Vincent van Gogh Green field 1888

Presented as a surprise.
• Global Economic Growth Has Peaked, Warns OECD (G.)
The west’s leading economic thinktank has warned that the expansion in the global economy may have peaked after cutting its growth forecasts for an array of rich and developing countries. In its latest update on the health of the world economy, the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development said the outlook for both 2018 and 2019 was less good than it had predicted in May. The Paris-based OECD called for immediate action to halt the “slide towards protectionism”, noting that trade tensions were already having an impact on confidence and investment. “The expansion may now have peaked,” the OECD said in its interim economic outlook. “Global growth is projected to settle at 3.7% in 2018 and 2019, marginally below pre-crisis norms, with downside risks intensifying.”
The OECD said it was cutting its 2018 forecast by 0.1 percentage points and its 2019 forecast by 0.3 points. Britain has had its growth forecast shaved by 0.1 points in both years to 1.3% and 1.2%, respectively – with the OECD saying the squeeze on living standards was affecting consumer spending and uncertainty about Brexit leading to soft investment. [..] The US is expected to be the fastest growing of the G7 group of industrialised countries in both 2018 and 2019, and the OECD said that in contrast to the broad-based expansion in late 2017 there were widening differences in growth performance between countries.

You break it, you own it.
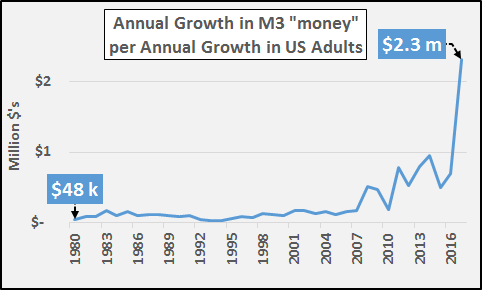
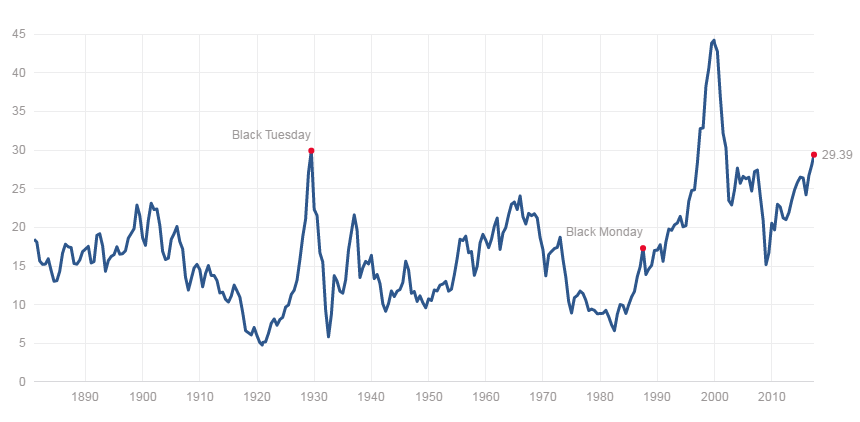
• Why Trump’s Stock Market Cheering Is Dangerous (Colombo)
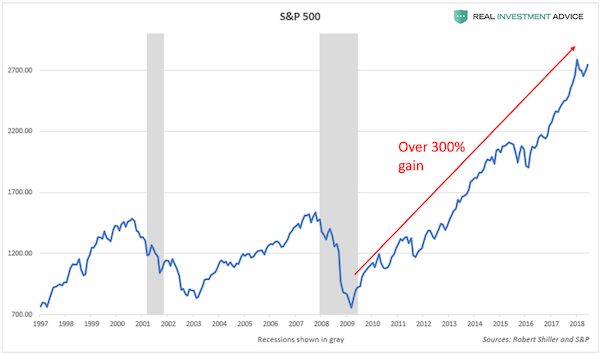
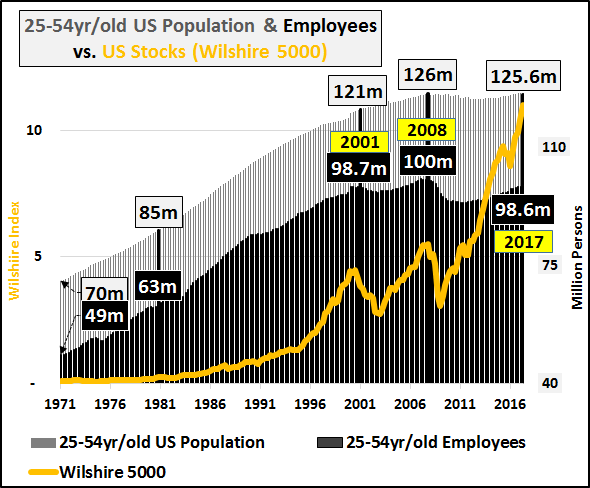
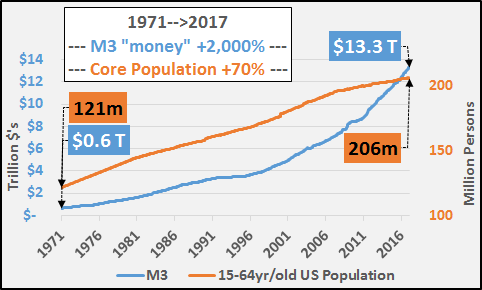
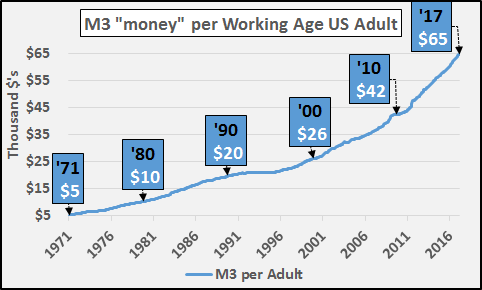
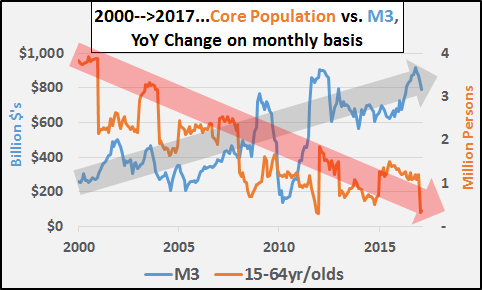
The S&P 500 hit another all-time high today and president Donald Trump tweeted, in his usual fashion, “S&P 500 HITS ALL-TIME HIGH Congratulations USA!” Though I am a conservative myself, president Trump’s stock market cheerleading angers me because he’s fanning the flames of a dangerous asset bubble, which is extremely irresponsible. I believe that the current stock market bubble will cause severe damage to the economy and our society when it ultimately pops. Imagine if George W. Bush constantly touted how surging U.S. housing prices were making Americans rich in the mid-2000s? We all know how that ended. Well, that’s what president Trump is doing with his stock market cheerleading – history will not look kindly upon it.
To make matters worse, Donald Trump knew that we were in a dangerous stock market bubble back in 2016 before he became president – he even called it a “big, fat, ugly bubble.” Now, the S&P 500 is 35% higher (and even more overvalued), but Trump is acting as if it’s an organic, sustainable boom rather than the debt-driven bubble that it really is. This is disingenuous behavior, plain and simple. The S&P 500 has surged over 300% since March 2009 due to the Federal Reserve’s pro-asset inflation policies:
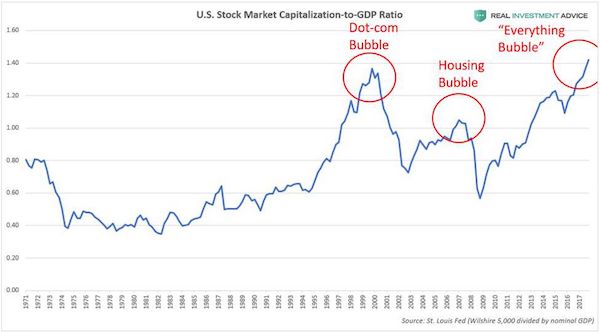
[..] According to the U.S. stock market capitalization-to-GDP ratio (also known as Warren Buffett’s “favorite indicator”), the market is more overpriced and inflated than it was during even the dot-com bubble:

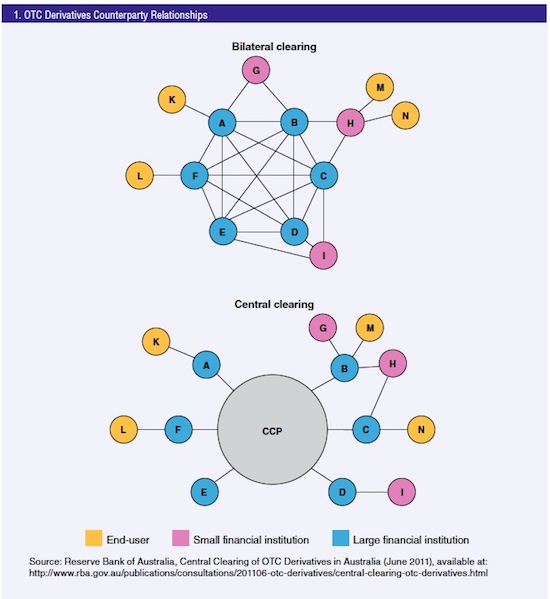
“..the crisis was a derivatives crisis, and not a housing crisis, as it is too commonly depicted.”
• Post Crisis Measures Have Failed To Tame Derivatives Risks (Yves Smith)
One of the frustrating aspects of the orgy of “ten years after Lehman” stories is that writers and pundits, many of whom are old enough to have missed the credit excesses that were evident in 2006 and 2007, are now screeching “A crisis is nigh” without necessarily focusing on likely triggers. As an aside, we are already in the midst of emerging market crises. The IMF agreed to give yet another monster bailout to Argentina. Pakistan is seeking an IMF rescue (or more accurately, trying to get shored up by any one other than the IMF but keeping the agency on the front burner in case other options fail). Turkey is still on the ropes. So calling a crisis is trivial because they are on now.
However, many of these writers are presumably anticipating something more like the global financial crisis, and too often are looking in the wrong places. There is a difference between market crashes that don’t impair the financial system, like the dot-com bust, because the assets that fell in price weren’t highly leveraged. You get real economy damage but not a financial crisis. You can also have lots of loans go bad and not impair the banking system because the credit risk was either well distributed among banks and/or significantly shifted onto investors who losses aren’t leveraged back to the financial system. However, one of the sources of systemic risk being overlooked is derivatives. That is particularly worrisome since the crisis was a derivatives crisis, and not a housing crisis, as it is too commonly depicted.
Even though the US and other housing markets were certain to suffer a nasty bust, a housing crisis alone would have resulted in something like a bigger, badder saving and loan crisis, not the financial coronary of September and October 2008. Derivatives allowed speculators to create synthetic exposures to the riskiest subprime housing debt that were 4-6 times its real economy value. Those bets wound up heavily at systemically important, highly leveraged financial institutions like Citigroup, AIG, the monolines, and Eurobanks.

“’I did not, and of course, I looked for it, looked for it hard..’
• Woodward: “No Evidence Of Trump-Russia Collusion, I Looked Hard” (DV)
After two years of exhaustive research for his book, Woodward says that he has found no evidence of collusion between Putin’s government and Donald Trump’s campaign in 2016. Zilch, nada, zero. And Woodward strained very hard looking for it. This largely ignored blockbuster admission came in a radio interview with Hugh Hewitt reported by Real Clear Politics [..] “In an interview with Hugh Hewitt on Friday, Bob Woodward said that in his two years of investigating for his new book, ‘Fear,’ he found no evidence of collusion or espionage between Trump and Russia. Woodward said he looked for it ‘hard’ and yet turned up nothing.
“’Did you, Bob Woodward, hear anything in your research in your interviews that sounded like espionage or collusion?’ Hugh Hewitt asked Woodward. “’I did not, and of course, I looked for it, looked for it hard,’ Woodward answered. ‘And so you know, there we are. …..’ “’But you’ve seen no collusion?’ Hewitt asked again to confirm. “’I have not,’ Woodward affirmed. “Hewitt would once again ask Woodward about collusion at the conclusion of the interview. “’Very last question, Bob Woodward, I just want to confirm, at the end of two years of writing this book, this intensive effort, you saw no effort, you, personally, had no evidence of collusion or espionage by the president presented to you?’ Hewitt asked. “’That is correct,’ Woodward said.”

“The most important lesson of the Brexit negotiation is that it is not a negotiation..”
“..no amount of diplomatic politesse can conceal Brexit’s reality: one part of the UK will be economically split from another.”
• Brexit: It’s A Border In The Irish Sea Or The Customs Union (G.)
Donald Tusk’s clear rejection of Theresa May’s Chequers plan at the Salzburg summit yesterday should not come as a surprise. The most important lesson of the Brexit negotiation is that it is not a negotiation, and never has been. Blessed with superior size, wealth and power, the EU has been able to dictate the framework and substance of the talks, and has refused any deviation from its red lines. The second most important lesson of the Brexit negotiation is that the EU will prioritise its economic and political cohesion above all else. That cohesion rests on two key outcomes: an undivided single market and an open border on the island of Ireland. It is these principles that have led us to Salzburg. The EU will not accept the Chequers plan, which proposes a single market in goods but not in services, capital or people.
It will also not accept any possibility of border infrastructure in Ireland, which is anathema to Dublin and, according to the Police Service of Northern Ireland, presents a credible risk of sectarian violence. That has duly paved the way for the Brexit endgame, which EU negotiator Michel Barnier has now confirmed: there will be a border for goods in the Irish Sea. The EU does not, however, want to antagonise or humiliate the UK, and has scrambled to defuse the drama of this development. Barnier stresses that most checks between Britain and Northern Ireland will take place in offices and warehouses, and only live animals and food products will need to be examined at ports themselves. But no amount of diplomatic politesse can conceal Brexit’s reality: one part of the UK will be economically split from another.

“..they left the day after so as not to have to deal with it.”
• Emmanuel Macron Calls Brexit Campaign Leaders ‘Liars’ (Ind.)
Emmanuel Macron has branded the leaders of the campaign for Brexit “liars”, in an extraordinary attack at the close of the Salzburg summit. The Leave victory was “pushed by those who predicted easy solutions”, the French president said, adding: “Those people are liars. They left the next day so they didn’t have to manage it.” At the press conference, Mr Macron also made clear he would not accept a “blind deal” – which would leave the nature of the UK’s future trading relationship with the EU to be decided after departure day. The stance is another blow to Theresa May, given that the EU’s rejection of her Chequers plan has increasingly left a “blind Brexit” as the only possible agreement.
Mr Macron did not name the “liars” behind Brexit, but he targeted those who had promised that leaving the EU would “bring a lot of money home”. The Vote Leave campaign, fronted by Boris Johnson and Michael Gove, infamously pledged it would deliver an extra £350m a week for the NHS – a claim now widely discredited. “Those who explain that we can easily live without Europe, that everything is going to be alright, and that it’s going to bring a lot of money home, are liars,” Mr Macron added. “It’s even more true since they left the day after so as not to have to deal with it.” Mr Macron made clear the prime minister would need to come up with fresh proposals by the next summit in October. “We all agreed on this today, the proposals in their current state are not acceptable, especially on the economic side of it. The Chequers plan cannot be take it or leave it.”

Someone’s going to take this to court.
• ‘Not Enough Time’ To Hold Referendum On Final Deal Before Brexit Day (G.)
A referendum on the Brexit deal would take at least six months to organise legally, making it very difficult to have a second vote before the UK is scheduled to exit the EU on 29 March next year, constitutional experts have said. As EU leaders including the Czech prime minister, Andrej Babis called on Theresa May to change firm government policy and put a vote to the people, academics said there was not enough time if article 50 is enacted as scheduled. There are indications that a delay to the enactment of article 50 could be acceptable to the EU, but without this agreement time stands in the way of a second referendum, experts believe.
“It is just possible to hold one within six months, but the shorter the timescale, the higher the chance of the question or other aspects of the referendum being challenged over their legitimacy,” said Prof Robert Hazell of the constitution unit at the department of political science, University College London. Fresh legislation, testing of the question by the Electoral Commission and a 10-week regulated period for a campaign are all required before a referendum can take place, he pointed out. David Cameron’s Brexit referendum took just over a year to get to the ballot box.

Liquidation. But: “Monuments are protected by the Constitution, they cannot be transferred or be sold..”
• Historical Monuments and Museums Moved to Greece’s Privatization Fund (KTG)
Archaeologists and sites Guards are up in arms after the Greek Finance Ministry issued a decision ordering the trasnfer several historical sites and buildings, museums, monuments and historical buildings to the Super Privatization Fund. “They belong de facto to the state and are off any trade,” the Greek Archaeologists Association said in a statement with the title “No to sale of the country’s monuments” issued on Wednesday. According to the archaeologists a total of 10,119 archaeological sites, museums and historical buildings have been transferred to the Privatization Fund, many of them from the area in and around Chania on the island of Crete.
“Monuments are protected by the Constitution, they cannot be transferred or be sold,” the Association said, adding that this unprecedented transfer became known when the catalogue of the monuments in and around Chania became public. Among those monuments and museums in Chania are the new Archaeological Museum, the archaeological museum located inside the St Francis Church, the National Museum Eleftherios Venizelos, the Historical Archive of Crete, several Venetian and Byzantine moats, fortifications and bastions as well as properties where important Minoan architectural remains have been discovered. “Is Acropolis next?” the Association of Guards at archaeological sites said in an equally angry statement on Thursday adding that also land plot where excavations take place have been transferred. They threaten with strikes.
“Our response will be very tough. Our cultural heritage belongs to all Greeks, no government has the right to negotiate about it or transfer ownership,” they said in their statement.

Yeah, smart species.
• Propping Up Glaciers To Avoid Cataclysmic Sea Level Rise (AFP)
As global warming outpaces efforts to tame it, scientists have proposed building massive underwater structures to prevent an Antarctic glacier the size of Britain from sliding into the sea and lifting the world’s oceans by several metres. The more modest of two engineering schemes — which is still on the scale of a Panama or Suez Canal — to shore up Thwaites Glacier would require the construction of Eiffel Tower-sized columns resting on the seabed to support the glacier’s ocean-facing edge, or ice shelf. Option Two is a 100-metre tall underwater wall, or berm, running 80-100 kilometres (55-60 miles) beneath the ice shelf to block bottom-flowing warm water that erodes the glacier’s underbelly, rendering it unstable.
The ambitious projects, detailed Thursday in the European Geophysical Union journal The Cryosphere, reflect a gathering awareness that slashing planet-warming greenhouse gas emissions — while essential — may not happen quickly enough to avoid catastrophic climate change impacts. “Thwaites could easily trigger a runaway ice sheet collapse that would ultimately raise global sea levels by about three metres,” said lead author Michael Wolovick, a researcher at Princeton University’s Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory. Nor will reducing carbon pollution be enough: any credible pathway to a world in which global warming is capped below two degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels (3.6º Celsius) — the target enshrined in the 2015 Paris climate treaty — depends on sucking large quantities of CO2 out of the air.

In the beginning there was nothing.
• 558 Million-Year-Old Fossils Identified As Oldest Known Animal (G.)
A fossilised lifeform that existed 558m years ago has been identified as the oldest known animal, according to new research. The findings confirm that animals existed at least 20m years before the so-called Cambrian explosion of animal life, which took place about 540m years ago and saw the emergence of modern-looking animals such as snails, bivalves and arthropods. The new fossils, of the genus Dickinsonia, are the remains of an oval-shaped lifeform and part of an ancient and enigmatic group of organisms called Ediacarans. These creatures are some of the earliest complex organisms on Earth, but their place within the evolutionary tree has long puzzled scientists. Suggestions as to what they were have ranged from lichens to failed evolutionary experiments to bacterial colonies.
Now, by identifying the remains of organic matter on newly discovered Ediacaran fossils as ancient cholesterol, the scientists have been able to confirm Dickinsonia was an animal, which makes it the oldest known animal. “It is the exact type and composition of that fat that was the giveaway that Dickinsonia was in fact an animal”, said Jochen Brocks of the Australian National University, one of the authors on the study. He added that the study solves “a decades-old mystery that has been the holy grail of palaeontology”. The fossils were discovered on two surfaces on a cliffside in the remote wilderness of north-west Russia by PhD student Ilya Bobrovskiy, who is lead author on the paper, published in the journal Science.

Dickinsonia fossils found in north-west Russia. Composite: Ilya Bobrovskiy/Ilya Bobrovskiy/ANU

“This generation being born now… is the last free generation..”
• Assange’s Last Interview Before Blackout (RT)
Before his links to the world was cut by his Ecuadorian hosts, WikiLeaks founder Julian Assange gave an interview on how technological advances are changing humankind. He said global surveillance will soon be totally unavoidable The interview was provided to RT by organizers of the World Ethical Data Forum in Barcelona. Assange, who is currently stranded in the Ecuadorean embassy in London with no outside communication except with his legal team, has a pretty grim outlook on where humanity is going. He says it will soon be impossible for any human being to not be included into global databases collected by governments and state-like entities.
This generation being born now… is the last free generation. You are born and either immediately or within say a year you are known globally. Your identity in one form or another –coming as a result of your idiotic parents plastering your name and photos all over Facebook or as a result of insurance applications or passport applications– is known to all major world powers. “A small child now in some sense has to negotiate its relationship with all the major world powers… It puts us in a very different position. Very few technically capable people are able to live apart, to choose to live apart, to choose to go their own way,” he added. “It smells a bit like totalitarianism – in some way.”