
Unknown Charleston, SC, after bombardment. Ruins of Cathedral of St John and St Finbar 1865



We’ve reached the end of a line. Not even the narrative works from here.
• Slowing Productivity Fast Becoming A Global Problem (Lebowitz)
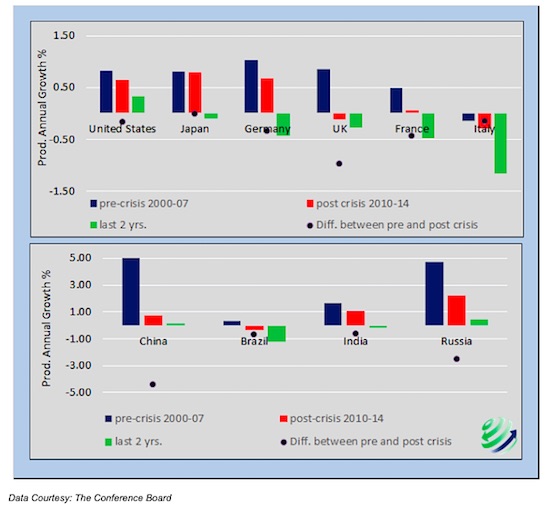
In “The Fed And Its Self-Defeating Monetary Policy” we focused our discussion on U.S. productivity, but weak and slowing productivity growth is not just an American problem. All of the world’s leading economies are, to varying degrees, exhibiting the same worrisome pattern. And slowing productivity is something investors across asset classes should pay attention to in 2016. The graph below compares annualized productivity trends from three time periods – the 7 years immediately preceding the financial crisis, the 5 years immediately following the crisis, and the 2 most recently reported years (2013 and 2014). The black dots display the change in trend from pre to post crisis.
In all cases the black dots are below zero representing slowing productivity growth. More troublesome, the world’s largest economies are most recently reporting either negligible productivity growth or a decline in productivity. Assuming that demographics are already “baked” and debt has been over-used to produce non-productive growth since well before the crisis, good old-fashioned productivity gains are what the global economy requires to produce durable organic growth in the developed world. Central bankers, politicians and investors are well advised to understand this dynamic.

Jobs numbers today will be big.
• Dow, S&P Off To Worst Four-Day Jan Start Ever As China Fears Grow (Reuters)
U.S. stocks sold off further on Thursday, giving the Dow and S&P 500 their worst four-day starts to a year ever, dragged down by another drop in Chinese equities and oil prices at 12-year lows. China allowed the biggest fall in its yuan currency in five months, adding to investor fears about the health of its economy, while Shanghai stocks were halted for the second time this week after another steep selloff. Oil prices fell to 12-year lows and copper prices touched their lowest since 2009, weighing on energy and materials shares. Shares of Freeport McMoran dropped 9.1% to $5.61. All 10 S&P 500 sectors ended in the red, though, and the Nasdaq Biotech index fell 4.1%. “People see the weakness in China and in the overall equity market and think there’s going to be an impact on corporations here in the United States,” said Robert Pavlik at Boston Private Wealth in New York.
“When you have a market that begins a year with weakness, people are sort of suspect anyway. The economy isn’t moving all that well, the outlook is modest at best, and they don’t want to wait for the long term. China creates more uncertainty.” The Dow Jones industrial average closed down 392.41 points, or 2.32%, to 16,514.1, the S&P 500 had lost 47.17 points, or 2.37%, to 1,943.09 and the Nasdaq Composite had dropped 146.34 points, or 3.03%, to 4,689.43. The Dow has lost 5.2% since the end of 2015 in the worst first four trading days since the 30-stock index was created in 1928. The S&P 500 is down 4.9% since Dec. 31, its worst four-day opening in its history, according to S&P Dow Jones Indices, while the Nasdaq is down 6.4%.

Serious losses and serious jitters.
• US Stock Markets Continue Plunge (Guardian)
US stocks continued to fall on Thursday as fears of an economic slowdown in China spooked investors around the world. The Dow Jones industrial average fell 392.41 points, or 2.32%, capping its worst four-day start to a year in more than a century. The S&P 500 posted its largest daily drop since September, losing 47.17 points, or 2.37%, to 1,943.09 and the Nasdaq Composite dropped 146.34 points, or 3%, to 4,689.43. The falls followed another day of turmoil on the world’s stock markets amid more signs that the Chinese economy is slowing. China moved early to try to head off more panic, scrapping a new mechanism that Beijing had initially hoped would prevent sharp selloffs.
Beijing suspended the use of “circuit breakers” introduced to halt trading after dramatic selloffs. The circuit breakers appear to have exacerbated the selloffs, as would-be sellers waited for the markets to open again in order to sell. The decision came after the breaker was tripped for the second time in a week as the market fell 7% within half an hour of opening. Signs of problems in the world’s second largest economy triggered selling in Europe. The German DAX was the worst performer, falling 2.29%, as manufacturing firms were hit by fears about China’s impact on the global economy. In London the FTSE 100 staged a late rally but still ended the day down 119 points, or 1.96%, at 5,954. That’s a three-week low, which wipes around £30bn ($43.86bn) off the index.

Well put.
• China Has Not One Insolvable Problem, But Many Of Them (Mish)
Yuan and Capital Flight
• China needs to prop up the yuan to slow capital flight.
• China needs to let the yuan drop to support exports.
• China needs to float the yuan and remove capital controls to prove it really deserves to be taken seriously as a reserve currency.
• If the yuan sinks, capital flight will increase and China risks the ire of US congress and those play into protectionist sentiment, notably Donald Trump.
• Artificial stabilization of the yuan will do nothing but create an oversized move down the road as we saw in Switzerland.SOEs and Malinvestments
• China needs to write off malinvestments in state owned enterprises (SOEs).
• If China does write off malinvestments in SOEs it will harm those investing in them, generally individual investors who believed in ridiculous return guarantees.
• If China doesn’t write off malinvestments it will have to prop up the owners of those enterprises, mainly the ruling class, at the expense of everyone else, delaying much needed rebalancing.Property Bubble
• China needs to fill tens of millions of vacant properties, but no one can afford them.
• If China makes the properties affordable it will have to cover the losses, or builders will suffer massive losses.
• If China subsidizes losses for the builders, there are still no real jobs in in the vacant cities.
• If China does not subsidize the losses, the builders and current investors will both suffer massive damage.Jobs
• China is losing exports to places like Vietnam that have lower wage points.
• Property bubbles, the overvalued yuan, SOEs, and capital flight all pose conflicting problems for a government desperate for job growth.Stock Market
• China’s stock market is insanely overvalued (as are global equity markets in general). Many investors are trapped. A sinking stock market and loss of paper profits will make overvalued properties even more unaffordable.
• Propping up the market, as China has attempted (not very effectively at that), encourages more speculation.Pollution
• Curtailing pollution will cost tens of millions of jobs.
• Not curtailing pollution will cost tens of millions of lives.

“Our new base case is that the Chinese government will simply let the debt party go on until it eventually collapses under its own weight..”
• Capital Flight Pushes China To The Brink Of Devaluation (AEP)
China is perilously close to a devaluation crisis as the yuan threatens to break through the floor of its currency basket, despite massive intervention by the central bank to defend the exchange rate. The country burned through at least $120bn of foreign reserves in December, twice the previous record, the clearest evidence to date that capital outflows have reached systemic proportions. “There is certainly a sense that the situation is spiraling out of control,” said Mark Williams, from Capital Economics. Mr Williams said the authorities botched a switch in early December from a dollar currency peg to a trade-weighted exchange basket, accidentally setting off an exodus of money. Skittish markets suspected – probably wrongly – that it was camouflage for devaluation. The central bank is now struggling to pick up the pieces.
Global markets are acutely sensitive to any sign that China might be forced to abandon its defence of the yuan, with conspiracy theories rampant that it is gearing up for currency war in a beggar-thy-neighbour push for export share. Any such move would send a powerful deflationary impulse though a world economy already on its knees, and risk setting off a chain-reaction through Asia, replicating the 1998 crisis on a larger and more dangerous scale. The confused signals coming from Beijing sent Brent crude crashing to an 11-year low of $32.20. They have also set off a parallel drama on China’s equity markets. The authorities shut the main exchange after the Shanghai Composite index plunged 7.3pc in less than half an hour, triggering automatic circuit-breakers. The crash wiped out $635bn of market capitalisation in minutes.
It was triggered by a witches’ brew of worries: a fall in China’s PMI composite index for manufacturing and services below the boom-bust line of 50, combined with angst over an avalanche of selling by company insiders as the deadline neared for an end to the share-sales ban imposed last year. Faced with mayhem, regulators have retreated yet again. They have extended the ban, this time prohibiting shareholders from selling more than 1pc of the total float over a three-month period. The China Securities Regulatory Commission said the move was to “defuse panic emotions”. The freeze on sales is an admission that the government is now trapped, forced to keep equities on life-support to stop the market crumbling. The commission said its “national team” would keep buying stocks if necessary, doubling down on its frantic buying spree to rescue the market last year.
[..] Jonathan Anderson, from Emerging Advisors Group in Shanghai, said the latest burst of stimulus – led by an 18pc rise in credit – is clear evidence that Beijing is unwilling to take its medicine and deflate the country’s $27 trillion loan bubble. “The debt ratio is rocketing upwards. China is still adding new leverage at a massive, frenetic pace,” he said. “The authorities have clearly shown that they have no intention of addressing leverage problems. Our new base case is that the Chinese government will simply let the debt party go on until it eventually collapses under its own weight,” he said.

Light. Tunnel. Oncoming freight train.
• China Stocks Rebound as State Funds Said to Buy Equities (BBG)
Chinese stocks gained in volatile trading after the government suspended a controversial circuit breaker system, the central bank set a higher yuan fix and state-controlled funds were said to buy equities. The Shanghai Composite Index rose 3% at 1:34 p.m. local time, after falling as much as 2.2% earlier. Regulators removed the circuit breakers after plunges this week closed trading early on Monday and Thursday. The central bank set the currency’s reference rate little changed Friday after an eight-day stretch of weaker fixings that roiled global markets. State-controlled funds purchased Chinese stocks on Friday, focusing on financial shares and others with large weightings in benchmark indexes, according to people familiar with the matter.
“The scrapping of the circuit breaker system will help to stabilize the market, but a sense of panic will remain, particularly among retail investors,” said Li Jingyuan, general manager at Shanghai Bingsheng Asset Management. “The ‘national team’ will probably continue to buy stocks significantly to stabilize the market.” While China’s high concentration of individual investors makes its stock-market notoriously volatile, the extreme swings this year have revived concern over the Communist Party’s ability to manage an economy set to grow at the weakest pace since 1990. The selloff has spread around the world this week, sending U.S. equities to their worst-ever start to a year and pushing copper to the lowest levels since 2009.
[..] The flip-flop in the circuit breaker rule adds to the sentiment among global investors that authorities are improvising – and improvising poorly – as they try to stabilize markets and shore up the economy. “They are changing the rules all the time now,” said Maarten-Jan Bakkum, a senior emerging-markets strategist at NN Investment Partners in The Hague with about $206 billion under management. “The risks seem to have increased.” Investors should expect more volatility in Chinese markets as the government attempts to shift away from a planned economy to one driven by market forces, Mark Mobius, chairman of the emerging markets group at Franklin Templeton Investments, wrote in a blog post on Thursday. Policy makers face a “conundrum” as they seek to maintain financial stability while at the same time loosening their grip on markets, he said.
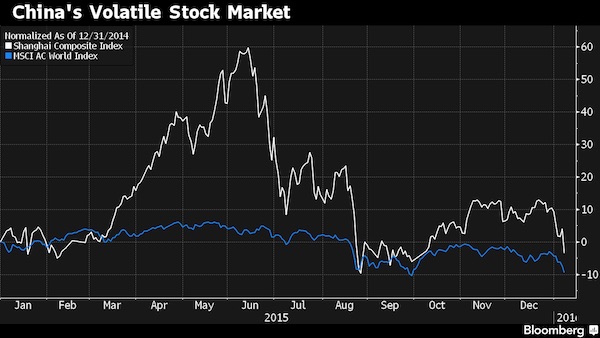

“Global shares have lost more than $4 trillion this year..”
• China’s Yuan Fixing Calms Markets as Asian Stocks Rally With Oil (BBG)
China’s efforts to stabilize its markets showed early signs of success as the yuan strengthened and regional equities rallied for the first time in five days. Treasuries and the yen fell as demand for havens eased. The Shanghai Composite Index gained 2.4% at the midday break after the securities regulator suspended a controversial circuit-breaker system. Asia’s benchmark share index pared its biggest weekly drop since 2011. The yuan rose 0.1% in onshore trading after the People’s Bank of China ended an eight-day stretch of setting weaker reference rates. Crude oil rallied, while Treasuries and the yen headed for their first declines this week. Global shares have lost more than $4 trillion this year as renewed volatility in Chinese markets revived doubts over the ruling Communist Party’s ability to manage the world’s second-largest economy.
The tumult has heightened worries over competitive devaluations and disinflation as emerging-market currencies tumbled with commodities. Investors will shift their attention to America’s economy on Friday as the government reports monthly payroll figures, a key variable for U.S. interest rates. “The PBOC may have been surprised at how badly China and global stock markets reacted to yuan depreciation,” said Dennis Tan at Barclays in Singapore. “They may want to keep the yuan stable for a while to help calm the stock market.” The PBOC set the yuan’s daily fixing, which restricts onshore moves to a maximum 2% on either side, at 6.5636 per dollar. That’s 0.5% higher than Thursday’s onshore effective closing price in the spot market and ends an eight-day reduction of 1.42%.
China’s markets regulator abandoned the circuit breaker just days after it was introduced, as analysts blamed the new mechanism for exacerbating this week’s selloff. Mainland exchanges shut early on Thursday and Monday after plunges of 7% in the CSI 300 triggered automatic halts. Chinese shares rallied after a volatile start to the day that sent the Shanghai Composite down as much as 2.2%. Producers of energy and raw-materials led the advance as investors gravitated to some of last year’s most beaten-down stocks and state funds were said to intervene to by purchasing shares with large index weightings.
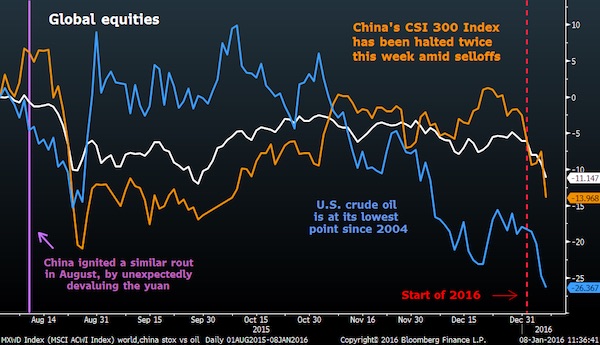

China will be exporting a crushing deflation.
• The Decline Of The Yuan Destroys Belief In Central Banking (Napier)
The key failure of control is in China because that failure will overwhelm other seeming successes. In 2012 this analyst labelled one chart “the most important chart in the world”. It was a chart of China’s foreign exchange reserves. It showed how they were declining and The Solid Ground postulated that this would produce a decline in real economic activity in China and higher real interest rates in the developed world. The result of these two forces would be deflation, despite the amount of wind puffed below the wings of the global economy in the form of QE. Of course, no sooner had this report been issued than China’s grand falconer got to work by borrowing hundreds of billions of USD through its so-called commercial banking system!
The alchemical process through which this mandated capital inflow supported the exchange rate while permitting money creation in China stabilized the global economy- for a while. However, by 2014 it was ever more difficult to borrow more money than the people of China were desperate to export and the market began to win. Since then foreign reserves have been falling and the grand falconer has tried to support the exchange rate while simultaneously easing monetary policy to boost economic growth. I’m no falconer but isn’t this akin to trying to get a bird to fly while tying back its wings? Some investors, well paid to believe six impossible things before breakfast, did not question the ability of the grand Chinese falconer to fly a falcon with tethered wings.
They changed their minds briefly as the bird plummeted earthwards in August 2015 but still the belief in the ability to reflate the economy and simultaneously support an overvalued exchange rate continued. In January 2016 this particular falcon, let’s call it the people’s falcon, was more ‘falling with attitude’ than flying. This bird does not fly and if this bird does not fly the centre does not hold. A major devaluation of the RMB is just beginning and the faith in all the falconers will wane as deflation comes to the world almost seven years after the falconers first fanned the winds of QE supposed to levitate everything.

Whack-a-mole.
• One Big Market Casualty: China Regulators’ Reputation (CNBC)
The wobbles in China that rocked financial markets this week have not only cast doubts over the economy, they’ve also shaken confidence in policymakers’ ability to stem the volatility. For two decades, China’s frenetic growth has been the source of the world’s envy, with investors placing faith in the ability of policymakers to help transform China from a manufacturing-led powerhouse to a consumer-driven economy . As the economy stutters and regulators scramble to contain wild moves in the yuan and stocks, analysts are calling out what appears to be a ham-fisted approach to managing market volatility.
“Market volatility this week suggests that nobody really knows what the policy is right now. Or if the government itself knows or is capable of implementing the policy even if there is one,” DBS said in a currency note Friday. “The market’s message was loud and clear that more clarity and less flip-flopping is needed going forward.” China-listed stocks plunged this week, with trade suspended completely in two sessions after the CSI 300 index dropped more than 7 percent, triggering a circuit breaker meant to limit market volatility. The China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC) suspended the circuit-breaker system, implemented for the first time on Monday, before the start of trade Friday. The quick regulatory flip-flops spurred a lot of derision among social media commentators.
“The CSRC all treated us as experiments to make history. When it failed, it concluded with ‘lacking experience,’ and that’s it,” Weibo user Li Hua posted. “I strongly call for resignation of related personnel who designed this policy! There’s no cost of failure so that decision makers can do whatever they want.” Another factor weighing on faith in China’s regulators: Policy makers at the central bank, the People’s Bank of China (PBOC), have tinkered again with its currency without providing much indication to the market about its endgame. On Thursday the PBOC allowed the yuan to fall by the most in five months, to the lowest level since the fixing mechanism was established in 2011.

Money will continue to flow out no matter what they do.
• China Orders Banks To Limit Dollar Buying This Month To Stem Outflows (CNBC)
China’s foreign exchange regulator has ordered banks in some trading hubs to limit dollar purchases this month, three people with direct knowledge said on Friday, in the latest attempt to stem capital outflows. The spread between the onshore and offshore markets for the yuan, or renminbi, has been growing since the devaluation last year, spurring Beijing to adopt a range of measures to curb outflows of capital. All banks in certain trading hubs, including Shenzhen, have been affected, the people added. China suspended forex business for some foreign banks, including Deutsche, DBS and Standard Chartered at the end of last year.

Beggar all of thy neighbors.
• Yuan Depreciation Risks Competitive Devaluation Cycle (Reuters)
The depreciation of the Chinese yuan risks triggering a cycle of competitive devaluation and is causing enormous worry in the world’s financial markets, Mexican Finance Minister Luis Videgaray said on Thursday. China allowed the biggest fall in the yuan in five months on Thursday, sending global markets down on concerns that China might be aiming for a devaluation to help its struggling exporters and that other countries could follow suit. “This is one of the worst starts of the year for all the world’s markets,” Videgaray said at an event in Mexico City. “There is a real worry that in the face of the slowing Chinese economy that the public policy response is to start a round of competitive devaluation,” he said.
Mexico has been committed to a freely floating currency since a devastating financial crisis in the mid-1990s and authorities refrain from some of the more direct forms of intervention seen in other emerging markets. Mexico’s peso slumped to a record low on Thursday, triggering two auctions of $200 million each by Mexico’s central bank to support the currency. The country’s program of dollar auctions, under which the central bank can sell up to $400 million a day, is set to expire on Jan. 29. Videgaray said policymakers would announce if the plan would be maintained or modified before that deadline. He noted the program’s goal is not to defend a certain peso level but to ensure sufficient order and liquidity in the market. “We have managed to achieve this objective in a satisfactory manner,” he said. “Up until now, there has been no decision to modify the mechanism.”

Can’t be a good sign no matter what they say.
• China’s Forex Reserves Post Biggest Monthly Drop On Record (Xinhua)
China’s foreign exchange reserves posted the sharpest monthly fall on record in December, official data showed Thursday. Foreign exchange reserves fell to $3.33 trillion at the end of last month, the lowest level in more than three years and down by 108billion dollars from November, according to the People’s Bank of China. The fall in December extended a month-on-month decline of $87.2 billion registered in November. The yuan has been heading south since the central bank revamped the foreign exchange mechanism in August to make the rate more market-based. The yuan has been losing ground as the Chinese economy is expected to register its slowest pace of growth in a quarter of a century in 2015.
Meanwhile, the United States raised interest rates in December and more rises are expected in 2016. The onshore yuan (CNY), traded in the Chinese mainland, declined 4.05% against the greenback in 2015. Li Huiyong, analyst with Shenwan Hongyuan Securities, said the faster decline indicated greater pressure for capital outflow as the yuan depreciated. On Thursday, the central parity rate of the yuan weakened by 332 basis points to 6.5646 against the U.S. dollar, its weakest level in nearly five years, according to the China Foreign Exchange Trading System. “An appropriate size for China’s forex reserves should be around 1.5 trillion U.S. dollars. There is still large room for necessary operations to sustain a stable yuan,” Li said.

They need to let it go. But won’t.
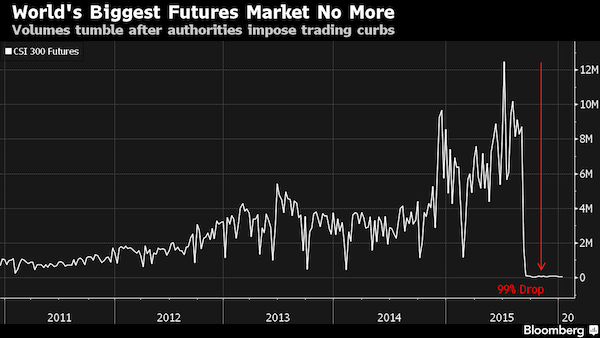
• China’s Stock Market Is Hardly Free With Circuit Breakers Gone (BBG)
China’s removal of market-wide circuit breakers after just four days still leaves investors facing plenty of restrictions in how they trade. A 10% daily limit on single stock moves and a rule preventing investors from buying and selling the same shares in a day remain in force. Volume in what was once the world’s most active index futures market is minimal after authorities curtailed trading amid a summer rout, making it more difficult to implement hedging strategies. Officials unveiled curbs Thursday on share sales by major stockholders just a day before an existing ban was due to expire. And the activity of foreign investors is limited by quotas, given either to asset managers or to users of the Hong Kong-Shanghai exchange link.
“Although there’s more ability now for offshore participation, it’s largely a market that’s restricted the domestic users,” said Ric Spooner at CMC Markets Asia Pacific. “That means it doesn’t get the arbitrage benefits that international investors bring. It’s a work in progress.” There’s also the prospect that regulators and executives will dust off last year’s playbook as they seek to stem losses. At the height of the summer rout, about half of China’s listed companies were halted, while officials investigated trading strategies, made it harder for investors to borrow money to buy equities and vowed to “purify” the market. Chinese equities seesawed in volatile trading on Friday, with the CSI Index rising 1.3% as of 10:02 a.m. local time after climbing 3.1% and sinking 1.7%.
The gauge slid 12% in the first four days of the week, two of which were curtailed as the circuit breakers triggered market-wide halts for the rest of the day. The flip-flop on using the mechanism, which was meant to help stabilize the market, is adding to investor concern that authorities are improvising. Policy makers weakened the yuan for eight days straight through Thursday, and authorities were said to intervene on Tuesday to prop up equities. Policy makers used purchases by government-linked funds to bolster shares as the CSI 300 plunged as much as 43% over the summer. State funds probably spent $236 billion on equities in the three months through August, according to Goldman Sachs.

Saudi rocket attack on embassy in Yemen.
• Iran Severs All Commercial Ties With Saudi Arabia (Reuters)
Relations between Iran and Saudi Arabia deteriorated even further on Thursday as Tehran severed all commercial ties with Riyadh and accused Saudi jets of attacking its embassy in Yemen’s capital. A row has been raging for days between Shi’ite Muslim power Iran and the conservative Sunni kingdom since Saudi Arabia executed cleric Nimr al-Nimr, an opponent of the ruling dynasty who demanded greater rights for the Shi’ite minority. Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, Sudan, Djibouti and Somalia have all broken off diplomatic ties with Iran this week, the United Arab Emirates downgraded its relations and Kuwait, Qatar and Comoros recalled their envoys after the Saudi embassy in Tehran was stormed by protesters following the execution of Nimr and 46 other men.
In a cabinet meeting chaired by Iran’s President Hassan Rouhani on Thursday, Tehran banned all imports from Saudi Arabia. Saudi Arabia had announced on Monday that Riyadh was halting trade links and air traffic with the Islamic Republic. Iran also said on Thursday that Saudi warplanes had attacked its embassy in Yemen’s capital, Sanaa, an accusation that Riyadh said it would investigate. “Saudi Arabia is responsible for the damage to the embassy building and the injury to some of its staff,” Foreign Ministry Spokesman Hossein Jaber Ansari was quoted as saying by the state news agency, IRNA. Residents and witnesses in Sanaa said there was no damage to the embassy building in Hadda district.

Aramco is so big, it may be impossible to value.
• Saudi Arabia Considers IPO For World’s Biggest Energy Company Aramco (Guardian)
Saudi Arabia is considering a stock market listing for its national oil group – the world’s biggest energy company and probably the most valuable company on the planet. Saudi Aramco is a highly secretive organisation but is likely to be valued at well over $1tn (£685bn). Any public share listing would be viewed as a potent symbol of the financial pain being wreaked by low prices on the world’s biggest crude exporting country. Prince Muhammad bin Salman, the country’s highly influential deputy crown prince, confirmed in an interview on Monday with the Economist magazine that a decision would be taken within months whether to raise cash in this way, even as oil company shares are depressed at this time.
“Personally I am enthusiastic about this step,” he said. “I believe it is in the interest of the Saudi market, and it is in the interest of Aramco, and it is for the interest of more transparency, and to counter corruption, if any, that may be circling around.” The sale via an initial public offering (IPO) of any part of Saudi Aramco would be a major change in direction for a country, which has jealously guarded its enormous – and cheaply produced – oil reserves. Aramco’s reserves are 10 times greater than those of Exxon, which is the largest publicly listed oil company. The prince, considered the power behind the throne of his father King Salman, is keen to modernise the largely oil-based Saudi economy by privatisation or other means but it also needs to find money.
The country is under pressure, with oil prices plunging to their lowest levels in 11 years and more than 70% below where they were in June 2014. This has put huge strain on Saudi public spending plans, which were drawn up when prices were much higher and pushed the public accounts into deficit.

A long way from salvation.
• VW Weighs Buyback of Tens of Thousands of Cars in Talks With US (BBG)
Volkswagen may buy back tens of thousands of cars with diesel engines that can’t be easily fixed to comply with U.S. emissions standards as part of its efforts to satisfy the demands of regulators, according to two people familiar with the matter. Negotiations between the German automaker and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency are continuing and no decisions have been reached. Still, a buyback would be an extraordinary step that demonstrates the challenge of modifying vehicles that were rigged to pass emission tests. VW has concluded it would be cheaper to repurchase some of the more than 500,000 vehicles than fix them, said the people, who declined to be cited by name.
One person said the number of cars that might be bought back from their owners totals about 50,000, a figure that could change as talks continue. “We’ve been having a large amount of technical discussion back and forth with Volkswagen,” EPA Administrator Gina McCarthy said Thursday, when asked about the possibility of VW having to buy back some vehicles. “We haven’t made any decisions on that.” McCarthy told reporters after an event in Washington Thursday that VW’s proposals to bring its cars into compliance with emissions standards have so far been inadequate. “We haven’t identified a satisfactory way forward,” McCarthy said. The EPA is “anxious to find a way forward so that the company can get into compliance,” she said.

“..the presence of isotopes from nuclear weapons testing..”
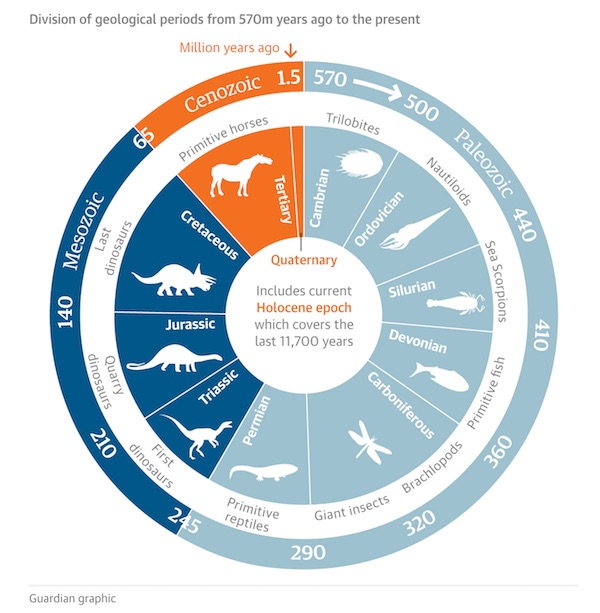
• Human Impact Has Pushed Earth Into The Anthropocene (Guardian)
There is now compelling evidence to show that humanity’s impact on the Earth’s atmosphere, oceans and wildlife has pushed the world into a new geological epoch, according to a group of scientists. The question of whether humans’ combined environmental impact has tipped the planet into an “anthropocene” – ending the current holocene which began around 12,000 years ago – will be put to the geological body that formally approves such time divisions later this year. The new study provides one of the strongest cases yet that from the amount of concrete mankind uses in building to the amount of plastic rubbish dumped in the oceans, Earth has entered a new geological epoch.
“We could be looking here at a stepchange from one world to another that justifies being called an epoch,” said Dr Colin Waters, principal geologist at the British Geological Survey and an author on the study published in Science on Thursday. “What this paper does is to say the changes are as big as those that happened at the end of the last ice age . This is a big deal.” He said that the scale and rate of change on measures such as CO2 and methane concentrations in the atmosphere were much larger and faster than the changes that defined the start of the holocene. Humans have introduced entirely novel changes, geologically speaking, such as the roughly 300m metric tonnes of plastic produced annually. Concrete has become so prevalent in construction that more than half of all the concrete ever used was produced in the past 20 years.
Wildlife, meanwhile, is being pushed into an ever smaller area of the Earth, with just 25% of ice-free land considered wild now compared to 50% three centuries ago. As a result, rates of extinction of species are far above long-term averages. But the study says perhaps the clearest fingerprint humans have left, in geological terms, is the presence of isotopes from nuclear weapons testing that took place in the 1950s and 60s. “Potentially the most widespread and globally synchronous anthropogenic signal is the fallout from nuclear weapons testing,” the paper says. “It’s probably a good candidate [for a single line of evidence to justify a new epoch] … we can recognise it in glacial ice, so if an ice core was taken from Greenland, we could say that’s where it [the start of the anthropocene] was defined,” Waters said.

It’s all become a joke.
• Europe’s Economy Faces Confidence Test as Borderless Ideal Fades (BBG)
Here’s the latest in a long line of threats to Europe’s economy: the border guard. Danish officers checking travel documents on the boundary with Germany this week aren’t out to stymie trade or hinder tourism – they’re under orders from politicians anxious to stem the flow of refugees. Even so, analysts are beginning to worry about what could happen to the already-embattled region when the free movement of people is called into question. Like the euro, the single currency used by 19 of the European Union’s 28 nations, the Schengen Agreement has long been touted by politicians as an irrevocable pillar of a multi-national union, allowing unimpeded travel between states for business or pleasure. So with an already fragile recovery, monetary policy stretched trying to fend off deflation and companies deferring investment, the mere threat that Schengen could unravel may be hard to shrug off.
“If in the migrant crisis Schengen were to disintegrate, this would send a disastrous signal to markets: the European project would be seen as in fact reversible,” said Wolfango Piccoli, managing director of Teneo Intelligence in London. “Nobody could blame investors if against that backdrop, they would suddenly start to re-evaluate the reliability of promises made by European institutions in the euro-zone crisis.” The EU says Europeans make over 1.25 billion journeys within the Schengen zone every year, which comprises 26 countries from the Barents Sea to the eastern Mediterranean. It also includes countries such as Iceland and Norway that aren’t part of the EU. Signed in 1985, Schengen took effect 10 years later. In normal times, it means travelers within the bloc aren’t subjected to border checks, and external citizens holding a visa for one country may usually travel without restriction to all.
These aren’t normal times and now the edifice of carefree travel across the continent is cracking. During 2015, the arrival of people fleeing wars and persecution in Asia, Africa and the Middle East exceeded 1 million, sparking political tension and public debate over how, and where, to settle the newcomers. Denmark’s decision to establish temporary controls seems, according to the EU, to be covered by Schengen rules that allow such curbs in emergencies. But it’s not the first; that move came hours after Sweden started systematic ID checks at its borders, while Germany was forced to take similar action in September along its frontier with Austria. Hungary erected a fence at its borders with Serbia and Croatia last year.

€3 billion, Angela.
• Turkey Does Nothing To Halt Refugee Flows, Says Greece (Kath.)
Turkey has not taken any action to clamp down on human traffickers and between 3,000 and 4,000 migrants and refugees are reaching Greece every day, Immigration Policy Minister Yiannis Mouzalas said Thursday. Mouzalas suggested in an interview on Skai TV that Ankara has not lived up to its pledges to stem the flow of people traveling across the Aegean to Greece. “It has not done anything to stop human trafficking, as is evident from the migratory flows.” The minister said that the high level of arrivals has continued because the news that some migrants are not being allowed through European borders has yet to filter through but, at the same time, refugees waiting to cross from Turkey are concerned that if they do not do so soon they will be prevented from reaching Central and Northern Europe.
“The high rate has to do with refugees’ fear that the borders will close for everyone,” he said, adding that he thought this possibility is “very likely.” “When the message reaches Morocco that Moroccans are not being allowed to cross into Europe but are being held and repatriated, the flows will drop.” Mouzalas said that around half of the people arriving in Greece over the last two months have been undocumented migrants.









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle January 8 2016