NPC George W. Cochran & Co., 709 14th Street NW, Washington DC 1920

Apparently Kuroda doesn’t buy enough yet.
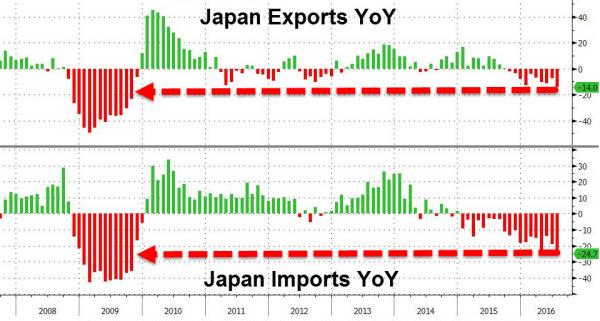
• Japanese Imports Drop -24.7%, Exports Crash -14.1% (ZH)
For the 19th month in a row, Japanese Imports plunged – dropping 24.7% YoY (worse than expected), the biggest drop since Oct 2009. Exports were just as dismal, also missing expectations, plunging 14.1% YoY – worst since Oct 2009. The biggest driver of the collapse of Japanese trade was a 44% crash in the Chinese trade balance. There’s no lipstick to put on this pig… it’s a disaster.. and worse still Yen is strengthening back below 100 against the USD.
Read more …

Why not simply admit that central bankers and economists alike have no idea what they’re doing?! Even if they ever had a clue, we’re now 8 years into ‘uncharted territory’, and it’s all anyone‘s guess. That’s what ‘uncharted territory’ means.
Moreover, central bankers and economists come in with dogmatic school book theories that don’t apply in ‘uncharted territory’, and those school book educations make sure they’re the very last candidates for finding creative solutions. Comparing economics to actual science does not help one bit.
• A Physics Lesson for Central Bankers (BBG)
The world is braced for the discovery of a fifth fundamental forces of nature – the four known ones being electromagnetism, gravity, and strong and weak nuclear forces – that subverts the so-called standard model of particle physics. Given the lackluster outlook for global growth, maybe economics needs a similar revolution. Quantitative easing’s failure to quash the threat of deflation is finance’s equivalent of the bump in the data that alerted physicists to the possibility of a new boson. The mismatch between economic theory and the real-world outcome of zero interest rates poses a direct challenge to the current orthodoxy that puts a 2% inflation target at the heart of monetary policy in most of the developed world.
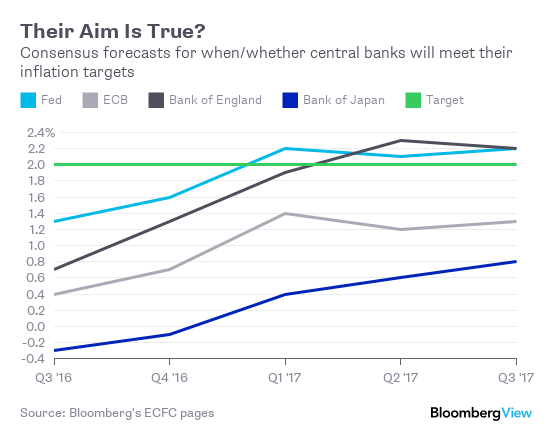
Figures earlier this week showed inflation running at an annual pace of just 0.8% in the U.S. and 0.6% in the U.K. Consumer prices in the euro zone are rising by about 0.2% a year; in Japan, prices dropped by 0.4% in June. The consensus forecast among economists surveyed by Bloomberg News is for none of the four central banks in those regions to meet their targets in 2016, and for the ECB and the BOJ to continue falling short for at least the next year:
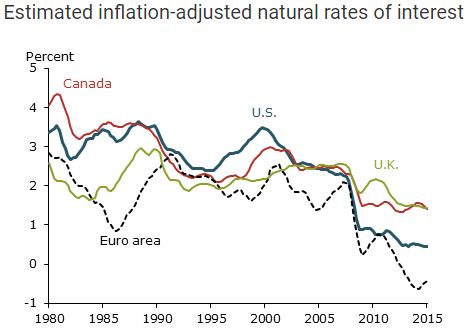
Years of pumping trillions of dollars, euros, yen and pounds into the economy by buying government debt and other securities hasn’t produced the rebound in inflation that economics textbooks predicted. Record low borrowing costs haven’t led to a surge in investment and spending that would lead to higher prices. That’s the kind of empirical evidence that should produce a reconsideration of what Rothschild Investment Trust Chairman Jacob Rothschild this week called “the greatest experiment in monetary policy in the history of the world.” Neil Grossman, director of Florida-based bank C1 Financial and former chief investment officer at TKNG Capital Partners, likens the need to abandon the current economic orthodoxy with the impact of quantum physics on science in the last century.
Read more …

“There is no science to this 2% number, it is all art.”
• The Idea Of The Fed Raising The Inflation Target Is Outrageous (Boockvar)
I can’t let an opportunity go by without criticizing a Fed official. I believe their feet should be held to the fire after creating a huge asset price bubble and culture of debt that is dragging down economic growth. Fed President John Williams comments yesterday really got me angry. First, he suggested possibly raising the Fed’s 2% inflation target. This reflects an amazing cluelessness of the damage this would do if realized. We are in an epic bond bubble globally where higher inflation would be kryptonite. With the bond monster central bankers have created, the last thing they should want is higher inflation. Also, many U.S. citizens are literally living paycheck to paycheck and a higher cost of living without a corresponding increase in wages or any interest income would damage the largest component of the U.S. economy and the lives of millions.
Second, he said, “Conventional monetary policy has less room to stimulate the economy during an economic downturn.” This we know is true. But he then added, “This will necessitate a greater reliance on unconventional tools like central bank balance sheets, forward guidance, and potentially even negative policy rates.” This last sentence proves he’s blind to the negative consequences of what unconventional tools have wrought and he believes in negative rates even in the face of all the evidence of how damaging the idea is. Let me expand on the first issue of inflation. Central banks in the U.S., Eurozone, UK and in Japan have tethered their monetary policy decisions on growth certainly but also the desire for 2% annual inflation. There is no science to this 2% number, it is all art.
The reason for this target and desire for this level of inflation is a matter of control. While they like to keep interest rates artificially low, they also understand the need to have them higher than they are in order to respond to any economic challenges. The fallacy with this theory that higher inflation is good and deflation is bad, is inflation is just a symptom of underlying supply and demand and technological improvements, and thus shouldn’t be manipulated.
Read more …

Stockman: “..earnings had fallen by 19% since then, even as the stock market moved from 1950 to nearly 2200 or 13% higher..”
• On The Impossibility Of Helicopter Money And Why The Casino Will Crash (DS)
[..] .. the S&P 500 companies posted Q2 2016 earnings for the latest 12 month period at $86.66 per share. So at the August bubble high the market was being valued at a lunatic 25.1X. Even in a healthy, growing economy that valuation level is on the extreme end of sanity. But actual circumstances are currently more nearly the opposite. That is, earnings have now been falling for six straight quarters in line with GDP growth that has slumped to what amounts to stall speed. In fact, reported earnings for the S&P 500 peaked at $106 per share in the 12 months ended in September 2014. That means that earnings had fallen by 19% since then, even as the stock market moved from 1950 to nearly 2200 or 13% higher.
This is called multiple expansion in the parlance of Wall Street, but it’s hard to find a more bubblicious example. Two years ago the market was trading at just 18.4X, meaning that on the back of sharply falling earnings the PE multiple had risen by 36%! Valuation multiples are supposed to go up only when the economic and profits outlook is improving, not when it’s unmistakably deteriorating as at present. But during the spring-summer melt-up these faltering fundamentals were blithely ignored on the hopes of a second half growth spurt and, failing the latter, that the Fed would again pull the market’s chestnuts out of the fire.
Read more …

Time for Yellen to buy those stocks? Buybacks were the no. 1 reason the S&P looked good till now. Better find something to replace them, or else…
• US Buyback Announcements Tumble to a 2012 Low (BBG)
Stock buybacks appear to be slowing down, suggesting either corporate America’s outlook has dimmed, stock valuations have become prohibitively high or, most optimistically, that companies are starting to listen to investors and put funds toward other uses. Buybacks announced for the second quarter’s earnings season between July 8 and August 15 totaled an average of $1.8 billion a day, the lowest volume in an earnings season since the summer of 2012, according to TrimTabs Investment Research.
Share repurchases have been a key driver of this year’s stock market rally, despite a notable deceleration relative to to the same period in 2015. In the first seven months of 2016, buybacks totaled $376.5 billion, according to TrimTabs.
That’s down 21% from $478.4 billion in the first seven months of last year. Equity buybacks last week totaled just $2.6 billion, while record highs in U.S. stocks triggered an increase in new equity offerings. “The reluctance to pull the trigger on share repurchases suggests corporate leaders are becoming less enthusiastic about what they see ahead,” David Santschi, chief executive officer of TrimTabs, said in a press release on Tuesday. That means “buybacks aren’t likely to provide as much fuel for the stock market as they have in the recent past.” According to TrimTabs, just five companies have announced buybacks of more-than $3 billion this earnings season: Biogen ($5 billion), Visa ($5 billion), CBS ($5 billion), AIG ($3 billion), and 21st Century Fox ($3 billion).
Read more …

Hard to admit to something that will cost you your livelihood. They all keep hoping for rising prices.
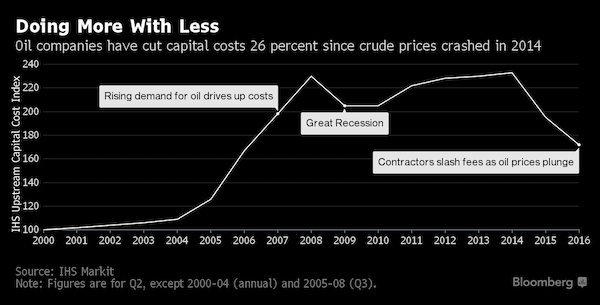
• Oil Drillers Have Slashed Spending For 2015-2020 By $1 Trillion
Mad Dog, BP’s drilling project deep in the Gulf of Mexico, could be Exhibit A in the oil industry’s war on cost. When the British oil giant announced the project’s second phase in 2011, it put the price at $20 billion. Last month, after simplifying plans and benefiting from a sharp drop in everything from steel to drilling services, Chief Executive Officer Bob Dudley said he could do the job for $9 billion.
Across the industry, companies have taken a chainsaw to expenses, slashing spending for the 2015-to-2020 period by $1 trillion through cutting staff, delaying projects, changing drilling techniques and squeezing outside contractors, according to consulting firm Wood Mackenzie. That’s cushioned businesses as oil prices plunged 60% since 2014. Now producers seek to show they can make the savings stick, while service providers try to reverse their losses. Industry costs “may be the defining issue of the next six to 12 months,” said J. David Anderson, a Barclays analyst in New York. “As you start ramping up, the fact is you’re going to need more services and they’re going to have to come in at a higher price.”
Read more …

Someone will come with an across the board forgiveness plan. But it’ll be contentious.
• Only 37% Of Borrowers Are Paying Down Their Student Loans (WSJ)
A largely overlooked report released in February by the Government Accountability Office suggests that the Obama administration’s policies have exacerbated student debt, which equals nearly a quarter of annual federal borrowing. With only 37% of borrowers actually paying down their loans, the federal student-loan program more closely resembles the payday-lending industry than a benevolent source of funds for college. As this newspaper reported in April, “43% of the roughly 22 million Americans with federal student loans weren’t making payments as of Jan. 1,” and a staggering “1 in 6 borrowers, or 3.6 million, were in default on $56 billion in student debt.”
If student debt continues to skyrocket, the federal government may have to deal with as much as a $500 billion write-down when future defaults and loan-forgiveness programs are factored in. In 2010, the Obama administration dispensed with the private intermediaries that had administered federal loans since the 1960s. It put in their place Direct Lending, a program administered by the Education Department. At the time, the Congressional Budget Office estimated that Direct Lending would save $62 billion from 2010 to 2020. That didn’t happen. The program’s advocates failed to anticipate how two other Obama-backed college affordability initiatives—Income-Driven Repayment and loan forgiveness—would create a cataclysmic hit to the federal student-loan program’s finances.
There are more than 20 Income-Driven Repayment programs, but they all work essentially the same way. Students struggling financially can defer their payments. When no or limited payments are made, their balances grow. Today, over 20 million borrowers are watching their loan balances increase thanks to these programs. The average balance ballooned to approximately $25,000 in 2014 from $15,000 in 2004, according to the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and has grown still larger since then.
Read more …

In their dreams.
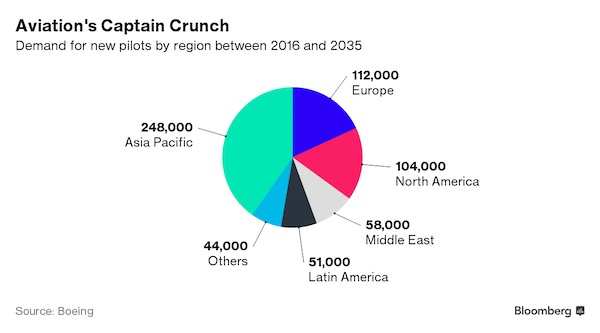
• Chinese Airlines Need To Hire 100 Pilots A Week For The Next 20 Years (BBG)
Chinese airlines need to hire almost 100 pilots a week for the next 20 years to meet skyrocketing travel demand. Facing a shortage of candidates at home, carriers are dangling lucrative pay packages at foreigners with cockpit experience. Giacomo Palombo, a former United Airlines pilot, said he’s being bombarded every week with offers to fly Airbus A320s in China. Regional carrier Qingdao Airlines promises as much as $318,000 a year. Sichuan Airlines, which flies to Canada and Australia, is pitching $302,000. Both airlines say they’ll also cover his income tax bill in China. “When the time to go back to flying comes, I’ll definitely have the Chinese airlines on my radar,” said Palombo, 32, now an Atlanta-based consultant for McKinsey. “The financials are attractive.”
Air traffic over China is set to almost quadruple in the next two decades, making it the world’s busiest market, according to Airbus Group SE. Startup carriers barely known abroad are paying about 50% more than what some senior captains earn at Delta Air Lines, and they’re giving recruiters from the U.S. to New Zealand free rein to fill their captains’ chairs. With some offers reaching $26,000 a month in net pay, pilots from emerging markets including Brazil and Russia can quadruple their salaries in China, said Dave Ross, Las Vegas-based president of Wasinc International. Wasinc is recruiting for more than a dozen mainland carriers, including Chengdu Airlines, Qingdao Airlines and Ruili Airlines. “When we ask an airline, ‘How many pilots do you need?,’ they say, ‘Oh, we can take as many as you bring,”’ Ross said. “It’s almost unlimited.”
Read more …

Incredible, but he really said it: “..there’s not a single case where hydraulic fracking has created an environmental problem for anyone..”
• Hillary Clinton Picks TPP and Fracking Advocate To Set Up Her White House (IC)
Two big issues dogged Hillary Clinton during the Democratic primary: the Trans-Pacific Partnership trade agreement (TPP) and fracking. She had a long history of supporting both. Under fire from Bernie Sanders, she came out against the TPP and took a more critical position on fracking. But critics wondered if this was a sincere conversion or simply campaign rhetoric. Now, in two of the most significant personnel moves she will ever make, she has signaled a lack of sincerity. She chose as her vice presidential running mate Tim Kaine, who voted to authorize fast-track powers for the TPP and praised the agreement just two days before he was chosen.
And now she has named former Colorado Democratic Senator and Interior Secretary Ken Salazar to be the chair of her presidential transition team — the group tasked with helping set up the new administration should she win in November. That includes identifying, selecting, and vetting candidates for over 4,000 presidential appointments. As a senator, Salazar was widely considered a reliable friend to the oil, gas, ranching and mining industries. As interior secretary, he opened the Arctic Ocean for oil drilling, and oversaw the botched response to the BP oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico. Since returning to the private sector, he has been an ardent supporter of the TPP, while pushing back against curbs on fracking.
The TPP would enhance the ability of corporations to sue to overturn environmental regulations, but Salazar helped a pro-TPP front group, the “Progressive Coalition for American Jobs,” argue the opposite. In a November 2015 USA Today op-ed that Salazar co-wrote with Bruce Babbitt, the two men argued that the TPP would be the “the greenest trade deal ever” by promoting sustainable energy. Both Salazar and Babbitt cited their former positions as interior secretaries to boost their credibility. The following month, Salazar authored a Denver Post op-ed with two former Colorado governors also affiliated with PCAJ, arguing that the agreement would protect the state’s scenic beauty: “And as a state rich with natural wonder and a long history of conservation, Colorado can be proud that the TPP includes the highest environmental standards of any trade agreement in history.”
Shortly after leaving his post at the Obama administration, Salazar appeared at an oil and gas industry conference to argue in favor of fracking. “We know that, from everything we’ve seen, there’s not a single case where hydraulic fracking has created an environmental problem for anyone,” Salazar told the attendees, who included the vice president of BP America, another keynote speaker at the conference. “We need to make sure that story is told.”
Read more …

Not confirmed. But moving them out of Turkey seems logical. Not exactly a safe third country these days.
• Is US Moving Nuclear Weapons From Turkey to Romania? (EurA)
Two independent sources told EurActiv.com that the US has started transferring nuclear weapons stationed in Turkey to Romania, against the background of worsening relations between Washington and Ankara. According to one of the sources, the transfer has been very challenging in technical and political terms. “It’s not easy to move 20+ nukes,” said the source, on conditions of anonymity. According to a recent report by the Simson Center, since the Cold War, some 50 US tactical nuclear weapons have been stationed at Turkey’s Incirlik air base, approximately 100 kilometres from the Syrian border.
During the failed coup in Turkey in July, Incirlik’s power was cut, and the Turkish government prohibited US aircraft from flying in or out. Eventually, the base commander was arrested and implicated in the coup. Whether the US could have maintained control of the weapons in the event of a protracted civil conflict in Turkey is an unanswerable question, the report says. Another source told EurActiv.com that the US-Turkey relations had deteriorated so much following the coup that Washington no longer trusted Ankara to host the weapons. The American weapons are being moved to the Deveselu air base in Romania, the source said. Deveselu, near the city of Caracal, is the new home of the US missile shield, which has infuriated Russia.
Read more …

It doesn’t sit well with me at all that the NYT editors are saying this. Far too much blood on those hands. It doesn’t feel right one bit.
• America Is Complicit in the Carnage in Yemen (NYT Editorial Board)
A hospital associated with Doctors Without Borders. A school. A potato chip factory. Under international law, those facilities in Yemen are not legitimate military targets. Yet all were bombed in recent days by warplanes belonging to a coalition led by Saudi Arabia, killing more than 40 civilians. The United States is complicit in this carnage. It has enabled the coalition in many ways, including selling arms to the Saudis to mollify them after the nuclear deal with Iran. Congress should put the arms sales on hold and President Obama should quietly inform Riyadh that the United States will withdraw crucial assistance if the Saudis do not stop targeting civilians and agree to negotiate peace.
The airstrikes are further evidence that the Saudis have escalated their bombing campaign against Houthi militias, which control the capital, Sana, since peace talks were suspended on Aug. 6, ending a cease-fire that was declared more than four months ago. They also suggest one of two unpleasant possibilities. One is that the Saudis and their coalition of mostly Sunni Arab partners have yet to learn how to identify permissible military targets. The other is that they simply do not care about killing innocent civilians. The bombing of the hospital, which alone killed 15 people, was the fourth attack on a facility supported by Doctors Without Borders in the past year even though all parties to the conflict were told exactly where the hospitals were located.
In all, the war has killed more than 6,500 people, displaced more than 2.5 million others and pushed one of the world’s poorest countries from deprivation to devastation. A recent United Nations report blamed the coalition for 60% of the deaths and injuries to children last year. Human rights groups and the United Nations have suggested that war crimes may have been committed.
Read more …

Today Yemen, yesterday California. Maybe if we stop trying to hide the past, we’re less likely to repeat it?!
• California Slaughter: The State-Sanctioned Genocide of Native Americans (NW)
The tally is relentlessly grim: a whole settlement wiped out in Trinity County “excepting a few children”; an Indian girl raped and left to die somewhere near Mendocino; as many as 50 killed at Goose Lake; and, two months later, as many as 257 murdered at Grouse Creek, scores of them women and children. There were the four white ranchers who tracked down a band of Yana to a cave, butchering 30. “In the cave with the meat were some Indian children,” reported a chronicle published later. One of the whites “could not bear to kill these children with his 56-calibre Spencer rifle. ‘It tore them up so bad.’ So he did it with his 38-calibre Smith and Wesson revolver.”
Read more …

We might as well stop speaking about western ‘civilization’.
• Uncovering The Brutal Truth About The British Empire (G.)
Help us sue the British government for torture. That was the request Caroline Elkins, a Harvard historian, received in 2008. The idea was both legally improbable and professionally risky. Improbable because the case, then being assembled by human rights lawyers in London, would attempt to hold Britain accountable for atrocities perpetrated 50 years earlier, in pre-independence Kenya. Risky because investigating those misdeeds had already earned Elkins heaps of abuse. Elkins had come to prominence in 2005 with a book that exhumed one of the nastiest chapters of British imperial history: the suppression of Kenya’s Mau Mau rebellion. Her study, Britain’s Gulag, chronicled how the British had battled this anticolonial uprising by confining some 1.5 million Kenyans to a network of detention camps and heavily patrolled villages.
It was a tale of systematic violence and high-level cover-ups. It was also an unconventional first book for a junior scholar. Elkins framed the story as a personal journey of discovery. Her prose seethed with outrage. Britain’s Gulag, titled Imperial Reckoning in the US, earned Elkins a great deal of attention and a Pulitzer prize. But the book polarised scholars. Some praised Elkins for breaking the “code of silence” that had squelched discussion of British imperial violence. Others branded her a self-aggrandising crusader whose overstated findings had relied on sloppy methods and dubious oral testimonies. By 2008, Elkins’s job was on the line. Her case for tenure, once on the fast track, had been delayed in response to criticism of her work.
To secure a permanent position, she needed to make progress on her second book. This would be an ambitious study of violence at the end of the British empire, one that would take her far beyond the controversy that had engulfed her Mau Mau work. That’s when the phone rang, pulling her back in. A London law firm was preparing to file a reparations claim on behalf of elderly Kenyans who had been tortured in detention camps during the Mau Mau revolt. Elkins’s research had made the suit possible. Now the lawyer running the case wanted her to sign on as an expert witness. Elkins was in the top-floor study of her home in Cambridge, Massachusetts, when the call came. She looked at the file boxes around her. “I was supposed to be working on this next book,” she says. “Keep my head down and be an academic. Don’t go out and be on the front page of the paper.”
She said yes. She wanted to rectify injustice. And she stood behind her work. “I was kind of like a dog with a bone,” she says. “I knew I was right.” What she didn’t know was that the lawsuit would expose a secret: a vast colonial archive that had been hidden for half a century. The files within would be a reminder to historians of just how far a government would go to sanitise its past. And the story Elkins would tell about those papers would once again plunge her into controversy.
Read more …

But not everyone has lost it: “If it happens again, everyone will do the exact same thing: We will help.”
• Greek Villagers Rescued Refugees. Now They Are the Ones Suffering. (NYT)
Stratis Valamios revved the motor on his small white boat and steered under a thumbnail moon out of the harbor of this fishing village, perched on the northern tip of Lesbos, Greece’s third-largest island. Skies were clear enough to see the purple mountains of Turkey a short distance across the Aegean Sea. It would be easy on this tranquil evening to catch calamari. These days, he needed a good haul to make ends meet. A year ago, he and other fishermen in the tiny village, Skala Sikaminias, were making a more unusual catch: thousands of sea-drenched asylum seekers who streamed across the Aegean to escape conflict and poverty in the Middle East and Africa.
As one of the landfalls in Greece that is closest to Turkey, Skala Sikaminias, with its 100 residents, fast became ground zero for the crisis, the first stop in Europe for people trying to reach Germany in a desperate bid to start new lives. “I’d be in the middle of the sea, and I would see 50 boats zigzagging toward me,” Mr. Valamios said, gazing across the narrow channel. “I would speed toward them, and they would throw their children into my boat to be saved.” Today the migrants have mostly stopped coming. The coastline, once littered with orange life vests and wrecked boats, has been cleaned to a near-spotless white. But the human drama has left an imprint here, and across all of Lesbos, in ways that have only begun to play out.
The village is nearly empty of tourists this year as Germans, Swedes and other visitors who had long flocked to the crystalline waters of Lesbos go elsewhere, wary of spending their vacations in a place now associated with human desperation. Business at the island’s hotels and tavernas has slumped around 80%, especially along the 7.5-mile stretch between Skala Sikaminias and the vacation town of Molyvos, where many of the more than 800,000 migrants who survived the crossing last year washed ashore. Mr. Valamios used to supplement his income as a fisherman by working five months of the year at Myrivilis’ Mulberry taverna, facing the bucolic port where fishermen mend yellow nets beneath oleanders and village cats prowl for fish. This year, he was asked to work just one month amid a dearth of customers. Nearly 1,000 Greeks in the area have lost seasonal employment.
[..] The villagers no longer experience the sea in the same way. When they look at the horizon, some say they think for a split second that another refugee boat is coming. “We have to be ready,” Mr. Valamios said. “If it happens again, everyone will do the exact same thing: We will help.”
Read more …