
Pablo Picasso Self portrait with palette 1906

Excellent lenghty takedown by Bill Mitchell.
• The Destruction Of Greece – “Only A Down Payment” According To The IMF (Bilbo)
With Greece still wallowing in the depths of recession, it is clear that the IMF hasn’t finished with the destruction of that formerly independent nation. The destruction to date (27% contraction and increased poverty) are considered by the IMF to be “only a down payment” on what Greece has to do so satisfy the Troika. At what point do people start to realise that the on-going costs of this austerity dwarf the significant costs that would accompany exit? And the Troika is not done with Greece yet. They intend to screw it down even further. And the costs of remaining in the dysfunctional monetary union escalate by the day. At some point, the Greeks will realise they have been dudded. What is left is anyone’s guess – but it won’t be pretty. The destruction of Greece is “only a down payment” according to the IMF – keep that mentality in mind when you are working out whether Greece should remain obedient or tell them all to f*ck off and regain their currency independence and restore prosperity.
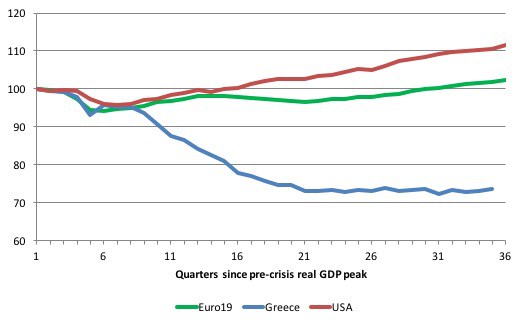
[..] The ‘event’ that brought Greece to heal in June 2015 was the ECB decision to starve the Greek banks of liquidity – in total violation of its charter to maintain financial stability within its jurisdiction. How many Greek people lost income over that blackmail? How many took their own lives? How many plunged into mental illness? Did the IMF come up with a measure of their sordid part in all that? And now Thomsen is back – threatening and haranguing a subservient polity in Greece who call themselves Socialists but have done more damage to their own nation by taking the obedience option that the conservatives could have ever dreamed of doing. The Troika are now claiming (largely at the behest of the IMF) that if Greece cuts further it will receive debt relief.
Why the Greeks are worried about their external debt is beyond me. Why not just refuse to pay it and let the debtors (largely the ECB these days as a result of the deals done with the previous bailouts (which insulated the private German and French banks from exposure) sort out the implications of that? Why not threaten Brussels with default (redenomination) and exit if they don’t allow the Greek government to expand its fiscal deficit to stimulate growth – along the lines of Spain, which only is growing because its fiscal position is in violation with the fiscal rules – conveniently ignored by Brussels as it wanted the PP government returned? Why not demand that the ECB include Greek government debt in its QE program – thereby ‘funding’ the deficit. If not, we leave!
Then the bullies would be on call and the compromises would come thick and fast. But the spinelessness of the Greek polity combined with the sociopathological joy of the Troika in bringing this rogue nation to heel will ensure no such confrontation occurs and Greece will continue to wallow at the bottom of the Eurozone. It is forecast that Greece currently needs an injection of around “€100 billion in emergency bailout cash” to stay afloat for a while. This would further add to its “already massive debt burden, that could also deepen the budget cuts and economic overhauls required to get Athens’ balance sheets back into the black and prolong what has already been a near decadelong ordeal for the country.” And the costs of staying in – huge and getting bigger.
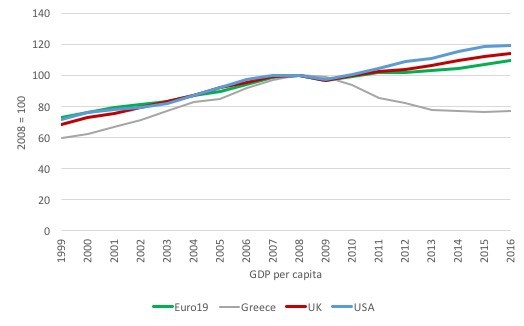

A “dramatic drop in consumption of basic commodities such as milk and bread..”
• Greek Supermarkets Report Dramatic Recession (K.)
The supermarket sector in Greece is experiencing a deep recession ranging from 8 to 15% year-on-year across its categories, according to the marketing and strategic planning director of AB Vassilopoulos, Zeta Cheimonidou. Her statements at a corporate event confirmed the general mood in the industry and data compiled by researchers surveying the sector. Cheimonidou went on to estimate that 2017 will see a 4 to 5% decline in supermarket turnover compared with 2016. “The market is experiencing a much steeper decline than last year. There is a very deep recession,” Cheimonidou stated, although she added that it would be safer to wait and see how demand evolves up until the end of May before drawing any conclusions for the entire year.
If proven correct, her estimate for a 4% drop in turnover will come on the back of a major decline in 2016 compared to 2015, which, depending on the surveying company, ranges from 4.5 to 6.5%. In its recent annual general meeting, the Hellenic Food Industry Federation (SEVT) noted the dramatic drop in consumption of basic commodities such as milk and bread, while a senior market research company official told Kathimerini that “our clients, suppliers and retailers, were crying in the first quarter.”

Congress wil have to address this soon.
• US Student Loan Implosion (PolCal)
The Consumer Federation of America recently put out a press release that reports that they’ve found that 1.1 million student loan borrowers in the United States have gone 270 or more days without making payments on their Federal Direct Student Loans, with more than $137 billion worth of the loans issued by the U.S. government now qualifying as being in default by that standard. Data from the CFA’s press release has made the rounds among multiple news outlets, but we have a pretty basic question: Are those big numbers? They certainly seem like big numbers, what with all the millions and billions being thrown about, but how do these numbers fit into the bigger U.S. government-issued student loan story? Let’s start with the biggest numbers, where we discover that $137 billion worth of Federal Direct Student Loans are in default, against the larger total of $1.3 trillion worth of Federal Direct Student Loans that have been issued through the end of December 2016.
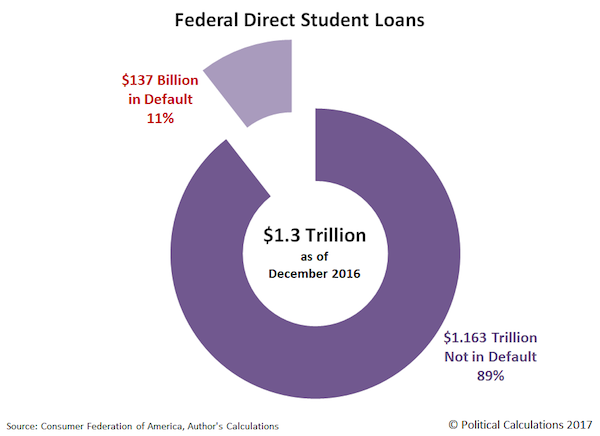
Here, we calculate that the percentage of student loans that have gone 270 or more days without having had a payment made upon them represents about 11% of the total amount borrowed. That means that some 1.1 million people whose student loans require that they make some sort of scheduled payment went more than 9 months without making any. To tell if that’s a big number or not requires that we put that number into some kind of context. Here, we’ll draw on the U.S. Federal Reserve’s data for the delinquency rates on loans and leases issued by all commercial banks in the U.S., where for the fourth quarter of 2016, we find that the total delinquency rate is 2.04%. That value had previously peaked at 7.4% back in the first quarter of 2010, following the bottoming of the Great Recession.
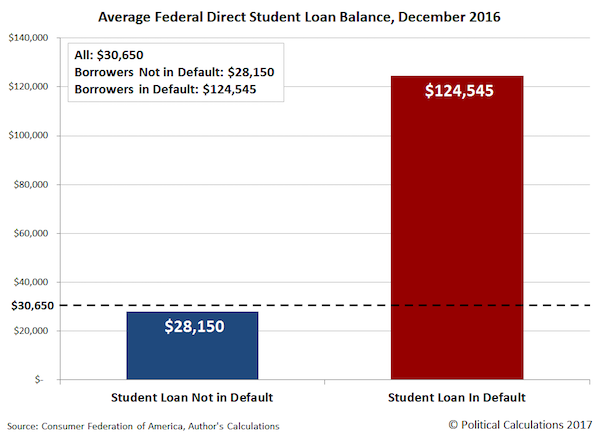
But another important thing to consider is that delinquency rate would include all private-sector issued loans and leases that have payments that are past due, including those that have gone without payment for much less than 270 days. That figure tells us that the default rate of 11% for Federal Direct Student Loans is, to put it in Trumpian terms, “Yuge!” [..] The average student loan balance in the U.S. is $30,650. For Americans who haven’t defaulted on their student loans, that average figure drops to $28,150. But for Americans who have defaulted on their payments to their U.S. government creditor, the average balance on their Federal Direct Student Loan is $124,545.

If you were not scared yet…
• If Mortgage Rates Rise, What Happens to Canada’s House Price Bubble? (WS)
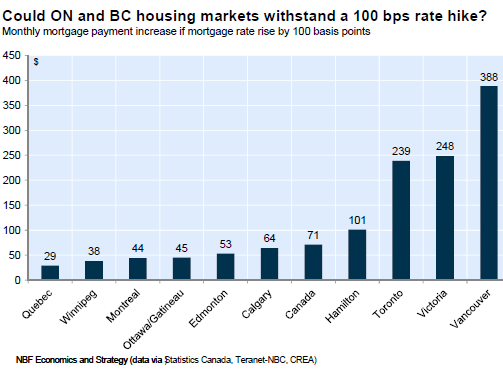
Housing affordability is a function of down payment, monthly payment, and household income. With home prices skyrocketing while household incomes were lagging far behind, low mortgage rates were the grease that kept it going. But what happens when mortgage rates begin to tick up? A “payment shock.” “An increase in interest rates of 100 bps [1 percentage point] on a 5 year term would represent a rise of C$388 for the monthly mortgage payment in the Vancouver market (+9% to C$4,669) and C$239 in Toronto (+7% to C$3,692). With housing affordability problem in these markets being already acute, we doubt current home prices could resist such an interest rate hike.”
This chart via NBF Economics and Strategy shows by how much monthly mortgage payments would rise if mortgage rates ticked up just 1 percentage point. Note the impact on monthly payments for homes in Toronto (Ontario) and Victoria and Vancouver (British Columbia):
So just how big is the Canadian housing bubble? The chart below by NBF Economics and Strategy compares US home prices (Case-Shiller 20-City index) to Canadian home prices (Teranet-National Bank 26-city index). Both indices are based on similar methodologies of comparing pairs of sales of the same home over time. The shaded areas denote recessions in Canada. The brief dip during the last recession in Canada pales against the multi-year housing bust in the US:
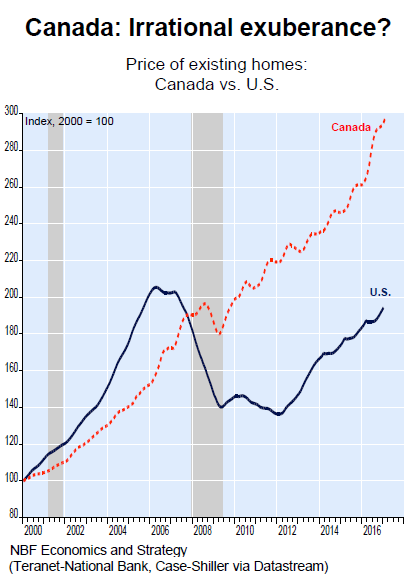
Like so many other assets classes in central-bank nirvana, this one too has reached ludicrous levels. But there’s a difference. People don’t live in stocks, bonds, classic cars, or art, and these asset bubbles have less impact on the real economy. But people do have to live in homes. Now that the results are clearer than daylight, central banks and governments worry about the consequences: Bubbles don’t just plateau. Now they wonder, belatedly, how to get out of it without bringing the whole construct down. The fact that a 1-percentage point increase in mortgage rates poses existential questions for some of the hottest markets shows how far policy makers have painted themselves into a corner.

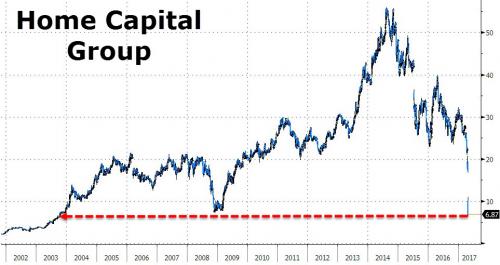
“Home Capital shares dropped by 61% in Toronto..”
• Canada’s Housing Bubble Explodes As Biggest Lender Crashes (ZH)
Call it Canada’s “New Century” moment. We first introduced readers to the company we said was the “tip of the iceberg in Canada’s magnificent housing bubble” nearly two years ago, in July 2015 when we exposed a major problem that we predicted would haunt Home Capital Group, Canada’s largest non-bank mortgage lender: liar loans in particular, and a generally overzealous lending business model with little regard for fundamentals. In the interim period, many other voices – most prominently noted short-seller Marc Cohodes – would constantly remind traders and investors about the threat posed by HCG.
Today, all those warnings came true, when the stock of Home Capital Group cratered by over 60%, its biggest drop on record, after the company disclosed that it struck an emergency liquidity arrangement for a C$2 billion ($1.5 billion) credit line to counter evaporating deposits at terms that will leave the alternative mortgage lender unable to meet financial targets, and worse, may leave it insolvent in very short notice. As part of this inevitable outcome, one which presages the company’s eventual disintegration and likely liquidation, Bloomberg reports that the non-binding rescue loan with an unnamed counterparty will be secured by a portfolio of mortgage loans originated by Home Trust, the Toronto-based firm said in a statement Wednesday.
Home Capital shares dropped by 61% in Toronto to the lowest since 2003, dragging down other home lenders. Equitable fell 17%, Street Capital fell 13%, while First National declined 7.6%. In short, the Canadian mortgage bubble has finally burst. refundable commitment fee of C$100 million, while standby fee on undrawn funds is 2.5%. The initial draw must be C$1 billion. The loan has an effective – and very much distressed – interest rate of 22.5% on the first C$1 billion, declining to 15% if fully utilized, according to a note from Jaeme Gloyn, an analyst at National Bank of Canada. Home Capital said the credit line is intended to “mitigate” a sharp drop in Home Trust’s high-interest savings account balances, which sank by $591 million from March 28 to April 24, at which point the total balance was $1.4 billion. Home Capital warned on Wednesday that further outflows are anticipated. Translated: what until last night was a depositor bank jog just became a sprint.

Dangerous shoptalk: “..overvaluation has been downgraded to moderate from a previously strong assessment..”
• Canada’s Housing Watchdog Warns of ‘Problematic Conditions’ (BI)
Canada’s housing watchdog maintained its view that there is “strong evidence of problematic conditions” in the market that some economists have classified as being in a bubble. The market is characterized by imbalances, defined as when demand and prices are far from their historical averages, Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation said in second-quarter report. “While the overall assessment of problematic conditions remains strong for Canada, overvaluation has been downgraded to moderate from a previously strong assessment,” CMHC said.
“Careful analysis by geography shows that local differences continue to divide the Canadian housing market into several markets: centers in the East are showing weak evidence of overvaluation, while centres in Southern Ontario and the West are showing moderate to strong evidence of overvaluation,” it added. In Victoria, for example, the CMHC determined that overvaluation had accelerated from “moderate” to “strong.” The Teranet and National Bank of Canada house-price index showed a 24.8% gain year-on-year in March. It jumped 12.2% for Vancouver. Separately on Wednesday, shares of Canada’s home lenders fell after Home Capital Group said it obtained a $1.5 billion credit line to cope with falling deposits. Home Capital shares plunged by more than 60%.

“George Washington used to complain about British lumber coming in from Canada..”
• It’s Tough Being Canada These Days (BBG)
It’s tough being Canada these days. There’s no other way, really, to explain why the Trump administration announced on Tuesday that it was imposing tariffs on exports of Canadian softwood lumber – tariffs that will cost the Canadian lumber industry $1 billion annually. The Canadian dairy industry is also in Trump’s crosshairs, as he made plain in a threatening tweet Tuesday morning. Trump spent much of his campaign railing about China’s “unfair” trade practices, and all the “American jobs” that have migrated to Mexico. But now that he’s president, he’s apparently been made to understand that slapping tariffs on Chinese goods could lead to a catastrophic trade war. And any moves that might destabilize Mexico would have negative consequences for the U.S.
Ah, but hit Canada with a tariff, and you get all of the political upside of looking tough with no downside. This is not just because Canadians are nice. It’s because the Canadian economy is more U.S.-dependent than any other. “20% of Canada’s GDP relies on the U.S.,” said Laura Dawson, the director of the Canada Institute at the Wilson Center. “And 70% of Canada’s exports go to the U.S.” Even if Canada wanted to retaliate, what exactly could it do? Stop the Ford plants in Canada from shipping cars to Ford in Detroit? A rational administration would never let these minor disputes get in the way of a smooth-functioning economic relationship with Canada. To start with, there’s the fact that Canada is the staunchest U.S. ally, which you would think would count for something.
And the U.S. benefits enormously from trade with Canada, which buys 18% of all American exports, more than any other country. Last year, Canada’s trade surplus with the U.S. was a minuscule $11.2 billion. The integration of the two economies has been beneficial to both. Nor are the two disputes anything new. The American lumber industry has been complaining about Canadian softwood lumber since pretty much forever. “George Washington used to complain about British lumber coming in from Canada,” Dawson said with a chuckle. The basic allegation is that most timberland in Canada is owned by its provinces, which sell logging rights at below-market prices. The U.S. views this as a government subsidy, a notion Canada rejects. Although Americans and the Canadians have never been able to put this dispute to rest, they have been able to negotiate a truce on three separate occasions since the early 1980s.

Advisers can’t agree.
• Trump Tells Canada, Mexico, He Won’t Terminate NAFTA Treaty Yet (R.)
U.S. President Donald Trump told the leaders of Canada and Mexico on Wednesday that he will not terminate the NAFTA treaty at this stage, but will move quickly to begin renegotiating it with them, a White House said. The announcement came after White House officials disclosed that Trump and his advisers had been considering issuing an executive order to withdraw the United States from the trade pact with Canada and Mexico, one of the world’s biggest trading blocs. The White House said Trump spoke by telephone with Mexican President Enrique Pena Nieto and Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau and that he would hold back from a speedy termination of NAFTA, in what was described as a “pleasant and productive” conversation.
“President Trump agreed not to terminate NAFTA at this time and the leaders agreed to proceed swiftly, according to their required internal procedures, to enable the renegotiation of the NAFTA deal to the benefit of all three countries,” a White House statement said. “It is my privilege to bring NAFTA up to date through renegotiation. It is an honor to deal with both President Peña Nieto and Prime Minister Trudeau, and I believe that the end result will make all three countries stronger and better,” Trump was quoted as saying in the statement. The Mexican and Canadian currencies rebounded in Asian trading after Trump said the U.S. would stay in NAFTA for now. The U.S. dollar dropped 0.6% on its Canadian counterpart and 1% on the peso.

This is not going to be easy to pass.
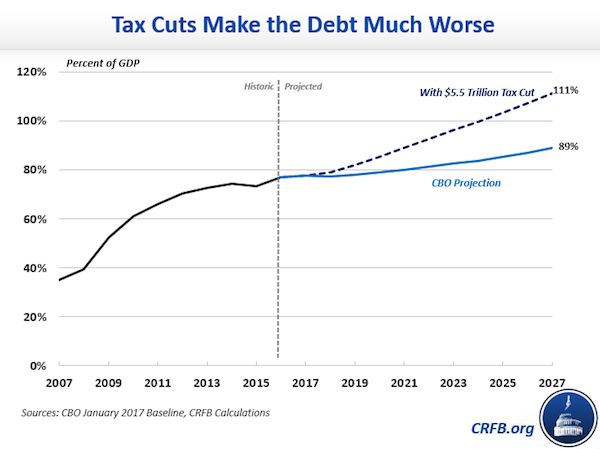
• Trump Tax Plan Would Raise US Debt by $5.5 Trillion, 20% of 2027 GDP (CRFB)
The White House released principles and a framework for tax reform today. We applaud the President’s focus on tax reform, but the plan includes far more detail on how the Administration would cut taxes than on how they would pay for those cuts. Based on what we know so far, the plan could cost $3 to $7 trillion over a decade– our base-case estimate is $5.5 trillion in revenue loss over a decade. Without adequate offsets, tax reform could drive up the federal debt, harming economic growth instead of boosting it. The framework proposes a number of specific changes including: consolidating and reducing individual income tax rates to 10, 25, and 35%; doubling the standard deduction; cutting the business tax rate to 15% on both corporations and pass-through businesses; repealing the Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) and estate tax; repealing the 3.8% investment surtax from the Affordable Care Act (“Obamacare”); moving to a territorial tax system; and imposing a one-time tax on money held overseas.
The plan also includes some vaguer proposals, including “providing tax relief for families with child and dependent care expenses” and eliminating “targeted tax breaks that mainly benefit the wealthiest taxpayers.” Although the framework itself is vague on the latter, at their press conference Secretary of the Treasury Steven Mnuchin and National Economic Director Gary Cohn seemed to imply it meant repealing all individual deductions unrelated to savings, charitable giving, or mortgage interest (revenue would come mostly from repealing the state and local tax deduction). Even with the detailed portions of the plan, there are not enough parameters specified to provide a certain revenue estimate of the tax plan. But making some assumptions based on prior proposals, our best rough estimate suggests the specified parts of the plan would cost $5.5 trillion. Assuming tax break limits only apply only to higher earners, that cost could be as high as $7 trillion; assuming credits and exclusions are eliminated as well as deductions, it would cost $3 trillion.

“..as much as 91 cents on the dollar went to share repurchases, even though that, along with compensation increases, was an expressly prohibited use by Congress.”
• What Happened Last Time US Companies Got A Break On Overseas Profits (CNBC)
The Trump administration wants to give companies a break on profits earned overseas and brought back to the United States — a program that’s been tried before to little effect. Current estimates put the total stockpile that U.S firms are holding abroad so as to avoid U.S. taxes at somewhere in the $2.5 trillion range. Back in 2004, Congress approved a plan to “repatriate” such overseas funds that companies could bring back home at a reduced rate. The program was part of the American Jobs Creation Act. The hope then, as now, was that companies would shovel that money back into the economy in the form of investment and job creation. It didn’t quite work out that way. Contrary to the intent, the benefits skewed toward a select few companies in a select few industries.
Rather than use the money for hiring and capital purchases, companies plowed the cash into share buybacks and dividends, and many of the biggest beneficiaries actually cut American jobs in the years after the repatriation. “While empirical evidence is clear that this provision resulted in a significant increase in repatriated earnings, empirical evidence is unable to show a corresponding increase in domestic investment or employment,” the Congressional Research Service, Congress’ nonpartisan think tank, said in a report. The CRS cited a series of reports into the benefits of repatriation, with a common theme that the 2004 program was “an ineffective means of increasing economic growth.” In the 2004 case, 9,700 companies were eligible to take part in a tax holiday that would bring the overseas cash back at a rate of 5.25%, well below the 35% rate for profits earned abroad.
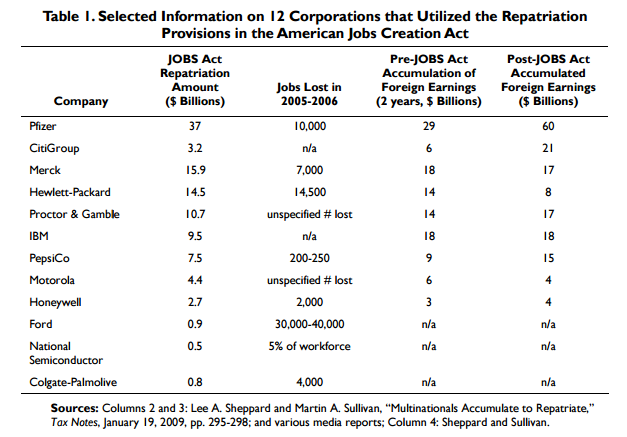
Of that group, 843 firms participated. They brought home $312 billion in qualified earnings, or about one-third of the total cash held overseas, according to the CRS. That translated into total deductions of $265 billion. [..] In the 2005-06 time frame, Pfizer, which repatriated $37 billion, slashed 10,000 jobs. Merck, which brought back $15.9 billion, cut 7,000 jobs, and HP pared its employment rolls by 14,500 after repatriating $14.5 billion. Most of the money went to repairing balance sheets and rewarding shareholders, according to the CRS. According to one study cited, as much as 91 cents on the dollar went to share repurchases, even though that, along with compensation increases, was an expressly prohibited use by Congress.

Once was a nice country.
• New Zealand Plans Spending Splurge to Keep ‘Growing Like Sydney’ (BBG)
New Zealand’s government announced plans to substantially increase infrastructure spending to help sustain economic growth and cope with a swelling population. In its May 25 budget, the government will allocate NZ$11 billion ($7.6 billion) in additional spending on infrastructure like schools, roads, hospitals and housing between 2017 and 2020, Finance Minister Steven Joyce said in a speech in Wellington Thursday. When added to already-planned investments, a total of around NZ$23 billion would be spent over the four-year period, representing “the biggest addition to the government’s capital stock in decades,” he said. New Zealand’s economy is among the fastest-growing in the developed world, expanding at around 3% a year, and the government predicts rising budget surpluses.
Growth is being driven in part by record immigration and fewer New Zealanders seeking work abroad, which is straining infrastructure. “As a country we are now growing a bit like South-East Queensland or Sydney, when in the past we were used to growing in fits and starts,” Joyce said. “That’s great because we used to send our kids to South-East Queensland and Sydney to work, and now they come back here.” Details of the first tranche of spending would be unveiled in the budget, and Joyce said the government wants to make greater use of public-private partnerships and joint ventures to boost infrastructure further.
[..] The government will aim to cut net debt to 10-15% of GDP by 2025, from an estimated 24.3% at June 30 this year. Its current target is to reduce net debt to 20% of GDP by 2020. Joyce said the government borrowed heavily to help the country through the global financial crisis and a devastating earthquake in Christchurch in 2011. “Shocks can come along at any time, and sometimes they come in pairs,” he said. “We are a geologically young country, and we are also a small country in an often turbulent world – so there are plenty of shocks ahead of us.”

“I just want any example of Russia spreading fake news, just show me one example.. I can present you tons, dozens, billions of examples of Western media spreading false news about Russia..”
• Russian Spokeswoman On ‘Ridiculous’ Airstrikes In Syria, Fake News (Y!)
Recent U.S. airstrikes against Syria were “ridiculous,” according to Russian Foreign Ministry spokesperson Maria Zakharova. In a blunt, at times contentious, interview with Yahoo Global News Anchor Katie Couric, Zakharova called the strikes “unacceptable” and said they violated international law and made no military or political sense. “They brought the situation nowhere,” she said. She went on to say that the goal of the West to oust Syrian President Bashar Assad is “not a way out, it is a dead end.” When pressed on whether Assad was responsible for the chemical attacks that led to the U.S. military action, she said, “Our decisions should be based on real evidence,” detailing Russia’s desire to have independent investigators determine blame.
She pointed to U.S. claims in 2003 that Iraq had weapons of mass destruction, which later turned out to be false. “That was the worst thing that happened to the Security Council, to the United States, to the Middle East region,” Zakharova said. The wide-ranging, exclusive conversation began with Zakharova objecting to Couric’s characterization of the Russian government as a “regime.” “I think if a president is elected by the people of his country, it’s not about being a regime, it’s about being a democracy,” she said. Zakharova said that relations between the U.S. and Russia began to deteriorate during the Obama administration, in part because of what she called “fake news” reports about her country that were disseminated during those years.
“What I’m facing today is, the main role of the media is to separate people (in order) to divide the world into separate parts. I think it’s dangerous.” She dismissed claims from American and European intelligence officials that, in actuality, Russia is disseminating fake news to achieve its geopolitical goals. “I just want any example of Russia spreading fake news, just show me one example,” she said. “I can present you tons, dozens, billions of examples of Western media spreading false news about Russia,” she told Couric.

Germany forces Greece to take measures that are illegal under German law. Both are -equal- members of an economic union.
• German Court Upholds Greek Teacher’s Case Against Pay Cut (AP)
A German federal court has upheld a complaint by a teacher at a Greek school in Germany against a pay cut that the Greek government imposed at the height of the country’s financial crisis. The teacher, a Greek citizen, works at a Greek government-run school in Nuremberg but his contract is subject to German law. He sued after his pay was cut in 2010. A lower court granted his demand for some €20,000 ($21,780) in extra pay for Oct. 2010-Dec. 2012 — the amount by which his salary was lowered. The Federal Labor Court said Wednesday it has rejected a Greek appeal against that ruling. It ruled that Greek austerity legislation isn’t directly applicable on German territory and that Greece doesn’t have legal immunity over the labor contract.









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle April 27 2017