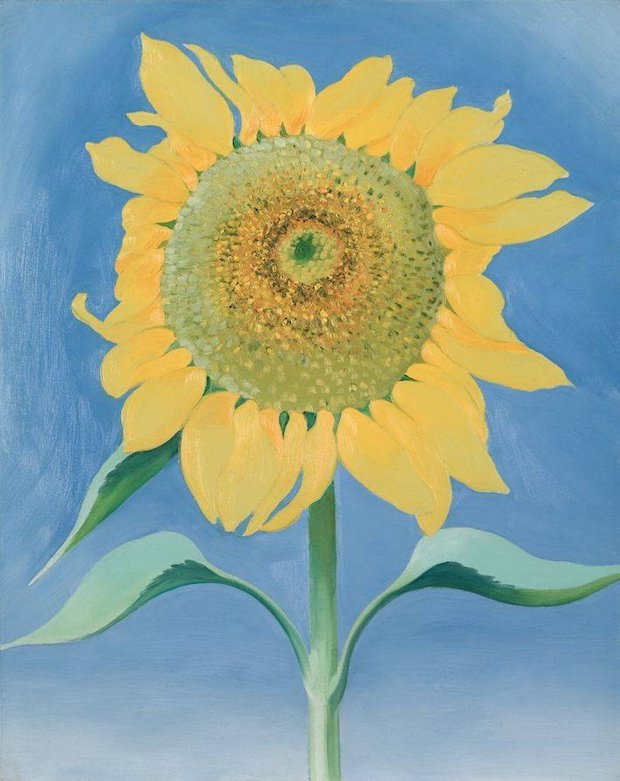
Georgia O’Keeffe Sunflower, New Mexico I 1935



Putin
Putin: What is the problem with "Empire"? They think they are so powerful, that they can afford mistakes. But issues accumulate, until eventually, they become unsolvable. The U.S. is confidently striding in the same direction as the Soviet Union. pic.twitter.com/HN0DS0H9Jf
— Geopolitics & Empire (@Geopolitics_Emp) February 6, 2023



Ausexit
https://twitter.com/i/status/1622679275466891264





Gonzalo: Zelensky going to Brussels? Now? Really. Just as Bakhmut is about to fall—and the Russians launch their offensive. Just as all his supporters have been purged from the government—and he might be next. I bet Zelensky doesn’t return to Kiev from this trip. I bet he’s running.
When I first heard how long the training was for Western weaponry, I surmised that all the operators would have to be former NATO troops working under the fiction of being military contractors.
Here, an Austrian officer confirms exactly what I thought.pic.twitter.com/yWj3OHhfBy
— Gonzalo Lira (@GonzaloLira1968) February 6, 2023


“We need to wake up – and get to work..” Well, what are you waiting for? Get a peace conference together.
• World Heading Into ‘Wider War’ – UN chief (RT)
The world has come close to a global conflict, UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres warned on Monday. The global community is not “sleepwalking” into “a wider war” but marches towards it “with its eyes wide open,” he stressed in a speech to the General Assembly. “The prospects for peace keep diminishing. The chances of further escalation and bloodshed keep growing,” Guterres said, denouncing the lack of “strategic vision” and “bias” that prevent political decision-makers from taking steps in the right direction. “This near-term thinking is not only deeply irresponsible – it is immoral,” he argued, adding that politicians and entrepreneurs became too absorbed with clinging to power and their business cycles.
The secretary-general also blasted the erosion of international law and order based on UN principles, which, according to him, led to the present sorry state of affairs. “If every country fulfilled its obligations under the [UN] Charter, the right to peace would be guaranteed,” he noted, calling on UN members to “to transform our approach to peace by recommitting to the Charter – putting human rights and dignity first, with prevention at the heart.” “We need to wake up – and get to work,” Guterres said, adding that 2023 had placed humanity in front of a “confluence of challenges unlike any in our lifetimes.”
The UN chief also pointed to the fact that scientists have moved the symbolic “Doomsday clock,” which reflects the potential annihilation of humanity, from 90 seconds to midnight – the closest it has ever been to a possible Armageddon. The UN chief’s words came after the US and its allies vowed to send dozens of Western-designed modern battle tanks to Ukraine amid the ongoing conflict between Moscow and Kiev. The Pentagon also announced supplying the Ukrainian forces with munitions that have a 150-kilometer range, adding that it would allow Kiev to use them as it sees fit. Moscow has previously repeatedly warned that continued weapons supplies to Ukraine by the US and its allies risk further escalation that might spiral into a direct conflict between Russia and NATO.

There are videos floating around.
• Ukraine Using Chemical Weapons In Donetsk – DPR leader (TASS)
A search for additional ways to protect troops from the chemical weapons that Ukrainian forces are using is underway in the Donetsk People’s Republic (DPR), the region’s Acting Head Denis Pushilin said on Monday.”We currently seek to equip our units [with chemical protection suits]. Then again, we have some of the things that we need but it’s not always comfortable to constantly wear chemical protection suits while in position. Certainly, it makes it harder for our forces to perform their missions so we are looking for additional ways to protect our troops,” he told the Rossiya-24 TV channel. Pushilin pointed out that experts had not yet had the chance to figure out what substances the Ukrainian forces were using.
“They trigger coughing, followed by watery eyes and general discomfort,” he said, describing the effect of the Ukrainian chemical weapons. Yan Gagin, an advisor to the Donetsk People’s Republic’s (DPR) leader, said earlier that the Kiev regime’s forces had used chemical weapons along the Soledar and Artyomovsk frontlines on February 5. He stressed that it wasn’t the first time that Ukraine had used chemical weapons. Gagin added that the Ukrainian military made no secret that it had prohibited weapons, posting videos showing imported gas grenades and drones designed for discharging them. Pushilin said on Monday that evidence corroborating the use of chemical weapons by the Armed Forces of Ukraine had also been found along the Ugledar frontline.

“Ukrainians feel like the masters of Lithuania here. No one talks about this, but in Lithuania, almost every administrative institution has a flag of Ukraine. In our parliament, the flag of Ukraine also hangs.”
• Ukrainian Refugees Are Becoming A Burden To The Baltic States (Milacic)
Every conflict, including this one in Ukraine, always leads to refugees. Considering the size of Ukraine, it is not surprising that a large number of Ukrainian refugees are in Russia and in Europe. Ukrainian refugees were the topic of an interesting online conference, where you could hear very interesting information from experts about Ukrainian refugees in the Baltics. The name of the online conference was “Ukrainian refugees in the Baltic States, social aspects of integration into society”. During the meeting, experts from the Baltic countries discussed the problem of Ukrainian refugees and their impact on the lives of Latvia, Lithuania and Estonia. The conference was held in Russian. It is curious that even 32 years after the collapse of the USSR, the inhabitants of the Baltic countries prefer Russian rather than English in interstate communication.
[..] “Ukrainians feel like the masters of Lithuania here. No one talks about this, but in Lithuania, almost every administrative institution has a flag of Ukraine. In our parliament, the flag of Ukraine also hangs. This is very painful for us Lithuanians!” The Baltics are also annoyed by “imaginary” refugees who travel to European countries from regions where there are no hostilities. And they require special treatment and all kinds of support. Allan Hantsom, editor-in-chief of the Estonian newspaper Delovye Vedomosti: “There are people who are fleeing the war, but the majority quietly leave those regions where there are no hostilities or rocket attacks. Very different people. Some come on buses with trunks, others – on expensive cars, and they also demand free rations and free accommodation. Especially now there is a crisis in the countries and now the Europeans are more and more concerned about their own problems: inflation, shortage of fuel and housing.”
After all, Europe’s resources for accepting refugees from Ukraine are running out, which leads to the curtailment of assistance programs and the cessation of accepting new migrants. At the same time, the Baltics should be prepared for the fact that refugees from Ukraine will remain there for many years even after the end of the conflict. The inhabitants of the Baltics are increasingly tired of forced guests, but they can’t do anything, because the course of the authorities is the same: “Everything for the sake of Ukraine, and let their residents survive somehow on their own!
Because of that, Estonians began to object. Why does a person who came from a foreign country, who does not know the language and has nothing to do with Estonia, get everything, and local people from the provinces are forced to live in poverty, work at low-paid jobs? Why not provide them with conditions? A refugee arrives in the capital – here’s a ration for you, here’s your living allowance. A lot of people from the Estonian hinterland would also like to live in hotels and on ferries, so that the state pays for everything. Ukrainian refugees, instead of learning the language and considering the Baltic states as their “second homeland”, impose their customs and rules of behavior.

They should ask for Ukraine’s money back too. That would make it real funy.
• FTX Demands Politicians Return Millions In SBF Donations (ZH)
Just when you thought the FTX travesty couldn’t get any more bizarre, the now bankrupt company is trying to claw back political donations and other spending that took place at the direction of former CEO Sam Bankman-Fried. A press release made its way out mid-day Sunday that FTX’s debtors and the company had sent “confidential messages to political figures, political action funds, and other recipients of contributions or other payments that were made by or at the direction of the FTX Debtors, Samuel Bankman-Fried or other officers or principals of the FTX Debtors” requesting the funds back. “These recipients are requested to return such funds to the FTX Debtors by February 28, 2023,” the release states. It continues: “The messages follow the December 19, 2022, announcement by the FTX Debtors that they have established arrangements for such recipients to return funds voluntarily by contacting (FTXrepay@ftx.us).”
Then, the release threatens legal action to those who are unwilling to return funds: “To the extent such payments are not returned voluntarily, the FTX Debtors reserve the right to commence actions before the Bankruptcy Court to require the return of such payments, with interest accruing from the date any action is commenced.” “Recipients are cautioned that making a payment or donation to a third party (including a charity) in the amount of any payment received from a FTX Contributor does not prevent the FTX Debtors from seeking recovery from the recipient or any subsequent transferee,” the release says. We noted back in December that $73 million in political donations were now at risk as a result of the bankruptcy. SBF also donated to Democratic Rep. Ritchie Torres of New York, who last year was one of 8 members of Congress who lobbied against regulating crypto. “Nobody ends up looking great in this,” said University of Rochester political science professor, David Primo, at the time.
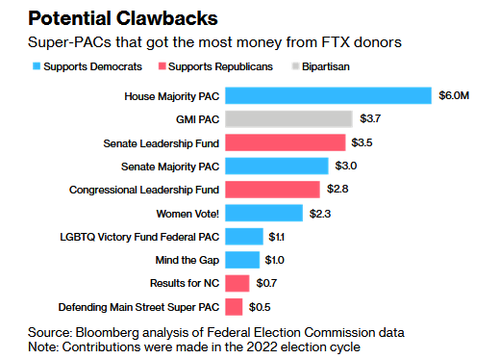
“While there’s precedent for forcing political entities to return contributions in cases of fraud, recovery prospects are unclear in FTX’s case. Recouping campaign funds as part of the bankruptcy proceedings is a complicated and lengthy process, and the scope of the total funds eligible for clawback depends on myriad federal and state laws. It is also subject to the bankruptcy lawyers’ judgment on what money, which may be long spent by the time the FTX trustees try to go after it, is worth the effort. Bankman-Fried is facing additional scrutiny for recently saying he gave equally to Republicans and Democrats, but funded conservatives through “dark money” groups that don’t identify donors. The claim is almost impossible to verify unless the recipients voluntarily disclose they received money from him.” -Bloomberg

“..Abe was not willing to sell off Japan as a satrapy, however, that was exactly what the western diktat was essentially demanding of Japan..”
Worth reading the whole piece.
• Why Shinzo Abe Was Assassinated (Chung)
Former Prime Minister of Japan Shinzo Abe was assassinated July 8th, 2022, and though no longer in the position of Prime Minister of Japan at the time of his assassination (having served from 2006-2007 and 2012- September 16, 2020) he was the longest serving prime minister in Japanese history and continued to exert major influence on policy-shaping within Japan. News of Abe’s assassination was received around the world with an admixture of very strong emotion from both extremes. Some were horrified by his death and praised what he had done for Japan as something almost saintly. Others ecstatically celebrated his death, thinking no possible good could come from him due to his attempts to revive the dark side of Japan’s imperial past and his public displays of tribute to the Japanese fascists from WWII. When the news was still fresh and the frenzy of confusion at its peak, many even blamed China for the orchestration of Abe’s death, thinking they were clearly the ones to benefit from such an act.
It is true that Abe had a very dangerous and destructive mission to restore Japan to its status as an imperialistic empire. He was a corrupt insider who pushed for the dangerous privatization of the Japanese government and increased the gap between the wealthy and middle-class citizens. However, it is also too simplistic as to celebrate his death as an absolute triumph. As we can clearly see seven months after Abe’s assassination, Japan has not become more peaceful and ready for dialogue with its eastern partners but rather has become much more bellicose and stauncher in its cooperation with the increasingly war frenzied western demands. Japan has also greatly severed motion towards greater economic and political cooperation with Russia and China, which was still moving forward when Abe was alive.
It is also interesting to note that Abe was assassinated weeks before Pelosi’s Circus Tour to Taiwan. Although Pelosi’s provocation did not amount to any military confrontation, we cannot say that that was not its intention, nor that things could have played out very differently in terms of a military confrontation between China and the United States. The reader should be reminded that in 2014, Japan had changed or “reinterpreted” its constitution which gave more powers to the Japan Self-Defense Forces, allowing them to “defend other allies” in case of war being declared upon them. The United States, of course, fully supported the move. This “reinterpretation” of Japan’s constitution effectively entered it into NATO. In December 2022, Japan announced a new national security strategy. This new strategy would double defense spending. Japan also plans to invest in counter-strike capabilities, including buying U.S. Tomahawk cruise missiles and developing its own weapons systems.
It was precisely Abe’s grand vision of Japan returning to its “glory” days as an empire that was problematic for the League of Nations vision, for if Japan saw itself on par with other great empires, or perhaps even greater, it meant that it did not ultimately intend to bend the knee. That is, Abe was not willing to sell off Japan as a satrapy, however, that was exactly what the western diktat was essentially demanding of Japan. Under this western diktat Japan was being ordered to accept its fate to collapse economically and sink into desperation, become increasingly militaristic and extremist and lead a kamikaze charge into a war with China and Russia which would lead to the ruination of the Japanese civilization. It does not look like Abe was going to go along with that stark vision for Japan.

“I will be very frank,” Puri said, “we will play the market card …”
• India Predicts 500% Increase In Domestic Natural Gas Demand (ZH)
Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi on Monday projected that the country’s gas demand would rise 500% due to the rapid pace of development, while its share of global oil demand would more than double. While the Indian prime minister did not offer a specific time frame for this major boost in demand, he said that the country’s energy demand would be highest in the present decade. Modi’s statement, delivered during the opening ceremony of India Energy Week 2023, coincides with a recent OPEC report that expects India to be the largest contributor to incremental demand, with the country expected to add some 6.3 million bpd until 2045. Overall, OPEC said it saw demand increasing to 110 million bpd in 2045, up from 97 million bpd in 2021. Modi predicts India’s share in global oil demand will increase from 5% to 11%.
The Indian prime minister used the occasion to highlight the country’s plans to boost exploration and production, which he said would provide opportunities for investors. Right now, India relies on imports for some 85% of its energy needs, with India and China being the largest importers of oil and gas in the world. With this in mind, India will remove significant restrictions on exploration, reducing “no-go” areas for E&P companies. India also plans to expand its refining capacity, along with its LNG import capacity by 2030. Asia is now the biggest buyer of Russian crude since the imposition of Western sanctions following Putin’s invasion of Ukraine. Some 70% of Russian Urals January loading cargoes were bound for India, according to Reuters data. India’s oil minister, Hardeep Singh Puri, also said on Monday that regardless of Western sanctions, the country would not shun Russian oil, which it receives at a discount to Brent crude. “I will be very frank,” Puri said, “we will play the market card …”

LNG.
• India and Russia Ditching Dollar In Energy Deal – Novatek (RT)
Russia’s largest independent gas producer, Novatek, is in talks with India over long-term contracts on supplies of liquefied natural gas (LNG), the company’s CEO, Leonid Mikhelson, announced on Monday. Negotiations with several Indian companies are underway as Russia is keen to invest in the country’s energy sector and further expand cooperation, he told reporters on the sidelines of the India Energy Week forum. “We want to be not just LNG suppliers, Indian engineering companies are already taking part in our projects and there’s a certain share of Indian suppliers in equipment. We want to expand and increase it,” Novatek’s CEO pointed out.
Mikhelson added that his company was interested in a broader investment into the Indian market, including the construction of regasification terminals for LNG production. He also revealed that the sides were considering settling LNG supply payments in national currencies – rupees or rubles – bypassing US dollar transactions. “We discussed it with the energy minister [Hardeep Singh Puri],” Mikhelson confirmed without specifying exact numbers. Earlier, Reuters reported that India’s main gas distributor GAIL was discussing the terms of a long-term contract on LNG imports with Novatek. The companies are close to signing a preliminary agreement, according to sources in the industry.

We’re all saying that. Question is the timing.
• ‘Doctor Doom’ Says US Dollar Reign Is Ending (RT)
The US dollar’s status as the world’s main reserve currency is in jeopardy, renowned economist Nouriel Roubini, who predicted the global financial crisis of 2008, wrote in an article for the Financial Times on Sunday. While no currency is yet capable of replacing the greenback on the pedestal altogether, the US currency is quickly losing its competitive advantage to the Chinese yuan, Roubini said. “Given the increased weaponization of the dollar for national security purposes, and the growing geopolitical rivalry between the west and revisionist powers such as China, Russia, Iran and North Korea, some argue that de-dollarization will accelerate…In a world that will be increasingly divided into two geopolitical spheres of influence – namely those surrounding the US and China – it is likely that a bipolar…currency regime will eventually replace the unipolar one,” the economist, dubbed ‘Doctor Doom’ by Wall Street for his tendency toward grim predictions, stated.
Sceptics note that the yuan cannot become a true reserve currency unless Beijing lifts capital controls, accepts permanent current account deficits, and the yuan’s exchange rate becomes more flexible. But the economist argues that such points are no longer valid, as Washington is actively undermining the allure of its currency with sanctions. “Complete exchange rate flexibility and international capital mobility is not necessary in order for a country to achieve reserve currency status…And while China may have capital controls, the US has its own version that may reduce the appeal of dollar assets among foes and relative friends. These include financial sanctions against its rivals, restrictions to inward investment in many national security-sensitive sectors and firms, and even secondary sanctions against friends who violate the primary ones,” Roubini argued.
The economist also noted that China has been stepping up yuan transactions with its foreign partners, and said this trend will likely continue, with more emerging market economies welcoming “the ability to trade oil in [yuan] and to hold a greater share of their reserves in the Chinese currency… given that they do a great deal more trade with China than the US.” He added that new technologies, like CBDCs, Alipay-like payment systems, swap lines between China and its partners and national analogs of the SWIFT messaging system, “will hasten the advent of a bipolar global monetary and financial system.” “For all these reasons, the relative decline of the US dollar as the main reserve currency is likely to occur over the next decade. The intensifying geopolitical contest between Washington and Beijing will inevitably be felt in a bipolar global reserve currency regime as well,” Roubini concluded.

“This year the government’s annual interest bill will break $1 trillion. Combine that with the soaring cost of Medicare and Social Security as millions of Baby Boomers retire, and Washington is looking at $2 trillion a year just in just interest and entitlements..”
John Rubino has been a strong supporter of the Automatic Earth since the start. Which reminds me, I totally forgot that we had our 15th anniversary on Jan. 22.
• Welcome To the Death Spiral (John Rubino)
Gold bugs and other long-suffering critics of fiat currency and endless credit expansion have for decades been predicting that soaring debt would eventually blow up the financial world. As the story went, governments with unlimited printing presses would spend and borrow too much, forcing their central banks to keep interest rates unnaturally low to make interest costs manageable, which would encourage even more credit growth, causing inflation to spike, and so on, until everyone loses faith in fiat currencies and the misbegotten things fall to their intrinsic value of zero. That’s a bit hard to visualize when it’s explained in long, convoluted sentences. But it’s a lot clearer when you line up the relevant charts. So let’s start with US government debt, which has gone parabolic.
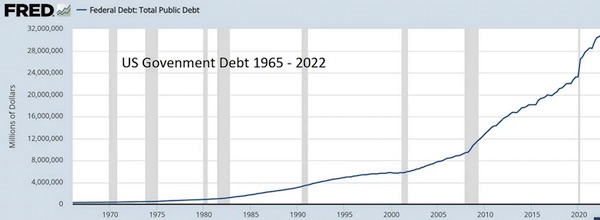
Ever-increasing debt is manageable if interest rates fall concurrently so the interest on that debt doesn’t change. And that’s what happened between 1980 and 2021. The Fed pushed down interest rates, which minimized interest costs, which lulled a shockingly gullible investment community and political class into the belief that this process could continue forever.
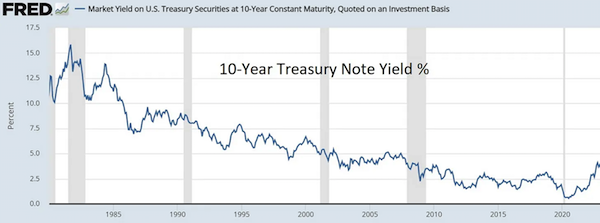
But of course it couldn’t continue forever. As the critics predicted, soaring debt required ever greater currency creation which eventually caused the cost of living to jump by 10% in 2022, leading regular people to demand that it stop. So the Fed now has to raise interest rates to counter inflation. You can see this happening on the far right of the above chart. As the US borrows more money and its existing debts roll over at higher rates, the cost of that debt is soaring. This year the government’s annual interest bill will break $1 trillion. Combine that with the soaring cost of Medicare and Social Security as millions of Baby Boomers retire, and Washington is looking at $2 trillion a year just in just interest and entitlements, which it will have to borrow to fund, which will send interest costs even higher, which will require more borrowing, and so on, until it all comes crashing down.
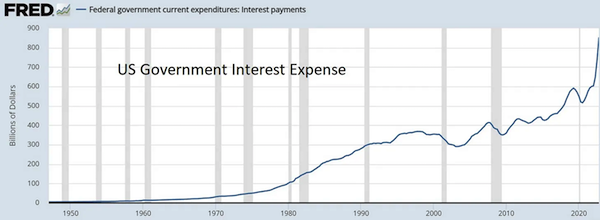

Part of the death spiral.
• Incentives Matter (Denninger)
An interesting data point: A stunning percentage of those young people without children now never intend to have them. In fact one relatively recent survey found the number was as high as one third. The most-common reason cited? Its too expensive. Now you can try to point to this as some sort of selfishness but that’s a dodge on the real issue: You, that is us older people, made it too expensive. Specifically homes and medical care are two places where all the “older people” cheer; we get the “best” but the next can’t buy it at all. Our federal government tries to interfere in both markets and allows blatantly illegal activity when it comes to medical care, specifically as relates to price fixing, which has been a felony for over 100 years. Nobody cares and nobody will prosecute.
Since all criminal offenses in the United States are “the people .v. whoever” — that is, there’s no right of private prosecution as there is with a lawsuit, it never ends since nobody goes to jail and in fact there is a formal government policy not to indict large corporations for felony criminal acts (which could debar them permanently from government and some private activity) after Arthur Anderson. Health care has gone from about 4% to 20% of our domestic output; that is, it has multiplied in price by five. Just having a child is expensive, never mind the near-inevitable little thing here and there. Your kid breaking a leg playing a sport could bankrupt you in this country, and God forbid said child contracts a serious childhood disease such as Leukemia.
Then there’s the always-required housing. One or more kids means more bedrooms, of course; at least one more. When a one-bedroom apartment runs $12,000 a year exactly how am I supposed to pay for that if I don’t make at least $40,000 annually? Oh, we’ll just “subsidize” that you say? Uh, no you won’t because all that does is force the price even higher by throwing printed government credit at it, since the government refuses to tax what it spends first. The last two years have made clear what all the credit emission does: Food, anyone? And kids are hungry, especially teens. I had one; she was a vacuum cleaner in the fridge and pantry and boys are worse. That’s normal. How are you going to pay for it?
Of course nobody seems to think this is a problem, not even Jerome Powell at The Fed, who is saying that he has “the tools” to make inflation come down to 2%. Eventually. Note that what he didn’t say is that he will tighten credit until the price of houses returns to what it was before the 2006-2007 bubble, which was in fact still ridiculously expensive in terms of average wages which is why the bubble happened in the first place — people running up the price by using hinky financial engineering. No, importing millions of people from other lands, most with no skills, will not fix this. They come here with no skills but a willingness to pop out some kids — which makes it worse. That’s basic economics: No skills means low or no wages but demand for goods and services which of course makes the price go up even more.

One more independent voice silenced.
• GB News Presenter Quits After Channel Tries To Make Him Pay Ofcom Fines (G.)
One of GB News’s leading presenters has quit after the channel tried to make him personally responsible for paying fines issued by the media regulator Ofcom. Mark Steyn, who presented the station’s 8pm peak-time slot, is already subject to two investigations by the media regulator after he used his show to cast doubt on the safety of Covid vaccines. The presenter’s departure has led some viewers of GB News – which has given airtime to conspiracy theorists warning of a globalist elite takeover – to suggest the channel has itself sold out to shadowy globalist forces. Steyn, who has been off-air since last year after suffering two heart attacks, told fans on his personal website that the station bosses initially insisted he could not return unless a defibrillator was fitted in the studio.
He said this was fixed with a call to “Defibrillators R Us”, only for Angelos Frangopoulos, GB News’s chief executive, to demand Steyn agree to personally cover the costs of dealing with Ofcom and paying any fines for breaches of the broadcasting code. This is a highly unusual situation given the fines are the legal responsibility of the broadcast licence holder, not the individual presenter. Steyn, who was employed on a freelance basis, said his response was that “you may be a homicidal maniac intent on bringing on a third fatal heart attack but you’ll have to do better than this”. The presenter said he used to call GB News’s in-house compliance officer “Ofcom’s bitch” when they argued about what he was allowed to say on air. “Well Ofcom’s bitch has had his revenge now,” said Steyn in his video.
Steyn said the proposal would be untenable. “I’m on the hook for Ofcom fines but I don’t have any say in our defence against an Ofcom complaint – that’s all done by GB News. Ofcom’s bitch, as I call the compliance officer, will be making the weedy defence to Ofcom and then I’m the one who has to pay the £40,000 fine,” he added. Although Ofcom has the ability to regulate the content of broadcast television and radio channels, it has no control over online streams – meaning Steyn is able to broadcast whatever he wants online to a potentially bigger audience without any intervention. The contractual terms offered to Steyn suggest GB News bosses are concerned about the impending judgment in the Ofcom investigations – which could scare away some of its remaining advertisers. Earlier this year all staff were put on mandatory Ofcom training.

Time for a hearing under oath. In public.
• Fauci Makes Absurd Amount of Money for “Speaking Engagements” (TP)
Dr. Anthony Fauci faced criticism online on Sunday after reports emerged about his speaking fee. Critics were stunned to discover that the once highest-paid federal U.S. government employee is charging up to $100,000 for speaking engagements. This news has raised questions about Fauci’s financial motivations and independence in light of his high-profile role as a public health expert during the COVID-19 pandemic. The information was brought to light by Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis’ rapid response director, Christina Pushaw, who tweeted a screenshot from the Leading Motivational Speaker’s Agency’s website. The screenshot showed that Fauci is listed as a motivational and healthcare keynote speaker, with a fee ranging from $50,000 to $100,000.
Many argued that his high speaking fee undermines his credibility and raises ethical concerns, regardless of the public response. On October 19, 2020, President Trump called Dr. Fauci “a disaster.” The chief medical adviser to Biden is scheduled to deliver the 2023 Yale Medical School commencement speech in May. He has also been a keynote speaker at several other university commencement ceremonies, including the University of Maryland, Roger Williams University, and The City College of New York. According to a Freedom of Information Act request, Fauci was once considered the highest-paid employee of the U.S. government, earning more than even the president. In 2019, Fauci’s income reached a record high of $417,608.00, and over the previous two years, he earned $384,625.00.
Between 2010 and 2019, Forbes reported that Fauci, as head of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, earned $3.6 million. Watchdog group OpenTheBooks found that the Fauci family’s net worth expanded from $7.5 million in 2019 to $12.6 million by the end of 2021, due to investment gains, awards, compensation, and royalties.

“..approximately one-quarter of a million American lives were lost during the first year of the catastrophic COVID-19 vaccine campaign..”
• Mind-Blowing Reality of Death after Injection (MOL)
Many individuals around the globe appear to have fallen into a trance where those who have undergone COVID-19 vaccination do not recognize, nor do they care when large numbers of individuals are dying suddenly without explanation days or months also after taking one of the COVID-19 vaccines. In this issue of the Report, we have an excerpt from the Headwinds documentary “The Psychology of Totalitarianism,” where Dr. Mattias Desmet, Ph.D., gives a summary of mass formation and some of the behaviors it explains, including the fear-driven affiliation with a group who believes so strongly in the vaccine, that they will do unimaginable things to the unvaccinated. Broken families, job loss, and careers ruined for the unvaccinated by those in the formation who are hell-bent on every last person taking a COVID-19 vaccine.
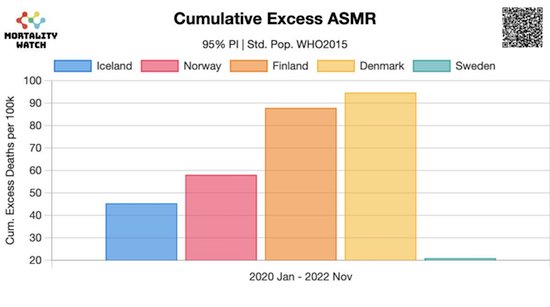
Cumulative excess deaths Scandinavia.
At the same time, the United States is facing catastrophic casualties with the mass vaccination program. Several sources of data emerged in 2021, pointing to a biopharmaceutical public health disaster with the COVID-19 vaccine campaign. Pfizer recorded 1223 deaths occurring shortly after administration of their product within the first 90 days of use starting December 10, 2020. Pantazatos and Seligmann reported an excess in all-cause mortality from vaccine administration and US census data during 2021 between 146k and 187k, with a midpoint of 166k deaths. By the end of December 2021, the CDC VAERS system had reported ~8K with an under-reporting factor of 30; the casualty estimate from that source was 240k. In a recent paper published in BMC Infectious Diseases, Dr. Mark Skidmore used a valid representative survey to learn from population reporting.
A total of 22% knew of someone who was seriously injured by the vaccine, and the estimate based upon deaths attributed to the vaccine by respondents was 278K deaths. In the Skidmore analysis, the average age of death reported was 48 years. This paper is important since it triangulates with two other sources for the same time interval with a conclusion that approximately one-quarter of a million American lives were lost during the first year of the catastrophic COVID-19 vaccine campaign. During 2021 the Delta outbreak took an additional toll, with lives lost to the infection, and there was no evidence to support a tradeoff. That is, no randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of COVID-19 vaccination demonstrated a reduction in death as a component of a primary or secondary endpoint. The consent form for immunization does not list mortality reduction as an expected benefit, yet it mentions death is possible with the vaccine. I anticipate more direct sources of information will become available, including vaccine administration information from the CDC linked with the National Death Index.
Unvaxxed women
https://twitter.com/i/status/1622705584435867648

“..200 feet tall, weighed thousands of pounds, and its payload was the size of a jetliner..”
• Chinese Spy Balloon Carried Explosives To Self-detonate (PM)
Following the shooting down of a Chinese spy balloon over the weekend, Pentagon officials have revealed that the balloon potentially was carrying explosives to destroy itself. According to the Daily Mail, Air Force Gen. Glen D. VanHerck, commander of US Northern Command, revealed in a Monday call with reporters that the Balloon, in addition to potentially carrying explosives, was 200 feet tall, weighed thousands of pounds, and its payload was the size of a jetliner. VanHerck’s comments came following a briefing by National Security Council spokesman John Kirby, who defended Biden’s decision to wait to shoot down the balloon until the weekend. “Because the president decided they wouldn’t shoot it down until he could do so safely, and that meant over water, that afforded us a terrific opportunity to gain a better understanding, to study the capabilities of this balloon,” Kirby said.
On the coast of South Carolina on Saturday afternoon, the US military, using an F-22 fighter jet, shot down the balloon with a missile. Shortly before the balloon was shot down, Federal Aviation Administration had issued a ground stop for three airports in the Carolinas located in Wilmington, North Carolina, Charleston, South Carolina, and Myrtle Beach, South Carolina. The balloon had entered US airspace on January 28 and was known to the Biden administration for nearly a week before its report in the news on Thursday, February 2. The White House reportedly tried to keep its presence secret to not disrupt Secretary of State Antony Blinken scheduled trip to China, which was postponed after the public’s discovery of the balloon.




C seeds
https://twitter.com/i/status/1621997452445229056


Ring
https://twitter.com/i/status/1622408086081396737


Funeral sheep
An Australian farmer couldn't attend the funeral for his aunt so he laid out grain in the shape of a heart so "she can see it through the clouds.” pic.twitter.com/f9L2Ud3r7X
— Historic Vids (@historyinmemes) February 6, 2023
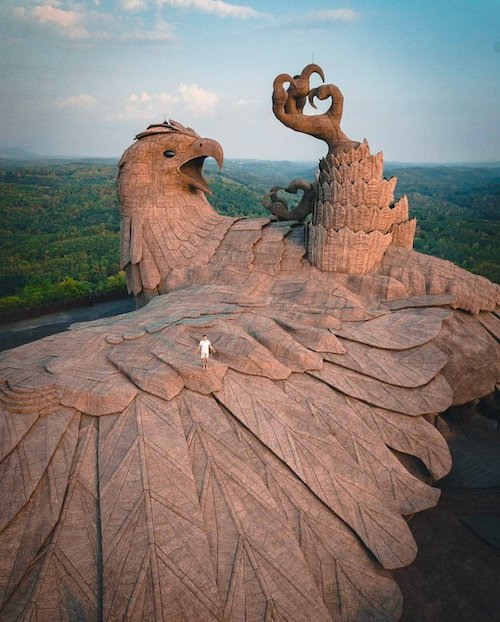


A massive sculpture of a legendary bird has taken shape at Jatayu Earth’s Center in Kerala, India, in 2020. Jatayu, the noble bird of divine origin, as recreated in concrete at the Center is 61 meters long, 46 meters wide, and 21 meters tall


Support the Automatic Earth in virustime with Paypal, Bitcoin and Patreon.