
Lewis Wickes Hine 12-year-old newsie, Hyman Alpert, been selling 3 years, New Haven CT 1909

Never mind public debt. $100 trillion in private debt is the big number.
• World Is Swimming In Record $152 Trillion In Debt: IMF (R.)
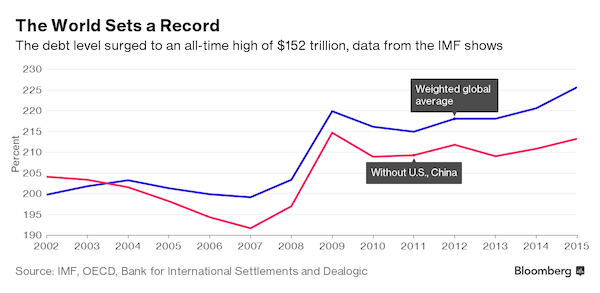
The world is swimming in a record $152 trillion in debt, the IMF said on Wednesday, even as the institution encourages some countries to spend more to boost flagging growth if they can afford it. Global debt, both public and private, reached 225% of global economic output last year, up from about 200% in 2002, the IMF said in its new Fiscal Monitor report. The IMF said about two thirds of the 2015 total, or about $100 trillion, is owed by private sector borrowers, and noted that rapid increases in private debt often lead to financial crises. While debt profiles vary by country, the report said that the sheer size of the debt could set the stage for an unprecedented private deleveraging that could thwart a still-fragile economic recovery.
“Excessive private debt is a major headwind against the global recovery and a risk to financial stability,” IMF Fiscal Affairs Director Vitor Gaspar told a news conference. “Financial recessions are longer and deeper than normal recessions.” While the United States has de-leveraged since the 2008-2009 financial crisis, the report cited the buildup of private debt in China and Brazil as a significant concern, fueled in part by a long era of low interest rates. The report comes as IMF managing director Christine Lagarde is urging the Fund’s 189 member governments that have “fiscal space” – the ability to sustainably borrow and spend more – to do so to boost persistently weak growth.
The Fund’s call for targeted fiscal support for consumer demand comes is accompanied by calls for continued accommodative monetary policy and accelerated structural reforms aimed at boosting countries’ economic efficiency. If a major deleveraging of private debt were to occur, the IMF report recommends that fiscal policy should include targeted interventions to restructure private debt or repair bank balance sheets to mininize damage to the overall economy.

An Australian take on the IMF debt report, which singles out the country along with Canada.
• Australia Private-Sector Debt Rises Faster Than Almost Anywhere Else (Aus.)
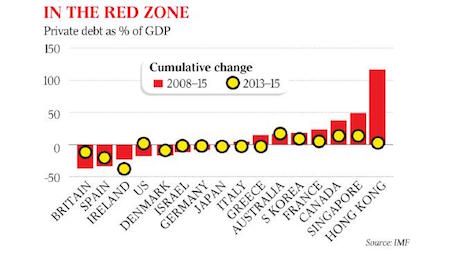
Private-sector debt is rising faster in Australia than almost anywhere else in the world, according to the IMF, which is concerned record debt globally may be setting the stage for a future downturn. The fund estimates that total debt levels have kept climbing since the global financial crisis, and are now equivalent to 225% of global GDP, up from 200% before the crisis. “Excessive private debt is a major headwind against the global recovery and a risk to financial stability”, said the head of the fund’s fiscal department, Vitor Gaspar, releasing the fund’s latest review of government finances. T�h�e� �I�M�F� �s�a�y�s� �p�r�i�v�a�t�e�-�s�e�c�t�o�r� �d�e�b�t� �i�n� �m�o�s�t� �a�d�v�a�n�c�e�d� �c�o�u�n�t�r�i�e�s� �r�e�a�c�h�e�d� �a� �p�e�a�k� �i�n� �2�0�1�2� �a�n�d� �s�t�a�r�t�e�d� �c�o�m�i�n�g� �d�o�w�n�,� �w�i�t�h� �t�h�e� �b�i�g�g�e�s�t� ��r�e�d�u�c�t�i�o�n�s� �r�e�c�o�r�d�e�d� �i�n� �c�o�u�n�t�r�i�e�s� �s�u�c�h� �a�s� �I�r�e�l�a�n�d� �a�n�d� �S�l�o�v�e�n�i�a� �t�h�a�t� �e�n�t�e�r�e�d� �t�h�e� �f�i�n�a�n�c�i�a�l� �c�r�i�s�i�s� �w�i�t�h� ��e�l�e�v�a�t�e�d� �d�e�b�t�s�.�
The IMF says private-sector debt in most advanced countries reached a peak in 2012 and started coming down, with the biggest reductions recorded in countries such as Ireland and Slovenia that entered the financial crisis with elevated debts. In some cases, however, private debt has continued to accumulate at a fast pace-notably, Australia, Canada, and Singapore, the fund says. The IMF estimates that, since 2013, private debt has risen as a share of GDP by 15 percentage points, more than in any other advanced nation. Private debt in Australia has risen from 188% of GDP to 225% since the global financial crisis, mostly driven by lending to households. Mr Gaspar said the risk was not just that private debt could revert to the government in a crisis, as occurred when many advanced country governments had to take over banks during the financial crisis.
“Rapid increases in private debt often end up in financial crises and financial recessions are longer and deeper than normal recessions”, he said. The fund says even without a financial crisis, high private-sector debt will hamper growth because highly indebted borrowers eventually cut back their consumption and investment. It says there is no consensus about the threshold at which debt levels start affecting growth, but says the longer that debt keeps rising, the greater becomes the sensitivity of the economy to any unexpected shocks. The IMF report shows that Australia s federal and state government debt remains one of the lowest in the advanced world, projected to peak at 21.6% of GDP in 2018, compared with an average of 80.5% for the advanced countries in the G20.

Why Draghi said there are too many banks in Europe. M&A can hide a lot of debt, or have taxpayers shoulder it.
• One-Third Of European Banks Fail IMF Stress Test: (WSJ)
Historic debt levels and dwindling policy ammunition risk derailing the meager recovery forecast for next year. Anemic global growth is “setting the stage for a vicious feedback loop in which lower growth hampers deleveraging and the debt overhang exacerbates the slowdown,” the emergency lender warned. The IMF lays out three major risks to the financial system. First, European banks are facing a chronic profitability crisis. Many haven’t been able to clear the legacy debt off their balance sheets and investors are increasingly skeptical they’ll be remain profitable based on their current structures. But it’s not just market perceptions. The IMF estimates that the recent plunge in bank equity price could curb lending until 2018.
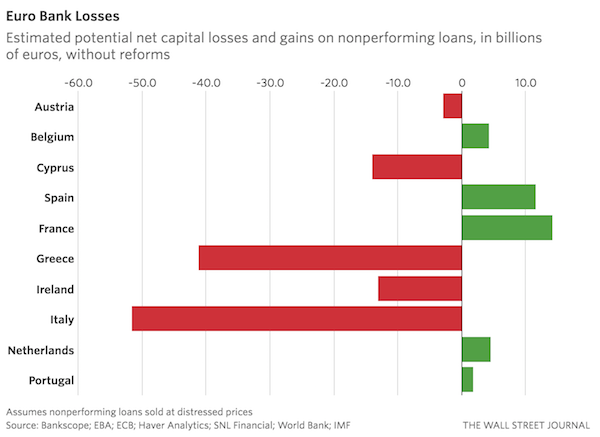
It also conducted a survey of more than 280 banks covering most of the banking systems in the U.S. and Europe to see if an economic recovery would be enough to propel them into long-term profitability. While a large majority of U.S. banks passed, nearly one-third of Europe’s banking system flunked. “A cyclical recovery helps but is not enough,” Mr. Dattels says. Those banking duds—representing $8.5 trillion in assets—remain weak and unable to generate sustainable profits even if growth picks up in the fund’s stress test. “Banks and policy makers need to tackle substantial structural challenges to survive in this new era.” Banks need to first resolve the massive stock of nonperforming loans. That requires banking authorities to fix their insolvency rules, a problem the IMF has been bugging Europe about for years. If officials could finally resolve that problem, it could turn a net capital cost to European banks of €85 billion to a net gain of €60 billion, the fund estimates.

One goal in mind: save large financial institutions. Not citizens.
• EU Readies Plan for Derivatives Clearing Crisis, the New Too-Big-to-Fail (BBG)
The EU plans to give authorities sweeping powers to tackle ailing derivatives clearinghouses to prevent their failure from wreaking havoc throughout the financial system. Draft EU legislation seen by Bloomberg sets out rules on saving or shuttering clearinghouses that would apply to firms such as London-based LCH. The proposals cover everything from the creation of resolution authorities to the powers they would have when winding a company down, including writing down shares, debt and collateral. Having forced most clearing to go through central counterparties to manage risk in the financial system, the EU will come out with recovery and resolution proposals by year-end. Clearing has come into focus after emerging as a pawn in the post-Brexit battle for London’s financial-services industry.
“If we are going to rely more on CCPs, we need to have a clear system in place to resolve them if things go wrong,” Valdis Dombrovskis, the EU’s financial-services chief, said last month. Governments around the world were spooked by the damage inflicted by derivatives trades that went awry during the financial crisis. Since then, they’ve taken steps to ensure trading in the contracts is reported and centrally cleared. Clearinghouses stand between the two sides of a derivative wager and hold collateral, known as margin, from both in case a member defaults. Many transactions were previously conducted directly between traders without a third party requiring collateral. Swaps trading, when it was largely unregulated, amplified the 2008 meltdown and prompted a $182 billion U.S. rescue of AIG.

“The very system they are built around is a corrupt and unsustainable model, and I hold that this is by design.”
• The Noose Is Tightening Quickly On The Global Economy (Alt-M)
The supposed “catalyst” for the 2008 crash is primarily attributed to the fall of Lehman Brothers. I highly recommend any of the “bullish” economists out there arguing today that the central banks intend to prolong a stock rally indefinitely examine the statements made in the mainstream about Lehman and by Lehman leading up to their eventual death rattle. Then, absorb and really think on some of the recent statements and tactics used by Deutsche Bank. Specifically, note Lehman’s use of accounting and derivatives gimmicks and the cycling of funds through various accounts in order to make the company appear solvent. Then, take a look at revelations coming out of places like Italy that Deutsche Bank has been using the same model of false accounts and market manipulation, once again, with derivatives as a main tool for fraud.
Also notice the same outright dismissals of all pertinent evidence that Deutsche Bank might be suffering a capital shortfall, as CEO John Cryan blames “speculators” for the companies losses. Lehman’s Dick Fuld and Bear Stearns’ Jimmy Cain both blamed “speculators” and “rumors and conspiracies” for the fall of their companies during the derivatives debacle eight years ago. It would seem that history doesn’t just rhyme, it sometimes repeats exactly. Below is a rather revealing chart from the folks at Zero Hedge comparing the collapse of Lehman Brothers stock value to the steady decline of Deutsche Bank. To be clear, Lehman was no catalyst. It was only a litmus test for a system completely devoid of tangible value and drowning in toxic debt. Lehman was a part of a much larger problem, it was not the cause of the problem. The same is true for Deutsche Bank.
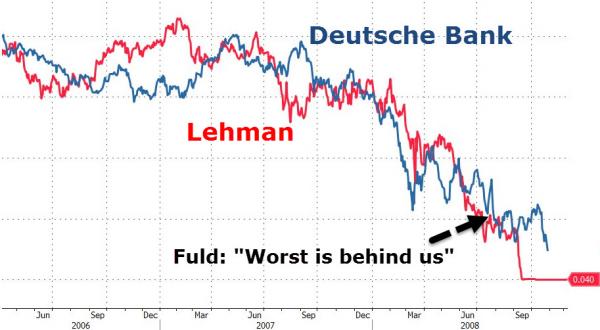
The panic growing around Germany’s second largest financial institution, Commerzbank, as it moves to lay off nearly 10,000 employees and suspend its dividend is another crisis indicator separate from Deutsche Bank. The clear solvency issues in Italy’s major banks, including Monte dei Paschi, are yet another explosive element.
Keep in mind that when these edifices begin to crumble and Europe enters a state of financial emergency, the mainstream media and numerous governments will continue to blame speculators. They will also claim that the entire disaster was set in motion through a “domino effect”; the first domino probably being Deutsche Bank. This will be a lie. There is no line of dominoes. One bank will not be bringing down the other banks — yes, there is terrible interdependency, but the real issue is that ALL of these banks are falling due to their own cancerous behaviors. The very system they are built around is a corrupt and unsustainable model, and I hold that this is by design.

Wow, he presents what has long been obvious as some sort of epiphany: “We could be stuck in a new longer-run equilibrium characterized by sluggish growth.”
• Fed’s Fischer Says Low Neutral Rate A Sign Of Potential Economic Trouble (R.)
Evidence that the so-called natural rate of interest has fallen to low levels could mean the economy is stuck in a low-growth rut that could prove hard to escape, Federal Reserve Vice Chair Stanley Fischer said on Wednesday. Speaking to a central banking seminar in New York, the Fed’s second-in-command said he was concerned that the changes in world savings and investment patterns that may have driven down the natural rate could “prove to be quite persistent…We could be stuck in a new longer-run equilibrium characterized by sluggish growth.” As a result, he said, central bankers may face a future where the short-term interest rates set by policymakers never get far above zero, and the unconventional tools used during the financial crisis become a “recurrent” fact of life.
“Ultralow interest rates may reflect more than just cyclical forces,” Fischer said, but “be yet another indication that the economy’s growth potential may have dimmed considerably.” Fischer’s remarks did not address current Fed policy or interest rate plans. It is not the first time a Fed official has openly expressed concerns about an underlying decline in U.S. economic potential, or fretted that the crisis shifted savings and investment patterns in a damaging way. Over the past year in particular there has been a vigorous debate, backed up by fresh research, about the “natural” rate of interest. Sometimes referred to as a neutral or equilibrium rate, it is in many ways an abstraction – not a rate that is set by the Fed or used in transactions, but an estimate of the underlying rate that would keep the price level stable while the economy grows at potential.
A number of developments have led many at the Fed to conclude that the natural rate is currently very low, and that its decline may reflect a loss of economic potential. There are immediate implications for the Fed: a low natural rate means the Fed could not move its short-term federal funds rate very high before policy becomes too tight.

Nothing new here either.
• Goldman Warns Of “Upward Shock” To Rates, Hints At Trillions In Losses (ZH)
[..] “The total face value of all US bonds, including Treasuries, Federal agency debt, mortgages, corporates, municipals and ABS, is $40 trillion (Securities Industry and Financial Markets Association). The Barclays US aggregate is a smaller number, $17 trillion, as the index excludes some categories of debt, such as money markets, with low duration. To end up with a more palatable number, Goldman uses the Barclays measure of debt outstanding, although it admits this may lead to an understatement of the total loss potential. Using either measure, total debt outstanding has grown by over 60% in real Dollars since 2000.”
[..] Doing the math, and combining a duration estimate of 5.6 years with the SIFMA total estimated notional exposure of $40trn, and current Dollar price of bonds of $105.6, indicates that, to first order, a 100bp shock to interest rates would translate into a market value loss estimate would be $2.4 trillion. That is the part Garzarelli forgot to write about. Which is ironic, because in trying to paint a bullish picture, the Goldman strategist in effect admitted that not just the Fed, but the entire world is trapped: should the global economy continue to contract, global bond yields will continue to sink, with trillions more bonds going negative yield, leading to even more debt issuance, and resulting in a ZIRP (and NIRP) trap from which there is no escape.
On the other hand, if – as Goldman hopes – inflation does materialize, however briefly, the resultant MTM loss will be staggering. Keep in mind that $2.4 trillion is only in the US. Now add tens of trillions of record low yielding global debt, including some $10.5 trillion in negative yield bonds around the globe, and one can make the case that the global MTM hit from an even 1% rise in rates would be somewhere between $5 and $8 trilion dollars! So, according to Goldman, here is the rather unpleasant choice facing the world: continue slowly sinking into a deflationary singularity, coupled with ever greater systemic leverage which makes escape from the ZIRP/NIRP trap impossible as social unrest builds up and ultimately spills over into the streets, or unleash an inflationary impulse, one which crushes countless debt holders, leads to trillions in losses, and requires yet another consolidated bailout…. oh, and also more social unrest.

If Italy leaves, there’s no EU left.
• Stiglitz Sees Italy, Others Leaving Euro Zone In Coming Years (R.)
Nobel Prize-winning economist Joseph Stiglitz predicted in a interview out on Wednesday that Italy and other countries would leave the euro zone in coming years, and he blamed the euro and German austerity policies for Europe’s economic problems. Europe lacks the decisiveness to undertake needed reforms such as the creation of a banking union involving joint bank deposit guarantees, and also lacks solidarity across national boundaries, Stiglitz was quoted as saying by Die Welt newspaper. “There will still be a euro zone in 10 years, but the question is, what will it look like? It’s very unlikely that it will still have 19 members. It’s difficult to say who will still belong,” the paper quoted Stiglitz as saying. “The people in Italy are increasingly disappointed in the euro.”
“Italians are starting to realize that Italy doesn’t work in the euro,” he added. He said Germany had already accepted that Greece would leave the euro zone, noting that he had advised both Greece and Portugal in the past to exit the single currency. Concerns about the euro zone have escalated in Germany in recent months amid growing concern about a shift away from austerity in southern Europe, the loose money policies of the ECB and the rise of the right-wing Alternative for Germany party. Stiglitz told the paper the euro and austerity policies in Germany were at fault for Europe’s economic malaise. The break-up of the single currency or the division into a north euro and a south euro were the only realistic options for reviving Europe’s stalled economy, the paper quoted him as saying.

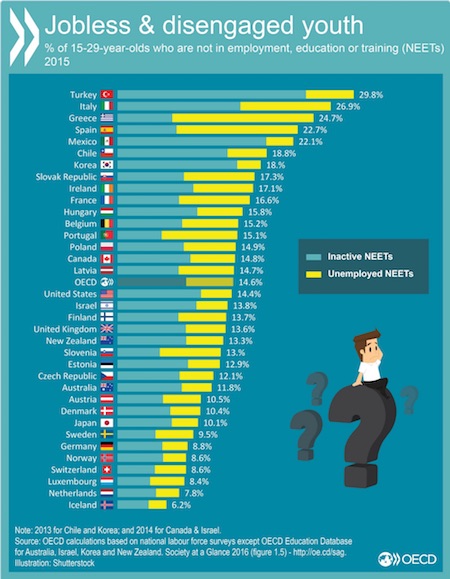
‘Target groups’ may be somewhat confusing: one survey looks at 15-29 year-olds, the other at 18-34 year-olds. But the trends are clear enough.
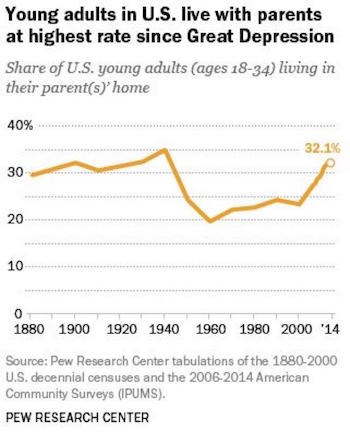
• Two Thirds Of Young American Adults Live With Their Parents (ZH)
As part of its periodic report on “Society at a Glance” which looks at how youth across member states are faring in terms of several social indicators, such as employment, poverty, marriage and health, the OECD also provided a unique glimpse into modern household composition, namely the%age of young adults, those aged 15-29, living at home. What it found is that since the Great Recession, there have been significant shifts worldwide in the number of young adults living at home. From 2007 to 2014, the number of youth living at home in countries belonging to the OECD increased by 0.7%, rising to 59.4%.
As expected, the nations hit hardest by the global economic slowdown such as Italy, Slovenia and Greece had the highest%age of youth living at home with their parents, at 80.6%, 76.4% and 76.3%, respectively. In itself, that is hardly surprising, since countries like Greece and Italy were not only among the harfest hit by the recession, and have a culture of young adults living longer at home, but also have some of the highest unemployment rates for young people. In fact, as the chart below shows, some 15% of young adults in OECD countries, or a whopping 40 million, were what the report classifies as NEET: not in employment, education or training, with both Italy and Greece at the very top, just behind Turkey.
On the other end of the spectrum, Canada had the lowest%age of youth living with parents, with just 30% of the country’s youth still living at home. The Nordic countries, including Denmark, Sweden, Finland and Norway, also had low numbers of young adults living at home. In terms of deterioration, France was by far the leader, with the number of young people cohabitating with their parents rising 12.5% to 53.5% from 2007 to 2014. Report authors attribute the increase in part to the high numbers of young adults in France who are not in the workforce or in education. In France, some 16.6% of young adults were not in a job or education institution in 2015, also a notable an increase over the previous few years.
Cited by US News, Claire Keane, an economist with the OECD’s social policy division said that “we really think this is a crisis story,” In France, she says, many benefits flow through families to reach young people. “They are relying on parents for financial support.” As for the US, there has been a 3.9% increase in the proportion of youth living with their parents from 2007 to 2014, significantly higher than the OECD average. As a result, today, about 66.6% of American 15- to 29 year-olds live with their parents as opposed to on their own or with a roommate, compared to around 62.8% before the crisis.

Syria was a relatively wealthy country not long ago. So was Libya. Guess what happened?
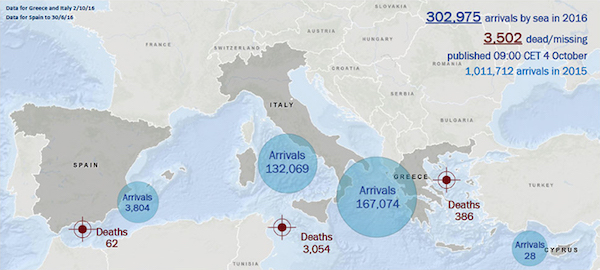
• The Math of Escaping From Syria (R.)
– Duration of Syrian Civil War: 5 years, 6 months, approximately. – Number of refugees through Oct. 1: 302,975. – Number of refugees drowned en route to Europe: 3,502 We’ve seen the pictures. We’ve read the stories. The numbers are stark. A single boat crossing on the Mediterranean cost $2,200 per passenger in the summer of 2015, up from an average $1,500 a year earlier, according to refugees’ accounts. For Syrians, as with most migrants seeking asylum, money is scarce; a report by the Syrian Economic Forum showed average monthly income for a citizen of Aleppo was around $80 last year. So if you’re a refugee, you face the prospect of spending as much as two years of your wages for a journey on which 1 of 87 refugees have drowned.
How bad is the economy you’re leaving behind? Let’s take the Great Recession of 2007 to 2009 in the U.S. as a comparison. GDP decreased at an average annual rate of 3.5%. Unemployment reached a high of 10% in Oct. 2009. In that year, 14.3% of the U.S. were living below the poverty line. In Syria, GDP fell 30% in 2013 and another 36% in 2014; 82% of the population lives below the poverty line; unemployment is at 60%. And 2016 looks pretty bleak as well. And that’s leaving aside falling bombs, chemical weapons and woefully inadequate medical care. Also connecting with international aid groups takes time, as many Syrians are located in hard to reach areas.
And let’s not forget you are probably a kid. More than 50% of refugees are under the age of 18 – and haven’t had educational access for years; not to mention the added trauma of witnessing extreme violence. So spending up to two years of your wages and risking your life to get to a safe haven, versus staying in a country where it’s likely you will die a violent death suddenly seems like a remarkably sound decision.

How many billions have been spent on ending world hunger? Or maybe we should ask how many have been spent on warfare.
• Nearly Half Of All Children In Sub-Saharan Africa Live In Extreme Poverty (G.)
Nearly half of all children in sub-Saharan Africa are living in extreme poverty, according to a joint Unicef-World Bank report released on Tuesday, with figures showing that almost 385 million children worldwide survive on less than $1.90 (£1.50) a day, the World Bank international poverty line. Extreme poverty leads to stunted development, limited future productivity as adults, and intergenerational transmission of poverty, the report (pdf) says. The figures – based on data from 89 countries, and representing 84% of the developing world’s population – indicate that much work will be needed to meet the sustainable development goal of eradicating extreme poverty by 2030.
Children are disproportionately affected by extreme poverty – they make up just a third of the population studied, but comprise half of the extreme poor. They are twice as likely as adults to be living on less than $1.90 a day, the report claims, with 19.5% of children in developing countries living in extremely poor households, compared to just 9.2% of adults. “It’s almost a double blow – firstly, that children are twice as likely as an adult to live in extreme poverty, but also that children are much less likely than an adult to be able to cope with extreme poverty because of stunting, infant mortality, and early childhood development,” said Unicef’s deputy executive director, Justin Forsyth. “Extreme poverty can either kill you, or ruin your potential for the rest of your life.”









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle October 6 2016