
G. G. Bain Navy dirigible, Long Island 1915



A lot of people and funds are long Apple, and own sizable chunks of it.
• Apple Just Wiped Out $40 Billion In Value (BI)
Apple’s disappointing earnings report on Tuesday sent the stock down more than 7% in after-hours trading. That’s a lot for any company, but particularly dramatic for Apple, which is the most valuable in the world. Before the market closed today, Apple’s market cap was $578 billion. That means a 7% drop erases more than $40 billion worth of value. But the bad news doesn’t end there. Shares of some of Apple’s suppliers are also down, with Bloomberg reporting that Cirrus Logic has lost more than 8%. By way of comparison, Alphabet’s market cap is around $485 billion. How long until it passes the leader?
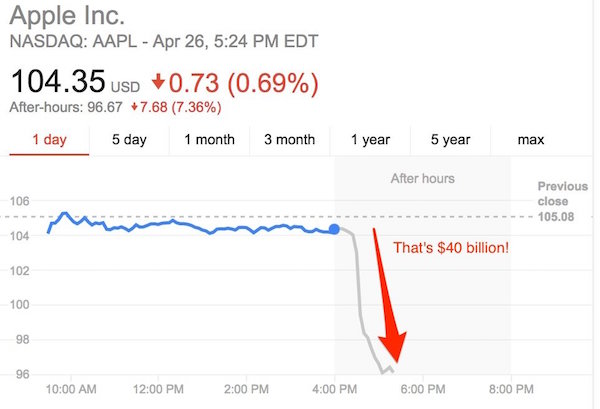

Peak Apple is now in the rearview mirror.
• Rotten Apple: Stock Plunges 8% On Earnings, Revenue Miss (CNBC)
Apple reported quarterly earnings and revenue that missed analysts’ estimates on Tuesday, and its guidance for the current quarter also fell shy of expectations. The tech giant said it saw fiscal second-quarter earnings of $1.90 per diluted share on $50.56 billion in revenue. Wall Street expected Apple to report earnings of about $2 a share on $51.97 billion in revenue, according to a consensus estimate from Thomson Reuters. That revenue figure was a roughly 13% decline against $58.01 billion in the comparable year-ago period — representing the first year-over-year quarterly sales drop since 2003. Shares in the company fell more than 8% in after-hours trading, erasing more than $46 billion in market cap.
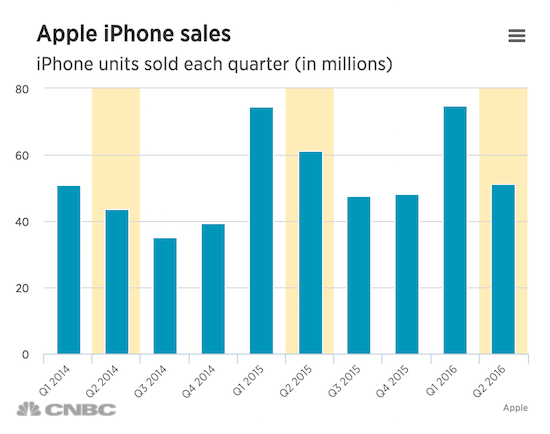
That after-hours loss is greater than the market cap of 391 of the S&P 500 companies. Importantly, the company announced a 10% dividend increase and a $50 billion increase to its capital return program. Under that new plan, Apple expects to spend a total of $250 billion of cash by the end of March 2018, it said. On the dividend, Apple said its board had declared a dividend of $.57 per share, payable on May 12, 2016 to shareholders of record as of the close of business on May 9. A key reason for the declining revenue was Apple’s year-over-year decrease in iPhone sales. Despite this, Apple CEO Tim Cook told CNBC Tuesday that the company is in “the early innings of the iPhone.”
In fact, Apple beat Wall Street’s estimates on iPhone shipments, reporting 51.19 million for the quarter. Analysts had expected 50.3 million, according to StreetAccount. Still, that iPhone unit count was a 16% decline from the 61.17 million shipped during the same period last year. For his part, however, Cook described the iPhone business as “healthy and strong” on the call. In fact, Cook said the company added more switchers from Android and other platforms in the first half of the year than in any other six month period ever.

Tim Cook is spinning. Reality says the next great gadget is long overdue; the iPhone is a Jobs idea, the iWatch a failure, and what has Apple done for you lately?
• Apple China Sales Drop 26% (CNBC)
Apple’s sales in China tumbled in the second quarter after currency headwinds hurt Hong Kong sales, the company said in Tuesday’s earnings. “The vast majority of the weakness sits in Hong Kong,” Apple CEO Tim Cook told analysts in an earnings call. “The Hong Kong dollar being pegged to the U.S. dollar, and therefore it carries the burden of strength of U.S. dollar. And that has driven tourism, trade and international shopping down significantly compared to what it was in the year ago.” The company reported quarterly earnings and revenue that missed analysts’ expectations, with revenue declining year-over-year in every region. But China saw the biggest share of declines: Greater China sales, once the tech giant’s fastest growing market, fell to $12.49 billion in the second quarter, the company said, a 26% year-over-year decline.
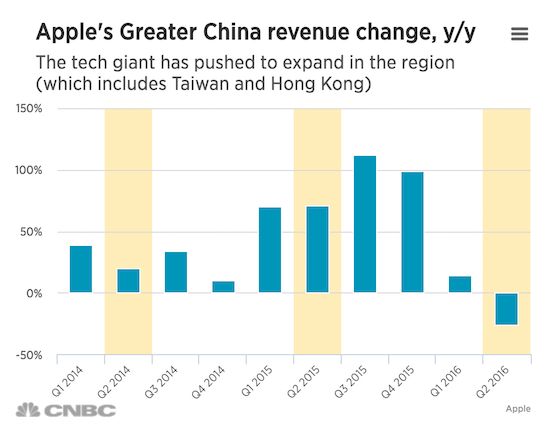
Excluding Hong Kong and Taiwan, mainland China saw sales decline 11% on a reported basis, and 7% on a constant currency basis, Cook said. But people need to look under the numbers, Cook said, as LTE adoption increases and more Apple stores open in the region. “When I look at the larger picture, I think China is not weak as is talked about,” Cook said. “I see China as … a lot more stable than what I think is the common view of it. We remain really optimistic about China.” Chief financial officer Luca Maestri said the business in China was “better than the numbers might suggest.” “We had significant inventory channel reductions and currency weakness which affected our reported revenue,” Maestri said in an earnings call.
“Keep in mind that we were up against an extremely difficult year-ago compare when our mainland China revenue grew 81%. We remain very optimistic about the China market over the long-term, and we are committed to investing there for the long run.” But speaking in January, Cook warned that the company had seen “some signs of economic softness” in the Greater China region. That business segment, which includes mainland China, Taiwan and Hong Kong, is a key area of growth for the U.S. tech giant, but Cook acknowledged in January that it had been something of a “turbulent environment.” China has seen its pace of economic expansion slowing in recent quarters, and its stock markets have taken investors on a roller coaster ride during that time.

Buybacks are fizzling out. They’re too expensive an option to continue propping up shares.
• Alarm Over Corporate America’s Debt And Stalled Earnings (Authers)
Corporate America is swimming in cash. There is no great news about this, and no great mystery about where it came from. Seven years of historically low interest rates will prompt companies to borrow. A new development, however, is that investors are starting to ask in more detail what companies are doing with their cash. And they are starting to revolt against signs of over-leverage. That over-leverage has grown most blatant in the last year, as earnings growth has petered out and, in many cases, turned negative. This has made the sharp increases in corporate debt in the post-crisis era look far harder to sustain. Perhaps the most alarming illustration of the problem compares annual changes in net debt with the annual change in earnings before interest, tax, depreciation and amortisation, which is a decent approximation for the operating cash flow from which they can expect to repay that debt. As the chart shows, debt has grown at almost 30% over the past year; the cash flow to pay it has fallen slightly.
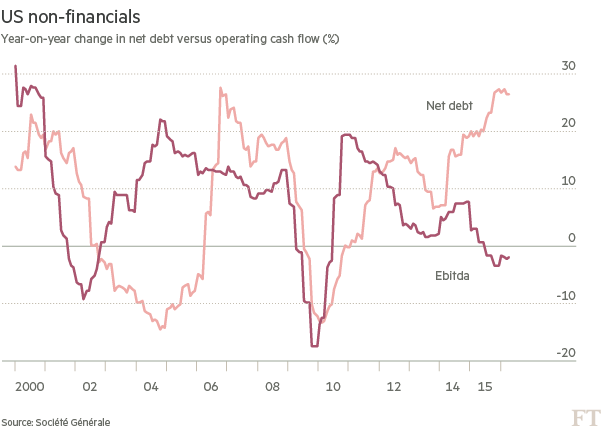
According to Andrew Lapthorne of Société Générale, the reality is that “US corporates appear to be spending way too much (over 35% more than their gross operating cash flow, the biggest deficit in over 20 years of data) and are using debt issuance to make up the difference”. The decline in earnings and cash flows in the past year has accentuated the problem, and brought it to the top of investors’ consciousness. A further issue is the uses to which the debt has been put. As pointed out many times in the post-crisis years, it has generally not gone into capital expenditures, which might arguably be expected to boost the economy. It has instead been deployed to pay dividends, or to buy back stock — or to buy other companies. Shifts in these uses of cash are now affecting markets.
Cash-funded mergers and acquisitions are at a record. In the four quarters to the end of last September, according to Ned Davis Research, S&P 500 companies spent $376bn on acquisitions, 43% above the prior high in 2007, ahead of the credit crisis. Buyback activity remains intense. According to S&P Dow Jones, for each of the seven quarters up to the third quarter of last year, between 20% and 23% of S&P 500 companies bought back enough shares to reduce their total shares outstanding at a rate of 4% per year. In the last quarter of 2015, 25.8% of companies did so.

“First-quarter GDP growth estimates are as low as a 0.3% rate.”
• Weak US Factory, Consumer Confidence Data Cloud Growth Outlook (R.)
Orders for long-lasting U.S. manufactured goods rebounded far less than expected in March as demand for automobiles, computers and electrical goods slumped, suggesting the downturn in the factory sector was far from over. Tuesday’s report from the Commerce Department also implied that business spending and economic growth were weak in the first quarter. Prospects for the second quarter darkened after another report showed an ebb in consumer confidence in April. The data came as Federal Reserve officials started a two-day policy meeting. The U.S. central bank is expected to leave its benchmark overnight interest rate unchanged on Wednesday. The Fed raised rates in December for the first time in nearly a decade.
“These disappointing reports will likely add to the caution at the Fed. Given the weak performance in these two key segments of the economy, we expect the rebound in growth momentum in the second quarter to be quite weak,” said Millan Mulraine, deputy chief economist at TD Securities in New York. The Commerce Department said orders for durable goods, items ranging from toasters to aircraft meant to last three years or more, increased 0.8% last month after declining 3.1% in February. Non-defense capital goods orders excluding aircraft, a closely watched proxy for business spending plans, were unchanged after a downwardly revised 2.7% decrease in the prior month. These so-called core capital goods orders were previously reported to have decreased 2.5% in February.
Economists had forecast durable goods orders advancing 1.8% last month and core capital goods increasing 0.8%. Shipments of core capital goods – used to calculate equipment spending in the gross domestic product report – rose 0.3% after slumping 1.8% in February. Manufacturing, which accounts for 12% of the U.S. economy, is struggling with the lingering effects of the dollar’s past surge and sluggish overseas demand. [..] The durable goods report added to recent reports on retail sales, trade and industrial production in suggesting economic growth slowed further in the first quarter. The economy grew at an anemic 1.4% annualized rate in the fourth quarter. First-quarter GDP growth estimates are as low as a 0.3% rate. The government will publish its advance first-quarter GDP growth estimate on Thursday.

It’ll take a long time for people to acknowledge that globalization, centralization, global trade, are declining and are in essence over, since they are shrinking. And shrinkage=death in our system.
• Once Bustling Trade Ports in Asia and Europe Lose Steam (WSJ)
At a logistics park bordering Shanghai’s port last month, the only goods stored in a three-story warehouse were high-end jeans, T-shirts and jackets imported from the U.K. and Hong Kong, most of which had sat there for nearly two years. Business at the 108,000-square-foot floor warehouse dwindled at the end of 2015 after several Chinese wine importers pulled out, said Yang Ying, the warehouse keeper, leaving lots of empty space. The final blow came after a merchant turned away a shipment in December at the dock. “The client told the ship hands, just take the wine back to France,” Ms. Yang said. “Nobody wants it.” Pain is increasing among the world’s biggest ports—from Shanghai to Hamburg—amid weaker growth in global trade and a calamitous end to a global commodities boom.
Overall trade rose just 2.8% in 2015, according to the World Trade Organization, the fourth consecutive year below 3% growth and historically weak compared with global economic expansion. The ancient business of ship-borne trade has been whipsawed, first by a boom that demanded more and bigger vessels, and more recently by an abrupt slowing. That turnabout has roiled the container-shipping industry, which transports more than 95% of the world’s goods, from clothes and shoes to car parts, electronic and handbags. It has set off a frenzy of consolidation and costs cutting across the world’s fleets. Ashore, it is also slamming ports and port operators, the linchpin to global commerce. Nowhere is the carnage more painful than along the Europe-Asia trade route, measuring roughly 28,000 miles round trip.
A cooling Chinese economy and a high-profile crackdown by Beijing on corruption has damped demand for everything from commodities like iron ore to designer scarves and shoes. Meanwhile, Europe’s still sputtering recovery from the global economic crisis is hitting the flow of goods in the other direction. On Friday, the Hong Kong Marine Department reported throughput for its port in the first quarter was off 11% from the first three months of last year. Throughput for all of 2015 also dropped 11%. “It is the first time you see people in shipping being really scared,” said Basil Karatzas, of New York-based Karatzas Marine Advisors and Co.

Things are not well.
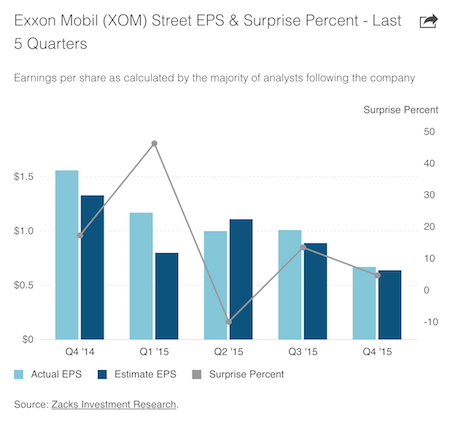
• Exxon Mobil Downgrade Leaves Just Two AAA-Rated Companies In The US (MW)
In a sign of deteriorating credit quality, Standard & Poor’s on Tuesday stripped oil giant Exxon Mobil of its pristine AAA rating, leaving just two U.S. non-financial companies with what is the highest possible rating on their debt. Microsoft and consumer goods giant Johnson & Johnson are now the only companies to enjoy an AAA rating, the strongest possible vote of confidence in their financial strength and discipline in meeting all of their debt obligations. As recently as 2008, there were six AAA-rated companies, but General Electric, Pfizer and Automatic Data Processing have been downgraded since then. “This shows that the corporate market is not immune from secular industry changes and deep cyclical troughs that materially impact the immediate-term credit outlook,” said Brian Gibbons at research firm CreditSights.
S&P cut Exxon’s rating by two notches to AA-plus, and said the outlook is stable, meaning it does not expect to adjust the rating in the near term. The rating agency had placed the rating on CreditWatch negative on Feb. 2, in the light of the lengthy slump in oil prices. “We believe Exxon Mobil’s credit measures will be weak for our expectations for a ‘AAA’ rating due, in part, to low commodity prices, high reinvestment requirements, and large dividend payments,” the agency wrote in a statement. Exxon has more than doubled its debt load in recent years, as it spends generously on major projects, said S&P. But the oil giant has also been rewarding its shareholders with dividend payments and share buybacks “that substantially exceeded internally generated cash flow.”
Exxon is likely to benefit from near-term production gains as some of those projects are completed, but maintaining production and replacing reserves will require more spending. “We believe the company may return cash to shareholders rather than building cash or reducing debt, limiting improvement in our projected credit measures when commodity prices improve,” said S&P. Gibbons said the two-notch downgrade is harsh, given Exxon’s status as the best-of-breed oil and gas company in the world, the strength of its balance sheet and earnings diversity through upstream and downstream businesses. “Its global reach positions it much better than any other energy peer, but it too is not immune to the depths of the cycle,” he said.

Zombie nation.
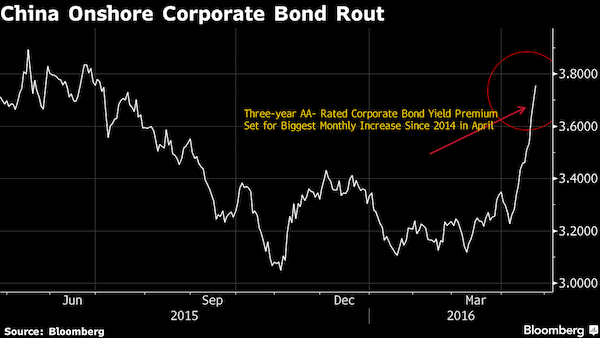
• China Ratings Downgrade Wave Seen as Next Driver of Bond Slump (BBG)
China’s slumping onshore bond market is braced for rating cuts, as companies report weaker earnings and prepare for unprecedented debt maturities. China Securities and HFT Investment Management predict downgrades will surge as a slumping economy makes financial reports due by April 30 a gloomy read. Companies in China must repay 547 billion yuan ($86 billion) of onshore notes in May, the most in any month ever, data compiled by Bloomberg show. Investors are avoiding risky debt, with the yield premium on three-year AA- rated local bonds, considered junk in China, widening 43 basis points in April, the most since 2014. “An explosion of credit risks is spreading,” said He Qian at HFT Investment Management. “The risks are spreading from privately held companies to state-owned companies, from overcapacity industries to all other industries.”
At least seven companies missed bond payment this year, up from only two in the same period of 2015 as Premier Li Keqiang tries to rid industries with overcapacity of zombie producers. Onshore agencies have cut 33 issuer ratings, almost double the 17 for the first four months of 2015, according to China Chengxin International Credit Rating Co. There have been 34 upgrades versus 37% a year ago. “We will see a wave of rating downgrades in the middle of this year,” said Wei Zhen at Bosera Asset Management. She oversees the Bosera Anfeng 18-Month Interval Bond Fund, whose 17% return in the past year was the best among fixed-income funds tracked by research firm Howbuy. “The rising credit risks may lead to a further correction in the corporate bond market.” Chinese investors have complained onshore ratings don’t fully reflect issuers’ credit risks.
More than 50% of Chinese locally-rated AAA bonds issued by listed firms may have default risk consistent with what Bloomberg’s quantitative, independent default-risk model deems below-investment-grade companies. Shi Yuxin at HuaAn Fund Management said in a report on April 18 that China’s “inflated” ratings will be under pressure to have “substantial” downgrades in 2016 as local governments cut their support for troubled companies. About 14.9% of listed Chinese companies have forecast losses for 2015, compared with 12.7% in 2014, according to data compiled by China International Capital Corp. Ministry of Finance data released on Tuesday showed that profit at state-owned companies slid 13.8% in the first quarter from a year earlier. Investors are fleeing the bond market. The market value of assets held by 718 onshore bond funds dropped last week, accounting for 95.6% of all the fixed-income funds tracked by Shanghai-based research firm Howbuy.

Beijing has lost the narrative.
• China’s Commodity Frenzy Spurs New Crackdown From Exchanges (BBG)
China’s commodity exchanges stepped up efforts to curb speculation in trading in everything from steel to iron ore and coking coal after prices soared amid a credit-fueled binge. Futures slumped on Wednesday. Bourses in Dalian, Shanghai and Zhengzhou have announced further measures, including higher fees and a reduction in night hours, adding to a raft of moves this month that have made it more expensive for investors to trade. Goldman Sachs said this week it was concerned about the surge in speculative trading in iron ore, adding daily volumes were so large that they sometimes exceed annual imports. Ore prices have surged 34% this year in Dalian, while steel reinforcement bar is up 39% in Shanghai.
Morgan Stanley said the spike in speculative trading had stunned global markets, citing a jump in activity for eggs, garlic and cotton as well as iron ore and steel. The explosive growth in trading has stoked concerns that the frenzy was triggered by a credit-fueled surge in liquidity echoing the stock market bubble in 2015 and is destined for a similar bust, according to Zheng Ge at CEFC Wanda Futures. China’s investors have been honing in on raw materials amid signs of a pickup in demand after policy makers talked up growth, added stimulus and the property market rebounded. Among the latest changes, the Dalian exchange raised trading fees for iron ore, coking coal and coke, while Shanghai said it would increase margin requirements for steel reinforcement bar and hot-rolled coil, and shorten trading hours.
The Zhengzhou exchange raised trading charges and margin requirements for some commodities. Iron ore futures plunged 4.1% on Wednesday, extending their decline in the past four days to 8.9%. Steel reinforcement bar lost 3.2% and coking coal slid 4.6% as prices responded to the exchange moves. “We’re trying to clampdown firmly on the trend of excessive speculation in some commodity trading,” the Dalian bourse said in a statement. “We’ll be highly vigilant and adopt further measures if necessary.”

Does SYRIZA have any fight left? If not, Europe is going to walk all over it.
• Eurogroup Meeting Cancelled, Tsipras To Ask For Special EU Summit (Kath.)
Greece and its lenders were unable on Tuesday to reach an agreement on how to line up €3.6 billion in contingent austerity measures, leading to plans for an extra meeting of eurozone finance ministers on Thursday being dropped. A spokesman for Eurogroup President Jeroen Dijsselbloem confirmed on Tuesday night that there would be no meeting this week to rubber-stamp an agreement between Athens and the institutions and conclude the first review of the third Greek bailout program. “More time needed,” tweeted Michel Reijns. “Meeting of first review, contingency package and debt at later stage,” he added, without suggesting when eurozone finance ministers might meet to discuss Greece.
Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras is expected to call European Council President Donald Tusk today to ask for an extraordinary EU leaders’ summit to discuss the Greek program as the SYRIZA leader feels that Athens has met its bailout commitments and that the lenders’ side is standing in the way of an agreement. Greek government sources said earlier that the details of an initial €5.4 billion package of tax hikes and pension cuts had been finalized. However, the standby measures, which total 2% of GDP, proved to be a stumbling block. Athens proposed that the government should commit to adopting corrective measures if fiscal targets are missed but that these interventions should only be specified after Greece’s fiscal data has been ratified by Eurostat.
This proposal is thought to have been rejected by the IMF and some eurozone member-states, which want Greece to legislate specific measures now and have them on standby in case they are needed. Sources said that Finance Minister Euclid Tsakalotos spoke with some of his eurozone counterparts on Tuesday in order to explain the situation to them. The Greek government believes that German Finance Minister Wolfgang Schaeuble showed understanding for Greece’s position and appeared to support the Greek proposal for a permanent mechanism to reduce spending when the adjustment program is not on track. Athens is adamant that the IMF’s insistence on specific standby measures being legislated now was the only factor that prevented Greece and the institutions reaching an agreement on Tuesday.

This battle is about contingency plans, not even actual ones, but what-ifs.
• Greece Faces New IMF Curve Ball to Unlock Aid (BBG)
Greek Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras has promised voters he’ll reject even one euro cent more of budget austerity than is needed under the country’s bailout. Greece’s international creditors say the program’s requirements may include €3.5 billion in extra fiscal tightening he hadn’t bargained for. The demand by the euro area and the IMF is a potential bombshell for the government, raising the threat of renewed instability in Greece. Tsipras rode to power in January 2015 railing against austerity and nearly steered Greece out of the euro before flip-flopping last summer to secure the nation’s third bailout in six years. Since then the Greek economy has slipped back into recession, unemployment has stayed stubbornly high at around 25% and public support for the euro has weakened.
Just like last year, Tsipras needs financial aid to avoid defaulting on payments to the ECB that come due in three months time. The prime minister’s current dilemma stems from a disagreement between the euro area and the IMF. While the European creditors say the government in Athens has committed to enough austerity to reach the targeted budget surplus before interest payments of 3.5% of gross domestic product in 2018, the IMF projects current Greek measures will produce an excess of just 1.5%. With Germany insisting on continued IMF involvement in the Greek aid program, the conflicting forecasts have led the creditors as a whole to call for “contingency measures” equal to 2% of GDP. These would kick in should the government in Athens stray off its budgetary course as the IMF projects.
So Tsipras and Finance Minister Euclid Tsakalotos face the delicate task of drawing up measures that can satisfy the creditors without breaking apart their coalition with the nationalist Independent Greeks. That balancing act would be a challenge for any Greek government, let alone one with an anti-austerity base, a deep dislike of the Washington-based IMF and a three-seat majority in parliament.

The fastest growing economy in North America for years. Gone.
• Moody’s Downgrades Canadian Province Of Alberta On Rising Debt (R.)
Moody’s Investors Service stripped Alberta of its Aaa credit rating on Monday, becoming the latest ratings agency to downgrade the Canadian province after the oil price shock pushed its finances deep into the red. Citing its worsening fiscal position and resulting rapid rise in debt, Moody’s downgraded the province’s long-term rating to Aa1 from Aaa and maintained a negative outlook. The downgrade “reflects the province’s growing and unconstrained debt burden, extended timeframe back to balance, weakened liquidity, and risks surrounding the success of the province’s medium-term fiscal plan,” Moody’s Assistant Vice President Adam Hardi said in a statement. Earlier this month, Dominion Bond Rating Service also downgraded the province after the provincial government forecast a budget deficit of C$10.4 billion ($8.21 billion) this fiscal year.
Standard & Poor’s stripped Alberta of its AAA credit rating in December. Alberta’s left-leaning NDP government expects the once-booming province to be C$57.6 billion in debt by 2019, while Finance Minister Joe Ceci said Alberta could run deficits until 2024. Ceci described the latest downgrade as a “disappointment” and reiterated the government’s commitment to maintaining funding for public services and infrastructure spending in a bid to spur growth. The province is home to Canada’s vast oil sands and is the No. 1 exporter of crude to the United States but the government expects oil and gas revenues this year to be almost 90% lower than 2014. Earlier this month the Canadian Association of Petroleum Producers said capital investment in the industry has dropped C$50 billion in two years and more than 100,000 oil and gas workers have been laid off.

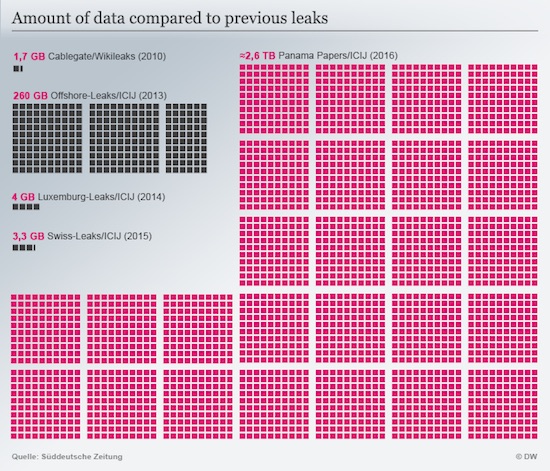
In order to pre-empt ‘authorities’, what the journalists should do is reach out to Wikileaks and find a means to release the data after redacting them in a way that prevents people from getting hurt. The ICIJ does not seem to have that ability. They will come to regret that, because pressure will rise.
• From Germany To The US, Authorities Want Access To Panama Papers (DW)
Germany’s federal states on Friday called for increased measures against tax havens and for media outlets to allow prosecutors to examine the contents of a cache of 11.5 million documents known as the “Panama Papers,” which had been leaked to the press. “If the data sets from the ‘Panama Papers’ are not made accessible, then we cannot draw any consequences,” said Lower Saxony’s Finance Minister Peter-Jürgen Schneider, Reuters news agency reported. However, the Munich-based newspaper Süddeutsche Zeitung’s (SZ) investigative unit on Tuesday said it would not hand over the cache nor would it publish the leak online, despite calls to do so by government officials and representatives of the whistleblowing organization WikiLeaks.
“As journalists, we have to protect our source: we can’t guarantee that there is no way for someone to find out who the source is with the data. That’s why we can’t make the data public,” the team said during an “Ask Me Anything” session on Reddit, which included journalist Bastian Obermayer, who was first contacted by the anonymous source. “You don’t harm the privacy of people, who are not in the public eye. Blacking out private data is a task that would require a lifetime of work – we have eleven million documents,” the unit added. In a letter to the International Consortium of Investigative Journalists (ICIJ) obtained by British newspaper The Guardian this week, US attorney for Manhattan Preet Bharara said the Justice Department “has opened a criminal investigation regarding matters to which the Panama Papers are relevant.”
“The office would greatly appreciate an opportunity to speak as soon as possible with any ICIJ employee or representative involved in the Panama Papers project in order to discuss this matter further,” Bharara said. ICIJ Director Gerard Ryle said on Thursday that the organization would not release unpublished data to the Justice Department or other government entities, although it welcomed the “US Attorney’s Office reviewing all of the information from the Panama Papers.” “ICIJ does not intend to play a role in that investigation. Our focus is journalism … ICIJ, and its parent organization, the Center for Public Integrity, are media organizations shielded by the First Amendment and other legal protections from becoming an arm of law enforcement,” Ryle said in a statement.

Thank you.
• ‘Largest Ever Airlift’ Flies 33 Circus Lions To Africa Sanctuary (AP)
Thirty-three lions rescued from circuses in Peru and Colombia are being flown back to their homeland to live out the rest of their lives in a private sanctuary in South Africa. The largest ever airlift of lions will take place on Friday and has been organised and paid for by Animal Defenders International. The Los Angeles-based group has for years worked with lawmakers in the two South American countries to ban the use of wild animals in circuses, where they often are held in appalling conditions. The lions suffered in captivity: some were declawed, one lost an eye and many were recovered with broken or rotting teeth.
The group said the first group of nine lions would be collected in the capital, Bogota, on a McDonnell Douglas cargo plane, which would pick up 24 more in Lima before heading to Johannesburg. From there they would be transported by land to their new home at the Emoya Big Cat Sanctuary in Limpopo province, where they would enjoy large natural enclosures. “It will be hugely satisfying to see these lions walking into the African bush,” said Tom Phillips, ADI’s vice-president, as he inspected the cages that will be used to transport the lions. “It might be one of the finest rescues I’ve ever seen; it’s never happened before taking lions from circuses in South America all the way to Africa,” he added. “It’s like a fairytale.”

Or, more likely, we’ll bash each other’s heads in. Bit too dreamy for me.
• How Less Stuff Could Make Us Happier – And Fix Stagnation (G.)
Has western society reached “peak stuff”? If reports that once-insatiable shoppers are starting to cut back are true, what are the consequences for the old economic theory that more consumption equals greater happiness? That is a question a Bank of England blogger has posed, with interesting and upbeat conclusions. Writing on Bank Underground, a blog where Bank of England staff can challenge prevailing orthodoxies, Dan Nixon wondered if rather than shopping our way to satisfaction, a Buddhism-inspired trend of mindfulness has taught us that less is more. Inspired by its message to appreciate the moment, perhaps we can achieve greater happiness by seeking to simplify our desires, rather than satisfy them, wrote Nixon, who works in the Bank’s stakeholder communications and strategy division.
The result of less consumption but greater wellbeing could be “especially important for debates around secular stagnation and ecological sustainability”, he says. In other words, if secular stagnation is nigh and there is a permanent downward shift in the potential growth rates of advanced economies, increased attention will naturally turn to alternative ways to increase wellbeing. “‘Less is more’ ideas could form one part of the solution,” said Nixon. There are also interesting implications in the field of environmental economics, given human wellbeing and ecological sustainability are often assumed to be in conflict. “The neat thing about the less is more critique is that it achieves less consumption without constraining people’s decisions,” said the Bank blogger.
The repeated Black Friday sales frenzies that have spilled across the Atlantic from the US to the UK and the continuing fortunes of big online retailers such as Amazon may feel at odds with all the less is more talk. But the rise of mindfulness, in media coverage, schools and workplaces – including at the Bank of England – has coincided with signs that shopping may be losing its appeal as our national pastime. Ikea, purveyor of flatpacks and tealights, recently claimed the appetite of western consumers for home furnishings had reached its peak. The Swedish furniture giant’s UK crammed car parks and long hotdog queues may suggest otherwise but Ikea’s head of sustainability, Steve Howard, has spoken of “peak curtains”.
His views were followed weeks later by official figures showing the amount of “stuff” used in the UK – including food, fuel, metals and building materials – had fallen dramatically since 2001. The Office for National Statistics data revealed that on average people used 15 tonnes of material in 2001 compared with just over 10 tonnes in 2013.

Fully in line with what I’ve often said. In a situation like this, you have to put people first, not politics, or you will create mayhem. This is a certainty. It’s too late already for Europe. The goodwill and moral high ground wasted over the past 18 months will take 100 years to regain, if ever.
• Europe’s Failure On Refugees Echoes The Moral Collapse Of The 1930s (G.)
In 1938, representatives from 32 western states gathered in the pretty resort town of Evian, southern France. Evian is now famous for its water, but back then, the delegates had something else on their minds. They were there to discuss whether to admit a growing number of Jewish refugees, fleeing persecution in Germany and Austria. After several days of negotiations, most countries, including Britain, decided to do nothing. On Monday, I was reminded of the Evian conference when British MPs voted against welcoming just 600 child refugees a year over the next half-decade. The two moments are not exactly comparable. History doesn’t necessarily repeat itself. But it does echo, and it does remind us of the consequences of ethical failure. Looking back at their inaction at Evian, delegates could claim they were unaware of what was to come.
In 2016, we no longer have that excuse. Nevertheless, both in Britain and across Europe and America, we currently seem keen to forget the lessons of the past. In Britain, many of those MPs who voted against admitting a few thousand refugees are also campaigning to unravel a mechanism – the EU – that was created, at least in part, to heal the divisions that tore apart the continent during the first and second world wars. Across Europe, leaders recently ripped up the 1951 refugee convention – a landmark document partly inspired by the failures of people such as the Evian delegates – in order to justify deporting Syrians back to Turkey, a country where most can’t work legally, despite recent legislative changes; where some have allegedly been deported back to Syria; and still more have been shot at the border.
Emboldened by this, the Italian and German governments have since joined David Cameron in calling for refugees to be sent back to Libya, a war zone where – in a startling display of cognitive dissonance – some of the same governments are also mulling a military intervention. Where many migrants work in conditions tantamount to slavery. Where three separate governments are vying for control. And where Isis runs part of the coastline.









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle April 27 2016