DPC Longacre Square, soon to be Times Square 1904



China went up on Friday, but Wall Street did not. Omen?
• Worst First Five Days of Year Ever For US Stocks Dim Outlook (WSJ)
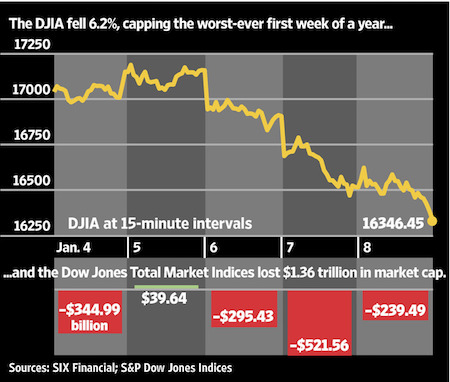
The Dow industrials tumbled more than 1,000 points this week, marking the worst first five days of any year, as volatility across the globe rattled investors. Traders said they are bracing for further big swings in the weeks to come. The Dow fell 1% Friday after starting the day in positive territory amid a strong U.S. jobs report and an uneventful session in China’s markets overnight. But shares slumped in afternoon trading as investors became unwilling to enter the weekend exposed to the risk of further losses. In all, U.S. stocks lost $1.36 trillion in value this past week.
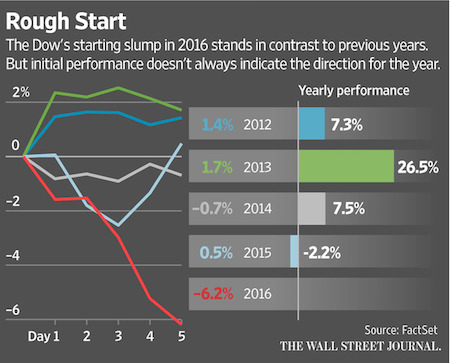
The unusually severe drop highlighted the precarious position of markets caught between relatively high valuations—attributable in part to years of easy money from central banks—and a new round of uncertainty about the fundamental underpinnings of key parts of the global economy. “The conundrum is there are parts of the world that are doing fine…and we have pockets that aren’t doing so well,” said Lawrence Kemp, head of BlackRock’s Fundamental Large Cap Growth team. “Given what’s going on in China and the rest of the world, the U.S. economy could grow a little more slowly.” The Dow Jones Industrial Average lost 1,078.58 points in the first week of 2016, down 6.2%. The broader S&P 500 was down 6%, also its worst five-day start to a year, and the Nasdaq Composite Index was down 7.3%.
Traders said the glum tone is likely to carry over into the coming week, as U.S. companies start reporting earnings for the last quarter of 2015. Corporate-earnings reports are widely expected to be underwhelming. The strong dollar is weighing on the competitiveness of U.S. exporters and the dollar value of companies’ overseas sales. Oil prices, which fell below $33 a barrel Friday in New York before closing at $33.16, continue to weaken. And China’s growth remains slow. Fourth-quarter earnings by companies in the S&P 500 are expected to come in 4.7% lower than they were a year earlier, according to FactSet.

Central banks
• The End of the Monetary Illusion Magnifies Shocks for Markets (BBG)
Central bankers are no longer the circuit breakers for financial markets. Monetary-policy makers, market saviors the past decade through the promise of interest-rate reductions or asset purchases, now lack the space to cut further or buy more. Even those willing to intensify their efforts increasingly doubt the potency of such policies. That’s leaving investors having to cope alone with shocks such as this week’s rout in China or when economic data disappoint, magnifying the impact of such events. “The monetary illusion is drawing to a close,” said Didier Saint Georges at Carmignac Gestion, an asset-management company. “With central banks becoming increasingly restricted in their stimulus policies, 2016 is likely to be the year when the markets awaken to economic reality.” Even against the backdrop of this week’s market losses, Fed officials signaled their intention to keep raising interest rates this year.
Those at the ECB and BoJ ended last year playing down suggestions they will ultimately need to intensify economic-aid programs. They have only themselves to blame for becoming agents of volatility, according to Christopher Walen at Kroll Bond Rating. He told Bloomberg TV this week that officials’ willingness to keep interest rates near zero and repeatedly buy bonds and other assets meant they became “way too involved in the global economy” and should have left more of the lifting work to governments. The handover to looser fiscal policy now needs to happen if economic growth and inflation are to get the spur they need, said Martin Malone at London-based brokerage Mint Partners. “Major economies have exhausted monetary and foreign-exchange policies,” he said. “Government action must take over from central-bank policies, triggering more confident private-sector investment and spending.”

Yeah, recovery.
• More Than 40% Of Young Americans Use Payday Loans Or Pawnshops (Ind.)
Young people are turning to desperate means to make ends meet. New figures that show 42% of Millennials, the generation born between 1980 and the mid-1990s, have turned to alternative finance including payday lenders and pawnshops in the past five years. The numbers come from a survey of more than 5,000 Millennials in the US by PriceWaterhouseCoopers and the Global Financial Literacy Excellence Center at George Washington University. Reports show that Millennials are high users of payday loans in the UK too. A 2014 report by the Financial Ombudsman Service showed that customers complaining about payday lenders were far more likely to be drawn from the 25-34 age group than any other.
The PwC study showed that a third of Millennials are very unsatisfied with their current financial situation and 81% have at least one long term debt, like a student loan or mortgage. That’s before they are saddled with interest on a payday loan that can be as much as 2000%. “They have already maxed out everything else and so they’re going to behavior that’s deemed even riskier,” said Shannon Schuyler, PwC’s corporate responsibility leader. The report also found that almost 30% of Millennials are overdrawn on their current accounts and more than half carry a credit card. Millennials are not the only generation suffering from rising debts. Earlier this week the Bank of England published a report showing that household borrowing surged in the run up to Christmas. The monthly cash rise in consumer credit for November 2015 was the highest since February 2008.

The shape of things to come. Who can afford a $5000-6000 funeral?
• British People Donating Bodies To Science To Avoid Funeral Costs (Tel.)
People are choosing to donate their body to science to avoid the cost of paying for a funeral, MPs have been warned. A leading forensic anthropologist said giving remains to anatomy departments can be seen as a way of avoiding the burden of funeral costs. However, science departments are not always able to take a person’s body, because of disease or because there is simply no space. Professor Sue Black, Director of the Centre for Anatomy and Human Identification at the University of Dundee, told the bereavement benefits inquiry families can be shocked to realise their loved one’s remains cannot be donated. “It is important that bequeathal is not viewed as an option to address funeral poverty although for some individuals it is unquestionably used in this manner,” she said.
As Dundee has one of the highest levels of child and adult poverty in Scotland, Professor Black said it is “not unusual for our bequeathal secretary to receive calls that will relate to concerns over funeral costs.” The Work and Pensions Committee is investigating funeral poverty after a freedom of information request by the BBC found the cost to local councils of so-called “paupers’ funerals” has risen almost 30pc to £1.7m in the past four years. The number of public health funerals, carried out by local authorities for people who die alone or whose relatives cannot afford to pay, has also risen by 11pc. [..] Bodies donated to science are mainly used for medical training and research.
But some are turned down because they are not suitable for educational use, for example if there has been a post-mortem and the body has already been dissected, or because the person has had a particularly destructive form of cancer, or if they have had an organ transplant. Potential donors must also make their wishes clear in their lifetime. “It’s really important that if people think that they want to donate their body, there are things that they must do. It’s not enough to say if verbally, they have to either find the consent forms or make a legal statement in a will or testament,” Professor Black said. The average cost of a basic funeral is now £3,702 according to a recent report.

Could be the major take-away from yesterday’s BLS report. Employment numbers do not reflect those of the employed.
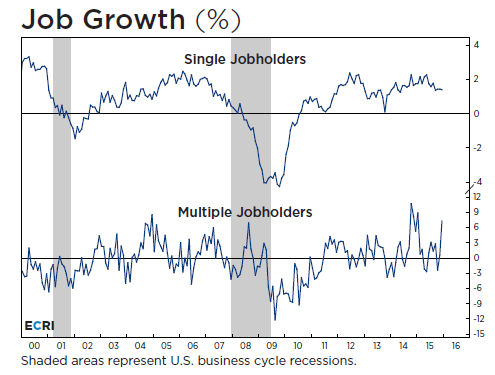
• Multiple Jobholders Responsible For 64% Of Net US Job Gains (ECRI)
The latest jobs report far exceeded consensus expectations as the economy added 292,000 nonfarm payroll jobs. But a closer look at the details reveals why concerns remain about the health of the labor market. In December, year-over-year (yoy) growth in multiple jobholders rose to an 11-month high, while yoy growth in single jobholders eased to a three-month low. Specifically, since May the number of multiple jobholders has increased by 752,000, while single jobholders have increased by 429,000. In other words, multiple jobholders have been responsible for 64% of the net job gains since last spring. The disproportionate importance of multiple jobholders – forced to cobble together a living – shows why the labor market is weaker than it seems. Notably, as long as these multiple jobholders log 35 hours of work per week – no matter how many part-time jobs that takes – they are considered full-time.

1967. Remember?
• First Profit Fall In 48 Years Looms Over US Energy Sector (MarketWatch)
The energy sector will depress U.S. fourth-quarter earnings and subdue growth for the entire S&P 500, making 2015 the weakest year for earnings since 2008, Goldman Sachs said Friday. The bank trimmed its S&P 500 earnings-per-share estimates for 2015, 2016 and 2017 in a note that highlighted three factors it expects to feature in earnings releases and on conference calls this year. The fourth-quarter and 2015 earnings season kicks off next week. The report from Aluminum producer Alcoa, scheduled for Monday after the market’s close, is seen as the unofficial start of several weeks of corporate news. The first factor Goldman highlighted is the energy sector, which the bank says is about to show a decline in operating earnings per share for 2015, its first negative reading since the bank started keeping records in 1967. “Energy EPS has collapsed along with crude oil prices,” analysts wrote in a note.
Energy EPS is highly sensitive to the price of oil, which Goldman is assuming will average $44 a barrel this year. Crude futures were trading below $33 a barrel early Friday, after hitting their lowest level since 2004 this week. Energy companies have been hammered by the slump in oil prices caused by oversupply, which has made some shale plays unprofitable and led companies to slash spending budgets, sell underperforming assets and cut staff and other costs. “The write-down in energy company assets has exacerbated the earnings hit from the 35% fall in Brent crude oil prices in 2015, following a 48% plunge in the commodity price in 2014,” said the note. In 2014, the energy sector accounted for $13, or 12%, of the overall S&P 500’s EPS reading of $113. In 2015, that contribution had tumbled to a loss of $2. That means energy contributed a $15 decline to S&P 500 earnings, which more than outweighed EPS gains in other sectors, said the note.

Much more downside to come.
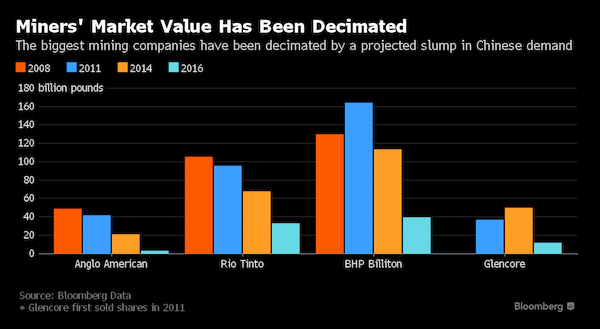
• Mining’s $1.4 Trillion Plunge Like Losing Apple, Google, Exxon Combined (BBG)
The $1.4 trillion lost in global mining stocks since 2011 exceeds the total market value of Apple, Exxon Mobil and Google’s parent Alphabet. When you’ve spent a decade building new mines from the Andean mountains to the West African jungle, it’s bad news when a downturn in China, your biggest customer, shows no signs of stopping. Investors have been unforgiving and concerns that it will only get worse pushed the Bloomberg World Mining Index to an 11-year low. “It’s terrible, there are no two ways about it,” said Paul Gait at Sanford C. Bernstein in London. “A lot of people were hoping at the start of 2016 to see at least some stabilization in the commodity performance in these stocks. Essentially people were looking to close the consensus short that has characterized 2015. This has clearly not happened.”
BHP Billiton and Rio Tinto were once among the world’s largest companies. Shares of the biggest commodity producers trading in London are now at least twice as volatile as the U.K.’s benchmark stock index. Raw-material prices slipped to the lowest since 1999 on Thursday, with China’s stock market suffering its worst start to the year in two decades after the central bank cut the yuan’s reference rate by the most since August. A weaker currency encourages exports from the nation and makes it costlier for it to import commodities, hurting those that supply them. Anglo American, worth almost £50 billion ($73 billion) in 2008, is now valued at £3.1 billion. The 99-year-old company, which is the world’s biggest diamond and platinum producer and owns some of the best copper and coal mines, is now worth less than mid-tier Randgold and copper miner Antofagasta.
Apple, the world’s most valuable company, is worth about $549 billion. Alphabet is valued at $510 billion and Exxon $321 billion. The Bloomberg mining index of 80 stocks slumped as much as 4.1% on Thursday to the lowest since 2004. Anglo closed down 11% in London to the lowest since it started trading in 1999. BHP tumbled 5% and Rio retreated 3.4%. Glencore settled down 8.3%.

They seem to get a lot wrong.
• Inventor of Market Circuit Breakers Says China Got It Wrong (BBG)
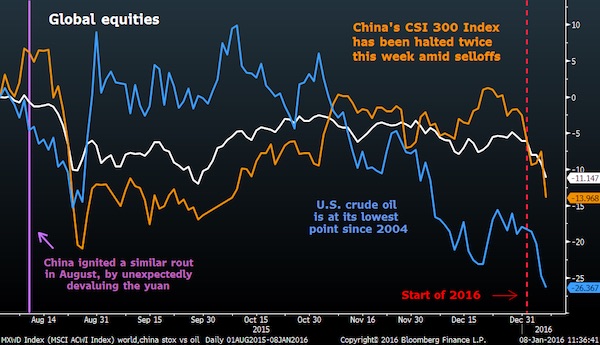
The man responsible for stock circuit breakers says Chinese officials must revise their safety net to avoid creating panic, joining critics who argue the nation’s trading halts are triggered too easily for such a volatile market. “They’re just on the wrong track,” said Nicholas Brady, 85, the former U.S. Treasury secretary who ran a committee that recommended the curbs on equity trading after the 1987 crash. “They need a set of circuit breakers that appropriately reflects their market.” Brady spoke Thursday after Chinese regulators suspended their newly introduced program that ends stock trading for the entire day after a 7% plunge. The halt was set off twice in its first week of operation, bolstering speculation China set its threshold too low. “The right thing to do is to widen their band,” Brady said in an interview.
The U.S. confronted a similar problem in the 1990s. The curb that the Brady Commission helped implement shut the market for the first time on Oct. 27, 1997, when the Dow Jones Industry Average lost 554 points. That was only a 7.2% decline, almost identical to the Thursday plunge in China’s CSI 300 Index. The trouble was that a decade-long surge in U.S. stock prices had diminished the value of each point in the Dow. The 1987 crash’s 508-point slump had amounted to a 23% tumble, three times greater than the decline that froze trading 10 years later. Regulators and exchanges pushed through a revision: If the Dow fell 10%, there would be an hour pause. At 20%, trading would cease for two hours, and at 30%, the day would end early.
In recent years, the benchmark that triggers the halts switched to the Standard & Poor’s 500 Index and the levels changed. Now it takes 7% and 13% drops to prompt a brief pause, and a 20% decline to close markets early for the day. Whereas 7% losses are rare in the U.S. – they were only common during the 2008 financial crisis, October 1987, and the Great Depression – Chinese shares have dropped about that much seven times in the past year. “I don’t think this is an exact science,” said Sang Lee, an analyst at financial-markets researcher Aite Group. With circuit breakers, “If you set these too low, instead of easing volatility it may increase volatility. That echoes the view of Brady, who was chairman of Wall Street powerhouse Dillon Read & Co. when President Ronald Reagan asked him to figure out what happened during the 1987 crash and propose solutions.

Lost in Beijing hubris.
• China Market Tsar In Spotlight Amid Stock Market Turmoil (Reuters)
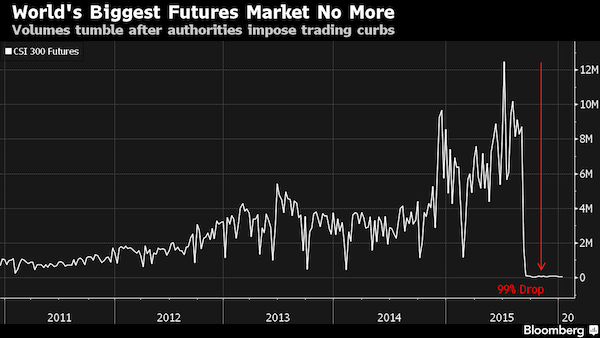
Xiao Gang, China’s stock market tsar, once remarked that the only thing he’d done right in life was marry his wife. No doubt the self-effacing Xiao, chairman of China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC), has done many other things right. Managing the stock market, though, might not be a high point of his career. Xiao faced internal criticism from the ruling Communist Party for his handling of the stock market crash last year, sources with ties to the leadership said at the time. In another blow, a “circuit breaker” mechanism to limit stock market losses that was introduced on Monday was deactivated by Thursday after it was blamed for exacerbating a sharp selloff. Online media had nicknamed Xiao “Mr Circuit Breaker”.
“There has to be responsibility. People are looking to the leader at the regulator. Xiao Gang is the public face,” said Fraser Howie, an independent China market analyst. “He was lucky to keep his job after the fiasco of July and August.” Xiao, 57, became chairman of the CSRC in the leadership churn when President Xi Jinping came into power, taking the helm of the regulator in March 2013. At the time, Chinese markets had been among the world’s worst-performing for six years – indeed they had not recovered from their collapse during the global financial crisis. Unfortunately for Xiao, they still haven’t. The challenge Xiao faced upon taking up the post was enormous: to attract fresh investment into equities from speculative bubbles in sectors like real estate, while defending against endemic insider trading.
To pull any of this off he needed to first convince China’s legions of small retail investors, who dominate transactions but are infamously fond of quick-hit speculative plays, that stocks are a safe place to park long-term capital. The urgency was heightened by the need to deal with China’s corporate debt overhang – Chinese firms had become almost entirely dependent on bank loans for financing, which naturally prejudiced economic development toward collateral-rich heavy industry and away from the innovative, nimble technology companies that tend to rely more on stock issuances to fund quick growth.

Chinese politics clash with economics. By default. It’s not just pushing a button or pulling a lever.
• As Growth Slows, China’s Era of Easy Choices Is Over (WSJ)
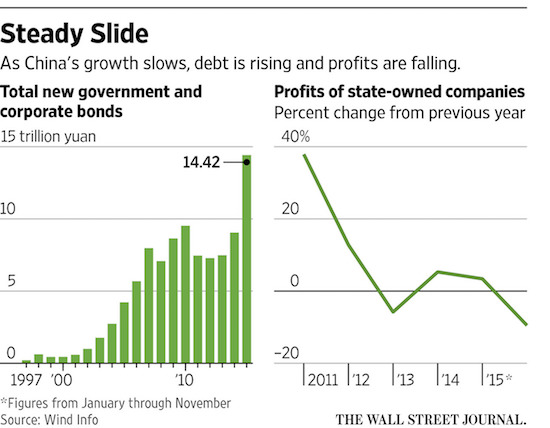
China has pulled hundreds of millions of people from poverty, supercharged its economy and burnished the pride of a nation that stood weak and isolated only decades ago. But swelling levels of debt, bloated state companies and an overall aversion to market forces are swamping the world’s second-largest economy, threatening to derail China’s ascent to the ranks of rich countries. As Beijing battles another bout of stock-market turmoil—and global markets shudder in response—the risks of doing nothing about these deep-seated problems are rising, economists said. Without a change in course, they said, China faces a period of low growth, crimped worker productivity and stagnating household wealth. It’s a condition known as “the middle-income trap.” “The era of easy growth is over,” said Victor Shih, professor at the University of California-San Diego.
“It’s increasingly about difficult choices.” Some economists don’t rule out an abrupt drop in growth, a hard landing that would see bad debts soar, consumer confidence tank, the Chinese yuan plunge, unemployment spiral and growth crater. More likely is that Beijing will continue to prop up growth, steering more capital to money-losing companies, unneeded infrastructure and debt servicing, depriving the economy of productive investment and leading to the sort of protracted malaise seen in Japan in recent decades. But China is less prosperous than Japan. An anemic China would weaken global growth at a time of low demand and prolong the downturn for big commodity producers like Brazil that have been dependent on the Asian economic giant. “They don’t want to take the pain,” said Alicia Garcia Herrero at investment bank Natixis. “But the longer they wait, the more difficult it becomes.”
Chinese leaders are aware of the risks. On Tuesday, Premier Li Keqiang called for a greater focus on innovation to spur new sources of economic growth and to revitalize traditional sectors, according to the Xinhua. A far-reaching economic blueprint laid out in 2013 after President Xi Jinping came to power vowed to let markets take a “decisive” role and build out a legal framework to restructure the economy and benefit consumers and small businesses, rather than industry. Progress to date, economists said, has been disappointing. Political objectives stand in the way. Mr. Xi has committed the government to meeting a goal of doubling income per person between 2010 and 2020, the eve of the 100th anniversary of the ruling Communist Party. That means, in Mr. Xi’s eyes, that growth must reach 6.5% annually. With global demand slipping and fewer Chinese entering the workforce, Beijing will need to resort to stimulus spending to get there, analysts said, delaying the reckoning with restructuring.

“As of September, China’s outstanding foreign debt stood at $1.53 trillion. More than two-thirds of that amount is expected to come due within a year..”
• Why China Shifted Its Strategy for the Yuan, and How It Backfired (WSJ)
The IMF’s decision on Nov. 30 to declare the yuan an official reserve currency removed an incentive for the central bank to keep propping up the currency. Rather, it aims to let it gradually depreciate with an eye toward sending it modestly higher in this year’s second half, according to advisers to the PBOC. That is when Beijing will host leaders from the Group of 20 major economies and will be eager to showcase China’s economic might. But that strategy is fraught with risks. Chief among them, analysts say, is the difficulty in reversing continued market expectations for a still-weaker yuan. In Hong Kong, where the yuan can be bought and sold freely, the Chinese currency now trades at a steep discount to its mainland cousin, whose trading is limited within a government-dictated band.
The gap has led some investors to try to profit from the different exchange rates, causing irregular flow of funds across China’s borders. By intervening in the Hong Kong market Thursday to try to cap the offshore yuan rate and at the same time allowing the onshore rate to weaken faster, the central bank appears to be attempting to find “a near-term market equilibrium level that can help the exchange rates converge,” analysts at HSBC wrote in a research note. The central bank also doesn’t want a too-weak yuan to exacerbate capital outflows and make it more difficult for Chinese companies to pay off their dollar-denominated debt. As of September, China’s outstanding foreign debt stood at $1.53 trillion. More than two-thirds of that amount is expected to come due within a year, according to government data.
Among the big foreign-debt holders are Chinese property companies, which have more than $60 billion of dollar debt outstanding, according to data provider Dealogic. Wary of continued weakening of the yuan, some Chinese companies are moving to pay off their debt early. State-run airliner China Eastern Airlines paid down $1 billion of dollar debts on Monday, citing the need to reduce its exposure to exchange-rate fluctuations. For many years, the prevailing investor sentiment had been the yuan had no way to go but up as China’s trade surplus surged. Investors have now shifted their mind-set to the other extreme.

Will they have any FX reserves left a year from now? It’s not all that obvious.
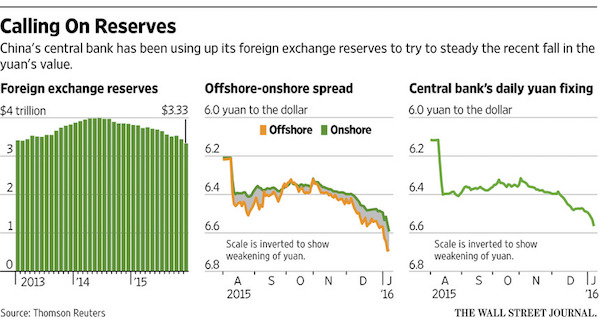
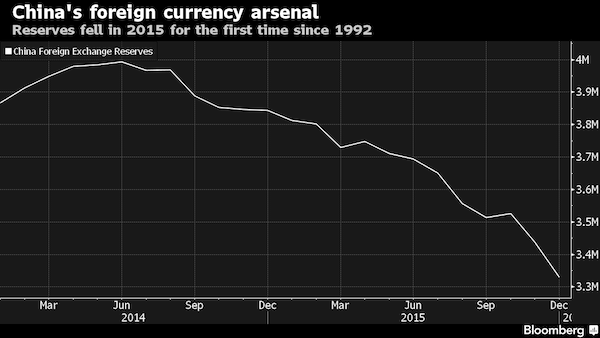
• China Finds $3 Trillion Just Doesn’t Pack the Punch It Used To (BBG)
China’s $3 trillion-plus in foreign currency reserves, the biggest such stockpile in the world, would seem to be a gold-plate insurance policy against the country’s current market chaos, a depreciating currency and torrent of capital leaving the country. Maybe not, say economists. First off, data point to an alarming burn rate of dollars at the People’s Bank of China. The nation’s stockpile of foreign exchange reserves plunged by $513 billion, or 13.4%, in 2015 to $3.33 trillion as the nation’s central bank coped with a weakening yuan and an estimated $843 billion in capital that left China between February and November, the most recent tally available according to data compiled by Bloomberg. “My greatest worry is the fast depletion of FX reserves,” said Yu Yongding, a member of China’s monetary policy committee when the currency was revalued in 2005.
True, trillions of dollars under the central bank’s care are thought to be invested in safe liquid securities, including Treasury bonds. The U.S. measure of China’s holdings of Treasuries, the benchmark liquid investment in dollars, stood at $1.25 trillion in October, according to the U.S. Treasury Department, which cautions that the figures may not reflect the true ownership of securities held in a custodial account in a third country. In China, like some other countries, the exact composition of China’s reserves is a state secret. But analysts worry the currency armory may not be as strong as it looks. That’s because some of the investments may not be liquid or easy to sell. Others may have suffered losses that haven’t been accounted for.
In addition, some Chinese reserves may have already been committed to fund pet government projects like the Silk Road fund to build roads, ports and railroad across Asia or tens of billions in government-backed loans to countries such as Venezuela, much of which is repaid through oil shipments. Then there are other liabilities that China needs to cover, such as the nation’s foreign currency debt to finance and manage imports denominated in overseas currencies. When those factors are taken into account, some $2.8 trillion in reserves may already be spoken for just to cover its liabilities, according to Hao Hong at Bocom International. “Considering China’s foreign debt, trade and exchange rate management, it needs around $3 trillion in foreign exchange reserves to be comfortable.” he said.
[..] “Where is the line in the sand, and what happens when we get there?,” said Charlene Chu, the former Fitch analyst known for her warnings over China’s debt risks. “China’s large hoard of foreign reserves gives the country considerable power and influence globally, and I would think they would want to protect that. If there is such a line in the sand, it is very possible we hit it in 2016.” To be sure, intervention isn’t the only thing dragging China’s reserves lower. There’s also a valuation impact from fluctuating currencies. Some of the fall may also reflect authorities accounting for its investments. Chu reckons much of the decline up to June 2015 was mostly due to investments in illiquid assets and valuation changes rather than capital outflows.

“The company could be worth anything from $1 trillion to upwards of $10 trillion..”
• Shock, Laughter Greet Plan for Saudi Arabia’s Record Oil IPO (BBG)
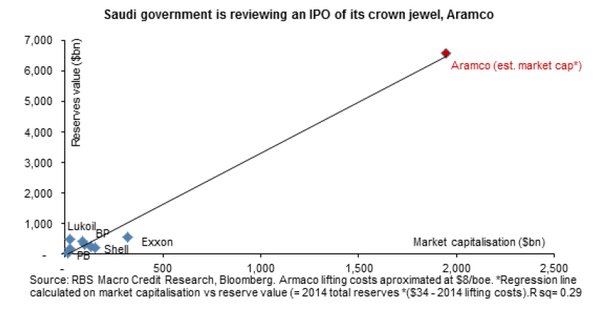
When one financial adviser heard about Saudi Arabia’s plans to list a company larger than the economies of most nations, he had to pull over his car because he was laughing so hard. Saudi Arabian Oil Co., or Aramco, the world’s largest oil producer, said Friday it’s considering an initial public offering. It confirmed an interview with Deputy Crown Prince Mohammad bin Salman published in the Economist Thursday. The news was greeted with incredulity in the financial industry, according to interviews with a half dozen bankers who do business in the Middle East. They asked not to be identified to protect their business interests. For one thing, Aramco’s inner workings are opaque, making its true value a mystery. Then there’s the timing. The price of crude oil is near its lowest level in more than a decade.
Discussions with Aramco about selling assets in the past had been about much smaller parts of the business, five of the people said. An initial public offering of the entire enterprise had only ever been discussed as a joke, one of the people said. The company could be worth anything from $1 trillion to upwards of $10 trillion, which would make it the most valuable company in the world, according to a note from Jason Tuvey at research firm Capital Economics. The last mega IPO from the oil industry was a decade ago, when Russia’s OAO Rosneft raised more than $10 billion. Even if Saudi Arabia sells a small stake, a listing could easily surpass that of Alibaba whose $25 billion IPO is the largest on record. Still, Aramco is unlikely to list on the biggest exchanges, according to Bloomberg oil strategist Julian Lee.
That would require the government to give investors more detailed information about Aramco’s reserves and production capacity, something oil-producing nations consider state secrets, he said. Aramco is considering selling an “appropriate%age” of its shares in the capital markets or listing a bundle of its subsidiaries, it said in the statement. Saudi Arabia typically sells stakes in state-owned companies to the public at below market value as part of its efforts to redistribute wealth. National Commercial Bank raised $6 billion in 2014 in the Middle East’s largest share sale. As the bankers do the sums, a big IPO won’t necessarily translate into big fees. Governments often pay low fees on their exits.

“.. it’s hard not to see talk of floating Aramco as a defensive move forced on a kingdom that is under pressure on the financial, political and military fronts.”
• Saudi Aramco’s Fire Sale (BBG)
That strange and rather unappetizing sound you just heard was the world’s energy bankers simultaneously salivating over the prospect of the oil deal of the century. In an interview published Thursday by The Economist, Saudi Arabia’s deputy crown prince Muhammad bin Salman said his country is considering privatizing Saudi Aramco. A quick back-of-the-envelope calculation for a company whose oil reserves dwarf those of Exxon Mobil yields a potential market capitalization of: gajillions. Apart from anything else, Aramco’s role in supplying roughly a tenth of the world’s oil would make its earnings guidance required reading not merely for sell-side analysts, but central bankers, government leaders and generals, too.There are many caveats here, beginning with the fact that the privatization is “something that is being reviewed.”
And if privatization were to proceed, it might well involve listing shares in some downstream part of Aramco such as petrochemicals, rather than the core upstream business or parent company. The bigger issue, though, is the idea appearing to have any traction at all and being spoken of publicly by no less a figure than the deputy crown prince. It adds a further twist to a narrative emanating from Saudi Arabia that suggests the global oil market is undergoing epochal change. The interview was wide-ranging, touching on relations with Iran and the U.S., women in the workforce, tax reform and possible privatization in many sectors, not just energy. And the deputy crown prince was in expansive mode, agreeing with his interviewer’s supposition that the autocratic kingdom is undergoing a “Thatcher revolution” and answering one question on attracting foreign investors with an almost Trumpian “I’m only giving out opportunities.”
The context for this sweeping vision, though, is the OPEC benchmark oil price having just slipped below $30 a barrel. The rational time to sell shares in Aramco would have been, let’s see, about 18 months ago, when oil was still trading in triple digits and the MSCI Emerging Markets Index was nudging 1100 rather than languishing below 750. Of course, other things play a part in deciding to privatize any state jewel of this scale – such as, in the words of the deputy crown prince, fostering transparency and strengthening the domestic stock market. Such factors were there, for example, in the privatization of China’s oil majors at the start of this century. Yet it’s hard not to see talk of floating Aramco as a defensive move forced on a kingdom that is under pressure on the financial, political and military fronts.
Saudi Arabia still sits on sizable foreign reserves. But the increases in (heavily subsidized) domestic fuel prices announced recently, as part of the country’s annual budget, indicate Riyadh’s desire to hunker down for a prolonged period of low oil prices. Indeed, it is possible that raising money from an Aramco IPO would be designed to show that the state is making its own sacrifices. [..] Change is clearly in the air. Riyadh is due later this month to unveil a medium-term “National Transformation Plan” aimed at, among other things, streamlining a public sector where wages swallow up nearly a fifth of GDP and diversifying the country’s tax base. This comes soon after a decision to open the country’s stock market to foreign investors. And, of course, it is happening amid an ongoing policy to maximize oil production in a suddenly much more competitive global oil market.
In one unnerving respect, this is bullish for oil: Ossified political structures are highly vulnerable precisely when they seek even partial reform. Any destabilization in Saudi Arabia could provide the supply shock that clears the glut in oil and raises oil prices. But don’t forget the warnings given by Saudi Arabia’s petroleum minister just over a year ago that global oil demand growth may face a “black swan” in the next few decades. Viewed through that lens, the policy of pumping more barrels out now looks like not merely a strategy to maintain market share but also to simply monetize reserves that might otherwise be left to mire underground. Take it one step further, and you might say the same of Riyadh suddenly deciding it’s time to cash in on Saudi Aramco now, oil price be damned.

“VW cited German law as its reason for not co-operating.”
• US Accuses Volkswagen Of Poor Co-Operation With Probe (FT)
Volkswagen is failing to co-operate sufficiently with a US investigation into the emissions scandal, according to New York attorney-general Eric Schneiderman, who warned that the authorities’ patience was “wearing thin”. Mr Schneiderman said on Friday that VW’s co-operation with a probe involving 47 state attorneys-general had been “spotty” and “slow”, adding to the German carmaker’s mounting troubles in the US. On Monday, the Department of Justice sued VW in a civil case, seeking at least $45bn in penalties. The US authorities’ clash with VW came as the company said that its annual sales had fallen last year for the first time in more than a decade.
A combination of the emissions scandal and turmoil in emerging markets has taken a toll on Europe’s biggest carmaker, pushing group-wide sales below 10m units in 2015. VW admitted in September that it had installed “defeat devices” in up to 11m cars, including 482,000 in the US, that served to understate the diesel-powered vehicles’ emissions of nitrogen oxides during official tests. The 47 state attorneys-general, plus prosecutors in Washington DC, are investigating whether VW violated environmental laws and misled consumers. The justice department is pursuing a similar probe now relating to almost 600,000 VW cars in the US.
“Volkswagen’s co-operation with the states’ investigation has been spotty — and frankly, more of the kind one expects from a company in denial than one seeking to leave behind a culture of admitted deception,” Mr Schneiderman said. He added that VW had been slow to produce documents from its US files, had sought to delay responses until it completed its own investigation, and had “failed to pursue every avenue to overcome the obstacles it says that German privacy law presents to turning over emails from its executives’ files in Germany”. “Our patience with Volkswagen is wearing thin,” Mr Schneiderman said. The New York Times first reported that VW was not handing over documents to the US authorities. VW cited German law as its reason for not co-operating.

Not long ago the very idea was considered heresy.
• Visible Light From Black Holes Detected For First Time (Guardian)
Astronomers have discovered that black holes can be observed through a simple optical telescope when material from surrounding space falls into them and releases violent bursts of light. The apparent contradiction emerges when a black hole’s gravity pulls in matter from nearby stars, producing light that can be viewed from a modest 20cm telescope. Japanese researchers detected light waves from V404 Cygni – an active black hole in the constellation of Cygnus, the Swan – when it awoke from a 26-year-long slumber in June 2015. Writing in the journal Nature, Mariko Kimura of Kyoto University and others report how telescopes spotted flashes of light coming from the black hole over the two weeks it remained active. The flashes of light lasted from several minutes to a few hours. Some of the telescopes were within reach of amateur astronomers, with lenses as small as 20cm.
“We now know that we can make observations based on optical rays – visible light, in other words – and that black holes can be observed without high-spec x-ray or gamma-ray telescopes,” Kimura said. The black hole, one of the closest to Earth, has a partner star somewhat smaller than the sun. The two objects circle each other every six-and-a-half days about 8,000 light years from Earth. Black holes with nearby stars can burst into life every few decades. In the case of V404 Cygni, the gravitational pull exerted on its partner star was so strong that it stripped matter from the surface. This ultimately spiralled down into the black hole, releasing a burst of radiation. Until now, similar outbursts had only been observed as intense flashes of x-rays and gamma-rays.
At 18.31 GMT on 15 June 2015, a gamma ray detector on Nasa’s Swift space telescope picked up the first signs of an outburst from V404 Cygni. In the wake of the event, Japanese scientists launched a worldwide effort to turn optical telescopes towards the black hole. The flickers of light are produced when x-rays released from matter falling into the black hole heat up the material left behind. Poshak Gandhi, an astronomer at Southampton University, said the black hole looked extremely bright when matter fell in, despite being veiled by interstellar gas and dust. “In the absence of this veil, V404 Cygni would have been one of the most distant objects in the Milky Way visible in dark skies to the unaided eye in June 2015,” he writes in the journal.

Death stalks Europe.
• Refugees Struggle In Sub-Zero Temperatures In Balkans (BBC)
Medics working at refugee aid camps in the Balkans say they are seeing a spike in the number of migrants falling ill as freezing temperatures arrive. It has fallen to as low as -11C (12F) in the region. The medical charities International Medical Corps and Medecins Sans Frontieres say most patients are suffering with respiratory problems such as bronchitis and flu. There are also concerns about people refusing or not seeking treatment. Migrants are offered medical assistance, warm clothes and food at the main refugee points at the Serbian border with Macedonia to the south, and Croatia to the north. International Medical Corps runs a makeshift clinic at the train station in the tiny town of Sid, in northern Serbia “Last week, when temperatures were a bit less, we were seeing around 50 to 60 people a day,” said Sanja Djurica, IMC team leader.
“This week, now that temperatures have fallen, it’s more like 100 or so a day.” “Almost all of them are suffering with respiratory illnesses brought on by the cold.” I met the Al-Maari family, who are making the journey as the snow falls thick and fast. They fled Syria three weeks ago, and have been on the road ever since. They are travelling with four children, the youngest is just two years old. His brother Mohammad, seven, is suffering with fever and a chest infection. “We are on a journey of death,” said Mohammad’s uncle, Iyad Al-Maari. “We can endure. But I am worried about the children – the cold, disease and hunger.” Mohammad is not thought to be seriously ill. Iyad said the family are determined to continue to Germany, where the children’s father is waiting for them.
“Some people are refusing further medical help after we’ve assessed them,” said Tuna Turkmen from MSF in Serbia. “Even if they are referred to hospital, most don’t go. They just want to keep moving… in case borders suddenly close and they are left stranded.” With tears in her eyes, Mohammad’s mother, Malak, said: “We didn’t want any of this… we just want the war to end in Syria.” The stress and anxiety can be seen clearly on Malak’s face. She is traumatised and desperate. Medics have also highlighted the enormous psychological impact on those making these journeys. International Medical Corps has psychologists on hand in Sid, and even though people only tend to stay there for a few hours, medics and aid workers do have some time to deliver “psychological first aid”. “It’s emotional comfort, empathetic listening and encouraging coping techniques,” said Sanja Djurica.

Checking those who filled in when Europe was a no-show. What a joke.
• Greek Police, Frontex To ‘Check’ Volunteers On Islands Receiving Migrants (Kath.)
The Greek Police and [EU border agency] Frontex are to carry out checks on non-governmental organizations and volunteers on islands of the northern Aegean which have been receiving large numbers of migrants, sources have told the Athens-Macedonia News Agency. “Our goal is not to offend the volunteers and employees of NGOs nor to disrupt their work but to simply highlight the presence of the police on the coastline and generally in areas where migrants and refugees are disembarking,” a police source told AMNA. There will also be an investigation into reports that certain individuals posed as refugees in order to steal the personal belongings of refugees or the smuggling boats on which they reach the islands. The broader checks will seek to determine that people declaring themselves as volunteers are working for an accredited organization. The aim is to restore a sense of security on the islands, police source said, not to prevent the work of the NGOs.