
Thin White Duke



Bowie’s secret: hard work.
• David Bowie Dies Aged 69 From Cancer (Reuters)
David Bowie, a music legend who used daringly androgynous displays of sexuality and glittering costumes to frame legendary rock hits “Ziggy Stardust” and “Space Oddity”, has died of cancer. He was 69. “David Bowie died peacefully today surrounded by his family after a courageous 18-month battle with cancer,” read a statement on Bowie’s Facebook page dated Sunday. Born David Jones in the Brixton area of south London, Bowie took up the saxophone at 13. He shot to fame in Europe with 1969’s “Space Oddity”. But it was Bowie’s 1972 portrayal of a doomed bisexual alien rock star, Ziggy Stardust, that propelled him to global stardom. Bowie and Ziggy, wearing outrageous costumes, makeup and bright orange hair, took the rock world by storm.
Bowie said he was gay in an interview in the Melody Maker newspaper in 1972, coinciding with the launch of his androgynous persona, with red lightning bolt across his face and flamboyant clothes. He told Playboy four years later he was bisexual, but in the eighties he told Rolling Stone magazine that the declaration was “the biggest mistake I ever made”, and he was “always a closet heterosexual”. The excesses of a hedonistic life of the real rock star was taking its toll. In a reference to his prodigious appetite for cocaine, he said: “iI blew my nose one day in California,” he said. And half my brains came out. Something had to be done.”
Bowie kept a low profile after undergoing emergency heart surgery in 2004 but marked his 69th birthday on Friday with the release of a new album, “Blackstar”, with critics giving the thumbs up to the latest work in a long and innovative career. British Prime Minister David Cameron tweeted: “I grew up listening to and watching the pop genius David Bowie. He was a master of re-invention, who kept getting it right. A huge loss.” Steve Martin from Bowie’s publicity company Nasty Little Man confirmed the Facebook report was accurate. “It’s not a hoax,” he told Reuters.�

Close to circuit breaker again. Plunge protection.
• Chinese Stocks Down 5%, As Rout Ricochets In Asia (MarketWatch)
China shares slid Monday, and losses in other regional markets deepened, as a rout that knocked trillions of dollars off global stocks last week ricochets back to Asia. The Shanghai Composite Index fell 5.3% to 3,018 and the smaller Shenzhen Composite Index was last down 3.5%. Shares in Hong Kong sank to their lowest in roughly 2.5 years. The Hang Seng Index was off 2.4% at 19,970, on track to close below 20,000 for the first time since June 2013. A gauge of Chinese firms listed in the city fell 3.5%. Australia s benchmark was down 1.3%, and South Korea’s Kospi fell 0.7%. Japan s market was closed for a national holiday. Worries about weakness in the Chinese yuan and how authorities convey their market expectations continue to unnerve investors.
Poorly telegraphed moves last week exacerbated volatility in China, and triggered selling that spread to the rest of the region, the U.S. and Europe. Concerns about China’s stalling economy, with the yuan weakening 1.5% against the U.S. dollar last week, has sparked selling in commodities and currencies of China s trading partners, and sent investors to assets perceived as safe. “There’s no reason for Chinese stock to move up for now”, said Jiwu Chen, CEO of VStone Asset Management. He said investors are closely watching for hints in coming days from officials on their outlook for shares and the yuan, noting that authorities have nudged the yuan stronger starting Friday.
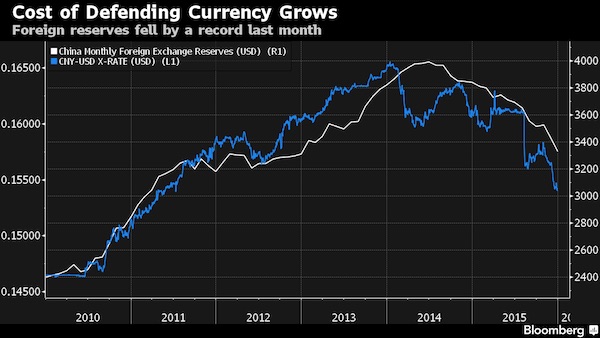
Earlier Monday, China’s central bank fixed the yuan at 6.5833 against the U.S. dollar, guiding the currency stronger from its 6.5938 late Friday. It was the second day the bank guided the yuan stronger, after eight sessions of weaker guidance. The onshore yuan can trade up or down 2% from the fix. The onshore yuan, which trades freely, was last at 6.6727 to the U.S. dollar, compared with 6.6820 late Friday. It reached a five-year low of 6.7511 last Thursday. China’s central bank appears to have spent huge amounts of dollars to support the yuan amid decelerating economic growth and the onset of higher U.S. interest rates. The country’s foreign-exchange regulator said over the weekend that its reserves are relatively sufficient. Reserves dropped by $107.9 billion in December, the biggest monthly drop ever.

“Policy makers have to be cautious in using intervention as they can’t rescue the market all the time.”
• Chinese Stocks Extend Rout as Economic Growth Concerns Deepen (BBG)
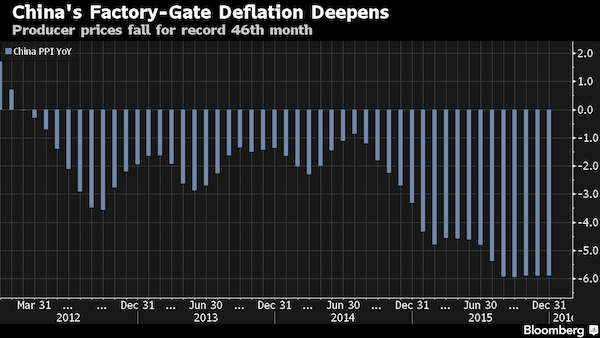
Chinese stocks fell, extending last week’s plunge, as factory-gate price data fueled concern the economic slowdown is deepening. The Shanghai Composite Index slid 2.4% to 3,109.95 at the break, led by energy and material companies. The producer price index slumped 5.9% in December, extending declines to a record 46th month, data over the weekend showed. The Hang Seng China Enterprises Index tumbled 3.5% at noon, while the Hang Seng Index fell below the 20,000 level for the first time since 2013. “Pessimism is the dominant sentiment,” said William Wong at Shenwan Hongyuan Group in Hong Kong. “The PPI figure confirms the economy is mired in a slump. Market conditions will remain challenging given weak growth and volatility in external markets and the yuan’s depreciation pressure.”
Extreme market swings this year have revived concern over the Communist Party’s ability to manage an economy set to grow at the weakest pace since 1990. Policy makers removed new circuit breakers on Friday after blaming them for exacerbating declines that wiped out $1 trillion this year. [..] The offshore yuan erased early losses after China’s central bank kept the currency’s daily fixing stable for the second day in a row, calming markets after sparking turmoil last week. While state-controlled funds purchased Chinese stocks at least twice last week, according to people familiar with the matter, there was little evidence of intervention on Monday. “Sentiment is very poor,” said Castor Pang, head of research at Core Pacific Yamaichi Hong Kong. “I don’t see any clear signs of state buying in the mainland market. Policy makers have to be cautious in using intervention as they can’t rescue the market all the time.”

Yuan shortage.
• Yuan Liquidity Extremely Tight, Interbank Rates Soar In Hong Kong (BBG)
Interbank yuan lending rates in Hong Kong climbed to records across the board after suspected intervention by China’s central bank last week mopped up supplies of the currency in the offshore market. The city’s benchmark rates for loans ranging from one day to a year all set new highs, with the overnight and one-week surging by the most since the Treasury Markets Association started compiling the fixings in June 2013. The overnight Hong Kong Interbank Offered Rate surged 939 basis points to 13.4% on Monday, while the one-week rate jumped 417 basis points to 11.23%. The previous highs were 9.45% and 10.1%, respectively. “Yuan liquidity is extremely tight in Hong Kong,” said Becky Liu, senior rates strategist at Standard Chartered in the city.
“There was some suspected intervention by the People’s Bank of China last week, and the liquidity impact is starting to show today.” The offshore yuan rebounded from a five-year low last week amid speculation the central bank bought the currency, an action that drains funds from the money market. Measures restricting overseas lenders’ access to onshore liquidity – which make it more expensive to short the yuan in the city – have also curbed supply. The PBOC has said it wants to converge the yuan’s rates at home and abroad, a gap that raises questions about the currency’s market value and hampers China’s push for greater global usage as it prepares to enter the IMF’s reserves basket this October. The offshore yuan’s 1.7% decline last week pushed its discount to the Shanghai price to a record, prompting the IMF to say that it will discuss the widening spread with the authorities.

What would make one think this is not a crisis?
• London Hedge Fund Omni Sees 15% Yuan Drop, and More in a Crisis (BBG)
Omni Partners, the $965 million London hedge fund whose wagers against China helped it beat the industry last year, said the yuan may fall 15% in 2016, and even more if the nation has a credit crisis. The currency, which tumbled to a five-year low last week, would have to drop to 7 or 7.5 a dollar to meaningfully reverse its appreciation and be commensurate with the depreciation of other slowing emerging markets, Chris Morrison, head of strategy of Omni’s macro fund, said in a telephone interview. The yuan slumped 1.4% last week to around 6.59 in Shanghai. “While Chinese authorities have been intervening heavily in the dollar-yuan market, they cannot ultimately fight economic fundamentals,” Morrison said, adding that even the 7-7.5% forecast would be too conservative if China were to have a credit crisis.
“You’ll be talking about the kind of moves that Brazil and Turkey have seen, more like 50%, and that’s how you can create serious numbers like 8, 9 and 10 against the dollar.” The yuan’s biggest weekly loss since an Aug. 11 devaluation prompted banks including Goldman Sachs and ABN Amro Bank, which Bloomberg data show had the most-accurate forecasts for the yuan over the past year, to cut their estimates for the currency. The options market is also signaling that the yuan’s slide has plenty of room to run, with the contracts indicating there’s a 33% chance that the yuan will weaken beyond 7 a dollar, data compiled by Bloomberg show.
The declining currency, a debt pile estimated at 280% of GDP and a volatile equity market are complicating Premier Li Keqiang’s efforts to boost an economy estimated to grow at the slowest pace in 25 years. While intervention stabilized the yuan for almost four months following an Aug. 11 devaluation, the action led to the first-ever annual decline in the foreign-exchange reserves as capital outflows increased. Policy makers also propped up shares in the midst of a $5 trillion rout last summer, including ordering stock purchases by state funds. While a weaker yuan would support China’s flagging export sector, it also boosts risks for the nation’s foreign-currency borrowers and heightens speculation that the slowdown in Asia’s biggest economy is deeper than official data suggest.

A hard rain is gonna fall.
• Australia Bet The House On Never-Ending Chinese Growth (Guardian)
Over the last couple of decades, China has undergone profound change and is often cited as an economic growth miracle. Day by day, however, the evidence becomes increasingly clear the probability of a severe economic and financial downturn in China is on the cards. This is not good news at all for Australia. The country is heavily exposed, as China comprises Australia’s top export market, at 33%, more than double the second (Japan at 15%). A considerable proportion of Australia’s current and future economic prospects depend heavily on China’s current strategy of building its way out of poverty while sustaining strong real GDP growth.
To date, China has successfully pulled hundreds of millions of its people out of poverty and into the middle class through mass provision of infrastructure and expansion of housing markets, alongside a powerful export operation which the global economy has relied upon since the 1990s for cheap imports. Though last week’s volatile falls on the Chinese stock markets alongside a weakening yuan sent shockwaves through the global markets, Australia’s exposure lies much deeper within the Chinese economy. The miracle is starting to look more and more fallible as it slumps under heavy corporate debts and an over-construction spree which shall never again be replicated in our lifetimes or that of our children.
As of the second quarter of 2015, China’s household sector debt was a moderate 38% of GDP but its booming private non-financial business sector debt was 163%. Added together, it gives a total of 201% and its climbing rapidly. This may well be a conservative figure, given it is widely acknowledged the central government has overstated GDP growth. Australia, though it frequently features high on lists of the world’s most desirable locations, currently has the world’s second most indebted household sector, at 122% of GDP, soon to overtake Denmark in first place. Combined with private non-financial business sector debt, Australia has a staggering total of 203%, vastly larger than public debts at all levels of government.

There’ll be alot of this.
• India Concerned About Chinese Currency Devaluation (Reuters)
India on Friday called the slide in China’s yuan a “worrying” development for its flagging exports and said it was discussing possible measures to deal with a likely surge in imports from its northern neighbour. Trade Minister Nirmala Sitharaman said the yuan’s fall would worsen India’s trade deficit with China. While the government would not rush into any action, it had discussed likely steps it could take to counter an expected flood of cheap steel imports with domestic producers and the finance ministry, she said. The comments came a day after China allowed the biggest fall in the yuan in five months, pressuring regional currencies and sending global stock markets tumbling as investors feared it would trigger competitive devaluations.
“My deficit with China will widen,” she told reporters. India’s trade deficit with China stood at about $27 billion between April-September last year compared with nearly $49 billion in the fiscal year ending in March 2015. India steel companies such as JSW Ltd have asked the government to set a minimum import price to stop cheap imports undercutting them. A similar measure was adopted in 1999. “We have done ground work but are not rushing into it,” Sitharaman said when asked if India would impose a minimum import price for steel.

?? “..even during an enormous steel glut last year, China had to import certain high-quality steel products, such as the tips of ballpoint pens. ..”
• China PM: We’ll Let Market Forces Fix Overcapacity (Reuters)
China will use market solutions to ease its overcapacity woes and will not use investment stimulus to expand demand, Premier Li Keqiang said during a recent visit to northern Shanxi province, according to state media. “We will let the market play a decisive role, we will let businesses compete against each other and let those unable to compete die out,” the state-run Beijing News quoted Li as saying. “At the same time, we need to prioritize new forms of economic development.” Li said the country needed to improve existing production facilities because even during an enormous steel glut last year, China had to import certain high-quality steel products, such as the tips of ballpoint pens.
China needed to set ceilings on steel and coal production volumes and government officials should use remote sensing equipment to check companies, the premier also said, according to the article, which was re-posted on the State Council’s website. During his visit to Chongqing earlier this month, President Xi Jinping said China would focus on reducing overcapacity and lowering corporate costs.

As I said from the start. ZH did too. Seems such an easy thing to predict, because such a large part of our economies depend on jobs connected with oil.
• Fed’s Williams: “We Got It Wrong” On Benefits Of Low Oil Prices (ZH)
In late 2014 and early 2015, we tried to warn anyone who cared to listen time and time and time again that crashing crude prices are unambiguously bad for the economy and the market, contrary to what every Keynesian hack, tenured economist, Larry Kudlow and, naturally, central banker repeated – like a broken – record day after day: that the glorious benefits of the “gas savings tax cut” would unveil themselves any minute now, and unleash a new golden ago economic prosperity and push the US economy into 3%+ growth. Indeed, it was less than a year ago, on January 30 2015, when St. Louis Fed president Jim Bullard told Bloomberg TV that the oil price drop is unambiguously positive for the US. It wasn’t, and the predicted spending surge never happened. However, while that outcome was not surprising at all, what we were shocked by is that on Friday, following a speech to the California Bankers Association in Santa Barbara, during the subsequent Q&A, San Fran Fed president John Williams actually admitted the truth.
The Fed got it wrong when it predicted a drop in oil prices would be a big boon for the economy. It turned out the world had changed; the US has a lot of jobs connected to the oil industry.
And there you have it: these are the people micromanaging not only the S&P500 but the US, and thus, the global economy – by implication they have to be the smartest people not only in the room, but in the world. As it turns out, they are about as clueless as it gets because the single biggest alleged positive driver of the US economy, as defined by the Fed, ended up being the single biggest drag to the economy, as a “doom and gloomish conspiracy blog” repeatedly said, and as the Fed subsequently admitted. At this point we would have been the first to give Williams, and the Fed, props for admitting what in retrospect amounts to an epic mistake, and perhaps cheer a Fed which has changed its mind as the facts changed… and then we listened a little further into the interview only to find that not only has the Fed not learned anything at all, but is now openly lying to justify its mistake. To wit:
I would argue that we are seeing [the benefits of lower oil]. We are seeing them where we would expect to see them: consumer spending has been growing faster than you would otherwise expect.
Actually John, no, you are not seeing consumer spending growing faster at all; you are seeing consumer spending collapse as a cursory 5 second check at your very own St. Louis Fed chart depository will reveal:
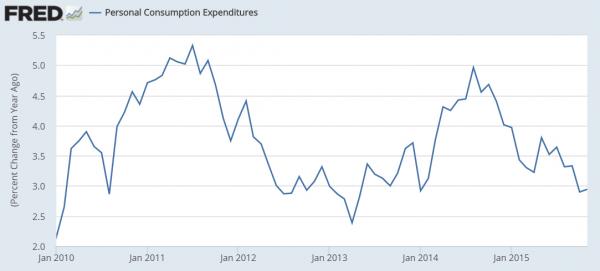
But the absolute cherry on top proving once and for all just how clueless the Fed remains despite its alleged epiphany, was Wiliams “conclusion” that consumers will finally change their behavior because having expected the gas drop to be temporary, now that gas prices have been low for “over a year” when responding to surveys, US consumers now expect oil to remain here, and as a result will splurge. So what Williams is saying is… short every energy company and prepare for mass defaults because oil will not rebound contrary to what the equity market is discounting. We can’t wait for Williams to explain in January 2017 how he was wrong – again – that a tsunami of energy defaults would be “unambiguously good” for the US economy.

Capital controls, protectionism, we’ll see all this and more.
• Free Capital Flows Can Put Economies In A Bind (Münchau)
When Margaret Thatcher took power in Britain in 1979, one of her first decisions as prime minister was to scrap capital controls. It was the beginning of a new era and not just for Britain. Free capital movement has since become one of the axioms of modern global capitalism. It is also one of the “four freedoms” of Europe’s single market (along with unencumbered movement of people, goods and services). We might now ask whether the removal of the policy instrument of capital controls may have contributed to a succession of financial crises. To answer that, it is instructive to revisit a debate of three decades ago, when many in Europe invested their hopes in a combination of free trade, free capital mobility, a fixed exchange rate and an independent monetary policy — four policies that the late Italian economist, Tommaso Padoa-Schioppa, called an “inconsistent quartet”.
What he meant was that the combination is logically impossible. If Britain, say, fixed its exchange rate to the Deutschmark, and if capital and goods could move freely across borders, the Bank of England would have to follow the policies of the Bundesbank. In the early 1990s, Britain put this to the test, joining the single European market and pegging its currency to Germany’s. The music soon stopped; after less than two years in the exchange-rate mechanism, sterling went back to a floating exchange rate. Other European countries took a different course, sacrificing monetary independence and creating a common currency. Both choices were internally consistent. What has changed since then is the rising importance of cross-border finance. Many emerging markets do not have a sufficiently strong financial infrastructure of their own.
Companies and individuals thus take out loans from foreigners denominated in euros or dollars. Latin America is reliant on US finance, just as Hungary relies on Austrian banks. With the end of quantitative easing in the US and rising interest rates, money is draining out of dollar-based emerging markets. Theoretically, it is the job of a central bank to bring the ensuing havoc to an end, which standard economic theory suggests it should be able to do so long as it follows a domestic inflation target. But if large parts of the economy are funded by foreign money, its room for manoeuvre is limited — as the French economist Hélène Rey has explained. In the good times, Prof Rey finds, credit flows into emerging markets where it fuels local asset price bubbles. When, years later, liquidity dries up and the hot money returns to safe havens in North America and Europe, the country is left in a mess.

Unease.
• Pensions, Mutual Funds Turn Back to Cash (WSJ)
U.S. public pension plans and mutual funds are sheltering more of their holdings in cash than they have in years, a sign of growing stress in financial markets. The ultradefensive stance reflects investors’ skittishness about global economic growth and uncertain prospects for further gains in assets. Pension funds have the added need to cut more checks as Americans retire in greater numbers, while mutual funds want cash to cover the risk that investors spooked by volatile markets will pull out more of their money. Large public retirement systems and open-end U.S. mutual funds have yanked nearly $200 billion from the market since mid-2014, according to a Wall Street Journal analysis of the most recent data available from Wilshire Trust Universe, Morningstar and the federal government.
That leaves pension funds with the highest cash levels as a percentage of assets since 2004. For mutual funds, the percentage of assets held in cash was the highest for the end of any quarter since at least 2007. The data run through Sept. 30, but many money managers say they remain very conservative. Pension consultants say some fund managers are considering socking even more of their assets into cash as they wait for the markets to calm down. “Some clients are asking us, ‘Would we be crazy to put 10% or 15% of our assets into cash?’,” said Michael A. Moran Goldman Sachs. Public pensions and mutual funds collectively manage $16 trillion, close to the value of U.S. gross domestic product, so even small shifts in their holdings can ripple through the trading world.
The movement of longer-term money to the sidelines has left the market increasingly in the hands of investors such as hedge funds, high-speed traders and exchange-traded funds that buy and sell more frequently, potentially leaving it more vulnerable to sharp swings, according to some money managers. [..] Managers of some pension plans and mutual funds said they limited their losses last year by moving more of their holdings into cash. Returns on cash-like securities were basically zero in 2015, while the Dow Jones Industrial Average fell 2.2% and the S&P 500 declined 0.7%. New York City’s $162 billion retirement system has more than tripled its cash holdings since mid-2014 to cut the plan’s interest-rate exposure. As a result, New York City’s allocations to plain vanilla stocks and fixed-income securities have fallen.

“In the US following the December rate rise the cost of mortgages has soared by 50pc. ”
• UK House Price To Crash As Global Asset Prices Unravel (Tel.)
House prices have broken free from reality and defied gravity for far too long, but they are an asset like anything else, and there are six clear reasons a nasty correction looms in the coming year . Asset prices around the world soared as central bankers embarked on the greatest money printing experiment in history. While much of that money flowed into the stock market, a great deal also found its way into house prices. What we are now witnessing on trading screens around the world is the unwinding of the era of monetary excess, and house prices will not escape the fallout. The end of easy money began when the US stopped its third QE programme in October 2014. That date marks the point the US balance sheet, or amount of money in the system, stopped rising, having soared from $800m in 2008 to more than $4 trillion.
Without an ever-increasing supply of money the world economy is now slowing sharply. The first assets to be impacted by the downturn were commodities. The price of things such as oil are set daily in one of the largest and most highly traded markets across the world and as a result it is highly sensitive to any changes in demand and supply. Admittedly there are also supply-side factors impacting the oil price, but the weak demand from a slump is still a major factor. The next asset to fall was share prices. There was a delay of about 12 months because even though shares are also traded daily, their value depends on the profits of the company, and the impact of the commodity collapse took about a year to feed through. There is a delayed effect on property prices because the market is so inefficient.
Transactions can take up to three months to complete and the property itself may have to languish on the market for even longer. The prices are also dictated by estate agents, who have an interest in inflating them to raise fees. The number of transactions is also still about 40pc below that of 2006 and 2007, which allows prices to stray from the fundamentals for a longer period. It is true that Britain is suffering from a housing shortage, which drove UK house prices to a record high of an average of £208,286 in December, but like all asset prices they are on borrowed time. The fundamentals of demand and supply in UK housing will undergo a huge shift in the year ahead. A large portion of the demand for UK housing will fall away as the benefits of buy-to-let have effectively been killed off in recent budgets.
George Osborne slapped a huge tax increase on buy-to-let in the summer Budget, which will take effect from 2017 onwards. The removal of mortgage interest relief was the first stage and was followed by hiking stamp duty four months later in the November review. This could prove a double whammy on the housing market, turning potential buyers into sellers, and flooding the market with additional supply. A survey of landlords suggested 200,000 plan to exit the sector. The rapid growth of buy-to-let during the past decade looks set to be slammed into reverse.

Implosion.
• The West Is Losing The Battle For The Heart Of Europe (Reuters)
A little over a quarter of a century ago, Europe celebrated the healing of the schism that Communism enforced on it since World War Two, and which produced great tribunes of freedom. Lech Walesa, the Polish shipyard electrician, climbed over his yard wall in Gdansk to join and then lead a strike in 1980 – lighting the fuse to ignite, 10 years and a period of confinement later, a revolution that couldn’t be squashed. He was elected president in 1990. Vaclav Havel, the Czech writer and dissident who served years in prison for his opposition to the Communist government, emerged as the natural leader of the democrats who articulated the frustration of the country. He was elected president of the still-united Czechoslovakia in 1989.
Jozsef Antall, a descendant of the Hungarian nobility who opposed both the Hungarian fascists and communists, was imprisoned for helping lead the 1956 revolt against the Soviet Union. And he was foremost in the negotiations to end Communist rule in the late 1980s. He survived to be elected prime minister in 1990. These men were inspirations to their fellow citizens, heroes to the wider democratic world and were thought to be the advance guard of people who would grow and prosper in a Europe eschewing every kind of authoritarianism. Havel could say, with perfect certainty, that the Communists in power had developed in Czechs “a profound distrust of all generalizations, ideological platitudes, clichés, slogans, intellectual stereotypes… we are now largely immune to all hypnotic enticements, even of the traditionally persuasive national or nationalistic variety.”
It isn’t like that now. Poland, largest and most successful of the Central European states has, in the governing Law and Justice Party, a group of politicians driving hard to remold the institutions of the state so that their power withstands all challenge. The government has sought to pack the constitutional court with a majority of its supporters; extended the powers of the intelligence services and put a supporter at their head; and signed into law a measure which puts broadcasting under direct state control.

Democracy under scrutiny.
• Newly Elected Catalan President Vows Independence From Spain By 2017 (RT)
The Catalan parliament has sworn in Carles Puigdemont as the president of Catalonia. He will lead the region in its push towards independence from Spain by 2017. “We begin an extremely important process, unparalleled in our recent history, to create the Catalonia that we want, to collectively build a new country,” Puigdemont told the Catalan parliament, vowing to continue with his predecessor Artur Mas’ initiative to pull the region into independence. Puigdemont’s candidacy was backed by 70 lawmakers while 63 voted against, with two abstentions. The parliament has been in deadlock since Spain’s ruling party won most of the seats in September elections but failed to obtain a majority.
The Catalan parties had to agree on a new leader before Monday to avoid holding new regional elections. In a “last minute change”, Catalonia’s former president Artus Mas agreed to step down on Saturday and not seek reelection as pro-independence ‘Together for Yes’ coalition representative. The new candidate was backed by the anti-capitalist Popular Unity Candidacy (CUP) party, whose 10 seats has allowed them to secure a majority in the 135-seat chamber. The Catalan 18-month roadmap to independence suggests the approval of its own constitution and the building of necessary institutions, such as a central bank, judicial system and army.
Meanwhile Spanish Prime Minister Mariano Rajoy reiterated on Sunday that he would block any Catalan move towards independence to “defend the sovereignty” and “preserve democracy and all over Spain.” Catalonia has a population of 7.5 million people and represents nearly a fifth of Spain’s economic output. The local population has been dissatisfied with their taxes being used by Madrid to support poorer areas of the country.

Shut up! Show some respect for democracy.
• Dutch ‘No’ To Kiev-EU Accord Could Trip Continental Crisis: Juncker (AFP)
European Commission chief Jean-Claude Juncker urged Dutch voters Saturday not to oppose an EU cooperation deal with Ukraine, saying such a move “could open the doors to a continental crisis”. A citizens’ campaign in the Netherlands spearheaded by three strongly eurosceptic groups garnered more than 300,000 votes needed to trigger a non-binding referendum on the deal, three months from now. Observers said the vote, set for April 6, pointed more towards broader euroscepticism among the Dutch than actual opposition to the trade deal with Kiev, which fosters deeper cooperation with Brussels. A Dutch ‘no’ “could open the doors to a continental crisis,” Juncker told the authoritative NRC daily newspaper in an interview published on Saturday.
“Let’s not change the referendum into a vote about Europe,” Juncker urged Dutch voters, adding: “I sincerely hope that (the Dutch) won’t vote no for reasons that have nothing to do with the treaty itself.” Should Dutch voters oppose the deal, Russia “stood to benefit most,” he said. The 2014 association agreement provisionally came into effect on January 1 and nudges the former Soviet bloc nation towards eventual EU membership. On a visit to the Netherlands in November, Ukranian President Petro Poroshenko hailed the deal as the start of a new era for the Ukraine. Dutch Prime Minister Mark Rutte has said his government was bound by law to hold the referendum, and would afterwards assess the results to see if any change in policy was merited.
Although the results are not binding on Rutte’s Liberal-Labour coalition, the referendum is likely to be closely watched as eurosceptic parties – including that of far-right politician Geert Wilders – rise in the Dutch polls ahead of elections due in 2017. Russia has been incensed by the EU’s move to bring Ukraine closer to the European fold.

Ambrose won’t let go of his techno dreams.
• Britain Abandons Onshore Wind Just As New Technology Makes It Cheap (AEP)
The world’s biggest producer of wind turbines has accused Britain of obstructing use of new technology that can slash costs, preventing the wind industry from offering one of the cheapest forms of energy without subsidies. Anders Runevad, CEO of Vestas, said his company’s wind turbines can compete onshore against any other source of energy in the UK without need for state support, but only if the Government sweeps away impediments to a free market. While he stopped short of rebuking the Conservatives for kowtowing to ‘Nimbyism’, the wind industry is angry that ministers are changing the rules in an erratic fashion and imposing guidelines that effectively freeze development of onshore wind. “We can compete in a market-based system in onshore wind and we are happy to take on the challenge, so long as we are able to use our latest technology,” he told the Daily Telegraph.
“The UK has a tip-height restriction of 125 meters and this is cumbersome. Our new generation is well above that,” he said. Vestas is the UK’s market leader in onshore wind. Its latest models top 140 meters, towering over St Paul’s Cathedral. They capture more of the wind current and have bigger rotors that radically change the economics of wind power. “Over the last twenty years costs have come down by 80pc. They have come down by 50pc in the US since 2009,” said Mr Runevad. Half of all new turbines in Sweden are between 170 and 200 meters, while the latest projects in Germany average 165 meters. “Such limits mean the UK is being left behind in international markets,” said a ‘taskforce report’ by RenewableUK. The new technology has complex electronics, feeding ‘smart data’ from sensors back to a central computer system.
They have better gear boxes and hi-tech blades that raise yield and lower noise. The industry has learned the art of siting turbines, and controlling turbulence and sheer. Economies of scale have done the rest. This is why average purchase prices for wind power in the US have fallen to the once unthinkable level of 2.35 cents per kilowatt/hour (KWh), according to the US energy Department. At this level wind competes toe-to-toe with coal or gas, even without a carbon tax, an increasingly likely prospect in the 2020s following the COP21 climate deal in Paris. American Electric Power in Oklahoma tripled its demand for local wind power last year simply because the bids came in so low. “We estimate that onshore wind is either the cheapest or close to being the cheapest source of energy in most regions globally,” said Bank of America in a report last month.

This is where EU, Turkey wish to send people back into.
• 400,000 Syrians Starving In Besieged Areas (AlJazeera)
As aid agencies prepare to deliver food to Madaya, on the outskirts of Damascus, and two other besieged towns in Idlib province, an estimated 400,000 people are living under siege in 15 areas across Syria, according to the UN. A deal struck on Saturday permits the delivery of food to Madaya, currently surrounded by forces loyal to Syrian President Bashar al-Assad, and the villages of Foua and Kefraya in Idlib, both of which are hemmed in by rebel fighters. Due to a siege imposed by the Syrian government and the Lebanese Hezbollah group, an estimated 42,000 people in Madaya have little to no access to food, resulting in the deaths of at least 23 people by starvation so far, according to the charity Doctors Without Borders (MSF).
Reports of widespread malnutrition have emerged, some of them suggesting that Madaya residents are resorting to eating grass and insects for survival. In Kefraya and Foua, about 12,500 people are cut off from access to aid supplies by rebel groups, including al-Nusra Front. On December 26, Syrian government forces set up a checkpoint and sealed off the final road to Moadamiyah, a rebel-controlled town on the outskirts of Damascus, demanding that opposition groups lay down their arms and surrender. The Moadamiyah Media Office, run by pro-opposition activists, estimates that 45,000 civilians are stuck in the area for more than two weeks. The organisation said on Saturday that a siege that started in April 2013 and lasted a year, resulted in the deaths of 16 local residents due to a lack of food and medicine. It said the current one has killed one local resident so far this year: an eight-month-old boy who died from malnutrition on January 10.

As we enter another crisis ourselves, we will need to become more generous. Or face chaos.
• World’s Poor Lose Out As Aid Is Diverted To The Refugee Crisis (Guardian)
Sweden is one of the most generous countries in the world when it comes to international aid. Along with other Scandinavian countries, it has given bounteously to less fortunate nations for many years. With a population of under 10 million, it also takes more than its fair share of asylum seekers – an estimated 190,000 last year, with a further 100,000 to 170,000 expected to arrive in 2016. This is proving to be an expensive business. The Swedish migration agency says the cost of assimilating such a large number of asylum seekers will be €6.4bn (£4.4bn) this year – and a debate is raging about whether the aid budget should be raided to help meet the bill. In 2015, 25% of the aid budget was spent on refugees. One proposal is to raise that figure to 60%.
Other countries are responding in similar fashion. Italy raised its aid spending in 2015, but the extra money was mostly spent domestically on those who successfully made the dangerous voyage across the Mediterranean from north Africa. Final figures for development assistance collated by the OECD show that global aid spending rose to a record level of $137.2bn (£94bn) in 2014 – an increase of 1.2% on the previous year. But the money is not going to those countries that are in the greatest need. Spending on the least developed countries (LDCs) fell by almost 5% and as a share of the total fell below 30% for the first time since 2005. Donor countries are increasingly dipping into their aid budgets to deal with the migration crisis or diverting money that would previously have gone to sub-Saharan Africa to countries that are deemed to be fragile, such as Egypt, Pakistan and Syria, but are not classified as LDCs.
What’s more, the trend is likely to have continued and accelerated in 2015, a year that saw far more people arriving in Europe from north Africa and the Middle East. Italy was already spending 61% of its aid budget on refugees in 2014. For Greece, the other country on the front line, the figure was 46%. It is hardly surprising that the governments in Rome and Athens have responded in this way. Both have had austerity measures foisted upon them and are seeking to make ends meet as best they can. The fact is, though, that the entire development assistance system is creaking under the strain at a time when demands for aid are increasing.









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle January 11 2016