing economy. Striking a deal with the country’s aggrieved bondholders was central to getting that done.
How Argentina and the hedge funds were able to break the long stalemate and reach a deal in a matter of weeks is a story of furious back-channeling and clashes that nearly derailed an agreement. Details of those negotiations have emerged from interviews with eight people who were involved in those meetings, as well as court filings and emails reviewed by The New York Times. Many of those people spoke on condition of anonymity because they were not authorized to speak publicly. There were moments when the talks nearly fell apart. Three days before a deal was signed with Elliott, Mr. Caputo, exasperated by a back-and-forth with bondholders over whether they would return government assets they had seized, emailed the court-appointed mediator: “THIS IS A JOKE; NO DEAL.”

” The whole world’s financial machinery [..] all comes down to (the threat of) physical force.”
• You Don’t Own That! The Evolution of Property (Roth)
There are a large handful of things that make humans uniquely different from animals. In many other areas — language, abstract reasoning, music-making, conceptions of self and fairness, large-scale cooperation, etc. — humans and animals vary (hugely) in degree and kind. But they still share those phenotypic behavioral traits. I’d like to explore one of those unique differences: ownership of property. Animals don’t own property. Ever. They can and do possess and control goods and territories (possession and control are importantly distinct), but they never “own” things. Ownership is a uniquely human construct. To understand this, imagine a group of tribes living around a common water source. A spring, say. There’s ample water for all the tribes, and all draw from it freely. Nobody “owns” it.
Then one day a tribe decides to take possession of the spring, take control of it. They set up camp surrounding it, and prevent other tribes from accessing it. They force the other tribes to give them goods, labor, or other concessions in return for access to water. The other tribes might object, but if the controlling tribe can enforce their claim, there’s not much the other tribes can do about it. And after some time, maybe some generations, the other tribes may come to accept that status quo as the natural order of things. By eventual consensus (however vexed), that one tribe “owns” the spring. Other tribes even come to honor and respect that ownership, and those who claim and enforce it. That consensus and agreement is what makes ownership ownership. Absent that, it’s just possession and control.
It’s not hard to see the crucial fact in this little fable: property rights are ultimately based, purely, on coercion and violence. If the controlling tribe can’t enforce its claim through violence, their “ownership” is meaningless. And those claimed rights are not just inclusionary (the one tribe can use the water). Property rights are primarily or even purely exclusionary. Owners can prevent others from doing anything with the owners’ property. Get off my lawn! When push comes to shove (literally), when brass tacks meet the rubber on the road (sorry, couldn’t resist), ownership and property rights are based purely on violence and the threat of violence. Full stop, drop the mic.
In the modern world we’ve largely outsourced the execution of that violence, the monopoly on violence, to government. If a family sets up a picnic on “your” lawn, you can call the police and they’ll remove that family — by force if necessary. And we’ve multiplied the institutional and legal mechanics and machinery of ownership a zillionfold. The whole world’s financial machinery — the immensely complex web of claims, claims on claims, and claims on claims on claims, endlessly and densely iterated and interwoven — all comes down to (the threat of) physical force.

Newspeak goes global.
• UN To Urge Media To Take More ‘Constructive’ Approach To News (G.)
The United Nations is to call for the world’s media to take a more “constructive” and “solutions-focused” approach to news to combat “apathy and indifference”. UN director general Michael Møller is to meet broadcast, print and online journalists in London on Wednesday to to discuss how new ways of covering the world with the help of the UN and the Constructive Voices programme run by the National Council for Voluntary Organisations. Constructive Voices incorporates an online resource designed to help journalists find case studies that provide practical solutions to problems. The UN has separately launched GAVDATA, an online portal providing access to a huge store of information from the the UN and other international organisations and NGOs. Speaking ahead of the event, director general Michael Møller said many people feel “disempowered” by the news and unable to influence decisions.
He said: “The choices we make are determined by the information we are given. These are fundamental to how we shape a better world together.” “In a world of 7 billion people, with a cacophony of voices that are often ill-informed and based on narrow agendas, we need responsible media that educate, engage and empower people and serve as a counterpoint to power. We need them to offer constructive alternatives in the current stream of news and we need to see solutions that inspire us to action. Constructive journalism offers a way to do that.” “It’s vital too that we have data and different points of view.” The UN and the NCVO also claims that the public are turned off by overwhelmingly negative news, and are more likely to share stories that offer solutions to problems, providing a commercial incentive for media organisations to include more positive stories.
NCVO chair Sir Martyn Lewis, a former BBC News presenter in the 80s and 90s who covered the death of Princess Diana, said the organisations were not asking the media to abandon its traditional approach, but to supplement it with journalism that helps solve problems. “It’s 23 years almost to the day that I first spoke out about the need for more balanced news agenda. I have been misunderstood in the past, with people believing I just wanted fluffy, feelgood news at the expense of covering real news,” said Lewis. “This is not the case at all. I’d like to see the media engage in solutions-driven journalism which not only reports problems but explores potential solutions to those problems as well.” “I would stress that this approach absolutely does not mean giving up the traditional approach to journalism, but is complementary to it and, interestingly, there is growing evidence that it makes a lot of commercial sense as well.”

How the human brain is designed.
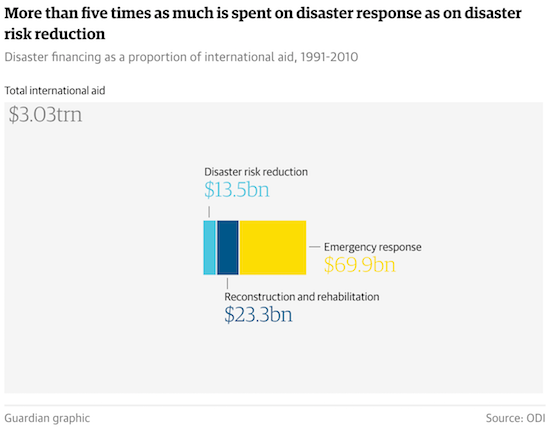
• World Heads For Catastrophe In Failure to Prepare For Natural Disasters (G.)
The world’s failure to prepare for natural disasters will have “inconceivably bad” consequences as climate change fuels a huge increase in catastrophic droughts and floods and the humanitarian crises that follow, the UN’s head of disaster planning has warned. Last year, earthquakes, floods, heatwaves and landslides left 22,773 people dead, affected 98.6 million others and caused $66.5bn of economic damage. Yet the international community spends less than half of one per cent of the global aid budget on mitigating the risks posed by such hazards. Robert Glasser, the special representative of the secretary general for disaster risk reduction, said that with the world already “falling short” in its response to humanitarian emergencies, things would only get worse as climate change adds to the pressure.
He said: “If you see that we’re already spending huge amounts of money and are unable to meet the humanitarian need – and then you overlay that with not just population growth … [but] you put climate change on top of that, where we’re seeing an increase in the frequency and severity of natural disasters, and the knock-on effects with respect to food security and conflict and new viruses like the Zika virus or whatever – you realise that the only way we’re going to be able to deal with these trends is by getting out ahead of them and focusing on reducing disaster risk.” Failure to plan properly by factoring in the effects of climate change, he added, would result in a steep rise in the vulnerability of those people already most exposed to natural hazards. He also predicted a rise in the number of simultaneous disasters.
“As the odds of any one event go up, the odds of two happening at the same time are more likely. We’ll see many more examples of cascading crises, where one event triggers another event, which triggers another event.” Glasser pointed to Syria, where years of protracted drought led to a massive migration of people from rural areas to cities in the run-up to the country’s civil war. While he stressed that the drought was by no means the only driver of the conflict, he said droughts around the world could have similarly destabilising effects – especially when it came to conflicts in Africa. “It’s inconceivably bad, actually, if we don’t get a handle on it, and there’s a huge sense of urgency to get this right,” he said. “I think country leaders will become more receptive to this agenda simply because the disasters are going to make that obvious. The real question in my mind is: can we act before that’s obvious and before the costs have gone up so tremendously? And that’s the challenge.”