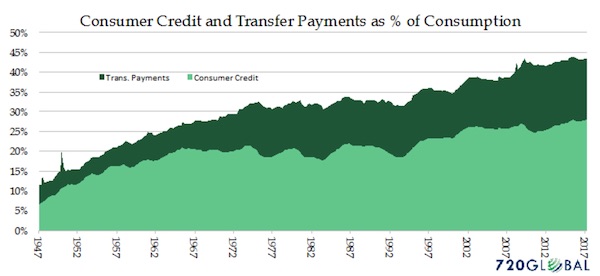
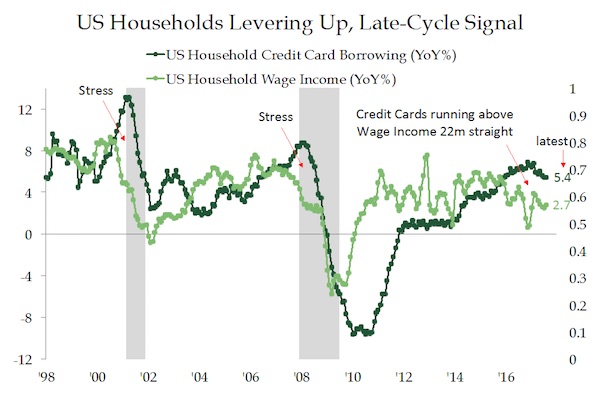
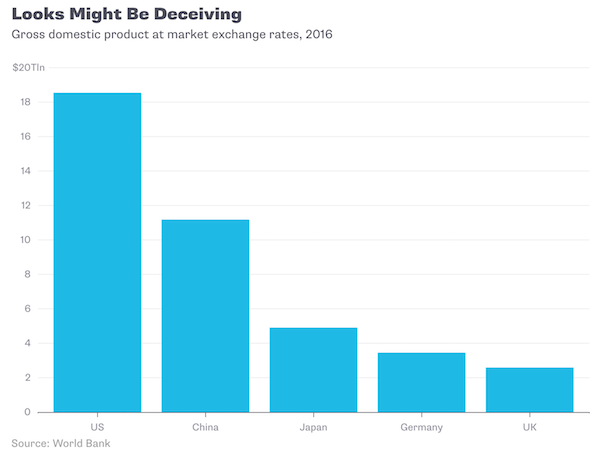
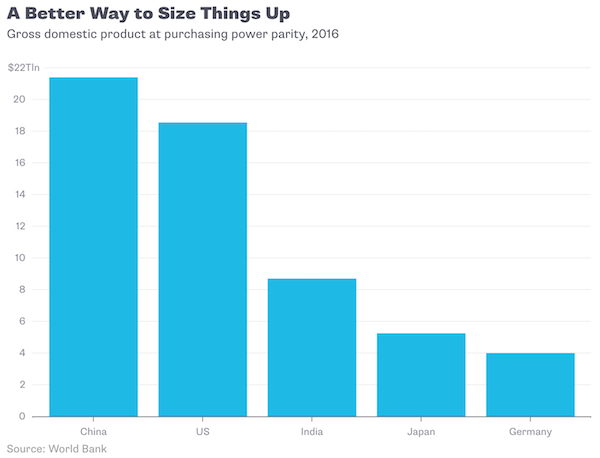
John French Sloan East Entrance, City Hall, Philadelphia 1901

Don’t think it will happen without an overall economic collapse.
• Carbon Bubble To Destroy Trillions Of Dollars Of Global Wealth (Ind.)
Trillions of dollars of fossil fuel wealth will be wiped out at some point over the next 17 years even if governments fail to impose binding carbon emissions limits on industry to curb global warming, according to a major new study. Environmentalists and policymakers have long warned of the threat of a “carbon bubble” and “stranded assets” for listed energy companies, based on the possibility they will never be able to realise the value of their vast stores of oil, gas and coal if politicians actually deliver on their decarbonisation promises.
But today a group of scientists and analysts from Cambridge, Nijmegen, Macao and the Open University take that warning a step further by arguing that these assets are destined to be stranded regardless of official policies to discourage the use of fossil fuels because clean energy technologies are now developing so rapidly that those polluting assets will be worthless in any case. “Our analysis suggests that, contrary to investor expectations, the stranding of fossil fuels assets may happen even without new climate policies. This suggests a carbon bubble is forming and it is likely to burst,” said Professor Jorge Viñuales from Cambridge University. If policymakers did deliver on the decarbonisation programmes, the loss for investors would be even more rapid.
The research is at odds with work from the International Energy Agency, which projects steady price rises for fossil fuels until 2040. And Donald Trump’s decision last year to pull the United States out of the Paris Agreement on climate change has also done nothing to persuade most investors to take the stranded assets warning seriously. But the researchers’ new “simulation-based, energy-economy-carbon-cycle climate” model suggests investing in fossil fuel firms today is likely to prove a disastrous bet, suggesting that between $1 trillion and $4 trillion could be wiped off the value of global fossil fuel assets by 2035.

Steel and concrete prices better not rise.
• The Effects Of Trump’s Steel Tariffs On Red State Energy (F.)
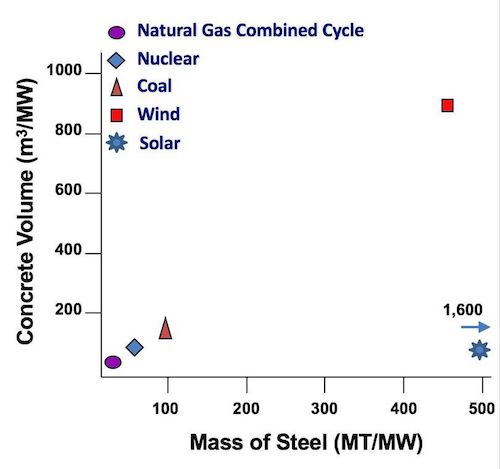
Electricity production is heavily dependent on materials like steel, concrete, copper and aluminum, for both producing electricity and moving it around to where it’s needed (see figure). Solar and Wind energy take more steel than any other energy source. Natural gas and nuclear take the least. Solar needs 1,600 tons of steel per MW, wind energy needs over 400 tons of steel, while gas and nuclear need only 4 and 40 tons, respectively. Wind and solar also require ten times more transmission, also heavily steel-intensive, since they are usually sited far away from where the energy is used.
The average high-voltage transmission tower includes about 30 tons of steel and transmission wire contains about a ton of steel per mile. Going from our biggest solar array, located in the Mohave Desert, to Los Angeles is almost 300 miles, requiring on the order of 10,000 tons of steel depending on specific design. While we tend to think of renewables as associated with Blue States, they are actually growing faster in Red States. Four of the five states with the most installed wind energy are Texas (20,321 MW), Iowa (6,917 MW), Oklahoma (6,645 MW) and Kansas (4,451 MW). The only Blue State in the top five is California (5,662 MW).

Prop up your stock some more.
• US Firms To Pour $2.5 Trillion Into Buybacks, Dividends, M&A This Year (CNBC)
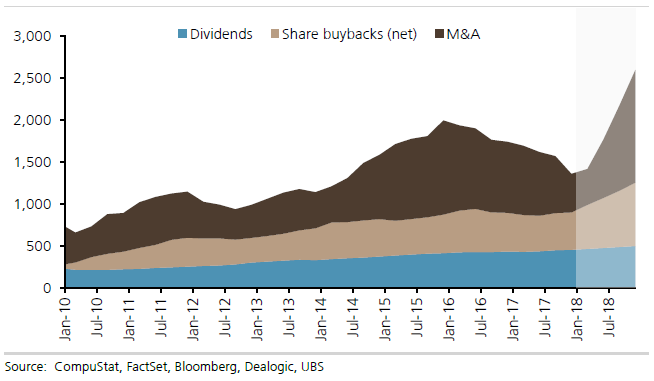
Money is pouring into the U.S. economy and in turn helping provide support for the otherwise struggling stock market. If current conditions persist, corporations are likely this year to inject more than $2.5 trillion into what UBS strategists term “flow” — the combination of share buybacks, dividends, and mergers and acquisitions activity. The development comes as companies find themselves awash in cash, thanks primarily to years of stashing away profits plus the benefits of a $1.5 trillion tax break this year that slashed corporate rates and encouraged firms to bring back money idling overseas. Companies have nearly $2.5 trillion in cash parked domestically, according to the Federal Reserve, and as much as $3.5 trillion overseas, various estimates have shown.
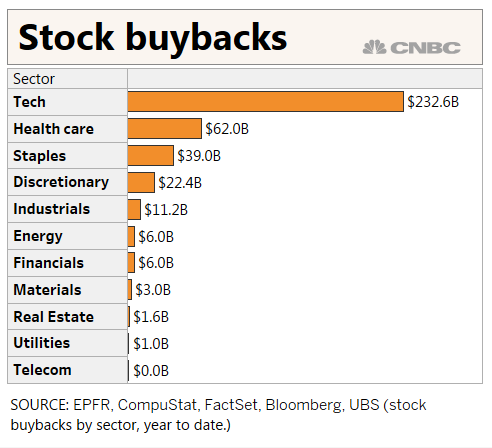
When all is said and done for 2018, UBS expects dividend issuance to top $500 billion, buybacks to range from $700 billion to $800 billion, and M&A to constitute about $1.3 trillion. If the numbers pan out, they would equate to about 10% of the S&P 500’s market cap and 12.5% of GDP. “Assuming improving growth and stable rates, we expect the positive positioning/flow backdrop to support US equities, which is important as the daily corporate flow slows from mid-June to mid-July,” UBS strategist Keith Parker said in a note. Parker pointed out that the firm has overweight positions in both tech and health care as the two sectors are leading the buyback boom.
Buybacks specifically have been on a torrid pace and are helping provide a floor to a market that for much of 2018 had looked tired and volatile after a 20% S&P 500 gain the year before. Repurchases are up 83% year to date, far ahead of the 9% gain in dividends, while M&A activity involving U.S. companies has surged 130%, according to UBS. [..] UBS estimates that the combination of buybacks, dividends and demand flows account for some 40% in performance this year. The S&P 500 has nudged 2.6% higher and the Dow industrials are just ahead of breakeven.

The Fed retreats and the Treasury issues new debt.
• India Central Banker Sees Sudden “Evaporation” Of Dollar Funding (ZH)
In an op-ed published overnight in the FT, a central banker writes that when it comes to the turmoil gripping the world’s Emerging Markets, whether it is the acute, idiosyncratic version observed in Argentina and Turkey, which according to JPM may be doomed, or the more gradual selloffs observed in places like Indonesia, Malaysia, Brazil, Mexico and India, don’t blame the Fed’s rate hike cycle. Instead blame the “double whammy” of the Fed’s shrinking balance sheet coupled with the dollar draining surge in debt issuance by the US Treasury.
That’s the message from the current Reserve Bank of India, Urjit Patel, who writes that “unlike previous turbulence, this episode cannot be attributed to the US Federal Reserve’s moves on interest rates, which have been rising steadily since December 2016 in a calibrated manner.” But does that mean that the Fed is not to blame for what increasingly looks like another budding EM crisis? Not at all: according to Patel, the dollar funding shortage “upheaval” stems from what he sees as the confluence of two significant events of which the Fed’s balance sheet reduction is one, while the second is the dramatic increase in US Treasury issuance to pay for Trump’s tax cuts; what is notable is that both events are drastically soaking up dollar liquidity.
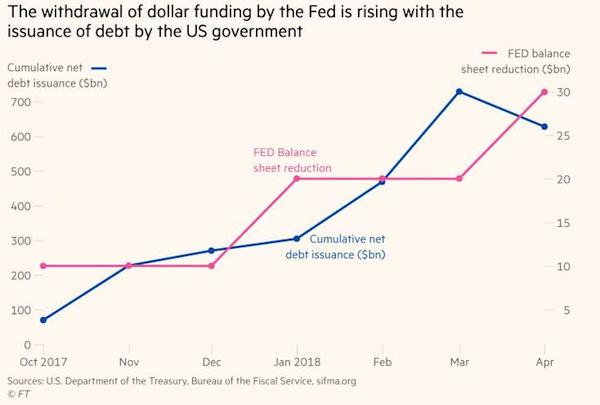
As a result, Patel blames a lack a coordination between the Fed and Treasury on the adverse flow through across global funding markets as a result of this decline in dollar liquidity, and writes that “given the rapid rise in the size of the US deficit, the Fed must respond by slowing plans to shrink its balance sheet. If it does not, Treasuries will absorb such a large share of dollar liquidity that a crisis in the rest of the dollar bond markets is inevitable.” Putting these two parallel processes – which threaten to materially impair dollar funding markets – in context, on one hand there is QT, or the gradual decline in the Fed’s balance sheet which is set to peak at a rate of $50BN/month by October, while at the same time US net Treasury issuance is set to jump to $1.2 trillion in 2018 and 2019 to cover the forecasted budget deficit of $804BN and $981BN in 2018 and 2019, respectively.
And in a curious coincidence, the withdrawal of dollar funding by the Fed in monthly terms, as it reduces its reinvestment of income received, is proceeding at roughly the same pace as that of net issuance of debt by the US government. Furthermore, both processes are open ended which means that over the next few years, the government’s net issuance will stabilize, albeit at a high level, whereas the Fed’s balance-sheet reduction will keep rising. Both are terrible news for Emerging Markets, which are in desperate need of reversing the ongoing dollar outflows; however as long as Trump continues to make America great, and funds said stimulus with excess debt issuance, emerging market turmoil is virtually guaranteed.
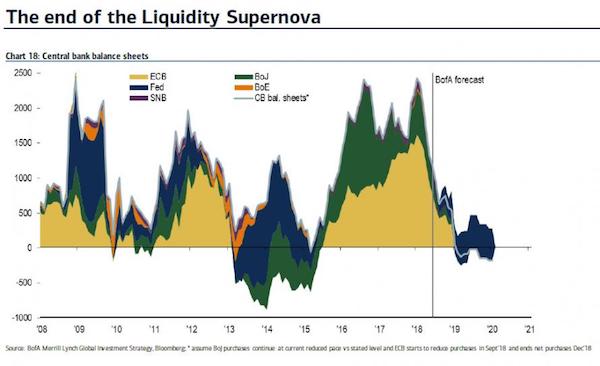

China retreats, too.
• China’s Debt Crackdown To Hurt Emerging Markets, Oil, Metals – Fitch (R.)
China’s debt crackdown is a key risk to the country’s economic growth and will have significant knock-on effects for the global economy, particularly emerging markets with high commodity dependence or close Chinese trade links, Fitch Ratings said. Beijing’s campaign to put a lid on debt could also lead to a sharp slowdown in business investment, Fitch said late on Sunday, forecasting that growth in the world’s second-biggest economy would slow to around 4.5% over the medium term. Fitch said the implications of this scenario for the global economy would be significant but not dramatic, unlike a full-scale hard landing.
One of the most significant effects would be on commodity prices, with Fitch expecting oil and metal prices to fall 5 to 10% from its baseline scenario, reflecting China’s large role as a commodity consumer. In April, a Reuters poll of 72 institutions showed economists expected China’s economic growth to slow to 6.5% this year and 6.3% next year as Beijing extends its crackdown on riskier lending practices. GDP in 2017 expanded 6.9% in real terms and 11.2% in nominal terms. Beijing’s financial crackdown, now in its third year, has slowly pushed up borrowing costs and is choking off alternative, murkier funding sources for companies such as shadow banking.
The ratio of Chinese corporate debt to GDP is already very high by international standards – at 168% in 2017 – and is expected to start rising again as nominal GDP growth declines towards 8% from the unusually high rate of more than 11% in 2017, Fitch said. If the government aims to stabilize its corporate debt ratio by 2022, Fitch said China’s nominal economic growth rate could fall by 1 percentage point a year over the medium term while business investment growth would drop 5percentage points per year.

Restructuring Target2. That should be fun.
• Italy’s Long, Hot Summer (Carmen Reinhart)
The political upheaval and social unrest fueling the current crisis in Italy should surprise no one. On the contrary, the only uncertainty was when exactly matters would come to a head. Now they have. Italy’s per capita GDP in 2018 is about 8% below its level in 2007, the year before the global financial crisis triggered the Great Recession. And the International Monetary Fund’s projections for 2023 suggest that Italy will still not have fully recovered from the cumulative output losses of the past decade. Among the 11 advanced economies that were hit by severe financial crises in 2007-2009, only Greece has suffered a deeper and more protracted economic depression.
Greece and Italy were the two economies carrying the highest debt burdens at the outset of the crisis (109% and 102% of GDP, respectively), leaving them poorly positioned to cope with major adverse shocks. Since the crisis erupted a decade ago, economic stagnation and costly banking weaknesses have propelled debt burdens higher still, despite a decade of exceptionally low interest rates. Greece has already faced more than one “credit event” and, while Italy has also had a couple of close calls, the spring of 2018 is turning out to be its most tumultuous episode yet. The summer will probably be worse, bringing Italy closer to a sovereign debt crisis. On the surface, general government debt appears to have stabilized since 2013, at around 130% of GDP. However, as I have stressed here and elsewhere, this “stability” is misleading.
General government debt is not the whole story for Italy, even setting aside the private debt loads and the recent renewed upturn in nonperforming bank loans (a daunting legacy of the financial crisis). When evaluating Italy’s sovereign risk, the central bank’s debts (Target2 balances) must be added to those of the general government. As the most recent available data (through March) show, these balances increase the ratio of public-sector debt to GDP by 26%. With many investors pulling out of Italian assets, capital flight in the more recent data is bound to show up as an even bigger Target2 hole. This debt, unlike pre-1999, pre-euro Italian debt, cannot be inflated away. In this regard, it is much like emerging markets’ dollar-denominated debts: it is either repaid or restructured.
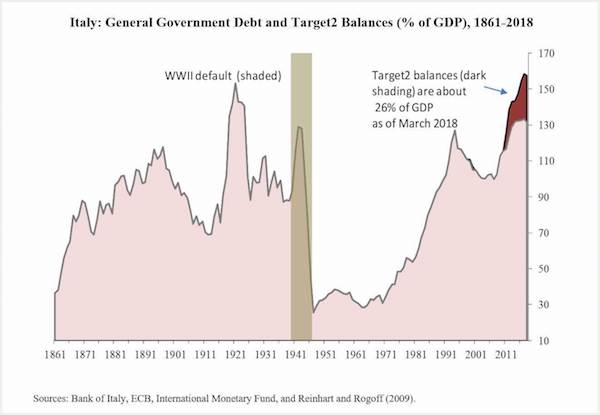

What the euro has meant for Greece and Italy: lower wages, higher unemployment and higher current account deficit.
• Why The Euro Was Created (ZH)
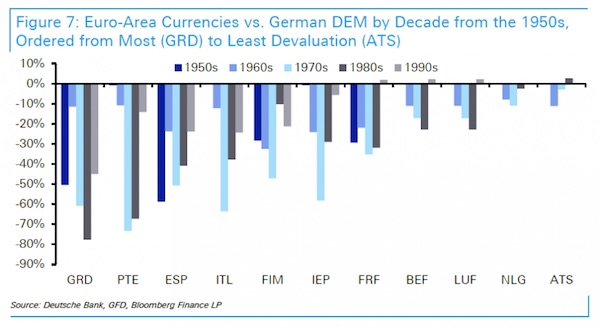
[..] we thought it would be a good idea to remind readers why the euro exists in the first place. The briefest possible answer: to make sure the Deutsche Mark does not. As presented in the chart below – which shows the performance for each of the EU12 countries against the German DEM in every decade from the 1950s to the start of the Euro in 1999 – apart from a small revaluation of core countries in the 1990s, every country devalued to Germany in every decade between the 1950s and the start of the Euro. Said otherwise, the Deutsche Mark appreciated in value against all of its European peers for 5 consecutive decades, a condition which if left unchanged, would have led to an economic and trade crisis.
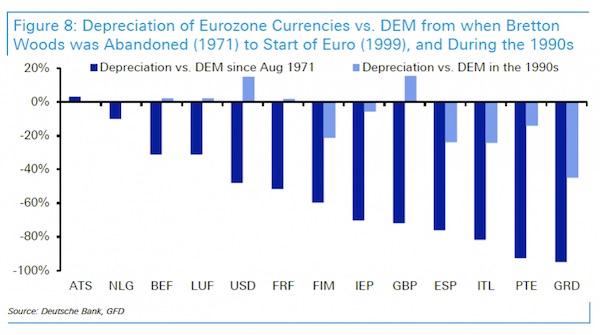
And as a bonus chart, here is same data (with the US and UK added) from the end of the Bretton Woods system in 1971 to the start of the Euro (Lira -82% devaluation to German DM) and during the 1990s (-24% devaluation) – the decade immediately leading up to the Euro start. As can be seen Italy is amongs the weakest performers relative to the German DM over these periods and showed the momentum that existed in the period leading up to the start of the Euro.
And while the fixed exchange of the Euro for European nations allowed the German export industry to go into overdrive, the lack of the possibility for an external, i.e. currency, devaluation, meant that Italy has been forced to do it all by engaging in internal devaluation, i.e., lower wages, higher unemployment and boosting its current account deficit, which however is made virtually impossible given Italy’s deteriorating demographics. This is what DB’s Jim Reid said of Italy’s potential future: Looking forward, Italy will not find it easy to grow out of its problems as its facing one of the worst set of demographics of the G20 countries. Its population size has peaked (according to the UN) and is expected to decline out to 2050. Its working age population (15-64 year olds as a proxy) is set to fall -24% over the same period and is again one of the worst placed in the G20.

“Home sales plunged 22% in May compared to a year ago..”
• Toronto’s House Price Bubble Not Fun Anymore (WS)
Housing in the Greater Toronto Area is, let’s say, retrenching. Canada’s largest housing market has seen an enormous two-decade surge in prices that culminated in utter craziness in April 2017, when the Home Price Index had skyrocketed 32% from a year earlier. But now the hangover has set in and the bubble isn’t fun anymore. Home sales plunged 22% in May compared to a year ago, to 7,834 homes, according to the Toronto Real Estate Board (TREB). It affected all types of homes, even the once red-hot condos: • Detached houses -28.5% • Semi-detached houses -29.4% • Townhouses -13.4% • Condos -15.5%.
It was particularly unpleasant at the higher end: Sales of homes costing C$1.5 million or more plummeted by 46% year-over-year to 508 homes in May 2018, according to TREB data. Compared to the April 2017 peak of 1,362 sales in that price range, sales in May collapsed by 63%. But it’s not just at the high end. At the low end too. In May, sales of homes below C$500,000 – about 68% of them were condos – fell by 36% year-over-year to 5,253 homes. The TREB publishes two types of prices – the average price and its proprietary MLS Home Price Index based on a “composite benchmark home.” Both fell in May compared to a year ago.
The average price in May for the Greater Toronto Area (GTA) fell 6.6% year-over-year to C$805,320, and is now down 12.3%, or an ear-ringing C$113,000, from the crazy peak in April 2017. There are no perfect measures of home prices in a market. Each has its own drawbacks. Average home prices can be impacted by the mix and by a few large outliers – but over the longer term, it gives a good impression of the direction. The chart below shows thepercentage change in average home prices in the GTA compared to a year earlier:
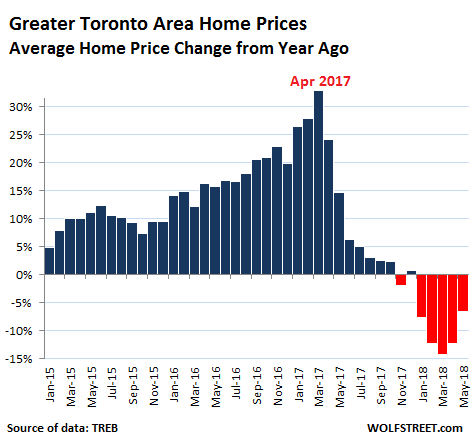

Because the boom was a bubble.
• Why Australia’s Great Banking Boom Has Ended (SMH)
It doesn’t feel all that long ago that Australian banks were the envy of the world. In March 2009, when stress-testing of US financial institutions drove the final spasm of the previous year’s credit crisis, you could have bought all the shares in Citigroup, Royal Bank of Scotland Group and Barclays with their $US8.4 trillion ($11 trillion) of gross assets for less than you’d pay for the equity of Westpac, with $US347 billion of assets. Commonwealth Bank of Australia’s share price peaked six years later just a sliver south of three times the value of its net assets, an extraordinary level in a business where price-book ratios have struggled to break above one times over the past decade.
With the current Royal Commission inquiring into practices in the country’s financial services industry and a slew of court cases, those high-flyers have come to earth with a bump. CBA on Monday agreed to pay $700 million to settle a money laundering case in which it admitted that a software update allowed about 54,000 reportable transactions to go unreported over a period of almost three years. On Friday, ANZ and local units of Deutsche Bank and Citigroup announced they were facing possible criminal cartel charges over their handling of a $2.5 billion placement of ANZ shares in 2015. Having executives hauled up before government inquiries and paying out hundreds of millions in court settlements isn’t great for headlines, but it would be a mistake to see the declines in Australia’s banking sector as purely a result of this.
When your annual net income is in the region of $10 billion, as CBA’s is, a $700 million charge is more than just a rounding error. But the 1.2 per cent jump in the company’s stock after the settlement was announced Monday is an indication that the cost is worth less to shareholders than the benefit of putting the issue firmly in the past. The greater risk to Australia’s banks lurks not in the papers of regulators and inquisitors, but on the streets of the country’s sprawling suburbs. As we’ve argued before, the most ominous indicator to watch is also a favourite one of the Reserve Bank of Australia. Rents, as measured by the Australian Bureau of Statistics, have been increasing at less than 1 per cent for nine consecutive quarters , the worst performance for the measure since the housing crash of the early 1990s.

The spirit of Steve Jobs?!
• Apple Jams Facebook’s Web-Tracking Tools (BBC)
Apple will attempt to frustrate tools used by Facebook to automatically track web users, within the next version of its iOS and Mac operating systems. “We’re shutting that down,” declared Apple’s software chief Craig Federighi, at the firm’s developers conference. He added that the web browser Safari would ask owners’ permission before allowing the social network to monitor their activity. The move is likely to add to tensions between the two companies. Apple’s chief executive Tim Cook had previously described Facebook’s practices as being an “invasion of privacy” – an opinion Facebook’s founder Mark Zuckerberg subsequently denounced as being “glib”.
At the WWDC conference – held in San Jose, California – Mr Federighi said that Facebook keeps watch over people in ways they might not be aware of. “We’ve all seen these – these like buttons, and share buttons and these comment fields. “Well it turns out these can be used to track you, whether you click on them or not.” He then pointed to an onscreen alert that asked: “Do you want to allow Facebook.com to use cookies and available data while browsing?” “You can decide to keep your information private.”
One cyber-security expert applauded the move. “Apple is making changes to the core of how the browser works – surprisingly strong changes that should enable greater privacy,” said Kevin Beaumont. “Quite often the changes companies make around privacy are small, incremental, they don’t shake the market up much. “Here Apple is allowing users to see when tracking is enabled on a website – actually being able to visually see that with a prompt is breaking new ground.”

Building on the Ring of Fire.
• A West Coast State of Mind (Jim Kunstler)
It’s only been in the last thirty years that Seattle hoisted up its tombstone cluster of several dozen office and condo towers. That’s what cities do these days to demonstrate their self-regard, and Seattle is perhaps America’s boomingest city, what with Microsoft’s and Amazon’s headquarters there — avatars of the digital economy. A megathrust earthquake there today would produce a scene that even the computer graphics artistes of Hollywood could not match for picturesque chaos. What were the city planners thinking when they signed off on those building plans?
I survived the journey through the Seattle tunnel, dogged by neurotic fantasies, and headed south to California’s Bay Area, another seismic doomer zone. For sure I am not the only casual observer who gets the doomish vibe out there on the Left Coast. Even if you are oblivious to the geology of the place, there’s plenty to suggest a sense of impossibility for business-as-usual continuing much longer. I got that end-of-an-era feeling in California traffic, specifically driving toward San Francisco on the I-80 freeway out in the suburban asteroid belt of Contra Costa County, past the sinister oil refineries of Mococo and the dormitory sprawl of Walnut Creek, Orinda, and Lafayette.
Things go on until they can’t, economist Herb Stein observed, back in the quaint old 20th century, as the USA revved up toward the final blowoff we’ve now entered. The shale oil “miracle” (so-called) has given even thoughtful adults the false impression that the California template for modern living will continue indefinitely. I’d give it less than five years now.

Snowden deserves as much support as Assange does.
• Edward Snowden: ‘The People Are Still Powerless, But Now They’re Aware’ (G.)
Edward Snowden has no regrets five years on from leaking the biggest cache of top-secret documents in history. He is wanted by the US. He is in exile in Russia. But he is satisfied with the way his revelations of mass surveillance have rocked governments, intelligence agencies and major internet companies. In a phone interview to mark the anniversary of the day the Guardian broke the story, he recalled the day his world – and that of many others around the globe – changed for good. He went to sleep in his Hong Kong hotel room and when he woke, the news that the National Security Agency had been vacuuming up the phone data of millions of Americans had been live for several hours.
Snowden knew at that moment his old life was over. “It was scary but it was liberating,” he said. “There was a sense of finality. There was no going back.” What has happened in the five years since? He is one of the most famous fugitives in the world, the subject of an Oscar-winning documentary, a Hollywood movie, and at least a dozen books. The US and UK governments, on the basis of his revelations, have faced court challenges to surveillance laws. New legislation has been passed in both countries. The internet companies, responding to a public backlash over privacy, have made encryption commonplace.
Snowden, weighing up the changes, said some privacy campaigners had expressed disappointment with how things have developed, but he did not share it. “People say nothing has changed: that there is still mass surveillance. That is not how you measure change. Look back before 2013 and look at what has happened since. Everything changed.” The most important change, he said, was public awareness. “The government and corporate sector preyed on our ignorance. But now we know. People are aware now. People are still powerless to stop it but we are trying. The revelations made the fight more even.”

Bayer-Monsanto: “It will effectively control nearly 60% of the world’s supply of proprietary seeds, 70% of the chemicals and pesticides used to grow food, and most of the world’s GM crop genetic traits..”
• Who Should Feed The World: Real People Or Faceless Multinationals? (Vidal)
Unless there is a major hiccup in the next few days, an incredibly powerful company will shortly be given a licence to dominate world farming. Following a nod from Donald Trump, powerful lobbying in Europe and a lot of political arm-twisting on several continents, the path has been cleared for Monsanto, the world’s largest seed company, to be taken over by Bayer, the second-largest pesticide group, for an estimated $66bn (£50bn). The merger has been called both a “marriage made in hell” and “an important development for food security”.
Through its many subsidiary companies and research arms, Bayer-Monsanto will have an indirect impact on every consumer and a direct one on most farmers in Britain, the EU and the US. It will effectively control nearly 60% of the world’s supply of proprietary seeds, 70% of the chemicals and pesticides used to grow food, and most of the world’s GM crop genetic traits, as well as much of the data about what farmers grow where, and the yields they get. It will be able to influence what and how most of the world’s food is grown, affecting the price and the method it is grown by. But the takeover is just the last of a trio of huge seed and pesticide company mergers.
Backed by governments, and enabled by world trade rules and intellectual property laws, Bayer-Monsanto, Dow-DuPont and ChemChina-Syngenta have been allowed to control much of the world’s supply of seeds. You might think that these mergers would alert the government, but because political parties in Britain are so inward-looking, and because most farmers in rich countries already buy their seeds from the multinationals, opposition has barely been heard.