
Arthur Rothstein Highway marker in Polk County, Florida 1937

I’m so tired of this. No, ‘trust us’ is not good enough anymore. That is why Trump won, because it’s no longer enough to say ‘because we say so’. People don’t trust CIA et al. And you can’t turn that back on its head and demand trust now. You lost! I get so frustrated they even locked up my Facebook account again. There’s always people who want to complain about those who don’t toe lines.
• Here Is The US Intel Report Accusing Putin Of Helping Trump Win (ZH)
The farce is complete. One week after a joint FBI/DHS report was released, supposedly meant to prove beyond a reasonable doubt that Russia intervened in the US presidential election, and thus served as a diplomatic basis for Obama’s expulsion of 35 diplomats, yet which merely confirmed that a Ukrainian piece of malware which could be purchased by anyone, was responsible for spoofing various email accounts including that of the DNC and John Podesta, moments ago US intelligence agencies released a more “authoritative”, 25-page report, titled “Assessing Russian Activities and Intentions in Recent US Elections”, and which not surprisingly only serves to validate the media narrative, by concluding that Russian President Vladimir Putin ‘ordered’ an effort to influence U.S. presidential election.
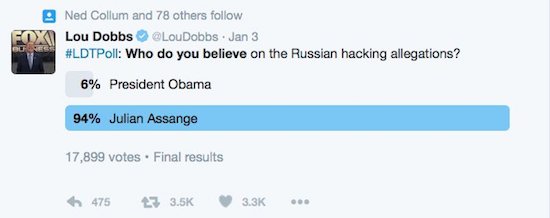
Specifically, the report concludes the following: “We assess Russian President Vladimir Putin ordered an influence campaign in 2016 aimed at the US presidential election. Russia’s goals were to undermine public faith in the US democratic process, denigrate Secretary Clinton, and harm her electability and potential presidency. We further assess Putin and the Russian Government developed a clear preference for President-elect Trump.” What proof is there? Sadly, again, none. However, as the intelligence agencies state, “We have high confidence in these judgments”… just like they had high confidence that Iraq had weapons of mass destruction. And while the report is severely lacking in any evidence, it is rich in judgments, such as the following:
“We assess Russian President Vladimir Putin ordered an influence campaign in 2016 aimed at the US presidential election. Russia’s goals were to undermine public faith in the US democratic process, denigrate Secretary Clinton, and harm her electability and potential presidency. We further assess Putin and the Russian Government developed a clear preference for President-elect Trump. We have high confidence in these judgments. “We also assess Putin and the Russian Government aspired to help President-elect Trump’s election chances when possible by discrediting Secretary Clinton and publicly contrasting her unfavorably to him. All three agencies agree with this judgment.”
At this point a quick detour, because the intel agencies responsible for drafting the report then explain how “confident” they are: “CIA and FBI have high confidence in this judgment; NSA has moderate confidence.” What do these distinctions mean? High confidence generally indicates judgments based on high-quality information, and/or the nature of the issue makes it possible to render a solid judgment. However, high confidence judgments still carry a risk of being wrong. Moderate confidence generally means credibly sourced and plausible information, but not of sufficient quality or corroboration to warrant a higher level of confidence. In other words, while not carrying the infamous DHS disclaimer according to which last week’s entire joint FBI/DHS report is likely garbage, the US intel agencies admit they may well be “wrong.”

“Trump is supposed to side with the CIA which is trying to destroy him.”
• A Case Study in the Creation of False News (Paul Craig Roberts)
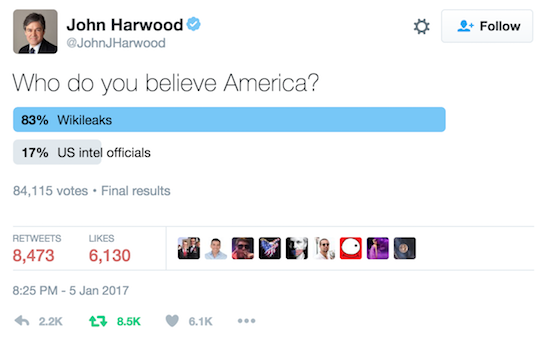
For many weeks we have witnessed the extraordinary attack by the CIA and its assets in Congress and the media on Donald Trump’s election. In an unprecedented effort to delegitimize Trump’s election as the product of Russian interference in the election, the CIA, media, senators and representatives have consistently made wild accusations for which they have no evidence. The CIA’s message to Trump is clear: Get in line with our agenda, or we are going to mess you over. It is clear that the CIA is warring against Trump. But the CIA’s media assets have turned the facts on their head and are blaming Trump for having a negative view of the CIA. Consider the January 4 Wall Street Journal article by Damian Paletta and Julian E. Barnes, which begins: “President-elect Donald Trump, a harsh critic of U.S. intelligence agencies . . .”
The two presstitutes set up their false news story by putting the shoe on the other foot. It is Trump who is the harsh critic rather than the victim of the CIA’s harsh accusations. Set up this way, the story continues: “White House officials have been increasingly frustrated by Mr. Trump’s confrontations with intelligence officials. ‘It’s appalling,” the official said. “No president has ever taken on the CIA and come out looking good.’” Now that the story is Trump taking on the CIA and not the CIA taking on Trump, the case can be built against Trump: Analysts accustomed to more cohesion with the White House are “jarred” by Trump’s skepticism of the CIA’s assessment that Putin got him elected. Trump is supposed to respond to the allegation by saying: I am not legitimate. Here take back the presidency.
WikiLeaks’ Assange has stated unequivocally that there was no hack. The information came to WikiLeaks as a leak, which suggests that it came from inside the Democratic National Committee. That Trump sees it this way means, according to one unidentified official that “It’s pretty horrifying to me that he’s siding with Assange over the intelligence agencies.” You see, Trump is supposed to side with the CIA which is trying to destroy him. Has the CIA shot itself in both feet? How can the agency control policy by manipulating the information fed to the President when the President does not trust the agency?

Leonard Peltier has been in jail for 40 years for a set-up. Forget about Snowden and Chelsea. Not going to happen.
• Obama Set For Pardon Frenzy As He Leaves Office (AFP)
A Rastafarian prophet, a former Taliban captive and thousands of minor drug traffickers have one thing in common: Their names have been submitted to President Barack Obama for clemency before he leaves office in two weeks. Some US presidents have used this regal power of leniency in a pointed way near the end of their term in office. On the last day of his term in 2001, Democratic president Bill Clinton granted pardon in a highly controversial move to late fugitive trader Marc Rich, whose ex-wife had been a major donor to Democrats. Sixteen years later, Obama is fielding pressure from all sides to grant unlikely pardons or commutations of sentences to people whose supporters say have been unjustly sentenced or sought out by the justice system.
Among them is Bowe Bergdahl, a US Army sergeant held captive for five years by the Taliban before his release in a prisoner swap, who is due to be court-martialed for desertion. Leonard Peltier, a Native American activist convicted for the 1975 deaths of two FBI agents in what his supporters say was a setup, is also hoping to enjoy Obama’s good graces. Then there’s Edward Snowden, who made the shattering revelation in 2013 of a global communications and internet surveillance system set up by the United States. The 33-year-old, a refugee in Russia, is backed by numerous celebrities like actress Susan Sarandon and singer Peter Gabriel, as well as Amnesty International and the American Civil Liberties Union. If Obama fails to pardon Snowden, his supporters say he may face the death penalty under the incoming administration of Republican Donald Trump, who has called him a “terrible traitor.”
In another leak case, Chelsea Manning is serving a 35-year sentence in solitary confinement for handing 700,000 sensitive military and diplomatic documents to WikiLeaks, some of them classified. Activists say her sentence is excessive and point to the psychological frailty of the transgender soldier who has already made two suicide attempts. Even though the White House has dismissed a possible pardon for Snowden and Manning, their supporters are still hoping for a final magnanimous gesture from a president about to leave the constraints of his high office on January 20.

We know.
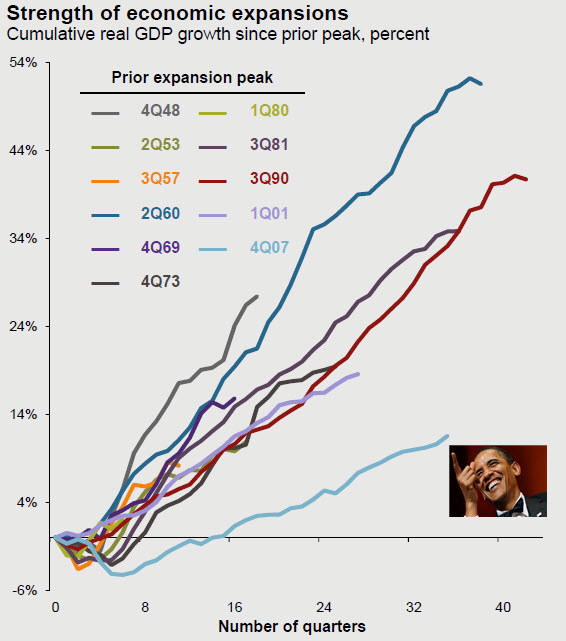
As the champagne glasses clink in Washington over a record-breaking streak of job growth on record (as the percent of the population employed slumped), and the fastest wage growth since the start of the recovery (for managers), we just wanted to remind a few blinkered media types that Obama’s “recovery” has officially been the worst recovery in US history (despite adding almost $10 trillion to the national debt)… When ‘fake news’ and ‘peddling fiction’ meet fact… Not quite as rosy an economic handover to Trump as The White House would like everyone to believe.

Peace, man!
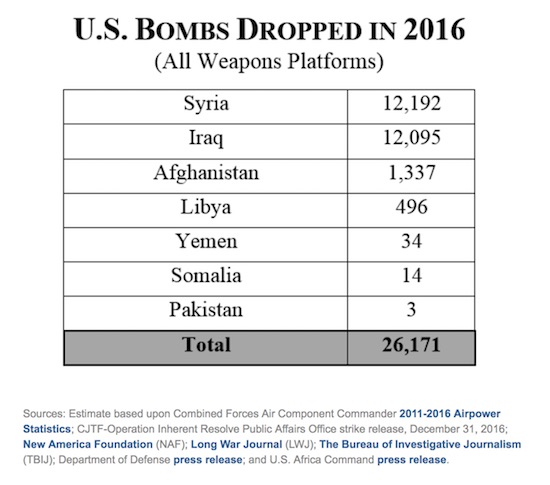
• How Many Bombs Did the United States Drop in 2016? (CFR)
As President Obama enters the final weeks of his presidency, there will be ample assessments of his foreign military approach, which has focused on reducing U.S. ground combat troops (with the notable exception of the Afghanistan surge), supporting local security partners, and authorizing the expansive use of air power. Whether this strategy “works”—i.e. reduces the threat posed by extremists operating from those countries and improves overall security and governance on the ground—is highly contested. Yet, for better or worse, these are the central tenets of the Obama doctrine.
In President Obama’s last year in office, the United States dropped 26,171 bombs in seven countries. This estimate is undoubtedly low, considering reliable data is only available for airstrikes in Pakistan, Yemen, Somalia, and Libya, and a single “strike,” according to the Pentagon’s definition, can involve multiple bombs or munitions. In 2016, the United States dropped 3,027 more bombs—and in one more country, Libya—than in 2015.
Most (24,287) were dropped in Iraq and Syria. This number is based on the percentage of total coalition airstrikes carried out in 2016 by the United States in Operation Inherent Resolve (OIR), the counter-Islamic State campaign. The Pentagon publishes a running count of bombs dropped by the United States and its partners, and we found data for 2016 using OIR public strike releases and this handy tool.* Using this data, we found that in 2016, the United States conducted about 79% (5,904) of the coalition airstrikes in Iraq and Syria, which together total 7,473. Of the total 30,743 bombs that the coalition dropped, then, the United States dropped 24,287 (79% of 30,743).
To determine how many U.S. bombs were dropped on each Iraq and Syria, we looked at the percentage of total U.S. OIR airstrikes conducted in each country. They were nearly evenly split, with 49.8% (or 2,941 airstrikes) carried out in Iraq, and 50.2% (or 2,963 airstrikes) in Syria. Therefore, the number of bombs dropped were also nearly the same in the two countries (12,095 in Iraq; 12,192 in Syria). Last year, the United States conducted approximately 67% of airstrikes in Iraq in 2016, and 96% of those in Syria.

Quick, Carney, cause chaos, or Le Pen will win…
• Le Pen Says Brexit Isn’t a Disaster and France Should Be Next (BBG)
French presidential candidate Marine Le Pen said the U.K. economy is weathering Brexit, giving her confidence to seek an immediate renegotiation of France’s relationship with the European Union if elected. “Brexit has not been a disaster,” Le Pen said at a meeting with English-language reporters in Paris on Friday. “The economic signals are good.” National Front leader Le Pen, who polls suggest will reach the presidential runoff in May, said she would seek talks with France’s EU partners “the day after my election” and put the result to a national referendum. She said the goal is to take back what she called “the four sovereignties”: control of borders, economic policy, money and legislation. France should dump the euro and return to a national currency, though the exchange rate could be linked to some sort of European currency mechanism, Le Pen said.
“I’ll give six months to these talks, and if at the end we have won back our sovereignty, I will tell the French to vote to stay in this Europe of nations and liberty,” she said. “If we don’t, I’ll suggest that they vote to leave.” Polls suggest Le Pen would finish second in the first round of France’s presidential elections on April 23, and lose a May 7 runoff to center-right candidate Francois Fillon. An Elabe poll released Thursday showed independent Emmanuel Macron gaining on Le Pen, taking second place in some hypothetical matchups. Le Pen, whose party received a $8.5 million loan from a Russian bank in 2014, said she doesn’t fear Russian meddling in France’s election. That follows U.S. intelligence findings that Russian officials directed hacking attacks to help elect Trump, whom she said she supports because his anti-globalist views were better for France.
“Every time big corporations, big finance don’t get what they want, they say it’s a conspiracy of the Russians,” she said. “It makes one laugh.” While the U.S. shouldn’t lecture anyone given its history of spying on allies, improved ties between Russia and the U.S. are in France’s interest, especially if they can cooperate on combating Islamic militants, Le Pen said. “I think that Mr. Trump and Putin can repair ties, and I hope so,” she said. “We don’t want to see an increase in tensions between the U.S. and Russia for a very selfish reason: we are in the middle.”

Should we let economists ‘heal’ their own field, or is it too late for that?
• Economics Is Driven By Ideology, Not Science (Pettifor)
As someone who correctly predicted the financial crisis (first in 2003 and later in a 2006 book) I support Andy Haldane’s assertion that the economics profession is “to some degree in crisis”. He is not the first to argue this. The retiring head of the UK Treasury admitted in 2016 that economists failed to spot the build-up of risk before 2007 and were guilty of what he called “a monumental collective intellectual error”. It is a collective intellectual failure that I believe has played a key role in the rise of political populism. The Bank of England’s chief economist was also right to compare the challenges facing economists to the famous “Michael Fish” moment, where everyone was assured that a hurricane wouldn’t hit before it did, bringing with it much devastation, in 1987.
Meteorologists have since transformed their field and improved forecasts. But that is not true of the economics profession. The dominant economic model of financial liberalisation, monetary policy dominance and fiscal austerity remains intact. In their defence, economists can’t be faulted for getting forecasts wrong. Political events such as Brexit are not easy to predict. But unlike economists, meteorologists have a deep understanding of the major forces shaping outcomes in their fields, even when they get precise forecasts wrong. Mainstream economists, by contrast, lack that deep understanding of the economic forces driving outcomes. The reason is not hard to understand. The field of meteorology is not underpinned by policy or by an agenda. Economics, by contrast, is dogged by ideology.
It is ideology, not science, that leads economists to wrongly assert that the market in money is like the market in widgets, and must not be regulated or tampered with by governments. That financial flows across borders must be “free”, regardless of whether they cause instability. That bankers are simply intermediaries between savers and borrowers – and do not create credit out of thin air. That monetary and fiscal policies that serve the finance sector with bailouts are tolerable, while those that serve the poor must be resisted. That the reasoning that informs the micro-economy can be extrapolated to reach conclusions about the macro-economy. In other words, the fallacy that the budgets of households (the micro-economy) can be aggregated and compared to the budgets of governments (the macro-economy).
Unsurprisingly, these flawed theories and models are a great comfort to financial elites – which is why so many economists are hired and funded by big banks, corporations and the wealthy. And it explains why their words and ideas are repeated by the media outlets that faithfully serve the status quo or “the establishment”. Very little has been done to transform the dominant economic model of financial and trade liberalisation or to limit economists’ almost religious belief in the efficiency of markets and hostility to public intervention.

“Let me take a long last look, before we say goodbye..”
• The Labor Market: The End Of The Innocence? (DiMartino Booth)
One of the first of life’s lessons we all learned is that we need not rush life; it will do that for us and in the end against our will. The inspiration for this wisdom could well have sprung from Ecclesiastes wherein we read these peaceful words: To every thing there is a season, and a time to every purpose under the heaven. Co-writers Don Henley and Bruce Hornsby embraced the spirit of this message as the 1980’s were coming to a close. You must agree 1989’s The End of the Innocence, that haunting and mournful ballad, was just the coda needed to move on to the last decade of the last century. “Let me take a long last look, before we say goodbye,” the song asks of the listener who can’t help themselves but to listen.
Many veteran investors, those who don’t need to be reminded about the Reagan era because they were there, may be feeling a bit more wistful as they peer over the horizon. They have lived through extraordinary economic times and maybe even recall the early 1970’s, the last time initial jobless claims were at their current historically low levels. They know, in other words, this can’t go on forever, that we are nearing the end of our own innocence. Federal Reserve Chair Janet Yellen has been adamant that economic cycles can’t die of old age. At the end of this month, we can proclaim to be living through the third longest expansion in postwar times. The parlor game occupying those on the Street these days entails devising scenarios that can push us into the second, or dare we dream, longest expansion of all.
The Wall Street Journal perfectly captures the infectious optimism, the yearning to keep that dream alive, by asking this in a headline: How Low Can the Unemployment Rate Go? Rather than keep you in suspense, the article’s answer is as follows: “Assuming the economy adds around 200,000 jobs a month in 2017 and the labor-force participation rate stays relatively constant, the unemployment rate would fall to 3.9% by the end of the year, according to a model maintained by the Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta.” If we do get there, a big if, we are sure to be staring down the barrel of appreciably higher interest rates and a flat, if not by then, inverted yield curve. The only precedent is, you guessed it, that which occurred in 2000, when the unemployment rate hit 3.6% as the longest cycle of all time was finally flaming out. Economics 101 teaches one tenet above all – that the unemployment rate is the most lagging within the data universe.
A recent visit with Dr. Gates, that steel-eyed sleuth, corroborated this maxim. “The unemployment rate is the single, most visible economic indicator for households. It’s easy to understand, black and white. Up is bad, down is good,” Gates observed. “If we keep getting downside surprises, it will feed even more consumer optimism. That happens late in the cycle.” What goes hand in hand with these late cycles guideposts? Since you asked, that optimism Gates cites tends to correlate with households overreaching their paychecks, which is exactly what we’re seeing. When adjusted for inflation, credit card borrowing is up 4.5% over last year, a full two percentage points above wage income, which is up 2.5% over the same period. That’s a new high for the current cycle. At 2.9%, inflation-adjusted spending is also running ahead of wage income.
These data are validated by separate data that shows state withholding tax collections are way off last year’s figures. “Vulnerabilities in household demand don’t happen overnight; they take time to rise to the surface,” Gates cautioned. “Households aren’t overstretched yet, but they’re getting there. Just like corporations substitute debt for profits late in the cycle, households also are starting to do just as they ride the wave of Trump optimism. Eventually this will run its course.”

So is Canada going to stand up to him?
• Canadian Woman Arrested In Turkey For Saying Erdogan Jails Journalists (CBC)
A Canadian woman has been arrested in Turkey for allegedly insulting the country’s president in comments posted on Facebook, her Turkish lawyer said Thursday. Ece Heper, 50, was arrested in the city of Kars in northeastern Turkey, and charged on Dec. 30, Sertac Celikkaleli told The Canadian Press. Heper, a dual Canadian-Turkish citizen, had been in the country since mid-November, according to her friends. “She is intense and opinionated, for sure,” Birgitta Pavic said from her Toronto home. “But everything is intense over there right now, especially criticizing the government.” At issue, her friends and lawyer said, are several recent Facebook posts about Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan.
In one posted on Dec. 28, Heper accused Erdogan of jailing journalists who suggest there is evidence Turkey is supporting the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant, known as ISIS or ISIL. Global Affairs Canada said they are aware of a Canadian citizen detained in Turkey and are providing consular assistance, but wouldn’t divulge further information, citing privacy laws. Heper has a log home in Norwood, Ont., about 150 kilometres northeast of Toronto, Pavic said, where she lives with five dogs she rescued from Turkey “that are like her children.” Her parents are dead and she is estranged from her brother, Pavic said, so her friends are taking up the cause to help her out.

We’re just going to watch it happen, ain’t we? That’s all we’re capable of.
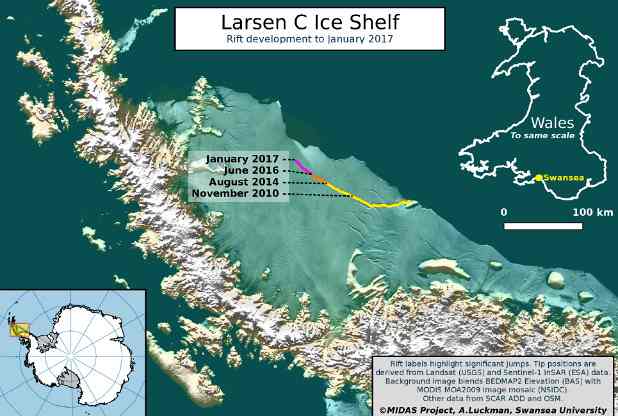
• Giant Iceberg Poised To Break Off From Larsen C Antarctic Shelf (G.)
A giant iceberg, with an area equivalent to Trinidad and Tobago, is poised to break off from the Antarctic shelf. A thread of just 20km of ice is now preventing the 5,000 sq km mass from floating away, following the sudden expansion last month of a rift that has been steadily growing for more than a decade. The iceberg, which is positioned on the most northern major ice shelf in Antarctica, known as Larsen C, is predicted to be one of the largest 10 break-offs ever recorded. Professor Adrian Luckman, a scientist at Swansea University and leader of the UK’s Midas project, said in a statement: “After a few months of steady, incremental advance since the last event, the rift grew suddenly by a further 18km during the second half of December 2016. Only a final 20km of ice now connects an iceberg one quarter the size of Wales to its parent ice shelf.”
The separation of the iceberg “will fundamentally change the landscape of the Antarctic Peninsula” and could trigger a wider break-up of the Larsen C ice shelf, he added. “If it doesn’t go in the next few months, I’ll be amazed,” Luckman told BBC News. Ice shelves are vast expanses of ice floating on the sea, several hundred metres thick, at the edge of glaciers. Scientists fear the loss of ice shelves will destabilise the frozen continent’s inland glaciers. And while the splitting off of the iceberg would not contribute to rising sea levels, the loss of glacial ice would. Martin O’Leary, also of Swansea University, said: “It just makes the whole shelf less stable. If it were to collapse there would be nothing holding the glaciers up and they would start to flow quite quickly indeed.”









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle January 7 2017