
Jules Bastien-LePage The annunciation to the shepherds 1875

Santa = faith in the good of mankind. As is Jesus. Still, hard to rhyme with copious dinners while others starve in the dark and cold, and $900 spent on gifts on average per American. That can’t be it.
• Yes, Virginia, There Is A ‘Santa Rally’ (Roberts)
Eight-year-old Virginia O’Hanlon wrote a letter to the editor of New York’s Sun, and the quick response was printed as an unsigned editorial Sept. 21, 1897. The work of veteran newsman Francis Pharcellus Church has since become history’s most reprinted newspaper editorial, appearing in part or whole in dozens of languages in books, movies, and other editorials, and on posters and stamps
THE EDITORIAL
DEAR EDITOR:I am 8 years old.
Some of my little friends say there is no Santa Claus.
Papa says, ‘If you see it in THE SUN it’s so.’
Please tell me the truth; is there a Santa Claus?VIRGINIA O’HANLON.
115 WEST NINETY-FIFTH STREET.“VIRGINIA, your little friends are wrong. They have been affected by the skepticism of a skeptical age. They do not believe except they see. They think that nothing can be which is not comprehensible to their little minds. All minds, Virginia, whether they be men’s or children’s, are little. In this great universe of ours, man is a mere insect, an ant, in his intellect, as compared with the boundless world about him, as measured by the intelligence capable of grasping the whole of truth and knowledge.
Yes, VIRGINIA, there is a Santa Claus. He exists as certainly as love and generosity and devotion exist, and you know that they abound and give to your life its highest beauty and joy. Alas! how dreary would be the world if there were no Santa Claus? It would be as dreary as if there were no VIRGINIAS. There would be no childlike faith then, no poetry, no romance to make tolerable this existence. We should have no enjoyment, except in sense and sight. The eternal light with which childhood fills the world would be extinguished.
Not believe in Santa Claus! You might as well not believe in fairies! You might get your papa to hire men to watch in all the chimneys on Christmas Eve to catch Santa Claus, but even if they did not see Santa Claus coming down, what would that prove? Nobody sees Santa Claus, but that is no sign that there is no Santa Claus. The most real things in the world are those that neither children nor men can see. Did you ever see fairies dancing on the lawn? Of course not, but that’s no proof that they are not there. Nobody can conceive or imagine all the wonders there are unseen and unseeable in the world.
You may tear apart the baby’s rattle and see what makes the noise inside, but there is a veil covering the unseen world which not the strongest man, nor even the united strength of all the strongest men that ever lived, could tear apart. Only faith, fancy, poetry, love, romance, can push aside that curtain and view and picture the supernal beauty and glory beyond. Is it all real? Ah, VIRGINIA, in all this world there is nothing else real and abiding.
No Santa Claus! Thank God he lives, and he lives forever. A thousand years from now, Virginia, nay, ten times ten thousand years from now, he will continue to make glad the heart of childhood.”

Do they know it’s Christmas time at all?
• Homelessness In England Rises By 75% Among Vulnerable Groups Since 2010 (G.)
Homelessness among people with mental and physical health problems has increased by around 75% since the Conservatives came to power in 2010, and there has been a similar rise in the number of families with dependent children who are classed as homeless. According to official figures collated by the Department for Communities and Local Government, the number of homeless households in England identified by councils as priority cases because they contain someone who is classed as vulnerable because of their mental illness, has risen from 3,200 in 2010 to 5,470 this year. Over the same period, the number of families with dependent children – another priority homeless group identified by councils – has increased from 22,950 to 40,130.
The number of homeless households with a family member who has a physical disability has increased from 2,480 to 4,370. After a week in which the prime minister has come under renewed attack over homelessness, housing charities have called on the government to urgently build more affordable housing and reverse a squeeze on benefits which has left vulnerable people unable to pay their rents. “With homelessness soaring, it is no surprise that the number of vulnerable groups – including families with children – who are having to turn to their council for help is on the rise,” said Polly Neate, chief executive of charity Shelter.
“As wages stagnate, rents continue to rise and welfare is cut, many people are struggling to keep a roof over their head. Eviction is now the number one cause of homelessness. “Our services across the country are seeing an increase in the number of people with multiple and complex needs, and we think this may be because other services are failing to provide the help that people need. The solution to our housing crisis must be to urgently build more affordable homes and, in the short term, end the freeze on housing benefit that is increasingly pushing people over the precipice into homelessness.”

Shaking the tree.
• Ten Years In, Nobody Has Come Up With A Use For Blockchain (Hackernoon)
Everyone says the blockchain, the technology underpinning cryptocurrencies such as bitcoin, is going to change EVERYTHING. And yet, after years of tireless effort and billions of dollars invested, nobody has actually come up with a use for the blockchain – besides currency speculation and illegal transactions. Each purported use case – from payments to legal documents, from escrow to voting systems – amounts to a set of contortions to add a distributed, encrypted, anonymous ledger where none was needed. What if there isn’t actually any use for a distributed ledger at all? What if, ten years after it was invented, the reason nobody has adopted a distributed ledger at scale is because nobody wants it?
The original intended use of the blockchain was to power currencies like bitcoin – a way to store and exchange value much like any other currency. Visa and MasterCard were dinosaurs, everyone proclaimed, because there was now a costless, instant way to exchange value without the middleman taking a cut. A revolution in banking was just the start& governments, unable to issue currency by fiat anymore, would take a back seat as individual citizens transacted freely outside any national system. It didn’t take long for that dream to fall apart. For one thing, there’s already a costless, instant way to exchange value without a middleman: cash. Bitcoins substitute for dollars, but Visa and MasterCard actually sit on top of dollar-based banking transactions, providing a set of value-added services like enabling banks to track fraud disputes, and verifying the identity of the buyer and seller.
It turns out that for the person paying for a product, the key feature of a new payment system – think of PayPal in its early days – is the confidence that if the goods aren’t as described you’ll get your money back. And for the person accepting payment, basically the key feature is that their customer has it, and is willing to use it. Add in points, credit lines, and a free checked bag on any United flight and you have something that consumers choose and merchants accept. Nobody actually wants to pay with bitcoin, which is why it hasn’t taken off.

Crypto vs democracy: “To Varoufakis, money is inherently political. The decisions regarding whether money is produced or not, how it is distributed and who receives it, all have significant political consequences, benefiting certain social groups over others.”
• Varoufakis: Bitcoin is The Perfect Bubble, Blockchain A Great Solution (Wired)
While acknowledging the limitations of bitcoin and other technical solutions to political problems, Varoufakis does see potential in blockchain technologies. For him, “the algorithm that operates behind bitcoin, caught my attention right from the beginning. I consider this to be a remarkable technology. As early as 2012, Varoufakis was toying with ideas for using blockchain to help solve Europe’s financial woes. By the time he was appointed Finance Minister of Greece in 2015, within days his anti-austerity programme was met with the direct threat from the Troika to close Greece’s banks. With no banking system, the country would grind to a halt. To counter this threat, Varoufakis devised an audacious plan to keep Greece’s financial system operating. Effectively Varoufakis proposed creating an alternative, peer-to-peer payments system based on the blockchain.
This would disintermediate the financing they were receiving from the Troika and from the money markets. But with no money coming from the Troika, Varoufakis would need to create a parallel payments system, that would leverage the tax that all citizens and companies of Greece need to pay, as a new form of money. This is what he would eventually brand, “fiscal money.” To understand how fiscal money works, imagine that a pharmaceutical company in Greece is owed money by the state. Due to the constraints of the crisis, it may take years to pay the company in normal central bank euros. However what if there was an alternative option? What if the Greek State created a reserve account for the company under its tax file number, in which it placed tax credits of one million euros? This IOU could then also be used by the company to pay other organisations and individuals within the country.
One of the most disruptive aspects of this unrealised plan, was to enable the state to borrow directly from citizens and vice versa. In effect, Varoufakis was attempting to use new digital technologies, such as blockchain, to cut out the European lending authorities and build new lending relationships between citizens, companies and the state. The risk this system faced was the threat of corruption and the subsequent decline in public trust of authorities, something that Varoufakis admits is “in very limited supply” in a country like Greece. For example, what if Greek authorities abused these tax credits and began to distribute this new fiscal money to close allies and friends? This is where Varoufakis saw blockchain’s potential. “If the payments system was based on the blockchain, this would allow the combination of anonymity but perfect transparency, regarding the total aggregate size of the transactions of the currency….blockchain would overcome the trust problem as we know it.”

Japan and China suffer the same fate: aging populations.
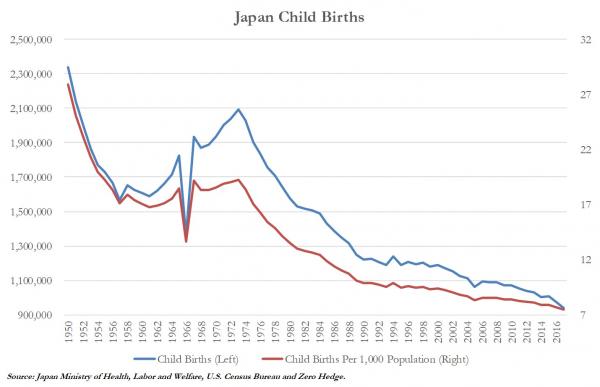
• Japan Births Plunge To Lowest Level Ever Recorded (ZH)
Back in 2013 we asked “Why Have Young People In Japan Stopped Having Sex?” And while that might sound like nothing more than a clever headline intended for The Onion, it was prompted by a very serious survey conducted by the Japan Family Planning Association which found that 45% of Japanese women aged 16-24 and 25% of men were “not interested in or despise sexual contact”…a growing trend that has revealed itself via the nation’s persistently declining birth rates. In fact, “celibacy syndrome” has become of such great concern for the Japanese government that it is considered a bit of a looming national catastrophe….a catastrophe that seems to be getting worse at an accelerating rate. According to data released today by Japan’s Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare, child births in Japan will drop to just 941,000 in 2017, the lowest since data first started being recorded in 1899, and nearly 65% below the peak birth rate from the late 1940’s.

China is building “..a housing bubble for a population that is never coming..”
• China Raging Against the Dying of the Light (Hamilton)
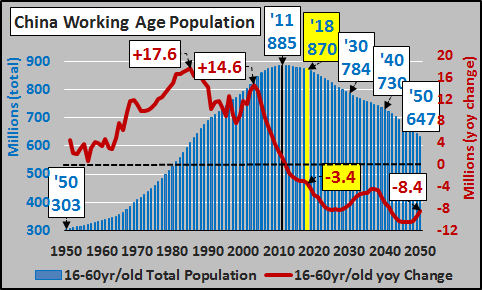
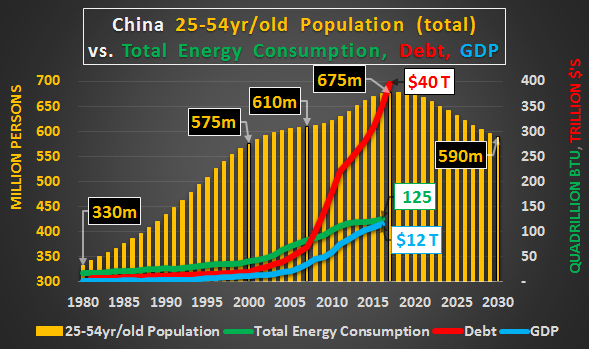
China’s working age population is clearly defined as those aged 16 to 50 years old for females (55 for “white collar” females) and 16 to 60 years old for males. China mandates retirement at these outer age limits. Perhaps of some interest should be that this working age population peaked in 2011 and has been declining since. This decline will continue indefinitely as China has a collapsing childbearing population (detailed HERE), net emigration (outflow), and a still decidedly negative birthrate. There is no evidence to believe the working age declines will abate any decade soon. As the chart below shows, China’s potential workforce will be shrinking indefinitely…and by 2030 China’s potential workforce will be over 100 million fewer than the 2011 peak (an 11% decline)…and only further down from there..
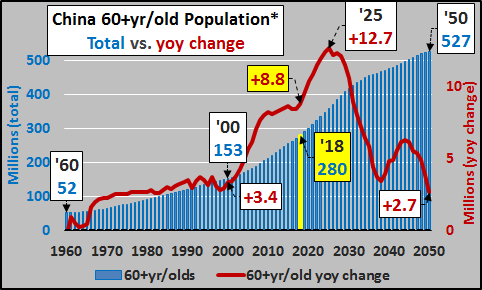
China has one of the youngest average retirement ages in the developed world. On average, according to a recent study (HERE), Chinese leave the work force by age 55 compared to age 63 in the US (Norway has the latest average departure at age 67). So, perhaps China will be raising the retirement age to curb the ballooning 60+yr/old population entering retirement (chart below…chart shows retirement population, 55+ females and 60+ males)? More on that later..
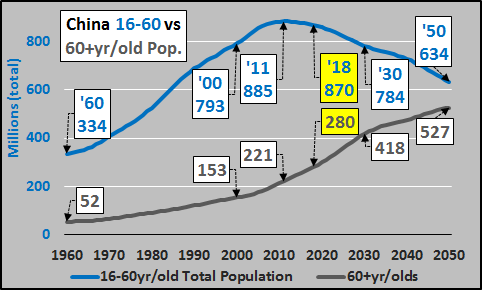
Comparing the working age population versus the 60+yr/old population (chart below…again, showing the 55+ females, 60+ males). A shrinking potential workforce since peaking in 2011 and a rapidly growing elderly population.
[..] While China’s GDP and energy consumption have led the world, they have not responded in kind to China’s debt explosion and exponentially more will be necessary to continue to show “growth”. Over a third and perhaps half of all the debt has been mal-invested in a housing bubble for a population that is never coming. What comes next isn’t going to be good for China nor the rest of the world as China looks to flood a depopulating nation with new debt only creating more housing overcapacity…China will look to beat the Japanese at the debt game.

Outflows are by no means over.
• US Tax Cut and Rate Hikes Threaten China Currency (Schmid)
Seven was the line in the sand. But the Chinese yuan never crossed that line vis-à-vis the U.S. dollar. It only crept up to 6.96 yuan per dollar on Dec. 16, 2016, before starting an impressive comeback, down to 6.5 in the middle of this year. Last year was a bad one for the Chinese economy. Growth was slow, and the world was worried China would finally land the hard way, as many have been predicting for years. And more than GDP growth or any other metric, the Chinese currency was the barometer of whether China could keep things stable – stability is the mantra of the ruling communist regime – or suffer a crisis of debt deflation. If it declined in value, it meant citizens and companies were moving money out of the country in droves because they didn’t believe in the Chinese dream anymore. So another measure of how bad things had gotten in the second-largest economy of the world was capital outflows.
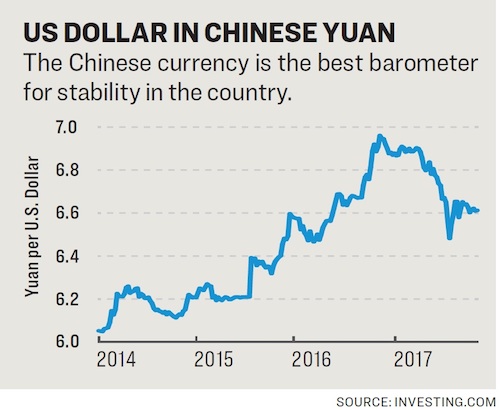
According to the Institute of International Finance (IIF), a record $725 billion left China in 2016, putting pressure on the currency and the Chinese interbank market. All these factors have changed in favor of the dollar in the last quarter, and it’s going to be hard for China to compete. Trying to stem the tide, the central bank sold record amounts of foreign currency. Chinese foreign exchange reserves, $4 trillion at the peak in 2014, went down to $3 trillion, and analysts started to question whether this was enough to finance the world’s largest trading economy. Then, miraculously in time for the 2017 National Congress of the Communist Party, all of this stopped. The yuan never went above 7, the exchange reserves never went below 3 trillion, and capital outflows subsided thanks to draconian regulations making it harder for individuals and companies to move money out of the country.

Beppe all the way.
• Italy’s Ruling PD Slides Further In Polls As Election Nears (R.)
Italy’s ruling Democratic Party (PD), hit by internal divisions and a banking scandal, is continuing to slide in opinion polls, with a new survey on Saturday putting it more than six points behind the anti-establishment 5-Star Movement. The survey by the Ixe agency, commissioned by Huffington Post Italia, comes just days before parliament is expected to be dissolved to make way for elections in March. It gives the center-left PD just 22.8% of voter support, down almost five points in the last two months, compared with 29.0% for 5-Star, which has gained almost two points in the same period. Silvio Berlusconi’s center-right Forza Italia (Go Italy!) is given 16.2%, with its right-wing allies the Northern League and Brothers of Italy on 12.1% and 5.0% respectively.
This bloc is expected to win most seats at the election but not enough for an absolute majority, resulting in a hung parliament. With the PD’s support eroding in virtually all opinion polls, several political commentators have speculated that its leader Matteo Renzi may choose or be forced to announce he will not be the party’s candidate for prime minister at the election. Renzi has given no indication so far he will take this step. The PD has split under his leadership, with critics complaining he has dragged the traditionally center-left party to the right. Breakaway groups united this month to form a new left-wing party called Free and Equal (LeU), which now has 7.3% of support, according to Ixe. The PD’s popularity seems to have also been hurt by a parliamentary commission looking into the collapse of 10 Italian banks in the past two years.

What kills faith in mankind.
• How Sea Shepherd Lost Battle Against Japan’s Whale Hunters In Antarctic (G.)
A fleet of Japanese ships is currently hunting minke whales in the Southern Ocean. It is a politically incendiary practice: the waters around Antarctica were long ago declared a whale sanctuary, but the designation has not halted Japan’s whalers, who are continuing a tradition of catching whales “for scientific research” in the region. In the past, conservation groups such as Sea Shepherd have mounted campaigns of harassment and successfully blocked Japan’s ships from killing whales. But not this year. Despite previous successes, Sea Shepherd says it can no longer frustrate Japan’s whalers because their boats now carry hardware supplied from military sources, making the fleet highly elusive and almost impossible to track. As a result the whalers are – for the first time – being given a free run to kill minke in the Southern Ocean.
“We have prevented thousands of whales from being killed in the past and we have helped ensure that the quota of minkes that Japan can take now is much lower than in the past,” said Peter Hammarstedt, a Sea Shepherd captain. “But they have put such resources into this year’s whaling that we cannot hope to find their fleet and stop them. It is simply a matter of us not wasting our own resources. We have other battles to fight.” Japan is not the only nation to hunt whales. Norway has a commercial operation in its own waters, for example. But what infuriates conservationists is that Japan is hunting and killing whales in a conservation zone, the Southern Ocean whaling sanctuary, that surrounds Antarctica. Japan claims that it does so only for scientific purposes.
“Essentially, they are exploiting a loophole in the rules – introduced in the 80s – that govern the banning of commercial whaling,” said Paul Watson, the founder of Sea Shepherd. Originally Japan set out to catch more than 900 minkes every year, as well as 50 humpbacks and 50 fin whales. However, its fleet was rarely able to reach these quotas because of actions by groups like Sea Shepherd. “We physically got in between the whalers and the whales and stopped the latter being killed,” said Hammarstedt. “One year we stopped Japan getting all but 10% of its quota. Their ships were nearly empty when they got back home.”

The further north the larger the differences.
• Climate Change In The Land Of Santa Claus (Ind.)
Lapland occupies a happy space in the popular imagination as a winter wonderland, occupied by reindeer, elves and Father Christmas. The real life Lapland, however, is increasingly facing up to the grim reality of global warming. Besides being the name of Swedish and Finnish provinces, Lapland is the English name for a region largely above the Arctic Circle that stretches across the north of Norway, Sweden, Finland and Russia. Research has revealed the disproportionate impact of climate change in the Arctic, where temperatures are currently rising at double the rate of the global average. The far north is bearing the brunt of global warming, and, as much of Lapland’s population relies on its polar climate for their livelihoods, the effects are starting to be felt.
Rovaniemi, the administrative capital of the Finnish province of Lapland, has done a good job of capitalising on the region’s Christmas-themed reputation. It is the self-proclaimed “Official Hometown of Santa Claus”, where the man himself can be visited 365 days a year. However, with his official residence there only constructed in 1950, Santa Claus is a relative newcomer to Lapland. The wider region is the ancient home of the indigenous Sami people, who refer to it as Sapmi. Owing to its remote location and freezing temperatures, much of Lapland remains relatively pristine wilderness, and it is this wilderness that provides the Sami with space to practise their ancient tradition of reindeer herding. As temperatures rise and begin to disrupt the unspoiled environment, the future prosperity of all Lapland’s inhabitants – from the Sami to Santa Claus – is at risk.
Dr Stephanie Lefrere first came to Finnish Lapland 18 years ago to study reindeer behaviour. Since then, she has observed dramatic changes in the region’s weather patterns, and subsequent effects on its wildlife. “In my very first fieldwork, 300km (186 miles) above the Arctic Circle, it was 20°C below zero on 31 October – really the Arctic feeling by the end of October,” she said. “We don’t have that any more. “Recently there have been ‘black Christmases’ with no snow at all in the southern part of Finland.” Decades of work in the region have cemented her view that climate change is having far-reaching effects on Lapland’s environment, affecting animal migratory routes, habitats and behaviour. “I became worried as a scientist, and also as an individual who is fascinated by the Arctic,” said Dr Lefrere.
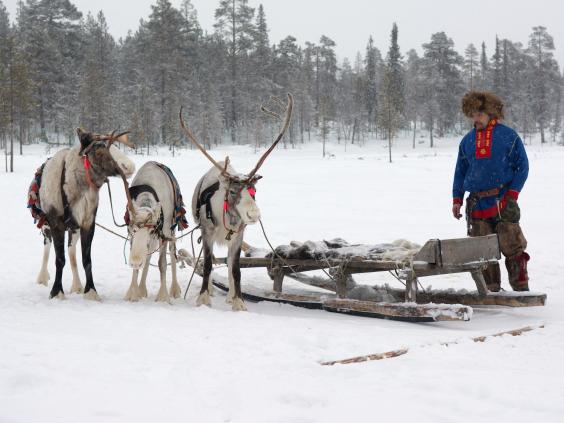

Sami culture is based around reindeer, but only a fraction still keep their animals due to environmental change (Getty)








