Henri Cartier Bresson Juvisny, France 1938

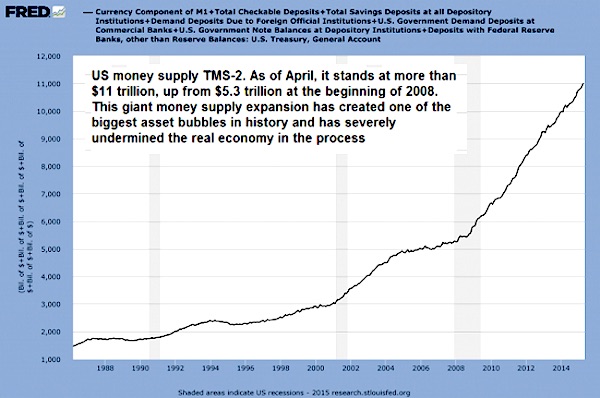
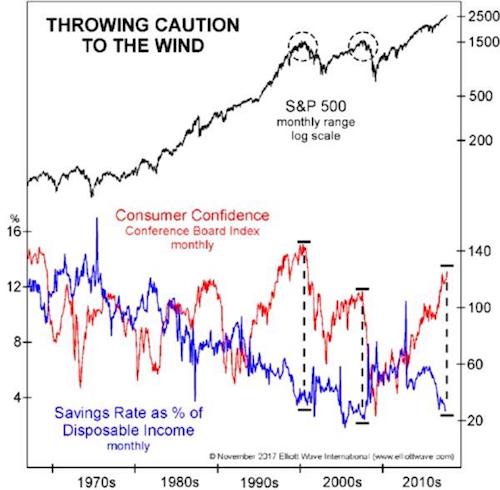
Powerful graph from Bob Prechter.
• Consumers Are Both Confident And Broke (John Rubino)
Elliott Wave International recently put together a chart (click here or on the chart to watch the accompanying video) that illustrates a recurring theme of financial bubbles: When good times have gone on for a sufficiently long time, people forget that it can be any other way and start behaving as if they’re bulletproof. They stop saving, for instance, because they’ll always have their job and their stocks will always go up. Then comes the inevitable bust. On the following chart, this delusion and its aftermath are represented by the gap between consumer confidence (our sense of how good the next year is likely to be) and the saving rate (the portion of each paycheck we keep for a rainy day). The bigger the gap the less realistic we are and the more likely to pay dearly for our hubris.

“Prior to 2000, debt was able to support a rising standard of living..” Two decades later, it can’t even maintain the status quo. That’s what you call a breaking point.
• You Have Been Warned (Lance Roberts)
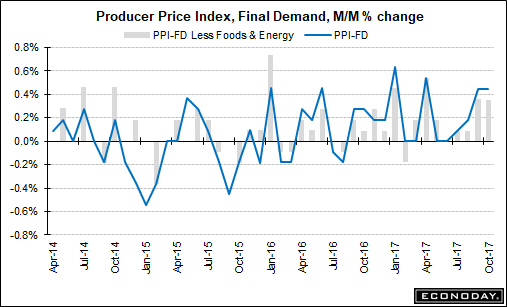
There is an important picture that is currently developing which, if it continues, will impact earnings and ultimately the stock market. Let’s take a look at some interesting economic numbers out this past week. On Tuesday, we saw the release of the Producer Price Index (PPI) which ROSE 0.4% for the month following a similar rise of 0.4% last month. This surge in prices was NOT surprising given the recent devastation from 3-hurricanes and massive wildfires in California which led to a temporary surge in demand for products and services.
Then on Wednesday, the Consumer Price Index (CPI) was released which showed only a small 0.1% increase falling sharply from the 0.5% increase last month.
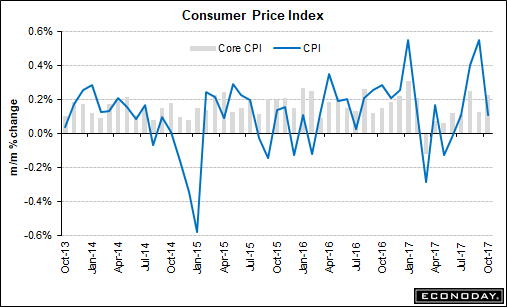
This deflationary pressure further showed up on Thursday with a -0.3 decline in Export prices. (Exports make up about 40% of corporate profits) For all of you that continue to insist this is an “earnings-driven market,” you should pay very close attention to those three data points above. When companies have higher input costs in their production they have two choices: 1) “pass along” those price increase to their customers; or 2) absorb those costs internally. If a company opts to “pass along” those costs then we should have seen CPI rise more strongly. Since that didn’t happen, it suggests companies are unable to “pass along” those costs which means a reduction in earnings. The other BIG report released on Wednesday tells you WHY companies have been unable to “pass along” those increased costs.
The “retail sales” report came in at just a 0.1% increase for the month. After a large jump in retail sales last month, as was expected following the hurricanes, there should have been some subsequent follow through last month. There simply wasn’t. More importantly, despite annual hopes by the National Retail Federation of surging holiday spending which is consistently over-estimated, the recent surge in consumer debt without a subsequent increase in consumer spending shows the financial distress faced by a vast majority of consumers. The first chart below shows a record gap between the standard cost of living and the debt required to finance that cost of living. Prior to 2000, debt was able to support a rising standard of living, which is no longer the case currently.
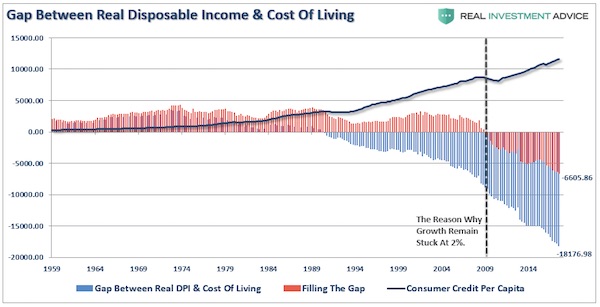
With a current shortfall of $18,176 between the standard of living and real disposable incomes, debt is only able to cover about 2/3rds of the difference with a net shortfall of $6,605. This explains the reason why “control purchases” by individuals (those items individuals buy most often) is running at levels more normally consistent with recessions rather than economic expansions.
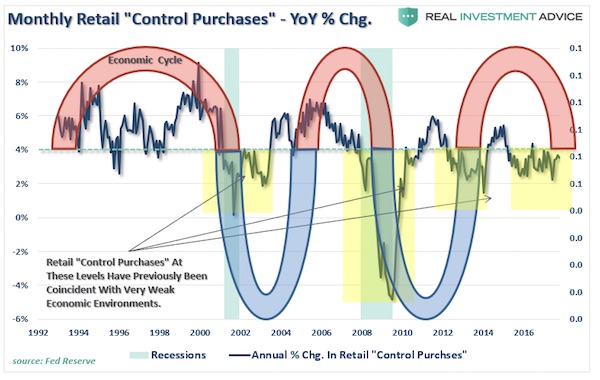
If companies are unable to pass along rising production costs to consumers, export prices are falling and consumer demand remains weak, be warned of continued weakness in earnings reports in the months ahead. As I stated earlier this year, the recovery in earnings this year was solely a function of the recovering energy sector due to higher oil prices. With that tailwind now firmly behind us, the risk to earnings in the year ahead is dangerous to a market basing its current “overvaluation” on the “strong earnings” story.

Another way to push up prices?
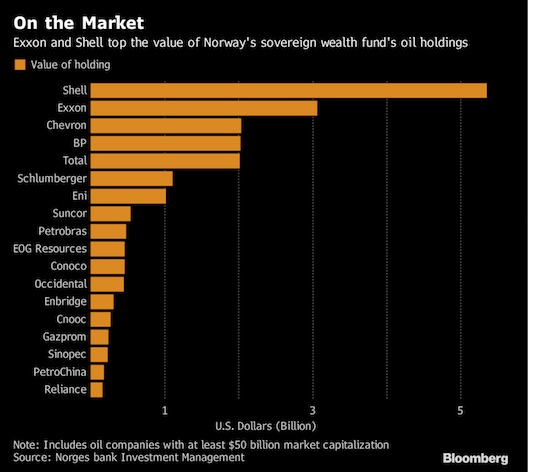
• Norway Plan to Sell Off $35 Billion in Oil, Gas Stocks Rattles Markets (BBG)
Norway’s proposal to sell off $35 billion in oil and natural gas stocks brings sudden and unparalleled heft to a once-grassroots movement to enlist investors in the fight against climate change. The Nordic nation’s $1 trillion sovereign wealth fund said Thursday that it’s considering unloading its shares of Exxon Mobil, Royal Dutch Shell and other oil giants to diversify its holdings and guard against drops in crude prices. European oil stocks fell. Norges Bank Investment Management would not be the first institutional investor to back away from fossil fuels. But until now, most have been state pension funds, universities and other smaller players that have limited their divestments to coal, tar sands or some of the other dirtiest fossil fuels. Norway’s fund is the world’s largest equity investor, controlling about 1.5% of global stocks. If it follows through on its proposal, it would be the first to abandon the sector altogether.
“This is an enormous change,” said Mindy Lubber, president of Ceres, a non-profit that advocates for sustainable investing. “It’s a shot heard around the world.” The proposal rattled equity markets. While Norwegian officials say the plan isn’t based on any particular view about future oil prices, it’s apt to ratchet up pressure on fossil fuel companies already struggling with the growth of renewable energy. Norway’s Finance Ministry, which oversees the fund, said it will study the proposal and will take at least a year to decide what to do. The fund has already sold off most of its coal stocks. “People are starting to recognize the risks of oil and gas,” said Jason Disterhoft of the Rainforest Action Network, which pushes banks to divest from fossil fuels.

From the biggest wealth fund to the biggest wealth manager.
• The World’s Biggest Wealth Manager Won’t Touch Bitcoin (BBG)
UBS, the world’s largest wealth manager, isn’t prepared to make portfolio allocations to bitcoin because of a lack of government oversight, the bank’s chief investment officer said. Bitcoin has also not reached the critical mass to be considered a viable currency to invest in, UBS’s Mark Haefele said in an interview. The total sum of all cryptocurrencies is “not even the size of some of the smaller currencies” that UBS would allocate to, he said. Bitcoin has split investors over the viability of the volatile cryptocurrency and UBS is among its critics. Bitcoin capped a resurgent week by climbing within a few dollars of a record $8,000 on Friday. Still, events such as a bitcoin-funded terrorist attack are potential risks which are hard to evaluate, he said.
“All it would take would be one terrorist incident in the U.S. funded by bitcoin for the U.S. regulator to much more seriously step in and take action, he said. “That’s a risk, an unquantifiable risk, bitcoin has that another currency doesn’t.” While skeptics have called bitcoin’s rapid advance a bubble, it has become too big an asset for many financial firms to ignore. Bitcoin has gained 17% this week, touching a high of $7,997.17 during Asia hours before moving lower in late trading. The rally through Friday came after bitcoin wiped out as much as $38 billion in market capitalization following the cancellation of a technology upgrade known as SegWit2x on Nov. 8.

Former (and current?!) TAE contributor Alastair Crooke draws his conclusions.
• Trump’s Saudi Scheme Unravels (Alastair Crooke)
Aaron Miller and Richard Sokolsky, writing in Foreign Policy, suggest “that Mohammed bin Salman’s most notable success abroad may well be the wooing and capture of President Donald Trump, and his son-in-law, Jared Kushner.” Indeed, it is possible that this “success” may prove to be MbS’ only success. “It didn’t take much convincing”, Miller and Sokolski wrote: “Above all, the new bromance reflected a timely coincidence of strategic imperatives.” Trump, as ever, was eager to distance himself from President Obama and all his works; the Saudis, meanwhile, were determined to exploit Trump’s visceral antipathy for Iran – in order to reverse the string of recent defeats suffered by the kingdom.
So compelling seemed the prize (that MbS seemed to promise) of killing three birds with one stone (striking at Iran; “normalizing” Israel in the Arab world, and a Palestinian accord), that the U.S. President restricted the details to family channels alone. He thus was delivering a deliberate slight to the U.S. foreign policy and defense establishments by leaving official channels in the dark, and guessing. Trump bet heavily on MbS, and on Jared Kushner as his intermediary. But MbS’ grand plan fell apart at its first hurdle: the attempt to instigate a provocation against Hezbollah in Lebanon, to which the latter would overreact and give Israel and the “Sunni Alliance” the expected pretext to act forcefully against Hezbollah and Iran.
Stage One simply sank into soap opera with the bizarre hijacking of Lebanese Prime Minister Saad Hariri by MbS, which served only to unite the Lebanese, rather than dividing them into warring factions, as was hoped. But the debacle in Lebanon carries a much greater import than just a mishandled soap opera. The really important fact uncovered by the recent MbS mishap is that not only did the “dog not bark in the night” – but that the Israelis have no intention “to bark” at all: which is to say, to take on the role (as veteran Israeli correspondent Ben Caspit put it), of being “the stick, with which Sunni leaders threaten their mortal enemies, the Shiites … right now, no one in Israel, least of all Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu, is in any hurry to ignite the northern front. Doing so, would mean getting sucked into the gates of hell”.

Targeting the military means MbS does not feel safe. How desperate is he?
• Saudi ‘Corruption’ Probe Widens: Dozens Of Military Officials Arrested (ZH)
After jailing dozens of members of the royal family, and extorting numerous prominent businessmen, 32-year-old Saudi prince Mohammed bin Salman has widened his so-called ‘corruption’ probe further still. The Wall Street Journal reports that at least two dozen military officers, including multiple commanders, recently have been rounded up in connection to the Saudi government’s sweeping corruption investigation, according to two senior advisers to the Saudi government. Additionally, several prominent businessmen also were taken in by Saudi authorities in recent days. “A number of businessmen including Loai Nasser, Mansour al-Balawi, Zuhair Fayez and Abdulrahman Fakieh also were rounded up in recent days, the people said. Attempts to reach the businessmen or their associates were unsuccessful.”
It isn’t clear if those people are all accused of wrongdoing, or whether some of them have been called in as witnesses. But their detainment signals an intensifying high-stakes campaign spearheaded by Saudi Arabia’s 32-year-old crown prince, Mohammed bin Salman. There appear to be three scenarios behind MbS’ decision to go after the military: 1) They are corrupt and the entire process is all above board and he is doing the right thing by cleaning house; 2) They are wealthy and thus capable of being extorted (a cost of being free) to add to the nation’s coffers; or 3) There is a looming military coup and by cutting off the head, he hopes to quell the uprising. If we had to guess we would weight the scenarios as ALL true with the (3) becoming more likely, not less.
So far over 200 people have been held without charges since the arrests began on November 4th and almost 2000 bank accounts are now frozen, which could be why, as The Daily Mail reports, Saudi prince and billionaire Al-Waleed bin Talal has reportedly put two luxury hotels in Lebanon up for sale after being detained in his country during a corruption sweep. The Saudi information ministry previously stated the government would seize any asset or property related to the alleged corruption, meaning the Savoy hotel could well become the state property of the kingdom. ‘The accounts and balances of those detained will be revealed and frozen,’ a spokesman for Saudi Arabia’s information ministry said. ‘Any asset or property related to these cases of corruption will be registered as state property.’

France and Germany play completely different roles. Hariri has said he will return to Lebanon by Wednesday.
• Hariri Arrives in Paris With Family Amid Saudi-Iran Tensions (BBG)
Saad Hariri arrived in France with his family amid mounting concern that his country, Lebanon, may once again turn into a battleground for a showdown between Saudi Arabia and Iran. The Lebanese prime minister and his family were invited to France by President Emmanuel Macron. French officials say they can’t say how long Hariri will stay. On Saturday, Macron and Hariri will meet at noon for talks, following which the Lebanese leader and his family will have lunch at the Elysee Palace. Hariri, 47, hasn’t returned to Lebanon since his shock resignation announcement from Saudi Arabia on Nov. 4, which sparked fears of an escalating regional conflict between the kingdom and Iran. The Saudi government has denied accusations it was holding Hariri against his will. The kingdom recalled its ambassador to Germany in response to comments made by Foreign Minister Sigmar Gabriel.
Hariri weighed in on the spat, suggesting that Gabriel has accused the kingdom of holding him hostage. “To say that I am held up in Saudi Arabia and not allowed to leave the country is a lie. I am on the way to the airport, Mr. Sigmar Gabriel,” he said on Twitter. In limited public comments and on Twitter, Hariri has sought to dispel speculation that Saudi Arabia asked him to resign because he wouldn’t confront Hezbollah, an Iranian-backed Shiite Muslim group that plays a key role in Lebanon’s fragile government. The group is considered a terrorist organization by countries including Israel and the U.S., and it has provided crucial military support to President Bashar al-Assad’s regime in Syria’s war.
Macron, who met with Saudi Arabia Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman in Riyadh, said last week that the two agreed that Hariri “be invited for several days to France.” He also reiterated France’s pledge to help protect Lebanon’s “independence and autonomy.” Hariri will be welcomed in France “as a friend,” Foreign Minister Jean-Yves Le Drian said a press conference in Riyadh on Thursday after meeting with Saudi authorities. French officials have said they still regard Hariri as Lebanon’s prime minister since the country’s president, Michel Aoun, rejected his resignation on the grounds that it must be handed over on Lebanese soil.

And if you weren’t confused enough yet, there’s this:
• Qatar Says It Has US Backing in Lingering Gulf Crisis (BBG)
Qatar’s foreign minister said the tiny emirate has U.S. backing to resolve the ongoing crisis with a Saudi-led alliance, but the country is also prepared should its Gulf Arab neighbors make military moves. The Trump administration is encouraging all sides to end the dispute and has offered to host talks at the Camp David presidential retreat, but only Qatar has agreed to the dialogue, Foreign Minister Sheikh Mohammed Al-Thani said Friday. Four countries in the Saudi-led bloc severed diplomatic and transport links with Qatar in June, accusing it of backing extremist groups, a charge Doha has repeatedly denied. Saudi Arabia closed Qatar’s only land border. Sheikh Mohammed said he will meet Secretary of State Rex Tillerson next week after having talks this week with Senate Foreign Relations Committee chairman Bob Corker and ranking member Ben Cardin as well as other congressional leaders.
“The Middle East needs to be addressed as the top priority of the foreign policy agenda of the United States,” he told reporters in Washington on Friday. “We see a pattern of irresponsibility and a reckless leadership in the region, which is just trying to bully countries into submission.” The Middle East has been a key foreign policy issue for the Trump administration, with much of it centered around support for the Saudis. The White House has backed the kingdom’s “anti-corruption” campaign that has ensnared top princes and billionaires once seen as U.S. allies, it has provided support for the Saudis in their war in Yemen and it has been muted in criticism of the crisis sparked when Lebanon’s prime minister unexpectedly resigned this month while in Saudi Arabia. Meanwhile, mediation attempts by Kuwait and the U.S. have failed to settle the spat with the Saudi-led bloc and Qatar.
Sheikh Mohammed accused Saudi Arabia of interfering in other countries’ affairs, citing the resignation of Lebanese Prime Minister Saad Hariri as an example of the oil-rich kingdom’s overreach and warning that other countries could be next. Asked about the prospect of the Saudi-led bloc taking military action, Sheikh Mohammed said though Qatar hopes that won’t happen, his country is “well-prepared” and can count on its defense partners, including France, Turkey, the U.K. and the U.S., which has a base in Qatar. “We have enough friends in order to stop them from taking these steps,” but “there is a pattern of unpredictability in their behavior so we have to keep all the options on the table for us,” he said. On the U.S. military presence, “if there is any aggression when it comes to Qatar, those forces will be affected,” he added.

There is nothing secret about land tax. Nor is it anything new. It can be implemented tomorrow morning.
• House Prices Aren’t The Issue – Land Prices Are (G.)
While reporting on the recent court case where controversial landlord Fergus Wilson defended (but lost) his right to refuse to let to Indians and Pakistanis, I learned something about how he’s now making money. He is now far from being Britain’s biggest buy-to-let landlord. He’s down to 350 homes, from a peak of 1,000. And what’s he doing with the cash made from sales? Buying agricultural land close to Kent’s biggest towns. One plot he bought for £45,000 is now worth, he boasted, £3m with development permission. And therein lies the reason why we have a housing crisis.
As long ago as 1909, Winston Churchill, then promoting Lloyd George’s “people’s budget” and its controversial measures to tax land, told an audience in Edinburgh that the landowner “sits still and does nothing” while reaping vast gains from land improvements by the municipality, such as roads, railways, power from generators and water from reservoirs far away. “Every one of those improvements is effected by the labour and the cost of other people … To not one of those improvements does the land monopolist contribute, and yet by every one of them the value of his land is sensibly enhanced … he contributes nothing even to the process from which his own enrichment is derived.”
When Britain’s post-war housebuilding boom began, it was based on cheap land. As a timely new book, The Land Question by Daniel Bentley of thinktank Civitas, sets out, the 1947 Town and Country Planning Act under Clement Attlee’s government allowed local authorities to acquire land for development at “existing use value”. There was no premium because it was earmarked for development. The New Towns Act 1946 was similar, giving public corporation powers to compulsorily purchase land at current-use value. The unserviced land cost component for homes in Harlow and Milton Keynes was just 1% of housing costs at the time. Today, the price of land can easily be half the cost of buying a home..

Democracy in 2017.
• ECB Denies EU Auditors Access To Information On Greek Bailouts (EuA)
The European Central Bank (ECB) challenged an attempt by the European Court of Auditors (ECA), the watchdog of EU finances, to examine the Bank’s role in the Greek bailout and reform programmes and refused to provide access to some requested information, citing banking confidentiality. The European Court of Auditors published a report assessing the effectiveness and results of the Greek bailouts on Thursday (16 November). “In line with the ECA’s mandate to audit the operational efficiency of the management of the ECB, we have attempted to examine the Bank’s involvement in the Greek Economic Adjustment Programmes. However, the ECB questioned the Court’s mandate in this respect,” the report reads. The auditors examined the role of the European Commission and found some shortcomings in its approach, which they said overall lacked transparency.
They made a series of recommendations to improve the design and implementation of the Economic Adjustment Programmes. “These recommendations have been accepted in full,” the report said. However, the ECB had invoked the banking confidentiality and denied access to specific information. “It [ECB] did not provide sufficient amount of evidence and thus we were unable to report on the role of the ECB in the Greek programmes,” the auditors said. The report pointed out that the European Parliament had specifically asked the Court to analyse the role of the ECB in financial assistance programmes. It noted that EU auditors had faced similar problems with obtaining evidence from the ECB when reviewing the Single Supervisory Mechanism.
The report highlighted the ECB’s decision on 4 February 2015 to suspend the waiver for accepting Greek government bonds as loan collateral, thereby automatically increasing short-term borrowing costs for the banks. That happened during the tough negotiations between Greece’s leftist government and its international lenders before the third bailout. Many believed it was meant to put additional pressure on Alexis Tsipras’ government to back down and respect the obligations undertaken by the country’s previous governments.

It just gets crazier all the time. If your intention was to make sure an economy slowly dies, this is the way to go.
“Retirees on low pensions will effectively have to return the handout they get in late December at the end of January..”
• Greek Pensioners Forced To Return ‘Social Dividend’ (K.)
Salary workers, retirees on low pensions, property owners and families with three or more children will bear the brunt of the new austerity measures accompanying the 2018 budget, which come to 1.9 billion euros. Next year the primary budget surplus will have to rise to 3.5% of GDP, therefore more cuts will be required, with low-income pensioners – the recipients of next month’s so-called “social dividend” – set to contribute most, according to the new measures. Retirees on low pensions will effectively have to return the handout they get in late December at the end of January, as the cost of pension interventions according to the midterm fiscal strategy plan amounts to 660 million euros. This is just 60 million euros shy of the social dividend’s 720 million euros that Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras promised this week.
The new measures for 2018 are set to be reflected in the final draft of the budget that is to be tabled in Parliament on Tuesday. They are likely to further increase the amount of expired debts to the state, after the addition of 34 billion euros from unpaid taxes and fines in the last three years, owing to the inability of most taxpayers to meet their obligations to the tax authorities. Plans for next year provide for the further reduction of salaries in the public sector in the context of the single salary system, additional cuts to pensions and family benefits, as well as the abolition of the handout to most low-income pensioners (EKAS). Freelance professionals are also in for an extra burden in 2018, due to the increase in their social security contributions that will be calculated on the sum of their taxable incomes and the contributions they paid in 2017.

The UN should be all over this.
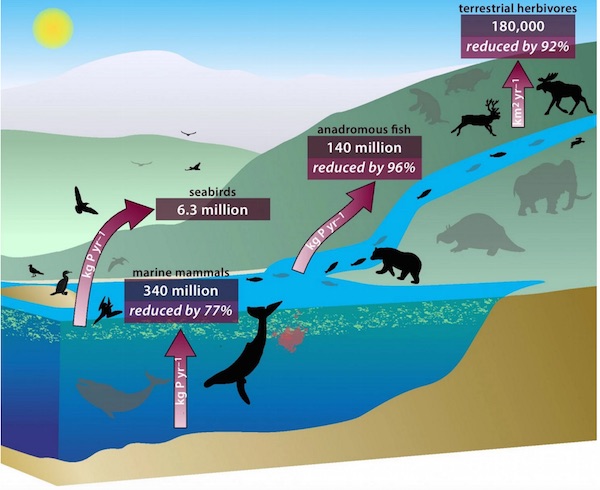
• UK Considers Tax On Single-Use Plastics To Tackle Ocean Pollution (G.)
The chancellor, Philip Hammond, will announce in next week’s budget a “call for evidence” on how taxes or other charges on single-use plastics such as takeaway cartons and packaging could reduce the impact of discarded waste on marine and bird life, the Treasury has said. The commitment was welcomed by environmental and wildlife groups, though they stressed that any eventual measures would need to be ambitious and coordinated. An estimated 12m tonnes of plastic enters the oceans each year, and residues are routinely found in fish, sea birds and marine mammals. This week it emerged that plastics had been discovered even in creatures living seven miles beneath the sea. The introduction just over two years ago of a 5p charge on single-use plastic bags led to an 85% reduction in their use inside six months.
Separately, the environment department is seeking evidence on how to reduce the dumping of takeaway drinks containers such as coffee cups through measures such as a deposit return scheme. Announcing the move on plastics, the Treasury cited statistics saying more than a million birds and 100,000 sea mammals and turtles die each year from eating or getting tangled in plastic waste. The BBC series Blue Planet II has highlighted the scale of plastic debris in the oceans. In the episode to be broadcast this Sunday, albatrosses try to feed plastic to their young, and a pilot whale carries her dead calf with her for days in mourning. Scientists working with the programme believed the mother’s milk was made poisonous by pollution. The call for evidence will begin in the new year and will take into account the findings of the consultation on drinks containers.
Tisha Brown, an oceans campaigner for Greenpeace UK, said the decades-long use of almost indestructible materials to make single-use products “was bound to lead to problems, and we’re starting to discover how big those problems are”. She said: “Ocean plastic pollution is a global emergency, it is everywhere from the Arctic Ocean at top of the world to the Marianas trench at the bottom of the Pacific. It’s in whales, turtles and 90% of sea birds, and it’s been found in our salt, our tap water and even our beer.

It’s either Christ or Santa Claus. Makes sense.
• Irish Catholic Priest Urges Christians To Abandon The Word Christmas (G.)
An Irish Catholic priest has called for Christians to stop using the word Christmas because it has been hijacked by “Santa and reindeer”. Father Desmond O’Donnell said Christians of any denomination need to accept Christmas now has no sacred meaning. O’Donnell’s comments follow calls from a rightwing pressure group for a boycott of Greggs bakery in the UK after the company replaced baby Jesus with a sausage roll in a nativity scene. “We’ve lost Christmas, just like we lost Easter, and should abandon the word completely,” O’Donnell told the Belfast Telegraph. “We need to let it go, it’s already been hijacked and we just need to recognise and accept that.”
O’Donnell said he is not seeking to disparage non-believers. “I am simply asking that space be preserved for believers for whom Christmas has nothing to do with Santa and reindeer. “My religious experience of true Christmas, like so many others, is very deep and real – like the air I breathe. But non-believers deserve and need their celebration too, it’s an essential human dynamic and we all need that in the toughness of life.”