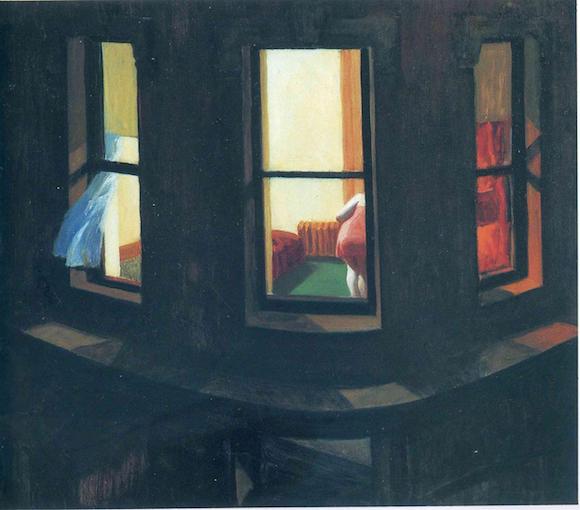
Edward Hopper Night windows 1928

If she knows she’s always wrong, why doesn’t she resign?
• Yellen Concedes Inflation Models Could Be Off “In Some Fundamental Way” (BBG)
Janet Yellen still has faith, but she’s open to converting. In a wide-ranging speech on inflation, the Fed chair wrestled with an issue that’s flummoxing policy makers everywhere: Why is inflation not only low, but in some instances going south? At this point in an expansion that’s lasted the better part of a decade and has returned jobless levels to pre-recession levels, leading economic models would ordinarily tell us to expect inflation to rise. Kudos to her for admitting the uncertainty. The question is one of the pre-eminent themes of the modern economic era. It’s perhaps fitting she air the issues not in a political environment like Congress or the Federal Open Market Committee, which calls for decisions, but in what might be her last address to the National Association for Business Economics.
Yellen conceded that some assumptions about how the modern economy works could be wrong. She is not operating on the premise that they are wrong, but she is prepared to entertain the prospect. She did so in a very rational way, and she urged no sharp about-turns in policy. If officials’ understanding of the link between inflation and the labor market and, more broadly, inflation itself, ends up being flawed, then there is an obligation to recalibrate policy. Neither Yellen nor the FOMC are there yet. And to be clear, the committee still believes inflation will again start to edge up and stabilize around the Fed’s 2% target. Under that scenario, a bit more tightening of policy is required. Not a ton, and the steps should be gradual. As they have been.
If the scenario proves off, then think again. As Yellen said in her remarks, a couple of things could be at work in explaining the bad behavior of inflation. For one, it’s not necessarily that the model linking low unemployment with wages and inflation is wrong; it may be that in the post-recession world the jobless level at which inflation kicks in could be lower. (The jobless rate in the U.S. now is 4.4%.) But it’s also plausible that policy makers misunderstand inflation on a more fundamental level. “Our framework for understanding inflation dynamics could be misspecified in some fundamental way, perhaps because our econometric models overlook some factor that will restrain inflation in coming years despite solid labor market conditions,” Yellen said.

Amen.
• Fed’s Beautiful Model in Pictures (Mish)
Pictures say more than words, especially when it comes to Fed hubris. Two pictures make the case.
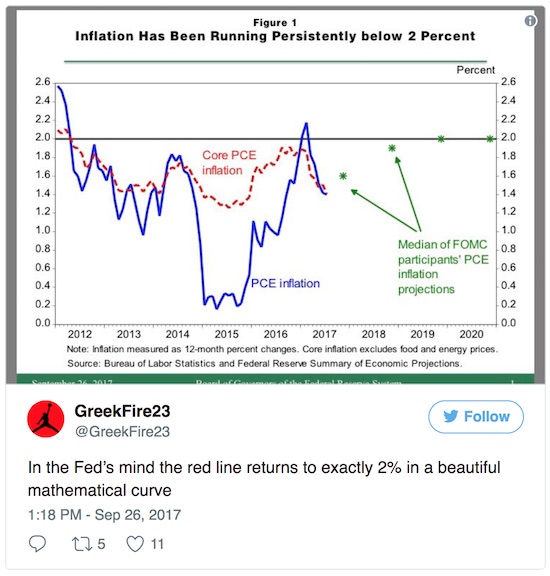

Don’t worry. That the Fed is consistently wrong on growth and inflation is purely transitory.

“..if the Jones Act did not exist, then neither would the public debt of Puerto Rico.”
• The Law Strangling Puerto Rico (NYT)
Hurricane Maria was the most powerful storm to hit Puerto Rico in more than 80 years. It left the entire island without electricity, which may take six months to restore. It toppled trees, shattered windows, tore off roofs and turned streets into rivers throughout the island. President Trump declared that “Puerto Rico was absolutely obliterated” and issued a federal disaster declaration. But the United States needs to do more. It needs to suspend the Jones Act in Puerto Rico. After World War I, America was worried about German U-boats, which had sunk nearly 5,000 ships during the war. Congress enacted the Merchant Marine Act of 1920, a.k.a. the Jones Act, to ensure that the country maintained a shipbuilding industry and seafaring labor force. Section 27 of this law decreed that only American ships could carry goods and passengers from one United States port to another.
In addition, every ship must be built, crewed and owned by American citizens. Almost a century later, there are no U-boats lurking off the coast of Puerto Rico. The Jones Act has outlived its original intent, yet it is strangling the island’s economy. Under the law, any foreign registry vessel that enters Puerto Rico must pay punitive tariffs, fees and taxes, which are passed on to the Puerto Rican consumer. The foreign vessel has one other option: It can reroute to Jacksonville, Fla., where all the goods will be transferred to an American vessel, then shipped to Puerto Rico where — again — all the rerouting costs are passed through to the consumer. Thanks to the law, the price of goods from the United States mainland is at least double that in neighboring islands, including the United States Virgin Islands, which are not covered by the Jones Act.
Moreover, the cost of living in Puerto Rico is 13% higher than in 325 urban areas elsewhere in the United States, even though per capita income in Puerto Rico is about $18,000, close to half that of Mississippi, the poorest of all 50 states. This is a shakedown, a mob protection racket, with Puerto Rico a captive market. The island is the fifth-largest market in the world for American products, and there are more Walmarts and Walgreens per square mile in Puerto Rico than anywhere else on the planet. A 2012 report by two University of Puerto Rico economists found that the Jones Act caused a $17 billion loss to the island’s economy from 1990 through 2010. Other studies have estimated the Jones Act’s damage to Puerto Rico, Hawaii and Alaska to be $2.8 billion to $9.8 billion per year. According to all these reports, if the Jones Act did not exist, then neither would the public debt of Puerto Rico.
[..] Food costs twice as much in Puerto Rico as in Florida. Jones Act relief will save many Puerto Ricans — especially children and seniors — from potential starvation. Jones Act relief will also enable islanders to find medicine, especially Canadian pharmaceuticals, at lifesaving rates. And it will give islanders access to international oil markets — crucial for running its electric grid — devoid of a 30% Jones Act markup. And suspending or repealing the law is crucial to the arduous rebuilding process ahead. In one town alone, 70,000 people were evacuated because of a failing dam. Jones Act relief will enable residents to buy materials, rebuild their homes and prevent an explosion of homelessness.

Either prices fall or sales do. People can’t afford homes anymore.
• US Housing Market “Unhealthy And Mismatched With Today’s Buyers” (CNBC)
From a broad view, the U.S. housing market looks very healthy. Demand is high, employment and wages are growing, and mortgage rates are low. But the nation’s housing market is assuredly unhealthy; in fact, it is increasingly mismatched with today’s buyers. While the big numbers don’t lie, they don’t tell the real truth about the affordability and availability of U.S. housing for the bulk of would-be buyers. First, several reports out this week point to both continued heat in home values as well as pushback from homebuyers. Prices remain nearly 6% higher than they were a year ago, nationally, with some local markets seeing double-digit annual price gains. Those prices are being driven by a severe lack of supply at the low end of the market, which is where the most demand exists. That means lower-priced homes are seeing bigger price gains than higher-priced homes because of the competition.
At the same time, sales are falling, again, because there are too few homes on the low end, and the homes that are available are very expensive. “It sets up a situation in which the housing market looks largely healthy from a 50,000-foot view, but on the ground, the situation is much different, especially for younger, first-time buyers and/or buyers of more modest means,” wrote Svenja Gudell, chief economist at Zillow in a response to the latest home-price data. “Supply is low in general, but half of what is available to buy is priced in the top one-third of the market.” Supply on the low end is tight because during the housing crash investors large and small bought hundreds of thousands of foreclosed properties and turned them into rentals. There are currently 8 million more renter-occupied homes than there were in 2007, the peak of the housing boom, according to the U.S. Census.
Investors could take the opportunity of high prices and high demand to sell these properties, but today’s high rents offer them better returns. Low supply of homes for sale might also seem like a great opportunity for the nation’s homebuilders. Yes, they went through an epic housing crash, but they have since consolidated market share and righted their balance sheets. Homebuilders are simply not building enough inexpensive houses that the market needs. [..] Just 2% of newly built homes sold in August were priced under $150,000, and just 14% priced under $200,000. Compare that with the existing home market, where more than half of homes sold in August were priced under $250,000.

“..a sharp reduction in property sales which tumbled 73.7% from the same quarter a year earlier.”
• Home Prices, Sales In Beijing Are Falling Fast (BI)
According to the Caixin website, citing data from the research arm of 5I5J Group, the average price of existing homes in Beijing fell 5%, continuing the slide that began in the June quarter. The fall corresponded with a sharp reduction in property sales which tumbled 73.7% from the same quarter a year earlier. According to survey, turnover alone fell 43.7% in the quarter to 2.06 million units based on measurements using online contracts, the lowest quarterly total since 2015. The sharp decline in turnover and prices follows a series of measures introduced by Beijing’s municipal government to quash speculative activity in the city’s property market. Since October last year, it has raised borrowing costs and minimum downpayment requirements for mortgages for second homes.
It has also introduced requirements for non-local buyers to provide tax or social security payment records for at least 60 consecutive months and increased scrutiny on “strategic divorces” as ways to squeeze speculation out of the market, said Caixin. “In the spirit of central government’s directive that ‘homes are for living in, not speculating on,’ the real estate market in Beijing will continue to be under tight control, thus the existing home market in Beijing is likely to remain tepid in the near term,” Hu Jinghui, vice president of 5I5J Group’s research arm, told Caixin. The measures introduced in Beijing mirror similar efforts from authorities in other large cities to curb rapid price growth seen since the middle of 2015. Previously limited to large tier-one cities initially, restrictions on both buyers and sellers have been rolled out across an increasing number of centres in recent months, including in smaller cities, in an attempt to limit speculators from moving from one market to another.

Deleveraging is just a word.
• China Still Stocking Up On Metals And Credit – Beige Book (CNBC)
The China-driven surge in commodity prices could soon come to an end, according to a private survey of Chinese businesses. Contrary to “markets’ unremitting faith in the Chinese government campaign to combat” oversupply in metals, “firms are saying quite the opposite. For the sixth quarter in a row, coal, aluminum, steel, and copper each saw capacity rise on net,” according to the China Beige Book’s early brief of third-quarter data released Tuesday. “Sector-wide growth took a dive across the board—revenue, profits, output, export orders, volumes, hiring, capex, borrowing, wages, and sales prices,” the report said. The China Beige Book is a quarterly survey of Chinese companies in an attempt to present a more accurate picture of growth. Many question the accuracy of most Chinese government data, since officials may have incentive to inflate or deflate the figures they report in order to show compliance with central policy.
“There has been for the past year and a half a desire to not think too much about China,” Leland Miller, chief executive officer of China Beige Book, told CNBC. “I think you’re at a point right now where there’s been a complacency on the part of the Chinese economy that is lending itself to unrealistic expectations about the economy that are not going to be met.” Copper prices have rallied more than 25% this year to a three-year high on bets for stronger global growth, primarily out of the world’s second-largest economy, China. But the metal has since come off those levels to trade about 16.5% higher for the year. Morgan Stanley echoed some of the China Beige Book’s concern in a Monday report.
“So in fact, the strongest price performances of 2017 (aluminium, zinc, lead, copper, nickel, alumina, iron ore) are based on either China’s reform-based supply shocks or global currency trades – not a sustained improvement in demand growth,” equity strategist Tom Price and a team of analysts said. They have negative price forecasts on aluminum, copper, iron ore and steel. In its third-quarter survey of 3,300 firms and 160 bankers across 34 industries, the China Beige Book also found that companies borrowed at the second-highest rate in four years, contrary to widespread beliefs that China is reducing its use of credit to fuel growth. “Most of the year when the Chinese government has been talking about deleveraging that has not been evidenced in China Beige Book data,” Miller said. “At least part of the time corporations have had even easier access to capital and even when conditions have been tightening it has not contributed to deleveraging or slower deleveraging.”

Yeah, the US should do the same.
• China Tells Entrepreneurs They Must Put Patriotism Over Profit (BBG)
The Chinese government underlined that patriotism is a core element of entrepreneurship, with official media saying it had for the first time defined what enterprise means for the world’s second-biggest economy. The joint statement issued late Monday by the Communist Party’s Central Committee and the State Council urged entrepreneurs to advance patriotism and professionalism, as well as innovation and social responsibility. It called for stronger party guidance of entrepreneurs and for them to endorse party leaders. It also promised to create a environment where they can thrive. The guideline “has defined the core meaning of Chinese entrepreneurship under the new era,” with being patriotic and professional core components, the official Xinhua News Agency said. It’s the first edict “of its kind that focused on entrepreneurial spirit” and is intended “to spur market vitality,” Xinhua said.
The call for patriotic entrepreneurs underscores the trend of emphasizing the national missions of both private and state-run businesses under President Xi Jinping, who has sought to shore up the state sector and build “national champions.” It reflects internal concern about capital outflows and acquisitions, which have put downward pressure on the yuan in recent years. “Key elements of the document relate to the phenomenon of Chinese firms going on massive overseas shopping sprees,” said Han Meng, a senior researcher at the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences Institute of Economics in Beijing. “If not reined in, this could hurt China’s economic base. Patriotic entrepreneurs are those who can do more to benefit the domestic economy and society.”

Great time to call for more centralization.
• Macron Lays Out Vision For ‘Profound’ Changes In EU (G.)
The French president, Emmanuel Macron, has set out his plans for a “profound transformation” of the EU with deeper political integration to win back the support of disgruntled citizens, but suggested a bloc moving forward at differing speeds could become somewhere the UK may “one day find its place again”. Macron, a staunchly pro-European centrist who came to power in May after beating the Front National’s Marine Le Pen, pleaded for the EU to return to its founders’ “visionary” ideas, which were born out of the disaster of two world wars. In what was hailed on Tuesday as one of the most pro-European speeches by an EU leader in years, he spoke up for common EU policies on defence, asylum and tax, called for the formation of European universities, and promised to play Ode to Joy, the EU anthem, at the Paris Olympics in 2024.
He said time was running out for the EU to reinvent itself to counter the rise of far-right nationalism and “give Europe back to its citizens”. With Brexit looming, Macron warned the rest of Europe against the dangers of anti-immigrant nationalism and fragmentation. “We thought the past would not come back … We thought we had learned the lessons,” he told a crowd of European students at Sorbonne University in Paris. Days after a far-right party entered the German parliament for the first time in 70 years, Macron said an isolationist attitude had resurfaced “because of blindness … because we forgot to defend Europe. The Europe that we know is too slow, too weak, too ineffective”.

Uber will leave Canadian province of Québec in October.
• Uber’s New ‘Good Cop’ Tack Will Face Test in US City Tussles (BBG)
Uber is testing out a new conciliatory tone in London, where officials said they wouldn’t renew the ride-hailing service’s operating license. It’s going to have ample opportunity to see if that approach will work in the U.S. San Francisco’s city attorney is investigating whether Uber Technologies Inc. is a public nuisance. In New York, officials are mulling ways to tighten controls on ride-hailing, including requiring a quarter of all trips come with wheelchair-accessible vehicles. And Seattle has passed an ordinance to make it easier for Uber drivers to unionize. “Uber is at a turning point with big-city governments,” Jon Orcutt, director of communications and advocacy for the TransitCenter, said of Uber and other ride-sharing companies. “London’s action to threaten to withdraw their license really could turn the corner in a more normal regulatory situation for Uber.”
London officials said Friday the city would not renew Uber’s operating license, which is set to expire Sept. 30, because it isn’t “fit and proper to hold a private hire operator license.” The city cited a failure to do sufficient background checks on drivers, report crimes and a program called “Greyball” used to avoid regulators. In response, newly minted Chief Executive Officer Dara Khosrowshahi released an open letter Monday apologizing “for the mistakes we’ve made” and acknowledging that the company “got things wrong along the way” during its rapid growth. London is a critical global market for Uber, which could encourage the company to make regulatory concessions to remain on the streets, Orcutt said. That stands in contrast with the company’s sharp-elbowed approach under co-founder and former CEO Travis Kalanick.
Uber ruffled feathers in city halls in several major U.S. cities that struggled to corral the company during its growth. It raised the ire of local officials and incumbent taxi drivers by compiling a track record of skirting traditional taxi-industry regulations and refusing to share trip data and other records sought by city officials. San Francisco City Attorney Dennis Herrera in July requested court orders for Uber and competitor Lyft Inc. to hand over years worth of records after the companies refused to comply with an earlier subpoena for the records. Herrera’s office is investigating whether the companies and their estimated 45,000 drivers in the city are creating a public nuisance, a finding that could subject the companies to civil monetary penalties and expose them to court injunctions restricting their operations in the city.

Wait. If the mines don’t function, gold gets scarcer, right?
• Hedge Fund Paulson & Co Declares War On Poor Gold Mining Returns (R.)
New York-based Paulson & Co, led by longtime gold bull John Paulson, called on Tuesday for the world’s biggest investors in gold-mining stocks to form a coalition to tackle miners’ “dreadful” performance. Speaking at the Denver Gold Forum, the industry’s top annual event, Paulson & Co partner Marcelo Kim launched the blistering attack on the sector, saying the hedge fund was looking for fellow founding members for a body to speak out on issues including high executive pay, cozy board appointments and value-destroying mergers and acquisitions. “If we don’t do anything to change, then as investors we will continually be disappointed with shareholder returns and the industry will slowly dig itself into a hole of irrelevance and oblivion,” Kim told a packed room of delegates.
The “shareholders’ gold council” would focus solely on the gold sector, issuing vote recommendations to shareholders on issues including company takeovers and chief executive officer pay, Kim said. He said that fellow large sector investor, Tocqueville, had endorsed the council idea. Average total shareholder returns from gold mining investments, including world No.1 producer Barrick, are a negative 65% since 2010 over a period when the CEOs of 13 of the largest companies have cumulatively received $550 million in pay, Kim said. In that time, the gold price rose by 20% and the price of oil, a major input cost for miners, fell by 28%, he said. Since 2010, the industry has written off $85 billion due to overpaying for acquisitions and massive cost overruns on mine builds, he said.
Amongst large producers, the weakest performer was Canadian miner Eldorado, which had destroyed shareholder value through M&A, he said. Eldorado could not immediately be reached for comment. Not all gold miners had performed poorly, Kim said, singling out Africa-focused Randgold as a role model. Shareholders have no one to blame but themselves for rubber stamping mergers, CEO pay packages and board appointments, Kim said, adding that there was little industry engagement with company boards or activism.

Lack of focus.
• The Case For The 3-Hour Workday (BI)
Over the course of an eight-hour workday, the average employee works for about three hours — two hours and 53 minutes, to be more precise. The rest of the time, according to a 2016 survey of 1,989 UK office workers, people spend on a combination of reading the news, browsing social media, eating food, socializing about non-work topics, taking smoke breaks, and searching for new jobs (presumably, to pick up the same habits in a different office). The research has been clear for awhile that long workdays hardly get the best from people. Some research has found people can only concentrate for about 20 minutes at a time. One study found people struggled to stay on task for more than 10 seconds.
Toward the end of the day, performance begins to flatline or even worsen, K. Anders Ericsson, an expert on the psychology of work, said. “If you’re pushing people well beyond that time they can really concentrate maximally, you’re very likely to get them to acquire some bad habits,” Ericsson told Business Insider in 2016. Ericsson is the foremost expert on the topic of building expertise. He’s made a career out of studying the most successful people on Earth, and figuring out what exactly helps them rise so high. Turns out the mantra “practice makes perfect” is true, but only if people engage in a certain kind of practice known as “deliberate practice.” Experts don’t spend hours upon hours honing their craft, Ericsson has found. They spend a few hours at a time purposefully trying to improve, and then they stop.

A very tense weekend is coming.
• Spain Deploys Ever More Police To Prevent Catalan Independence Vote (G.)
Police will be deployed at polling stations to prevent people from voting in the Catalan independence referendum, the Spanish government has confirmed. Although the Catalonia regional government has insisted the unilateral poll will go ahead on Sunday, the Spanish government has vowed to stop the vote, which it says is a clear violation of the constitution. Spain’s constitutional court has suspended the legislation underpinning the referendum while it rules on its legality. A spokesman for the Spanish government’s Catalan delegation said on Tuesday that the region’s prosecutor had ordered the Mossos d’Esquadra, Catalonia’s police force, to take control of polling booths and identify those in charge. “The order has been conveyed and it will be executed with all normality,” he said.
The Spanish government said the steps it had taken over the past week, including raiding Catalan government offices, arresting 14 officials and seizing almost 10m ballot papers, meant the vote could not take place. “Today we can affirm that there will be no effective referendum in Catalonia,” the Spanish government’s representative in Catalonia, Enric Millo, told reporters on Tuesday. “All the referendum’s logistics have been dismantled.” In an order to police issued on Monday, the prosecutor’s office said it would take the names of anyone participating in the vote and confiscate relevant documents. Anyone in possession of the keys or entrance codes to a polling booth could be considered a collaborator to crimes of disobedience, misuse of office and misappropriation of funds, the order said.
However, despite the words and actions of the Spanish government, not to mention the deployment of thousands of extra police officers to Catalonia, the regional government is adamant that the referendum cannot be stopped. Catalonia’s regional president, Carles Puigdemont, has accused the Spanish prime minister, Mariano Rajoy, of acting “beyond the limits of a respectable democracy” in his efforts to prevent the referendum. He has also compared the Spanish government’s behaviour to the repression of the Franco era and said it is only serving to drive more Catalans towards independence.

People want to be independent all over.
• Banned West Papua Independence Petition Handed To UN (G.)
A petition banned by the Indonesian government, but bearing the signatures of 1.8 million West Papuans – more than 70% of the contested province’s population – has been presented to the United Nations, with a demand for a free vote on independence. Exiled West Papuan independence campaigner Benny Wenda presented the bound petition to the UN’s decolonisation committee, the body that monitors the progress of former colonies – known as non-self-governing territories – towards independence. The petition was banned in the provinces of Papua and West Papua by the Indonesian government, and blocked online across the country, so petition sheets had to be “smuggled from one end of Papua to the other”, Wenda told the Guardian from New York.
Independence campaigners have been jailed and allegedly tortured in Papua for opposing the rule of Indonesia, which has controlled Papua (now Papua and West Papua) since 1963. Those signing the petition risked arrest and jail. “The people have risked their lives, some have been beaten up, some are in prison. In 50 years, we have never done this before, and we had to organise this in secret,” Wenda said. “People were willing to carry it between villages, to smuggle it from one end of Papua to the other, because this petition is very significant for us in our struggle for freedom.”

Atlantis down under.
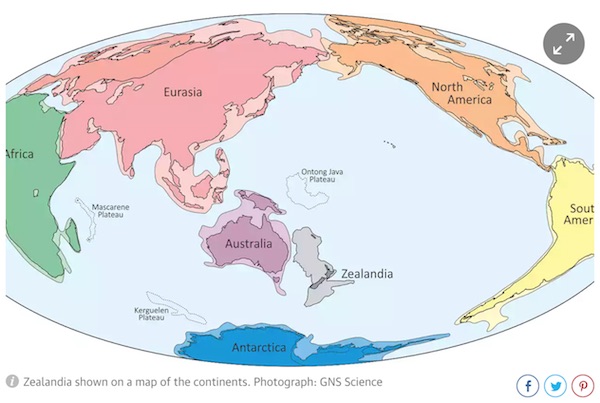
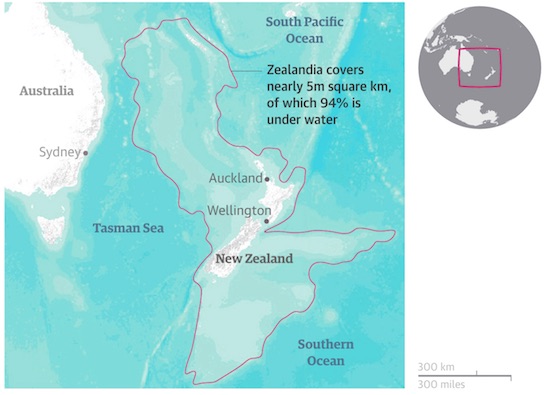
• Zealandia Drilling Reveals Secrets Of Sunken Lost Continent (G.)
The mostly submerged continent of Zealandia may have been much closer to land level than previously thought, providing pathways for animals and plants to cross continents from 80m years ago, an expedition has revealed. Zealandia, a for the most part underwater landmass in the South Pacific, was declared the Earth’s newest continent this year in a paper in the journal of the Geological Society of America. It includes Lord Howe Island off the east coast of Australia, New Caledonia and New Zealand. On Wednesday researchers shared findings from their two-month-long expedition, one of the first extensive surveys of the region, announcing fossil discoveries and evidence of large-scale tectonic movements.
“The discovery of microscopic shells of organisms that lived in warm shallow seas, and spores and pollen from land plants, reveal that the geography and climate of Zealandia was dramatically different in the past,” said Prof Gerald Dickens of Rice University. Researchers drilled more than 860 metres below the sea floor in six different sites across Zealandia. The sediment cores collected showed evidence of tectonic and ecological change across millions of years. “The cores acted as time machines for us, allowing us to reach further and further back in time,” said Stephen Pekar, a researcher on board the scientific drilling vessel, in August. “As one scientist put it: ‘We are rewriting the geologic and tectonic history of Zealandia at this drill site.’”
The 5 million sq km continent, roughly the size of the Indian subcontinent, is believed to have separated from Australia and Antarctica, as part of Gondwana, about 80m years ago. On Wednesday Prof Rupert Sutherland from New Zealand’s Victoria University said the expedition had discovered “big geographic changes”. “[The research] has big implications for understanding big scientific questions, such as how did plants and animals disperse and evolve in the South Pacific? The discovery of past land and shallow seas now provides an explanation: there were pathways for animals and plants to move along.”