
Jack Delano “Lower Manhattan seen from the S.S. Coamo leaving New York.” 1941

It looks like the facemask issue is being absolved by US politics. That is a shame because it’s not as if we have such a wide array of initial defense options against COVID19.
Trump gets scolded for calling Fauci an alarmist, but what he actually said was “a bit of an alarmist”. And that’s really a nice way of putting it, because would anyone want to question that he is? The man has said some strange things.
That goes back to what I’ve covered before, a long time ago already, that in the initial phase of dealing with an unknown pathogen, epidemiologists are not the people to listen to, because it’s unknown to them as well. You need basic risk assessment, and basic tools. Lockdowns and masks are prominent among those tools.
Today, we know so little still, even if many would claim we’ve gathered a lot of knowledge, that they remain those tools. And now they’re being lost to arguments that have nothing at all to do with the pathogen. Maybe that is inevitable as distancing is not an inborn human trait, but the consequences are potentially huge.

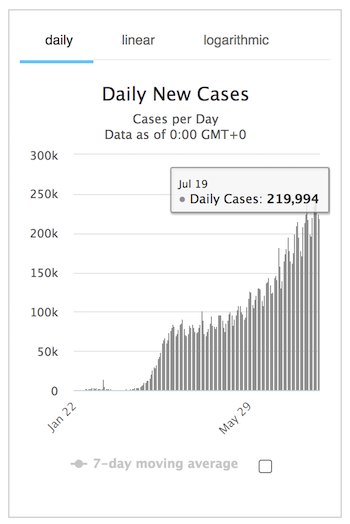
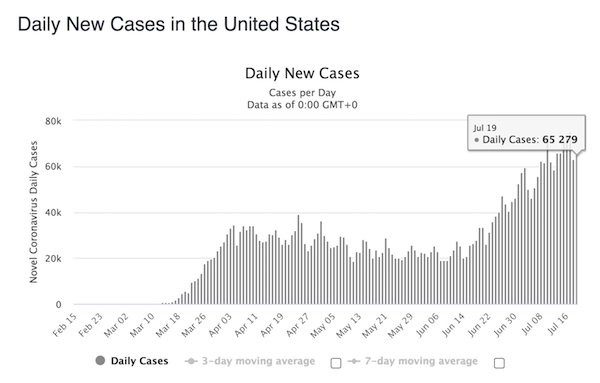

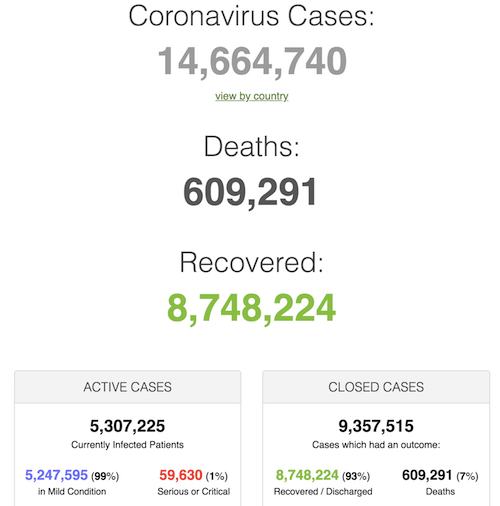

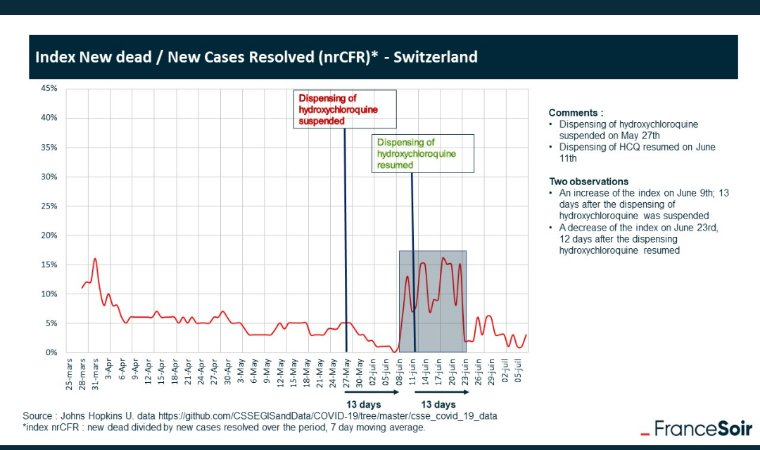
A cautionary tale from Switzerland, where a New Dead/New Case index shot up after the use of HCQ was stopped and went back down when it was resumed.

“With relatively low levels of natural immunity in the population, no vaccine and few effective treatments, there’s no pressure on it to adapt.”
• Are Mutations Making Coronavirus More Infectious? (BBC)
This coronavirus is actually changing very slowly compared with a virus-like flu. With relatively low levels of natural immunity in the population, no vaccine and few effective treatments, there’s no pressure on it to adapt. So far, it’s doing a good job of keeping itself in circulation as it is. The notable mutation – named D614G and situated within the protein making up the virus’s “spike” it uses to break into our cells – appeared sometime after the initial Wuhan outbreak, probably in Italy. It is now seen in as many as 97% of samples around the world. The question is whether this dominance is the mutation giving the virus some advantage, or whether it’s just by chance. Viruses don’t have a grand plan. They mutate constantly and while some changes will help a virus reproduce, some may hinder it. Others are simply neutral.
They’re a “by-product of the virus replicating,” says Dr Lucy van Dorp, of University College London. They “hitch-hike” on the virus without changing its behaviour. The mutation that has emerged could have become very widespread just because it happened early in the outbreak and spread – something known as the “founder effect”. This is what Dr van Dorp and her team believe is the likely explanation for the mutation being so common. But this is increasingly controversial. A growing number – perhaps the majority – of virologists now believe, as Dr Thushan de Silva, at the University of Sheffield, explains, there is enough data to say this version of the virus has a “selective advantage” – an evolutionary edge – over the earlier version.
[..] When studied in laboratory conditions, the mutated virus was better at entering human cells than those without the variation, say professors Hyeryun Choe and Michael Farzan, at Scripps University in Florida. Changes to the spike protein the virus uses to latch on to human cells seem to allow it to “stick together better and function more efficiently”. When it comes to looking at the population as a whole, it’s difficult to observe the virus becoming more (or less) infectious. Its course has been drastically altered by interventions, including lockdowns.
But Prof Korber says the fact the variant now appears to be dominant everywhere, including in China, indicates it may have become better at spreading between people than the original version. Whenever the two versions were in circulation at the same time, the new variant took over. In fact, the D614G variant is so dominant, it is now the pandemic. And it has been for some time – perhaps even since the start of the epidemic in places like the UK and the east coast of the US. So, while evidence is mounting that this mutation is not neutral, it doesn’t necessarily change how we should think about the virus and its spread.

Global trade was a useless bubble anyway. COVID can teach us the value of localizing again. If we’re wise.
• When The US Sneezes, The World Catches A Cold. Now It Has Severe COVID19 (R.)
During a blue-sky moment in 2018 near the end of a decade-long economic expansion, it was the United States that helped pull the world along as the extra cash from tax cuts and government spending flowed through domestic and global markets. But if it was U.S. policy that pushed the world higher then, it is U.S. policy that threatens to pull the world under now as the country’s troubled response to the coronavirus pandemic emerges as a chief risk to any sustained global recovery. Officials from Mexico to Japan are already on edge. Exports have taken a hit in Germany, and Canada looks south warily knowing that any further hit to U.S. growth will undoubtedly spill over.
“Globally there will be difficult months and years ahead and it is of particular concern that the number of COVID-19 cases is still rising,” the International Monetary Fund said in a review of the U.S. economy that cited “social unrest” due to rising poverty as one of the risks to economic growth. “The risk ahead is that a large share of the U.S. population will have to contend with an important deterioration of living standards and significant economic hardship for several years. This, in turn, can further weaken demand and exacerbate longer-term headwinds to growth.”
[..] The U.S. economy accounts for about a quarter of world gross domestic product. Though much of that is service-related, and much of the direct impact of the virus is tied up in industries like restaurants with weak links to the global economy, the connections are still there. A lost job leads to lower consumer spending leads to fewer imports; weak business conditions lead to less investment in the equipment or supplies that are often produced elsewhere. Year-to-date U.S. imports through May are down more than 13%, or roughly $176 billion. In Germany, whose measures to contain the pandemic are considered to have been among the most effective, exports to the United States plunged 36% year-over-year in May. Analysts see little prospect for improvement, with year-to-date U.S. auto sales through June down nearly 24% from a year earlier.

But some will insist the global trade bubble must be reinvented.
• S&P Says Governments Must Spend To Support Coronavirus-Hit Economy (CNBC)
With the coronavirus pandemic exacerbating a slowdown in the global economy, governments around the world may have no choice but to increase spending to support businesses and households well into the next year, according to an economist from S&P Global Ratings. Many governments have announced large amounts of fiscal support in the wake of the pandemic. But some countries, including the U.S., have shown “a degree of fiscal fatigue” and are considering rolling back some of the stimulus, said Shaun Roache, the ratings agency’s chief economist for Asia Pacific.
“We’re seeing some fiscal policymakers think about pulling back some of their measures or maybe letting them expire without renewing them, and that’s quite a dangerous thing to do when demand in the rest of the economy still remains quite suppressed,” he told CNBC’s “Squawk Box Asia” on Monday. “So we expect and we hope to see some of those fiscal measures being renewed, pushed forward into the next year. That is going to mean more fiscal easing but at the moment there is no alternative to that,” he added. Roache explained that additional spending will worsen the balance sheets of governments, but it’s necessary to “prevent things from getting even worse.” That’s especially so when authorities have to take actions that suppress economic activity to contain the virus given the absence of an apparent medical solution to the outbreak, he added.

They’re trying to comply with both Chinese and US demands at the same time. Good luck with that.
• Global Banks Scrutinize Their Hong Kong Clients For Pro-Democracy Ties (R.)
Global wealth managers are examining whether their clients in Hong Kong have ties to the city’s pro-democracy movement, in an attempt to avoid getting caught in the crosshairs of China’s new national security law, according to six people with knowledge of the matter. Bankers at Credit Suisse Group, HSBC, Julius Baer and UBS, among others, are broadening scrutiny under their programs that screen clients for political and government ties and subjecting them to additional diligence requirements, these people said. The designation, called politically exposed persons, can make it more difficult or altogether prevent people from accessing banking services, depending on what the bank finds about the person’s source of wealth or financial transactions.
The checks at some wealth managers have involved combing through comments made by clients and their associates in public and in media, and social media posts in the recent past, these people said. The new law prohibits what Beijing describes broadly as secession, subversion, terrorism and collusion with foreign forces, with up to life in prison for offenders. The sources, who requested anonymity because of the sensitivity of the situation, said the broadened scrutiny of clients also applied to Hong Kong and Chinese officials who had implemented the law in anticipation of any U.S. sanctions against them. One banker at a global wealth manager that holds more than $200 billion in assets said the audit of its clients could go back as far as 2014 in some cases to gauge a client’s political stance since Hong Kong’s 2014 pro-democracy “umbrella” movement. Protesters at the time used umbrellas to shield themselves from tear gas and pepper spray deployed by police.

Fine by me.
• Global Real Estate Investment Plunges 33% Amid Covid Pandemic (BBC)
Global real estate investment fell by 33% in the first half as the coronavirus pandemic battered economies and disrupted deals. The Asia-Pacific region took the biggest hit, with volumes down 45% from the year-earlier period, because it was the first struck by the outbreak, according to a report from broker Savills Plc. Investment dropped by 36% in the Americas and 19% in Europe, the Middle East and Africa. With the tourism industry shut down for months by government lockdowns, hotels saw investment decline by 59% in the first half of the year, followed by a 41% drop for retail properties, according to the Savills report. Industrial and residential properties fared better.
Investment is “expected to remain well below pre-pandemic levels for the rest of 2020 as investors wait for market clarity,” Simon Hope, Savills head of global capital markets, said in a statement on Monday. “However, certain sectors are expected to outperform as investors focus on secure assets, namely logistics, residential and life sciences.” The IMF has forecast that global GDP will shrink 4.9% this year as the pandemic wears on. IMF chief economist Gita Gopinath has said the cumulative loss for the world economy this year and next as a result of the recession is expected to reach $12.5 trillion. Still, the investment decline was less severe than at the start of the last financial crisis in the first half of 2008, when investment cratered by 49% and kept falling until the middle of 2009, Sophie Chick, director of Savills World Research team, said in the statement.

Good for the planet.
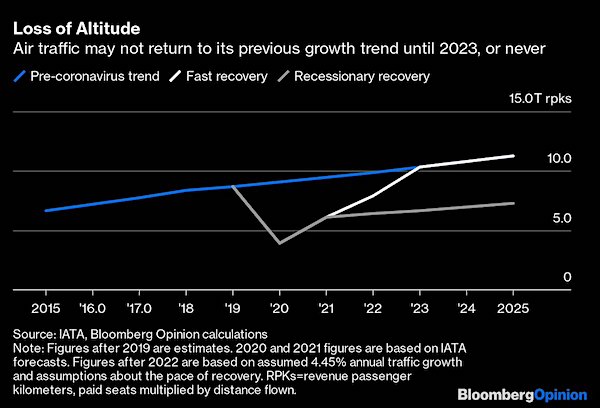
• Global Air Travel Demand Won’t Recover Till At Least 2023 – Moody’s (RT)
Airline passenger numbers are not expected to recover to the levels before the Covid-19 pandemic, which resulted in nationwide shutdowns around the world, for at least three years, Moody’s Investors Service warns. The drop in demand could last even longer as the recovery depends on how fast health and safety concerns are relieved, according to the agency’s recent research. Noting the rising number of infections across the US, Moody’s analysts said that passenger demand “may ultimately align with its slower recovery case, or worse,” if strict quarantine measures are reinforced. Airlines saw demand plunge by more than 90% shortly after the pandemic struck.
Given that the industry supports economic activity across many sectors, providing thousands of jobs and supporting fuel demand, the severe blow will affect a broad swath of the global economy “well into 2022 and beyond,” according to the report. “Passenger demand for air travel drives demand for key stakeholders in the aviation industry, including airport operators, aircraft leasing companies and aircraft manufacturers, as well as a multitude of service providers that keep airlines and airports running,” Moody’s Senior Vice President Jonathan Root said in a statement. He added that demand for the key stakeholders’ products and services may fall between 40 and 50 percent or even more this year, while they are expected to feel the impact of the coronavirus crisis for at least the next three years.
While the recovery for airlines and airports will be largely aligned, followed by aircraft lessors, plane makers will be the last to regain their 2019 footing. “To the extent that an environment characterized by fits and starts of health safety confidence levels and ensuing passenger demand persists beyond 2021, the risk of more extensive industry disruption and a more protracted recovery period would escalate further,” Moody’s Associate Managing Director Russell Solomon said.

Nothing that a new big bailout can’t fix.
• Boeing Is Running Out Of Space To Park Its Newly-Built 787 Dreamliners (ZH)
While Morgan Stanley continues to stubbornly repeat that the US economy is undergoing a jolly V-shaped recovery, one would be very hard pressed to observe that in either the number of airline passengers, or the commercial aerospace sector in general, where Boeing has become a poster child for how quickly the fate can turn… and it’s not just the company’s ill-fated Boeing 737 MAX which may or may not fly again. According to Bloomberg, Boeing is now also running out of space to stash newly-built 787 Dreamliners, as unsold jetliners are now crammed onto “every available patch of pavement on airfields near its factories in Washington and South Carolina.”
Citing people familiar with the situation, Bloomberg writes that “dozens of the planes are sitting on the company’s premises” with Uresh Sheth, a closely followed blogger who meticulously tracks the Dreamliners rolling through Boeing’s factories, putting the total somewhere above 50. That’s more than double the number of jets typically awaiting customers along Boeing’s flight lines. According to Sheth, brand-new widebodies are lined up on a closed off runway at the airport that abuts Boeing’s hulking plant north of Seattle. In North Charleston, 787s are tucked around the delivery center and a paint hangar. The U.S. planemaker has even started sending aircraft to be stored in a desert lot in Victorville, California.
Boeing’s troubles with parked jets are nothing new: last year Boeing had so many 737 Maxes after their global ground when it emerged that Boeing had drastically cut corners to save on costs even if it meant risking people’s lives, that it commandeered an employee parking lot to store surplus aircraft. Now, as it finally starts to emerge from that crisis, another critical source of cash – the company’s marquee jet, the 787 Dreamliner – is under pressure but not do to airworthiness concerns but simply due to the global depression that commercial air traffic has found itself in.

The rich governments have their rich voters to appease.
• ‘Diametrically Opposed Positions’ in EU On Coronavirus Rescue Package (EN)
There is still no agreement among EU leaders on a massive coronavirus recovery package after three days of intense meetings in Brussels. Leaders left the marathon summit early Monday morning and are set to resume talks at 16:00 CET. The summit was originally planned to end on Saturday. Talks have focussed on a proposed €1.68 trillion package, a seven-year budget and a coronavirus recovery fund. Eastern Europe leaders have opposed attaching rule of law conditions, while southern European countries are rejecting demands from the so-called frugal four, now five, countries – Netherlands, Austria, Finland, Sweden and Denmark – for a great sum bound by economic reform requirements.
EU Council President Charles Michel urged leaders to set aside disagreements on Sunday night. “Are the 27 EU leaders capable of building European unity and trust or, because of a deep rift, will we present ourselves as a weak Europe, undermined by distrust,” he said in a copy of the speech obtained by the AP. Early Monday morning, Austrian Prime Minister Sebastian Kurz tweeted that “tough negotiations had ended” but that leaders can be “very happy with today’s result.” Dutch prime minister Mark Rutte has provided the strongest opposition to the plans on the table – said to be insisting on a cap of €350 billion worth of grants – preferring loans of strict conditions.
The recovery fund had originally set €500 billion to be handed out as grants and €250 billion in loans. Differences were so great that Sunday’s resumption of talks by all 27 leaders together was pushed back several hours as small groups worked on new compromise proposals. “The actual size of the package in terms of the scale of the package and the balance within the package between grants and loans, that’s where significant disagreement still remains, notwithstanding movement yesterday and overnight,” said Irish Taoiseach, Micheál Martin. Luxembourg Prime Minister Xavier Bettel said in his seven years’ experience of European meetings he “had never seen positions as diametrically opposed as this.”

To an economist, everything may well look like an economics issue, because everything is about money, we get it. But is this really the appropriate time to discuss this? Is Southern Europe had been destroyed by a hurricane or an earthquake, would you want to have the same conversation? And we get it, the north has been hit too, but they’re in much better shape. The essence is that solidarity is not an economics issue, and perhaps that should chase economists away from the negotiating table. If you had just decided on coronabonds, none of this would have been necessary. It all simply shows that the north are determined to continue profiting from the south, and that solidarity is an alien concept to them.
• The “Frugal” Countries Are Right (Lacalle)
There is no solidarity without responsibility. The European Union Recovery Fund cannot be used as an excuse to perpetuate bloated political spending and create a transfer union where governments use taxpayers’ money to increase bureaucracy, because it would be the end of the European project. A union based on excess spending, debt and extractive policies would be destroyed in a few years. The strength of a unified group of countries comes from diversity and responsibility. No one denies the challenges created by the Covid-19 crisis, but there are countries that have used the excuse of the pandemic to inflate political spending and now demand free money.
The Spanish government has doubled the cost of government, maintained all the spending it increased during the growth period and increased the number of ministerial seats and advisors despite the crisis. Additionally, the government has approved a basic income plan that had no budget or fiscal space. There has been no management of costs whatsoever to allow budget room for automatic stabilizers, health, and unemployment costs. A government that increased the deficit in 2019 by 24% in a year of 2% GDP growth and record tax revenues has doubled the cost of government in the crisis and now demands no conditions or scrutiny from other member states.
Why would a serious government oppose a detailed scrutiny of the funds received? It should welcome it. Why would a government that calls itself reformist and states its commitment to budget stability reject any structural reform proposed by other member states? They should be implementing them now. Furthermore, why would a government that talks about an unprecedented emergency prefer to receive less funds than to accept the member states’ monitoring of grants? One could suspect that they are not aiming to use the funds in the most effective way.

We’ve heard that too much. You have 3.5 months.
• Meadows Signals Imminent Indictments In Durham Probe (Fox)
White House Chief of Staff Mark Meadows said Sunday that it’s “time for people to go to jail” as part of U.S. Attorney John Durham’s probe into FBI misconduct — prompting ex-Trump aide George Papadopoulos to sound a celebratory note on Twitter. The comments came as Fox News learned this weekend that Jennifer Boone, a senior FBI official who oversaw the flawed probe into former Trump adviser Carter Page, has received a major promotion to lead a field office — and the bureau won’t say why. Meadows, during his Sunday interview with Fox News’ “Sunday Morning Futures,” also previewed the Trump administration’s soon-to-be-released plans for reopening schools and implementing new economic stimulus measures.
More details, Meadows said, would be coming this week. However, Meadows’ comments on the Durham probe were among his most suggestive yet. They followed Attorney General Bill Barr’s comments to Fox News earlier this year that Durham’s findings have been “very troubling” and that familiar names are currently being probed. “I think the American people are expecting indictments,” Meadows told anchor Maria Bartiromo. “I expect indictments based on the evidence I’ve seen. Lindsey Graham did a good job in getting that out. We know that they not only knew that there wasn’t a case, but they continued to investigate and spy.”
Internal FBI documents that emerged in April showed that Peter Strzok — the now-disgraced anti-Trump former head of FBI counterintelligence — ordered the investigation of former National Security Adviser Michael Flynn to remain open even after it was slated to be closed due to a lack of so-called “derogatory” information. Strzok pursued an investigation based on the Logan Act, a law never used in a successful prosecution and that was intended to prevent individuals from falsely representing the U.S. government abroad in a pre-telephone era. “And yes, I use the word spy on Trump campaign officials and actually even doing things when this president was sworn in,” Meadows continued. “And after that and doing in an inappropriate manner, you’re going to see a couple of other documents come out in the coming days that will suggest that not only was the campaign spied on, but the FBI did not act appropriately as they were investigating. It’s all starting to come unraveled. And I tell you, it’s time that people go to jail and people are indicted.”

RussiaRussia every day. We mustn’t forget it.
• BBC’s Andrew Marr Suggests Scottish Independence Is A Russian Plot (Nat.)
In the latest bizarre series of rumours from Unionists, Andrew Marr has suggested that Scottish independence is a Russian plot. Marr asked Russian Ambassador Andrey Vladimirovich Kelin if he is “interested in the cause of Scottish nationalism” in an interview on his show. Kelin replied: “Our interest in Scotland is only one. We are open for business.” Marr said: “The reason I ask is that there are many people in this Government and the Conservative party at least, who feel that Russia is enthusiastic about breaking up the UK.”
That’s despite the Tories receiving £3.5 million from Russian donors, according to an invesigation in The Ferrett in November last year. It comes as a report is expected to reveal that Russian interference may have influenced the Brexit and independence referendums. The Russia report by the Intelligence and Security Committee (ISC), released on Tuesday, is expected to raise concerns about Moscow’s interference in aspects of Scottish politics. The development comes just days after Dominic Raab, the foreign secretary, revealed that Russian “actors” were highly likely to have interfered in December’s General Election.
Brilliant. Hoping v much I’ll have to deal with “you pursuing the right to national self-determination is actually a fiendish Russian plot” in next few years. Will have to adopt subtle Roosky signifiers to drive UK establishment nuts. Some kind of hat? pic.twitter.com/KTU5yXvx67
— Pat Kane (@thoughtland) July 19, 2020

We try to run the Automatic Earth on donations. Since ad revenue has collapsed, your support is now an integral part of the process.
Thank you.





Support the Automatic Earth in virustime.







