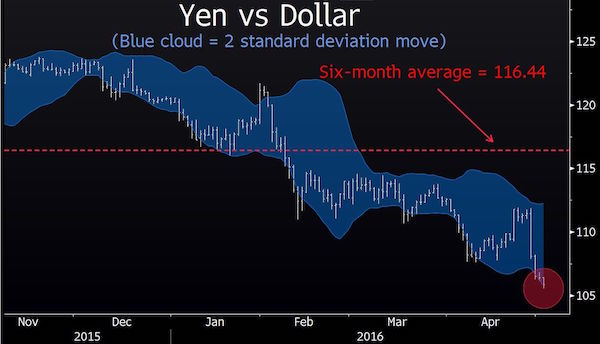
DPC Peanut stand, New York 1900



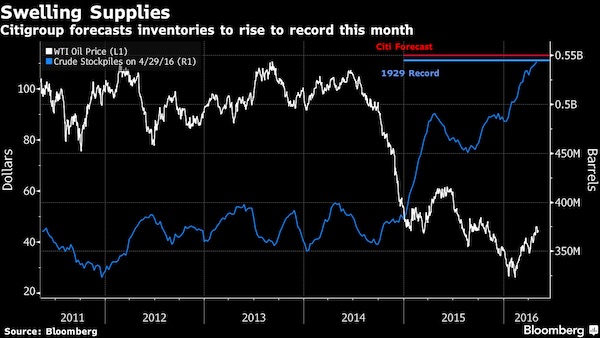
Panic in Riyadh.
• Saudi Arabia’s Oil ‘Maestro’ Exits As Young Prince Flexes Muscles
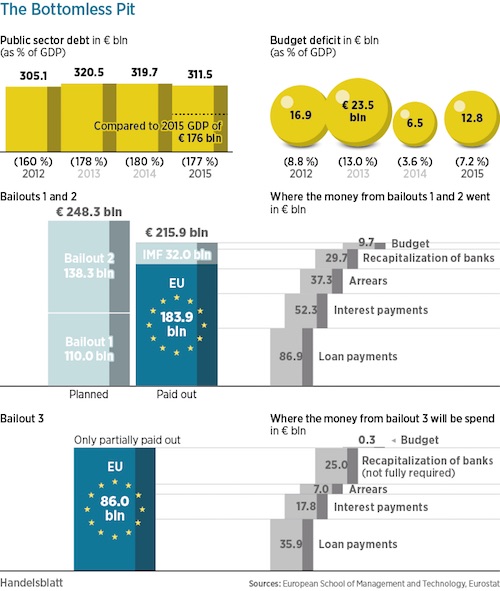
The end of Ali al-Naimi’s more than two-decade tenure as Saudi Arabia’s oil minister signals a new era for crude markets, analysts said on Saturday, and appeared to be a reaffirmation of Saudi policy to let oil set its own pricing. On Saturday, Saudi Arabia issued a royal decree that replaced al-Naimi with Khalid al-Falih, chairman of Saudi Aramco, as part of a broad reshuffling of the cabinet. The move came as the world’s largest oil producer continues to grapple with the fallout from the global bear market in crude oil. Al Naimi was the most watched figure in the oil world, and was often described as a “maestro” of the market. His utterances on production levels could swing prices and drive the direction of oil for months. Last month, a high-stakes summit in Doha between OPEC and non-OPEC producers failed to produce an agreement to freeze output, in what was seen as the product of tensions between Saudi Arabia and Iran.
The failure of Doha reinforced what many analysts have said for months: That the oil cartel was quickly losing its ability to set the agenda of world oil markets, and influence prices. Al-Naimi battled to manage the price of oil throughout his time as minister. In his absence, the Saudis may allow market forces to play a greater role in setting the cost of crude, according to observers. “What that means is you’ll have much more market volatility. You’ll have higher highs and lower lows if you don’t manage” crude prices, Pira Energy Group founder and executive chairman Gary Ross told CNBC on Saturday. Al-Naimi was a “stabilizing force,” and markets could react negatively to his absence, said Ross, who has known al-Naimi for more than 20 years. Although savvy observers say the aging al-Naimi was ready to vacate his post, the implications of the shake up are still far reaching. “The Saudi put is gone,” Ross added.

Say what? “..encouraging Saudis to spend money at home by creating more entertainment opportunities.”
• Saudi Shake-Up Rolls On With Big Reshuffle Of Economic Posts (R.)
Saudi Arabia’s King Salman on Saturday replaced his veteran oil minister and restructured some big ministries in a major reshuffle apparently intended to support a wide-ranging economic reform programme unveiled last week. The most eye-catching move was the creation of a new Energy, Industry and Natural Resources Ministry under Khaled al-Falih, chairman of the state oil company Aramco. He replaces the 80-year-old oil minister Ali al-Naimi, in charge of energy policy at the world’s biggest oil exporter since 1995. But major changes were also made to the economic leadership, with Majed al-Qusaibi named head of the new Commerce and Investment Ministry, and Ahmed al-Kholifey made governor of the Saudi Arabian Monetary Agency (SAMA), the central bank.
The changes, announced in a series of royal decrees, go far beyond Salman’s previous reshuffles since he became king in January last year, and also put the stamp of his son, Deputy Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman, author of the Vision 2030 reform programme, on the government. Prince Mohammed’s programme has been presented as a sweeping rethink of the entire way that Saudi Arabia’s government and economy will function to prepare for a future that is less dependent on oil income. Some of the most important elements of the plan, which will be fleshed out in coming weeks, involve creating a massive sovereign wealth fund, privatizing Aramco, cutting energy subsidies, expanding investment and streamlining government. The plan also seeks to boost revenues by increasing the number of foreign pilgrims outside the main annual Haj, and encouraging Saudis to spend money at home by creating more entertainment opportunities.

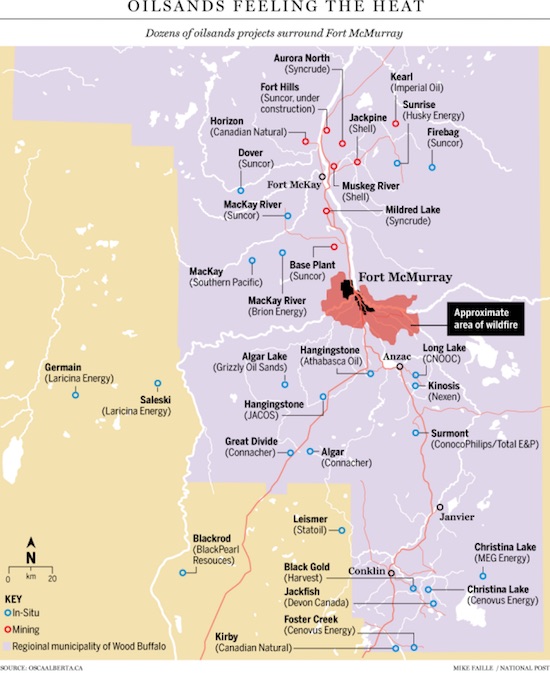
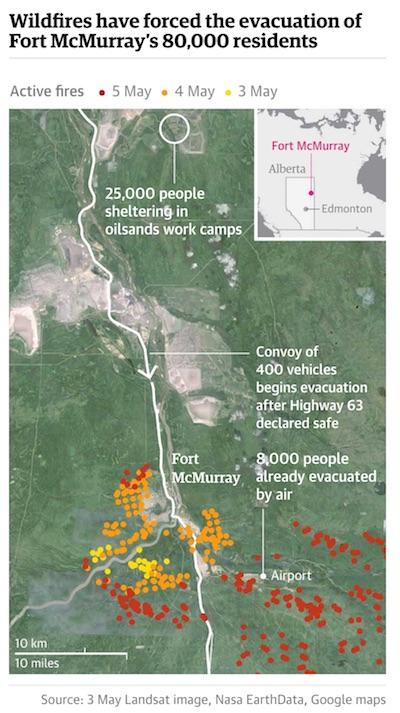
The Alberta blaze is so big smoke from the fire is being detected in Florida.. It’s now threatening to cross the border into both Sasketchewan and the Northwest Territories too. It’ll take months to get it under control.
• Canada Fire ‘Out Of Control,’ Doubles In Size (AFP)
A ferocious wildfire wreaking havoc in Canada doubled in size and officials warned that the situation in the parched Alberta oil sands region was “unpredictable and dangerous.” “This remains a big, out of control, dangerous fire,” Public Safety Minister Ralph Goodale said of the raging inferno bigger than London that forced the evacuation of the city of Fort McMurray. Winds were pushing the flames east of the epicenter around the oil city late Saturday, as nearly all 25,000 people who were still trapped to the north finally left town, either via airlift or convoys on the roads. The wildfire had doubled in size in one day, covering more than 200,000 hectares (494,000 acres) by midnight and continuing to grow, the Alberta Emergency Management Agency said in an update late Saturday. “Fire conditions remain extreme,” it said.
Low humidity, high temperatures nearing 30 degrees Celsius (86 Fahrenheit) and gusty winds of 40 kilometers (25 miles) in forests and brush dried out from two months of drought are helping fan the flames. Still, in a glimmer of positive news, the authorities have recorded no fatalities directly linked to the blaze that began almost a week ago. Cooler, moist air with some chance of rainfall could help slow the fires in the coming days, Alberta Fire Service director Chad Morrison said. However, “we need heavy rain,” he cautioned. “Showers are not enough.” The only “good news,” he said, was that the wind was pushing the fires away from Fort McMurray and oil production sites to the northeast, presenting less threat to people although causing serious damage to the environment.
The government has declared a state of emergency in Alberta, a province the size of France that is home to one of the world’s most prodigious oil industries. In the latest harrowing chapter, police convoys shuttling cars south to safety through Fort McMurray resumed at dawn. Making their way through thick, black smoke, the cars were filled with people trapped to the north of the city, having sought refuge there earlier in the week. Police wearing face masks formed convoys of 25 cars, with kilometers (miles) of vehicles, smoke swirling around them, patiently awaiting their turn. Separate convoys of trucks carried essential equipment to support “critical industrial services,” according to the Alberta government. With elevated risk that something could go wrong, the convoys along Highway 63 were reduced in size compared to the previous day.
Those being evacuated – for a second time, after first abandoning their homes – had fled to an area north of the city where oil companies have lodging camps for workers. But officials concluded they were no longer safe there because of shifting winds that raised the risk of them becoming trapped, and needed to move south to other evacuee staging grounds and eventually to Edmonton, 400 kilometers away. Some 2,400 vehicles made it to safety on Friday. But concerns are growing about the effect on the oil industry, the region’s economic mainstay, as the fires come dangerously close to extraction sites. Syncrude, one of several oil companies in the region, announced that it had shut down its facility 50 kilometers (31 miles) north of Fort McMurray due to smoke, followed by Suncor, after the local authorities ordered them to evacuate personnel. The military dispatched C130 aircraft to help evacuate 4,800 Syncrude employees.

Hard to see how the tar sands industry could ever be rebuilt.
• 70,000 Fort McMurray Foreign Workers May Have To Leave Canada (AFP)
Jonathan Infante fled for his life from wildfires ravaging Canada’s remote Athabasca oil-producing region, and now he and other migrant workers face the grim prospect of having to altogether leave Canada. Their residency here is tied to their employment and if that is now gone – literally up in smoke – they could be forced to leave this country. The wildfires in northern Alberta have forced the evacuation of 100,000 people. Among the evacuees were almost two dozen distraught migrant workers who arrived late Friday at a government shelter in Edmonton, Alberta’s capital. Marco Luciano of the migrant advocacy group Coalition for Migrant Worker Rights in Canada, who was on hand to greet them, said many showed up in their work uniforms.
“They had been evacuated from work and did not have time to stop at home to pick up any of their clothes or belongings,” Luciano told AFP. “They’re not sure what’s coming… Because they no longer have work, their (residency) status has become precarious.” “Many are bracing for the worst,” he said. Infante’s wages support a wife and two children back in the Philippines. The Wendy’s fast food restaurant in Fort McMurray where he worked is believed to have survived the wildfires, so far. “Our employer told us to wait and see,” Infante said outside an evacuation center in Lac La Biche, about 300 kilometers (185 miles) south of Fort McMurray. According to Luciano’s group, there are about 70,000 temporary foreign workers accredited in Alberta. There’s no breakdown available of how many were displaced by the fires.

“April imports dropped 10.9% from a year earlier, falling for the 18th consecutive month. ”
• China April Exports, Imports Decline More Than Expected (R.)
China’s exports fell more than expected in April, reversing the previous month’s brief recovery, as weak global demand weighed on trade out of the world’s second-largest economy. Exports fell 1.8% from a year earlier, the General Administration of Customs said on Sunday, supporting the government’s concerns that the foreign trade environment will be challenging in 2016. April imports dropped 10.9% from a year earlier, falling for the 18th consecutive month. The continued decline in imports suggests domestic demand remains weak, despite a pickup in infrastructure spending and record credit growth in the first quarter. China had a trade surplus of $45.56 billion in April, versus forecasts of $40 billion. [..]
An official factory survey and Caixin’s private-sector gauge for April painted a mixed picture of the health of the manufacturing sector. The official purchasing managers’ index (PMI) showed factory activity expanded for the second month in a row in April but only marginally, while Caixin’s manufacturing PMI pointed to 14 straight months of sector contraction. Concerns of a hard-landing in China had eased after the strong March economic data, but analysts have warned that the rebound may be short-lived. Economists expect a slowdown in credit growth and industrial production in April although inflation could accelerate. Key economic data is expected over the next two weeks. [..] Amid shrinking global demand, China still managed to grow its share of world exports to 13.8% last year from 12.3% in 2014, indicating the country’s export sector remains competitive despite higher costs.

“..I worry that it is discriminatory..” Well, what is more discriminatory? A person not being able to buy a second home, or a person not having access to any home?
• Britain Braced For A Ban On Second Homes (DM)
Councils across the UK are set to consider banning people who already own homes from buying holiday cottages after a historic vote yesterday. More than 80% of voters in St Ives, Cornwall, backed proposals that will mean new housing developments will only get planning permission if homes there are reserved for full-time residents. And now councils in the Lake District, Derbyshire Dales, north Devon and the Isle of Wight are all looking at schemes to prevent outsiders buying holiday homes. But ministers are poised to oppose the ban, saying it could be regarded as unfair and discriminatory. Tory MP Mark Garnier told The Times: ‘The only home I own is in St Ives but I live in rented properties elsewhere. Would it be considered as a second home? ‘I worry that it is discriminatory – that one person can buy a home but another can’t.’
The mayor of Aldeburgh on the Suffolk coast, Michael Kiff, admitted that he would be watching what happened in St Ives with interest, and Liberal Democrat MP Norman Lamb said that a vote to ban second homes would be ‘entirely justified’ in his North Norfolk constituency, which has a high percentage of holiday homes. The St Ives vote comes after figures revealed that 48% of homes in the town centre were second homes or holiday lets. Planning minister Brandon Lewis will meet the St Ives’ MP Derek Thomas on Monday to urgently discuss the ban – which is subject to a legal challenge by a firm of architects from Penzance. The town has been dubbed Kensington-on-Sea because of the number of rich holidaymakers who own houses there, and concerns were raised that local people in the town were struggling to stay in the area thanks to increasingly expensive house prices, and rents that spiral during the summer months.

You’d almost hope they try to push it through regardless. Germany badly needs a wake-up call that is not right-wing and racist.
• The TTIPing Point: German Protests Threaten Trade Deal (Spiegel)
As the battle over TTIP was lost, Angela Merkel feigned resolution yet one more time. “We consider a swift conclusion to this ambitious deal to be very important,” her spokesperson said on her behalf on Monday. And this is the government’s unanimous opinion. But the German population has a very different one. More than two-thirds of Germans reject the planned trans-Atlantic free trade agreement. And even in circles within Merkel’s cabinet, the belief that TTIP will ever become a reality in its currently planned form is disappearing. That’s because on Monday morning, Greenpeace published classified documents from the closed-door negotiations. Even if the papers only convey the current state of negotiations and do not document the end results, they still confirm the worst suspicions of critics of TTIP.
The 248 pages show that bargaining is taking place behind the scenes, even in areas which the EU and the German government have constantly maintained were sacrosanct. These include standards on the environment and consumer protection; the precautionary principle, a stricter EU policy that sets high hurdles for potentially dangerous products; the legislative self-determination of the countries involved, etc. Even the pledge made on the European side that there would be no arbitration courts has turned out to be wishful thinking. So far, the Americans have insisted on the old style of arbitration court. The result is that Merkel’s grandly staged meeting with US President Barack Obama in Hanover eight days earlier had been nothing more than a show – one aimed at hiding the fact that the two sides are anything but united in their positions.
The leaks have resulted in a failed attempt to bypass 800 million European citizens as they negotiate the world’s largest bilateral free trade agreement. From the very beginning, the government underestimated the level of resistance these incursions on virtually all aspects of life would unleash among the people. What began as a diffuse discomfort over opaque backroom dealings grew into a true public initiative, especially in Germany. It was fueled by an international alliance of non-government organizations that has acted in a more professional and networked way than anything that has come before.

We need discussions on this. Big ones. On pensions and on health care. But we’re not having them. Not everything can be optimized for profit. What happens when the profit is gone, what happens when the economy crashes? We’re going to dump our elderly?
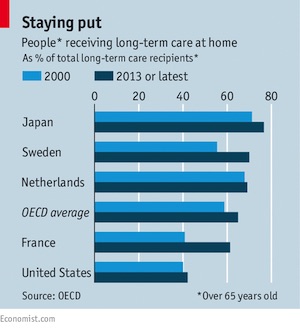
• Is For-Profit Care For The Elderly The Answer? (Economist)
The forecasts are clear: by 2050 the number of people aged over 80 will have doubled in OECD countries, and their share of the population will rise from 3.9% to 9.1%. Around half will probably need help with daily tasks—particularly those with enduring chronic illnesses such as Alzheimer’s, heart disease and osteoporosis. Health systems designed only to offer hospital care for acute cases will struggle to provide such support. To maintain the well-being of wrinkly populations, hospital stays can be replaced by residencies in purpose-built facilities at less cost. A forthcoming report covering 20 countries from KPMG, a consultancy, suggests the number of care-home residents could grow by 68% over the next 15 years. How care is managed in any one country reflects a tussle between cultural attitudes, national budgets and gritty demographic realities.
The increasing availability of technology that would allow the elderly to stay in their homes for longer will also affect demand for such options. Residential care in America and Japan is flourishing. But in an era of tight public finances, some governments are trimming the payments they offer to cover, or subsidise, care-home places. Some operators now struggle to make money; in western Europe, for example, governments are encouraging the elderly to stay in their own houses for longer. This is why the length of stays in care homes has declined from an average of three to four years a decade ago to 12 to 18 months today, says Max Hotopf, the boss of Healthcare Business International, a publishing company. Thousands of residential beds in the Netherlands and Sweden have disappeared as a result. About 5,000 debt-laden British care homes—a quarter of the total—may close within three years.
This makes emerging markets a more attractive prospect, at least for European care firms. Senior Assist, a Belgian company which manages residential facilities and home help, is now expanding in Chile and Uruguay. But China is the big prize. The Chinese will rely heavily on residential care, thanks to the country’s one-child policy and increasing urbanisation: two parents and four grandparents often depend on one child far away. Families in other developing countries are more hesitant about handing Granny over to strangers, however. In Brazil, India and richer countries of the Middle East, such as Saudi Arabia, elderly care remains centred around hospitals. In Brazil taking the old from their neighbourhoods is frowned upon. In India and the Middle East, families are expected to look after their elderly when they are not in hospital.

Let’s make our armies do something useful.
• On The Frontline Of Africa’s Wildlife Wars (G.)
Brigadier Venant Mumbere Muvesevese, a 35-year-old father of four, became the 150th ranger in the last 10 years to be killed protecting lowland gorillas, elephants and other wildlife in Virunga national park last month. He and his young Congolese colleague, Fidèle Mulonga Mulegalega, were surrounded by local militia, captured and then summarily executed. For Emmanuel de Mérode, the Belgian head of Virunga, himself shot and wounded by militia in 2014, the two killings in Africa’s oldest park, in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, were yet another atrocity in the brutal wildlife wars raging through southern Sudan, the Central African Republic, Congo and parts of Uganda, Chad and Tanzania. “These two rangers were killed in situations that may amount to war crimes in any other conflict,” he said. “We cannot sustain these kind of losses in what is still the most dangerous conservation job in the world.”
Virunga has lost five rangers so far this year. Speaking to the Observer from the park’s fortified HQ in Goma, De Mérode said security had got worse in recent months. “We lost people in January, too. We have a state of armed conflict, a low-intensity war being fought over the exploitation of natural resources in the park,” he said. “For the rangers it is not impossible to work, but it is now very dangerous. We are training 100 new rangers now and there will be 120 more next year. We are still very committed and optimistic.” The battle for central Africa’s wildlife has exploded as heavily armed militia target elephants and rhino and gun down anyone trying to protect them. Three rangers were killed and two wounded in a shootout in the vast Garamba national park in DRC last week; others were killed in Kahuzi-Biéga park near the city of Bukavu in March; in northern Tanzania, poachers killed British helicopter pilot Roger Gower in January.
The five rangers shot in Garamba were working for African Parks, a Johannesburg-based nonprofit conservation group that sends South African and other military officials to train rangers in the 10 wildlife parks it manages on behalf of governments. According to Peter Fearnhead, African Parks director, Garamba is now the heart of the illegal African wildlife trade. Its 300-odd armed guards combat helicopters and drones and find poachers from as far afield as the Central African Republic, Uganda, Sudan, Chad, Somalia, Kenya and Tanzania. “We have lost probably 30 people in Garamba alone in seven years. Hundreds of elephants are killed every year. This is the last stronghold of elephant and giraffe in Congo, but probably the toughest park in Africa. Every elephant poached can turn into a firefight,” said Fearnhead. “Life for a wildlife ranger is now very dangerous in some countries, probably more risky than being in a national army.”
[..] “Last week we buried three people but morale is as strong as ever. When [the rangers] were told that their colleagues had been shot, they all wanted to respond. The poachers use automatic weapons, even grenades. Being a ranger is not about chasing people through the bush and arresting them. It’s war. The rangers put their lives on the line every day, and are under real siege in Garamba. We are not militia but it requires a militaristic response to defend wildlife. [Groups of militia] are now bidding for contracts to get tons of ivory. It’s big business with groups of armed people crossing multiple borders. These people have phenomenal bush skills, with AK-47s. They shoot for the head. They are a total law unto themselves.”

Stop talking and do it already.
• German Vice Chancellor Urges Debt Relief For Greece (R.)
German Vice Chancellor Sigmar Gabriel urged euro zone finance ministers to start talks on debt relief for Greece, saying it made no sense to crush the green shoots of economic recovery with further austerity measures. The finance ministers of the euro zone’s 19 countries are due to meet in Brussels on May 9 to discuss Greece’s debt and a new set of contingency measures that Athens should adopt to ensure it will achieve agreed fiscal targets in 2018. “The euro group meeting on Monday must find a way to break the vicious circle,” Gabriel, who is also Economy Minister, said in an emailed statement to Reuters on Saturday. “Everyone knows that this debt relief will have to come at some point. It makes no sense to shirk from that time and time again,” he added.
The IMF wants Greece’s European partners to grant Athens substantial relief on its debt, which it sees as vital for its long term sustainability. But Germany’s hardline Finance Minister Wolfgang Schaeuble opposes any debt relief, arguing it is not necessary. Thrice-bailed-out Greece needs to secure an overdue aid payment of €5 billion to repay IMF loans, bonds held by the ECB maturing in July, and growing state arrears. “It doesn’t help the people and the country to have to fight every 12 months to get new credit to pay off old loans,” Gabriel said. “Greece needs debt relief.” Gabriel spoke out against further austerity measures and said Athens had managed to achieve better economic growth than expected. “It makes no sense to destroy these tender shoots once again with new austerity measures,” he added.

“Tsakalotos warned of the price of a “failed state” if the crucial talks on Monday run aground.”
• Greece Has ‘Basically Achieved’ Reform Goals, Says Juncker (AFP)
Greece has “basically achieved” the objectives of the reforms required by its creditors and its eurozone partners will begin discussing possible debt relief for the country, according to European Commission head Jean-Claude Juncker. “We are now at the time of the first review of the programme (to aid Greece) and the objectives have been basically achieved,” Juncker said in an interview to be published on Sunday in Funke Mediengruppe newspapers in Germany. Greece’s creditors carried out the review intended to evaluate progress on reforms by the Athens government as it hopes to unlock the next tranche of its €86bn bailout agreed in July. The Eurogroup, comprised of the 19 finance ministers of the euro area countries, is set to meet on Monday in Brussels and take up this review of Greek reforms.
They will also “start the first discussions about how to make Greece’s debt sustainable in the long term”, Juncker told the German papers. Approval of the reforms is needed before any consideration of Greek debt relief, but despite months of talks, Greece’s reforms have yet to win the backing of all its creditors largely due to differences between the EU and the IMF, which has demanded more reforms. Juncker’s comments come as Greek finance minister Euclid Tsakalotos Saturday called on his eurozone partners to back Greece’s reform package of cuts worth €5.4 billion, and to put aside the creditors’ call for €3.6 billion of additional measures. “Any package in excess of €5.4 billion is bound to be seen by both Greek citiziens and economic agents, within and beyond Greece, as socially and economically counter-productive,” he wrote in a letter to the Eurogroup. Tsakalotos warned of the price of a “failed state” if the crucial talks on Monday run aground.

History rhymes.
• 1,700 Years Ago, Mismanagement Of A Migrant Crisis Cost Rome Its Empire (Q.)
On Aug. 3, 378, a battle was fought in Adrianople, in what was then Thrace and is now the province of Edirne, in Turkey. It was a battle that Saint Ambrose referred to as “the end of all humanity, the end of the world.” The Eastern Roman emperor Flavius Julius Valens Augustus—simply known as Valens, and nicknamed Ultimus Romanorum, (the last true Roman)—led his troops against the Goths, a Germanic people that Romans considered “barbarians,” commanded by Fritigern. Valens, who had not waited for the military help of his nephew, Western Roman emperor Gratian, got into the battle with 40,000 soldiers. Fritigern could count on 100,000. It was a massacre: 30,000 Roman soldiers died and the empire was defeated. It was the first of many to come, and it’s considered as the beginning of the end of the Western Roman Empire in 476.
At the time of the battle, Rome ruled a territory of nearly 600 million hectares, with a population of over 55 million. The defeat of Adrianople didn’t happen because of Valens’s stubborn thirst for power or because he grossly underestimated his adversary’s belligerence. What was arguably the most important defeat in the history of the Roman empire had roots in something else: a refugee crisis. Two years earlier the Goths descended toward Roman territory looking for shelter. The mismanagement of Goth refugees started a chain of events that led to the collapse of one of the biggest political and military powers humankind has ever known. It’s a story shockingly similar to what’s happening in Europe right now—and a it should serve as a cautionary tale.