
Edward S. Curtis Crow Scout in Winter 1908

And I have a bridge in Brooklyn.
• The US Economy Suddenly Looks Like It’s Unstoppable (CNBC)
In the face of persistent fears that the world could be facing a trade war and a synchronized slowdown, the U.S. economy enters June with a good deal of momentum. Friday’s data provided convincing evidence that domestic growth remains intact even if other developed economies are slowing. A better-than-expected nonfarm payrolls report coupled with a convincing uptick in manufacturing and construction activity showed that the second half approaches with a tail wind blowing. “The fundamentals all look very solid right now,” said Gus Faucher, chief economist at PNC. “You’ve got job growth and wage gains that are supporting consumer spending, and tax cuts as well. There’s a little bit of a drag from higher energy prices, but the positives far outweigh that. Business incentives are in good shape.”
The day started off with the payrolls report showing a gain of 223,000 in May, well above market expectations of 188,000, and the unemployment rate hitting an 18-year low of 3.8%. Then, the ISM manufacturing index registered a 58.7 reading — representing the%age of businesses that report expanding conditions — that also topped Wall Street estimates. Finally, the construction spending report showed a monthly gain of 1.8%, a full point higher than expectations. Put together, the data helped fuel expectations that first-quarter growth of 2.2% will be the low-water point of 2018. “May’s rebound in jobs together with yesterday’s report of solid income growth and the rise in consumer confidence points to the economy functioning very well,” the National Retail Federation’s chief economist, Jack Kleinhenz, said in a statement.
“Solid fundamentals in the job market are encouraging for retail spending, as employment gains generate additional income for consumers and consequently increase spending.” The most recent slate of widely followed barometers could see economists ratchet up growth expectations. Already, the Atlanta Fed’s GDPNow tracker sees the second quarter rising by 4.8%. While the measure also was strongly optimistic on the first quarter as well, at one point estimating 5.4% growth, other gauges are positive as well. CNBC’s Rapid Update, for instance, puts the April-to-June period at 3.6%.

The unemployment rate is meaningless. Is that why it keeps being reported?
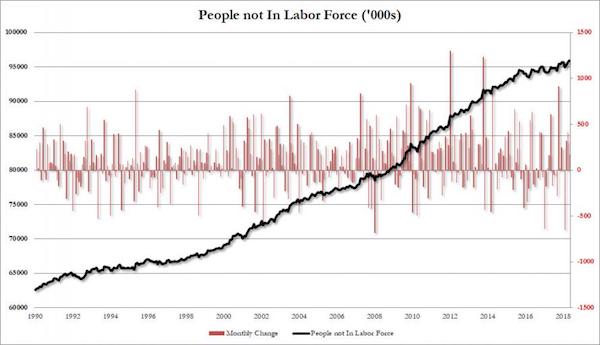
• Record 95.9 Million Americans Are No Longer In The Labor Force (ZH)
In what was otherwise a solid jobs report – one which Donald Trump may or may not have leaked in advance – in which the establishment survey reported that a higher than expected 223K jobs were added at a time when numbers below 200K are expected for an economy that is allegedly without slack, the biggest surprise was not in the Establishment survey, but the household, where the unemployment rate tumbled once more, sliding to a new 18 year low of 3.8%, even as the participation rate declined once again, as a result of a stagnant labor force, which was virtually unchanged (161.527MM in April to 161.539MM in May, even as the total civilian non-inst population rose by 182K to 257.454LMM).
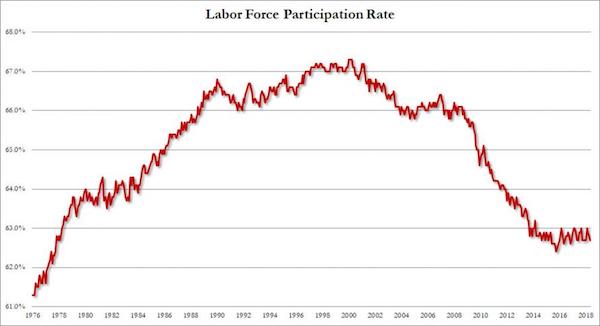
What was perhaps more interesting, however, is that for all the talk that the slack in the labor force is set to decline, precisely the opposite is taking place, because in May, the number of people not in the labor force increased by another 170K, rising to 95.915 million, a new all time high. Adding to this the 6.1 million currently unemployed Americans, there are 102 million Americans who are either unemployed or out of the labor force (and it is also worth noting that of those employed 26.9 million are part-time workers). In other words, contrary to prevailing economist groupthink, there is a lot of slack in the economy, and if as the latest Beige Book revealed, employers are now hiring drug addicts and felons to make up for the shortage of qualified candidates, a long time will pass before wages see significant gains.

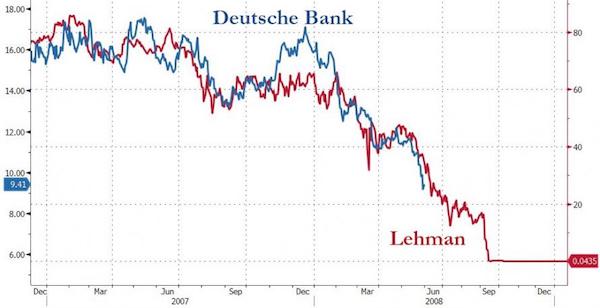
Deutsche is dangerous.
• The Pause That Refreshes (Roberts)
As long as interest rates remain low and negative in some cases, debt can continue to be accumulated even with weaker rates of economic growth. More importantly, as long as rates remain low, the banking system can continue to play the “hide-the-debt game” through derivatives, swaps and a variety of other means. But rates are rising, and sharply, on the shorter-end of the curve. Historically, sharply rising rates have been a catalyst for a debt related crisis. As long as everything remains within the expected ranges, the complicated “math” behind trillions of dollars worth of financial instruments function properly. It is when those boundaries are broken that things “go wrong” and quickly so.
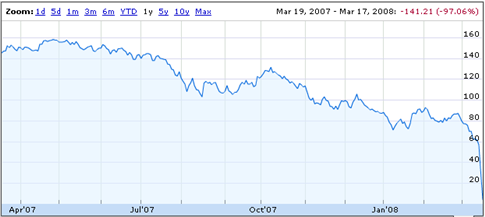
People have forgotten that in 2008 a major U.S. financial firm crashed as its derivative based exposure “blew up.” No, I am not talking about Lehman Brothers, the poster-child of the financial crisis, I am talking about Bear Stearns. In just 365-days, Bear Stearns stock went from $159 to $2, with about half of the loss occurring within a few weeks. Bear Stearns was the warning shot for the financial markets in early 2008 that no one heeded. Within a couple of months, the markets dismissed Bear Stearns as a “non-event” and rallied to a higher level than prior to the event, and almost back to highs for the year. Remember, there was “nothing to worry about” at the time, even though the Fed was increasing interest rates, as the “Goldilocks economy” could handle tighter monetary policy.
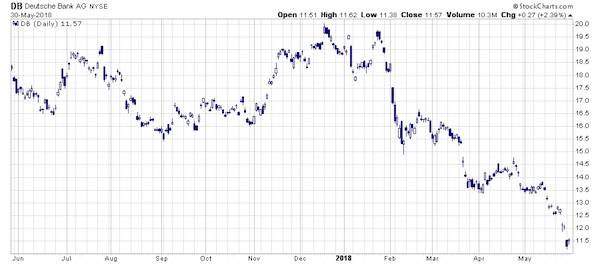
Sure, housing had been slowing down, mortgage delinquencies were rising, along with credit card defaults, but there wasn’t much concern. Today, we are seeing similar signs.Interest rates are rising, along with delinquencies, defaults, and a slowing housing market. But no one is concerned as the “Goldilocks economy” can clearly offset these mild risks. And no one is paying attention to, what I believe to be, one of the biggest risks to the global financial markets – Deutsche Bank.

Globalization in reverse.
• EU Joins Global Battle Against Trump Tariff Onslaught (AFP)
The EU on Friday launched its first counteroffensive against Washington’s punishing steel and aluminum tariffs while the US began meetings in Canada with outraged finance ministers from its top trading partners. Meanwhile in Washington, US President Donald Trump floated the possibility of scrapping the 24-year-old North American Free Trade Agreement in favor of separate bilateral deals with Canada and Mexico. And in another leg of Trump’s multi-front trade offensive, Commerce Secretary Wilbur Ross arrived in Beijing to continue fraught talks with Chinese officials. Trump has vowed to press ahead with tariffs on as much as $50 billion in imports from China.
Brussels and Ottawa on Friday filed legal challenges at the World Trade Organization against Washington’s decision. The EU, Canada and Mexico also threatened stiff retaliatory tariffs as they pushed back against Trump’s moves. Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau said Friday he was dumbfounded by Washington’s national security basis for the tariffs, given that US and Canadian troops had fought together in World War II, Afghanistan and elsewhere. “This is insulting to them,” he told NBC News. British Prime Minister Theresa May said she was “deeply disappointed” and reiterated a call for Britain and the EU to be “permanently exempted” from the “unjustified” metals tariffs.
At the Group of Seven ministerial meeting in Canada, US Treasury Secretary Steven Mnuchin faced stern reactions from his counterparts, who accused Trump of jeopardizing the world economy with steps that would prove job killers for all concerned. “The French, British and Germans held firm,” French Finance Minister Bruno Le Maire told reporters. “Everyone expressed their complete incomprehension of the American decisions and everyone said it was up to the Americans to take the next step since they were the ones who imposed the tariffs.”

This is like the owner of a sports team publicly declaring the coach has their full support. Bad sign.
• Eurozone Not Facing New Debt Crisis – Juncker (R.)
There is no threat of a new sovereign debt crisis in the euro zone despite an anti-establishment coalition government taking power in Italy, European Commission President Jean-Claude Juncker said in remarks published on Saturday. Asked by the RND network of German newspapers if the single currency bloc faced a new crisis, Juncker said: “No. The reactions of the financial markets are irrational. People should not draw political conclusions from every fluctuation in the stock market. Investors have been wrong on so many occasions before.” A governing coalition comprising two parties hostile to the euro was installed in Italy on Friday, calming markets spooked by the possibility of a new election that might have become a referendum on quitting the single currency. “I am certain the Italians have a keen sense of what is good for their country,” Juncker said. “They will sort it out.”

It will just take one little spark.
• Three Critical Lessons From Europe’s Recent Mini-Meltdown (Black)
1) On the day that the finance minster was rejected, financial markets worldwide tanked. Italy’s stock market plunged 5%, which is considered a major drop. But curiously, the stock market in the US fell as well, with the Dow Jones Industrial Average shedding 400 points. Even markets in China and Japan had significant drops as a result of the Italy turmoil. Now, it’s easy to see why Italy’s markets fell. And even the rest of Europe. But the entire world? Granted, a lot of people made a really big deal out of this event, concluding that it signals the end of the euro.. or Europe itself… or some other such drama. Sure, maybe. But it’s almost impossible to foretell a trend as significant as ‘the end of the euro’ based on a single event.
At face value, the rejection of a cabinet minister in Italy should have almost -zero- relevance on economies as large and diversified as the US, China, and Japan. To me, this is another sign that we’re near the peak of the bubble… and possibly already past it. Markets are so stretched, and investors are on such pins and needles, that even a minor, insignificant event induces panic. And it makes me wonder: if financial markets are so tightly wound that something so irrelevant can cause such an enormous impact, how big will the plunge be when something serious happens?
2) It wasn’t just stocks either. Bond markets were also keenly impacted. Bear in mind that stocks are volatile by nature; prices move much more wildly than other asset classes. But bonds, on the other hand, are supposed to be safe, stable, boring assets. Especially government bonds in highly developed nations. In Italy the carnage was obviously the worst. Investors dumped the 2-year Italian government bond, and yields (which move opposite to prices) surged from 0.9% to 2.4% in a matter of hours. Simply put, that’s not supposed to happen. And it hadn’t happened in at least three decades. Again, though, even in the United States, yields on the US 10-year note dropped 16 basis points overnight, from 2.93% to 2.77% (which means US bond prices increased).
That’s considered MAJOR volatility for US government bonds. To put it in context, the only day over the past few YEARS that saw 10-year yields move more than that was the day after Donald Trump won the US Presidential Election in 2016. So it was a pretty big deal. Again, this leads me to wonder: if safe, stable assets like government bonds can react so violently from such an insignificant event, how volatile will riskier assets be when there’s an actual crisis? Just imagine what’s going to happen to all the garbage assets out there (like unprofitable, heavily indebted businesses) when a real downturn kicks in.

No, they supported setting up a fund for countries in trouble.
• EU Lawmakers From Italy’s Coalition Parties Seek Funds To Quit Euro (R.)
European Union lawmakers from the two parties forming Italy’s new government coalition backed this week a rejected proposal to set up EU funds to help countries quit the euro, a sign of the Italian leadership’s ambivalent position on the common currency. Their vote came as the anti-establishment 5-Star Movement and far-right League were finalising a deal to form an executive in Rome, under pledges that leaving the euro was not in their government programme. The government was sworn in on Friday. An earlier attempt to form a government foundered after the parties proposed as economy minister an economist who had devised a plan for Italy’s departure from the euro zone, prompting his rejection by the head of state.
Despite the declared intentions to stay in the euro, all six EU lawmakers from the League and all but one of the 14 5-Star Members of the European Parliament voted on Wednesday for a document that called for the establishment of programmes of financial support “for member states that plan to negotiate their exit from the euro.” The document voted on by their EU lawmakers called for compensation for “the social and economic damages caused by the euro zone membership.” The document was an amendment to a European Parliament resolution on the EU budget for the 2021-2027 period. The proposal, advanced by three leftist MEPs, was backed by 90 lawmakers but was rejected by a majority of the 750 MEPs.

Sure this is very recognizable across the globe.
• Canada Auditor General To Public Service: Stop Ignoring My Reports (CBC)
Canada’s auditor general says he’s getting tired of filing annual reports recommending reforms to the way the government does business — only to see those recommendations disappear down the memory hole afterward. Michael Ferguson released his spring audits on Tuesday. They included scathing criticisms of the government’s performance on the Phoenix pay system, Indigenous services and military justice. Many of these problems have been highlighted in Ferguson’s reports in the past. And that, he told CBC News, is the problem. “We always get the department agreeing to our recommendation but then somehow we come back five years later, 10 years later and we find the same problems,” he told host Chris Hall on CBC Radio’s The House on Wednesday.
“It almost is like the departments are trying to make our recommendations and our reports go away by saying they agree with our recommendations.” His work has made one thing clear, he said: the federal government has a culture problem that makes meaningful change difficult. “They need to do things to make the results better.” Part of the problem stems from political pressure on the public service, said Ferguson. Politicians tend to think from election to election, he said, which can undermine public servants’ efforts to bring in a longer-term plan. “It seems like the political side of things ends up having more weight in the conversation.” In Parliament, he said — and particularly with respect to Indigenous Services — progress tends to be measured on the basis of how much money the government spends on a particular policy file, and not on measurable outcomes.

“.. it is clear there were strong interests to see Greece’s public wealth turned over into other peoples’ hands..”
• Greece’s Busiest Port Reveals the Perils of Privatization (Nation)
In 2015, as a condition of the $100 billion European Union bailout that followed the 2008 financial crisis, the Greek government agreed to privatize a number of state-held assets including the Piraeus Port Authority, which manages the port’s container and passenger terminals. The Greek state sold a majority stake for $330 million to COSCO. For the Chinese company, the purchase had a clear financial logic. About 80 percent of China’s imports and exports to and from Europe are transported by sea, and by avoiding the need to sail to busy Northern European ports like Rotterdam or Hamburg, COSCO could offload containers in Piraeus, reducing the time it takes cargo to get to Europe by nearly a week. Plus, by owning the port authority, COSCO could help determine how much its own ships would have to pay itself in port fees.
As part of the deal, COSCO pledged to participate in financing $410 million worth of investment in the port, including a repair of port equipment and the dredging of Piraeus’s central port. Supporters of privatization argue these improvements signal a coming maritime renaissance at Piraeus—already the busiest port in the eastern Mediterranean. Nektarios Demenopolous, the deputy manager for investor relations at Piraeus Port Authority, told me, “There are 300 million euros [$350 million] of investment to come in the next five years, followed by another 50 million. Privatization has made the port much more dynamic and will reboot activities at the port like ship repair that have been in recession. It will be remembered as a success story.”
But a “success story” for whom? The dockworkers of Piraeus say they and their families have seen little of the alleged gains brought by COSCO. As Piraeus Port Authority boasts of widening profit margins and increasing maritime traffic, wages for dockworkers haven’t budged since they were slashed from 1500 euros ($1,750) per month to 600 euros after the financial crisis. Beyond that, COSCO now hires few dockworkers as full-time employees, and tends to enlist unskilled laborers for complex container unloading. COSCO also primarily remunerates people on an ad hoc basis as subcontractors, leaving dockworkers and their families entirely dependent on the ebb and flow of traffic into Piraeus. It also means their traditional retirement benefits have disappeared.
The long list of Greek public assets in the privatization pipeline includes Athens International Airport, the oil refiner Hellenic Petroleum, and the electric-grid operator. To date, some roughly $5 billion in Greek state assets, including the Port of Piraeus and Greece’s regional airport network, have been sold, and it is expected that the Greek government will sell nearly $55 billion worth of state assets within the next decade. There is no conclusive evidence that privatized state assets are more efficiently managed than their state-owned predecessors, but privatization is undoubtedly an effective means for a cash-strapped government to raise funds when its creditors are getting impatient. “Piraeus was always a profitable port. However, it is clear there were strong interests to see Greece’s public wealth turned over into other peoples’ hands,” said Giorgos Gogos, head of the Piraeus dockworkers’ union.

How corrupt is Juncker?
• EU Scraps Plans To Tackle Antibiotics Abuse (G.)
The EU has scrapped plans for a clampdown on pharmaceutical pollution that contributes to the spread of deadly superbugs. Plans to monitor farm and pharmaceutical companies, to add environmental standards to EU medical product rules and to oblige environmental risk assessments for drugs used by humans have all been discarded, leaked documents seen by the Guardian reveal. An estimated 700,000 people die every year from antimicrobial resistance, partly due to drug-resistant bacteria created by the overuse, misuse and dumping of antibiotics. The UK’s chief medical officer, Dame Sally Davies, has warned that failing to act could lead to a post-antibiotic apocalypse, spelling “the end of modern medicine” as routine infections defy effective treatment.
Some studies predict that antimicrobial resistance could cost $100tn (£75tn) between now and 2050, with the annual death toll reaching 10 million over that period. An EU strategy for pharmaceuticals in the environment was supposed to propose ways to avert the threat, but leaked material shows that a raft of ideas contained in an early draft have since been diluted or deleted. Proposals that have fallen by the wayside include an EU push to have environmental criteria for antibiotic use included in international agreements as “good manufacturing practice requirements”. This would have allowed EU inspectors to visit factories in Asia or Africa, sanctioning them were evidence of pharmaceutical pollution found.
[..] The pharmaceutical industry spent nearly €40m on lobbying EU institutions in 2015, according to voluntary declarations, and enjoys infamously easy access to officials. Public records show that the European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industries and Associations had more than 50 meetings with the Juncker commission in its first four and a half months of office. In the same period, GlaxoSmithKline had 15 meetings with the commission, Novartis had eight engagements, Sanofi and Johnson & Johnson had six sessions apiece, while Pfizer and Eli Lilly both met with EU officials five times each.









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle June 2 2018