
Giotto Lamentation 1306

Again: look at dollar-denominated debt in the world. And then check interest rates. The dollar will be in great demand.
• What Could Dethrone the Dollar as Top Reserve Currency? (WS)
What will finally pull the rug out from under the dollar’s hegemony? The euro? The Chinese yuan? Cryptocurrencies? The Greek drachma? Whatever it will be, and however fervently the death-of-the-dollar folks might wish for it, it’s not happening at the moment, according to the most recent data. The IMF just released its report, Currency Composition of Official Foreign Exchange Reserves (COFER) for the fourth quarter 2017. It should be said that the IMF is very economical with what it discloses. The COFER data for the individual countries – the total level of their reserve currencies and what currencies they hold – is “strictly confidential.” But we get to look at the global allocation by currency.
In Q4 2017, total global foreign exchange reserves, including all currencies, rose 6.6% year-over-year, or by $709 billion, to $11.42 trillion, right in the range of the past three years (from $10.7 trillion in Q4 2016 to $11.8 trillion in Q3, 2014). For reporting purposes, the IMF converts all currency balances into dollars. Dollar-denominated assets among foreign exchange reserves rose 14% year-over-year in Q4 to $6.28 trillion, and are up 42% from Q4 2014. There is no indication that global central banks have lost interest in the dollar; on the contrary:
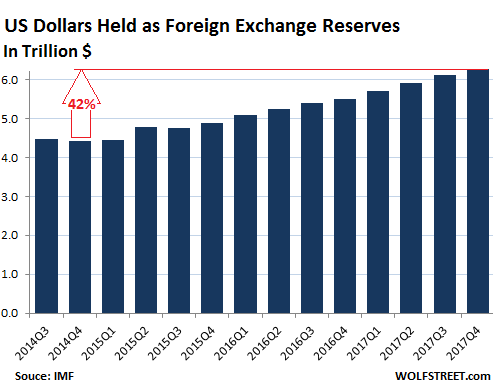
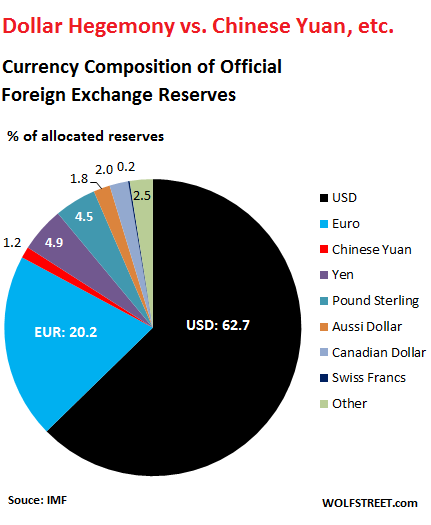
Over the decades, there have been some efforts to topple the dollar’s hegemony as a global reserve currency, which it has maintained since World War II. The creation of the euro was the most successful such effort. Back in the day, the euro was supposed to reach “parity” with the dollar on the hegemony scale. And it edged up for a while until the euro debt crisis derailed those dreams. And now there’s the ballyhooed Chinese yuan. Effective October 1, 2016, the IMF added it to its currency basket, the Special Drawing Rights (SDR). This anointed the yuan as a global reserve currency. But not all central banks disclose to the IMF how their foreign exchange reserves are allocated. In Q4, the allocation of 12.3% of the reserves hadn’t been disclosed.
These “unallocated reserves” have been plunging. Back in Q4 2014, they still accounted for 41% of total reserves. They’re plunging because more central banks report to the IMF their allocation of foreign exchange reserves, and the COFER data is getting more detailed. So among the 87.7% of the “allocated” reserve currencies in Q4 2017, the pie was split up this way, with changes since 2014: Disappointingly for many folks, the Chinese yuan – the thin red sliver in the pie chart above — didn’t exactly soar since its inclusion in the SDR basket. Its share ticked up by a minuscule amount to a minuscule share of 1.2% of allocated foreign exchange reserves in Q4. In other words, central banks seem to lack a certain eagerness, if you will, to hold yuan-denominated assets.

Nobody has a clue why LIBOR rises, including whoever wrote this. A wild guess: $200 trillion?! It’s that dollar-denominated debt problem again.
• How Many Trillions In Debt Are Linked To Soaring LIBOR? (ZH)
[..] we have commented extensively on what may (or may not) be behind the Libor blow out: if as many claim, the move is a benign technicality and a temporary imbalance in money market supply and demand, largely a function of tax reform (including the Base Erosion Anti-Abuse Tax) or alternatively of the $300BN surge in T-Bill supply in the past month, the Libor move should start fading. If it doesn’t, it will be time to get nervous. But no matter what the reason is behind the Libor move, the reality is that financial conditions are far tighter as a result of the sharp move higher in short-term rates in general, and Libor in particular, which for at least a few more years, remains the benchmark rate referenced by trillions in fixed income instruments.
Which brings us to a logical follow up question: ignoring the reasons behind the move, how does a higher Libor rate spread throughout the financial system, and related to that, how much notional debt is at risk of paying far higher interest expense, if only temporarily, resulting in even tighter financial conditions. For the answer, we look at the various ways that Libor, and short-term rates in general “channel” into the economy. Here, as JPMorgan explains, the key driver is and always has been monetary policy, which controls short-term rates, which affect the economy via various channels and pathways.

45% feels like a lot.
• Bitcoin Is On Track For Its Worst First Quarter Ever (CNBC)
Bitcoin is having a terrible first quarter, in fact the worst its ever seen. The price of the cryptocurrency has fallen from $13,412.44 on January 1 to $7,266.07 on March 30, marking a more than 45% decline, according to data from CoinDesk, a site which tracks the price of different digital coins. The quarter ends on Saturday. So far this quarter, $114.9 billion of market capitalization or value has been wiped off of bitcoin. The price decline this quarter is the biggest first quarter decline in bitcoin’s history. The previous biggest decline was a near 38% fall in the price in the first quarter of 2014, according to data from CoinDesk. It tracks the price of bitcoin back to the middle of 2010.
CNBC looked at bitcoin’s price performance in the first quarters of each year beginning in 2011. Bitcoin has recorded a decline in 5 of the 8 first quarters tracked, which includes the current 2018 Q1. The biggest price rise was a 599% surge in the price of bitcoin in the first quarter of 2013. Bitcoin saw a huge run up in price in 2017 and hit a record high above $19,000 towards the end of last year. But it has faced tougher regulatory scrutiny in 2018 and some of the air has come out of the market. At a G-20 meeting this month, Argentina’s central bank governor outlined a summer deadline for members to have “specific recommendations on what to do” and said task forces are working to submit proposals by July. Italy’s central bank leader told reporters after the meeting in Buenos Aires, Argentina, that cryptocurrencies pose risks but should not be banned, according to Reuters.

What’s the recall of 123,000 cars going to cost?
• Tesla’s ‘Day Of Reckoning’ Is Near (CNBC)
Tesla’s big stock drop this month will have negative implications for its ability to raise critically-needed funds, according to Wall Street analysts. The company’s shares declined 22% in March on concerns over a fatal car crash in California last week and worries over its Model 3 production rate. Tesla’s 5.3% bond, issued last August and maturing in 2025, also fell 4% to 87.25 cents Wednesday with a yield of 7.6%, according to FactSet. The bond’s price declined 8% this month. Morgan Stanley on Wednesday warned Tesla shareholders the stock’s fall could be a “self-fulfilling” prophecy for further declines.
“A lower share price begets a lower share price … For a company widely expected to continue to fund its strategy through external capital raises, a fall in the share price can take on a self-fulfilling nature that further exacerbates the volatility of the share price,” analyst Adam Jonas wrote. Jonas said the company needs to accelerate its rate of Model 3 production if it wants to raise funds at an attractive price for the company. “The precise timing of when Tesla can achieve a 2,500/week and then a 5,000/week production run-rate for its mass market sedan can make the difference between whether Tesla is potentially raising capital from a position of weakness at a price near our $175 bear case or whether it can access capital from a position of strength with a stock price near our $561 bull case,” he wrote.
Another financial firm is already pessimistic over Telsa’s Model 3 manufacturing capability. Moody’s downgraded Tesla’s credit ratings after the close Tuesday and changed the outlook to negative from stable, citing the “significant shortfall” in the Model 3 production rate and its tight financial situation. Tesla had $3.4 billion in cash or cash equivalents at year end 2017. The company lost nearly $2 billion last year and burned about $3.4 billion in cash after capital investments. Given the company’s cash burn rate and how it has $230 million of debt due in Nov. 2018 and another $920 million in Mar. 2019, Moody’s believes the company has to raise new capital soon.

This is a week old, but we can’t repeat often enough how insane this is. Germany’s economy is supposedly soaring, but Draghi keeps saving its banks. “To boost inflation..” Bigger nonsense was never heard. Those banks are simply not doing well. But even then, let Germany solve the mess.
• ECB To Buy More German Bank Bonds To Keep Stimulus Flowing (R.)
The European Central Bank will start buying bonds from a further seven state-owned German banks under its stimulus program, it said on Thursday, in a bid to avoid running out of debt to buy after three years of massive purchases. The seven regional banks, which include the Investitionsbank Berlin and Bavaria’s LFA Förderbank Bayern, join a small group of German development lenders whose debt the ECB has already been buying as part of its efforts to boost inflation. The move slightly enlarges the pool of German debt which the ECB can tap as part of its 2.55 trillion euro ($3.14 trillion) quantitative easing scheme, thereby pushing back a looming cap on owning more than a third of any one country’s public debt.
With euro zone inflation now comfortably above 1%, the ECB is widely expected to wind down its bond purchases this year and even start raising interest rates towards the middle of 2019. With Germany running a fiscal surplus, however, finding enough German bonds to buy has already become harder for the ECB, which has reduced its purchases of debt from Europe’s largest economy more than for other large countries in recent months. The ECB has set out to buy government bonds in proportion to the amount of capital that each country has paid into the central bank, which in turn depends on the size of its economy. Deviations from this so called “capital key”, however, have been substantial, with France, Italy and Spain enjoying oversized purchases while smaller countries such as Estonia and Portugal have fallen behind.

And the whole time I’m thinking: why do they have so many people out there? What do they do all day long?
• UK Must Bring Home ‘Just Over 50’ Of Its Diplomats From Russia (R.)
Russia has told Britain it must send home “just over 50” more of its diplomats in a worsening standoff with the West over the poisoning of a former Russian spy and his daughter in Britain. Russia has already retaliated in kind against Britain and ejected 23 British diplomats over the poisoning of former Russian spy Sergei Skripal and his daughter Yulia. London says Moscow stood behind the attack, something Russia denies. British Ambassador Laurie Bristow was summoned again on Friday and told London had one month to cut its diplomatic contingent in Russia to the same size as the Russian mission in Britain.
On Saturday, Foreign Ministry Spokeswoman Maria Zakharova told Reuters that meant Britain would have to cut “a little over 50” of its diplomats in Russia. “We asked for parity. The Brits have 50 diplomats more than the Russians,” said Zakharova. When asked if that meant London would have to bring home exactly 50 diplomats, she said: “A little over 50.”

It doesn’t feel as if demanding internet access for Julian quite cuts it. He could be in much bigger trouble.
• Jammers Stop Assange From Using Internet (PA)
Electronic jammers have been placed inside the Ecuadorian embassy in London to prevent WikiLeaks founder Julian Assange having access to the internet or social media, sources say. The Ecuadorian government took the measure on Tuesday evening, stopping Assange from tweeting, using the internet or phone. He has also been refused any visitors to the embassy, where he has been living since June 2012, believing he will be extradited to the US for questioning over the activities of WikiLeaks if he leaves. The measures follow the publication of an article in the Ecuadorian press concerning Assange’s tweets about the arrest of former Catalan president Carles Puigdemont in Germany earlier this week.
In a phone call to Assange’s lawyer on Tuesday, an adviser to Ecuadorian Foreign Minister Maria Fernanda Espinosa said the WikiLeaks founder must stop tweeting about the Catalan issue. He was also asked to erase a tweet which said: “In 1940 the elected president of Catalonia, Lluis Companys, was captured by the Gestapo, at the request of Spain, delivered to them and executed. Today, German police have arrested the elected president of Catalonia, Carles Puigdemont, at the request of Spain, to be extradited.” Assange did not erase the tweet. His lawyer was told that a decision had been taken to isolate Assange by preventing him from communicating with the outside world and that this was “by order of the president”, say sources.
The serving Ecuadorian ambassador to Washington DC Francisco Carrion tweeted on Thursday: “The decision of the government of Ecuador to prevent Assange from tweeting is correct.” The Ecuador government said in a statement: “The government of Ecuador has suspended the systems that allow Julian Assange to communicate to the outside of the Ecuador embassy in London. “The measure was adopted due to Assange not complying with a written promise which he made with the government in late 2017, by which he was obliged not to send messages which entailed interference in relation to other states.” WikiLeaks sources said there was no such agreement.

Who needs Orwell? Or Facebook, for that matter?! Only difference is China does it openly.
• China’s Social Credit System Punishes Untrustworthy Citizens (ABC.au)
Chinese authorities claim they have banned more than 7 million people deemed “untrustworthy” from boarding flights, and nearly 3 million others from riding on high-speed trains, according to a report by the country’s National Development and Reform Commission. The announcements offer a glimpse into Beijing’s ambitious attempt to create a Social Credit System (SCS) by 2020 — that is, a proposed national system designed to value and engineer better individual behaviour by establishing the scores of 1.4 billion citizens and “awarding the trustworthy” and “punishing the disobedient”.
Liu Hu, a 43-year-old journalist who lives in China’s Chongqing municipality, told the ABC he was “dumbstruck” to find himself caught up in the system and banned by airlines when he tried to book a flight last year. Mr Liu is on a “dishonest personnel” list — a pilot scheme of the SCS — because he lost a defamation lawsuit in 2015 and was asked by the court to pay a fine that is still outstanding according to the court record. “No one ever notified me,” Mr Liu, who claims he paid the fine, said. Like the other 7 million citizens deemed to be “dishonest” and mired in the blacklist, Mr Liu has also been banned from staying in a star-rated hotel, buying a house, taking a holiday, and even sending his nine-year-old daughter to a private school. And just last Monday, Chinese authorities announced they would also seek to freeze the assets of those deemed “dishonest people”.
As the national system is still being fully realised, dozens of pilot social credit systems have already been tested by local governments at provincial and city levels. For example, Suzhou, a city in eastern China, uses a point system where every resident is rated on a scale between 0 and 200 points — every resident starts from the baseline of 100 points. One can earn bonus points for benevolent acts and lose points for disobeying laws, regulations, and social norms. According to a 2016 report by local police, the top-rated Suzhou citizen had 134 points for donating more than one litre of blood and doing more than 500 hours of volunteer work. The city said the next step was to use the credit system to punish people for transgressions such as dodging transport fares, cheating in video games, and restaurant no-shows.

Tried to make sense of this, several times. Still sounds entirely hollow.
• China ‘Environment Census’ Reveals 50% Rise In Pollution Sources (G.)
China’s environment ministry has said the number of sources of pollution in the country has increased by more than half in less than a decade. Releasing preliminary results of an ongoing “environmental census”, China’s ministry of ecology and environment said the number of sources of pollution in the country stands at about 9m, compared to 5.9m in its first census, in 2010. “The objectives and scope of the second census is different from those of the first one,” said Hong Yaxiong, head of the pollution survey at the ministry, Thursday. “But overall, there are more pollution sources.” The census did not say whether pollution had increased but declines in airborne pollution in major cities have been recorded in other studies.
Hong said factories flouting emissions standards were the main problem. The ministry found 7.4m sources of industrial pollution, compared to a million in rural areas and 500,000 in urban locations. Five years ago, China declared a “war against pollution.” Since then, new coal plants have been barred from opening and existing ones have been ordered to cut emissions. Major cities restrict the number of cars allowed on the roads. This past winter, residents in Beijing were left without heat after their coal boilers were removed. As part of the campaign, officials this month expanded the powers of the country’s 10-year-old ministry of environmental protection to include water management, emissions reductions, agricultural pollution, and other duties previously managed by half a dozen other ministries.

No, it’s not just the birds and the bees. Fish are gone too.
• Overfishing Turns Mediterranean Dolphins Into Thieves (Ind.)
Dolphins short on prey are resorting to underhand tactics to find a meal – tearing into nets to access the fish inside. Researchers studying interactions between dolphins and fishermen in northern Cyprus found nets were six times more prone to damage when dolphins were in the vicinity. They concluded that the marauding marine mammals were therefore the most likely culprits. “It seems that some dolphins may be actively seeking nets as a way to get food,” said Dr Robin Snape, an ecologist at the University of Exeter, who led the study. Net damage is irritating for the fishermen themselves, and can cost individuals thousands of euros every year. This is particularly problematic as most operations in the region are small scale.
However, the scientists suggested the fishermen must take some share of the blame, as overfishing in the region is a likely driver for the dolphins’ unusual behaviour. Dr Snape highlighted a “vicious cycle” that is “probably driven by falling fish stocks, which also result in low catches – meaning more nets are needed and higher costs for fishers”. “Effective management of fish stocks is urgently needed to address the overexploitation that is causing this vicious cycle,” he said.









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle March 31 2018