
Unknown A couple wearing smog masks, London 1953

“The curve is flattening; we can end lockdown now”
=
“This parachute has slowed my rate of descent; I can take it off now”

Compare Spain and Greece: What difference does two weeks make? 100X pic.twitter.com/6GATJpyXJo
— Yaneer Bar-Yam (@yaneerbaryam) April 19, 2020

• Cases 2,345,476 (+ 84,051 from yesterday’s 2,261,425)
• Deaths 161,196 (+ 6,462 from yesterday’s 147,378)

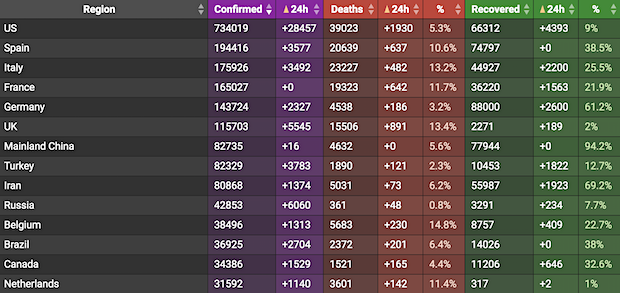
From Worldometer yesterday evening -before their day’s close-
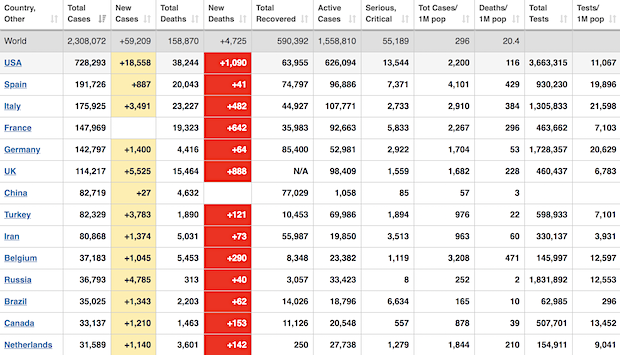
From Worldometer – NOTE: among Active Cases, Serious or Critical fell to 3%
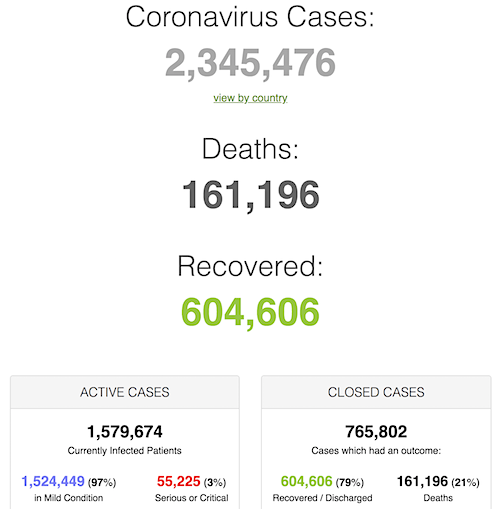
From SCMP:
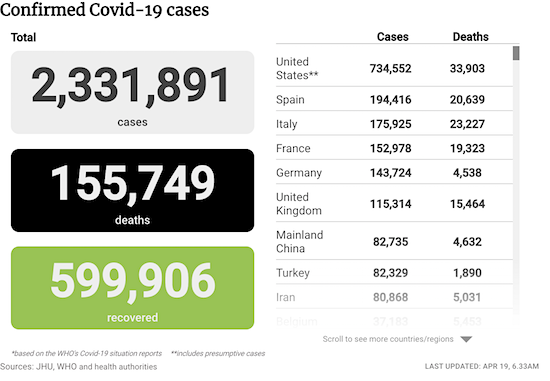
From COVID19Info.live:

Just as everyone says it was the lab.
• Did COVID19 Outbreak Start Months Earlier And Not In Wuhan? (RT)
The novel coronavirus may have first passed to humans somewhere in southern China months before the outbreak in the city of Wuhan, a new study found, cutting against widely held theories about the origins of the pandemic. Mapping a “network” of coronavirus genomes and tracing mutations over time, a team of researchers led by a Cambridge University geneticist determined the first Covid-19 infection may have come as early as September in a region south of Wuhan, noting the pathogen could have been carried by humans well before it mutated into a more lethal form. “The virus may have mutated into its final ‘human-efficient’ form months ago, but stayed inside a bat or other animal or even human for several months without infecting other individuals,” geneticist Peter Forster told the South China Morning Post.
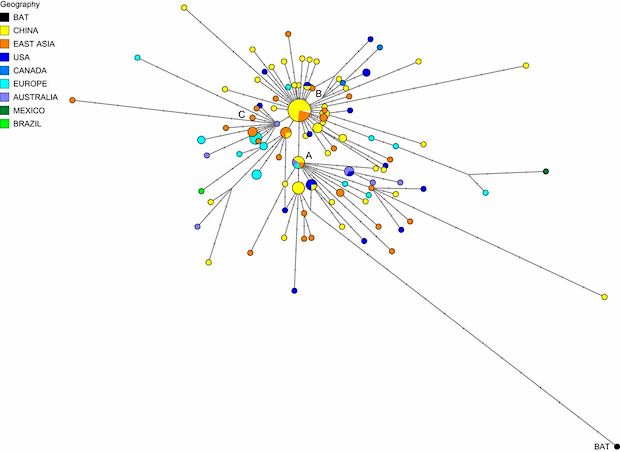
Phylogenetic network of 160 SARS-CoV-2 genomes © PNAS / Peter Forster
He leads the ongoing yet to be peer-reviewed research, recently published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences journal. “Then, it started infecting and spreading among humans between September 13 and December 7, generating the network we present in [the study]”. Though the virus is thought to have transmitted from bats to another host animal – pangolins are a popular candidate – and finally to humans, the new findings could overturn prevailing ideas as to precisely how, when and where it made the interspecies leap. Initial theories posited the jump to humans took place at a wet market in Wuhan, but the new study has called that into question, suggesting Covid-19 might have originated south of the central-Chinese city.
“If I am pressed for an answer, I would say the original spread started more likely in southern China than in Wuhan.” Any solid conclusions, however, could only be made after analyzing more bats and other potential host animals, as well as tissue samples from early patients, Forster cautioned. “But it is the best assumption we can make at the moment, pending analysis of further patient samples stored in hospitals during 2019,” the researcher told Newsweek in a separate interview.

For two whole months, Shinzo Abe had just one thing in mind: the Olympics. Everything else had to be pushed aside.
• New Wave Of Infections Threatens To Collapse Japan Hospitals (AP)
Hospitals in Japan are increasingly turning away sick people as the country struggles with surging coronavirus infections and its emergency medical system collapses. In one recent case, an ambulance carrying a man with a fever and difficulty breathing was rejected by 80 hospitals and forced to search for hours for a hospital in downtown Tokyo that would treat him. Another feverish man finally reached a hospital after paramedics unsuccessfully contacted 40 clinics. The Japanese Association for Acute Medicine and the Japanese Society for Emergency Medicine say many hospital emergency rooms are refusing to treat people including those suffering strokes, heart attacks and external injuries.
Japan initially seemed to have controlled the outbreak by going after clusters of infections in specific places, usually enclosed spaces such as clubs, gyms and meeting venues. But the spread of virus outpaced this approach and most new cases are untraceable. The outbreak has highlighted underlying weaknesses in medical care in Japan, which has long been praised for its high quality insurance system and reasonable costs. Apart from a general unwillingness to embrace social distancing, experts fault government incompetence and a widespread shortage of the protective gear and equipment medical workers need to do their jobs. Japan lacks enough hospital beds, medical workers or equipment. Forcing hospitalization of anyone with the virus, even those with mild symptoms, has left hospitals overcrowded and understaffed.
[..] Medical workers are now reusing N95 masks and making their own face shields. The major city of Osaka has sought contributions of unused plastic raincoats for use as hazmat gowns. Abe has appealed to manufacturers to step up production of masks and gowns, ventilators and other supplies. A government virus task force has warned that, in a worst-case scenario where no preventive measures were taken, more than 400,000 could die due to shortages of ventilators and other intensive care equipment. Prime Minister Shinzo Abe has said the government has secured 15,000 ventilators and is getting support of Sony and Toyota Motor Corp. to produce more.
Japanese hospitals also lack ICUs, with only five per 100,000 people, compared to about 30 in Germany, 35 in the U.S. and 12 in Italy, said Osamu Nishida, head of the Japanese Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Italy’s 10% mortality rate, compared to Germany’s 1%, is partly due to the shortage of ICU facilities, Nishida said. “Japan, with ICUs not even half of Italy’s, is expected to face a fatality overshoot very quickly,” he said. Japan has been limiting testing for the coronavirus mainly because of rules requiring any patients to be hospitalized. Surging infections have prompted the Health Ministry to loosen those rules and move patients with milder symptoms to hotels to free up beds for those requiring more care.

Wherever you put large groups of people together, this happens with a highly contagious virus.
• Florida Prison System Begins To Reveal Ravages Of Coronavirus (MH)
For weeks the Florida Department of Corrections refused to address rumors that inmates with coronavirus-like symptoms — or those who had come into contact with symptomatic inmates or staff — were being segregated by the hundreds from the general population. That changed on Friday, when the agency acknowledged that more than 4,500 inmates are being isolated in one way or another as COVID-19, the highly infectious disease caused by the novel coronavirus, has spread throughout the third-largest prison system in the country. As of Friday evening, 45 inmates and 71 staff members had tested positive for COVID-19, according to the FDC. Four inmates had died, all of whom had been incarcerated at Blackwater River Correctional Facility, a compound near Pensacola run under contract by the Geo Group.
The medical examiner in Santa Rosa County revealed the deaths. The new data was made public amid a growing chorus of criticism by a handful of lawmakers, including an influential Republican, state Sen. Jeff Brandes, who is vice chairman of the Senate Criminal Justice Committee. The department found itself on the defensive this week when those four deaths were revealed not by prison administrators — including its communication staff, which has ignored questions from reporters for several weeks — but by journalists who sought out information from the Santa Rosa County medical examiner. After the first two deaths were reported by the News Service of Florida, confirmation was hastily posted on the department’s website.

About 20 times higher.
• UK Care Home Deaths ‘Far Higher’ Than Official Figures (BBC)
New data has added to growing evidence that the number of deaths linked to coronavirus in UK care homes may be far higher than those recorded so far. The National Care Forum (NCF) estimates that more than 4,000 elderly and disabled people have died across all residential and nursing homes. Its report comes amid calls for accurate data on virus-linked deaths. Only 217 such care home deaths have been officially recorded in England and Wales up to 3 April. The NCF, which represents not-for-profit care providers, said its findings highlight significant flaws in the official reporting of coronavirus-related death statistics.
It collected data from care homes looking after more than 30,000 people in the UK, representing 7.4% of those people living in one of the country’s thousands of care settings. It said that, across those specific homes, in the week between 7 April and 13 April, there had been 299 deaths linked to coronavirus. That was treble the figure for the previous week and double that in the whole of the preceding month. If that number was reflected across all residential and nursing homes, NCF estimated there have been 4,040 coronavirus-related deaths in care homes which are not yet included in official figures.

And then the nurses start dying too.
• Anger In Sweden As Elderly Pay Price For Coronavirus Strategy (O.)
It was just a few days after the ban on visits to his mother’s nursing home in the Swedish city of Uppsala, on 3 April, that Magnus Bondesson started to get worried. “They [the home] opened up for Skype calls and that’s when I saw two employees. I didn’t see any masks and they didn’t have gloves on,” says Bondesson, a start-up founder and app developer. “When I called again a few days later I questioned the person helping out, asking why they didn’t use face masks, and he said they were just following the guidelines.” That same week there were numerous reports in Sweden’s national news media about just how badly the country’s nursing homes were starting to be hit by the coronavirus, with hundreds of cases confirmed at homes in Stockholm, the worst affected region, and infections in homes across the country.
Since then pressure has mounted on the government to explain how, despite a stated aim of protecting the elderly from the risks of Covid-19, a third of fatalities have been people living in care homes. Last week, as figures released by the Public Health Agency of Sweden indicated that 1,333 people had now died of coronavirus, the country’s normally unflappable state epidemiologist Anders Tegnell admitted that the situation in care homes was worrying. “This is our big problem area,” said Tegnell, the brains behind the government’s relatively light-touch strategy, which has seen it ask, rather than order, people to avoid non-essential travel, work from home and stay indoors if they are over 70 or are feeling ill.
The same day prime minister Stefan Löfven said that the country faced a “serious situation” in its old people’s homes, announced efforts to step up protections, and ordered the country’s health inspectorate to investigate. Lena Einhorn, a virologist who has been one of the leading domestic critics of Sweden’s coronavirus policy, told the Observer that the government and the health agency were still resisting the most obvious explanations. “They have to admit that it’s a huge failure, since they have said the whole time that their main aim has been to protect the elderly,” she said. “But what is really strange is that they still do not acknowledge the likely route. They say it’s very unfortunate, that they are investigating, and that it’s a matter of the training personnel, but they will not acknowledge that presymptomatic or asymptomatic spread is a factor.”
The agency’s advice to those managing and working at nursing homes [..] is that they should not wear protective masks or use other protective equipment unless they are dealing with a resident in the home they have reason to suspect is infected. Otherwise the central protective measure in place is that staff should stay home if they detect any symptoms in themselves. “Where I’m working we don’t have face masks at all, and we are working with the most vulnerable people of all,” said one care home worker, who wanted to remain anonymous. “We don’t have hand sanitiser, just soap. That’s it. Everybody’s concerned about it. We are all worried.” “The worst thing is that it is us, the staff, who are taking the infection in to the elderly,” complained one nurse to Swedish public broadcaster SVT. “It’s unbelievable that more of them haven’t been infected.”

No more of this.
• A Scam To Enrich Execs: COVID19 Bailouts Fuel More Share Buybacks (Feierstein)
To anyone doubting the Covid-19 bailouts will line executives’ pockets, American Airlines CEO Doug Parker says he’ll “find a way around” the rules against it. This after making $150 million while AAL’s stock plummeted 70%. Stock buybacks are the ultimate vehicle of self-enrichment. Consider the following as a ‘case study’ of Wall Street’s legal fraud. Under CEO Doug Parker’s leadership from 2013-2020, American Airlines has seen its stock plummet 70%. When one looks at Parker’s pay awarded vs the company’s three-year average economic profits, his pay-for-performance metrics are abominable. The media worships Parker for his stewardship of AAL during this crisis and reports that, for the past three years, Parker’s salary and bonus were zero.
However, they fail to mention that AAL’s legal Ponzi stock-buyback scheme saw Parker’s 2016-2018 take-home pay rocket to $70.2 million. (According to the FT, Parker’s total award from selling stock since 2013 is $150 million). It’s not bad for Parker, but it’s horrendous for AAL employees, shareholders and American taxpayers who will be stuffed with a $20 billion bailout. Fair? Not on your life. Debt-fuelled stock buybacks and dividend payments are engineered to artificially increase stock prices so that self-interested CEOs like Parker can “earn” higher compensation. Increasing debt creates an illusion of better earnings. However, buybacks cannibalize corporate balance sheets, leaving taxpayers exposed to unlimited “bailouts” when these leveraged bets go wrong.
What’s the difference between rogue hedge fund managers and airline CEOs? Not much, except some airline CEOs have been given golden parachutes to the tune of nearly $17.5 million. So who is enabling these CEOs to line their pockets with taxpayer money? Last summer, the US Federal Reserve released the results of its annual Comprehensive Capital Analysis and Review (CCAR). The CCAR is a bank stress test, which all the banks passed, and after passing the stress test, the Federal Reserve approved $125 billion in share buybacks! Yet, even though the banks all passed the stress test, the Financial Times recently reported that the president and chief executive of the Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis (who oversaw TARP during the GFC of 2008) is recommending big US banks raise $200 billion in capital now to act as a buffer against economic shock from the “coronavirus pandemic.” This is a bit like putting on your seatbelt after your airbag has already deployed.
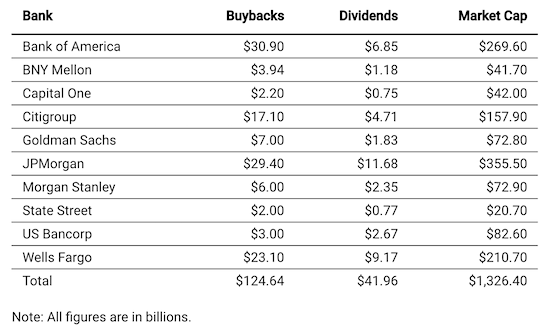

“..80% of the benefit of the bill went to just 43,000 taxpayers each earning over $1 million a year. The average tax break for those 43,000 individuals was $1.6 million..”
• The Trickle-Up Bailout (Matt Taibbi)
Because the CARES Act was rushed to the floor, members didn’t have all of the information they might have wanted before the vote. After the bill passed, Democratic staffers sent these tax provisions in the CARES Act, sections 2303 and 2304, to the Joint Committee on Taxation, to be scored. They were stunned to learn they would cost $195 billion over ten years. In other words, what seemed like a run-of-the-mill offhand legislative pork provision ended up dwarfing the airline bailout and other main parts of the bill. “The cost of caring for this small slice of the wealthiest one percent is greater than the CARES Act funded for all hospitals in America,” says Texas Democrat Lloyd Doggett. “It’s greater than CARES provided for all state and local governments.”
The JCT analysis found that 80% of the benefit of the bill went to just 43,000 taxpayers each earning over $1 million a year. The average tax break for those 43,000 individuals was $1.6 million, an interesting number when one considers the loudness of the controversy over $1,200 relief checks for everyone else. Doggett joined Rhode Island Senator Sheldon Whitehouse in sending a letter to the Trump administration, demanding to know the provenance of these tax breaks. “This irresponsible provision must be repealed,” he says. It’s possible we’ll find out someday whose idea it was to insert those breaks. By then, however, other windfalls from the Covid-19 rescue might have rendered the $195 billion bailout appetizer quaint.
With the Fed’s announcement on April 9th of a $2.3 trillion program that includes purchases of junk bonds, the toolkit for support of the financial economy now encompasses nearly every conceivable official response apart from subsidy of stock markets. The sheer quantity of money raining down on the finance sector appears transformational, a “joyful noise” heard around the world.

Russia has done something very wrong.
• Russia Reports Record Daily Rise In Coronavirus Cases (R.)
Russia on Sunday reported a record rise of 6,060 new coronavirus cases over the previous 24 hours, bringing its nationwide tally to 42,853, the Russian coronavirus crisis response center said. The number of coronavirus cases in Russia began rising sharply this month, although it had reported far fewer infections than many western European countries in the outbreak’s early stages.

There should be different ways.
• Spain To Allow Children Outside After Six Weeks (BBC)
Spanish children have been kept indoors since 14 March, under strict measures to curb the spread of Covid-19. Now Prime Minister Pedro Sánchez aims to relax the rule on 27 April so they can “get some fresh air”. Barcelona Mayor Ada Colau, who has young children herself, this week pleaded with the government to allow children outside. Spain has seen more than 20,000 deaths since the start of the pandemic and almost 200,000 reported cases. In a televised briefing on Saturday evening, Mr Sánchez said Spain had left behind “the most extreme moments and contained the brutal onslaught of the pandemic”.
But he said he would ask parliament to extend Spain’s state of alarm to 9 May as the achievements made were “still insufficient and above all fragile” and could not be jeopardised by “hasty decisions”. Another 565 deaths were reported on Saturday, well down from the peak of the pandemic, and the government allowed some non-essential workers to resume construction and manufacturing last Monday. However, the main lockdown measures remain in place, with adults only allowed out to visit food shops and pharmacies or work considered essential. Children have been barred from leaving their homes completely.

“The number of positives was shocking, but the fact that 100 percent of the positives had no symptoms was equally shocking..”
• CDC Reviewing ‘Stunning’ Testing Results From Boston Homeless Shelter (B25)
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is now “actively looking into” results from universal COVID-19 testing at Pine Street Inn homeless shelter. The broad-scale testing took place at the shelter in Boston’s South End a week and a half ago because of a small cluster of cases there. “It was like a double knockout punch. The number of positives was shocking, but the fact that 100 percent of the positives had no symptoms was equally shocking,” said Dr. Jim O’Connell, president of Boston Health Care for the Homeless Program, which provides medical care at the city’s shelters. O’Connell said that the findings have changed the future of COVID-19 screenings at Boston’s homeless shelters.
“All the screening we were doing before this was based on whether you had a fever above 100.4 and whether you had symptoms,” said O’Connell. “How much of the COVID virus is being passed by people who don’t even know they have it?” The 146 people who tested positive were immediately moved to two different temporary isolation facilities in Boston. According to O’Connell, only one of those patients needed hospital care, and many continue to show no symptoms. “If we did universal testing among the general population, would these numbers be similar?” said Lyndia Downie, president and executive director at the Pine Street Inn.
“I think there are no many asymptomatic people right now. We just don’t know. We don’t have enough data on universal testing to understand how many asymptomatic people are contagious.” Hundreds of tests are now set to be conducted at additional Boston homeless shelters in the coming days. “It tells you, you don’t know who’s at risk. You don’t know what you need to do to contain the virus if you don’t actually have the details or facts,” said Marty Martinez, Boston’s chief of Health and Human Services.

His own party appears to be after his head.
• 38 Days When Britain Sleepwalked Into Disaster (Times)
On the third Friday of January a silent and stealthy killer was creeping across the world. Passing from person to person and borne on ships and planes, the coronavirus was already leaving a trail of bodies. The virus had spread from China to six countries and was almost certainly in many others. Sensing the coming danger, the British government briefly went into wartime mode that day, holding a meeting of Cobra, its national crisis committee. But it took just an hour that January 24 lunchtime to brush aside the coronavirus threat. Matt Hancock, the health secretary, bounced out of Whitehall after chairing the meeting and breezily told reporters the risk to the UK public was “low”.
This was despite the publication that day of an alarming study by Chinese doctors in the medical journal, The Lancet. It assessed the lethal potential of the virus, for the first time suggesting it was comparable to the 1918 Spanish flu pandemic, which killed up to 50 million people. Unusually, Boris Johnson had been absent from Cobra. The committee — which includes ministers, intelligence chiefs and military generals — gathers at moments of great peril such as terrorist attacks, natural disasters and other threats to the nation and is normally chaired by the prime minister. Johnson had found time that day, however, to join in a lunar new year dragon eyes ritual as part of Downing Street’s reception for the Chinese community, led by the country’s ambassador.
It was a big day for Johnson and there was a triumphal mood in Downing Street because the withdrawal treaty from the European Union was being signed in the late afternoon. It could have been the defining moment of his premiership — but that was before the world changed. That afternoon his spokesman played down the looming threat from the east and reassured the nation that we were “well prepared for any new diseases”. The confident, almost nonchalant, attitude displayed that day in January would continue for more than a month. Johnson went on to miss four further Cobra meetings on the virus.
As Britain was hit by unprecedented flooding, he completed the EU withdrawal, reshuffled his cabinet and then went away to the grace-and-favour country retreat at Chevening where he spent most of the two weeks over half-term with his pregnant fiancée, Carrie Symonds. It would not be until March 2 — another five weeks — that Johnson would attend a Cobra meeting about the coronavirus. But by then it was almost certainly too late. The virus had sneaked into our airports, our trains, our workplaces and our homes. Britain was on course for one of the worst infections of the most deadly virus to have hit the world in more than a century. Last week, a senior adviser to Downing Street broke ranks and blamed the weeks of complacency on a failure of leadership in cabinet. In particular, the prime minister was singled out. “There’s no way you’re at war if your PM isn’t there,” the adviser said.
6 days ago, in an answer to a Parliamentary Question, the Canadian Deputy Prime Minister said all governments of The Five Eyes were informed by their intelligence agencies in early January of the dangers posed by the coronavirus: https://t.co/tHeIjxVHmH
— Leighton Jenkins (@jenkinsleighto) April 18, 2020

If Osaka can ask for raincoats to be donated as hazmat suits, so can Britain. No shortage of raincoats.
• UK Medical Staff Face Weeks Without Protective Gowns (O.)
Doctors and nurses treating Covid-19 patients face shortages of protective full-length gowns for weeks to come, it has emerged, as anger builds over the failure to stockpile the garments. Critical shortages of the gowns have meant that some trusts have already had to make do with the best available alternatives as a result of the shortages, which forced a sudden change in Public Health England (PHE) guidelines on the use of gowns on Friday. Concerns are being raised within the NHS over why the gowns did not form part of the government’s pandemic stockpile. It is understood shortages are already forcing some NHS workers to use the controversial new guidelines, which tell them to wear a plastic apron with coveralls should the specialist fluid-repellent gowns run out. Workers are also advised to reuse washed aprons.
Meanwhile, surgeons are being told by senior colleagues not to put themselves at risk should they be unable to wear a protective gown. Professor Neil Mortensen, from the Royal College of Surgeons of England, said surgeons should not risk their health if fluid-repellent gowns or coveralls could not be used. “We are deeply disturbed by this latest change to personal protective equipment (PPE) guidance, which was issued without consulting expert medical bodies,” he said. “After weeks of working with PHE and our sister medical royal colleges to get PPE guidance right, this risks confusion and variation in practice across the country.”
Health unions warned that staff could begin to refuse to work if they felt the new guidelines put them at serious risk of contracting the coronavirus. Sara Gorton, Unison’s head of health, said: “Managers must be truly honest with health workers and their union reps over the weekend. If gowns run out, staff in high-risk areas may well decide that it’s no longer safe for them to work.” Last night, the British Medical Association (BMA) also warned that it would support doctors who refused to work with inadequate PPE. “There are limits to the level of risk staff can be expected to expose themselves and their patients to,” said Dr Chaand Nagpaul, BMA council chair.

No kidding, there’s a video somewhere here entitled: “Flocks of chickens to be slaughtered over coronavirus.. “
• Lockdown Puts Increasing Strain On Britain’s Food System (Ind.)
From a mosque in Banbury, taxi drivers left out of work during the lockdown are picking up an unusual fare: hundreds of doughballs and garlic dip that had been destined for local pizza restaurants and are now being diverted to people’s homes. Yasmin Kaduji, who runs Banbury Community Fridge is one of thousands of people working overtime across the UK to get meals to three million people thought to be going hungry due to the coronavirus pandemic. Yet, at the same time British farmers are warning they have been forced to throw millions of gallons of milk down the drain because it no longer has a buyer, cheesemakers are binning artisan cheese and meat processors have an overabundance of sirloin, rib-eye steaks and prime roasting joints. Supply and demand are severely misaligned.
While supermarket stocks have returned closer to normal after being plundered last month, more deep-rooted problems lay ahead for Britain’s food supplies which are set to come under increasing strain as lockdown is extended for at least another three weeks and could go on for much longer. The problem is not that there is not enough food but that the well-established routes that supply it have been upended so abruptly. When we saw empty shelves last month, the primary cause was not inconsiderate stockpilers, as some government ministers claimed, but the fact that a massive part of the food industry had been shut down overnight without a plan in place for how hundreds of millions of meals would be redirected.
Tim Lang, professor of food policy, at London’s City University, argues that the coronavirus pandemic has exposed the fragility of our food system; a system which stretches out over thousands of miles, dozens of countries, and is reliant on migrant labour and air freight. That system has been reshaped, according to Professor Lang’s analysis, largely to suit the interests of nine companies which sell 90 per cent of the food we buy. Supermarkets have been happy to rely on sprawling supply chains that are left exposed during a crisis, as long as the price is right and the product sells. This, along with a “dangerously complacent” government, has left the UK vulnerable in the current situation, Professor Lang argues.

But the incumbent order always protests violently first.
• Pandemics Have Reshaped The World In Unpredictable Ways Throughout History (ProsM)
In just four years—from 1347 to 1351—between a third and a half of the population of Europe died. That would be world-shaking enough in itself, but it also completely rewrote the social order. Before the Black Death, European society had for centuries been structured around what we’d later call feudalism: to over-simplify massively, the system by which poorer people would work for richer ones in exchange for access to their land, and put up with having no freedom of movement because otherwise they didn’t eat. But when plague caused the population to collapse, food and land prices plummeted, too. Land without workers turned out to be worthless, so the lords found themselves competing for labourers. Despite assorted ruling class efforts to overcome the laws of supply and demand, wages rose, and keeping peasants tied to particular scraps of land proved impossible.
The Black Death didn’t just kill people. It probably killed feudalism, too. It’s too early to know how coronavirus might reshape 21st-century society. But we can certainly speculate. Perhaps, as large chunks of the workforce simultaneously shift to working from home for the first time, it’ll kill the idea that you need to be in the office to get stuff done. If it turns out that employees will do their work even if they’re not literally in their managers’ line of sight, bosses could finally shake their addiction to presenteeism. That could have all sorts of unpredictable knock-on effects: less pressure on transport networks, lower emissions, even relief for overheated housing markets as people discover they can live further from work. Or perhaps it could drive an increase in mothers’ participation in the workforce: more flexible office culture, after all, would make it easier to combine work with caring responsibilities.
[..] Now that a fear of financial ruin might drive sick, contagious people to work when they should be in isolation, perhaps we can go back to talking about the state as the enabler of our freedoms rather than the barrier to them. Or perhaps it won’t: where this will take us, we just don’t know, and your guess is as good as mine. But pandemics have been reshaping the world in unpredictable ways throughout history. If this crisis is even a fraction as serious as it seems, don’t be surprised if the world afterwards looks very unlike the world before.

We would like to run the Automatic Earth on people’s kind donations. Since their revenue has collapsed, ads no longer pay for all you read, and your support is now an integral part of the process.
Thanks everyone for your wonderful donations to date.

Autriche ⬇️ pic.twitter.com/FV7mHMGNRC
— -VÉNOM- (@anthonysarti11) April 18, 2020

Pirro is certified nuts:
Holy fucking shit pic.twitter.com/7YR95gXisZ
— Quoth the Raven (@QTRResearch) April 19, 2020

This ad is nuts too:
This is the most devastating political ad I’ve seen in years. It reveals the truth about Trump and China, and that truth is ugly. pic.twitter.com/52cNf9Ay9u
— Joe Scarborough (@JoeNBC) April 18, 2020

And then there are the good people…
https://twitter.com/ValaAfshar/status/1251634686348210178



Support the Automatic Earth. It’s good for your mental health.








Home › Forums › Debt Rattle April 19 2020