
US photographer Margaret Bourke-White on top of the Chrysler Building, NYC 1931

If I were Beijing, I’d be a tad worried about the implication that Chine needs the US to be great again.
• America Makes China Great Again – People’s Daily (CNBC)
A Communist Party mouthpiece is crowing that malfunctioning U.S. leadership is making China “great again” on the eve of highly anticipated bilateral trade talks between the two countries. The op-ed published in the People’s Daily said the U.S. was in political chaos and suffered from a broken system, which was why Washington couldn’t get anything done. It also claimed the U.S. mess was giving China an opportunity to shine. “U.S. foreign policy is in total disarray, and world regard for the U.S. has plummeted. Indeed, America is making China ‘great again,'” the op-ed said. “Once the world’s model, the great American meltdown has turned the U.S. into some bizarre soap opera.” This isn’t the first time China has piggybacked off an American saying — remember President Xi Jinping’s “Chinese Dream” slogan?
This time around, the tone is a bit sharper, with Chinese state media not backing down ahead of annual bilateral talks that have been rebranded this year as the U.S.-China Comprehensive Economic Dialogue. Although both Beijing and Washington have indicated they understand the need to play nice, both sides are pushing their own agenda as expected. The U.S. wants to reduce the more than $300 billion trade deficit with China and make good on a campaign promise from President Donald Trump to pressure China on a number of fronts, such as opening up its markets to more foreign participation and to bring jobs back to America. China, on the other hand, has pushed back, saying Chinese investment has helped the U.S. But it’s clear that as the U.S. continues to face political turmoil, China is enjoying its time in the spotlight. That is, Beijing is explicitly seeking to fill the void the U.S. left as it backed out of various multilateral talks and agreements…

Got the money? Got the money? Show me the money!
• Pentagon Report Declares US Empire ‘Collapsing’ (Nafeez Ahmed)
An extraordinary new Pentagon study has concluded that the US-backed international order established after World War 2 is “fraying” and may even be “collapsing”, leading the United States to lose its position of “primacy” in world affairs. The solution proposed to protect US power in this new “post-primacy” environment is, however, more of the same: more surveillance, more propaganda (“strategic manipulation of perceptions”) and more military expansionism. The document concludes that the world has entered a fundamentally new phase of transformation in which US power is in decline, international order is unravelling, and the authority of governments everywhere is crumbling. Having lost its past status of “pre-eminence”, the US now inhabits a dangerous, unpredictable “post-primacy” world, whose defining feature is “resistance to authority”.
Danger comes not just from great power rivals like Russia and China, both portrayed as rapidly growing threats to American interests, but also from the increasing risk of “Arab Spring”-style events. These will erupt not just in the Middle East, but all over the world, potentially undermining trust in incumbent governments for the foreseeable future. The report, based on a year-long intensive research process involving consultation with key agencies across the Department of Defense and US Army, calls for the US government to invest in more surveillance, better propaganda through “strategic manipulation” of public opinion, and a “wider and more flexible” US military.
[..] Observing that US officials “naturally feel an obligation to preserve the US global position within a favorable international order,” the report concludes that this “rules-based global order that the United States built and sustained for 7 decades is under enormous stress.” The report provides a detailed breakdown of how the DoD perceives this order to be rapidly unravelling, with the Pentagon being increasingly outpaced by world events. Warning that “global events will happen faster than DoD is currently equipped to handle”, the study concludes that the US “can no longer count on the unassailable position of dominance, supremacy, or pre-eminence it enjoyed for the 20-plus years after the fall of the Soviet Union.” So weakened is US power, that it can no longer even “automatically generate consistent and sustained local military superiority at range.”

I can’t really do Bill Mitchell justice in this format, but the health care debate badly needs views such as his.
• A Government Can Always Afford High-Quality Health Care Provision (BIlbo)
The US is the only advanced nation that lacks universal health care. Even though it is the world’s richest nation, millions of US citizens cannot afford to see a doctor much less acquire more complex health care (for example, surgery). It it clear that in seeking private profits, the private health care insurers drive up the cost of health care which means, in nominal terms, the proportion of GDP expenditure devoted to it will rise. It is quite obvious that when private profits are included costs will rise unless efficiency is vastly improved. The ‘free market (not!)’ lobby always appeal to arguments that competitive systems are always more effective. The Commonwealth Report shows emphatically that strong (dare we call them socialist) government-dominated universal care systems like the NHS are vastly more effective than the profit-driven US system.
There also doesn’t seem to be any reason for private insurance in health care at all. And it is here that we enounter the ‘funding’ myths. Too often health care debates get stuck in irrelevant fiscal arguments about whether the government can afford to expand and/or invest in health care. The justification for private insurance is usually predicated on these ‘governments cannot afford’ to pay for the system type arguments. They are fallacious of course. In the pursuit of profits, private health insurance providers have an incentive to move towards the US model where they seek to avoid payment and set up exclusions etc. There is no ‘funding’ reason for the existence of these private insurance providers. The NHS in the UK demonstrates that clearly.
There has clearly been a strong private health industry lobby to privatise as much of the health care system as possible in places like Australia and the UK, where there are good fully-funded public systems of universal health care operating. That lobby has been powerful in the US and continually claims there will be a fiscal blow out and Americans will live in high-taxed penury forever because some latinos or blacks are getting health care for the first time as a result of the Obama changes. From a MMT perspective, the fiscal component of the debate is irrelevant.
The fiscal beat-up is framed in terms of ‘adding heavy costs’ to the ‘budget’ such that their will be soaring deficits, which will penalise future generations etc etc. What is a heavy cost? What is a soaring deficit? These are irrelevant concepts devoid of meaning. Any sophisticated society will deem health care to be a human right. The constitution of the World Health Organisation says: “The enjoyment of the highest attainable standard of health is one of the fundamental rights of every human being without the distinction of race, religion, political belief, economic or social condition.” The hallmark of a sophisticated nation is maximising the potential of its citizens. That must include placing health care under the responsibility of the currency-issuing government.

Line of the day: “Some market observers have said that a weaker dollar can help to boost earnings of S&P 500 companies and eventually justify their high valuations.”
• US Dollar Will Rebound In The Second Half Of 2017 – JPMorgan (CNBC)
The current weakness in the U.S. dollar may be short lived, as a pick-up in inflation and expected rate hikes by the Federal Reserve will support the greenback in the coming months, JPMorgan Asset Management said Wednesday. “We’re thinking that the dollar will actually rebound in the second half, and this is mainly as the markets re-price in interest rates hike. We’re of the view that inflation will actually be picking up in the U.S. and currently, markets have only priced in one rate hike now till end-2018,” Jasslyn Yeo, global market strategist at JPMorgan Asset Management, told CNBC’s “Street Signs.” “So, we think (markets) are going to do a bit of re-pricing and that will support a bit of a rebound in the dollar,” she added.
The U.S. dollar tumbled to a 10-month low on Tuesday after the Republican health-care bill aimed at replacing Obamacare failed to get enough backing to proceed to a debate. Some market observers have said that a weaker dollar can help to boost earnings of S&P 500 companies and eventually justify their high valuations. But Yeo said equity markets outside the U.S., such as Europe and Japan, have more upside potential. Yeo noted that margins in Europe are starting to improve and that could translate into stronger earnings growth, while Japan is likely to benefit from a weaker yen versus the U.S. dollar. “We still like certain spots in the U.S. market. Currently we still favor U.S. banks, which we like in terms of rate hike expectations, bond yields moving higher as well as the promise for financial deregulation in the banking system,” she said.

Sell it all off, who cares?
• Foreigners Snap Up Record Number Of US Homes (CNBC)
Foreign purchases of U.S. residential real estate surged to the highest level ever in terms of number of homes sold and dollar volume. Foreign buyers closed on $153 billion worth of U.S. residential properties between April 2016 and March 2017, a 49% jump from the period a year earlier, according to the National Association of Realtors. That surpasses the previous high, set in 2015. The jump follows a year-earlier retreat and comes as a surprise, given the current strength of the U.S. dollar against most foreign currencies, which makes U.S. housing even more expensive. Apparently, the value of a financial safe-haven is outweighing the rising costs. Foreign sales accounted for 10% of all existing home sales by dollar volume and 5% by number of properties. In total, foreign buyers purchased 284,455 homes, up 32% from the previous year.

Half of all foreign sales were in just three states: Florida, California and Texas. Chinese buyers led the pack for the fourth straight year, followed by buyers from Canada, the United Kingdom, Mexico and India. Russian buyers made up barely 1% of the purchases. But the biggest overall surge in sales in the last year came from Canadian buyers, who scooped up $19 billion worth of properties, mostly in Florida. They are also spending more, with the average price of a Canadian-bought home nearly doubling to $561,000. “There are more [baby] boomers now than ever before. It’s the demographic,” said Elli Davis, a real estate agent in Toronto who said she is seeing more older buyers downsize their primary home and purchase a second or third home in Florida. “The real estate here is worth so much more money. They all have more money. They’re selling the big city houses that are now $2 million-plus, where they went up so much in the last 10 to 15 years, so they’re cashing in.”

Noooo, that’s not late at all…
• Big Australian Banks Told To Hold More Capital, On Notice Over Mortgages (R.)
Australia on Wednesday ordered the country’s biggest banks to raise capital for the second time in two years and signalled further action to shore up their burgeoning mortgage books, potentially squeezing shareholder returns. The banking regulator said it would release a discussion paper later this year to include risk weights on mortgages among other changes, in-line with expected rules due to be finalised by global regulators. The warning on mortgages came as it raised the target for the four major banks’ common equity Tier 1 ratio – a key gauge of a lender’s strength – to at least 10.5%. That translates into an average increase of 100 basis points above the banks’ December 2016 levels. They are expected to meet the new benchmarks by January 2020.
The Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA) has now ordered the big banks to boost capital twice since 2015 as it seeks to make the sector impregnable to global shocks. Australia’s major lenders – Commonwealth Bank of Australia , Westpac Banking Corp, ANZ Banking Group and National Australia Bank – hold combined market share of more than 80%, raising fears their failure could fatally weaken the broader economy. “Capital levels that are unquestionably strong will undoubtedly equip the Australian banking sector to better handle adversity in the future and reduce the need for public sector support,” APRA Chairman Wayne Byres said in a statement.

Inevitable result of property bubbles.
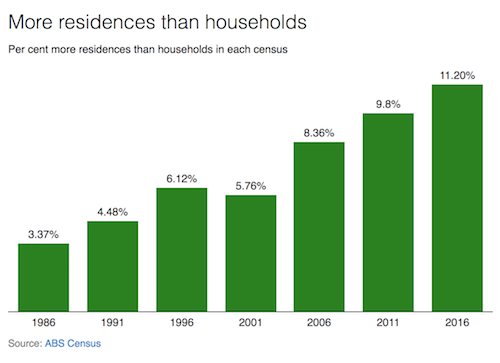
• One Million Homes Left Empty Across Australia (SMH)
Australia has 200,000 more homes sitting empty than it had a decade ago, new figures show, despite the country grappling with a housing supply shortage that is pushing the cost of a first home beyond many of its residents. The figures from the 2016 census have been described as “cruel and immoral” by leading UNSW urban policy expert Hal Pawson, who has warned the government must act to stem the growth in unoccupied housing. “There is gross under-occupation across Australia,” Mr Pawson said, adding that there were up to a million homes with three or more extra bedrooms than the owner required. “There is a growing realisation that our housing market is not working well. It doesn’t just create a problem for people on low incomes, it also hurts spending in the economy when housing is overvalued.”
The figures from the Australian Bureau of Statistics show up to 11.2% of properties are now unoccupied, up from 9.8% in 2006. In the space of two decades Australia has added 2.1 million homes to its property portfolio but an extra 360,000 are being left vacant. Separate analysis by the Grattan Institute, released on Monday, found the number of Australian home owners has been falling for three decades, with the spike in home ownership restricted to baby boomers. “Falling home ownership rates for younger Australians, especially 25 to 34-year-olds where home ownership rates are down 6% in the last decade alone, are just the latest evidence that the traditional Australian dream is slipping out of their reach,” said Grattan Institute fellow Brendan Coates.
[..] “The census showed empty property numbers up by 19% in Melbourne and 15% in Sydney over the past five years alone,” he said. “Considering that thousands of people sleep rough – almost 7000 on census night in 2011, more than 400 per night in Sydney in 2017 and that hundreds of thousands face overcrowded homes or unaffordable rents – these seem like cruel and immoral revelations.”

Better not lose your phone. Or the government can’t seeyou anymore.
• In Urban China, Nobody Uses Cash Or Cards Anymore (NYT)
There is an audacious economic experiment happening in China. It has nothing to do with debt, infrastructure spending or the other major economic topics du jour. It has to do with cash – specifically, how China is systematically and rapidly doing away with paper money and coins. Almost everyone in major Chinese cities is using a smartphone to pay for just about everything. At restaurants, a waiter will ask if you want to use WeChat or Alipay – the two smartphone payment options –before bringing up cash as a third, remote possibility. Just as startling is how quickly the transition has happened. Only three years ago there would be no question at all, because everyone was still using cash. “From a tech standpoint, this is probably one of the single most important innovations that has happened first in China, and at the moment it’s only in China,” says Richard Lim, managing director of the venture capital firm GSR Ventures.
There are certain parts of the Chinese internet that have to be seen to be believed. Coming from outside the country, it’s hard to comprehend that Facebook or Google can be completely blocked until you are forced to do without them. It’s tough to fathom how critical the messenger app WeChat is for everyday life until the sixth person of the day asks to scan your QR (quick response) code – a square-shaped barcode – to connect the two of you. What’s happening with cash in China is similar. For the past three years, I have been outside mainland China covering Asian technology from Hong Kong, which has a very different internet culture from the mainland. I knew that smartphone payments were taking over in China, as the statistics were stark: in 2016, China’s mobile payments hit £42 trillion ($5.5tn), roughly 50 times the size of America’s £860bn market, according to consulting firm iResearch.
[..] Some Scandinavian countries have also weaned themselves from cash but still use cards frequently. In China, the change has been to phones. One friend didn’t realise how reliant she had become on mobile payments until her bank called her. She had left her ATM card in the machine three weeks earlier and had not noticed its absence. In practical terms, this means that two Chinese companies – Tencent, which runs WeChat, and Alibaba, whose financial affiliate, Ant Financial, runs Alipay – are sitting atop a goldmine of staggering proportions. Both companies can make money off the transactions, charge other companies to use their payment platforms and all the while collect the payments data to be used in everything from new credit systems to advertising.

My wild guess: it’s not going to happen.
• Survivors Of 9/11 Urge May To Release Saudi Arabia Terror Report (Ind.)
Survivors of the 9/11 attacks have written to Prime Minister Theresa May – urging her to make public a British government report into the extent of Saudi Arabia’s funding of Islamist extremism in the UK. The report into the significance of the financing of Islamic extremists in Britain by Saudi Arabia and other nations was commissioned by Ms May’s predecessor, David Cameron, as part of a deal to obtain political support for a parliamentary vote on UK airstrikes on Syria. Last week, British Home Secretary Amber Rudd said the report was not being published “because of the volume of personal information it contains and for national security reasons”. Green Party co-leader Caroline Lucas suggested the refusal to make public the report was linked to a reluctance to criticise the kingdom, with which Britain has long had close strategic and economic ties.
Now, a group representing US survivors of the 9/11 attacks and the relatives of some of the almost 3,000 people who died, has urged Ms May to seize the chance to release the report, even if it is not fully complete. “The UK now has the unique historic opportunity to stop the killing spree of Wahhabism-inspired terrorists by releasing the UK government’s report on terrorism financing in the UK which, according to media reports, places Saudi Arabia at its centre of culpability,” says the letter, signed by 15 people. “The longer Saudi Arabia’s complicity is hidden from sunlight, the longer terrorism will continue. They must be stopped; but who will stop them? We submit that you are uniquely situated to shine the cleansing light of public consciousness.” It adds: “We respectfully urge you to release the report now, finished or unfinished. We ask you to consider all the victims of state-sponsored, Saudi-financed terrorism, their families and their survivors in the UK and all over the world.”

Completely insane. Lawless.
• West Virginians Are Fighting To Save Their Neighbors From Opioids (NewYorker)
Michael Barrett and Jenna Mulligan, emergency paramedics in Berkeley County, West Virginia, recently got a call that sent them to the youth softball field in a tiny town called Hedgesville. It was the first practice of the season for the girls’ Little League team, and dusk was descending. Barrett and Mulligan drove past a clubhouse with a blue-and-yellow sign that read “Home of the Lady Eagles,” and stopped near a scrubby set of bleachers, where parents had gathered to watch their daughters bat and field. Two of the parents were lying on the ground, unconscious, several yards apart. As Barrett later recalled, the couple’s thirteen-year-old daughter was sitting behind a chain-link backstop with her teammates, who were hugging her and comforting her.
The couple’s younger children, aged ten and seven, were running back and forth between their parents, screaming, “Wake up! Wake up!” When Barrett and Mulligan knelt down to administer Narcan, a drug that reverses heroin overdoses, some of the other parents got angry. “You know, saying, ‘This is bullcrap,’ ” Barrett told me. “ ‘Why’s my kid gotta see this? Just let ’em lay there.’ After a few minutes, the couple began to groan as they revived. Adults ushered the younger kids away. From the other side of the backstop, the older kids asked Barrett if the parents had overdosed. “I was, like, ‘I’m not gonna say.’ The kids aren’t stupid. They know people don’t just pass out for no reason.” During the chaos, someone made a call to Child Protective Services.
At this stage of the American opioid epidemic, many addicts are collapsing in public—in gas stations, in restaurant bathrooms, in the aisles of big-box stores. Brian Costello, a former Army medic who is the director of the Berkeley County Emergency Medical Services, believes that more overdoses are occurring in this way because users figure that somebody will find them before they die. “To people who don’t have that addiction, that sounds crazy,” he said. “But, from a health-care provider’s standpoint, you say to yourself, ‘No, this is survival to them.’ They’re struggling with using but not wanting to die.”

So?
• This Isn’t the First US Opiate-Addiction Crisis (BBG)
The U.S. is in the throes of an “unprecedented opioid epidemic,” reports the Centers for Disease Control. The crisis has spurred calls for action to halt the rising death toll, which has devastated many rural communities. It’s true that there’s an opioid epidemic, a public health disaster. It’s not true that it’s unprecedented. A remarkably similar epidemic beset the U.S. some 150 years ago. The story of that earlier catastrophe offers some sobering lessons as to how to address the problem. Opioids are a broad class of drugs that relieve pain by acting directly on the central nervous system. They include substances such as morphine and its close cousin, heroin, both derived from the opium poppy. There are also synthetic versions, such as fentanyl, and medications that are derived from a mix of natural and synthetic sources, such as oxycodone.

Opioid addiction can take many forms, but the current crisis began with the use and abuse of legal painkillers in the 1990s, and has since metastasized into a larger epidemic, with heroin playing an especially outsized role. All of this is depressingly familiar. The first great U.S. opiate-addiction epidemic began much the same way, with medications handed out by well-meaning doctors who embraced a wondrous new class of drugs as the answer to a wide range of aches and pains. The pharmacologist Nathaniel Chapman, writing in 1817, held up opium as the most useful drug in the physician’s arsenal, arguing that there was “scarcely one morbid affection or disordered condition” that would fail to respond to its wonder-working powers. That same year, chemists devised a process for isolating a key alkaloid compound from raw opium: morphine.
Though there’s some evidence that opiate dependency had become a problem as early as the 1840s, it wasn’t until the 1860s and 1870s that addiction became a widespread phenomenon. The key, according to historian David Courtwright, was the widespread adoption of the hypodermic needle in the 1870s. Prior to this innovation, physicians administered opiates orally. During the Civil War, for example, doctors on the Union side administered 10 million opium pills and nearly three million ounces of opium powders and tinctures. Though some soldiers undoubtedly became junkies in the process, oral administration had all manner of unpleasant gastric side effects, limiting the appeal to potential addicts.

The Koch brothers and the Fauxbel for economics.
• A Despot In Disguise: One Man’s Mission To Rip Up Democracy (Monbiot)
In 2013 she stumbled across a deserted clapboard house on the campus of George Mason University in Virginia. It was stuffed with the unsorted archives of a man who had died that year whose name is probably unfamiliar to you: James McGill Buchanan. She says the first thing she picked up was a stack of confidential letters concerning millions of dollars transferred to the university by the billionaire Charles Koch. Her discoveries in that house of horrors reveal how Buchanan, in collaboration with business tycoons and the institutes they founded, developed a hidden programme for suppressing democracy on behalf of the very rich. The programme is now reshaping politics, and not just in the US.
Buchanan was strongly influenced by both the neoliberalism of Friedrich Hayek and Ludwig von Mises, and the property supremacism of John C Calhoun, who argued in the first half of the 19th century that freedom consists of the absolute right to use your property (including your slaves) however you may wish; any institution that impinges on this right is an agent of oppression, exploiting men of property on behalf of the undeserving masses. James Buchanan brought these influences together to create what he called public choice theory. He argued that a society could not be considered free unless every citizen has the right to veto its decisions. What he meant by this was that no one should be taxed against their will. But the rich were being exploited by people who use their votes to demand money that others have earned, through involuntary taxes to support public spending and welfare.
Allowing workers to form trade unions and imposing graduated income taxes were forms of “differential or discriminatory legislation” against the owners of capital. Any clash between “freedom” (allowing the rich to do as they wish) and democracy should be resolved in favour of freedom. In his book The Limits of Liberty, he noted that “despotism may be the only organisational alternative to the political structure that we observe.” Despotism in defence of freedom. His prescription was a “constitutional revolution”: creating irrevocable restraints to limit democratic choice. Sponsored throughout his working life by wealthy foundations, billionaires and corporations, he developed a theoretical account of what this constitutional revolution would look like, and a strategy for implementing it. He explained how attempts to desegregate schooling in the American south could be frustrated by setting up a network of state-sponsored private schools. It was he who first proposed privatising universities, and imposing full tuition fees on students: his original purpose was to crush student activism.
He urged privatisation of social security and many other functions of the state. He sought to break the links between people and government, and demolish trust in public institutions. He aimed, in short, to save capitalism from democracy. In 1980, he was able to put the programme into action. He was invited to Chile, where he helped the Pinochet dictatorship write a new constitution, which, partly through the clever devices Buchanan proposed, has proved impossible to reverse entirely. Amid the torture and killings, he advised the government to extend programmes of privatisation, austerity, monetary restraint, deregulation and the destruction of trade unions: a package that helped trigger economic collapse in 1982. None of this troubled the Swedish Academy, which through his devotee at Stockholm University Assar Lindbeck in 1986 awarded James Buchanan the Nobel memorial prize for economics. It is one of several decisions that have turned this prize toxic.

Well, it would create a ton of chaos…
• Italy Mulls Temporary Humanitarian Visas For Migrants, Refugees (G.)
Italy has confirmed it is considering issuing temporary humanitarian visas that would allow tens of thousands of migrants who have arrived in the country from Libya to travel around the European Union. The move would provoke an immediate Austrian response, including the closure of the border with Italy at the Brenner Pass. The chances of Italy being able legally to grant unilateral humanitarian visas in this way is slight, but the threat is intended to concentrate minds in the EU after Italy failed to win clear practical support from Germany and France to take more people that have been arriving in increasing numbers from Libya.
The refugee crisis is putting growing political domestic pressure on the Democratic party (PD)-led government, with PD mayors refusing to take extra migrants and plans for legislation on citizenship being shelved at the weekend by the Italian prime minister, Paulo Gentiloni. In an interview with Il Manifesto, Mario Giro, the deputy foreign minister, said the government was looking at all options including the granting of temporary visas. Previously he had simply described the idea as speculation, and it had been dismissed by the interior minister. Giro said: “We are in a tug of war.” He said Italy wanted to avoid unilateral gestures, but was against the strict application of EU law which required migrants to remain in their first country of arrival.
“We don’t accept being turned into a European hotspot, or feeling guilty because we rescue people, so deciding what to do with the migrants who arrive is everyone’s responsibility,” he said. On Monday, the Italian foreign minister, Angelino Alfano, said the idea of humanitarian visas was not on the agenda. The EU high commissioner for external affairs, Federica Mogherini, insisted the issue was not discussed at the EU foreign affairs council meeting on Monday in Brussels. But the Italians are examining whether they could invoke the application of directive 2001/55, a measure approved following the Balkan wars, that allows the granting of humanitarian visas. It was too early to say when or how many such permits could be issued, Giro said, adding that the Italian authorities who received asylum requests already had the power to grant them.








