
Dorothea Lange Rear window tenement dwelling, 133 Avenue D, NYC 1936

“It never was a big deal because growing imports were portrayed as healthy demand in the US. The world loved it.”
• This Is How Out-Of-Whack US Trade Relationships Really Are (WS)
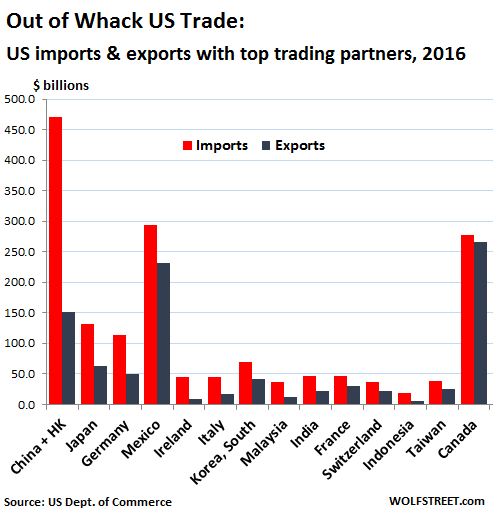
2016 marked another banner year for US trade, a banner year largely for other countries that at the initiative of Corporate America, whose supply chains weave all over the world, managed to load the US up with their merchandise. According to the Commerce Department’s report today, the US trade deficit in goods and services rose to $502.3 billion in 2016, the highest in four years. Exports of goods and services fell $52 billion in 2016 year-over-year to $2.21 trillion, and imports fell $50 billion to $2.71 trillion. That both exports and imports fell is a sign of weakening world trade, lackluster demand globally, and lousy economic growth in the US, where GDP in 2016 inched up by a miserable 1.6%, matching the growth rate of 2011, both having been the lowest growth rates since 2009.
Exports add to the economy and to GDP; imports subtract from GDP. And it’s a big number: the trade deficit in 2016 amounted to 2.7% of GDP. In overly simplified, scribbled-on-a-napkin-after-the-third-beer math: had trade been balanced, with imports about equal to exports, GDP growth would have been 2.7 percentage points higher in 2016. So 4.3%! OK, we’re dreaming. But that’s how a massive trade deficit whacks the economy. The overall trade balance is composed of trade in goods and services. It used to be years ago when the trade deficit in goods began to balloon that it was no big deal because America was exporting innovative services, such as complex financial services, and they would make up for the deficit in old-fashioned goods.
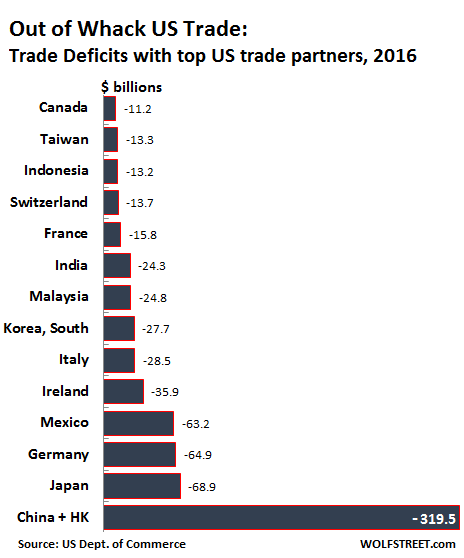
They did lessen the pain for a little while, and then they didn’t. And soon, even the overall US trade deficit ballooned, but it was no big deal because soaring imports showed that the US economy was healthy and brimming with consumer demand. Year after year, we heard this from economists and politicians. Beyond that, apathy was palpable. No one cared. It’s just the way it is. Dreaming of balanced trade was like so 1980s or whatever. Meanwhile, Corporate America was fine-tuning its game of offshoring production and importing from cheaper countries. The entire business model of Wal-Mart depends on it. US supply chains wind all over the globe, in search of the lowest production costs, whether it’s consumer gadgets or automotive components. It never was a big deal because growing imports were portrayed as healthy demand in the US. The world loved it.

Kelly’s a straight shooter. Wonder how long he can last.
• John Kelly, Homeland Security Chief, Says Travel Ban Rolled Out Too Quickly (WSJ)
Homeland Security Secretary John Kelly told Congress the Trump administration should have taken more time to inform Congress before implementing its controversial executive order temporarily blocking entry of people from seven nations. “The thinking was to get it out quick so potentially people coming here to harm us would not take advantage” of a delay, Mr. Kelly told the House Homeland Security Committee on Tuesday. In his first congressional appearance as a cabinet member, Mr. Kelly offered a forceful defense of the order, saying it wasn’t a ban on Muslims as critics have charged, but a “temporary pause” on immigrants and visitors from countries about whose residents the U.S. can’t access solid information. He sought to take responsibility for the chaotic rollout, saying the confusion was “all on me.”
“Going forward, I would have certainly taken some time to inform the Congress and certainly that’s something I’ll do in the future,” he said. The Wall Street Journal and others have reported that Mr. Kelly had little input in the order or its rollout, which was directed by the White House. The order, issued on the afternoon of Friday, Jan. 27, resulted in initial confusion and confrontation at airports around the country, as some travelers were detained for hours or sent away and protesters gathered at terminals to denounce the new rules. A federal court in Seattle temporarily put the order on hold on Friday, citing potential legal concerns. That action prompted President Donald Trump to question the judge’s credentials and say he could be to blame in the event of a terrorist attack. Mr. Kelly waded into that debate on Tuesday, likening judges to academics removed from on-the-ground realities.
“I have nothing but respect for judges, but in their world it’s a very academic, very almost in-a-vacuum discussion, and of course, in their courtrooms, they are protected by people like me, so they can have those discussions,” he said. “They live in a different world than I do. I’m paid to worst-case it, he’s paid to, in a very academic environment, make a call.” [..] Committee chairman Rep. Michael McCaul (R., Texas) said he backed the executive order, which a court order has put on hold. But he said it was poorly implemented. He said some U.S. permanent residents who are citizens of the targeted countries were initially not allowed to return to the country, while foreigners who aided the U.S. military and students attending American schools were “trapped overseas.”
“I applaud you for quickly correcting what I consider errors,” Mr. McCaul said. The congressman said he had suggested the approach President Donald Trump took when Mr. Trump was a candidate. His goal, Mr. McCaul said, was to help reframe the proposal from what Mr. Trump initially described as a Muslim ban, an approach he thought would have been unconstitutional.

It’s great to have the courts discuss this. That’s where it belongs. If Trump can win, we will know just how broad US presidents’ power had become, before Trump. And we can judge whether we like things that way. He either has the authority, or he doesn’t. That should be clear from the law, not a matter of taste or preference.
• Trump Travel Ban: Judges Skeptical About Arguments On Executive Order (G.)
A lawyer seeking to reinstate Donald Trump’s travel ban was grilled by a panel of three judges on Tuesday, facing questions over the president’s inflammatory campaign promise to close America’s borders to Muslims. August Flentje, of the Department of Justice, was put on the spot over why seven Muslim-majority countries had been targeted in Trump’s executive order, as well as past statements made by the president and his ally Rudy Giuliani. The hour-long hearing before the San Francisco-based ninth circuit court of appeals was the most significant legal battle yet over the ban. The judges said they would try to deliver a ruling as soon as possible but gave no indication of when. Flentje, reportedly called up for the hearing at short notice, asked the judges for a stay on the temporary restraining order placed on Trump’s travel ban by district court judge James Robart last week.
[..] During a hearing conducted by telephone between various locations, Flentje described the ban as putting a “temporary pause” on travelers from countries that “pose special risk”. He said the seven countries targeted had “significant terrorist presence” or were “safe havens for terrorism”. Trump’s actions were “plainly constitutional”, Flentje argued, as the president sought to strike a balance between welcoming visitors and securing the nation of the risk of terrorism. “The president has struck that balance,” he said. “The district court order upset that balance.” Flentje argued that the district court restraining order was too broad, giving rights to people “who have never been to the United States” and “really needs to be narrowed”. Judge Michelle Friedland asked: “Are you arguing then that the president’s decision in the regard is unreviewable?”
Flentje replied: “Yes, there are obviously constitutional limitations.” But Judge William Canby pointed out that people from the seven countries already could not come into the country without a visa and were subject to “the usual investigations”. How many of these people had committed terrorist attacks in the US, he wondered, before pointing out it was none. Flentje pointed to Congress’s determination that they were countries of concern, an argument that Judge Richard Clifton dismissed as “pretty abstract”. Trying to regain ground, the lawyer said: “Well, I was just about to at least mention a few examples. There have been a number of people from Somalia connected to al-Shabaab [an Islamist militant group] who have been convicted in the United States.” Friedland, who was appointed by Barack Obama, interjected: “Is that in the record? Can you point us to what, where in the record you are referring?” Flentje admitted: “It is not in the record.”

“..if you went to the local souk [bazaar] in Aleppo and brought one of the retail shop owners, he would do the same thing Trump is doing. Like making a call to Boeing and asking why are we paying so much..”
• ‘Trump Makes Sense To A Grocery Store Owner’ – Taleb (Hindu)
In Skin in the Game, you seem to build on theories from The Black Swan that give a sense of foreboding about the world economy. Do you see another crisis coming? Oh, absolutely! The last crisis [2008] hasn’t ended yet because they just delayed it. [Barack] Obama is an actor. He looks good, he raises good children, he is respectable. But he didn’t fix the economic system, he put novocaine [local anaesthetic] in the system. He delayed the problem by working with the bankers whom he should have prosecuted. And now we have double the deficit, adjusted for GDP, to create six million jobs, with a massive debt and the system isn’t cured. We retained zero interest rates, and that hasn’t helped. Basically we shifted the problem from the private corporates to the government in the U.S. So, the system remains very fragile.
You say Obama put novocaine in the system. How will the Trump administration be able to address this? Of course. The whole mandate he got was because he understood the economic problems. People don’t realise that Obama created inequalities when he distorted the system. You can only get rich if you have assets. What Trump is doing is put some kind of business sense in the system. You don’t have to be a genius to see what’s wrong. Instead of Trump being elected, if you went to the local souk [bazaar] in Aleppo and brought one of the retail shop owners, he would do the same thing Trump is doing. Like making a call to Boeing and asking why are we paying so much.
You’re seen as something of an oracle, given that you saw the 2008 economic crash coming, you predicted the Brexit vote, the outcome of the Syrian crisis. You said the Islamic State would benefit if Bashar al-Assad was pushed out and you predicted Trump’s win. How do you explain it? Not the Islamic State, but al-Qaeda at the time, and I said the U.S. administration was helping fund them. See, you have to have courage to say things others don’t. I was lucky financially in life, that I didn’t need to work for a living and can spend all my time thinking. When Trump was running for election, I said what he says makes sense to a grocery store owner. Because the grocery guy can say Trump is wrong because he can see where he is wrong. But with Obama, he can’t understand what he’s saying, so the grocery man doesn’t know where he is wrong.
Is it a choice between dumbing down versus over-intellectualisation, then? Exactly. Trump never ran for archbishop, so you never saw anything in his behaviour that was saintly, and that was fine. Whereas Obama behaved like the Archbishop of Canterbury, and was going to do good but people didn’t feel their lives were better. As I said, if it was a shopkeeper from Aleppo, or a grocery store owner in Mumbai, people would have liked them as much as Trump. What he says makes common sense, asking why are we paying so much for this rubbish or why do we need these complex taxes, or why do we want lobbyists. You can call Trump’s plain-speaking what you like. But the way intellectuals treat people who don’t agree with them isn’t good either. I remember I had an academic friend who supported Brexit, and he said he knew what it meant to be a leper in the U.K. It was the same with supporting Trump in the U.S.

Amen to that.
• Do Not Let Elliott Abrams Anywhere Near The State Department (Rand Paul)
I hope against hope that the rumors are wrong and that President Donald Trump will not open the State Department door to the neocons. Crack the door to admit Elliott Abrams and the neocons will scurry in by the hundreds. Neoconservative interventionists have had us at perpetual war for 25 years. While President Trump has repeatedly stated his belief that the Iraq War was a mistake, the neocons (all of them Never-Trumpers) continue to maintain that the Iraq and Libyan Wars were brilliant ideas. These are the same people who think we must blow up half the Middle East, then rebuild it and police it for decades. They’re wrong and they should not be given a voice in this administration.
One of the things I like most about President Trump is his acknowledgement that nation building does not work and actually works against the nation building we need to do here at home. With a $20 trillion debt, we don’t have the money to do both. I urge him to keep that in mind this week when he meets with Elliott Abrams, the rumored pick for second in command to the Secretary of State. Abrams would be a terrible appointment for countless reasons. He doesn’t agree with the president in so many areas of foreign policy and he has said so repeatedly; he is a loud voice for nation building and when asked about the president’s opposition to nation building, Abrams said that Trump was absolutely wrong; and during the election he was unequivocal in his opposition to Donald Trump, going so far as to say, “the chair in which Washington and Lincoln sat, he is not fit to sit.”
Why then would the president trust him with the second most powerful position in the State Department? Abrams was equally dismissive throughout Trump’s entire candidacy. As a Never-Trumper, he repeatedly said he would neither vote for Clinton nor Trump. He likened the choice to the one the nation faced of McGovern vs. Nixon. I voted for Rex Tillerson for secretary of state because I believe him to have a balanced approach to foreign policy. My hope is that he will put forward a realist approach. I don’t see Abrams as part of any type of foreign policy realism. Elliott Abrams is a neoconservative too long in the tooth to change his spots, and the president should have no reason to trust that he would carry out a Trump agenda rather than a neocon agenda. But just as importantly, Congress has good reason not to trust him – he was convicted of lying to Congress in his previous job.

It’s not only a broken record, it’s a really bad song too.
• EU Faces Crisis As IMF Warns Greek Debts Are On ‘Explosive’ Path (Tel.)
The EU faces a looming crisis which could threaten the sustainability of the eurozone as the IMF has warned Greece’s debts are on an “explosive” path despite years of attempted austerity and economic reforms. Global financiers at the IMF are increasingly unwilling to fund endless bailouts for the eurozone’s most troubled country, passing more of the burden onto the EU – at a time when Germany does not want to keep sending cash to Athens. The assessment opens up a fresh split with Europe over how to handle Greece’s massive public debts, as the IMF called on Europe to provide “significant debt relief” to Greece – despite Greece’s EU creditors ruling out any further relief before the current rescue programme expires in 2018. Jeroen Dijsselbloem, the Eurogroup President repeated that position last night, saying there would be no Greek debt forgiveness and dismissing the IMF assessment of Greece’s growth prospects as overly pessimistic.
“It’s surprising because Greece is already doing better than that report describes,” said Mr Dijsselbloem, who chairs meetings of eurozone finance ministers, adding that Greece was on track for a “pretty good recovery at the moment”. The renewed divisions over how to handle the Greek debt crisis has raised fresh questions over whether the IMF will be a full participant in the next phase of the Greek rescue – a key condition for backing from the German and Dutch parliaments. As Angela Merkel, the German chancellor, fights a tough reelection battle, Germany is particularly reluctant to send funds directly to Greece, with populist parties in Germany arguing that the payments amount to an unfair bailout from hard-working Germans to less deserving Greeks.
The IMF split came as Mrs May last night comfortably defeated a Brexit rebellion in the Commons as MPs rejected Labour plans to give Parliament a “meaningful” vote on the terms of a final deal. Despite suggestions that up to 30 Tory MPs could defy their party whip and back the Labour amendment just seven chose to do so. Mrs May stemmed the rebellion after the Government pledged to hold a vote in Parliament on the deal before it is sent to the European Parliament. However ministers said that MPs would have to “take or leave it”, meaning that Mrs May is prepared to walk away from Europe without a deal if Parliament rejects it. A fresh crisis over Greek debt could be triggered as soon as in July when Greece is due to repay some €7bn to its creditors – money the country cannot pay without a fresh injection of bailout cash.

As they do the same thing again and again, things only get worse. And then they have to do it again.
• Greece’s Debt Costs Rise Sharply As Worries Grow Over IMF Role (G.)
Fresh worries over Greece’s debts have pushed the country’s borrowing costs sharply higher amid renewed insistence from Athens it will not swallow further austerity demands from international lenders. The yields on two-year government bonds jumped to their highest level since last June and went above 10% to reflect growing anxiety on financial markets over Greece’s ability to keep up to date with debt repayments. Yields on 10-year government bonds were also higher at above 7.8%, the highest close since November. The renewed focus on Greece’s debts came as the International Monetary Fund revealed its board was split over how far spending cuts in the country should go, raising fresh doubts over its participation in rescue plans for the struggling Greek economy.
The fund has made repeated warnings that Greece’s debt burden of about €330bn is unsustainable despite the government pushing through spending cuts and tax increases that have badly hit popularity ratings for the government of prime minister Alexis Tsipras. The IMF declined to join other international lenders – the ECB and the EU – in funding the country’s third bailout, agreed in August 2015, and it is currently deciding whether to take part in a new chunk of rescue funds needed by mid-2018. Germany has warned the IMF’s involvement is crucial if support for Greece is to continue. News of a split on the IMF board raised new questions over whether Germany will see its wish granted for the fund joining the next rescue. In its latest annual review of the Greek economy, the IMF revealed that its board members were in disagreement over whether Athens should enforce even more austerity to satisfy its lenders.

Barry Eichengreen basically says the euro will stay because of fear (of the consequences of leaving). That doesn’t seem a very stable foundation.
• Don’t Sell the Euro Short. It’s Here to Stay. (Eichengreen)
Two forms of glue hold the euro together. First, the economic costs of break-up would be great. The minute investors heard that Greece was seriously contemplating reintroducing the drachma with the purpose of depreciating it against the euro, or against a “new Deutsche mark,” they would wire all their money to Frankfurt. Greece would experience the mother of all banking crises. The “new Deutsche mark” would then shoot through the roof, destroying Germany’s export industry. More generally, those predicting, or advocating, the euro’s demise tend to underestimate the technical difficulties of reintroducing national currencies. They suggest briefly imposing capital controls to prevent holders of euros from fleeing while the new money, electronic or other, is quickly put in place.
This ignores the complexity of actually removing controls once they are adopted. Recall the experiences of Iceland and Cyprus, which required years, not days, to completely remove their “temporary” controls. The proponents advocate quickly restructuring the debts of banks, firms and households with euro-denominated liabilities, without realizing that one person’s debt is another’s asset. Moreover, because borrowing and lending occurs across borders, agreement on debt restructuring will require lengthy negotiation between countries if the country abandoning the euro is to avoid harsh retaliatory measures. This process would make the U.K.’s Brexit negotiations look like a stroll in the park.
For southern European countries, there is an additional complication. They would have a massive bill to the ECB, and by implication to the other member states that are shareholders in the ECB, in settlement of their so-called Target2 balances, liabilities incurred as a result of cross-border payments in central bank money. ECB President Mario Draghi recently made clear that countries abandoning the euro would be presented with this bill. For Italy, to pick a case not entirely at random, those balances currently stand at €360 billion ($383 billion), or approximately €6,000 for every man, woman and child. That’s about 10 times on a per capita basis what the U.K. likely owes the EU as alimony for its divorce. And if a country like Italy chooses to default on its Target2 obligations, it will be unceremoniously kicked out of the EU.
This brings us to the second form of glue: namely that European countries, Britain aside, still attach very considerable value to EU membership. That membership matters even more now that that President Trump has cast NATO into doubt and the United States is no longer seen as a reliable ally. The example of U.K. Prime Minister Theresa May, reduced to cozying up to Mr. Trump and Turkish Prime Minister Recep Tayyip Erdogan, is not one that many other European politicians care to follow. In a 2007 article, I too made a bet — namely that the euro, while flawed, wasn’t going away. I argued that it is the roach motel of currencies. Like the Hotel California of the song: you can check in, but you can’t check out. For 10 years I’ve been right. To be sure, past performance is no guarantee of future returns, as any prudent investor knows. Even so, unlike ambassador-in-waiting Malloch, I continue to think that shorting the euro is bad advice.

And this is before Trump.
• Money Is Pouring Out Of China, And The Government Can’t Stop It (R.)
China’s foreign exchange reserves unexpectedly fell below the closely watched $3 trillion level in January for the first time in nearly six years, even as authorities tried to curb outflows by tightening capital controls. Reserves fell by $12.3 billion in January to $2.998 trillion, compared with a drop of $41 billion drop in December. Economists polled by Reuters had forecast forex reserves would fall by about $10.5 billion to $3 trillion. While the $3 trillion mark is not seen as a firm “line in the sand” for Beijing, concerns are swirling in global financial markets over the speed at which the country is depleting its ammunition to defend the currency and staunch capital outflows.
Some analysts fear a heavy and sustained drain on reserves could prompt Beijing to devalue the currency. The yuan fell 6.6% against the rising dollar in 2016, its biggest annual drop since 1994. For 2016 as a whole, China burned through nearly $320 billion of reserves, on top of a record drop of $513 billion in 2015. The yuan has found some respite in recent weeks as the dollar retreated, helped also by recent steps to curb capital outflows. But analysts expect downward pressure on the yuan to resume, especially if the U.S. continues to raise interest rates, which would likely trigger fresh capital outflows from emerging economies such as China and test its enhanced capital controls.

“What was presented as a gradual depreciation of the yuan last year was in reality a significant 6% weakening of the currency versus the dollar as China’s domestic woes mounted. A collapse of the crawling peg could lead to yuan depreciation that is three times as large.”
• China’s Reserves Approach Breaking Point As Another Devaluation Looms (BBG)
In his first few weeks in office, President Donald Trump has ordered the U.S. to withdraw from the Trans-Pacific Partnership and confirmed his intention to renegotiate the North American Free Trade Agreement. The consensus is that it won’t be long before he turns his focus to China, which he calls a currency manipulator. China can weather such criticism, for now. But if Trump’s threats of trade sanctions and 45% tariffs become real, the economic impact for the world’s second-biggest economy would be meaningful and could upend financial markets, potentially leading to a global recession. With economic growth already slowing and capital fleeing the nation, China’s $11 trillion economy is operating from a position of weakness.
Here’s how it plays out: As the world’s dominant reserve currency, the dollar has no peer. IMF data show that the greenback accounts for 63.3% of global foreign-exchange reserves, with the euro next at 20.3%, followed by the British pound and Japanese yen, both at 4.5%. That means that in times of crisis, the dollar benefits from global investors seeking a haven, even if the strife and the the uncertainty emanates from the U.S. It’s possible that a trade war would drive flows into the dollar, putting upward pressure on the currency at the expense of other exchange rates. That would be on top of the natural demand for the greenback created by the anticipation of significant fiscal stimulus floated by the Trump administration and a faster pace of interest-rate increases by the Federal Reserve.
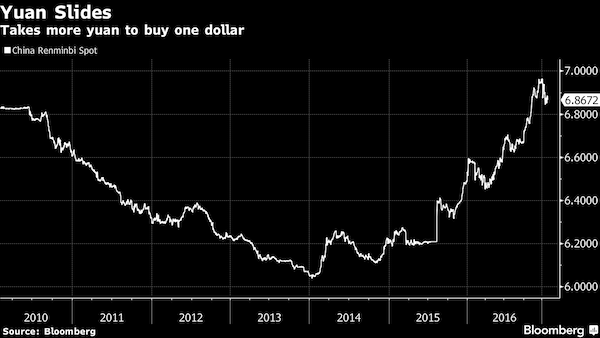
In terms of China, it’s important to remember that the yuan’s external value is managed by authorities in a way that isn’t compatible with a sharp appreciation pressure of the dollar vis-à-vis all other currencies. The currency is managed to achieve a stable, effective, trade-weighted exchange rate and to foster a gently crawling peg relative to the dollar. That peg would be threatened if a trade war weakened China’s economy at a faster rate than forecast. What was presented as a gradual depreciation of the yuan last year was in reality a significant 6% weakening of the currency versus the dollar as China’s domestic woes mounted. A collapse of the crawling peg could lead to yuan depreciation that is three times as large.

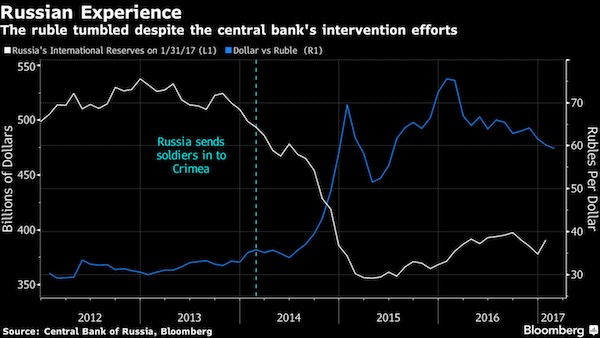
The ruble lost 50% vs the USD. A similar path for the yuan would be catastrophic.
• Russia Shows Why China Should Just Stop Burning Up Its Reserves (BBG)
China has wiped out about a quarter of the world’s heftiest foreign-currency stockpile over the past 18 months in its quest to keep the yuan stable. According to Commerzbank, such intervention is futile. Data Tuesday showed China’s foreign reserves slipped below $3 trillion in January, the first time they’ve breached that psychologically potent level in almost six years. Yet the experiences of some fellow BRICs show that drawing down the stockpile will probably have little effect on the currency’s long-term fate, Hao Zhou, Commerzbank’s Singapore-based senior emerging-markets economist, wrote in a research note late Tuesday.
While efforts by Russia and Brazil in recent years might have cushioned the blow of currency declines, they couldn’t change the market’s dynamics. In Russia’s case, a collapse in oil prices and the imposition of economic sanctions over the Crimea crisis proved more powerful drivers than the sale of a third of the country’s foreign-currency hoard between April 2013 and March 2015. The ruble fell more than 50% versus the dollar in the period.

Get out while you can.
• Cracks Are Appearing In Australia’s Trillion-Dollar Property Debt Pile (BBG)
The Reserve Bank of Australia frequently seeks feedback on the health of the economy. It might want to call the debt counsellors soon. Homeowners, consumers and property investors around Australia are making more calls to financial helplines as three warning signs back up the spike in demand: mortgage arrears are creeping up, lenders’ bad debt provisions have increased and personal insolvencies are near an all-time high. “It’s steadily out of control – I don’t know of too many financial counselling services where demand doesn’t exceed supply,” said Fiona Guthrie, chief executive officer of Financial Counselling Australia, who says the biggest increase in calls is from people suffering mortgage stress. “There are more people who have got mortgages that they can’t afford to pay.”
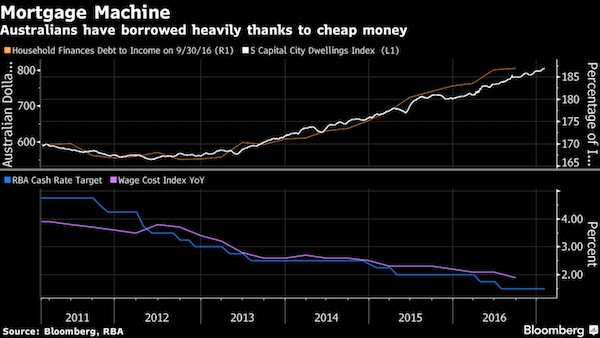
Australia’s households are among the world’s most-indebted after bingeing on more than $1 trillion of mortgages amid a housing boom that’s fizzled out in parts of the country, but still roaring in Sydney and Melbourne. While most are capably servicing their debts, a worsening of credit metrics has seen executives and analysts take a more cautious tone. It’s also a key factor in the central bank’s rate decisions this year, as RBA governor Philip Lowe places financial stability at the forefront of monetary policy. The concerns are understandable. Australians’ private debt has soared to 187% of their income, from about 70% in the early 1990s, encouraged by low interest rates. In a November speech, Lowe said that while most households are managing these levels of debt, many feel they are closer to their borrowing capacity than they once were.

Odd that this reaches the press.
• Putin Orders Russian Air Force To Prepare For ‘Time Of War’ (Ind.)
Russia’s air force has been ordered to prepare for a “time of war”. President Vladimir Putin has ordered a “snap check” of the country’s armed forces, accoording to defense minister Sergey Shoigu. As well as checking whether agencies and troops are ready for battle, the same order will ensure that systems are ready to fight, according to state news agency TASS. Those preparations have already begun, according to Russian ministers. “In accordance with the decision by the Armed Forces Supreme Commander, a snap check of the Aerospace Forces began to evaluate readiness of the control agencies and troops to carry out combat training tasks,” he said, according to TASS.
“Special attention should be paid to combat alert, deployment of air defense systems for a time of war and air groupings’ readiness to repel the aggression,” Shoigu added. The preparations come amid increasing concern about tensions between Russia and many of the world’s largest superpowers. Donald Trump has both condemned Russia’s military campaigns and been criticised for being too close to the country’s leaders, and Russia itself is standing in an increasingly tense relationship with some Nato countries. The country has been increasing movement of its military including the launch of the biggest Arctic military push since the fall of the Soviet Union, last month. It has also revealed plans to expand its military over 2017, including a huge boost in the number of tanks, armoured vehicles and aircraft controlled by the company.

Really? Trump is willing to strongarm veterans and Native Americans? Bad PR.
• Controversial Dakota Pipeline To Go Ahead After Army Approval (R.)
The U.S. Army will grant the final permit for the controversial Dakota Access oil pipeline after an order from President Donald Trump to expedite the project despite opposition from Native American tribes and climate activists. In a court filing on Tuesday, the Army said that it would allow the final section of the line to tunnel under North Dakota’s Lake Oahe, part of the Missouri River system. This could enable the $3.8 billion pipeline to begin operation as soon as June. Energy Transfer Partners is building the 1,170-mile (1,885 km) line to help move crude from the shale oilfields of North Dakota to Illinois en route to the Gulf of Mexico, where many U.S. refineries are located. Protests against the project last year drew drew thousands of people to the North Dakota plains including Native American tribes and environmental activists, and protest camps sprung up.
The movement attracted high-profile political and celebrity supporters. The permit was the last bureaucratic hurdle to the pipeline’s completion, and Tuesday’s decision drew praise from supporters of the project and outrage from activists, including promises of a legal challenge from the Standing Rock Sioux tribe. “It’s great to see this new administration following through on their promises and letting projects go forward to the benefit of American consumers and workers,” said John Stoody, spokesman for the Association of Oil Pipe Lines. The Standing Rock Sioux, which contends the pipeline would desecrate sacred sites and potentially pollute its water source, vowed to shut pipeline operations down if construction is completed, without elaborating how it would do so.
The tribe called on its supporters to protest in Washington on March 10 rather than return to North Dakota. “As Native peoples, we have been knocked down again, but we will get back up,” the tribe said in the statement. “We will rise above the greed and corruption that has plagued our peoples since first contact. We call on the Native Nations of the United States to stand together, unite and fight back.” Less than two weeks after Trump ordered a review of the permit request, the Army said in a filing in District Court in Washington D.C. it would cancel that study. The final permit, known as an easement, could come in as little as a day, according to the filing. There was no need for the environmental study as there was already enough information on the potential impact of the pipeline to grant the permit, Robert Speer, acting secretary of the U.S. Army, said in a statement.

The case is not that hard to make. You just need to erase the ideological resistance.
• Why Should A Libertarian Take Universal Basic Income Seriously? (Dolan)
In a recent post on EconLog, Bryan Caplan writes, “I’m baffled that anyone with libertarian sympathies takes the UBI [universal basic income] seriously.” I love a challenge. Let me try to un-baffle you, Bryan, and the many others who might be as puzzled as you are. Here are three kinds of libertarians who might take a UBI very seriously indeed. Philosophical issues aside, what galls many libertarians most about government is the failure of many policies to produce their intended results. Poverty policy is Exhibit A. By some calculations, the government already spends enough on poverty programs to raise all low-income families to the official poverty level, even though the poverty rate barely budges from year to year. Wouldn’t it be better to spend that money in a way that helps poor people more effectively?
A UBI would help by ending the way benefit reductions and “welfare cliffs” in current programs undermine work incentives. When you add together the effects of SNAP, TANF, CHIP, EITC and the rest of the alphabet soup, and account for work-related expenses like transportation and child care, a worker from a poor household can end up taking home nothing, even from a full-time job. A UBI has no benefit reductions. You get it whether you work or not, so you keep every added dollar you earn (income and payroll taxes excepted, and these are low for the poor). But, wait, you might say. Why would I work at all if you gave me a UBI? That might be a problem if you got your UBI on top of existing programs, but if it replaced those programs, work incentives would be strengthened, not weakened.
In which situation would you be more likely to take a job: one where you get $800 a month as a UBI plus a chance to earn another $800 from a job, all of which you can keep, or one where your get $800 a month in food stamps and housing vouchers, and anything extra you earn is taken away in benefit reductions? Or, you might say, a UBI might be fine for the poor, but wouldn’t it be unaffordable to give it to the middle class and the rich as well? Yes, if you added it on top of all the middle-class welfare and tax loopholes for the rich that we have now. No, if the UBI replaced existing tax preferences and other programs that we now lavish on middle- and upper-income households. Done properly, a UBI would streamline the entire system of federal taxes and transfers without any aggregate impact on the federal budget.









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle February 8 2017