
Underwood&Underwood Chicago framed by Gothic stonework high in the Tribune Tower 1952



China’s strongarming all of eastern Asia into submission to its exports. This could get very ugly.
• South Korea Exports To China Tumble 15.7% In Q1 (Yonhap)
South Korea suffered a 15.7% fall in exports to China in the first quarter this year, data showed Sunday, deepening its overall trade woes. It marks the biggest drop in seven years in South Korea’s outbound shipments to China, its single biggest market. China accounts for about 25% of South Korea’s total exports. Exports to China stood at $28.5 billion in the year’s first three months, down 15.7% from a year earlier, according to the Korea International Trade Association (KITA). By item, exports of semiconductors, flat panel displays, petrochemical products, car parts and synthetic resins recorded notable declines. Experts cited a structural problem and suggested a shift in trade strategy. “Over 70% of South Korean goods exported to China are intermediate goods. China’s demand for those is diminishing,” said Park Jin-woo, head of KITA’s strategic market research office.
“In particular, China is making massive investments and expanding facilities in such sectors as semiconductors, while reducing imports.” He stressed the need for targeting the consumer goods market instead. South Korea’s exports to the United States also sank 3.3% on-year to $16.8 billion in the January-March period and imports were down 4.9% to $10.1 billion. Trade with Japan remains in trouble as well. Exports fell 13.1% to $5.5 billion, representing a double-digit drop for the sixth consecutive quarter, and imports dwindled 11.2% to $10.6 billion. In contrast, exports to Vietnam, which has emerged as South Korea’s third-largest exports market, maintained an upward trend. Exports grew 7.6% to $7 billion, although growth rates showed signs of slowing.

Mom and pop, shadow banking, P2P, Hollywood, Ponzi, it’s all there.
• Chinese P2P Shadow Lender’s Woes Expose Its Global Tentacles (WSJ)
A crisis rocking a loosely regulated lending network is underlining the risks of a financing boom that has channeled Chinese household money into Hollywood movies and Wall Street deals Droves of teary-eyed investors from around China have descended on Shanghai Kuailu Investment Group’s swanky offices over the past week to demand their money back after the firm halted redemptions on wealth-management products for the roughly 250,000 clients of the firm and three affiliates. The uncertainty around investments handled by Kuailu could force a re-evaluation of a financing trend that has become widespread, in the latest knock to a financial system damaged by months of stock-market turmoil and a slowing economy.
Kuailu is one of thousands of finance companies in a universe of Chinese “shadow banks” that funnel investors funds to businesses and individuals, often with an assurance of high returns. Moody’s estimated credit extended by nonbank financing companies in China stood at $370 billion in mid-2015. Many Chinese refer to the diverse industry using English: P2P, as in peer-to-peer lending, though that business of matching small lenders and borrowers is just one segment of operations at Kuailu. Kuailu isn’t the first such lender to leave investors hanging amid recent collapses in the sector. What is distinctive is how its problems are exposing an international dimension to the industry, which bankers said is common but little understood.
The Shanghai firm invested in at least 20 feature films, including the coming release of “The Bombing” starring Bruce Willis, according to the company. Client money holds a slice of a $9 billion deal to privatize NYSE-listed Chinese Internet-security company Qihoo 360 Technology, firm marketing documents show. A crisis-management specialist that Kuailu’s founding chairman this month put in charge of sorting through $1.5 billion in liabilities told the WSJ it wasn’t a Ponzi scheme, a fear some investors have raised with the company. “No cash flow. That’s the issue,” said Xu Qi, who estimated assets cover about 90% of what is owed to investors, but that most of it is tied up in investments or projects that can’t be quickly converted to cash.
Companies like Kuailu got their start in peer-to-peer lending, initially a modest effort to supply money to Chinese households and entrepreneurs that was endorsed by top government officials as a way to power new streams of consumer activity. But crowdsourced lending has quickly expanded and now powers financing across China, from wedding loans to land speculation. Like banks, but with less regulation, such lenders compete aggressively for deposits, often via online platforms. Many attract money faster than they can thoroughly research investments, according to analysts.

B Movie.
• Doha Oil Freeze Talks Face Last-Minute Trouble (Reuters)
A meeting between OPEC and non-OPEC oil producers on an agreement to freeze output ran into last-minute trouble in Qatar on Sunday due to a new request by OPEC’s de facto leader Saudi Arabia, sources told Reuters. Oil ministers were heading into a meeting with the Qatari emir, Sheikh Tamim bin Hamad al-Thani – who was instrumental in promoting output stability in recent months – in an attempt to rescue the deal designed to bolster the flagging price of crude. “There is an issue. Experts are discussing how to find an acceptable solution. I’m confident they will come up with a solution,” one of the sources said. According to another source, Saudi Arabia said it wanted all OPEC members to participate in the talks, despite insisting earlier on excluding Iran because Tehran does not want to freeze production.
Saudi Arabia has taken a tough stance on Iran, the only major OPEC producer to have refused to participate in the freeze. Tehran says it needs to regain market share after the lifting of international sanctions against it in January. Deputy Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman told Bloomberg that the kingdom would restrain its output only if all other major producers, including Iran, agreed to freeze production. More than a dozen nations inside and outside OPEC have officially confirmed they would attend the meeting in Doha but the role of Iran has been the key issue overhanging the talks. “We have told some OPEC and non-OPEC members like Russia that they should accept the reality of Iran’s return to the oil market,” Iran’s oil minister, Bijan Zanganeh, was quoted as saying by his ministry’s news agency SHANA on Saturday.

Iran will go all out.
• Iran Central Banker Dismisses Idea Of Oil Output Cut (CNBC)
Iran’s top central banker is adding to growing doubts about an agreement to freeze output at a meeting of oil producers in Doha, Qatar on Sunday. Ahead of a pivotal meeting that may determine the near-term outlook for crude prices, Iran on Saturday announced that it would not participate in the conference. The country, still trying to recover from Western sanctions, is seen trying to preserve market share, and has steadfastly resisted any suggestions that Iran should freeze or curb output in order to prop up prices. On the sidelines of an IMF meeting in Washington, D.C., Valiollah Seif, head of Iran’s central bank told CNBC that asking Iran to freeze output right now is unfair.
“What Iran is doing right now is trying to get back and secure its share of the market,” Seif said, adding that “what Saudi Arabia is asking Iran to do is not a very fair [or] logical request.” On several occasions, the leadership of Saudi Arabia has repeatedly said they would agree to an output freeze as long as Iran did too. Currently, analysts believe the two rivals are unlikely to reach a near-term consensus. Seif told CNBC that Iran, as a member of OPEC, has a quota of 2.4 million barrels per day. Under sanctions for its nuclear program, that quota went unfilled.
At the same other members used their output to fill the gap. “And right now, Iran is trying to just take back the quota it is entitled to get, so we are going to do that and this is the main direction of our economy,” Seif added. He went as far as to say other OPEC members are to blame for the sharp fall in oil prices, which are down more than 37% year to date. “This request is coming from those countries which are responsible for this surplus production in the market, because they have exceeded output beyond their quota, and I think this is not fair,” Seif added. He cautioned that this was his personal viewpoint, and the ultimate decision lies with Iran’s oil minister, Bijan Zangeneh.

Predators experimenting on an entire nation.
• Greece’s Creditors Weigh Extra Austerity Measures to Break Deadlock (WSJ)
Greece’s creditors are considering seeking extra austerity measures that would be triggered if Athens misses its fiscal targets, in a bid to bridge differences between Europe and the IMF and break a deadlock threatening to unravel the Greek bailout. Under the proposal, say officials involved in the discussions, Greece would have to sign up to so-called contingency measures of up to about €3 billion, on top of the package of about €5 billion in tax increases and spending cuts Greece and its lenders are already negotiating. The country would only have to implement the extra measures if falls short of targeted budget surpluses for coming years that were set out in last year’s bailout agreement, the officials say.
The idea, which has support from the eurozone’s dominant power Germany, hasn’t yet been agreed upon, and officials on the creditors’ side say it would be politically hard for Greece’s embattled government to swallow. Creditors say the contingency-measures idea could finally overcome the monthslong disagreement between European institutions and the IMF about the outlook for Greece’s budget. That disunity has paralyzed talks about what Greece needs to do to secure a new IMF loan program and unlock rescue funding from Europe. Without billions of euros in fresh bailout funds, Greece faces bankruptcy in July, when large debts fall due. Months of talks without agreement have stoked concern in Europe about another Greek debt drama this summer, reviving fears the country could tumble out of the eurozone.
Athens has argued that imposing even-more austerity measures would go beyond what was agreed in the July 2015 bailout deal, according to people familiar with Athens’s thinking. The deadlock among creditors since last fall stems from Germany’s insistence that Greece get no more money from the eurozone’s bailout fund until the IMF agrees to lend more money too. Since Greece’s bailout odyssey began in 2010, German Chancellor Angela Merkel has insisted IMF involvement is essential. But the IMF is unconvinced by the math of the eurozone’s July 2015 bailout plan for Greece. The fund says it can’t resume lending to Greece unless there is a combination of a credible fiscal plan for Greece and debt relief from Europe.
The creditors and Greece agreeing on a fiscal plan would allow for the start of concrete talks on a second thorny issue: debt relief for Greece. Germany is deeply reluctant to offer much debt relief, but tends to agree with the IMF about the weaknesses of Greece’s budget, rather than with the more upbeat assessments of the European Union’s executive arm, the Commission. The Commission believes around €5 billion of austerity measures would be enough for Greece to hit a key target in the bailout plan: a primary budget surplus, meaning before interest payments, of 3.5% of gross domestic product. But the IMF is more pessimistic about Greek growth and finances. It insists about €8 billion of savings are needed to hit the target. The European side’s proposed measures, the IMF thinks, would only get Greece to a primary surplus of 1.5% of GDP.

Dream on.
• Panama and a New Copernican Revolution (Tett)
The name Nicolaus Copernicus is not usually mentioned in the same breath as corporate tax planning or Mossack Fonseca. This month, however, it probably should be. Six centuries ago, the Polish astronomer formulated a model of the universe that put the sun, rather than the earth, at the centre of the solar system. It was a paradigm shift that led to a transformation in the way that we view the universe. I suspect something similar might be happening with global finance. This month, the International Consortium of Investigative Journalists (ICIJ) published some 11.5 million documents leaked from the Panamanian law firm Mossack Fonseca. Among other things, these gave details about offshore companies the firm created for the elite.
The leak has already provoked a number of political scandals: last week, the Icelandic prime minister resigned after it emerged that he had an offshore company in Panama; and David Cameron, the British prime minister, has faced a steady stream of criticism about an offshore company created by his late father. Meanwhile, revelations about Chinese and Russian billionaires could spark further recriminations. To my mind, it is not just the revelations concerning the rich and famous that make the Panama Papers so fascinating; after all, it is not illegal to create such companies, unless they are used to evade taxes or launder money. Instead, the most interesting issue is whether this leak will create something akin to a Copernican moment.
Think about it. Most of us vaguely know that money flows through offshore centres but the details of this world are very shadowy and opaque. Thus, insofar as any of us have ever tried to visualise the 21st-century “map” of global finance, we assumed that the visible onshore activity was the “sun” that dominated this universe — and offshore finance just a fuzzy little planet, that hovered on the edge. But the Panama Papers have given contours to that fuzzy, offshore world. More specifically, anyone who wants to get a sense of what has been happening in Panama can now go on to the ICIJ website and search those 11.5 million documents with keywords. Try it out at home — it is as simple as a Wikipedia search.
As further details tumble out, it’s not just more names that will be generated but numbers too. Even before the data were readily available, activist groups such as the Tax Justice Network had claimed that some $21tn-$32tn was being stashed in offshore centres, but they had no real way of verifying the figure. With the Panama Papers online, more precise figures could emerge — and with that the ability to compare them with the overall picture of global banking. Could this spark a bigger policy change, such as a crackdown on tax avoidance or money laundering? A cynic might argue not. Remember, powerful vested interests are involved. But if you want to get a sense of what can happen when that mental map flips, think about how attitudes to shadow banking have changed in the past decade.

EU does not rhyme with democracy, and never will. We’re going to see a lot of crazy claims and numbers pre-referendum.
• Wolfgang Schäuble Warns UK Of Tough Brexit Negotiations (FT)
Wolfgang Schäuble, Germany’s finance minister, has warned British chancellor George Osborne that Berlin would be a tough negotiator if the UK votes to leave the EU. Speaking on the sidelines of the IMF spring meetings on Saturday, Mr Schäuble, one of the strongest forces in European politics, also jested that British football teams in a post-Brexit world should be excluded from the European champions league — something not actually linked to EU membership. His confirmation that Germany would not readily agree to an easy trading relationship with Britain after Brexit undermines the Leave campaign’s argument that the UK would be able to secure preferential EU trade deals without freedom of movement of people or the need for Britain to contribute to the EU budget.
The German finance minister, who is known for his unyielding negotiating positions, told German media that he wanted the UK to remain in the EU and did not want to inflame the British debate. But he added that if Britain were to leave, the process would not be easy. The Treasury confirmed that Mr Schäuble told Mr Osborne just how tough negotiations would be after Brexit during a bilateral meeting this weekend — and made the same joke about European football. In Washington this weekend, finance minsters from around the world have gradually been waking up to the possibility that Britain will seek to leave the EU within a matter of months. The IMF said it would wreak “severe damage” to the British and European economies.
Christine Lagarde, the IMF head, admitted this week that while she hoped Europe would avoid having to deal with Brexit, “the continued relationship with other countries in the EU would be at risk”. The difficulties of post-Brexit negotiations will be amplified by elections in Germany and France in 2017, European finance ministers said privately on the sidelines of the IMF meetings. With populist rightwing Eurosceptic parties threatening mainstream politics in both countries, the domestic incentives would prevent concessions to Britain as politicians would need to show their electorates that leaving the EU comes with a heavy price.
Many European officials and ministers have tried to avoid the subject of how they would negotiate with the UK after Brexit, saying instead that they hoped the British people would vote to remain. But some did speak out. Klaus Regling, head of the European Stability Mechanism, said that the leave campaign’s ambition to secure full access to the single market without accepting free movement of people and budget contributions “has never happened in Europe”. “I’m pretty certain [the negotiations ] would take quite a while — two years is not enough — so there would be several years of high uncertainty, which would have a negative impact on the UK economy,” Mr Regling said.

BlackRock and ‘corporate responsibility’.. Yeah, sure.
• BlackRock Wields Its Big Stick Like a Wet Noodle (Morgenson)
For several years, Laurence D. Fink, chairman and chief executive of BlackRock, the money management giant, has been on a crusade, exhorting corporations to change their short-term ways. Executives should forgo tricks that reward short-term stock traders, he argues, like share buybacks purchased at high valuations. Instead, corporate managers should focus on creating value for long-term shareholders. It’s an admirable argument that has won Mr. Fink wise-man status on Wall Street and accolades in the press. Hillary Clinton has echoed his ideas on the campaign trail. Certainly, as the head of BlackRock, Mr. Fink wields an outsize stick. With $4.6 trillion in assets and ownership of shares in roughly 15,000 companies, BlackRock is the world’s largest investment manager.
But if Mr. Fink really wants to get the attention of company executives on stock buybacks and other corporate governance issues, why doesn’t BlackRock vote more often against CEO pay packages of companies that play the short-term game? Executive compensation is inextricably linked to the shareholder-unfriendly actions Mr. Fink has identified; voting against pay packages infected by short-termism would help curb the problem. But BlackRock rarely takes such a stance. From July 1, 2014, to last June 30, according to Proxy Insight, a data analysis firm, BlackRock voted to support pay practices at companies 96.2% of the time. On pay issues, anyway, Mr. Fink’s big stick is more like a wet noodle. BlackRock’s “yes” percentage runs far higher than that of other money managers that express concern about corporate responsibility. Domini Funds supported pay practices only 6% of the time during the period, while Calvert Investments did so at 46% of companies.

As if Auckland real estate wasn’t bad enough yet.
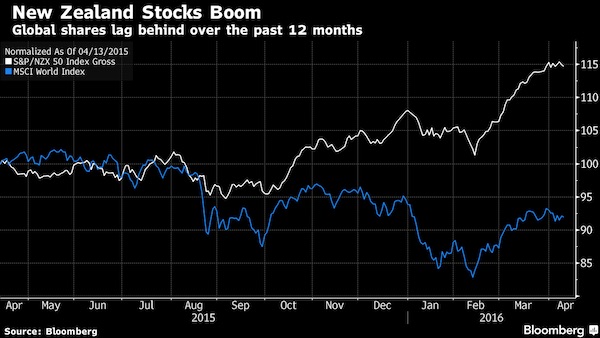
• Foreign Investment Turns New Zealand Stock Market Into A Casino (BBG)
As fund manager Mark Williams deliberated from his London office where next to invest, the world’s most remote stock market was just too good to pass up. That’s worrying locals, 11,000 miles away in New Zealand. The S&P/NZX 50 Index is the world’s best-performing developed stock gauge this year, climbing more than 7% to a record after overseas buying of equities jumped 21% in 2015. That’s driven stock valuations in the South-Pacific nation close to a record high, leaving them more expensive than anywhere else in the region. Funds from Henderson Global Investors to Liontrust Asset Management are buying into New Zealand, lured by dividends almost double the global average, rising earnings and expectations the central bank will cut interest rates to maintain growth.
Yet with a market cap of about $75 billion, smaller than the publicly traded value of Nike, opportunities are becoming more limited, says Matthew Goodson, an Auckland-based investor. “We’ve seen significant offshore inflows into larger-cap stocks and that’s driven their valuations to unusually high levels,” Goodson, who helps oversee about $1 billion at Salt Funds Management, said by phone. “It’s swamped the market and it leaves them very vulnerable. We’re somewhat nervous.” Foreigners now own about one third of New Zealand’s market, about three times the overseas ownership of U.S. equities, according to estimates from brokerage JBWere. Mark Williams, a money manager at Liontrust, is optimistic, given he expects the nation’s central bank will cut its key interest rate from an already record-low 2.25%.
While New Zealand accounts for less than 0.1% of the MSCI All Country World Index, Williams said he has 4.5% of his fund invested in the country. He bought Spark New Zealand and Fletcher Building in March, attracted by dividend yields of more than 5%. Spark, a communications provider, is the largest member by weighting of the S&P/NZX 50 gauge. “We find plenty of opportunities in New Zealand,” Williams, who helps manage $6.7 billion running an Asian equity-income fund at Liontrust, said by phone from London. “Interest rates remain relatively high, so that could lead to further cuts.”

This author gets it spectacularly wrong.
• Free Trade Has Won: Adapt Or Die Is The Only Option Left To Us (G.)
The Tata Steel sale has revived the battle between protectionists and free traders, a debate that became particularly acute in the run-up to the creation of the World Trade Organisation in 1995, which marked the success of “free traders” all around the world. In the protectionist camp, there is now a wide range of political parties from the extreme left to the extreme right: from Syriza to Ukip, from the Front National to Podemos. The common element for all these parties is that they dream of returning to a time when “we were in control”; when we could easily open or close our borders; when the world was manageable and small and we did not have to compromise. That is why they want national rules rather than international ones; and that is also why ultimately most of them despise the EU, because it is based not on direct control but on compromise.
The problem with that notion is that such a cosy world does not exist any more. The new generations expect to talk, travel and trade with each other all over the world, no matter where they are. My children, for example, know more about startup products released for crowdfunding around the world than about what is sold in shops in our high street; they respond to fashions that are created thousands of miles away; and they expect products to reach them almost instantaneously, no matter where they are made. Fluidity, speed, seamlessness and complexity define the 21st century. Fighting those trends makes sense only if you are of such an age and means that you can afford the luxury of whingeing about the present and dreaming nostalgically about the past, but if you are still trying to make your way in life, you have to embrace change and adapt.
Companies are rightly responding as quickly as possible to those new demands and, as a result, we are witnessing a level of international outsourcing that we could never have imagined. “Made in” labels mean little nowadays: companies based in the west often have their production plants elsewhere and use components sourced from third countries; and are financed by investors in yet other countries. If that were not complex enough, when countries impose trade barriers and erect controls, companies simply move overnight. Regulators and governments often do not stand a chance. That does not mean regulators should let modern trade become the Wild West. But it means they need to have the flexibility and tools to react better and faster.

Banks create money out of nothing. They’re not intermediaries.
• Economists Ignore One of Capitalism’s Biggest Problems (Steve Keen)
I like Joe Stiglitz, both professionally and personally. His Globalization and its Discontents was virtually the only work by a Nobel Laureate economist that I cited favourably in my Debunking Economics, because he had the courage to challenge the professional orthodoxy on the “Washington Consensus”. Far more than most in the economics mainstream—like Ken Rogoff for example—Joe is capable of thinking outside its box. But Joe’s latest public contribution—“The Great Malaise Continues” on Project Syndicate—simply echoes the mainstream on a crucial point that explains why the US economy is at stall speed, which the mainstream simply doesn’t get. Joe correctly notes that “the world faces a deficiency of aggregate demand”, and attributes this to both “growing inequality and a mindless wave of fiscal austerity”, neither of which I dispute.
But then he adds that part of the problem is that “our banks … are not fit to fulfill their purpose” because “they have failed in their essential function of intermediation”: Between long-term savers (for example, sovereign wealth funds and those saving for retirement) and long-term investment in infrastructure stands our short-sighted and dysfunctional financial sector… Former US Federal Reserve Board Chairman Ben Bernanke once said that the world is suffering from a “savings glut.” That might have been the case had the best use of the world’s savings been investing in shoddy homes in the Nevada desert. But in the real world, there is a shortage of funds; even projects with high social returns often can’t get financing. I’m the last one to defend banks, but here Joe is quite wrong: the banks have very good reasons not to “fulfill their purpose” today, because that purpose is not what Joe thinks it is.
Banks don’t “intermediate loans”, they “originate loans”, and they have every reason not to originate right now. In effect, Joe is complaining that banks aren’t doing what economics textbooks say they should do. But those textbooks are profoundly wrong about the actual functioning of banks, and until the economics profession gets its head around this and why it matters, then the economy will be stuck in the Great Malaise that Joe is hoping to lift us out of. The argument that banks merely intermediate between savers and investors leads the mainstream to a manifestly false conclusion: that the level of private debt today is too low, because too little private debt is being created right now. In reality, the level of private debt is way too high, and that’s why so little lending is occurring.
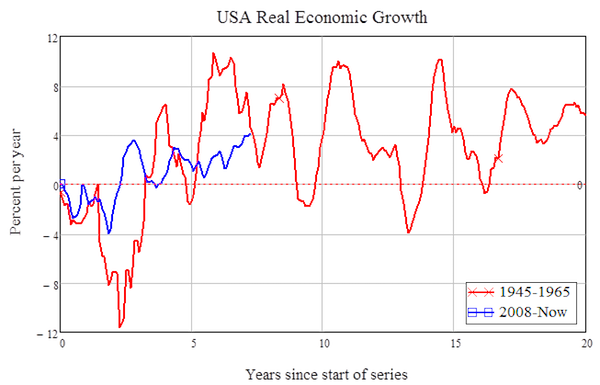
I can make the case empirically for non-economists pretty easily, thanks to an aside that Joe makes in his article. He observes that when WWII ended, many economists feared that there would be a period of stagnation: Others, harking back to the profound pessimism after the end of World War II, fear that the global economy could slip into depression, or at least into prolonged stagnation. In fact, the period from 1945 till 1965 is now regarded as the “Golden Age of Capitalism”. There was a severe slump initially as the economy changed from a war footing to a private one, but within 3 years, that transition was over and the US economy prospered—growing by as much as 10% in real terms in some years. (see Figure 1). The average from 1945 till 1965 was growth at 2.8% a year. In contrast, the average rate of economic growth since 2008 to today is precisely zero.

Time for Trump?!
• Saudi Arabia Warns of Economic Fallout if Congress Passes 9/11 Bill (NYT)
Saudi Arabia has told the Obama administration and members of Congress that it will sell off hundreds of billions of dollars’ worth of American assets held by the kingdom if Congress passes a bill that would allow the Saudi government to be held responsible in American courts for any role in the Sept. 11, 2001, attacks. The Obama administration has lobbied Congress to block the bill’s passage, according to administration officials and congressional aides from both parties, and the Saudi threats have been the subject of intense discussions in recent weeks between lawmakers and officials from the State Department and the Pentagon. The officials have warned senators of diplomatic and economic fallout from the legislation.
Adel al-Jubeir, the Saudi foreign minister, delivered the kingdom’s message personally last month during a trip to Washington, telling lawmakers that Saudi Arabia would be forced to sell up to $750 billion in treasury securities and other assets in the United States before they could be in danger of being frozen by American courts. Several outside economists are skeptical that the Saudis will follow through, saying that such a sell-off would be difficult to execute and would end up crippling the kingdom’s economy. But the threat is another sign of the escalating tensions between Saudi Arabia and the United States. The administration, which argues that the legislation would put Americans at legal risk overseas, has been lobbying so intently against the bill that some lawmakers and families of Sept. 11 victims are infuriated.
In their view, the Obama administration has consistently sided with the kingdom and has thwarted their efforts to learn what they believe to be the truth about the role some Saudi officials played in the terrorist plot. “It’s stunning to think that our government would back the Saudis over its own citizens,” said Mindy Kleinberg, whose husband died in the World Trade Center on Sept. 11 and who is part of a group of victims’ family members pushing for the legislation. President Obama will arrive in Riyadh on Wednesday for meetings with King Salman and other Saudi officials. It is unclear whether the dispute over the Sept. 11 legislation will be on the agenda for the talks. Saudi officials have long denied that the kingdom had any role in the Sept. 11 plot, and the 9/11 Commission found “no evidence that the Saudi government as an institution or senior Saudi officials individually funded the organization.”
But critics have noted that the commission’s narrow wording left open the possibility that less senior officials or parts of the Saudi government could have played a role. Suspicions have lingered, partly because of the conclusions of a 2002 congressional inquiry into the attacks that cited some evidence that Saudi officials living in the United States at the time had a hand in the plot. Those conclusions, contained in 28 pages of the report, still have not been released publicly. The dispute comes as bipartisan criticism is growing in Congress about Washington’s alliance with Saudi Arabia, for decades a crucial American ally in the Middle East and half of a partnership that once received little scrutiny from lawmakers. Last week, two senators introduced a resolution that would put restrictions on American arms sales to Saudi Arabia, which have expanded during the Obama administration.

French protests have been going on for a while. Not sure Yanis should desire a role in this.
• Varoufakis Joins French ‘Nuit Debout’ Anti-Labor Reform Protests (AFP)
Former Greek finance minister Yanis Varoufakis on Saturday addressed opponents of the French government’s workplace reforms at a protest in Paris, telling them the planned changes would “devalue labor.” “He (French President Francois Hollande) wants to devalue French labor… it can’t work,” Varoufakis told protesters as he paid a visit to the latest “Nuit Debout” (Up All Night) gathering at the city’s vast Place de la Republique. “Devaluing French labor can only deepen the crisis… I’m bringing to you solidarity from Athens,” he told the crowd. The labor reforms of France’s Socialist government aim to make it easier for struggling companies to fire people.
The government says they will make France’s rigid labor market more flexible but opponents say the reforms are too pro-business and will fail to reduce the 25% jobless rate among the young. Hundreds, at times thousands, of people have been demonstrating every night for the past two weeks at the Place de la Republique in central Paris. The labor reforms are a unifying theme of the gatherings but the so-called “Nuit Debout” movement is broader, embracing a range of anti-establishment grievances. The nightly protests have been marred by sporadic violence. The latest clashes erupted late Friday when, according to police, some 100 protesters set rubbish on fire and threw bottles and stones at officers, who responded with tear gas. Twenty-two people were arrested. The “Nuit Debout” demonstrations have spread to cities across France, becoming a major headache for the government.

I still can’t muster much enthousiasm about this. He should have used much harsher words. There are still 3,000 people locked up there, including many children.
• Pope Flies 12 Syrian Refugees to Vatican in Potent Symbol for EU (BBG)
Pope Francis made an emotional visit to the Greek island of Lesbos Saturday, plucking 12 Syrian refugees to take back to Rome with him and draw attention to what he called Europe’s most serious humanitarian crisis since the end of World War II. Francis, who has made migration a defining issue of his papacy, visited a refugee center as he appealed to the international community to deal with the migrants crisis as a humanitarian catastrophe. The pope said there was “reason to weep” on his visit to the refugees, and he brushed aside any political reasons for his invitation to have three families from Syria, 12 people including six children, accompany him on the flight home. “It is a purely humanitarian thing,” he told reporters on his chartered plane.
The Vatican will take financial responsibility for the families and an organization of volunteers, Comunità di Sant’Egidio, will initially host the groups, according to a statement. During the five-hour visit to Lesbos, the pontiff visited a refugee center with Ecumenical Patriarch Bartholomeos, the spiritual leader of the Orthodox Church, and was welcomed by Greek Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras. He also criticized the use of walls to keep migrants out. “In reality, barriers create divisions instead of promoting the true progress of peoples, and divisions sooner or later lead to conflicts,” Francis said in a speech at the port of Lesbos.
The visit was made days after migrants to Greece started being sent back to Turkey under a European Union agreement that has been criticized by the Vatican and denounced by human rights groups as impractical and legally suspect. Lesbos has become a repository for migrants seeking a better life in the EU: there were 3,560 refugees on the island as of Wednesday morning with more arriving each day, according to a daily tally issued by the Greek authorities. As he began the journey to Greece, the pope told reporters on his flight that the trip is marked by sadness. “This is important. It is a sad trip,” he said. “Refugees are not numbers, they are people who have faces, names, stories and need to be treated as such,” the pontiff said through his Twitter account.









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle April 17 2016