M. C. Escher Symmetry Drawing 1948

“Medical science has made such tremendous progress that there is hardly a healthy human left”
– Aldous Huxley

No infections, lots of excess deaths. Why?
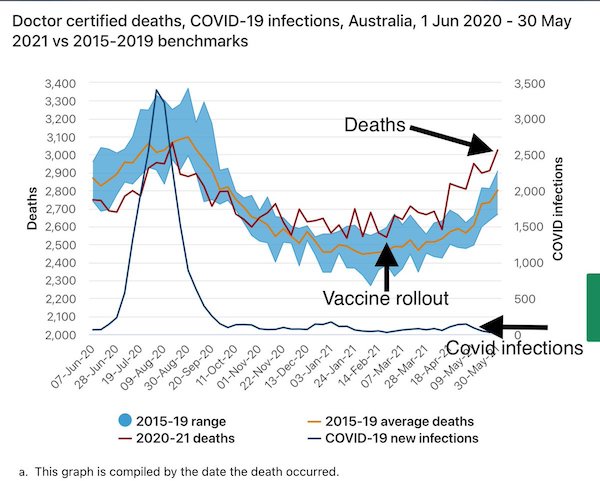


O’Looney

Launch 1,000 cases.
• Natural Immunity Emerges As Potential Legal Challenge To Vaccine Mandates (Y!)
The argument that natural immunity against COVID-19 is an alternative to vaccination is emerging as a potential legal challenge to federally mandated vaccination policies. Vaccination is already required for certain workers and some college students. The federal government, despite steeper legal hurdles to imposing vaccination, has also invoked the U.S. Department of Labor to mandate inoculation for health care workers and is expected to roll out a larger policy effectively mandating vaccination for a majority of U.S. workers. The stated goal behind mandatory vaccination policies is to protect against the spread of disease, meaning that the crux of any policy is immunity.
The notion that a previous COVID-19 infection provides natural immunity that can be at least as good as vaccination in some people is something a judge would likely need to consider in a challenge to a mandatory policy, especially against a government actor. “I think that a judge might reject a rule that’s been issued by a body, like the U.S. Department of Labor or by a state, that has not been sufficiently thought through as it relates to the science,” Erik Eisenmann, a labor and employment attorney with Husch Blackwell, told Yahoo Finance. Some recent research, which looks at hundreds of thousands of cases in Israel and has yet to undergo peer review, indicates that natural immunity might be at least as effective as vaccination in certain people.
Other peer-reviewed research cited by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), which looks at dozens of cases in the U.S., indicated that certain people who suffered from a COVID-19 infection did not create antibodies (ie, natural immunity) at all. In August, the CDC published a study of 246 Kentucky residents, concluding that vaccination offers higher protection than a previous COVID infection. The CDC said the study went through a “rigorous multi-level clearance process” before submission, though analysis was conducted before the Delta variant became prevalent in the U.S. The CDC says the Kentucky data indicates that vaccines offer better protection than natural immunity alone, and medical professionals widely recommend vaccination for everyone who is eligible — including those who have experienced a prior COVID-19 infection.
Legally challenging COVID-19 vaccine mandates involves both science and law. The scientific arguments are based on certain studies over the past year, including the Israel study, and studies out of Cleveland Clinic and Washington University. A June study that tracked 52,238 Cleveland Clinic employees found that within 1,359 previously infected and unvaccinated people, none contracted a subsequent COVID-19 infection over the five-month study. The findings led authors to conclude that prior infection makes a person “unlikely to benefit from COVID-19 vaccination.” Nevertheless, Cleveland Clinic stated afterwards that it continued to recommend vaccination for people previously infected, stressing that the research was conducted in late 2020 and early 2021 before the emergence of the Delta variant.

I don’t trust Jeffrey Sachs.
• Lancet Covid Origins Panel Disbanded Over Ties To Peter Daszak (DM)
The chairman of a COVID-19 origins task force affiliated with the Lancet scientific journals has disbanded the commission over its ties to controversial researcher Peter Daszak and his EcoHealth Alliance. Columbia University professor Jeffrey Sachs told the Wall Street Journal on Saturday that he was concerned with the links to Daszak, who led the task force until recusing himself from that role in June. Daszak, who lives in New York, devoted his career to championing so-called ‘gain of function’ research to engineer coronavirus to be more deadly to humans, arguing that it was the best chance to detect and prevent a global pandemic. Shocking documents released this week revealed his 2018 proposal to help the Wuhan Institute of Virology engineer bat coronaviruses to be more deadly, by inserting genetic features that are similar to those found in SARS-CoV-2.
There is still no conclusive proof as to whether COVID-19, a coronavirus linked to bats, first jumped to humans from a wild animal or in a lab setting. But from the early days of the pandemic, Daszak has made every effort to paint the lab origin hypothesis as a ‘conspiracy theory,’ including masterminding a letter in the Lancet that established a veneer of scientific consensus that natural origin was the only possibility. If the virus did emerge from a lab performing the experiments he championed, it would be a crushing blow to Daszak’s research. Natural origin, on the other hand, would vindicate his life’s work seeking to prevent the next pandemic. Several members of the disbanded Lancet task force have collaborated with Daszak or EcoHealth Alliance on projects in the past.
‘I just didn’t want a task force that was so clearly involved with one of the main issues of this whole search for the origins, which was EcoHealth Alliance,’ Dr. Sachs told the Journal. Sachs said a new Lancet Covid-19 Commission would continue studying the origins for a report to be published in mid-2022, but broaden its scope to include input from other experts on biosafety concerns, including risky laboratory research. It comes just days after the release of bombshell documents showing Daszak’s 2018 funding request to the US Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) seeking $14.2 million to fund gain-of-function research on bat coronaviruses at the Wuhan lab.

“Their data, official public health data, says that (1) the jabs wear off, (2) those who were jabbed are spreading the disease and (3) you who got jabbed are at high risk of getting ****ed.”
• Dear Idiot: I Will Laugh (Denninger)
So The Miami Herald — and Yahoo — think they can print this without consequence? “That’s why we were glad President Biden stopped asking nicely, started requiring vaccinations everywhere he had power to do so. We were also glad when employers followed suit. And if that’s a problem for you, then, yes, goodbye, sayonara, auf wiedersehen, adios and adieu. We’ll miss you, to be sure. But you’re asking us to choose between your petulance and our lives. And that’s really no choice at all.” Is that so? Well here’s a bit of science for you, *******: The jabs don’t work. In fact you admit they don’t work. If you believed they did work you wouldn’t care about us. You might call us stupid, but that’s the end of it right? You’re safe, we’re not. So what? You live your life and if we kill ourselves, so be it. You don’t ban beer because I can drink myself to death, right?
So why are you all up in arms? There’s only one answer: You know you did something stupid and put yourself in a worse position rather than a better one when you got vaccinated! So now, having done something that you know is dumb you insist others join you in your ritualized suicide cult, headed by Biden, Fauci and Rochelle. Have a look at Scotland if you think I’m wrong on this. Their data, official public health data, says that (1) the jabs wear off, (2) those who were jabbed are spreading the disease and (3) you who got jabbed are at high risk of getting ****ed. Not a little ****ed either. Indeed you traded what was 18 months to get rid of the extra 100lbs for a non-sterilizing, lightly-tested jab that on the history was very unlikely to work out well. It never had before for any coronavirus, so why would you believe, without years or even decades of evidence, that “this time its different”?
So when — not if, when — you get a so-called “breakthrough” infection the evidence is you will get screwed faster, harder, and more-certainly than someone never vaccinated. You’re at least as likely to die. Indeed, if you talk to clinicians they will tell you point-blank that once you get into the hospital being vaccinated has no statistical benefit on outcome. Oh sure, it appears being jabbed comes with a lower risk of death close in to your vaccination date, but remember, when you got vaccinated you also took a wildly-elevated risk of myocarditis which, on the data, progresses to heart failure a frightening part of the time within five years and which is asymptomatic until there is nothing you can do about it because the root, PAH, is not detectable from outside the body by non-invasive means.
If that turns out badly five years down the road you either get a heart transplant (at six-figure cost, permanent disability and permanent dependence on anti-rejection drugs) or you’re dead. Never mind those people who took the first jab, got hammered by it, couldn’t go back for the second due to the risk of immediate death and now are stuck with permanent compromise from infection and wildly elevated risk of mortality. By the way that’s in the data too and your demands and screaming are why those people are screwed. Just in case you missed that let me say it again: You screwed them. Many among us, myself included, calculated that the risk from infection was less than the risk from being jabbed. I was right. I got infected, placed no burden on the health care system, survived, recovered, I have no apparent bad lasting effects, my exercise tolerance is back to where it was and I gained durable, broad and deep immunity which the jabs do not confer.

“Coronavirus vaccines have been used in animals for years, with extremely unimpressive results.”
• We Are All Cattle Now (Eugyppius)
There is nothing surprising about the failure of our vaccines. In fact it was totally predictable. Coronavirus vaccines have been used in animals for years, with extremely unimpressive results. The problem is that coronaviruses infect the mucosal surfaces of the lungs, at what is basically the very edge of the reach of our immune systems. You could say that this their grand strategy. They work their way in from our least protected borders. Typically, nasal spray vaccines are preferred in animals to stimulate immunity in the mucosa. Unfortunately, even the sprays achieve immunity that „is often short-lived, requires frequent boosting, and may not prevent re-infection.“ This is after decades of vaccine development and the considerably reduced safety standards observed in veterinary medicine.
Our own SARS-2 vaccines, despite their fancy mRNA and virus vector technology, are entirely of a piece with veterinary standards. They have a poor side effect profile, they provide only temporary and partial protection against infection, and they are deployed on a vast scale with no regard for the evolutionary pressure they place on the virus or their broader consequences for infection dynamics. These are normal standards in the context of industrial livestock, where most animals are not raised to live very long in any event, and the risk of occasional accidents — inadvertently favouring or even causing lethal superstrains, or inflicting widespread vaccine injuries — can be weighed against the economic loss associated with mortality from infections.
Of all animal coronavirus vaccines, the most successful is that which prevents IBV, or infectious bronchitis virus, in chickens. IBV is mainly deadly to chicks, who are vaccinated almost immediately after hatching with a live, attenuated virus vaccine. These kinds of vaccines are preferred over deactivated virus vaccines in animals, because they elicit a better immune response. The reason is simple: The weakened vaccine virus actually infects you and your immune system remembers the event accordingly. Some SARS-2 attenuated virus vaccines are even in development for humans, but it is unlikely they will ever be used, because they are very dangerous. The attenuated virus, because it replicates in the cells of the vaccinated, can reacquire its prior virulence via mutations. This happened with early attenuated vaccines against poliovirus in humans.
And there is an added danger, that the recently vaccinated might come into contact with the wild virus, and recombination events might then combine splice together the genomes of both, yielding unpredictable, potentially very lethal, mutant strains. IBV vaccines protect the chickens from infection for only about nine weeks. That‘s long enough for the chickens destined to be eaten, but those raised for their eggs require constant boosters. They receive two or three attenuated virus vaccines at first, and then periodic deactivated virus boosters thereafter, to maintain their protection. Adenovirus vector vaccines have been tried in chickens, with efficacy similar to that induced by the attenuated virus vaccines. This is very likely an unstated reason that vaccine vector and mRNA messenger technology were used for our own SARS-2 jabs. It was known from experience with animals that deactivated virus vaccines would not work nearly as well, and that attenuated viruses were too dangerous.

You sure it’s not the league trying to push the players around?
• The NBA’s Anti-Vaxxers Are Trying to Push Around the League (RS)
One by one, the basketball players — non-vaccinated star here, fully-inoculated veteran on mute down there, a full-on anti-vaxxer front-and-center — logged into the video conference. The annual summer meeting of the powerful NBA union had gone virtual again on August 7, and high on the agenda for the season ahead was a proposed mandate from the league office that 100 percent of players get vaccinated against Covid-19. One response echoed from squares across the screen, according to players and an executive on the call: “Non-starter. Non-starter.” The NBA had relied on science above all to lead the sports world through the Covid nightmare, from the league’s outbreak-driven shutdown to a pandemic-proof playoff bubble in Disney World to game after game with fans back in the stands.
But after two plagued seasons of non-stop nasal swabbing, quarantining and distrust, unvaccinated players were pushing back. They made their case to the union summit: There should be testing this year, of course, just not during off-days. They’d mask up on the court and on the road, if they must. But no way would they agree to a mandatory jab. The vaccine deniers had set the agenda; the players agreed to take their demands for personal freedom to the NBA’s negotiating table. This month, league officials caught a break: Two of America’s most progressive cities, New York and San Francisco, would require pro athletes to show proof of one Covid-19 vaccination dose to play indoors, except with an approved medical or religious exemption. Which meant that one of the NBA’s biggest stars — one known for being receptive to conspiratorial beliefs — would be under heavy pressure to get a shot. And if Brooklyn Nets superstar Kyrie Irving could be convinced to take the vaccine, then maybe, just maybe, the whole league could create a new kind of bubble together.
When asked directly about Irving’s vaccination status — or his plans to change it — multiple people familiar with his thinking declined to answer directly. But one confidant and family member floated to Rolling Stone the idea of anti-vaxx players skipping home games to dodge the New York City ordinance… or at least threatening to protest them, until the NBA changes its ways. “There are so many other players outside of him who are opting out, I would like to think they would make a way,” says Kyrie’s aunt, Tyki Irving, who runs the seven-time All-Star’s family foundation and is one of the few people in his regular circle of advisors. “It could be like every third game. So it still gives you a full season of being interactive and being on the court, but with the limitations that they’re, of course, oppressing upon you. There can be some sort of formula where the NBA and the players can come to some sort of agreement.”

“..vaccine misinformation campaigns overwhelmingly popular in conservative circles..”
• How The US Vaccine Effort Derailed And Why We Shouldn’t Be Surprised (G.)
The cause of flagging vaccine uptake in the United States has flummoxed national health authorities, who in May loosened mask guidance in hopes it would encourage more people to get vaccinated, in July again recommended masks because of the Delta variant, and hoped August’s full FDA approval of the Pfizer Covid-19 vaccine would increase vaccine mandates. In a September speech, just days before the US slipped behind Japan, Joe Biden channeled national exasperation: “Many of us are frustrated with the nearly 80 million Americans who are still not vaccinated even though the vaccine is safe, effective and free.” He called for vaccine mandates impacting 100 million Americans, two-thirds of US workers.
However, all these strategies have failed to encourage more than 900,000 Americans per day to get vaccinated in recent weeks, far lower than nearly 3m doses administered per day in April, the height of the vaccination push. Finally, in mid-September, the country’s slow progress allowed Japan to surpass the US both in terms of vaccination rate per 100,000 people and percentage of the total population with one or both shots. There are very specific, well-documented reasons that Americans are hesitant to take vaccines. They vary from the troubling way the medical system treats people of color, to vaccine misinformation campaigns overwhelmingly popular in conservative circles, to logistical challenges.
But population health researchers, whose work considers how society as a whole is fairing, said low vaccine uptake may be looked at another way: as the predictable outcome of a campaign subject to entrenched social forces that have diminished American health and life expectancy since the 1980s. “When I look at this I do see a very familiar pattern,” said Dr Steven Woolf, a prominent population health researcher at Virginia Commonwealth University. “When Operation Warp Speed came out I thought I was just seeing a modern example of this old problem where the scientific community developed the vaccine at ‘warp speed,’ but the implementation system for getting it out into the community was inadequate”. Woolf calls this “breakthrough without follow-through”. In that light, the plodding vaccination campaign could be seen as one more aspect of the American “health disadvantage”.

“These and others in the anti-vax movement are basically enemies of society and need to be treated accordingly, without hesitation…”
• Treating Antisocial Elements For What They Are (K.)
Day-to-day life in Greece is excessively determined by people defying laws, rules and reason; it’s disappointing and extremely frustrating. But this, as former prime minister Kostas Simitis once said, is Greece and it doesn’t look like it’s changing much. It’s exhausting for citizens yearning for basic normalcy to be assailed by the prevalent delinquency and to feel that their quality of life is being constantly undermined, often with the tolerance of the state apparatus. Right now, events are being defined by our fellow citizens who refuse to get the Covid vaccine and by the obstinacy of deniers of all stripes. Whether they’re jerks, kooks, nitwits, thugs, vote-mongers or religious fanatics is neither here nor there. They are a swarm that is endangering the lives of the rest of us, having a negative impact on the quality of everyday life and obstructing the vital functions of society.
The state, therefore, has an obligation to all the “normal” people in this country to decisively deal with such antisocial elements. Admittedly, there are more antisocial Greeks out there. There are the unconscionable priests and monks who preach against the vaccines, the lawyers exploiting the anti-vax movement, the judges approving the exhumation of Covid victims, the relatives suing doctors for a payout, the parents calling the police on teachers implementing the law, the nurses and other state workers who refuse to be vaccinated but expect to keep getting paid… These and others in the anti-vax movement are basically enemies of society and need to be treated accordingly, without hesitation. Especially given that the overwhelming majority of the political world claims to support vaccinations.
The truth is that the antisocial behavior we are seeing right now is not the result of the pandemic. It may appear so, but is, in fact endemic and manifests in all sorts of ways: violence in the soccer arena and on the streets; interminable protest rallies and marches; sit-ins at schools and universities; increasingly aggressive and unruly driving; sound pollution; nasty graffiti; posters pasted willy-nilly on public walls; grimy bowls of water and food scattered here and there for strays; and, of course, in the inability or indifference of the state to these and so many other such phenomena. And even in the favorable decisions and amendments passed by every government to accommodate those breaking the rules and shirking their obligations. At the end of the day, it’s the suckers who dream of a different kind of Greece who end up paying the price.

Edward Snowden @Snowden: “Stop what you’re doing and read this. The CIA developed plans to kill or kidnap an award-winning journalist whose work they did not like — before they charged him with a crime. The case against Julian Assange must be dropped—and condemned.”
• Inside The CIA’s Secret War Plans Against Wikileaks (Y!)
In 2017, as Julian Assange began his fifth year holed up in Ecuador’s embassy in London, the CIA plotted to kidnap the WikiLeaks founder, spurring heated debate among Trump administration officials over the legality and practicality of such an operation. Some senior officials inside the CIA and the Trump administration even discussed killing Assange, going so far as to request “sketches” or “options” for how to assassinate him. Discussions over kidnapping or killing Assange occurred “at the highest levels” of the Trump administration, said a former senior counterintelligence official. “There seemed to be no boundaries.” The conversations were part of an unprecedented CIA campaign directed against WikiLeaks and its founder. The agency’s multipronged plans also included extensive spying on WikiLeaks associates, sowing discord among the group’s members, and stealing their electronic devices.
While Assange had been on the radar of U.S. intelligence agencies for years, these plans for an all-out war against him were sparked by WikiLeaks’ ongoing publication of extraordinarily sensitive CIA hacking tools, known collectively as “Vault 7,” which the agency ultimately concluded represented “the largest data loss in CIA history.” President Trump’s newly installed CIA director, Mike Pompeo, was seeking revenge on WikiLeaks and Assange, who had sought refuge in the Ecuadorian Embassy since 2012 to avoid extradition to Sweden on rape allegations he denied. Pompeo and other top agency leaders “were completely detached from reality because they were so embarrassed about Vault 7,” said a former Trump national security official. “They were seeing blood.”
The CIA’s fury at WikiLeaks led Pompeo to publicly describe the group in 2017 as a “non-state hostile intelligence service.” More than just a provocative talking point, the designation opened the door for agency operatives to take far more aggressive actions, treating the organization as it does adversary spy services, former intelligence officials told Yahoo News. Within months, U.S. spies were monitoring the communications and movements of numerous WikiLeaks personnel, including audio and visual surveillance of Assange himself, according to former officials. This Yahoo News investigation, based on conversations with more than 30 former U.S. officials — eight of whom described details of the CIA’s proposals to abduct Assange — reveals for the first time one of the most contentious intelligence debates of the Trump presidency and exposes new details about the U.S. government’s war on WikiLeaks. It was a campaign spearheaded by Pompeo that bent important legal strictures, potentially jeopardized the Justice Department’s work toward prosecuting Assange, and risked a damaging episode in the United Kingdom, the United States’ closest ally.
Isikoff
Watch: MSNBC speaks to Yahoo News' Chief investigative correspondent Michael Isikoff about todays bombshell Yahoo report on how the CIA planned to kidnap or kill Julian #Assange https://t.co/rA7hRgU7Tr pic.twitter.com/SQIzcFb7nC
— WikiLeaks (@wikileaks) September 27, 2021

With the Russians….
• CIA Was Ready To Wage Gun Battle In London Streets Over Assange (RT)
At the peak of preparations for hostilities in 2017, the CIA was allegedly expecting Russian agents to help Assange flee the Ecuadorian Embassy in London. In such a contingency, the Americans, together with the British, were planning to engage in street battles against the Russians, potentially starting a firefight, ramming a Russian diplomatic vehicle, or shooting at the tires of a Russian plane to prevent it from lifting off, the story said. The attempt to spring Assange was reportedly expected on Christmas Eve. “It was beyond comical,” a former senior official told the outlet regarding the situation in the vicinity of the embassy at the time. “It got to the point where every human being in a three-block radius was working for one of the intelligence services – whether they were street sweepers or police officers or security guards.”
The CIA was also deliberating plans to kill Assange and other members of WikiLeaks, the report said. Alternatively, the agency was considering snatching him from the embassy and bringing him to the US, or handing him over to the British authorities. At the time, the UK wanted Assange for skipping bail in an extradition trial on a request from Sweden – a case that has since been dropped. The possibility of carrying out a successful rendition or assassination were described as “ridiculous” by one intelligence official, because of the location. “This isn’t Pakistan or Egypt – we’re talking about London,” the source was quoted as saying. There was also resistance in the Trump administration because such an operation might be deemed illegal under US law. A source said using CIA powers meant only for spy-versus-spy activities would be “the same kind of crap we pulled in the War on Terror.”
As far as the CIA was concerned, WikiLeaks prompted these extreme measures after the so-called ‘Vault 7’ publications, which exposed a cyber-offensive toolkit used by US agents. The leak of those tools was a major humiliation for US intelligence, so “Pompeo and [then-Deputy CIA Director Gina] Haspel wanted vengeance on Assange,” Yahoo was told. Pompeo had to do some legal maneuvering so the agency could go more aggressively after Assange and WikiLeaks without having then-president Donald Trump sign off such operations. When, shortly after taking office, he infamously called WikiLeaks a “non-state hostile intelligence service” during a public speech, it was more than just rhetoric, according to the report. Designating in that way allowed the CIA to file its snooping under “offensive counterintelligence” activities, which it’s allowed to conduct on its own volition. “I don’t think people realize how much [the] CIA can do under offensive [counterintelligence] and how there is minimal oversight of it,” a former official said.
Credico Isikoff

Twitter thread.
• Mike Pompeo And The CIA’s War On WikiLeaks and Julian Assange (Gosztola)
Journalists for Yahoo! News finally confirmed a narrative around Mike Pompeo and the CIA’s war on WikiLeaks and its founder Julian Assange, which I outlined back in October 2019. It’s an important report. WikiLeaks’ publication of “Vault 7” materials from the CIA was hugely embarrassing. Even though the CIA had increased spying operations against WikiLeaks, they still were surprised the media organization obtained a trove of the agency’s extremely sensitive files.
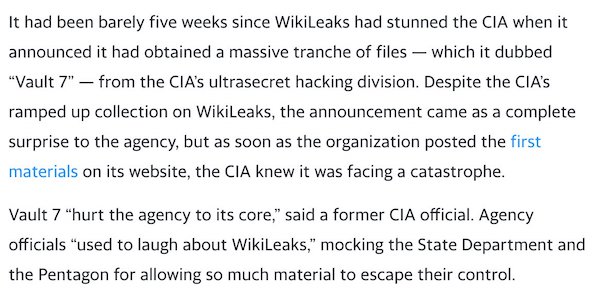
CIA director Mike Pompeo was afraid President Donald Trump would learn about the “Vault 7” materials and think less of him. “Don’t tell him, he doesn’t need to know.” But it was too important. Trump had to be informed.

[..] Recall, CIA director Mike Pompeo’s speech at CSIS, a Washington think tank, where he labeled WikiLeaks “a non-state hostile intelligence service.” That was all to fuel a climate for aggressive action targeted against Assange, WikiLeaks staff, and associates. The CIA could not prove WikiLeaks was working at the behest of the Russian government. So rather than claim authority to target WikiLeaks that way officials sought to reframe the organization as a “hostile entity.” Then it wouldn’t matter that they weren’t working for Russia.


Australian media are useless too.
• CIA’s Assange Abduction/Murder Plan Raises Questions For Australia (Crikey)
Revelations by a large number of former US officials, reported by Yahoo! News, that the CIA planned to abduct and render Julian Assange to the United States — and contemplated murdering him — raise more uncomfortable questions for the Australian government and its policy of trying to pretend Assange doesn’t exist. Yahoo’s investigation relies on accounts from eight former officials about the plan to kidnap Assange from the Ecuadorean embassy in London, among dozens of other sources about the Trump administration’s determination to go after Assange and WikiLeaks. The Trump administration went where even the whistleblower-hating Obama administration refused to go and launched a prosecution for espionage and conspiracy, but until now it was widely thought its plans were limited to legal extradition.
It is now clear the CIA — under Republican Mike Pompeo, who would go on to be Trump’s secretary of state — developed plans to abduct Assange and illegally render him to the US via a third country. There was discussion “at the highest levels” of the Trump administration of murdering him. There was also scenario planning about what violent measures US and UK agents might take to thwart a hypothetical Russian attempt to help Assange escape to Russia. The most obvious question for the Australian government is whether the CIA discussed with Australian intelligence officials its plans to abduct or murder an Australian citizen, or whether Trump administration figures — some of whom were alarmed by the CIA’s planning — alerted the Turnbull government at a political level.
It would say much about how unimportant Australia was, and how little we have spoken up for Assange, if the entire process was conducted without anyone bothering to raise it with the Australian government. The extent of Australian knowledge of the plans for Assange is likely never to be clarified because Australia’s intelligence agencies are able to operate behind a bipartisan wall of secrecy far stronger than that which applies to US agencies, where independent congressional oversight, a better-protected media, a stronger whistleblower culture and better disclosure laws mean much more scrutiny for intelligence agencies. In Australia there’s virtually none, with limited parliamentary oversight, brutal gag laws for intelligence officials, vexatious prosecutions and police raids on journalists willing to try to pierce the secrecy.
But there’s another angle that is also important. What sparked the CIA’s fury at WikiLeaks and set it to planning to kidnap or murder Assange was that WikiLeaks in 2017 revealed a trove of CIA software exploits, known as “Vault 7”, which had been stolen from the intelligence agency. That release was followed, within months, by news that the National Security Agency had had some of its own trove of software exploits stolen, which led to Microsoft publicly criticising intelligence agencies for failing to alert companies to exploitable software faults. The two cases illustrated how Western intelligence agencies were a key threat to our cybersecurity by intentionally leaving security weaknesses in commonly used systems so they could exploit them — leading to other states, or organised crime, to exploit them as well, in some cases using the very software tools bought or developed by intelligence agencies.









Support the Automatic Earth in virustime; donate with Paypal, Bitcoin and Patreon.