Paulus Potter De stier 1625

Dr. D today from an entirely unexpected angle: cattle farming from a engineer’s point of view. His interest here stems from the increasing numbers of people wanting to move “back to the land” in COVID time, who have very little idea what that entails. Well, here it is, here’s your manual:

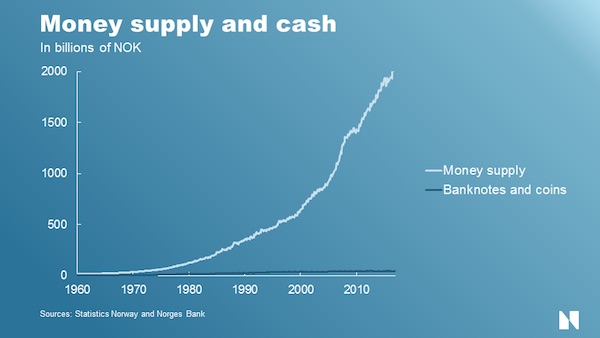
Dr. D: Since the idea of 1840 has come up, let’s do something useful and work out math on 1840’s factory-food system. That is to say, cows.
In 1840 the Victorian age had started, and the world was moving away from the post-medieval 18th century in important ways. Far from the millennia-long tradition of shepherds and commons punctuated by manor houses, life was moving towards distributed farmsteads integrated with modest small businesses in the nearest town. From centuries-old regional breeds, active breeding had developed powerful new plants and animals with new niche purposes overnight. And likewise, active management of pastures led to a revolution in hay and fodder unimagined a few years previously.
Although railroads and canals radically transformed nations overnight, permitting that specialization of labor and radically reduced costs that expertise and infrastructure bring – that is to say, “Capital” – nevertheless, life remained solidly local by our standards. A farm might have been cleared last year or 200 years previous. It might be attached to a railroad or be in the Alps. It might be under the eye of the Feudal Lord or might be a colony of Anabaptists. But the general structure was now one of single family ownership, large or small, with a central house and barn, with fields moving back from the house and road into ever-wilder, less human territory, eventually becoming impassible forest in the great beyond.
While there was a human transformation happening, daily items were more historic than we might credit: a farm might have few iron nails and hinges, few window panes, with turf cellars and wood box granaries that a Viking would recognize. Spinning and weaving existed on site or in the cots nearby. Although an explosion in factory goods was beginning, there was still little to buy, and few stores to buy things from. At the same time, the new availability of iron, of steel for blacksmiths, but also for saws and new wood mills made materials unimaginably cheap, as material science opened the world to new inventions. The revolution of Jethro Wood’s steel plow opened up soil to production unimaginable a few years before, and Jethro Tull’s grain drill was finally becoming common instead of simply tossing seeds by the handful for the birds on ox-harrowed ground.
American corn, maize, was transforming from Indian-flint grown in hills and hung on poles to endless fields of food, cattle feed even for cities and feedlots far away. And with it, the opening of the north, of feeding chickens, pigs, and horses in a newly-sawn Dutch barns all winter. And cows. Cows have a different place in human life. Unlike sheep, who need little and can stay faraway much of the year, or chickens which require daily tending, cows live in the middle place. They can stay in the field, but essentially must be fenced. They may not need humans, but when used for milk they require human attention twice daily all year.
They can be an expensive breakeven, but with the right support and infrastructure, they are highly profitable in diverse ways: Milk, butter, cheese, which may be too much for one farm without a nearby market. Meat, leather, bones, which again tie into the butchers, markets, prices, tanners and railroads. And oxen, the slow tractor of the small, as well as calves for sale, and the milk they cause, starting the year over again. So a cow is not a cow: it’s a system. The system has parts, and the parts are not only breeds, traditions, methods, but expensive standing infrastructure – barns, fences, wells, dairies, markets — Capital — or else they are put afield, Roman-style, and wild, near-subsistence living returns again.
Of course all methods, all areas, all answers are local, but let’s take your British/French/U.S. areas as an example. In these wet, temperate areas, land requirements are ~1 acre/cow. In addition, in the north, but also in the new scientific methods of Victorian Britain, they were no longer leaving cows to destroy winter pasture in the cold and rain, but haying and sheltering them in barns at the expense of a building, the fields…and the enormous time of mucking and haying. But still it was a well-paying improvement.
A 1,200lb cow eats 10,000lbs a year. At this time, the high-tech cow would be left to field 9 months of the year. So let’s say 3 months or 3,300lbs of hay per cow. You need more rare and expensive Capital of troughs, sheds, and stanchions to feed carefully at this time, so much is wasted. Estimate 5,000lbs dry hay per cow. Cows are not “cows”; they live in herds. To milk, you need calves. To calve you need bulls. Bulls are generally overhead as they are quickly too tough for the butcher, and too tough for the farmer without a very strong fence and strong britches.
You can’t have a herd of 500 cows either: they are too many and will trample the soil to powder anywhere within walk of the house and barn. So you’re set with 5, 10, 20 cows for a family stead, and not many more on a manor, when for the same reasons they will break off and sublet to a new barn and pasture. 10 cows x 5,000lbs = 50,000lbs of hay. 25 tons. They used the new haystacks, cranes, hay elevators, but let’s visualize in hay bales, a technology common 70 years later. At 50lbs/bale, it’s 1,000 bales. 10 high, 10 deep, 10 wide. That’s 30ft x 16 feet x 14 feet.
A modest 1-story house. Picture 2 semis packed tight, +4 semis loose hay. For only three months. Weather and yield vary wildly by area and year but let’s say hay fields produce 3 tons per acre, so10 acres guarded hay in addition to 10 acres fenced summer pasture. What do we get for it? Hard to figure exactly but +2 gal/day/cow for these hardier breeds which varies wildly with shelter, season, and diet. 2 gallons milk = 2 pounds of cheese. It takes 1 year to raise beef, so 7,500lbs of hay = 1,200lb cow = 750lb beef.
While you need 20 acres for the feed alone, you’ll also need crop rotation, a barn, a springhouse, a dairy, an implement shed, a repair garage, a human house and cellar, and because of humans on site to support the cows: a chicken coop, pigs to eat the leftover dairy, a smokehouse, a garden and orchard, as well as wood for heat. That’s 1 acre / face cord, so let’s say 20 acres for cows, 10 acres for crop rotation, 10 acres for wood, and 10 acres for the homestead, garden, and buildings. What is the common size of American farms from Cape Cod to Iowa? 50 acres. 20 hectares. How many people? 4-10/farm. 1-2 humans/acre.
Why do I bring this up? It gives you a rough sense of transforming a suburban housing development back into the farm it came from. First: there’s no longer any forest. That means no boards, no firewood. We have new materials and oil too, so let’s not dwell on this. There is an enormous surplus of existing buildings. How many acres per house? Presently, it’s 1/5 acre. How many people per house? There are unimaginable difficulties answering this, but let’s say 2 people/house. That’s 10 people per acre.
Pablo Picasso Bull – Plate 4 1945
Starting to see the problem? At merely the cow-size, even ignoring the existing buildings, using McMansions for hay, ignoring firewood, even using solar or (insert fantasy here) you have to displace 20 acres, or 200 people. But you only have 10 cows feeding those 200 people, or 1/20th of 20 gallons = 1 gal, or 1 quart of milk + 12 oz of cheese per day. No grains, no veg. You could halve the population density and it’s not much better. This is your 1840s reality.
They might say this explains why we must have no cows and become vegetarians. But aside from land that cannot be gardened – the entire U.S. cattle plains, for instance, or the Swiss Alps – this is just more false science. Howso? There are 30 calories per cup of kale, 200 calories/pound. There are 1,500 calories per beef pound – 1,900cal/lb dry (jerky). So you need to eat 7x more kale than meat. All you’re doing is concentrating vegetables into meat with a small efficiency loss. So you can EAT more as a vegetarian, but you also HAVE to eat much more to break even. So when they say they can create more food by outlawing meat, be careful of what they’re saying. They’re not creating more calories, more life stuff. They will also calculate the maintenance of a cow from birth on corn feed, which is foolhardy. High-cost, high-input corn or grain feed is only used – or should be – in the last weeks if at all.
Comparing your 1840 yields (i.e. without petroleum fertilizer), that’s 800lbs field corn/acre – a very productive crop. But we just said we have 750lbs/acre in grass-fed beef. The calories are 1,600cal dry corn vs 1,900cal dry beef. Where’s the savings? Where’s the rennet, the suet, the soap, the fertilizer, the leather that could greatly increase the use, the “profit”, the value? Where’s the diversity? Where’s the life?
Here’s the engineering reality: only 442BTUs of sunlight fall per square foot. It may fall evenly or more in summer and less in winter. It may fall on trees, grass, or houses. You can eat it as beef, sugar or kale. You can burn it in the stove. But that’s the energy input of a non-carbon world. And since photovoltaic is at 12% efficiency, solar may be the single least efficient way to capture and store these BTUs – and that’s beyond the rare-earths, glass smelting, world-wide transportation, back-end space-age infrastructure, transmission loss, and replacement problems. Trees, grass, and cows may be the best way. It depends on your goal.
Now can I increase yields from 1840 levels? Yes. A lot. And they did too – I’m describing only one food stream of many overlapping. And although the soil is ruined and the present structures are practically useless in what Kunstler calls “the largest misallocation of resources in world history,” we can still leverage perfect roads, electric, ditches, water lines and structures. But to do so we would need to un-misallocate them, completely convert them out of centralization and suburbia, out of consumption and back into production, and all that takes time, energy, and materials.
And to think I started this discussion calculating how many people and how many scythes to take in those 10 acres of hay. 2 acres per man per day x 5 men, 2 pounds of steel per scythe per man. 10 pounds of finest steel per hay barn. 9 million barns, 90 million pounds of fine scythe steel for this one tool alone. 35 million blades, 1 blade smithed per man per day, 35 million days…on and on and on.
So if you plan to adjust to a new rural world, might want to start early and beat the rush.

Albert Cuyp Cows in a river 1650

We try to run the Automatic Earth on donations. Since ad revenue has collapsed, you are now not just a reader, but an integral part of the process that builds this site.
Click at the top of the sidebars for Paypal and Patreon donations. Thank you for your support.

Support the Automatic Earth in virustime, election time, all the time. Click at the top of the sidebars to donate with Paypal and Patreon.