William Henry Jackson Hospital Street, St. Augustine, Florida 1897



This cannot end well.
• China Cuts Interest Rates, Reserve Ratios to Counter Slowdown (Bloomberg)
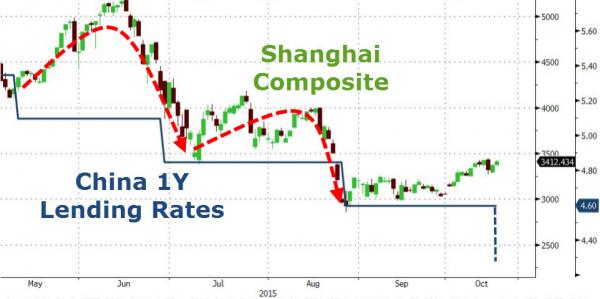
China’s central bank cut its benchmark lending rate and reserve requirements for banks, stepping up efforts to cushion a deepening economic slowdown. The one-year lending rate will drop to 4.35% from 4.6% effective Saturday the People’s Bank of China said on its website on Friday. The one-year deposit rate will fall to 1.5% from 1.75%. Reserve requirements for all banks were cut by 50 basis points, with an extra 50 basis point reduction for some institutions. The PBOC also scrapped a deposit-rate ceiling. The expanded monetary easing underscores the government’s determination to meet its 2015 growth target of about 7%. Moderated consumer inflation and a deeper slump in producer prices have given policy makers room for further easing.

If growth numbers were anywhere near the IMF’s predictions, China wouldn’t be cutting rates.
• China Interest Rate Cut Fuels Fears Over Ailing Economy (Guardian)
China fuelled fears that its ailing economy is about to slow further after Beijing cut its main interest rate by 0.25 percentage points. The unexpected rate cut, the sixth since November last year, reduced the main bank base rate to 4.35%. The one-year deposit rate will fall to 1.5% from 1.75%. The move follows official data earlier this week showing that economic growth in the latest quarter fell to a six-year low of 6.9%. A decline in exports was one of the biggest factors, blamed partly by analysts on the high value of China’s currency, the yuan. The rate cut sent European stock markets higher as investors welcomed the boost from cheaper credit in China, together with the hint of further monetary easing by the European Central Bank president, Mario Draghi, on Thursday.
Investors were also buoyed by the likelihood that the US Federal Reserve would be forced to signal another delay to the first US rate rise since the financial crash of 2008-2009 until later next year. The FTSE 100 was up just over 90 points, or 1.4%, at 6466, while the German Dax and French CAC were up almost 3%. The People’s Bank of China’s last rate cut in August triggered turmoil in world markets after Beijing combined the decision with a 2% reduction in the yuan’s value. Shocked at the prospect of a slide in the Chinese currency, investors panicked and sent markets plunging. Some economists have warned that the world economy is about to experience a third leg of post-crash instability after the initial banking collapse and eurozone crisis.
The slowdown in China, as it reduces debts and a dependence for growth on investment in heavy industry and property, will be the third leg. World trade has already contracted this year with analysts forecasting weaker trade next year. The IMF in July trimmed its forecast for global economic growth for this year to 3.1% from 3.3% previously, mainly as a result of China’s slowing growth. The Washington-based fund also warned that the weak recovery in the west risks turning into near stagnation. At its October annual meeting, it said growth in the advanced countries of the west is forecast to pick up slightly, from 1.8% in 2014 to 2% in 2015 while growth in the rest of the world is expected to fall from 4.6% to 4%.

“The continued and dramatic slowing of the Chinese economy in the years ahead is baked in the cake.”
• Why The Chinese Rate Cut Will Not Slow China’s Economic Decline (Coward)
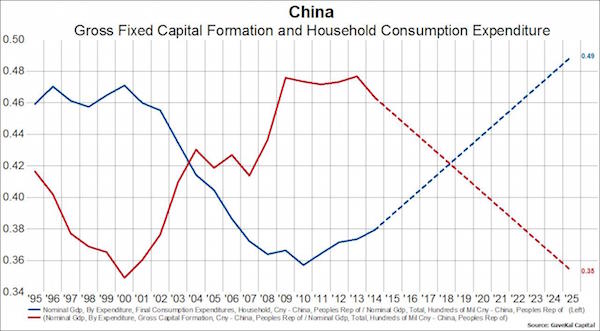
Today the Peoples Bank of China cut the benchmark interest rate by .25% and lowered banks’ reserve requirements by .5%. The measure is supposed to spur growth and make life a little easier on debt-ridden Chinese companies. In the immediate term it may give a slight boost to the economy, but there is no chance this measure, or others like it, will keep the Chinese economy from slowing much further in the years ahead. Let us explain… The continued and dramatic slowing of the Chinese economy in the years ahead is baked in the cake. For the last decade Chinese growth has been fueled by investment in infrastructure (AKA fixed capital formation). In an effort to sustain a high level of growth massive and unprecedented investment in fixed capital was carried out and fixed investment has now become close to 50% of the Chinese economy.
On the flip side, consumption as a% of GDP has shrunk from about 46% of GDP to only 38% of GDP. Most emerging market countries run with fixed investment of around 30-35% of GDP and with consumption accounting for about 40-50% of GDP – exactly the opposite dynamic of the Chinese economy. China has run into a ceiling in terms of the percentage of the economy accounted for by fixed investment and now fixed investment must shrink to levels more appropriate for China’s stage of economic development. This necessarily implies a slowing of the Chinese economy from what the government says is near 7% to something closer to 2-4%, and that is in the optimistic scenario in which consumption growth picks up the pace to mitigate the slowdown in investment.
This is why cuts in rates mean practically nothing for China’s long-term economic prospects. In the short-term rate cuts may postpone corporate bankruptcies by allowing companies to refinance debt at lower rates. Rate cuts may also make housing more affordable, on the margin. But these are cyclical boosts that act as tailwinds to China’s economic train.
No amount of wind, save a hurricane, is going to keep the train from slowing. As a reminder, it has not been working…

“..easing shows China is “getting more and more desperate” and that “things are really bad there.”
• Reactions To Rate Cut: “China Is Getting More And More Desperate” (Zero Hedge)
To say that China, which a few days ago reported GDP of 6.9% which “beat” expectations and which a few hours ago reported Chinese home prices rose in more than half of tracked cities for the first time in 17 months, stunned everyone with its rate cut on Friday night, meant clearly for the benefit of US stocks, as well as the global commodity market, is an understatement: nobody expected this. As a result strategists have been scrambling to put China’s 6th rate cut in the past year (one taking place just ahead of this weekend’s Fifth plenum) in context. Here are the first responses we have seen this morning. First, from Vikas Gupta, executive vice president at Arthveda Fund Management, who told Bloomberg that “China rate cut will spur fund flows to EMs.” He adds that “the move rules out U.S. rate increase this yr; Fed’s “hands are getting tied” concluding that “easing shows China is “getting more and more desperate” and that “things are really bad there.”
While there is no debate on just how bad things in China are, one can disagree that the Fed’s hands are tied – after all the Fed’s biggest “global” concern was China. The PBOC should have just taken that concern off the table. The second reaction comes from Citi’s Richard Cochinos: “Bottom line: Impacts of China rate announcements on the G10 are falling. Investors remain cautious ahead of this weekend’s announcements, and what policy cuts imply for the region. One day after a dovish ECB, China cuts interest rates by 25bp and RRR cut by 50bps. Accommodative policy begets accommodative policy it seems. Our economics team has been expecting further policy accommodation out of China, the issue was just a matter of timing.
Unlike other major central banks, the PBOC doesn’t announce policy on a set schedule – but this doesn’t mean there isn’t a pattern to it. Before today, it had announced cuts to the RRR or interest rate six times in 2015 – the last being on 25 August. So today was a surprise in terms of action, but not completely unexpected. We prefer to see the easing can be seen in the larger picture of China adjusting to weaker growth in a systematic and controlled manner, rather than a reaction to a new economic shock.”
This view helps explain the muted reaction in the G10. So far, AUDUSD (0.27%) and USDJPY (0.18%) have borne the bulk of price action, but we note price action so far is muted relative to April, June or August. Clearly stimulus is beneficial to both Japan and Australia – but we are cautious not to sound too optimistic. Today’s rate cut comes ahead of this weekend’s Fifth plenum, and previous ones haven’t been sufficient to reverse the economic slowdown. Additionally, this weekend it has been expected GDP targets for the next 5-years will be announced (currently at 7%, but broadly expected to fall), along with other fiscal plans and goals. Without knowing the full baseline of what China expects and is working towards, it is difficult to chase price action. The main drivers of EM Asia lower has been poor growth and trade in the region – hence we main cautious. Policy adjustments now could be a way to soften the impact of further weak economic growth.

Will adding more leverage save Beijing?
• China Takes ‘Riskiest’ Step by Ending Deposit-Rate Controls (Bloomberg)
China scrapped a ceiling on deposit rates, tackling what the central bank has called the “riskiest” part of freeing up the nation’s interest rates. The move came as the central bank cut benchmark rates and banks’ reserve requirements to support a faltering economy. The changes take effect on Saturday, the People’s Bank of China said in a statement on Friday. Scrapping interest-rate controls boosts the role of markets in the economy, part of efforts by Premier Li Keqiang to find new engines of growth. While officials must be on guard for any excessive competition for deposits that could increase borrowing costs for companies or lead to lenders going bust, weakness in the economy may be mitigating the risks.
Ending the ceiling is an important milestone but comes in the wake of “a tremendous amount of deposit-rate liberalization over the last several years,” especially in the shape of wealth management products, according to Charlene Chu at Autonomous Research Asia. Wealth products issued by Internet firms are increasingly siphoning away deposits, making rate controls less effective and adding urgency to accelerating reform, the central bank said in a question-and-answer statement after the move. History shows that the best time to deregulate rates is when they’re being cut and inflation is easing, it said. The risks may not be as high as they would’ve been two or three years ago, because competition for deposits has cooled, with weaker demand for funding and a decline in banks’ willingness to lend, Chu, formerly of Fitch Ratings, said ahead of the PBOC announcement. Banks aren’t fully using the deposit-rate flexibility that they already have, she said.

Remember that Draghi et al have no idea what the effect of negative rates will be. None. All they have is theories.
• Draghi’s Signal Adds $190 Billion to Negative-Yield Universe (Bloomberg)
With his confirmation that policy makers had discussed cutting the region’s deposit rate, Mario Draghi extended the euro area’s negative yield universe by $190 billion. Those comments by the ECB chief on Thursday sparked a rally that left yields on German sovereign securities at less than zero for as long as six years. Across the currency bloc, the value of securities issued by governments at negative yields rose to $1.57 trillion, from $1.38 trillion before Draghi’s comments. That’s equivalent to about a quarter of the market. German and French two-year yields set fresh record-lows Friday, while their longer-dated peers pared weekly gains. Draghi also said the ECB will re-examine its quantitative-easing plan in December.
“This is certainly an exceptional environment,” said Christian Lenk at DZ Bank in Frankfurt. “We have to admit that the discussion about the deposit rate being cut further came as a surprise. It takes the curve very much into negative territory. In the time being the short-end looks a bit artificial.” Germany’s two-year yield was little changed at minus 0.32% as of 9:58 a.m. London time, after earlier reaching a record-low minus 0.348%. The price of the 0% security maturing September 2017 was at 100.605% of face value. French two-year yields dropped to a record minus 0.292% on Friday, also below the current level of the deposit rate, which is at minus 0.20%. There are about $752 billion of securities in the euro region with yields below that rate, making them ineligible for the ECB’s €1.1 trillion bond-buying plan

Next major Brussels headache: “Public debt is 127pc of GDP and total debt is 370pc, worse than in Greece. Net external liabilities are more than 220pc of GDP.”
• Eurozone Crosses Rubicon As Portugal’s Anti-Euro Left Banned From Power (AEP)
Portugal has entered dangerous political waters. For the first time since the creation of Europe’s monetary union, a member state has taken the explicit step of forbidding eurosceptic parties from taking office on the grounds of national interest. Anibal Cavaco Silva, Portugal’s constitutional president, has refused to appoint a Left-wing coalition government even though it secured an absolute majority in the Portuguese parliament and won a mandate to smash the austerity regime bequeathed by the EU-IMF Troika. He deemed it too risky to let the Left Bloc or the Communists come close to power, insisting that conservatives should soldier on as a minority in order to satisfy Brussels and appease foreign financial markets. Democracy must take second place to the higher imperative of euro rules and membership.
“In 40 years of democracy, no government in Portugal has ever depended on the support of anti-European forces, that is to say forces that campaigned to abrogate the Lisbon Treaty, the Fiscal Compact, the Growth and Stability Pact, as well as to dismantle monetary union and take Portugal out of the euro, in addition to wanting the dissolution of NATO,” said Mr Cavaco Silva. “This is the worst moment for a radical change to the foundations of our democracy. “After we carried out an onerous programme of financial assistance, entailing heavy sacrifices, it is my duty, within my constitutional powers, to do everything possible to prevent false signals being sent to financial institutions, investors and markets,” he said. Mr Cavaco Silva argued that the great majority of the Portuguese people did not vote for parties that want a return to the escudo or that advocate a traumatic showdown with Brussels.
This is true, but he skipped over the other core message from the elections held three weeks ago: that they also voted for an end to wage cuts and Troika austerity. The combined parties of the Left won 50.7pc of the vote. Led by the Socialists, they control the Assembleia. The conservative premier, Pedro Passos Coelho, came first and therefore gets first shot at forming a government, but his Right-wing coalition as a whole secured just 38.5pc of the vote. It lost 28 seats. The Socialist leader, Antonio Costa, has reacted with fury, damning the president’s action as a “grave mistake” that threatens to engulf the country in a political firestorm. “It is unacceptable to usurp the exclusive powers of parliament. The Socialists will not take lessons from professor Cavaco Silva on the defence of our democracy,” he said.
Mr Costa vowed to press ahead with his plans to form a triple-Left coalition, and warned that the Right-wing rump government will face an immediate vote of no confidence. There can be no fresh elections until the second half of next year under Portugal’s constitution, risking almost a year of paralysis that puts the country on a collision course with Brussels and ultimately threatens to reignite the country’s debt crisis. The bond market has reacted calmly to events in Lisbon but it is no longer a sensitive gauge now that the ECB is mopping up Portuguese debt under quantitative easing. Portugal is no longer under a Troika regime and does not face an immediate funding crunch, holding cash reserves above €8bn. Yet the IMF says the country remains “highly vulnerable” if there is any shock or the country fails to deliver on reforms, currently deemed to have “stalled”. Public debt is 127pc of GDP and total debt is 370pc, worse than in Greece. Net external liabilities are more than 220pc of GDP.

“Europe has steadily departed from its principal founding goals, democracy, human rights and freedoms and the prosperity of its people and its societies..”
• Italy ex-PM Monti: Ignoring Greek Referendum A Violation Of Democracy (EurActiv)
By disregarding the resounding ‘No’ of the recent Greek referendum, Europe clearly violated democracy, said the former Italian premier, Mario Monti. At the “Regaining Public Trust in Europe” event organised this week in Brussels by Friends of Europe, Zoe Konstantopoulou, the former speaker of the Greek Parliament, strongly criticized the EU institutions for the unfolding humanitarian crisis in Greece. “Would you trust the EU if they told you that your vote or the court decisions in your countries do not matter?”, Konstantopoulou wondered. Zoe Konstantopoulou served as a speaker of the Greek parliament under the first term of Syriza coalition government and was a close ally of the Greek premier, Alexis Tsipras.
But shortly after the deal agreed on between Athens and its international creditors this summer, Konstantopoulou resigned from Syriza, and joined the newly established leftist Popular Unity party led by former energy minister Panagiotis Lafazanis. In the recent snap election in Athens, Popular Unity did not manage to enter the Greek parliament, scoring below the required 3% threshold. Konstantopoulou and Monti had a vivid dialogue during the panel discussion. The former Greek lawmaker was quite critical of the EU, and said that at times when the democratic principles of the EU are shaken, “it is our duty to speak clearly and honestly”.
“Europe has steadily departed from its principal founding goals, democracy, human rights and freedoms and the prosperity of its people and its societies,” she stressed. Konstantopoulou noted that “Greeks have been sacrificed and crucified for more than 5 years now, to pay a debt which has been evaluated to be wholly unsustainable ever since 2010 to the knowledge of the IMF and the EU.” “And it was baptised as public, although it was initially private, involving private banks in Germany, France and Greece,” she added.

Must. Read. Whole. Article.
• Rare Metals: The War Over the Periodic Table (Bloomberg)
A little past 9:30 on the morning of Sept. 7, 2010, a Japanese Coast Guard vessel in the East China Sea spots a Chinese fishing trawler off the coast of islands, known as Senkaku in Japanese and Diaoyu in Chinese. The Japanese have little tolerance for such incursions in the Senkakus, which they annexed in 1895 after the Sino-Japanese War. But recently China has asserted claims to these islands extending hundreds of years earlier. The island dispute is wrapped up in a morass of misunderstanding and oneupmanship, with an eye toward the rich seabed resources nearby. When you ask Japanese officials about the territorial dispute, they will look at you as if it is almost insulting to answer the question. “It’s our land,” one government official told me, as if an American diplomat had been asked if Hawaii is part of the US.
On that morning, the Japanese vessel pulls alongside the smaller Chinese trawler and blares messages to the crew in Chinese from loudspeakers: “You are inside Japanese territorial waters. Leave these waters.” Videos from the day show that instead of leaving, the Chinese boat bends toward the stern of the Japanese cutter, hitting it and then sailing on. Forty minutes later, the same captain veers into another Japanese coast guard ship. Tokyo has managed previous incursions with little fanfare. However, the newly elected Democratic Party of Japan detained the trawler’s crew and captain. It planned to put the captain on trial. China retaliated by detaining four Japanese citizens.
Then, on Sept. 21, Japanese trading houses informed its Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry that China was refusing to fill orders for rare-earth elements – a set of 17 different, obscure rare metals. What seemed like a battle over seabed resources became a new conflict, one that is potentially far larger, a War over the Periodic Table. Japanese officials and manufacturers were frightened. These elements – essential materials in Japan’s high-tech industry, well known for its high quality components – were virtually all produced in China. Beijing never acknowledged an export ban or said it would use the rare-metal trade as a political weapon. But no other country reported such delays. And Beijing never explained why all 32 of the country’s rare-earth exporters halted trade on the same day.
Restricting these exports was an astute move if Beijing’s goal was to escalate the political conflict between the two countries without the use of force. Tokyo worried that rare earths were just the beginning of what China might withhold because China is also the leading global producer of 28 advanced metals also vital to Japanese industry. Bowing to Beijing’s pressure, Tokyo quickly released the Chinese captain. But the damage to Japan and the rare-earth market had only just begun. Prices for rare earths started to climb, some as much as 2,000% over the next year and a half. Prices have since returned to lower levels, and China changed its export regime after being found in violation of global trade rules last year. But the lessons from this episode have not yet been fully realized as a fundamental market instability remains. A little perspective is in order.

It’s already much much more.
• $6.5 Billion in Energy Writedowns and We’re Just Getting Started (Bloomberg)
The oil and gas industry’s earnings season is barely underway, and already there’s been $6.5 billion in writedowns. On Thursday, Freeport-McMoRan reported a $3.7 billion charge for the third quarter, while Southwestern Energy – which has a market value of $4.5 billion – booked $2.8 billion. And that’s just the beginning. Barclays estimated in an Oct. 21 analysis that there could be $20 billion in charges among just six companies. Southwestern’s writedown was double Barclays’ forecast. Oil prices have tumbled 44% in the past year, and natural gas is down 35%, making the write-offs a foregone conclusion from an accounting standpoint. The companies use an accounting method that requires them to recognize a charge when estimates of future cash flow from their properties falls below what the companies spent buying and developing the acreage. The predictions of future cash flow have fallen along with prices.
Since it’s no secret oil and gas prices have plunged, “the majority of write-offs are typically non-events,” said Barclays’ analysts led by Thomas R. Driscoll in the report. Southwestern’s shares have declined 64% in the past year, and Phoenix-based Freeport-McMoRan’s are down 61%. Barclays predicted ceiling-test impairments for Apache, Chesapeake Energy , Devon Energy, Encana and Newfield. All five companies are scheduled to report third-quarter results in November. “Many companies will have writedowns as the price of oil is about half of where it once was and gas is also down,” Timothy Parker at T. Rowe Price said in an e-mail. “However, it won’t generally hurt the companies because very few have debt covenants that are linked to book value, which the writedowns affect.”

The troika wants to evict Greeks from their homes.
• Greece’s Creditors Demand Further Reform (La Tribune)
The European institutions and the IMF are increasing their demands on Greece, despite the recent reforms adopted by the Greek parliament. Athens can hardly afford to resist. Our partner La Tribune reports. Discussions between Greece and its creditors are tense, despite the major reforms accepted by the Greek parliament, the Vouli, on Monday (19 October). The talks between Greece and the new institutional ‘quartet’ began on Wednesday (21 October). The old troika of the Commission, the ECB and the IMF has been joined by the European Stability Mechanism (ESM). On Wednesday afternoon, Olga Gerovasili, a spokesperson for the Greek government, spoke of a “very hard battle” with the institutions.
At the heart of this battle are the Greek banks, which were severely weakened by the massive withdrawal of deposits in the first half of this year. Added to this is the increasing cost of debt. According to the Bank of Greece, in 2014 this represented 34% of the total deposits held by all the Hellenic banks put together. This figure has risen since 2014, and will continue to rise as Greek GDP contracts in 2015 and 2016. Fewer deposits mean more toxic debt: the Greek banking system needs a bailout. The Greek government says it needs a recapitalisation fund of €25 billion. But the creditors clearly hope to provide only the bare minimum. As the supervisor of the process, the ECB plans to carry out an asset quality review (AQR) to determine exactly how much money the banks need before bailing them out.
But the conditions attached to this bailout may create a raft of other problems. Greece’s creditors are now demanding that borrowers who cannot afford to repay their loans be evicted from their homes. The vacated properties would then be sold in order to settle the exact payment due on each loan. Up to now, households with modest incomes have been protected from eviction as long as their main residence was worth less than €250,000; a measure that has helped to keep many families hit by unemployment off the streets. But the creditors want this limit lowered so more bank loans can be recovered in this way. Olga Gerovasili said that the government was “fighting to maintain the protection of main residences”.
A similar issue arose in Cyprus last year. The Cypriot parliament refused to implement the tougher eviction conditions demanded by the troika, and the ECB responded by excluding Cyprus from its quantitative easing programme. The troika then froze all transfers to Nicosia, pushing the island to the verge of bankruptcy. Under pressure from the government, the parliament finally accepted the demand to make evictions easier to carry out.

Where and why debt deflation starts: “Companies have increased leverage massively, and that is starting to catch up..”
• Investment Grade Ain’t What It Used to Be in Nervous Bond Market (Bloomberg)
After six years of a credit boom in which investors distinguished less and less between ratings, rewarding companies across the spectrum with favorable borrowing costs, the market is becoming more discriminating. Fear of low growth, which has largely been focused on the riskiest of energy companies, is spilling over to other industries and into the lower rungs of investment grade as the strength of balance sheets comes back into focus. Just being investment grade, it seems, isn’t good enough anymore. “The chickens are coming home to roost,” said Freddie Offenberg at Andres Capital Management. “Companies have increased leverage massively, and that is starting to catch up, especially given the worries in the economy.” Earnings for Standard & Poor’s 500 companies contracted 1.7% last quarter, the most since 2009.
And more than half of companies in the index that reported earnings this quarter have disappointed analysts’ sales expectations. The credit-ratings companies have noticed: There have been 1.6 investment-grade companies upgraded for every one downgraded so far this year, compared with last year’s 3.5-1 ratio. “It’s not time to panic, but the market is paying closer attention to performance and quality, and rightly so,” said David Leduc at Standish Mellon Asset Management. Companies like Fossil are paying nearly half a percentage point more for their debt since May, based on secondary prices of comparable securities, according to Bank of America Merrill Lynch Indexes. Companies with the best balance sheets, such as Microsoft and Johnson & Johnson, only pay 0.05 percentage point more.
Among companies that have had to pay up in debt markets is Hewlett-Packard. The Baa2 rated computer maker sold $14.6 billion of bonds on Sept. 30 that yielded half apercentage point more than the average for bonds with similar ratings and maturities in the secondary market, according to Bank of America Merrill Lynch index data. That’s not good news for companies that still need to raise debt to finance $356 billion of takeovers that are expected to be completed by the end of the year. This includes Charter Communications, which is attempting to complete its $55.1 billion takeover of Time Warner Cable with the lowest investment-grade rating from S&P and Fitch Ratings, and a junk rating from Moody’s Investors Service.

“On the basis of its record, the financial system as constituted in the years 1900-1913 must be considered to have been successful to an extent rarely equalled in the United States.”
• An All Too Visible Hand (WSJ)
When Woodrow Wilson signed the Federal Reserve Act into law in 1913, the dollar was defined as a weight of gold. You could exchange the paper for the metal, and vice versa, at a fixed and statutory rate. The stockholders of nationally chartered banks were responsible for the solvency of the institutions in which they owned a fractional interest. The average level of prices could fall, as it had done in the final decades of the 19th century, or rise, as it had begun to do in the early 20th, without inciting countermeasures to arrest the change and return the price level to some supposed desirable average. The very idea of a macroeconomy—something to be measured and managed—was uninvented. Who or what was in charge of American finance? Principally, Adam Smith’s invisible hand.
How well could such a primitive system have possibly functioned? In “The New York Money Market and the Finance of Trade, 1900-1913,” a scholarly study published in 1969, the British economist C.A.E. Goodhart concluded thus: “On the basis of its record, the financial system as constituted in the years 1900-1913 must be considered to have been successful to an extent rarely equalled in the United States.” The belle epoque was not to be confused with paradise, of course. The Panic of 1907 was a national embarrassment. There were too many small banks for which no real diversification, of either assets or liabilities, was possible. The Treasury Department was wont to throw its considerable resources into the money market to effect an artificial reduction in interest rates—in this manner substituting a very visible hand for the other kind.
Mr. Lowenstein has written long and well on contemporary financial topics in such books as “When Genius Failed” (2000) and “While America Aged” (2008). Here he seems to forget that the past is a foreign country. “Throughout the latter half of the nineteenth century and into the early twentieth,” he contends, “the United States—alone among the industrial powers—suffered a continual spate of financial panics, bank runs, money shortages and, indeed, full-blown depressions.” If this were even half correct, American history would have taken a hard left turn. For instance, William Jennings Bryan, arch-inflationist of the Populist Era, would not have lost the presidency on three occasions. Had he beaten William McKinley in 1896, he would very likely have signed a silver-standard act into law, sparking inflation by cheapening the currency. As it was, President McKinley signed the Gold Standard Act of 1900, which wrote the gold dollar into the statute books.

Well, that’s a surprise…
• EU Negotiators Break Environmental Pledges In Leaked TTIP Draft (Guardian)
The EU appears to have broken a promise to reinforce environmental protections in a leaked draft negotiating text submitted in the latest round of TTIP talks in Miami.. In January, the bloc promised to safeguard green laws, defend international standards and protect the EU’s right to set high levels of environmental protection, in a haggle with the US over terms for a free trade deal. But a confidential text seen by the Guardian and filed in the sustainable development chapter of negotiations earlier this week contains only vaguely phrased and non-binding commitments to environmental safeguards. No obligations to ratify international environmental conventions are proposed, and ways of enforcing goals on biodiversity, chemicals and the illegal wildlife trade are similarly absent.
The document does recognise a “right of each party to determine its sustainable development policies and priorities”. But lawyers say this will have far weaker standing than provisions allowing investors to sue states that pass laws breaching legitimate expectations of profit. “The safeguards provided to sustainable development are virtually non-existent compared to those provided to investors and the difference is rather stark,” said Tim Grabiel, a Paris-based environmental attorney. “The sustainable development chapter comprises a series of aspirational statements and loosely worded commitments with an unclear dispute settlement mechanism. It has little if any legal force.” The document contains a series of broadly sympathetic statements about the importance of conservation and climate action.
But it offers no definitions of what core terms – such as “high levels of protection” for the environment or “effective domestic policies” for implementing them – actually mean. Last year, more than a million people across Europe signed a petition calling for the Transatlantic Trade and Investment Partnership (TTIP) talks to be scrapped. Their concern was that multinationals could use the treaty’s investor-state dispute settlement (ISDS) provisions to sue authorities in private tribunals, not bound by legal precedent. In one famous case, Lone Pine launched an unresolved $250m suit against the state of Quebec after it introduced a fracking moratorium, using ISDS provisions in the North American Free Trade Agreement (Nafta).
US officials maintain that few such cases are ever likely to be brought under the TTIP, which could wipe away tariffs in the world’s largest ever free trade deal. However, environmental cases accounted for 60% of the 127 ISDS cases already brought against EU countries under bilateral trade agreements in the last two decades, according to Friends of the Earth Europe. Europe’s taxpayers paid out at least $3.5bn to private investors as a result.

Seen this before: “..a shift in norms that will be difficult to get back under control.”
• Populist, Pernicious and Perilous : Germany’s Growing Hate Problem (Spiegel)
Germany these days, it seems, is a place where people feel entirely uninhibited about expressing their hatred and xenophobia. Images from around the country show a level of brutalization that hasn’t been witnessed for some time, and attest to primitive instincts long believed to have been relegated to the past in Germany. The examples are as myriad as they are shocking, and include the bloody attack in Cologne as well as the mock gallows for Angela Merkel and her deputy Sigmar Gabriel carried by a demonstrator at a Pegida rally in Dresden on Oct. 12.
But they also include the abuse shouted at the German chancellor when she visited a refugee hostel in Heidenau near Dresden in August, where she was called a “slut” and other insults, or the placards held aloft by demonstrators on the first anniversary of the Pegida rallies listing the supposed “enemies of the German state” – Merkel, Gabriel and their “accomplices.” The lack of inhibition when it comes to vicious tirades took on a whole new scale on Monday, when Turkish-born German author and Pegida supporter Akif Pirincci, said there are other alternatives in the refugee crisis, but “the concentration camps are unfortunately out of action at the moment.”
There have been more than twice as many attacks on refugee hostels during the first nine months of this year as in the whole of 2014. The rising tide of hatred is now reaching the politicians many hold responsible for the perceived chaos besetting Germany. The national headquarters of Merkel’s conservative Christian Democratic Union (CDU) party in Berlin fields thousands of hate mails every week. As the architect of the “we can do it” policy of allowing masses of refugees into the country, Chancellor Merkel is their primary target. Within the SPD, it is General Secretary Yasmin Fahimi, whose father is Iranian. “Open the doors to the showers, fire up the ovens. They’re going to be needed,” read one recent anonymous mail addressed to her.
The hatred comes in many forms. It’s expressed on the streets and on the Internet. Sometimes it’s loud. Other times it’s unspoken. It eminates from every class and every section of society. According to studies conducted by Andreas Zick, the respected head of the Institute for Interdisciplinary Research on Conflict and Violence at the University of Bielefeld, who has been researching German prejudices against different groups for many years, almost 50% of Germans harbor misanthropic views. Zick warns of a shift in norms that will be difficult to get back under control.

Rinse and repeat?!
• Germany To Push For Compulsory EU Quotas To Tackle Refugee Crisis (Guardian)
Germany is to push for more ambitious and extensive common European policies on the refugee crisis, according to policymakers in Berlin, with compulsory and permanent EU quotas for sharing probably hundreds of thousands of people to be brought to Europe directly from the Middle East. New European powers replacing some national authority over border control, and the possible raising of a special EU-wide levy to fund the new policies are also on Berlin’s agenda. The plans, being prepared in Berlin and Brussels, are certain to trigger bitter resistance and major clashes within the EU. Berlin backs European commission plans to make the proposed scheme “permanent and binding”. But up to 15 of 28 EU countries are opposed.
The plans will not apply to the UK as it is not part of the EU’s passport-free Schengen zone and has opted out of EU asylum policy, saying it will not take part in any proposed European refugee-sharing schemes. Angela Merkel, appears determined to prevail, as she grapples with a crisis that will likely define her political legacy. The German chancellor is said to be angry with the governments of eastern and central Europe who are strongly opposed to being forced to take in refugees. She is said to resent that these EU member states are pleading for “solidarity” against the threats posed by Russia and Vladimir Putin while they resist sharing the burdens posed by the refugee crisis. EU government leaders agreed last month to share 160,000 asylum seekers already inside the EU, redistributing them from Greece and Italy over two years.
But the decision had to be pushed to a majority vote overruling the dissenters, mainly in eastern Europe, with the Hungarian prime minister, Viktor Orban, accusing Merkel of “moral imperialism” by forcing the issue. It is highly unusual in the EU for sensitive issues of such deep national political impact to be settled by majority voting. But Berlin appears prepared to go there if no consensus can be reached. The opponents of quotas insist last month’s decision was a one-off. But according to policymakers in Berlin, Merkel now wants to go much further, shifting the emphasis of burden-sharing from redistribution of refugees inside the EU to those collecting en masse in third countries, notably Turkey where more than two million Syrians are hosted.
Under one proposal being circulated in Berlin, the EU would strike pacts with third countries such as Turkey agreeing to take large but unspecified numbers of refugees from them directly into Europe. In return the third country would need to agree on a ceiling or a cap for the numbers it can send to Europe and commit to keeping all other migrants and refugees, and accommodate them humanely. This effectively means Europe will be financing large refugee camps in those third countries, which will also be obliged to take back any failed asylum seekers returned from Europe.

Foreign cops on sovereign territory?
• Worried Slovenia Might Built Fence To Cope With Migrant Crisis (Reuters)
Slovenia said it will consider all options, including fencing off its border with Croatia, if European leaders fail to agree a common approach to the migrant crisis as thousands stream into the ex-Yugoslav republic. Migrants began crossing into Slovenia last Saturday after Hungary closed its border with Croatia. The Slovenian Interior Ministry said that a total of 47,000 had entered the country since Saturday, including some 10,000 in the past 24 hours. A Reuters cameraman said about 3,000 people broke the fence at the border crossing at Sentilj and walked in to Austria on Friday morning. Slovenian officials said the country is too small and does not have enough resources to handle such large numbers of people. Prime Minister Miro Cerar accused Croatia of transporting too many people too quickly to Slovenia.
When asked if there was the possibility of building a fence on the border, Cerar told Slovenian state TV: “We are considering also those options.” “At first we are seeking a European solution. If we lose hope on the European level, if we do not get enough on Sunday … then all options are possible as that would mean that we are on our own,” Cerar said. Several European leaders are due to meet in Brussels on Sunday under the auspices of the European Commission to discuss the latest developments in the migrant crisis, Europe’s biggest since World War. [..] According to Slovenia’s interior ministry, the cost of fencing off the 670-km long border with Croatia would be about €80 million. Slovenia has asked for the EU for assistance and officials said Austria, Germany, Italy, France, Hungary, the Czech Republic, Slovakia and Poland offered to send police reinforcements.








