Vincent van Gogh Field with Flowers near Arles 1888

All politics today, with one finance story (and one on recycling). Expect venture capital to plunge in 2019.
• Venture Capital Spending Hit All-Time High In 2018 In Tech Bubble 2.0 (Colombo)
Though most people look at record VC spending as a sign of a strong, healthy economy, my research has found that the current VC boom is the result of another tech bubble that inflated due to the Federal Reserves ultra-stimulative monetary policies of the past decade. Unfortunately, this tech bubble is going to end just like the late-1990s dotcom bubble did – in another disastrous bust. The chart below shows the monthly count of global VC deals that raised $100 million or more since 2007. According to this chart, a new “unicorn” startup was born every four days in 2018.
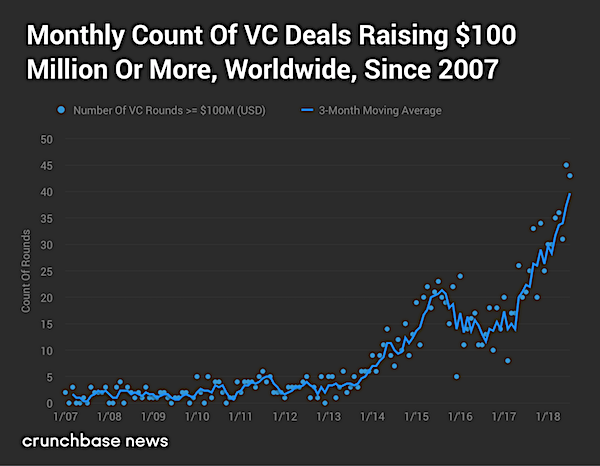
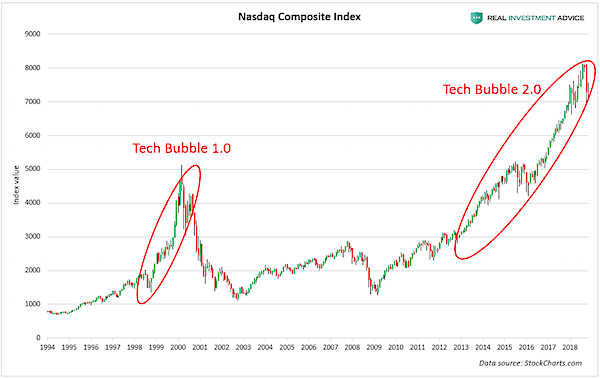
The chart below shows the Nasdaq Composite Index and the two bubbles that formed in it in the past two decades. Lofty tech stock prices and valuations encourage the tech startup bubble because publicly traded tech companies have more buying power with which to acquire tech startups and because they allow startups to IPO at very high valuations.
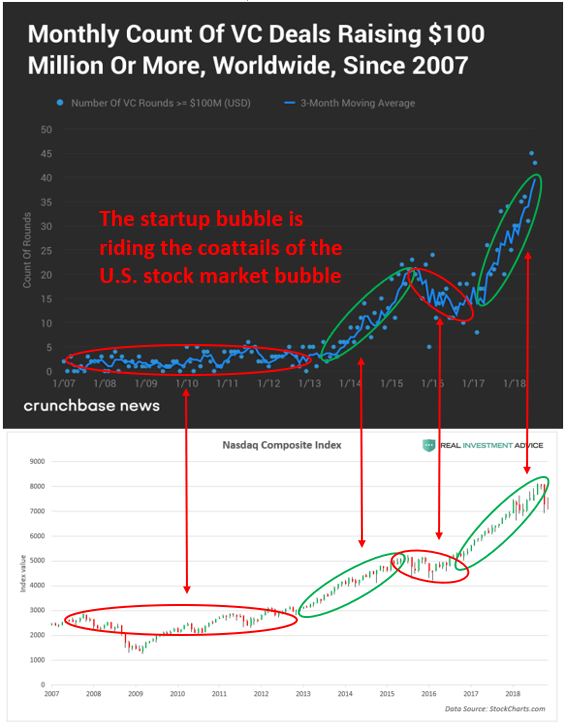
In the chart below, I compared the monthly global VC deals chart to the Nasdaq Composite Index and they line up perfectly. Surges in the Nasdaq lead to surges in VC deals, while lulls or declines in the Nasdaq lead to lulls or declines in VC deals.

The FBI has to be investigated over this (why was the probe launched?). But no-one has the power to do so.
• Trump Vents Fury Over Russia Stories (G.)
Donald Trump has strongly denied the stunning claim that he was secretly working on behalf of Russia and again threatened to declare a national emergency to fund a border wall. In 20-minute live phone interview with Fox News on Saturday night, he described as an “insult” the New York Times story that alleged the FBI launched an investigation into whether the he was acting as a Russian asset, against his own country’s interests. Trump said the story, which claimed the investigation opened after Trump fired the FBI director James Comey in May 2017, was “the most insulting article ever written”. “If you read the article you’ll see that they found absolutely nothing,” he said during the Fox News interview. “I think [the story] was a great insult and the New York Times is a disaster of a paper. It’s a very horrible thing they said.”
Citing anonymous sources, the Times said the investigation was part counterintelligence, to determine whether Trump was knowingly or unknowingly working for Moscow and posed a threat to national security. It was also part criminal, to ascertain whether Trump’s dismissal of Comey constituted obstruction of justice. The FBI effort was soon absorbed into the special counsel Robert Mueller’s investigation of Russian interference in the 2016 election and alleged collusion between Trump’s campaign and Moscow, the Times reported, adding that it was unclear if the counterintelligence aspect is still being pursued. The president again called Comey a “liar” and claimed the entire Russia investigation was a “terrible hoax”. “Everybody knows it. It’s really a shame because it takes time; it takes effort. Everybody knows there’s no collusion,” he said.
[..] Trump’s warm relationship with the Russian president, Vladimir Putin, has long set alarm bells ringing. The day after firing Comey, he hosted Russia’s foreign minister, Sergey Lavrov, in the Oval Office – and disclosed intelligence from an Israeli counterterrorism operation. At a summit in Helsinki last summer, Trump appeared to side with Putin over his own intelligence agencies on the question of election interference. On Saturday, the Washington Post reported that Trump took the notes from of a 2017 meeting with Putin in Hamburg from his own interpreter. Citing current and former US officials, the paper also said Trump instructed the linguist not to discuss what had transpired with other administration officials. Asked why he would not release the conversations, Trump said: “I would. I don’t care … I’m not keeping anything under wraps. I couldn’t care less.”

Sometimes you think they actually believe their Putin as bogeymen tales. But that can’t be true. They know as well as we do that there’s never been any proof, and you can’t base policy on innuendo alone. That would be dangerous.
• House Democrats Eye Reported FBI Probe Of Trump (R.)
A U.S. House of Representatives committee will look into a newspaper report that the FBI investigated whether President Donald Trump has been working on behalf of Russia, against U.S. interests, the panel’s Democratic chairman said on Saturday. The New York Times reported that the probe began in the days after Trump fired James Comey as director of the Federal Bureau of Investigation in May 2017 and said the agency’s counterintelligence investigators had to consider whether Trump’s actions constituted a possible threat to national security. Trump rejected the Times piece in a late Saturday night interview on Fox News as “the most insulting article I’ve ever had written” and lashed out at Comey and the FBI in half a dozen tweets.
House Judiciary Committee Chairman Jerrold Nadler said his panel “will take steps to better understand both the president’s actions and the FBI’s response to that behavior” in coming weeks. He also said lawmakers would seek to protect investigators from the president’s “increasingly unhinged attacks.” “There is no reason to doubt the seriousness or professionalism of the FBI, as the president did in reaction to this story,” Nadler, a New York Democrat, said in a statement. “We have learned from this reporting that, even in the earliest days of the Trump administration, the president’s behavior was so erratic and so concerning that the FBI felt compelled to do the unprecedented – open a counterintelligence investigation into a sitting president,” Nadler said.
House Intelligence Committee Chairman Adam Schiff said he could not comment on the specifics of the report, but said his committee would press ahead with its probe of Trump’s contacts with Russia. “Counterintelligence concerns about those associated with the Trump campaign, including the president himself, have been at the heart of our investigation since the beginning,” said Schiff, a California Democrat. Schiff said meetings, contacts and communications between Trump associates and Russians, as well as “the web of lies about those interactions, and the president’s own statements and actions,” have heightened the need to follow the evidence where it leads.

Schumer here moves on the basis of a collusion-themed link between Manafort and Deripaska.
But the article after this one says: “The Virginia judge who presided over Manafort’s first trial said the charges against him “manifestly don’t have anything to do with the [2016] campaign or with Russian collusion.” The collusion probe, the DC judge in Manafort’s second trial concurred, was “wholly irrelevant” to these charges.”
• Schumer To Force Vote On US Decision To Lift Sanctions On Russia Firms (R.)
U.S. Senate Democratic Leader Chuck Schumer said on Saturday he will force a vote soon on a resolution to disapprove the Trump administration’s decision to relax sanctions on three Russian companies connected to oligarch Oleg Deripaska. “I have concluded that the Treasury Department’s proposal is flawed and fails to sufficiently limit Oleg Deripaska’s control and influence of these companies and the Senate should move to block this misguided effort by the Trump Administration and keep these sanctions in place,” Schumer said in a news release.
The U.S. Treasury announced on Dec. 20 that it would lift sanctions imposed in April on the core businesses of Deripaska, including aluminum giant Rusal its parent En+ and power firm EuroSibEnergo, watering down the toughest penalties imposed since Moscow’s 2014 annexation of Crimea. After lobbying by European governments that followed the imposition of sanctions, Washington postponed enforcement of the sanctions and started talks with Deripaska’s team on removing Rusal and En+ from the blacklist if he ceded control of Rusal. The businessman, who has close ties to the Kremlin, also had ties with Paul Manafort, Trump’s former campaign manager, documents have showed.
An FBI agent said in an affidavit attached to a 2017 search warrant unsealed earlier this year that he had reviewed tax returns for a company controlled by Manafort and his wife that showed a $10 million loan from a Russian lender identified as Deripaska. On Thursday, U.S. Treasury Secretary Steven Mnuchin insisted that the Trump administration would keep tight control on companies linked to Deripaska, despite the decision to ease restrictions. Mnuchin said the firms would face consequences including the reimposition of sanctions if they failed to comply with the terms. Schumer said given Deripaska’s potential involvement with Manafort, and since special counsel Robert Mueller’s investigation into Trump’s ties with Russia has not yet concluded, “It’s all the more reason these sanctions must remain in place.”

It’s a shame I don’t have more speace for Aaron Maté’s piece. Click the link and read.
@yashalevine on Twitter about Kilimnik: “Yep, the supposed Russian intelligence asset linking Trump through Manafort to the Kremlin spent a decade on the payroll of a CIA cutout meddling in Russian politics. “
• The Manafort Revelation Is Not a Smoking Gun (Maté)
Partisans of the theory that Donald Trump conspired with the Kremlin to win the 2016 election believe that they have found their smoking gun. On Tuesday, defense attorneys inadvertently revealed that special counsel Robert Mueller has claimed that former Trump-campaign chairman Paul Manafort lied to prosecutors about sharing polling data with a Russian associate. Now we’re being told that the revelation “is the closest thing we have seen to collusion,” (former FBI agent Clint Watts), “makes the no-collusion scenario even more remote,” (New York magazine’s Jonathan Chait), and, “effectively end[s] the debate about whether there was ‘collusion.’” (Talking Points Memo’s Josh Marshall). But like prior developments in the Mueller probe that sparked similar declarations, the latest information about Manafort is hardly proof of collusion.
According to an accidentally unredacted passage, Mueller believes that Manafort “lied about sharing polling data…related to the 2016 presidential campaign,” with Konstantin Kilimnik, a Russian national who worked as Manafort’s fixer and translator in Ukraine. Manafort’s employment of Kilimnik has fueled speculation because Mueller has stated that Kilimnik has “ties to a Russian intelligence service and had such ties in 2016.”Yet Mueller’s only references that Kilmnik has Kremlin “ties” came in two court filings in 2017 and 2018, and it’s not clear what Mueller meant in either case. In April 2018, Manafort’s attorneys told a Virginia judge that they have made “multiple discovery requests” seeking any contacts between Manafort and “Russian intelligence officials,” but that the special counsel informed them that “there are no materials responsive to [those] requests.”
Kilimnik insists that he has “no relation to the Russian or any other intelligence service.” According to a lengthy profile in The Atlantic, “insinuations” that Kilimnik has worked for Russian intelligence during his years in Ukraine “were never backed by more than a smattering of circumstantial evidence.” All of this has been lost on US media outlets, who routinely portray Kilimnik as a “Russian operative” or an “alleged Russian spy.” [..] Rather than imagining it as part of some grand Trump-Russia conspiracy, there’s a more plausible explanation for why Manafort wanted public polling data to be forwarded to Ukrainian oligarchs. Manafort was heavily in debt when he joined Trump’s team. Being able to show former Ukrainian clients “that he was managing a winning candidate,” the Times noted, “would help [Manafort] collect money he claimed to be owed for his work on behalf of the Ukrainian parties.”
All of this highlights another inconvenient fact about Mueller’s case against Manafort: It is not about Russia, but about tax, bank, and lobbying violations stemming from his time in Ukraine. The Virginia judge who presided over Manafort’s first trial said the charges against him “manifestly don’t have anything to do with the [2016] campaign or with Russian collusion.” The collusion probe, the DC judge in Manafort’s second trial concurred, was “wholly irrelevant” to these charges.

And what goes for Aaron Maté’s piece is also valid for Stephen Cohen. Worth reading the whole thing.
• What Trump’s Syrian Withdrawal Really Reveals (Stephen Cohen)
First, no foreign-policy initiative undertaken by President Trump, however wise it may be in regard to US national interests, will be accepted by that establishment. Any prominent political figure who does so will promptly and falsely be branded, in the malign spirit of Russiagate, as “pro-Putin,” or, as was Senator Rand Paul, arguably the only foreign-policy statesman in the senate today, “an isolationist.” This is unprecedented in modern American history. Not even Richard Nixon was subject to such establishment constraints on his ability to conduct national-security policy during the Watergate scandals.
Second, not surprisingly, the condemnations of Trump’s decision are infused with escalating, but still unproven, Russiagate allegations of the president’s “collusion” with the Kremlin. Thus, equally predictably, the Times finds a Moscow source to say, of the withdrawals, “Trump is God’s gift that keeps on giving” to Putin. (In fact, it is not clear that the Kremlin is eager to see the United States withdraw from either Syria or Afghanistan, as this would leave Russia alone with what it regards as common terrorist enemies.)
Closer to home, there is the newly reelected Speaker of the House, Nancy Pelosi, who, when asked about Trump’s policies and Russian President Putin, told MSNBC’s Joy Reid: “I think that the president’s relationship with thugs all over the world is appalling. Vladimir Putin, really? Really? I think it’s dangerous.” By this “leadership” reasoning, Trump should be the first US president since FDR to have no “relationship” whatsoever with a Kremlin leader. And to the extent that Pelosi speaks for the Democratic Party, it can no longer be considered a party of American national security.
But, third, something larger than even anti-Trumpism plays a major role in condemnations of the president’s withdrawal decisions: imperial thinking about America’s rightful role in the world. Euphemisms abound, but, if not an entreaty to American empire, what else could the New York Times’ David Sanger mean when he writes of a “world order that the United States has led for the 73 years since World War II,” and complains that Trump is reducing “the global footprint needed to keep that order together”? Or when President Obama’s national-security adviser Susan Rice bemoans Trump’s failures in “preserving American global leadership,” which a Times lead editorial insists is an “imperative”?

The news about fake news has itself become fake news.
• Republican Baby Boomers More Likely To Share Fake News On Facebook (MW)
Social media doesn’t help people differentiate what is real from what is fake, but the phrase “fake news” has been used by social scientists to describe fictional articles online and perhaps more famously by President Donald Trump, who uses it as a cudgel against mainstream media outlets. Facebook, meanwhile, struggles to stem the flow of fake news and erroneous memes, though Chief Executive Mark Zuckerberg has said the world’s biggest social-media site is making progress in dealing with the problem. Trump’s relationship with the media has been acrimonious from the moment he embarked on his campaign for president.
Since then he has not only labeled as “fake” news outlets that have reported critically on his administration but described CNN, NBC, ABC, CBS and the New York Times as “the enemy of the American people.” The good news: Most Facebook users did not share any fake news articles during the 2016 U.S. presidential campaign, according to a study released Wednesday, but the small number who did were mostly Republican Americans over the age of 65. The findings suggest the need for “renewed attention” to educate “particular vulnerable individuals,” such as aging baby boomers, about fake news or misleading information that appears to resemble a fact-checked news article published by a legitimate and fact-based media outlet, researchers said.
[..] To shed light on the issue in the latest study of which users were more likely to share misleading facts on Facebook during the 2016 presidential election, Andrew Guess, an associate professor at Princeton University, and his colleagues disseminated an online survey to 3,500 people in three waves throughout the 2016 campaign. Of the respondents, 1,331 in the initial wave agreed to share their Facebook profile data, which allowed researchers to analyze the age and political affiliations of those people who were more likely to spread fake news.
The results showed that 90% of these users actually did not share misleading or fake articles and only 8.5% shared one or more fake news articles. A plurality, 18%, of the Facebook users who shared the fake stories were both self-identified Republicans and over the age of 65, the authors concluded, and these individuals shared nearly seven times as many fake news articles as respondents in the youngest age group, ranging in age from 18 to 29.

Catastrophe is inevitable for May.
• May Warns Of Catastrophe If Lawmakers Don’t Back Brexit Deal (R.)
British Prime Minister Theresa May has warned lawmakers that failure to back her plan to leave the European Union would be catastrophic for Britain, in a plea for support two days ahead of a vote in parliament that she is expected to lose. Lawmakers are set to vote on May’s Brexit deal on Tuesday, after she shelved plans for a vote in December when it became clear that not enough lawmakers from her own party or others would back the deal she agreed with Brussels. May looks little closer to securing the support she needs, but writing in the Sunday Express she said lawmakers must not let down the people who voted for Brexit.
“Doing so would be a catastrophic and unforgivable breach of trust in our democracy,” May said. “So my message to Parliament this weekend is simple: it is time to forget the games and do what is right for our country.” On Friday, her foreign minister Jeremy Hunt said Brexit might not happen at all if May’s deal was defeated. Britain, the world’s fifth largest economy, is scheduled to quit the European Union on March 29. The Sunday Times reported that rebel lawmakers were planning to wrest control of the legislative agenda away from May next week with a view to suspending or delaying Brexit, citing a senior government source.

Way too late.
• Labour Set To Call Vote To Topple Theresa May’s Government (G.)
Labour MPs have been told to prepare for Jeremy Corbyn to table a dramatic and immediate vote of no confidence in Theresa May’s government as early as Tuesday evening in an attempt to force a general election if – as expected – she suffers a heavy defeat this week on her Brexit deal. Messages have been sent to Labour MPs, even those who are unwell, to ensure their presence both for the “meaningful vote” on the prime minister’s Brexit blueprint on Tuesday and the following day. Labour whips have told MPs the no-confidence vote is likely to be tabled within hours of a government loss, with the actual vote taking place on Wednesday.
The news comes before what promises to be one of the most tumultuous 24 hours in recent parliamentary history in which, barring another delay, May will put her Brexit deal to parliament despite deep and widespread opposition across the Commons, including from many MPs inside her own party. A senior shadow cabinet member said: “There is now recognition that we cannot wait any longer. If May goes down to defeat and she does not resign and call an election, this is the moment we have to act.” Senior Tories said on Saturday that they could not see how the prime minister could win the meaningful vote “in any circumstances” and that a defeat by less than 100 would now be regarded as the best she could hope for.
But even if she suffered a loss of closer to 200, which many Tories fear could be the case, Conservative MPs and ministers still expect her to stagger on and seek to bring an improved offer back to the Commons for a further vote within weeks.

The number of protesters is increasing rapidly again.
• Police Use Water Cannon And Teargas On Paris Protesters (G.)
Gilets jaunes protesters engaged in a ninth weekend of protests all over France on Saturday as the president, Emmanuel Macron, prepared to stake his political future on an open letter to the French people and a national debate. Officials said that at least 84,000 demonstrators turned out across France, thousands more than last weekend, with about 8,000 of those in Paris where protests passed “without serious incident”. Gilets jaunes – named after the hi-vis yellow vests French motorists must carry in their vehicles – said the number was higher but did not give a figure. After the violence of previous weeks, the government put on a show of strength, deploying 80,000 police officers nationwide and about 7,000 in Paris.
[..] Macron has attempted to take the sting out of the protests by announcing a “great national debate” to sound out the public on four themes: taxation, state institutions, democracy and citizenship, but just days before the consultation is due to begin on Tuesday, there is still confusion over how it will be carried out. The president will publish an open letter to the French people on Monday to “explain what I intend to do”. He said the debate was “a vital and very useful moment for our country”. “It’s a great opportunity and everyone must take it … I want a real debate,” he said.

When are we going to stop producing the stuff that needs recycling?
• The Era Of Easy Recycling May Be Coming To An End (538)
On average, about 25 percent of the stuff we try to recycle is too contaminated to go anywhere but the landfill, according to the National Waste and Recycling Association, a trade group. Just a decade ago, the contamination rate was closer to 7 percent, according to the association. And that problem has only compounded in the last year, as China stopped importing “dirty” recyclable material that, in many cases, has found no other buyer. Americans love convenient recycling, but convenient recycling increasingly does not love us. Waste experts call the system of dumping all the recyclables into one bin “single-stream recycling.” It’s popular.
But the cost-benefit math of it has changed. The benefit — more participation and thus more material put forward for recycling — may have been overtaken by the cost — unrecyclable recyclables. On average, about 25 percent of the stuff we try to recycle is too contaminated to go anywhere but the landfill, according to the National Waste and Recycling Association, a trade group. Just a decade ago, the contamination rate was closer to 7 percent, according to the association. And that problem has only compounded in the last year, as China stopped importing “dirty” recyclable material that, in many cases, has found no other buyer.
Most recycling programs in the United States are now single stream. Between 2005 and 2014, these programs went from covering 29 percent of American communities to 80 percent, according to a survey conducted by the American Forest and Paper Association. The popularity makes sense given that single-stream is convenient and a full 66 percent of people surveyed by Harris Poll last October said that they wouldn’t recycle at all if it wasn’t easy to do. Some experts have credited single stream with large increases in the amount of material recycled. Studies have shown that people choose to put more stuff out on the curb for recycling when they have a single-sort system. And the growth of single-stream recycling tracks with the growth of recycling overall in this country. But it also pretty closely tracks with skyrocketing contamination rates.