
Tomb of the diver, Paestum c480 BCE

•The US recorded 1,635 #coronavirus deaths in the past 24 hours, bringing the total to 77,178, with a confirmed total of 1,283,829 cases
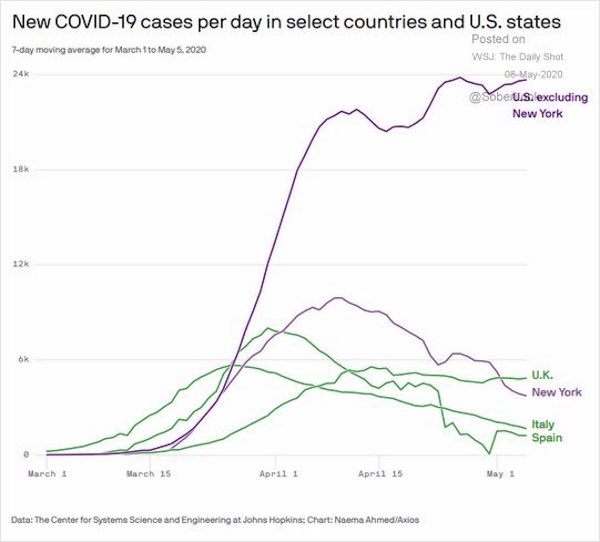
• Brazil today now 10,199, total near 150k
• Mexico 23% jump to 1,982, new high
• India today 3,362, small decrease after large increase
• Pakistan 1,791 new high
• Iran recent increasing trend continues 1,556
• Kuwait 641, Qatar 1,311 both new highs

• Cases 4,032,763 (+ 98,052 from yesterday’s 3,934,711)
• Deaths 276,677 (+ 5,582 from yesterday’s 271,095)

From Worldometer yesterday evening -before their day’s close-
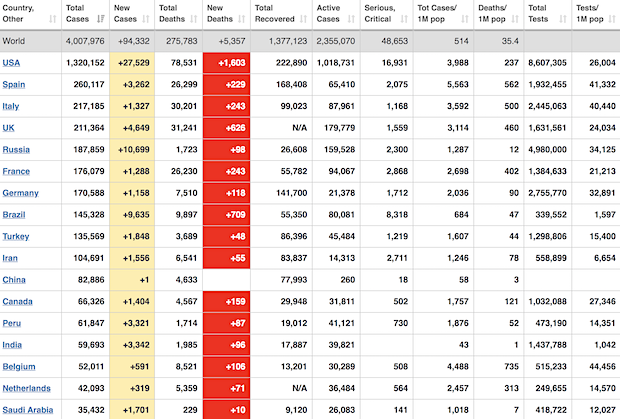
From Worldometer Deaths among Closed cases is down to 17%. That still needs to come down much more.
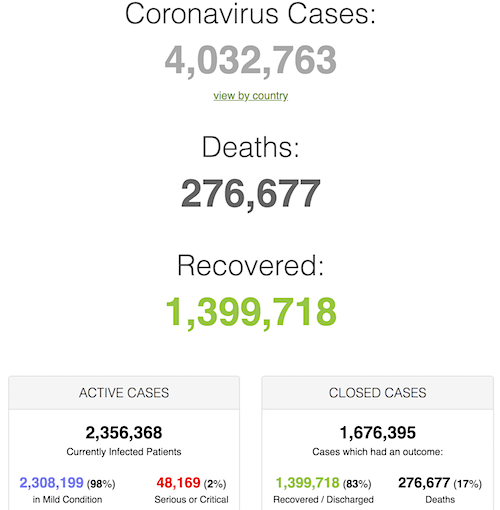
From SCMP:
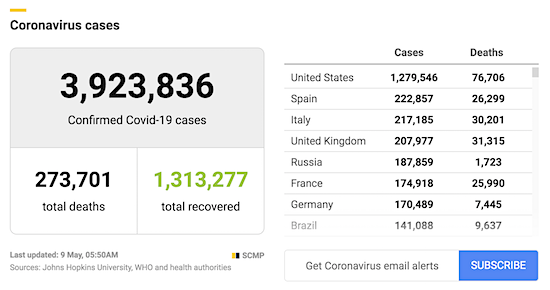
From COVID19Info.live:
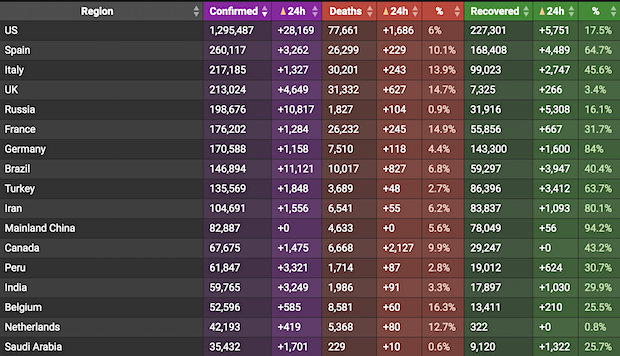

Total nonfarm payroll employment fell by 20.5 million in April, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, bringing the unemployment rate to 14.7%.
That is the highest rate and largest month-over-month increase since the report began in its current form in 1948.
• Ugly US Jobs Data Hides As Much As It Reveals (R.)
April really was the cruelest month. Over 20 million Americans lost their jobs, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, bringing the unemployment rate to an eye-popping 14.7% – the highest since at least the 1940s. But the headline number leaves out much of the Covid-19 economic story. The report makes for grisly – if unsurprising – reading. The economy shed roughly a decade of job gains. The figure dwarfs the 8.7 million jobs lost in the Great Recession that lasted from December 2007 to June 2009 and suggests an annualized second-quarter GDP contraction north of 30% is possible. It represents the highest recorded losses in the report’s seven-decade history, and includes the wipeout of almost half of the country’s leisure and hospitality jobs.
Comparing this to previous crises and slumps is of limited use, because the United States has never intentionally shut off almost 30% of its economy before. But other things are different too. For one, Friday’s figure doesn’t necessarily paint an accurate income picture. Federal stimulus has added $600 a week to jobless benefits, making them, on average, actually higher than normal salaries in a majority of states, according to the New York Times. This is only temporary and the levels vary by state, but it’s still a huge difference from previous crises. The $1,200 one-off payments made to many Americans also mean households, overall, might not see income decline as much as the depressing statistics would suggest.
Just as the record lows in unemployment before Covid-19 didn’t give a full picture, the highs present a similar problem. The headline unemployment figure leaves out workers who aren’t looking for jobs. And it classifies over 18 million workers as being on temporary layoff – but it’s impossible to know whether they will be rehired. After the lockdown, demand may remain depressed because people are scared to, say, go to restaurants or spend much at all. Jobless figures during the decade-plus expansion didn’t account for the low quality of jobs, limited benefits, and low labor-force participation rate. Unfortunately, Friday’s statistics mostly make clear what was already known – that the U.S. economy is in an induced coma – without giving clues on how or when it will wake up.

In a nutshell: by ignoring the WHO.
• How Australia Got On Top Of COVID19 (SMH)
It got really serious for Greg Hunt while he was at the cricket. It was a Saturday morning, February 1, while Australia’s Health Minister was watching his 10-year-old son play that he got the message. In between phone calls and text messages, Hunt was cheering his boy on as he walked laps around the Balnarring cricket oval on his home turf of Victoria’s Mornington Peninsula. “We now have sustained human-to-human transmission outside Wuhan,” read the message from Australia’s Chief Medical Officer, Brendan Murphy, as Hunt recalls it. “I think we are going to have to close the border to China.” It’s a morning that Hunt says he remembers clearly. The government was already on high alert.
It had been 12 days since Murphy had informed Hunt he was invoking the Biosecurity Act to list the novel coronavirus as a disease of pandemic potential. Behind closed doors, Prime Minister Scott Morrison had already told the national security committee of the cabinet that he’d resolved to “respect the medical advice” as the guiding principle in any response to the epidemic that was spreading in China. Now it was time to act. Hunt immediately connected with Morrison and Murphy on a three-way phone call. Murphy set out the facts and advised: “There’s a very strong risk of this spreading to Australia.” “Are you recommending that we close the border to China?” the Prime Minister asked. Yes, came Murphy’s answer. It was announced at 5pm that same day. It was to be, in Hunt’s words, “almost the biggest, one-day decision a government had made in 50 years”.
Beijing, predictably, put on a show of anger. The Chinese embassy gave Canberra a stern lecture, called Australia “xenophobic” and demanded compensation for Chinese students who were inconvenienced. The Australian government realised that something was badly wrong with the World Health Organisation, or WHO, around this time. The Geneva-based UN organisation kept insisting that there was no cause for countries to ban travel from China. Many nations, Britain and Canada among them, were trusting enough to take its advice. Australia wasn’t the first to shut down arrivals from China. The US and Singapore had done it a day earlier. Taiwan had barred tourists from China’s mainland earlier still, on January 26.
Australian officials since have reflected privately that, if Canberra had been watching China as closely as Taiwan does – and with as much scepticism of its official announcements – Australia would have acted at the same time. Taiwan is the standout global success story in managing COVID-19 to date. It’s an island with roughly the same population as Australia but only six deaths. Australia’s death toll is approaching 100. Taiwan’s restrictions on movement weren’t much more drastic than Australia’s but it moved sooner. Taiwan also was smart enough to put no faith in the WHO. Indeed, Beijing has barred Taiwan from membership of the WHO. Which, in this case, hasn’t done Taiwan any harm whatsoever.
Canberra announced other border closures in short order – Iran, Italy, South Korea. But then it paused before finally banning all foreign arrivals after March 19. Was it a mistake to wait so long? Should Australia have followed its China ban with a global ban sooner?

What comes before the fall?
• South Korea’s COVID19 Exceptionalism (Atl.)
By the end of February, South Korea had the most COVID-19 patients of any country outside China. New confirmed cases were doubling every few days, and pharmacies were running out of face masks. More than a dozen countries imposed travel restrictions to protect their citizens from the Korean outbreak, including the U.S., which had, at the time, recorded an official COVID-19 death toll low enough to count on one hand. But just as South Korea appeared to be descending into catastrophe, the country stopped the virus in its tracks. The government demanded that the Shincheonji Church turn over its full membership list, through which the Ministry of Health identified thousands of worshippers. All were ordered to self-isolate.
Within days, thousands of people in Daegu were tested for the virus. Individuals with the most serious cases were sent to hospitals, while those with milder cases checked into isolation units at converted corporate training facilities. The government used a combination of interviews and cellphone surveillance to track down the recent contacts of new patients and ordered those contacts to self-isolate as well. Within a month, the Korean outbreak was effectively contained. In the first two weeks of March, new daily cases fell from 800 to fewer than 100. (This morning, the nation of 51 million reported zero new domestic infections for the third straight day.) On April 15, the country successfully held a national parliamentary election with the highest turnout in three decades, without triggering another wave.
South Korea is not unique in its ability to bend the curve of daily cases; New Zealand, Australia, and Norway have done so, as well. But it is perhaps the largest democracy to reduce new daily cases by more than 90 percent from peak, and its density and proximity to China make the achievement particularly noteworthy. [..] In mid-March, the U.S. and South Korea had the same number of coronavirus-caused fatalities—approximately 90. In April, South Korea lost a total of 85 souls to COVID-19, while the U.S. lost 62,000—an average of 85 deaths every hour. That the U.S. population is approximately six times larger than South Korea’s does little to soften the horror of the comparison.

Uh-oh….
• South Korea Backtracks On Reopening After COVID19 Cases Jump (NW)
Despite recently reopening businesses amid an impressive decline in new coronavirus case, the South Korean government has issued a nationwide health advisory for bars and nightclubs to close down for 30 more days after health officials tracked 13 new cases to a single person who attended five nightclubs and bars in the country’s capital city of Seoul. “We believe we will have another community infection,” said Vice Health Minister Kim Gang-lip at a Friday press briefing. “The spread took place in enclosed and crowded spaces. Transmission with no known source of infection can lead to a widespread cluster infection and that is why the government is not letting its guard down.”
The man in question had no symptoms when he visited the nightspots. He eventually tested positive on Wednesday and gained admittance to a hospital in Suwon, a city south of Seoul, according to the UPI wire service. Officials think he may have come in contact with over 1,500 people during his night out. City officials are now using CCTV and credit card records to help identify visitors and are encouraging them to self-isolate and immediately report any coronavirus symptoms to local hospitals. With a decline in new cases, South Korea has allowed places of worship, museums venues, recreational facilities and nightclubs to recently resume business. The country’s high schools begin reopening next week and its lower schools will gradually reopen throughout May.
However, similar to the reopening plans of many U.S. states, South Korea has said it will pull back on and reverse reopenings if new cases emerge. While the number of coronavirus cases in South Korea originally exploded in late February and early March, the country’s Ministry of Health worked hard to conduct rigorous contact tracing, contacting anyone who had attended venues where patients with confirmed cases of coronavirus had gone. Using a combination of interviews and cellphone surveillance, anyone in proximity to these patients and their neighbors were widely tested and all encouraged to self-quarantine.

People lock themselves down.
• Enough With the Phoney ‘Lockdown’ Debate (Kay)
The skeptics who argue that lockdowns “don’t work” usually will support this claim by ticking off nations that have succeeded in fighting COVID-19 without imposing harsh government restrictions. But when you parse the actual data, what you find is that these tend to be high-trust, high-education, high-information societies—such as in Scandinavia and East Asia—where official lockdowns haven’t been necessary precisely because a critical mass of people have effectively locked themselves down on their own. If, say, spring-breakers in Miami were as conscientious and disciplined as, say, most office workers in Stockholm or Tokyo, the state’s governor wouldn’t have had to clear the beaches. But they’re not, so he did. Such spectacles tell us a lot about college students, but not much about lockdowns.
The crowdsourced aspect of lockdowns is bad news and good news. It’s bad news because getting all of society’s actors on the same page will take many months. And so we won’t be able to get our economies up and running on anything like the speedy timeline that most self-styled lockdown opponents are seeking. But it’s good news because a slower, crowdsourced form of lockdown lifting will be subject to a whole slew of negative feedback mechanisms whereby outbreaks naturally lead to corrections. And so we can avoid the problem, depicted in Ferguson’s graphs, by which sudden quantum shifts in centralized policy yield behavioural spikes whose catastrophic effects set off an endless wave of epidemiological boom and bust.

This should have been a January headline. Now all the clusters are in place.
• UK To Place All Incoming Travellers Under 14-Day Quarantine (R.)
British Prime Minister Boris Johnson will announce on Sunday that all travellers coming to the United Kingdom will be quarantined for a fortnight, The Times reported. “Passengers arriving at airports and ports including Britons returning from abroad, will have to self-isolate for 14 days,” the newspaper said, adding that travellers will have to provide the address sat which they will self-isolate on arrival. Travellers from Ireland, the Channel Islands and the Isle of Man will be exempt, as will lorry drivers bringing crucial supplies, the report added.
The authorities will carry out spot checks and those found to be breaking the rules are to face fines of up to 1,000 pounds or even deportation, the report added. According to The Times, travellers will have to fill in a digital form with details of where they plan to self-isolate themselves for the duration of the quarantine. The measures will help reduce the “transmission of the virus as we move into the next phase of our response,” the report said, citing a government source. The measures are expected to come into force in early June.

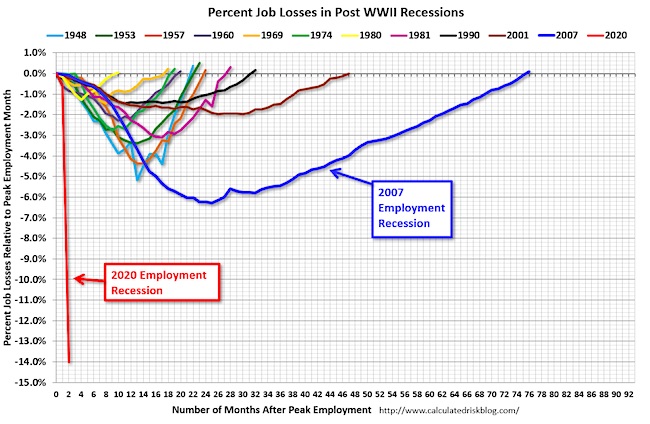
The all-cause death number. Hot potato.
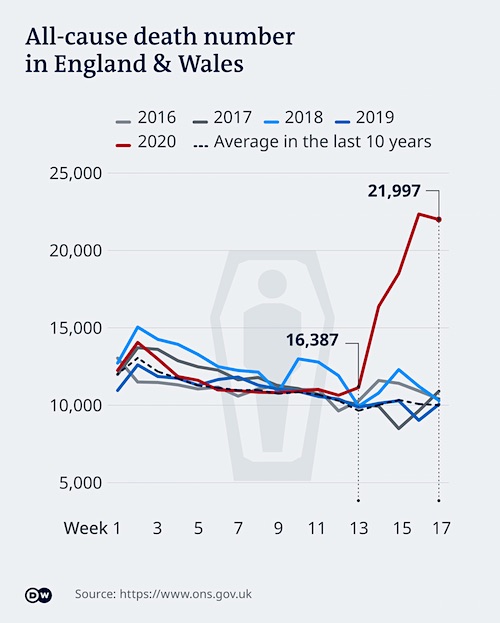
• COVID19 Death Rate Sinking? Data Reveals A Complex Reality (DW)
When is a COVID-19 death counted as a COVID-19 death? The answer is not as straightforward as one might think, because different countries have different methods for determining a COVID-19 case or declaring COVID-19 as a deceased person’s cause of death. Some countries, like Spain, carry out post-mortem COVID-19 tests, while in others like Germany, the UK, or Turkey it not a common practice. Belgium, for example, counts all coronavirus deaths outside hospitals in its daily statistics: This means the country includes people suspected of having died of coronavirus, without a confirmed positive test result, whereas countries like Italy only count deaths in hospitals. Spain only recently started to count non-hospitalized, coronavirus-related deaths from some regions.
Why is the all-cause death number relevant? There are a few essential lessons we can learn from all-cause death data. According to many scientific experts, it is the only unbiased information we can trust to measure the real impact of the pandemic, and create policies to minimize its effects. The number of people dying of COVID-19 is huge, but it still is not the leading cause of death in many countries. People are more reluctant to go to hospitals because they fear contagion, or simply do not want to burden the health system further. However, a scenario in which the leading causes of death, such as heart disease or cancer, increase by even 5% could translate into hundreds of thousands of people.
David Spiegelhalter, Professor of Public Understanding of Risk from the University of Cambridge, notes the differences in each country: “I would say the all-cause death number is the really unbiased measure of the impact of this epidemic. And it’s the one I look up far more closely,” he told DW. Data collected by DW both on all-cause deaths and COVID-19 deaths shows: Thousands more people are dying directly or indirectly due to COVID-19 than the official numbers suggest. DW’s data analysis focused on Spain, England and Wales, but indicates a pattern present in other countries too.

Success breeds success.
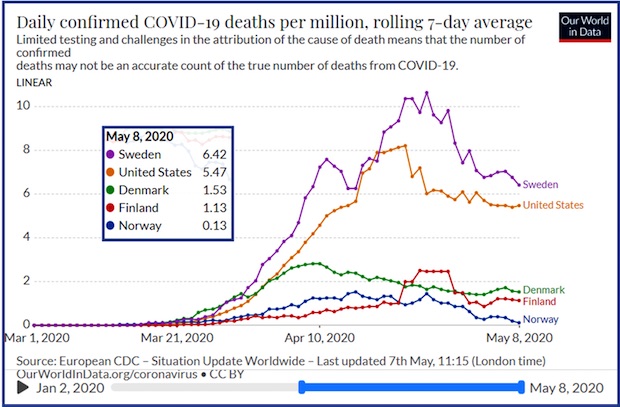
• Want To Be More Like Sweden? What If We Already Are? (Mish)
Unlike most of the rest of the world, Sweden did not mandate coronavirus lockdowns. Instead, most measures were voluntary, but it did cutoff access to nursing homes after a surge in deaths. It has been an experiment worth monitoring. And for weeks, many in the US have been clamoring for the US to be “more like Sweden”. But what do the results really show and what is Sweden saying now? Please note the head of Sweden’s no-lockdown coronavirus plan said the country’s Heavy Death Toll ‘Came as a Surprise’ “We never really calculated with a high death toll initially, I must say,” said epidemiologist Anders Tegnell. “We calculated on more people being sick, but the death toll really came as a surprise to us.”
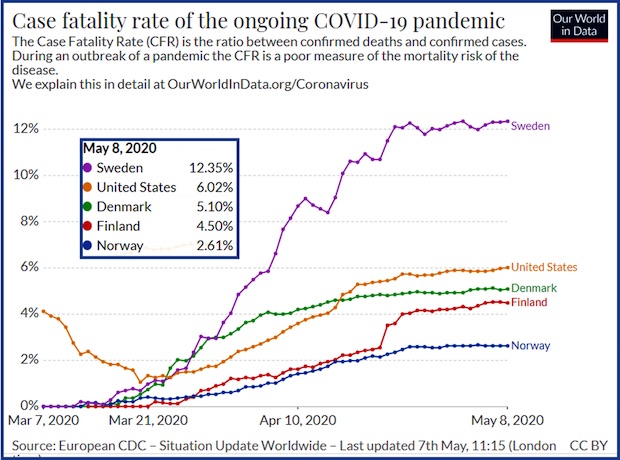
The deniers will point out that about half of Sweden’s deaths came from nursing homes as if those deaths don’t matter. When it comes to per-capita counts, the US is remarkably like Sweden. This can be portrayed two ways. • See, the lockdowns didn’t help. • Based on population density, Sweden is a total disaster. You should not compare a tiny Nordic country to the US but there it is anyway, for those clamoring to be more like Sweden. On a fatality rate basis, we better hope the US does not become more like Sweden. Clearly Sweden is not the success story widely claimed. Unfortunately, people will look at these charts, continue to make inane flu comparisons and continue to tout Sweden’s success. The one area of attack left open is whether or not the US approach was economically justified. I will not address that question because I will not change anyone’s mind.

“And will some of the employees returning to work have their limbs torn off and tossed into the air like a juggler tossing bowling pins? Undoubtedly.”
• Velociraptors Still On The Loose? No Reason Not To Reopen Jurassic Park (McS)
Hello, Peter Ludlow here, CEO of InGen, the company behind the wildly successful dinosaur-themed amusement park, Jurassic Park. As you’re all aware, after an unprecedented storm hit the park, we lost power and the velociraptors escaped their enclosure and killed hundreds of park visitors, prompting a two-month shutdown of the park. Well, I’m pleased to announce that, even though the velociraptors are still on the loose, we will be opening Jurassic Park back up to the public!
Now, I understand why some people might be skeptical about reopening an amusement park when there are still blindingly fast, 180-pound predators roaming around. But the fact of the matter is, velociraptors are intelligent, shifty creatures that are not going to be contained any time soon, so we might as well just start getting used to them killing a few people every now and then. Some might argue that we should follow the example of other parks that have successfully dealt with velociraptor escapes. But here at Jurassic Park, we’ve never been ones to listen to the recommendations of scientists, or safety experts, or bioethicists, so why would we start now?
As some of you know, Dr. Ian Malcolm, our lead safety consultant, had recommended that we wait until the velociraptors have been located and contained before reopening the park, so he wasn’t thrilled when we told him the news. I believe his exact words were “you were so preoccupied with whether you could reopen the park, you didn’t stop to think whether you should.” Talk about a guy on a high horse.
That said, you’ll be pleased to know that, rather than double down on our containment efforts, we’ve decided to dissolve the velociraptor containment task force altogether, and focus instead on how we can get people back into the park as quickly as possible. So rather than concentrating on so-called life-saving measures like “staying in designated safe areas” or “masking your scent,” we’ll be focusing on the details that will get our customers really excited, like a wider selection of fun hats, a pterodactyl-shaped gondola ride to the top of the island, and a brand new Gordon Ramsay designed menu at the Cretaceous Cafe.
In addition to satisfying our customers, the decision to reopen the park is also about allowing the furloughed employees of Jurassic Park to get back to the work they love. Could we have continued to pay their salaries for several months until we got the velociraptor situation under control? Definitely. We’re the wealthiest nature preserve on the planet after all. And will some of the employees returning to work have their limbs torn off and tossed into the air like a juggler tossing bowling pins? Undoubtedly. But we’re confident that with a few safety precautions put in place, we’ll be able to keep the level of workplace injuries and deaths just below levels that would elicit widespread public outrage.

Do these people really not understand securitization? To skip a few steps, US housing would collapse without these “miscalculations”. There’s now talk of a federal agency to take over for the “servicers”. Another bottomless pit.
• The Bailout Miscalculation That Could Crash the Economy (Taibbi)
When Donald Trump signed the $2 trillion CARES Act rescue on March 27, there was immediate praise across the political spectrum for section 4022, concerning homeowners in distress. Under the rule, anyone with a federally-backed mortgage could now receive instant relief. Forbearance, the law said: “…shall be granted for up to 180 days, and shall be extended for an additional period of up to 180 days at the request of the borrower.” Essentially, anyone with a federally-backed mortgage was now eligible for a six-month break from home payments. Really it was a year, given that a 180-day extension could be granted “at the request of the borrower.” It made sense. The burden of having to continue to make home payments during the coronavirus crisis would be crushing for the millions of people put out of work.
If anything, the measure didn’t go far enough, only covering homeowners with federally-backed (a.k.a. “agency”) mortgages. Still, six months or a year of relief from mortgage payments was arguably the most valuable up-front benefit of the entire bailout for ordinary people. Unfortunately, this portion of the CARES Act was conceived so badly that it birthed a potentially disastrous new issue that could have severe systemic ramifications. “Whoever wrote this bill didn’t have the faintest fucking clue how mortgages work,” is how one financial analyst put it to me. When homeowners take out mortgages, loans are bundled into pools and turned into securities, which are then sold off to investors, often big institutional players like pension funds.
Once loans are pooled and sold off as securities, the job of collecting home payments from actual people and delivering them to investors in mortgage bonds goes to companies called mortgage servicers. Many of these firms are not banks, and have familiar names like Quicken Loans or Freedom Mortgage. The mortgage servicing business is relatively uncomplicated – companies are collecting money from one group of people and handing it to another, for a fee – but these quasi-infamous firms still regularly manage to screw it up. “An industry that is just… not very good,” is the generous description of Richard Cordray, former head of the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau. Because margins in the mortgage service business are relatively small, these firms try to automate as much as possible. Many use outdated computers and have threadbare staffing policies.

Fully bipartisan.
• Wall Street-Friendly Lawmakers Sought Bailout For Shady Lenders (HuffPo)
A bipartisan group of House Financial Services Committee members asked the Federal Reserve in an April letter to extend an emergency loan program to a host of controversial financial firms that offer high-interest loans to low-income Americans. In other words, firms that offer Americans high-interest loans want a low-cost loan from the government. All 14 signatories of the April letter are recipients of campaign contributions this election cycle from the political action committee of the American Financial Services Association, or AFSA, which represents subprime lenders’ interests in Washington.
“It’s bad on the substance to have the Federal Reserve be lending to subprime consumer and small business lenders,” Graham Steele, a former Democratic counsel on the Senate Banking Committee, who now runs Stanford School of Business’ Corporations and Society Initiative. “It doesn’t look good when the members asking for that kind of bailout for these companies are also funded by those predatory lenders.” Writing to Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell, the lawmakers encouraged the Fed to expand eligibility for loans from its Term Asset-Backed Securities Loan Facility, or TALF, for “non-bank lenders and fintech platforms.” “Non-bank lenders” issue loans that are less regulated than loans made by traditional banks, but they are also willing to take greater risks. And “fintech platforms” are a kind of non-bank lender that operate online and through mobile apps.
The House members – seven Democrats and seven Republicans – were responding to a letter that the AFSA sent to Congress appealing for its members to become eligible for the program. In late March, the Fed reinitiated TALF, a program it created to shore up consumer lenders after the 2008 financial crisis, to address the economic fallout from the public health response to the COVID-19 pandemic. The Fed has said that every financial institution is eligible for the emergency loans, but it will not bail out some riskier forms of credit. In the letter, the House members make clear that they specifically want TALF to include loans issued by “installment” lending firms that the program currently excludes. Those firms offer high-interest loans for low-income borrowers to pay off in installments.

My first reaction is: that’s great, half a million fewer cars! Than I realize of course I’m not supposed to think that. “Bad, bad” for the economy!
• Auto Production Collapses By 99% In Mexico and Brazil (R.)
Auto production in Mexico and Brazil, Latin America’s top producers, plunged by an unprecedented 99% in April as a result of the coronavirus crisis, with the two countries building a total of just 5,569 vehicles. In normal times, Mexico and Brazil produce over half a million cars a month combined. The industry accounts for hundreds of thousands of jobs and several percentage points of their respective countries’ gross domestic products. “The situation is difficult and dramatic,” Luiz Carlos Moraes, president of Brazil’s automakers association, told reporters.
The statements on production, made on Friday by Mexico’s Inegi statistics association and Brazil’s Anfavea automakers association, are the first available window into the sheer extent of the crisis for automakers in Latin America. The coronavirus pandemic is putting jobs in peril and raising questions about the sustainability of the industry’s international supply chains, much of which go back to China. The poor results may also be used by auto executives to obtain government aid. Both countries have so far avoided layoffs but much hinges on when production can restart and whether there will be any demand for cars once that happens. Mexico could tentatively restart production on May 18, while Brazil’s top automakers are eyeing a June restart.

Jim quoted Comey in his headline -“I sent them”-, I changed that to a Strzok quote.
• Our Utter Incompetence Actually Helps Us (Kunstler)
“Our utter incompetence actually helps us,” declared Deputy Assistant Director of the FBI Peter Strzok to his confidante (10,000 text messages) and paramour, FBI attorney Lisa Page, when he discovered on January 4, 2017, that the agency had omitted to close the barren Crossfire Razor case against General Michael Flynn. There you have a perfect summary of the fantastic hubris at work in the agency-gone-rogue under then-FBI Director Jim “I sent them” Comey days before the swearing-in of a president somehow mistakenly elected by bamboozled voters — or so the thinking apparently went at the highest level there. Or what passed for thinking.
General Flynn, you see, having been anathematized by Barack Obama, and black-spotted by the so-called Interagency (i.e. the giant hairball of competing spy shops set up after the 9/11 fiasco), was about to assume the pivotal job of White House National Security Advisor, and it was known that he was fixing to change things up with all that. He had been director of one such shop, the Defense Intelligence Agency, for a few years and he had a fair idea just how lawlessly debauched the Intel Community had grown under CIA Director John Brennan and Director of National Intelligence James Clapper, not to mention Mr. Comey, and they all knew that.
So, General Flynn had to go, and then get squeezed hard to somehow rat-out his boss, the incoming President Trump, against whom the Interagency had nothing but a dossier of already discredited oppo research baloney courtesy of the Clinton campaign. The pretext was some conversations General Flynn had with Russian Ambassador Sergey Kislyak a few weeks before the inauguration. The FBI cooked up a “narrative” that it was criminal misbehavior for a duly appointed incoming NSA to confab with foreign diplomats – a completely specious notion, of course. The Interagency’s errand boys in the press ran with that preposterous story, and the inconsolable cohort of Hillary voters herding up to form “the Resistance” went along with the gag out of sheer, crazed bitterness.
Attorney General William Barr neatly disposed of that yarn Thursday in his remarkable chat with Catherine Herridge of CBS News (transcript here), saying: “[H]e [General Flynn] was the designated national security adviser for President-Elect Trump, and was part of the transition, which is recognized by the government and funded by the government as an important function to bring in a new administration. And it is very typical, very common, for the national security team of the incoming president to communicate with foreign leaders.”

Obama will be implicated.
• What Did Joe Biden Know About Michael Flynn? (York)
It takes a little digging, but there’s a Joe Biden connection deep inside the documents released as part of the Justice Department’s decision to drop charges against former national security adviser Michael Flynn. It is this: Sally Yates was Barack Obama’s Deputy Attorney General, and as such she played a key role in the Flynn investigation. She told special counsel Robert Mueller’s prosecutors in September 2017 that she did not know about the transition phone call between Flynn and Russian ambassador Sergey Kislyak until she was told about it by…President Barack Obama.
It happened on January 5, 2017. Yates was in a group that went to the Oval Office to brief Obama on the findings of the Intelligence Community investigation into Russian campaign meddling. The meeting had all the administration’s top national security officials: FBI Director James Comey, CIA Director John Brennan, National Intelligence chief James Clapper, national security adviser Susan Rice, and other National Security Council officials. “After the briefing, Obama dismissed the group but asked Yates and Comey to stay behind,” a memo of Yates’ interview read. “Obama started by saying he had ‘learned of the information about Flynn’ and his conversation with Kislyak about sanctions.” Yates was totally blindsided. “At that point, Yates had no idea what the president was talking about,” the interview write-up said.
What does that have to do with Biden? The interview notes made no mention of the vice president. But think back to one of the stranger moments in the Trump-Russia investigation: Rice, on January 20, 2017, at almost the exact minute the Obama administration left office, sent an email to herself documenting the January 5 meeting. This is how it began: “On January 5, following a briefing by IC leadership on Russian hacking during the 2016 presidential election, President Obama had a brief follow-on conversation with FBI Director Jim Comey and Deputy Attorney General Sally Yates in the Oval Office. Vice President Biden and I were also present.”
Oh — so Biden was there, too. The Rice memo-to-self always appeared to be an oddly-timed effort to cover for Obama. “President Obama began the conversation by stressing his continued commitment to ensuring that every aspect of this issue is handled by the intelligence and law enforcement communities ‘by the book,’ Rice wrote. “The president stressed that he is not asking about, initiating or instructing anything from a law enforcement perspective. He reiterated that our law enforcement team needs to proceed as it normally would by the book.” Got that? By the book.

” In this story, McCabe is not a news analyst. He is news. Instead of pressing him on these conflicts and allegations, he was allowed to rage against Trump, Barr, and Flynn. It is a new twist on echo journalism. McCabe the CNN analyst was echoing his own false account and calling it news analysis.”
• Andrew McCabe’s Bizarre CNN Interview (Turley)
CNN host John Berman interviewed McCabe. CNN has long used McCabe to give analysis on a host of Trump-related stories despite being fired by Trump, ridiculed for his prior bias, and referred (by career officials) for possible criminal charges. This interview, however, was even more remarkable. The documents released in the Flynn case referred to McCabe and his alleged misconduct. He was not asked about any of the specific allegations against him. Instead, he gave a revisionist history that quickly crossed into fantasy. McCabe told Berman that, in December 2016, they were considering the closure of the investigation involving Flynn but that it was a “close question.” We have previously discussed this history.
On January 4, 2017, the FBI’s Washington Field Office issued a “Closing Communication” indicating that the bureau was terminating “CROSSFIRE RAZOR” — the newly disclosed codename for the investigation of Flynn. CROSSFIRE RAZOR was formed to determine whether Flynn “was directed and controlled by” or “coordinated activities with the Russian Federation in a manner which is a threat to the national security” of the United States or a violation of federal foreign agent laws. The FBI investigated Flynn and various databases and determined that “no derogatory information was identified in FBI holdings.” Due to this conclusion, the Washington Field Office concluded that Flynn “was no longer a viable candidate as part of the larger CROSSFIRE HURRICANE umbrella case.”
After Strzok intervened to stop the closure of the investigation, he texted FBI lawyer Lisa Page “Razor still open. :@ but serendipitously good, I guess. You want those chips and Oreos?” Page replied “Phew. But yeah that’s amazing that he is still open. Good, I guess.” Strzok replied “Yeah, our utter incompetence actually helps us. 20% of the time, I’m guessing :)” So McCabe was left unchallenged in saying that at that time there was a close question as to whether to close Crossfire Razor when his investigators found nothing. Nothing. That made it a close question for McCabe whether to continue to investigate the incoming Trump National Security Adviser.
What McCabe stated next was truly incredible. He told Berman that he then learned that Flynn has arranged “surreptitious meetings” with the Russians. He explained that this was akin to investigating someone for drug dealing and then learning about his meeting with drug dealers. The problem is that there was no evidence of a crime of any kind against Flynn. Moreover, this was not a “surreptitious” meeting. There was no reason for McCabe to know about the communications of the incoming National Security Adviser with foreign officials. It was not “surreptitious.” Flynn reportedly told the transition team about the call and that the Russians wanted to talk after the newly imposed sanctions against them. It is not “surreptitious” just because McCabe did not know about it and he did not reach out to the Transition Team.

We try to run the Automatic Earth on people’s kind donations. Since their revenue has collapsed, ads no longer pay for all you read, and your support is now an integral part of the process.
Thank you.

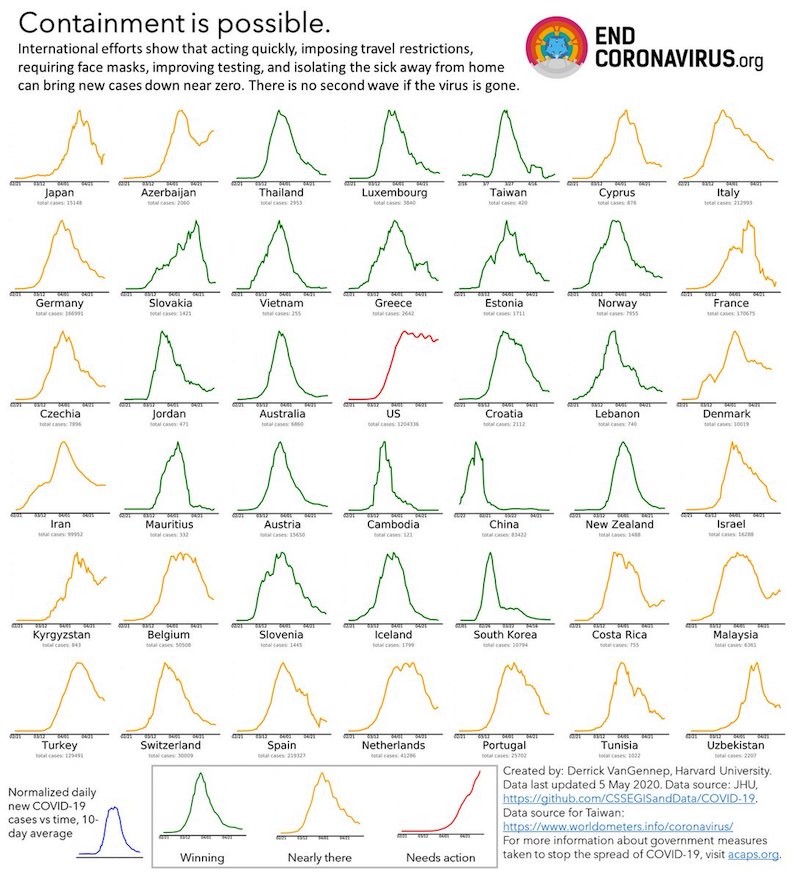
Winners prove: Containment is possible.
AND
There is no second wave (not now, not in the fall, not next year, not anytime) if the virus is gone. pic.twitter.com/L1VhYCpryq— Yaneer Bar-Yam (@yaneerbaryam) May 8, 2020

“Yesterday, upon the stair,
I met a man who wasn’t there!
He wasn’t there again today,
Oh how I wish he’d go away
Last night I saw upon the stair,
A little man who wasn’t there,
He wasn’t there again today
I think he’s from the CIA.
– Hughes Mearns et al

Support the Automatic Earth in virustime.








Home › Forums › Debt Rattle May 9 2020