
DPC Belle Isle Park Aquarium, Detroit 1905



Bill submitted to Greek parliament, vote due on Friday morning. Chances of a split in SYRIZA are large.
• Greek Debt Deal Reached But Targets Branded ‘Utterly Unachievable’ (Telegraph)
Greece has agreed the broad terms of a new three-year bail-out deal with its international creditors, though experts warned that severe austerity demands mean the country’s fiscal targets remained “utterly unachievable”. Technical details of the deal were finalised in the early hours of Tuesday morning, paving the way for Greece to unlock around €85bn in new loans. The measures include increases in the retirement age, opening up the energy and pharmaceutical industries and new taxes on shipping firms. More measures will follow in October. While Euclid Tsakalotos, Greece’s finance minister, said there were just “two or three” details remaining to reach an accord, Germany, the country’s biggest creditor, has called for more time to complete a deal.
Angela Merkel, the German Chancellor, is understood to have told Greek prime minister Alexis Tsipras that she would prefer to give Greece a second bridging loan rather than rush a deal through. Mr Tsipras rejected the idea, arguing that it would ride roughshod over an agreement with the eurozone that had been struck after marathon talks on July 12 and implemented by the Greek government. Under the terms of Greece’s third rescue package, the country will be required to post a primary deficit no larger than 0.25pc of GDP this year. In 2016, the country is required to post a surplus of 0.5pc of GDP rising to 1.75pc in 2017 and 3.5pc in 2018. Greece had previously proposed a primary surplus target of 1pc of GDP this year and 2pc in 2016.
Officials claimed the deal would reduce Greece’s obligations with regards to primary surpluses by 11pc of GDP over the next three years, meaning Greece would avoid austerity measures worth around €20bn over that period. The Greek parliament must now pass the reforms agreed with creditors, ahead of a meeting of eurozone finance ministers expected on Friday. However, Costas Lapavitsas, a Syriza MP and professor of economics at SOAS university in London, criticised the package, and suggested he would vote against it. “To lower the targets because the economy is in recession is one thing. To present this as lightening the recessionary burden is quite another and wrong. Nothing has been lightened because the tax rises have already been voted in,” he said.
Capital Economics described the fiscal targets as “fantasy” and “utterly unachievable”, while Raoul Ruparel, co-director at the think-tank Open Europe, said: “The new targets have not been so much negotiated as made inevitable by the recent economic destruction – claiming savings thanks to significant economic downturn has a touch of claiming success in cutting off your nose to spite your face,” he said.

Moving averages intersect.
• Dow Death Cross Is A Bearish Omen For The Stock Market (MarketWatch)
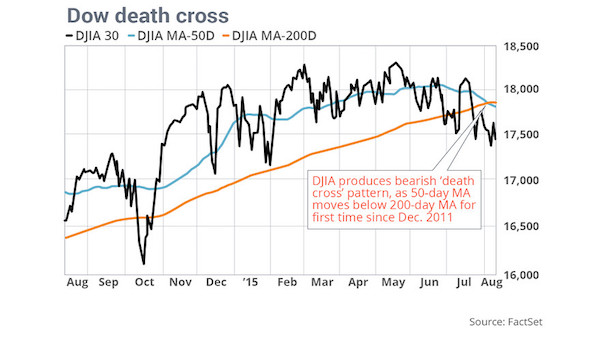
A rare “death cross” appeared Tuesday in the chart of the Dow Jones Industrial Average, suggesting the stock market may have already begun a new long-term downtrend. Although chart watchers have seen the bearish technical pattern coming for some time, it can still send a chill down bulls’ spines when it is finally confirmed. The fact that the Dow industrials’ death cross follows the appearance of one in its sister index, the Dow Jones Transportation Average, warns that this one is more than a one-off event. A death cross is said to have occurred when the 50-day simple moving average, which many use to track the short-term trend, crosses below the 200-day moving average, which is widely used to gauge the health of the longer-term trend.
For the Dow industrials, it marked the first time the 50-day moving average, which ended Tuesday at 17,806.99, was below the 200-day moving average, at 17,813.42, since Dec. 30, 2011, according to FactSet. Therefore, many technicians see the death cross as marking the spot that a shorter-term pullback morphs into a longer-term downtrend. The Dow closed down 1.2% suffer an eighth loss in the past nine sessions. It has lost 5% since its record close of 18,312.39 on May 19. Some argue that death crosses have very little predictive value, since some previous ones have appeared right around market bottoms. For example, a death cross appeared on July 7, 2010, when the Dow closed at 10,018.28. The Dow’s closing low for the year had actually been hit two sessions earlier, at 9,686.48.

One day after claiming it was a one-off.
• China Stuns Financial Markets By Devaluing Yuan For Second Day Running (Guardian)
China stunned the world’s financial markets on Wednesday by devaluing the yuan for the second day running, sparking fears that the world’s second largest economy is in worse shape than investors believed. The currency hit a four-year low on Wednesday after the People’s Bank of China set the yuan’s daily midpoint even weaker than in Tuesday’s devaluation. With the bank having said that Tuesday’s move was a “one-off depreciation”, the rapid drop in the value of China’s currency – around 4% in the last two days – dealt a blow to appetite for risky assets, and markets across the region plunged amid concerns that Beijing has embarked on a damaging currency war. Stocks, currencies and commodities came under heavy pressure as money managers feared it could ignite a currency war that would destabilise the global economy.
The Nikkei stock market index in Japan was down more than 1% while the Hang Seng in Hong Kong was down 1.64%. The Australian dollar, often seen as a proxy for the Chinese economy, fell again to a fresh six-year low of US$72.25c, having been sold off heavily on Tuesday. The US dollar, on the other hand, rose strongly again against all Asian currencies. Oil was hit, too, with Brent futures were down 31c at $48.87 per barrel at 0251 GMT. US crude was trading at $43.02 per barrel, down 6 cents from Tuesday when it marked its lowest settlement since March 2009. Key industrial and construction materials nickel, copper and aluminium also hit six-year lows. “China’s currency moves will hurt appetite for risky assets such as equities and commodities,” said Rajeev De Mello, head of Asian fixed income at Schroders in Singapore.

Well, the IMF says they like it.
• China Roils Markets Second Day as Yuan Cut by 1.6%; Bonds Rally (Bloomberg)
China’s unexpected decision on Tuesday to devalue the yuan and shift to a more market-determined rate sparked concern that the world’s second-largest economy is faltering. Vietnam widened the trading band on its currency Wednesday, underscoring the risk of competitive devaluations. Traders are seeking safety in government debt as China’s move reduces inflation expectations and eases pressure on the Federal Reserve to raise interest rates. China’s government “is focused on domestic issues rather than global implications at the moment, employing all the possible means to stabilize the economy,” said Ronald Wan at Partners Capital in Hong Kong. “A weaker yuan means weaker consumption power and Chinese demand for foreign products and commodities will weaken.”
The yuan is heading for its biggest two-day drop since 1994 and has returned to levels last seen in August 2011. There’s no economic or financial “basis” for the exchange rate to fall continuously, the PBOC said in a statement Wednesday. Traders increased bets on further movement in the currency, with options volume surging to more than triple the 5-day average for the time of day, Depository Trust & Clearing Corp. data showed. China’s central bank said Tuesday that market-makers who submit prices for the reference rate will have to consider the previous day’s closing spot rate, foreign-exchange demand and supply, as well as changes in major currency rates. Previous guidelines made no mention of those criteria.
The IMF welcomed China’s move to devalue the yuan and said it doesn’t directly impact the country’s push to win reserve-currency status. The devaluation is aimed at buying China some flexibility against continued dollar appreciation as the Fed prepares to lift rates, according to Goldman Sachs.

Beijing is way behind the ball.
• How The Dollar’s Rise Led To China’s Yuan Devaluation (MarketWatch)
The Obama administration, like many U.S. administrations before it, has long pushed China to allow the market to play a greater role in setting the exchange rate. U.S. officials have long argued that China’s currency is undervalued, giving the country’s exporters an unfair advantage over manufacturers in the U.S. and elsewhere. As recently as April, the Treasury Department praised China’s decision to allow the yuan to appreciate over recent years, but maintained the currency was still undervalued. But forex analysts note Beijing’s willingness to allow the yuan to appreciate over recent years, taking its cue from a rising U.S. currency. That’s made the yuan the second-best-performing emerging-market currency over the past 12 months, noted Jane Foley at Rabobank. China’s real effective exchange rate has been rising at the same time.
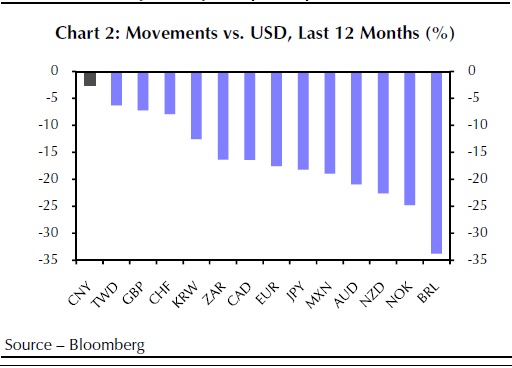
Kit Juckes, global macro strategist at Société Générale, noted that since the taper tantrum during the summer of 2013, the yuan has fallen 3% versus the dollar. But over the same time, the yen is down 23%, the euro is down 18% and other Asian currencies have dropped between 5% and 25%. Against the other so-called BRIC emerging market currencies—Brazil, Russia and India—the yuan has gained more than 50% over the last decade, Juckes said, in a note. The yuan’s valuation “has looked increasingly unsustainable as the others have seen their currencies tumble, and the 1.9% adjustment today is far too small to change that,” he said. “Via the dollar-yuan peg, China is in effective importing the Fed’s tighter policy bias at a time when its own economy is struggling,” said Rabobank’s Foley.
Much will depend on whether the devaluation is, as China says, a one-time move or if Beijing takes further action to weaken the yuan. “The renminbi will presumably come under additional downward pressure and a new gap has already opened up between the reference and market rates. But we expect the PBOC to resist this pressure—it has done over most of the past year—rather than continue to ratchet the reference rate lower,” said Julian Jessop at Capital Markets. “As well as the political sensitivities, allowing further big falls would encourage ‘one-way’ speculation and undermine the credibility of the description of today’s move as a one-time correction.” Nonetheless, China’s move is unwelcome news for its Asian neighbors, who saw their currencies knocked lower in the wake of the move. In that regard, China’s move is seen as a belated salvo in the so-called currency wars.

No doubt.
• Roach Sees Currency Wars Just Getting Worse After Yuan Decision (Bloomberg)
China’s shock move to devalue the yuan risks opening a new front in a currency war that stretches from the euro zone to Japan as nations look to energize their economies. The People’s Bank of China slashed the yuan’s fixing by a record 1.9% on Tuesday, sparking the currency’s biggest one-day loss since the official and market exchange rates were united in 1994. It triggered the steepest selloff among Asian currencies in almost seven years, led by slides in South Korea’s won and the Taiwan and Singapore dollars. The euro and the yen tumbled 18% against the greenback in the past 12 months as monetary policies diverged in the U.S., Europe and Japan.
“In a weak global economy, it will take a lot more than a 1.9% devaluation to jump-start Chinese exports,” said Stephen Roach, a senior fellow at Yale University and former Morgan Stanley chairman in Asia. “That raises the distinct possibility of a new and increasingly destabilizing skirmish in the ever-widening global currency war. The race to the bottom just became a good deal more treacherous.” China’s devaluation shook global markets just as the currency war appeared to be losing steam in Asia, with Australia and New Zealand toning down calls for weaker rates and Japan refraining from expanding stimulus this quarter.
Even with almost all major currencies losing ground against the dollar this year amid rising expectations for increased borrowing costs in the U.S., China maintained a de facto peg since March amid a push for the yuan to win reserve status at the International Monetary Fund. “They built into the market an expectation that they were keeping the currency stable,” said Ray Farris at Credit Suisse. “Then all of a sudden they blinked. Because they blinked today, markets will continue to look for similar conditions in the future. If exports are falling off a cliff, then against the background of this development, markets will expect more” depreciation, he said.

It’s like when you say you want a job done good, cheap and fast: pick two.
• China’s Devaluation And The Impossible Trinity (Beckworth)
So China devalued its currency peg almost 2% against the dollar. It happened just as I was wrapping up a twitter debate on this very possibility, a very surreal experience. Many more twitter discussions erupted after the announcement of this policy change and I got sucked into a few of them. My key takeaways from these discussions on the yuan devaluation are as follows. First, this devaluation was almost inevitable: the economic outlook in China had been worsening. The question is why? As I explained in my last post, the proximate cause is the Fed’s tightening of monetary conditions. China’s currency is quasi-pegged to the dollar and that means U.S. monetary policy gets imported into China.
The gradual tightening of U.S. monetary conditions since the end of QE3 has therefore meant a gradual tightening of Chinese monetary conditions. Recently, it has intensified with the Fed signalling its plans to tighten monetary policy with a rate hike. U.S. markets have priced in this anticipated rate hike and caused U.S. monetary conditions to further tighten. Through the dollar peg this tightening has also been felt in China and can explain the slowdown in economic activity. Consequently, China had to loosen the dollar choke hold on its economy via a devaluation of its currency.
There is, however, a more fundamental reason for the devaluation. China has been violating the impossible trinity. This notion says a country can only do on a sustained basis two of three potentially desired objectives: maintain a fixed exchange rate, exercise discretionary monetary policy, and allow free capital flows. If a country tries all three objectives then economic imbalances will build and eventually give way to some kind of painful adjustment. China was attempting all three objectives to varying degrees. It quasi-pegged its currency to the dollar, it manipulated domestic monetary conditions through adjustment of interest rates and banks’ require reserve ratio, and it allowed some capital flows. This arrangement could not last forever, especially given the Federal Reserve’s passive tightening of monetary policy.

Talk about lowballing…
• Yuan Move Threatens to Add $10 Billion to China Inc.’s Debt Costs (Bloomberg)
The biggest offshore borrowers in Asia are about to understand the costs of a devaluation. Chinese companies, which have $529 billion in dollar and euro bonds and loans outstanding, could see their debt costs jump by $10 billion after the People’s Bank of China devalued the yuan by 1.9%, according to Bloomberg-compiled data. The weaker yuan increases expenses for firms that have to exchange it into those currencies to pay interest and principal on offshore borrowings. Chinese corporations have sold bonds and gotten bank loans offshore at a record pace and now are the biggest component of major fixed-income indexes in the region. A narrow trading band for their home currency meant that many did not hedge against exchange losses that Tuesday’s devaluation, the biggest in two decades, now threatens.
“Most Chinese companies don’t hedge their forex exposure,” said Ivan Chung, an analyst at Moody’s Investors Service. “The sudden devaluation in the currency will add pressure to those with offshore dollar debt, especially the property sector that relies heavily on offshore debt.” The central bank cut its daily reference rate for the currency by a record, triggering the yuan’s biggest one-day loss since China unified official and market exchange rates in January 1994. “Chinese property developers have lots of offshore debt outstanding – more than 20% of their total debt for some – and the majority of them have high leverage and weak cash flow,” said Christopher Lee at Standard & Poor’s in Hong Kong. “If the yuan depreciation sustains, they will face pressure on servicing their debt.”

Carry me Carry.
• One of China’s Most Popular Trades May Be Coming to an End (Tracy Alloway)
Years of the Chinese yuan practically pegged to the U.S. dollar gave succor to a massive carry trade that involved mainland speculators borrowing from overseas banks at relatively low rates and then investing in higher-yielding renminbi-denominated assets. Pocketing the spread between the two netted hefty returns, but the era of “peak” China carry looks to be coming to an end following China’s move to devalue its currency. While the exact size of the carry trade is unknown, the Bank for International Settlements estimates that dollar borrowing in China jumped five-fold since 2008 to reach more than $1.1 trillion.
Global dollar borrowing is something like $6 trillion to $9 trillion, according to the BIS, thanks largely to an emerging market borrowing spree. The speed and nature of the China carry trade unwind will now depend largely on the pace of the dollar’s appreciation. It’s doubtful that Chinese authorities want to see a disorderly unwind of any sort. Still, the flipside is that China still has some pretty impressive foreign exchange reserves, which could soften the blow from an unwind of the carry trade. The devaluation may also have the added benefit of taking some of the froth out of a Chinese market that has arguably been overheated by foreign borrowing.

Duh..
• Goldman Says China Yuan Move Is Attempt to Get Ahead of the Fed (Bloomberg)
China’s shock devaluation of its currency is designed to cushion it from rising along with the dollar after a projected interest-rate increase from the Federal Reserve, according to Goldman Sachs. “This is about Fed liftoff most obviously and further dollar strength,” Goldman Sachs chief currency strategist Robin Brooks wrote in a note to clients. “It certainly makes sense for China’s policy makers to buy some flexibility ahead of Fed liftoff, in particular since the fix had become very peg-like in its stability in recent months.” Goldman Sachs projects the dollar strengthening 20% on a trade-weighted basis by the end of 2017. The yuan fell the most Tuesday since China ended a dual-currency system in January 1994 after the central bank cut its daily reference rate by 1.9%.
China has stepped up efforts to boost old growth drivers as new ones fail to offset slowing investment and trade. Developing markets are feeling the strain as domestic growth slows while the U.S. nears its first interest-rate increase in almost a decade. Until Tuesday, China had kept the yuan steady against the dollar, effectively pushing it higher against other emerging-market currencies and hurting its exporters. While the change is reminiscent of Swiss abandonment of the franc’s ceiling versus the euro in January, which anticipated quantitative easing from the ECB, China isn’t looking to push the currency significantly lower, according to Brooks. The change is a one-time correction, a spokesman for the People’s Bank of China said Tuesday. “Our bias is that the move overnight was more about buying flexibility as opposed to the beginning of a large devaluation trend,” New York-based Brooks wrote.

“..total credit outstanding (household, corporate, government and financial) has expanded by over $50 trillion in the past 30 years, while GDP has expanded by only $13 trillion.”
• The Fed Is In A Bind (Haselmann)
The intention of Fed policy over the past 30 years has been to self-correct business cycles into a ‘steadier state’ by easing interest rates into weakness and hiking them into strength. Unfortunately, there is political-asymmetry between easing and hiking which has resulted in the stair-stepping of official interest rates down to the zero lower bound. Interest rates that are held lower than the ‘natural or normal rate’ (discussed in a moment) may have short-term benefits, yet there are longer-term costs that aggregate and eventually need to be addressed. These costs are then typically dealt with by lowering interest rates even farther away from the normal or natural rate. Eventually the Fed ends up worsening the very business cycles they intended to smooth out.
The fact that rates today have reached zero means that the day of reckoning is quickly approaching, because monetary policy has reached the practical limits of what it can do. Thus, the multi-decade credit era is coming to an end. Credit-based consumption is unsustainable. US corporate issuance has broken a new record in four successive years. According to David Stockman, the amount of total credit outstanding (household, corporate, government and financial) has expanded by over $50 trillion in the past 30 years, while GDP has expanded by only $13 trillion. In addition, while the whole world has gotten significantly more indebted, it also has terrible demographics to contend with. The S&P over this same 30-year period has returned just over 6% adjusted for inflation, while real GDP has been just above 2%.
The market has risen 3 times faster than national output in real terms. A sizable equity market correction could happen merely because the bubble-blowing machine is losing its wind. Certainly, the magnitude of the monetary and debt-based fuel that has powered equities in the past will not be available going forward. An economy runs most efficiently in the long-run when the price of money, i.e., the official interest rate, does not veer too far from the level where savings and investment can find a clearing price (i.e., the natural rate of interest). This is called the Wicksellian Differential, i.e., the difference between the money rate and natural rate of interest. It postulates that when the natural rate is higher than the money rate, the disequilibrium will drive credit expansion.

Debts have shifted but not disappeared.
• An Economic Earthquake Is Rumbling (Livingston)
While the people sleep, an economic earthquake rumbles underneath. The day that they begin to feel the quake draws near. History will record that in this decade more people will lose more money (forget about the trillions of dollars already lost) than at any time in our history, including during the Great Depression. At the same time, a very small group has made and will make huge sums of money. During the Y2K scare (a real hoax) many people stored food. Then, after Y2K, many people wanted to dump their cache; and some did. We advised readers at the time to store food simply because of the crisis world we live in, but to store those foods that you could rotate and consume. Stored food is a hedge against inflation. It’s a hedge against natural disaster. It’s a hedge against economic collapse.
It was our advice before, and it has been our advice since. This advice is still valid. People who don’t have some stored food don’t realize how dependent they are on the system and government. Of course, the system was designed and created to make the people dependent on government. That makes them easier to control. Many people have been in hard times since 2008, thanks to bursting housing and derivatives bubbles — both fueled by the Federal Reserve’s money printing and both predicted by meand by many other writers. For those of us who are not well-connected (those of us who are not in the 1%), there has been no relief. While the banksters got bailouts and Wall Street and the banksters benefited from the money printers, the middle class was impoverished. Savings were wiped out.
More working-age people than ever before are not working. More young workers than ever before are still living with their parents because they are either out of work or working at low-paying jobs. More people than ever before are on the government dole. Welfare pays more than most jobs. Retirement funds have been cashed out and spent on living expenses. [..] The default rate of companies with the lowest credit rating is at its highest level since 2013. The auto loan debt bubble is at $900 billion, fueled by easy credit and long-term loans (more than 60 months on even used cars) that put the car buyer upside down as he drives off the lot and keeps him there. U.S. mortgage holders are carrying the most non-mortgage debt they’ve had in more than 10 years; 81% of that is automobile debt. Student loan debt held by mortgage holders is the highest it’s ever been, with the average balance owed at nearly $35,000. Almost 5.7 million homeowners remain underwater on their mortgages.

Externalities. Our economic systems’ highly destructive 800 pound gorilla.
• The Social Cost of Capitalism (Paul Craig Roberts)
Few, if any, corporations absorb the full cost of their operations. Corporations shove many of their costs onto the environment, the public sector, and distant third parties. For example, currently 3 million gallons of toxic waste water from a Colorado mine has escaped and is working its way down two rivers into Utah and Lake Powell. At least seven city water systems dependent on the rivers have been shut down. The waste was left by private enterprise, and the waste was accidentally released by the Environmental Protection Agency, which might be true or might be a coverup for the mine. If the Lake Powell reservoir ends up polluted, it is likely that the cost of the mine imposed on third parties exceeds the total value of the mine’s output over its entire life.
Economists call these costs “external costs” or “social costs.” The mine made its profits by creating pollutants, the cost of which is born by those who had no share in the profits. As this is the way regulated capitalism works, you can imagine how bad unregulated capitalism would be. Just think about the unregulated financial system, the consequences we are still suffering with more to come. Despite massive evidence to the contrary, libertarians hold tight to their romantic concept of capitalism, which, freed from government interference, serves the consumer with the best products at the lowest prices. If only. Progressives have their own counterpart to the libertarians’ romanticism. Progressives regard government as the white knight that protects the public from the greed of capitalists. If only.
[..] The two largest reservoirs, Lake Mead and Lake Powell, are at 39% and 52% of capacity. The massive lakes on which the Western United States is dependent are drying up. And now Lake Powell is faced with receiving 3 million gallons of waste water containing arsenic, lead, copper, aluminum and cadmium. Wells in the flood plains of the polluted rivers are also endangered. The pollutants, which turned the rivers orange, flowed down the Animas River from Silverton, Colorado through Durango into the San Juan River in Farmington, New Mexico, a river that flows into the Colorado River that feeds Lake Powell and Lake Mead. All of this damage from one capitalist mine.

Makes a lot of sense.
• Yanis Varoufakis Backs Wikileaks Bounty To Crack TTIP (Telegraph)
Yanis Varoufakis, the former Greek finance minister, has donated to a $110,000 bounty to reward whoever leaks the text of a major EU-US trade deal. Mr Varoufakis was named yesterday as one of a number of public figures said to have donated to a fund set up by Wikileaks, the secret-sharing website, to encourage the leaks of documents surrounding Transatlantic Trade and Investment Partnership (TTIP). Others said to have donated to the fund include Vivienne Westwood, the fashion designer; Daniel Ellsberg, the Pentagon papers leaker; Slavoj Zizek, the philosopher; and Evgeny Morozov, the journalist. Julian Assange, the Wikileaks founder, was also named as a donor. So far some $24,000 dollars has been raised of the target.
Wikileaks wants the text of the proposed deal to be leaked. It is not clear whether such a single text exists. The deal will break down tariff and regulatory barriers between the EU and US, adding around £94 billion to the European economy and cutting the price of goods such as jeans and cars. David Cameron is a major advocate, seeing it as essential to save the EU s economies from decline, and has pledged to put rocket boosters under the deal. It has met stiff opposition from the left and radical right in Britain and the continent, who argue it will allow corporations to sue the Government for market access and force greater private provision in the NHS.
Some French farmers claim it will allow the spread of US “Frankenfoods”, such as chlorine-washed chicken, genetically modified crops and hormone-treated beef. Advocates say most controversial element the ability of companies to challenge governments in the courts is commonplace in global trade deals. Mr Assange said: “The secrecy of the TTIP casts a shadow on the future of European democracy. Under this cover, special interests are running wild, much as we saw with the recent financial siege against the people of Greece. The TTIP affects the life of every European and draws Europe into long term conflict with Asia. The time for its secrecy to end is now. Mr Varoufakis, an economist, had a toxic relationship with EU officials and European leaders, and he left office before a bailout deal could be signed. I shall wear the creditors loathing with pride, he said on resigning in July.

Word of the week: Euroin.
• Euromaniacs: An Addiction To Euroin (Diego Fusaro)
Italy, and not only Italy but indeed all of the Eurozone countries should get out of the Euro as soon as possible because the Euro has proven to be a real financial coup d’état that has enabled the imposition of a neoliberal regime and the removal of all forms of social rights and the removal of any form of guaranteed healthcare and public ownership, all in favour of privatisation. The Euro has been the Trojan Horse with which neoliberalism has imposed its wishes and it’s a bit like a charging rhinoceros that is impossible to stop, to appease or for that matter to control in any way. You simply have to move out of its way before it tramples you! We simply have to get out of the Euro as soon as possible!
Generally speaking, and I use Gramsci’s words here, the Euro is a sort of Passive Revolution, in other words a revolution by which the dominant capitalist power after 1989 strengthened itself, strengthening its own structure and ridding itself of the ties and restrictions of the State and the public, of the Sovereign National Government, in order to impose the power of the unfettered economy, in other words the power of the banks and the Financial world no longer disciplined by the State and by what Hegel’s Philosophy would refer to as Ethical forces, i.e. those powers that are capable of disciplining the Economy and to place it at the service of the community. The Euromaniacs, and I am using this term that I have borrowed from my journalist friend Alessandro Montanari, are those people that are totally unable to overcome their absolute addiction to the Euro.
Just like drug addicts, these guys keeping on wanting more Euro and more Europe, even though the Euro continues to cause social and political catastrophes, including the end of public ownership, the end of social security and the downward spiral towards poverty here in Italy. They resort to using oracle-like, almost theological terminology such as: “What we need is more Europe! It’s paradoxical. No less paradoxical in fact than if someone were faced with the tragedy of a drug addict and said: “What we need are more drugs!Nowadays, anyone looking at the twin tragedies of Europe and the Euro and obsessively and compulsively repeats: “What we need is more Euro, more Europe!”is no more and no less than an addiction to Euroin.

A huge powderkeg.
• PKK Leader: Turkey Is Protecting Islamic State By Attacking Kurds (BBC)
The man leading the Kurdistan Workers’ Party (PKK) has accused Turkey of trying to protect the Islamic State group by attacking Kurdish fighters. Cemil Bayik told the BBC he believed President Recep Tayyip Erdogan wanted IS to succeed to prevent Kurdish gains. Kurdish fighters – among them the PKK – have secured significant victories against IS militants in Syria and Iraq. But Turkey, like a number of Western countries, considers the PKK a terrorist organisation. A ceasefire in the long-running conflict with the group appeared to disintegrate in July, when Turkey began bombing PKK camps in northern Iraq, at the same time as launching air strikes on IS militants. Observers say PKK fighters have been on the receiving end of far more attacks than IS.
But Turkish officials deny that the campaign against IS group is a cover to prevent Kurdish gains. On Wednesday, Turkey said it was planning a “comprehensive battle” against IS. “The Turkish claim they are fighting Islamic State… but in fact they are fighting the PKK,” Cemil Bayik told BBC’s Jiyar Gol. “They are doing it to limit the PKK’s fight against IS. Turkey is protecting IS. “[President] Erdogan is behind IS massacres. His aim is to stop the Kurdish advance against them, thus advancing his aim of Turkishness in Turkey.”

A 12-fold increase. And even now, where is the EU? This is sufficient reason NOT to remain a member: moral degenerancy.
• 50,000: More Migrants Reached Greece In July Than During All Of 2014 (Quartz)
It is a “crisis within a crisis.” That’s how prime minister Alexis Tsipras describes the massive influx of migrants to Greece, straining the resources of a country that is already strapped for cash. Nearly 50,000 migrants came to Greece in July—more than the whole of 2014. So far this year, more than 130,000 illegal border crossings have been made in Greece, according to Frontex, the EU’s border agency. The vast majority of migrants come from Syria and Afghanistan, seeking asylum in the EU after a treacherous journey in overcrowded, makeshift boats across the eastern Mediterranean—now the busiest route for people seeking a better life in Europe.
Even Greece’s shattered economy is better than what Afghans, Syrians, and others leave behind. But most migrants hope to travel further into Europe in search of jobs, stability, and states more receptive to asylum claims. But if they’re caught or rescued in Greece, in most cases they must be processed there. The UN recently described conditions for migrants in popular Greek landing spots as “total chaos,” with a severe lack of food, sanitation, and shelter. But an EU plan to distribute migrants more evenly across the bloc has stalled, with many countries rejecting proposed quotas. This weekend alone, the Greek coast guard pulled another 1,400 people out of the sea, according to reports. Tsipras recently called for urgent assistance from the rest of the EU: “This problem surpasses us,” he said.

Better instruct them well.
• Greece Sends Police Reinforcements To Kos In Migrant Crisis (Kathimerini)
The Greek Police (ELAS) has sent additional officers to the eastern Aegean island of Kos to help deal with a burgeoning migrant crisis there which escalated into violent clashes Tuesday. ELAS chief Dimitris Tsaknakis has dispatched 12 officers from the force’s immigration unit to the island, including one Arab-speaking employee, to help accelerate the process of identifying some 7,000 immigrants there, most believed to be Syrian. Local authorities allocated a municipal gymnasium and an old soccer field for officers to interview the immigrants and issue them with documents allowing them to remain in the country for six months. The officers arrived on the island on Monday and had interviewed around 750 migrants by late last night, a police source told Kathimerini.
The process of identifying the arrivals was brusquely interrupted Tuesday when a fracas broke out between migrants and police officers as the former were being transferred to the old soccer stadium. Police used truncheons and even fire extinguishers to keep back the immigrants in an apparent bid to avert a stampede amid a crush to enter the stadium. Responding to the rising tensions, ELAS ordered two riot police units to be flown to the island on a C-130 military transport aircraft. Tsaknakis also ordered the transfer of some 250 additional officers to be stationed on Kos and other islands in the eastern Aegean such as Lesvos and Samos which have been besieged by large numbers of immigrants. Kos Mayor Giorgos Kyritsis said local authorities were overwhelmed and warned of “bloodshed if the situation degenerates.”

UN equals special interests.
• United Nations Failing To Represent Vulnerable People, Warn NGOs (Guardian)
Vulnerable people are prevented from gaining representation at the United Nations by a committee dominated by countries with repressive regimes, according to concerned NGOs. Organisations have told the Guardian how they face lengthy hold-ups, bizarre questioning and intimidation as they negotiate with the UN committee on non-governmental organisations, the group which decides which organisations get official UN status, and is currently made up of countries including Cuba, China, Russia, Pakistan and Qatar. Last month, Freedom Now, which works with prisoners of conscience around the world, finally won a six year battle to get official status, in the face of fierce opposition from China.
It took an intervention from US ambassador Samantha Power, who said she was determined “to put an end to the inexcusable attempt to deny Freedom Now’s official NGO status”. But this case is far from unique, with NGO workers from around the world warning that vulnerable people are being denied representation at the UN by the dysfunctional nature of the NGO committee and its parent body the Economic and Social Council (Ecosoc), which produces policy and makes recommendations on economic, social and environmental issues at the UN. In order to work at the UN, make speeches and gain access to important officials, organisations need to submit applications for special consultative status to the NGO committee.
The UN offers no guidance or time limit on how long it takes for applications to be processed by the committee. The 19 members of the committee are elected by other states every four years. The committee must always contain a set number of countries from each region; with four from Asian states and five from African states, for example. Jessica Stern, from the International Gay and Lesbian Human Rights Commission which took three years to get special consultative status, told the Guardian that it is “almost impossible” for NGOs to operate in the UN as without this official status. She added that negotiating with the committee can be both costly and time-consuming, meaning that many organisations simply give up.









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle August 12 2015